Thermo-mechanical treatment strengthening technology of magnesium alloy sheet
A deformation heat treatment, magnesium alloy technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metals, can solve problems such as limited work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The magnesium alloy in this embodiment is composed of the following components by mass percentage: 7.8% Al, 0.7% Zn, impurity element Mn<0.12%, 0% Gd, and the rest is Mg.
[0044] Select a representative part from the smelted magnesium alloy ingot to cut a magnesium alloy sheet with a size of 40×40×4mm, and grind the upper and lower surfaces with sandpaper from coarse to fine to make it smooth for use.
[0045] The treated magnesium alloy sheet is subjected to solid solution treatment in a box-type resistance furnace: the heating temperature is 415° C., and the temperature is kept for 20 hours.
[0046] The sample after solution treatment was rolled at 150°C with a deformation of 15%, followed by aging treatment. The process parameters: heating temperature was 168°C, holding time was 8h, and air cooled to room temperature.
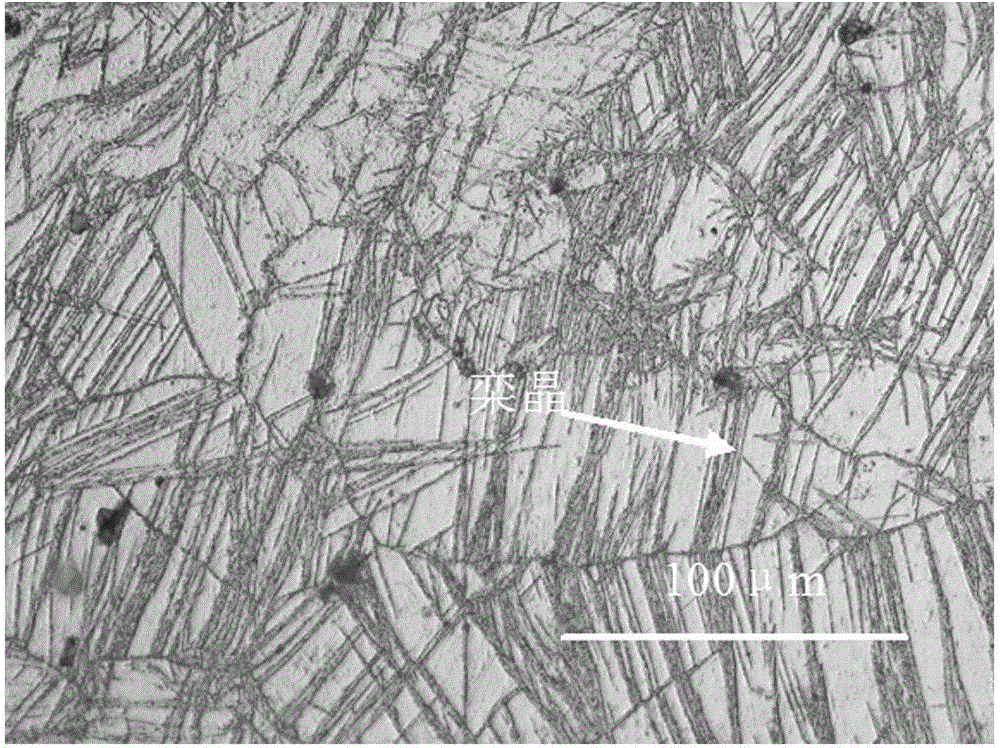
[0047] The microstructure of the high-strength and toughness magnesium alloy obtained in this embodiment is as follows: figure 1 shown, from fi...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The magnesium alloy in this embodiment is composed of the following components by mass percentage: 7.4% Al, 0.78% Zn, impurity element Mn<0.12%, 3.01% Gd, and the rest is Mg.
[0050] Select a representative part from the smelted magnesium alloy ingot to cut a magnesium alloy sheet with a size of 40×40×4mm, and grind the upper and lower surfaces with sandpaper from coarse to fine to make it smooth for use.
[0051] The treated magnesium alloy sheet is subjected to solid solution treatment in a box-type resistance furnace: the heating temperature is 415° C., and the temperature is kept for 20 hours.
