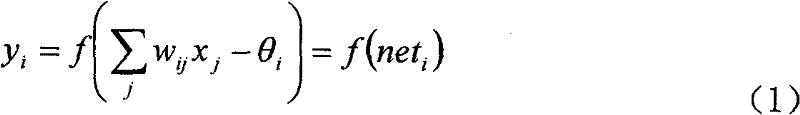Patents
Literature
101 results about "Ausforming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ausforming also known as Low and High temperature thermomechanical treatments is a method used to increase the hardness and toughness of an alloy by simultaneously tempering, rapid cooling, deforming and quenching to change its shape and refine the microstructure. This treatment is an important part in the processing of steel.
High-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistance copper alloy material and preparation method thereof
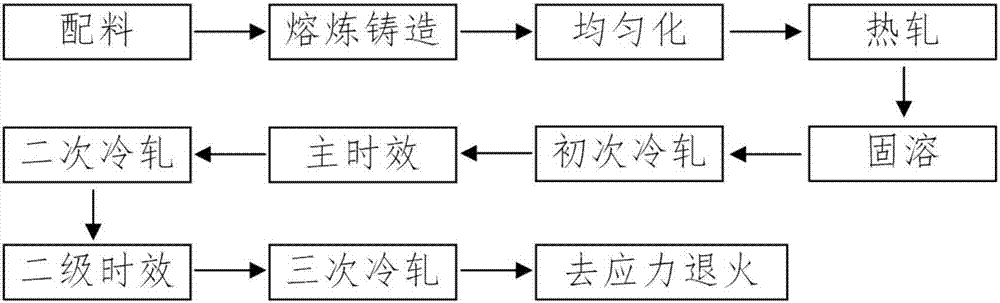
The invention discloses a high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistance copper alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistance copper alloy material comprises the following components: 0.2-1.0 wt% of Cr, 0.05-0.2 wt% of Mg, 0.03-0.2 wt% of Si, 0-0.1 wt% of Ni, 0-0.15 wt% of Ce, and the balance of Cu. The preparation method of the copper alloy comprises several steps of smelting-casting-homogenization-hot rolling-solid solution-combination, deformation and heat treatment. On component design of the copper alloy, cheap, easy-added and difficult-burnt elements are adopted to replace easy-burnt elements; through element component design of the alloy, the precipitation sequence of a precipitated phase and the nucleation and growth mechanism are changed, so that the alloy is excellent in high-temperature resistance and softening resistance; and through combination, deformation and heat treatment, the mechanical performance and the electric performance of the alloy are greatly improved, so that the tensile strength of the alloy reaches 530-620 MPa, and the electric conductivity reaches 75-87% IACS. The prepared high-strength, high-conductivity and heat-resistance copper alloy material is suitable for non-vacuum large-scale industrial manufacturing.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Ultralow-yield-ratio cold-rolled dual-phase steel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105420605AHigh work hardening rateUltra-low yield ratioChemical compositionDual-phase steel
The invention belongs to the technical field of steel materials, and relates to an ultralow-yield-ratio cold-rolled dual-phase steel and a manufacturing method thereof. Internal control chemical components of the dual-phase steel comprise 0.13%-0.18% of C, 0.30%-0.60% of Si, 1.7%-2.0% of Mn, 0.02%-0.070% of Al, 0.02%-0.05% of Nb and the balance Fe and other inevitable impurities. Simple chemical component design is adopted, the hot-rolling deformation heat treatment TMCP and the flexible continuous annealing process are combined to obtain a microscopic structure with fine grain ferrite, island martensite and 