[0052] The sample after solution treatment was rolled at 160°C with a deformation of 15%, followed by aging treatment, process parameters: heating temperature was 168°C, holding time was 16h, air cooled to room temperature.
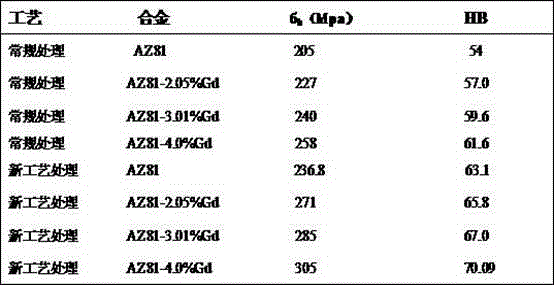
[0053] The high-strength and toughness magnesium alloy obtained in this embodiment has a tensile strength of 285 MPa and a hardness of 67HB.
Embodiment 3
[0055] The magnesium alloy in this embodiment is composed of the following components by mass percentage: 7.0% Al, 0.7% Zn, impurity element Mn<0.12%, 4.0% Gd, and the rest is Mg.
[0056] Select a representative part from the smelted magnesium alloy ingot to cut a magnesium alloy sheet with a size of 40×40×4mm, and grind the upper and lower surfaces with sandpaper from coarse to fine to make it smooth for use.
[0057] The treated magnesium alloy sheet is subjected to solid solution treatment in a box-type resistance furnace: the heating temperature is 415° C., and the temperature is kept for 20 hours.
[0058] The sample after solution treatment was rolled at 150°C with a deformation of 15%, followed by aging treatment, process parameters: heating temperature was 168°C and holding time was 12h, air cooled to room temperature.
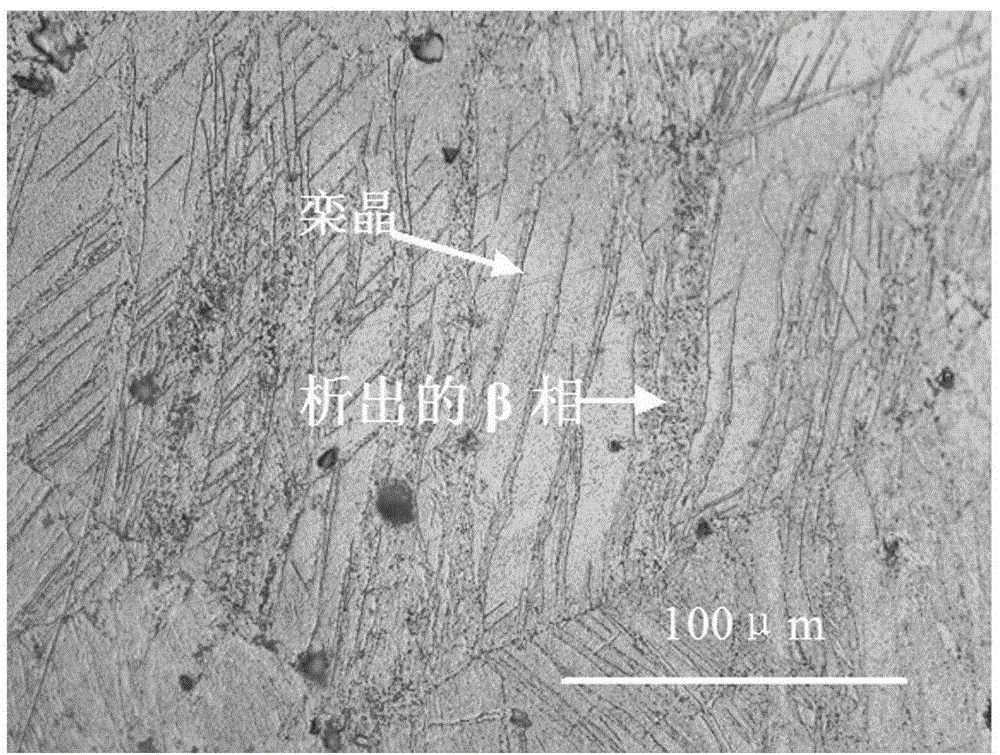
[0059] The microstructure of the high-strength and toughness magnesium alloy obtained in this embodiment is as follows: figure 2 shown, from figu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com