5%-7% of retained austenite, and therefore the uniform deformation capacity of materials is increased while the strong plasticity of the cold-rolled dual-phase steel is improved. The ultralow-yield-ratio cold-rolled dual-phase steel has the beneficial effects that good stamping performance, low process sensitivity and the ultralow yield ratio YS / TS which is smaller than or equal to 0.51 are achieved, springback generated after stamping can be reduced, and later deep machining of the automobile industry is facilitated.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
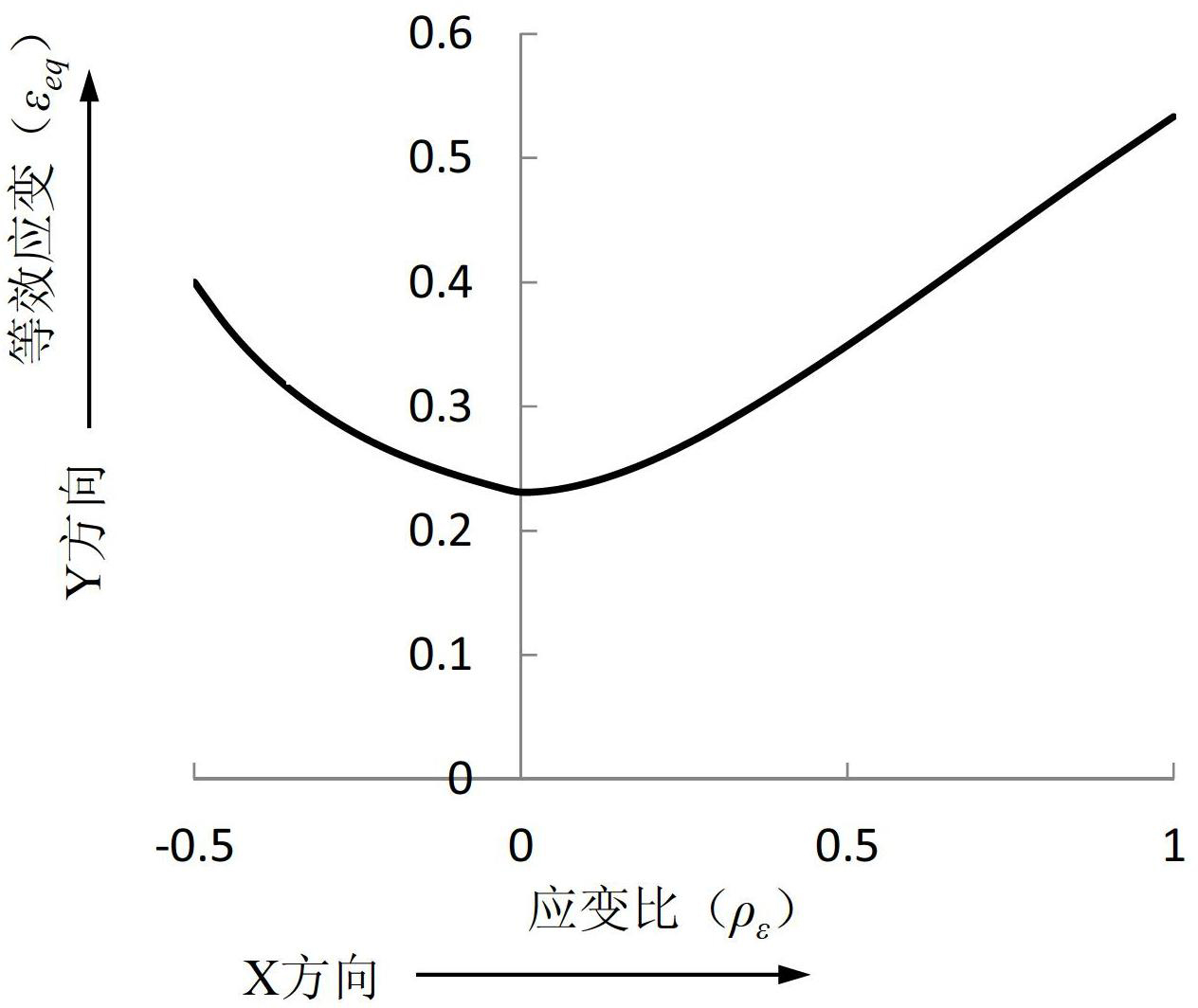
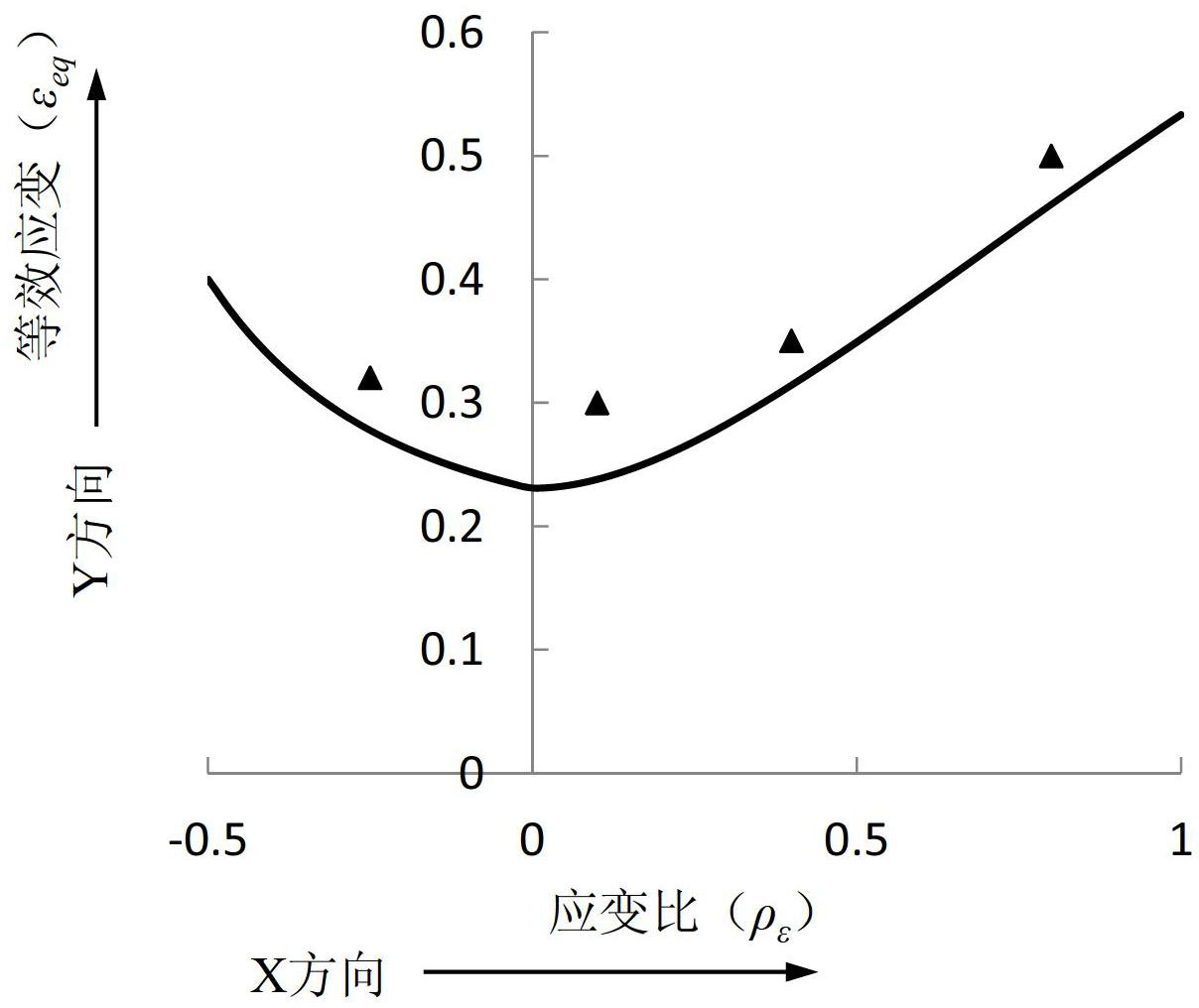
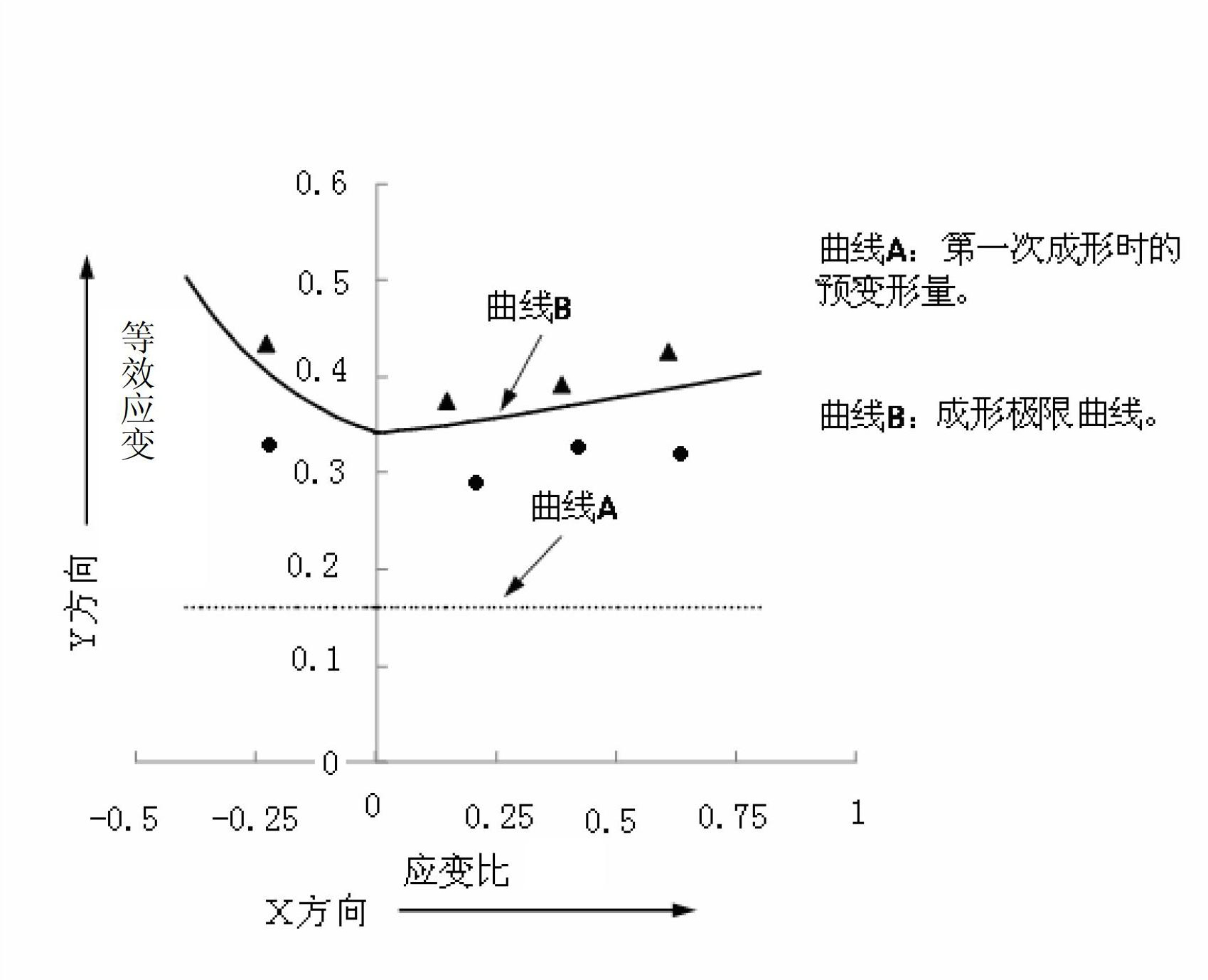
Method for establishing and using forming limit diagram of metal sheet material
InactiveCN102661899AForming limit judgmentInvestigating material ductilityStored energyForming limit diagram
The invention discloses a method for establishing and using a forming limit diagram of a metal sheet material. The method comprises the following steps of: A, establishing an XY coordinate system, wherein an X coordinate represents a strain ratio and a Y coordinate represents an equivalent strain; B, setting different values of the strain ratio, and calculating corresponding main strain and secondary strain according to the different strain ratios; C, calculating limit equivalent strain values at the different strain ratios through a formula according to the main strain and the secondary strain obtained in the step B; and D, marking the limit equivalent strain value corresponding to each strain ratio, which is obtained in the step C, on the XY coordinate system, and connecting marked points to be a curve, namely the forming limit curve shown by the limit equivalent strain values, wherein the XY coordinate system and the forming limit curve form the forming limit diagram of the metal sheet material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the equivalent strains are used as variable values. Each equivalent strain is the single variable value, so that the influences of deformation in a pre-forming process on deformation stored energy and a forming limit of a magnesium alloy sheet material after thermomechanical treatment can be reflected in a more direct manner.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
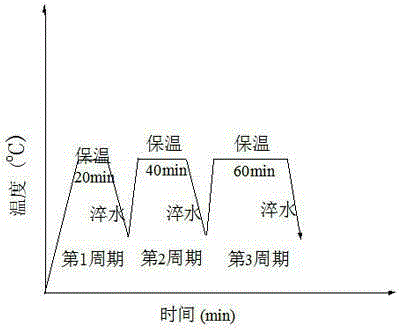
Method for increasing proportion of special grain boundaries in precipitation strengthened austenitic heat-resistance steel
ActiveCN105177262AImprove high temperature performanceImprove oxidation resistanceGrain boundaryMaterials science
The invention belongs to the field of precipitation strengthened austenitic heat-resistance steel and relates to a method for increasing the proportion of special grain boundaries in the precipitation strengthened austenitic heat-resistance steel. An optimization treatment process includes solid solution, cold rolling and annealing. The method is characterized in that solution treatment is performed at the temperature from 1150 DEG C to 1300 DEG C for 20 min to 60 min; indoor temperature rolling with the deformation ranging from 20% to 60% is then performed, the single pass reduction is not lower than 15%, and then at the temperature from 1100 DEG C to 1250 DEG C, periodical short-time annealing and water cooling are performed. After optimization treatment is performed, the special grain boundaries in a microscopic structure of the precipitation strengthened austenitic heat-resistance steel are evenly distributed, and the proportion is higher than 80%. By the adoption of the method, the strain storage energy is improved by increasing the indoor temperature deformation, recrystallization is promoted to occur in precipitation strengthened austenitic steel, the proportion of the special grain boundaries in the precipitation strengthened high-Cr and high-Ni austenitic heat-resistance steel is increased, the performance of the steel related to the grain boundaries is optimized, and corrosion resistance and irradiation swelling resistance are particularly optimized.
Owner:ANYANG INST OF TECH
Steel with good property and ultra-high strength for engineering machinery and manufacturing method thereof
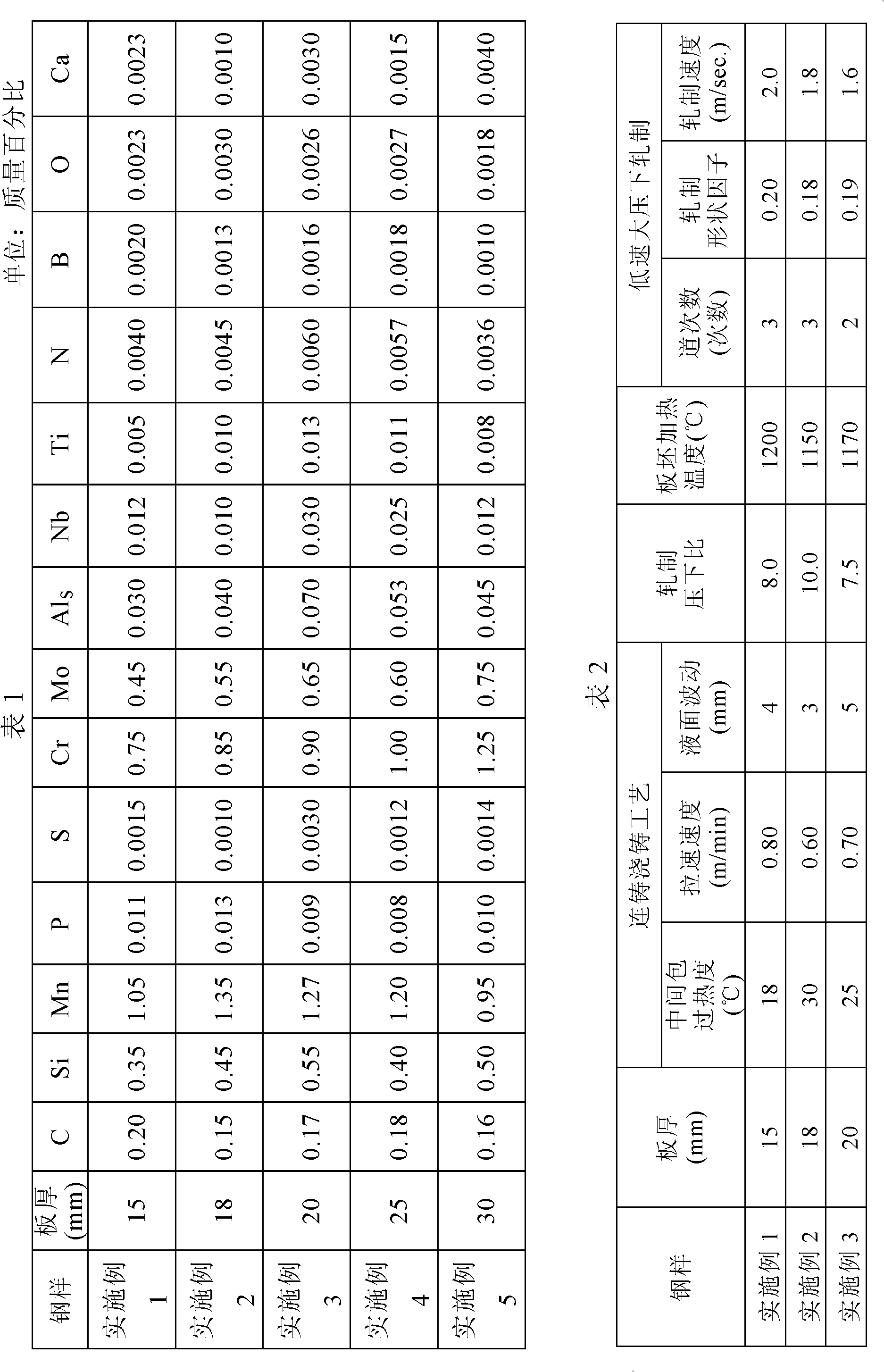
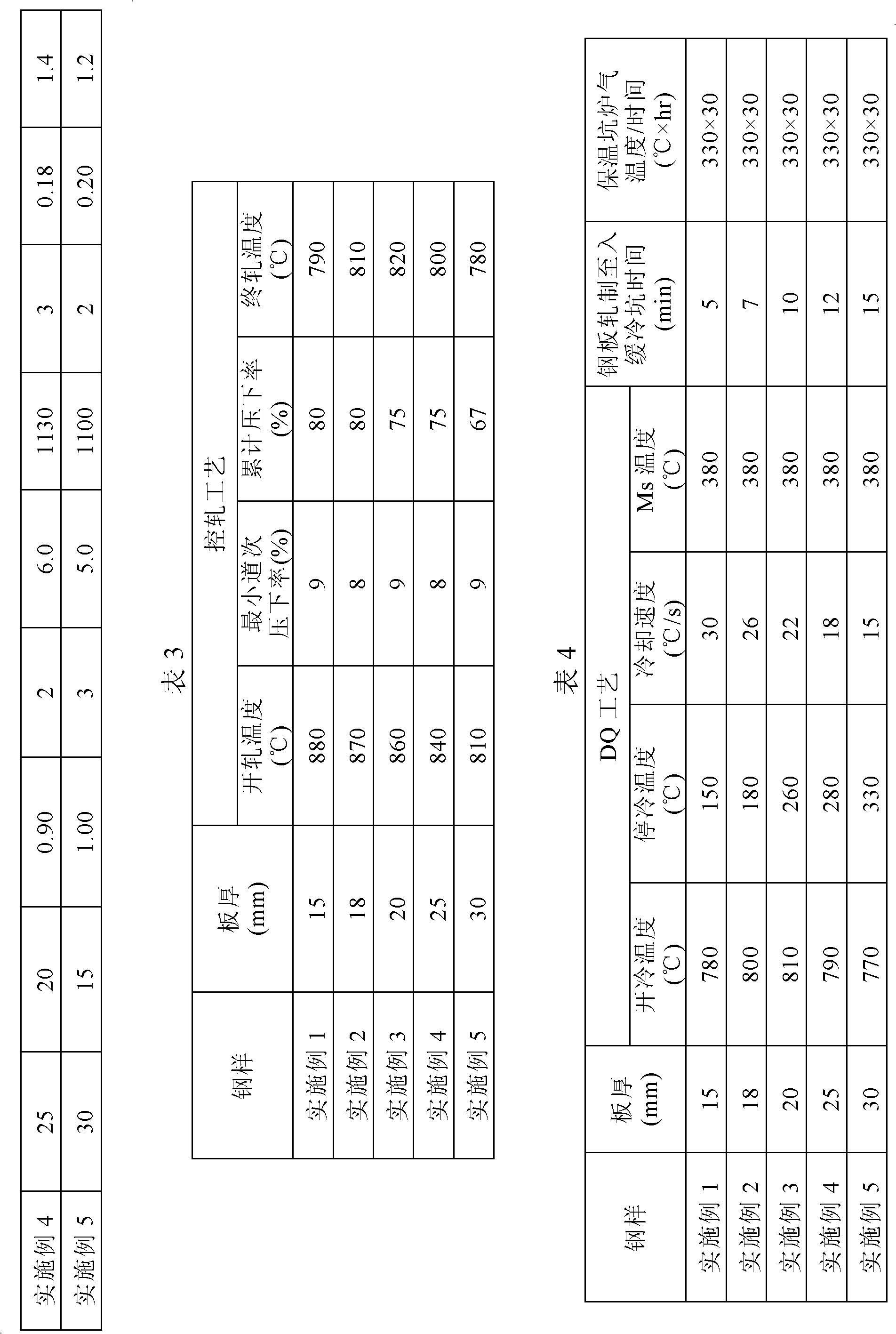
The invention discloses steel with good property and ultra-high strength for engineering machinery and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel comprises the following components by weight percent: 0.15 to 0.20 percent of C, 0.35 to 0.55 percent of Si, 0.95 to 1.35 percent of Mn, at most 0.013 percent of P, at most 0.0030 percent of S, 0.75 to 1.25 percent of Cr, 0.45 to 0.65 percent of Mo, 0.0010 to 0.0020 percent of B, 0.005 to 0.013 percent of Ti, 0.010 to 0.030 percent of Nb, 0.030 to 0.070 percent of Al, at most 0.0060 percent of N, at most 0.0030 percent of O, 0.001 to 0.004 percent of Ca, and Fe and inevitable impurities in balance. The invention optimizes the DQ and offline tempering process, adopts the ausforming process, ensures that the microscopic structure of finished steel plates becomes fine low-carbon tempered martensite and the average colony size is smaller than 20 micrometers, obtains ultra-high strength steel plates with good low-temperature flexibility, weldability and anti-delay cracks, solves the problem of overquenching of superficial layers of the ultra-high strength steel plates, and is particularly applicable to equipment manufacturing industries of large-scale engineering machinery and the like.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Production technique of high-damage-resistance aluminum alloy plate
InactiveCN103484738AReduce the chance of spawningIncrease resistance to expansionUltimate tensile strengthToughness
The invention discloses a production technique of a high-damage-resistance aluminum alloy plate. The aluminum alloy comprises the following elements in percentage by mass: 3.2-3.6% of Cu, 1.1-1.4% of Mg, 0.6-0.9% of Mn, 0.4-0.8% of Zr, 0.3-0.6% of Mo, 0.15-0.25% of Li, 0.1-0.2% of Ga, 0.05-0.15% of Co, 0.04-0.07% of Fe, 0.03-0.05% of Si, 0.06-0.12% of Er, 0.04-0.08% of Sc and the balance of Al. On the basis of lowering the Fe / Si ratio and Cu content, Zr, Er, Sc, Li and other elements are added for microalloying to reduce the solidified eutectic phase and heat treatment excess phase and reduce the fatigue crack generation probability; the microalloying forms a disperse phase coherent with the base to keep the deformation recovery subgrain structure; and the thermomechanical treatment improves the distribution uniformity of the precipitated phase to effectively enhance the fatigue crack propagation resistance, thereby greatly enhancing the damage resistance of the existing aluminum alloy material on the premise of ensuring the strength and toughness of the aluminum alloy material.
Owner:ANHUI SHENGDA QIANLIANG ALUMINUM
Method for locally softening automotive thermal forming part
ActiveCN106086364AImprove performanceIncrease the secondary heating processFurnace typesVehicle componentsCrash testEngineering
The invention discloses a method for locally softening an automotive thermal forming part. The method can be realized through the following manners: 1, controlling the temperature of sheet matal at different areas at the sheet matal heating phase of thermal forming technology; 2, controlling the temperature of inserts at different areas of a die at the die assembling phase of the thermal forming technology; 3, controlling the cooling rate of sheet matal at different areas at the die assembling phase of the thermal forming technology; and 4, after the thermal forming technology is finished, locally heating the thermal forming part for the second time. With adoption of the method, one thermal forming part has different mechanical properties at different areas, and the performance of the part in a vehicle crash test is optimized. The high-strength part of the performance-variable thermal forming part is mainly quenched martensite, and the tensile strength is equal to or greater than 1300 Mpa; and the low-strength part of the performance-variable thermal forming part is formed by one or combination of ferrite, pearlite, bainite and tempered martensite, and the tensile strength is equal to or less than 1000 Mpa.
Owner:COSMA AUTOMOTIVE (CHONGQING) CO LTD
Method for preparing aluminum lithium alloy superplastic plate
ActiveCN103882351ASolve the cracking problemRaise the annealing temperatureAluminium-lithium alloySuperplasticity
The invention discloses a method for preparing an aluminum lithium alloy superplastic plate. The process route of the method comprises the following steps: carrying out solid solution on a raw material, namely a 2A97 aluminum lithium alloy plate blank with certain initial thickness at 460-540 DEG C for 0.5-4 hours, carrying out water quenching, and then carrying out heat preservation at 400 DEG C for 8-48 hours; then rolling an alloy to 1.0-4.0 mm. Compared with the traditional thermomechanical treatment method, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively solving the problem of easiness for cracking of a large-sized plate during rolling by increasing the intermediate annealing temperature, enhancing the deformation stored energy of the alloy and solving the problem of low superplastic elongation percentage of a plate by changing the traditional warm rolling process into a cold rolling process by retaining 20%-30% of deformation amount and can be used for firstly preparing the 2A97 aluminum lithium alloy large-sized superplastic plate with good superplastic property.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Multi-stage combination deformation heat treatment method for ultrahigh-strength CuNiSn-series elastic copper alloy
The invention discloses a multi-stage combination deformation heat treatment preparation method for an ultrahigh-strength CuNiSn-series elastic copper alloy. The method comprises the steps that a casting is subjected to two-stage homogenization treatment, hot rolling, solid solution, pre-aging, first-time cold rolling, first-time aging, second-time cold rolling and second-time aging sequentially,wherein pre-aging has the technological parameters that the temperature is 350-380 DEG C and the time lasts for 30-60 minutes. According to the multi-stage combination deformation heat treatment technology for the alloy, the condition that cellular precipitation occurs in the alloy aging process can be effectively avoided, distribution of a precipitated phase of the CuNiSn-series alloy is controlled, the corrosion resistance and the abrasion resistance are significantly improved, and the electric conductivity and the strength and ductility product (the product of the strength and the ductility) can be increased. The CuNiSn-series elastic copper alloy prepared through the heat treatment technology has the characteristics of the ultrahigh strength, the high stress relaxation resistance and the like, is high in safety and reliability and can meet the requirements of the spaceflight industry, the aviation industry, the navigation industry and the electronic industry on a high-performance conductive elastic material.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
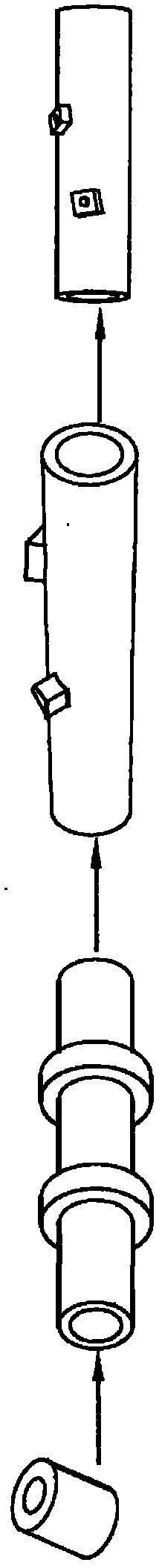
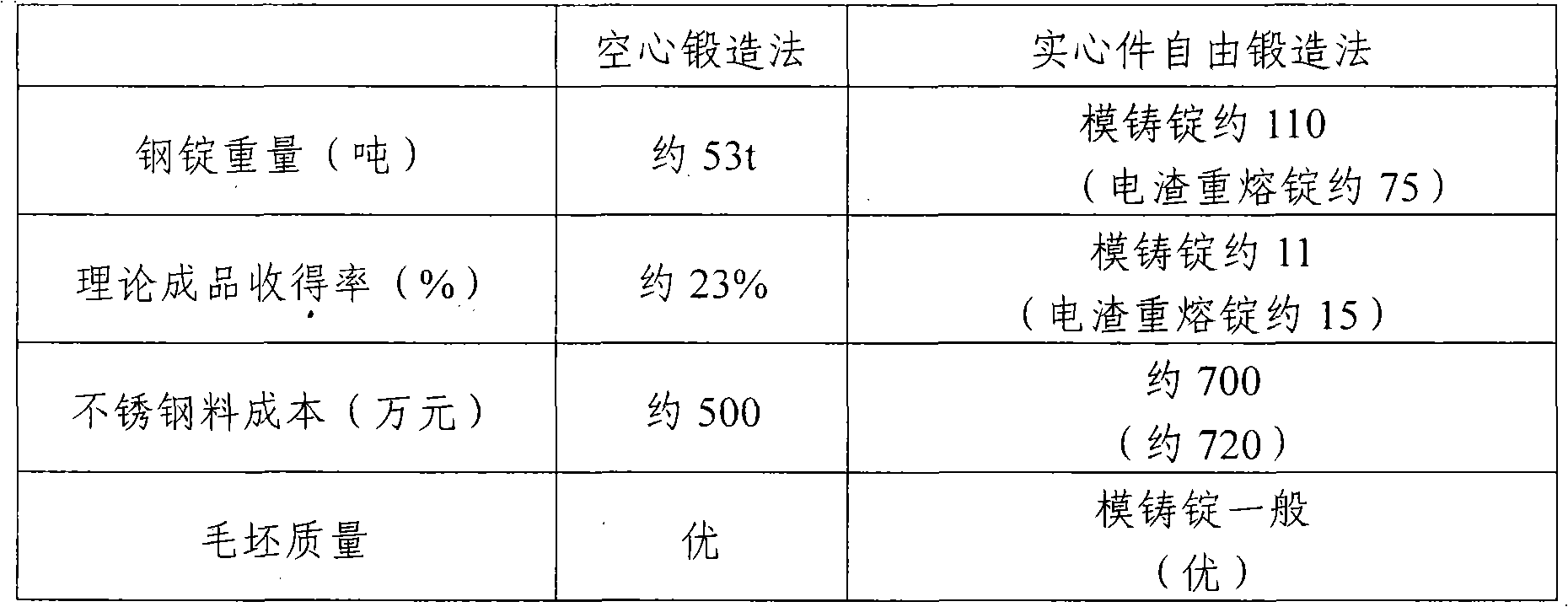
Forging molding process for integral hollow nuclear power main pipe
The invention discloses a forging molding process for an integral hollow nuclear power main pipe. The process includes steps: placing a TP316LN stainless steel hollow electroslag casting into a heating furnace to realize primary heating and heat insulation; secondarily heating after the heat insulation procedure is completed; thirdly heating after the secondary heating is completed; and forging after the third heating is completed. The forging procedure includes repeated drawing-out, necking and branching, then secondary drawing-out, tube blank molding and finally tube nozzle drawing-out and hole punching, When the temperature of a forged part is reduced to 880 DEG C during forging, the forged part needs to be returned to the furnace to be heated at a heating speed close to the temperature rise speed of the power of the heating furnace, and the temperature is kept. By the aid of the process, manufacturing cost of the nuclear power main pipe can be lowered, and the problems that the grain size is large and forging and heating are controlled difficultly due to the fact that 316LN stainless steel is austenite stainless steel and does not have allotropic transformation can be solved.
Owner:JIANGYIN NANGONG FORGING
Method for simultaneously improving strength and electric conductivity of Cu-Cr-Nb alloy
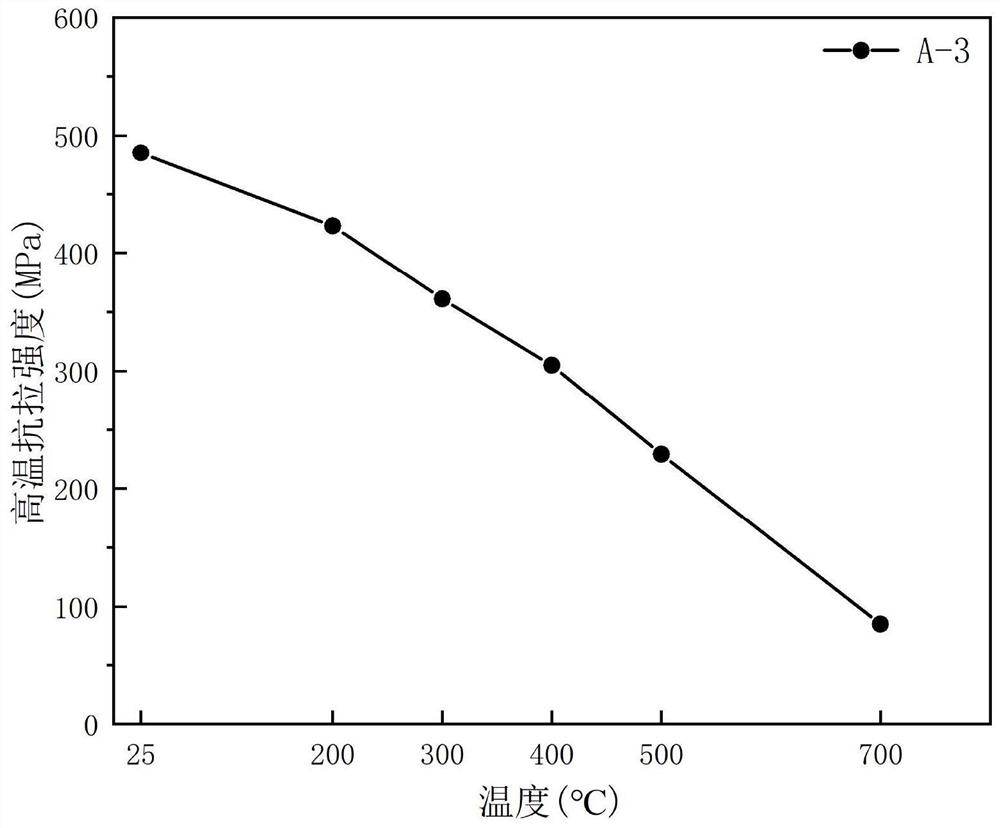
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously improving the strength and electric conductivity of a Cu-Cr-Nb alloy. The alloy comprises the components with percent by weight: 0.5-5.0% of Cr, 0.5-5.0% of Nb, 0.01-1.00% of M and the balance copper, wherein M is at least three components selected from RE, B, P, Si, Ca, Zr, Li, Mg, Ti, Ni, Fe, Sn and Mn; and RE is at least one component selected from Ce, La, Y, Pr, Nd, Sm and Sc. The Cu-Cr-Nb-M alloy is prepared through powder formation and thermo-mechanical treatment. Under the combined action of microalloying, rapid solidification, rapiddensification and the thermo-mechanical treatment, the microscopic structure of the alloy is regulated; and under the synergistic action of various strengthening mechanisms, the strength of the alloyis improved, and the comprehensive performance of the alloy is improved. The size of the second phase in the alloy prepared by using the method is smaller than or equal to 0.50 micrometer; the secondphase is uniformly distributed; the room-temperature tensile strength of the alloy is equal to or higher than 450 Mpa; and the electric conductivity is equal to or higher than 80% IACS. The tensile strength is equal to or higher than 95 MPa at the high temperature of 700 DEG C; and it is achieved that the electric conductivity and the strength of the Cu-Cr-Nb alloy are simultaneously improved andwell matched.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
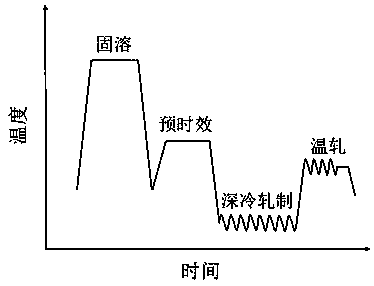
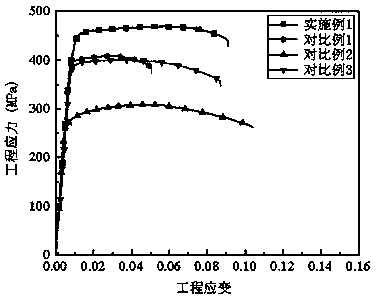
Ausforming method capable of improving mechanical property of aluminum alloy rolled plate
ActiveCN108018509AImprove acceleration performanceImprove plasticitySolution treatmentUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an ausforming method capable of improving the mechanical property of an aluminum alloy rolled plate. The ausforming method particularly comprises the following steps of (1) solution treatment, (2) preaging, (3) deep cooling rolling and (4) warm rolling. Compared with a traditional 6000 series aluminum alloy deep cooling rolled state plate, the intensity and plasticity of the aluminum alloy rolled plate machined by the ausforming method are improved significantly. Compared with a traditional peak-aging state plate, the intensity of the aluminum alloy rolled plate machined by the ausforming method is improved substantially and the aluminum alloy rolled plate and the traditional peak-aging state plate have similar plasticity. With the adoption of the ausforming method,the processes are simple, the cycle is short, the energy consumption is low, and the ausforming method has very high potential applications and value in industrial production.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
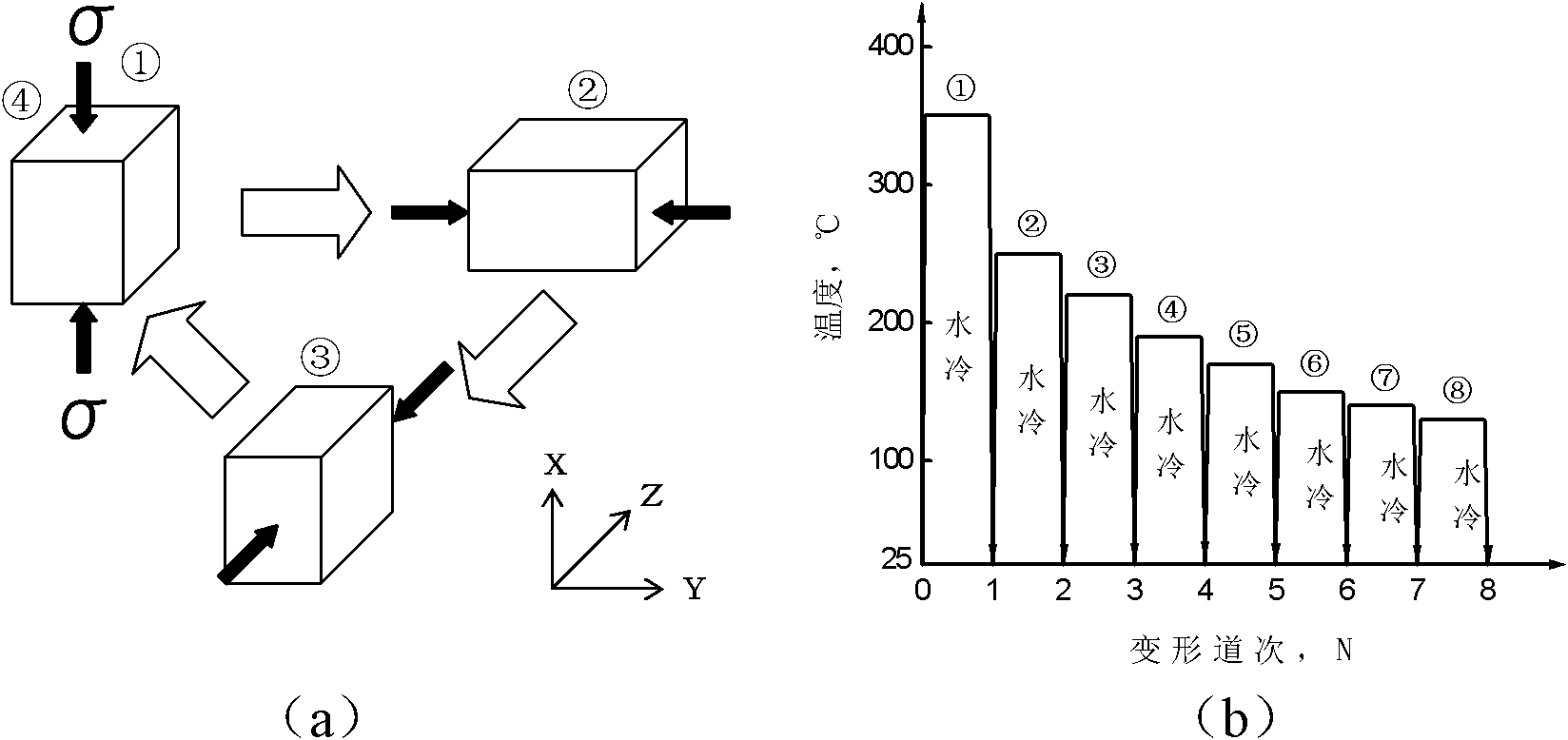
Thermomechanical treatment method for obtaining high-strength and high-toughness magnesium alloy
The invention relates to a thermomechanical treatment method for obtaining a high-strength and high-toughness magnesium alloy. The method comprises the following steps of: cutting a magnesium alloy ingot or a thermal deformation material into rectangular blocks; putting in a furnace, heating to 400-460 DEG C, keeping the temperature for 1-15 h, quenching in water and cooling; then, sequentially cooling by passes and multiaxially compressing and deforming along the three directions, i.e. the X-axis, the Y-axis and the Z-axis of the rectangular blocks from 300-460 DEG C; deforming and cooling to 10-120 DEG C for each pass and controlling the pass to have the true strain of 0.4-1 and the stress rate of 10<-4>-10<-1>s<-1>; aging for 0.5-10 h at 100-250 DEG C when the accumulated true strain is larger than or equal to 3 or carrying out cold deformation with a certain strain before aging to obtian the high-strength and high-toughness magnesium alloy with the tensile strength greater than 450 MPa and the elongation greater than 25 percent. The invention has reasonable process design, simple equipment requirement and convenience of operation, overcomes the problem that the delay is greatly reduced when the strength of the magnesium alloy is improved through grain refinement in the prior art and has favorable industrial application prospects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Thermo-mechanical treatment strengthening technology of magnesium alloy sheet
InactiveCN104451484AIncreased tensile strength at room temperatureHigh hardnessSolution treatmentHeat conservation
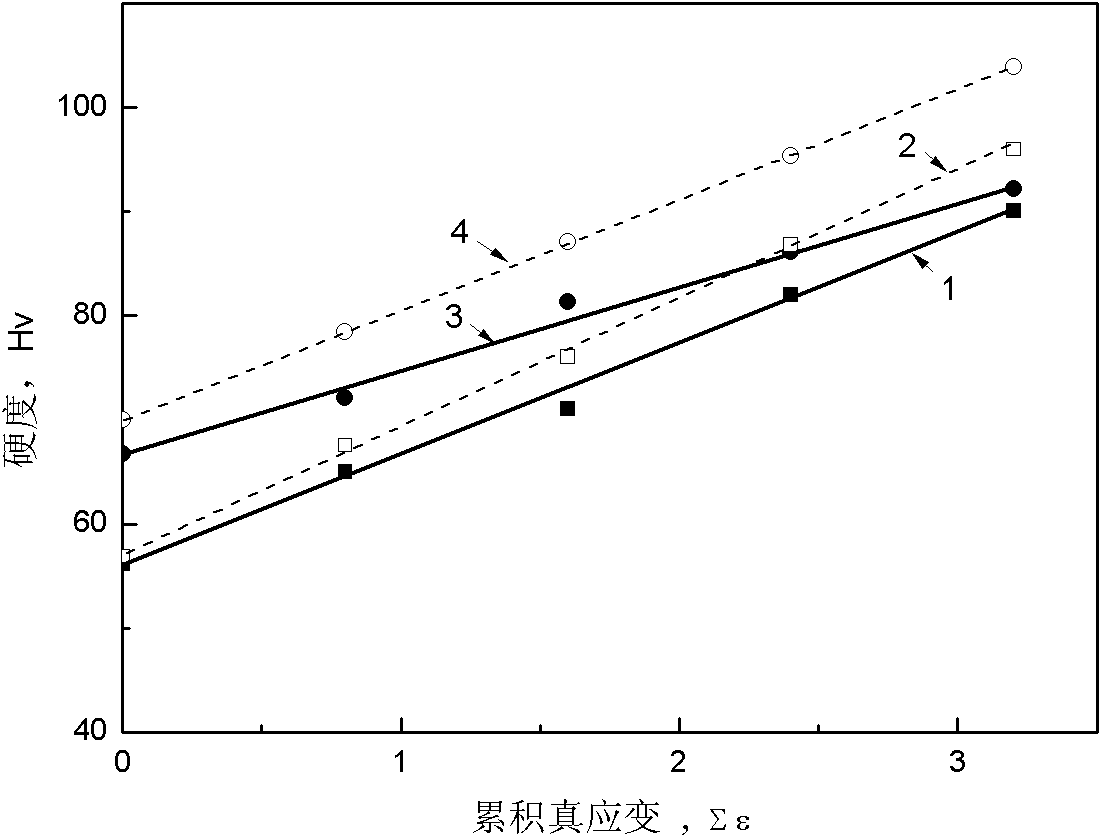
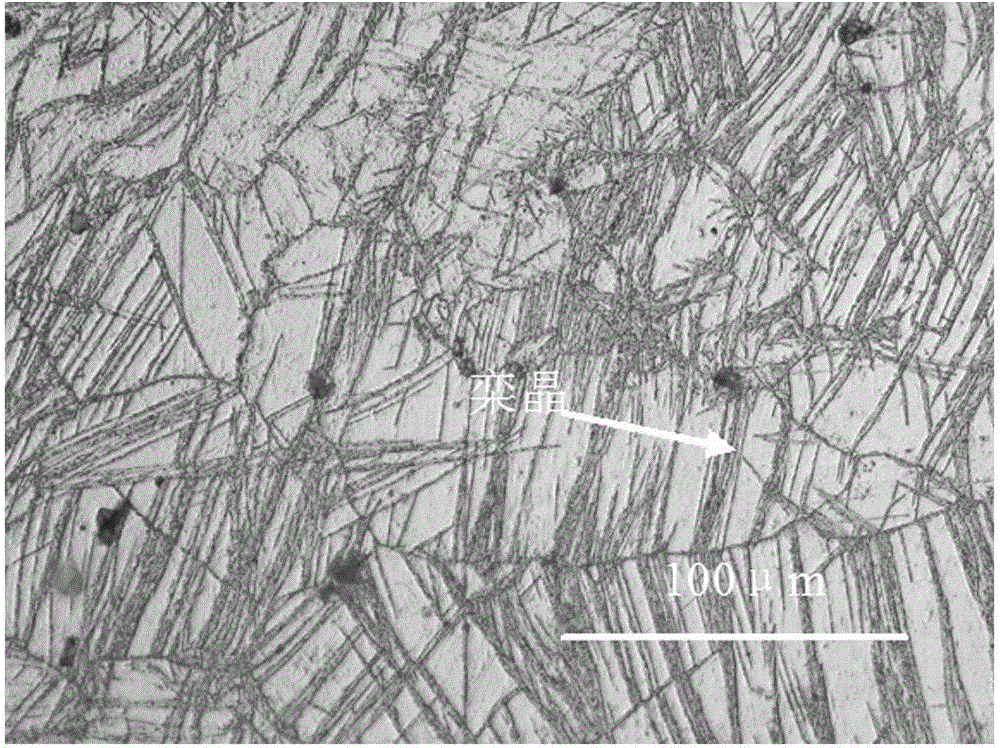
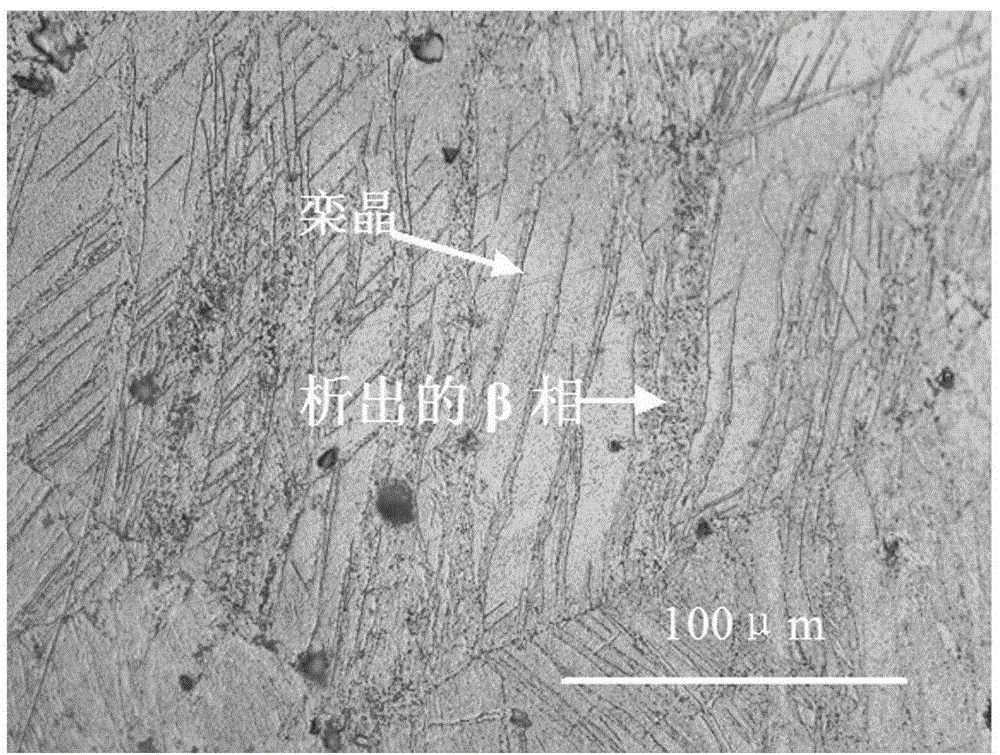
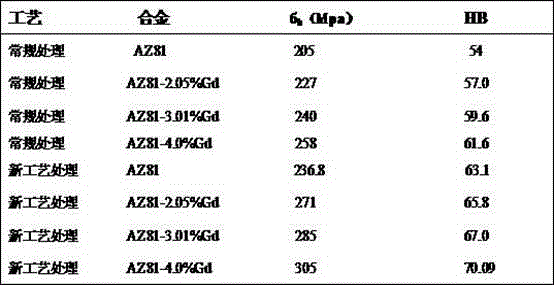
The invention discloses a thermo-mechanical treatment strengthening technology of a magnesium alloy sheet. The magnesium alloy sheet adopts an AZ81-series magnesium alloy sheet, and the thermo-mechanical treatment strengthening technology of the magnesium alloy sheet comprises steps as follows: the well-polished magnesium alloy sheet with the size of (40*40*40) mm is subjected to solution treatment, the heating temperature is 415 DEG C, and the heat preservation is performed for 20 hours; the magnesium alloy sheet is heated again to a range of 150-160 DEG C for rolling, and the deformation amount is 15%; and then the aging treatment is performed, the technological parameters include that the heating temperature is 168 DEG C and the heat preservation time is 8-16 hours, and the air cooling is performed to the room temperature. After the technological treatment, compared with the conventional heat treatment technology, mechanical properties of the alloy are improved, that is, the tensile strength sigma b of the alloy at the room temperature is improved by 15.5%-18.2%, and the hardness is improved by 12.4%-16.85%.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
High-strength high-conductivity copper alloy material, preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN111996411AHigh temperature softening resistanceReduce residual stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead frameUltimate tensile strength
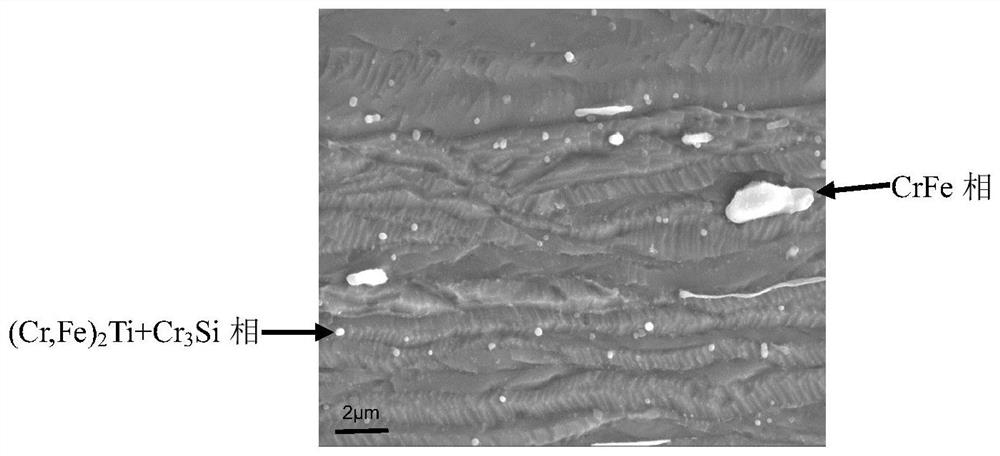
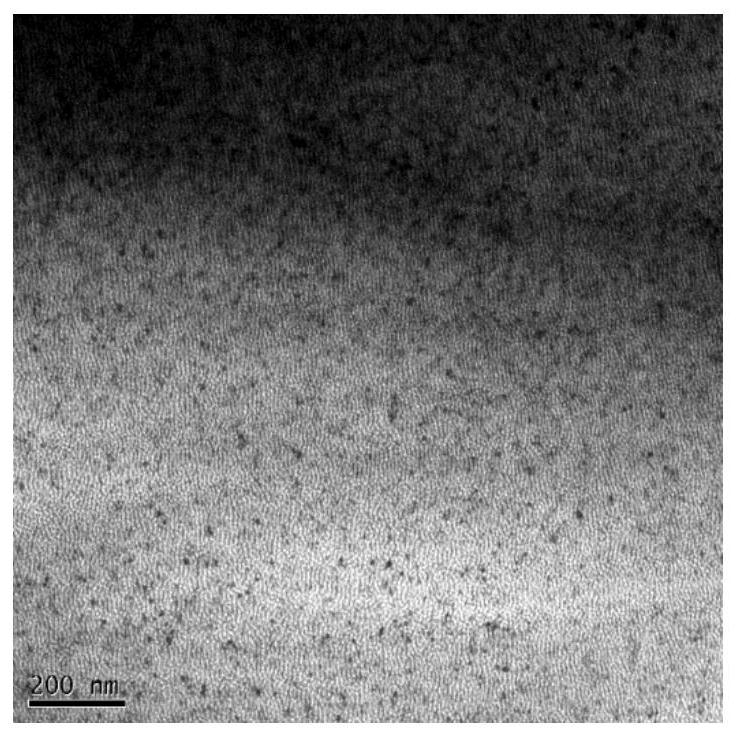
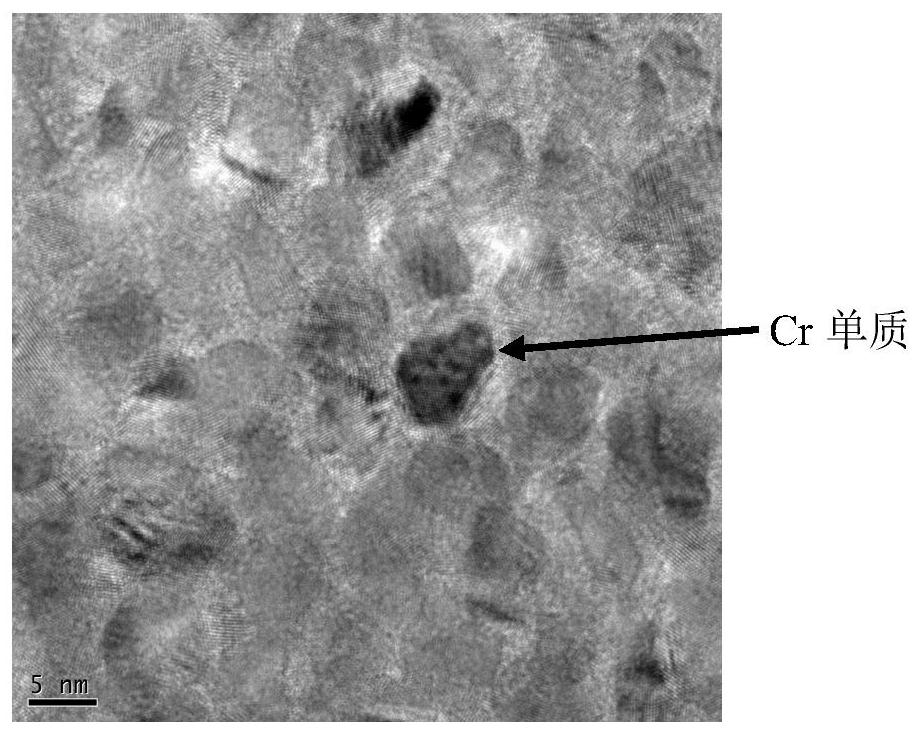
The invention discloses a high-strength high-conductivity copper alloy material. The high-strength high-conductivity copper alloy material comprises, by weight percentage, 0.3wt%-0.8wt% of Cr, 0.05wt%-0.5wt% of Fe, 0.05wt%-0.3wt% of Ti, 0.01wt%-0.1wt% of Si and the balance Cu and inevitable impurities. The high-strength high-conductivity copper alloy is prepared through the alloying design of Cr,Fe, Ti, Si and other elements and a thermo-mechanical treatment technology taking two-stage aging as a main process. By means of the control over the sizes and the densities of a CrFe phase, a (Cr, Fe)2Ti and Cr3Si composite precipitated phase and a Cr elementary substance phase in a microscopic structure of the alloy, the effects of strengthening the alloy and improving the conductivity of the alloy are achieved. The copper alloy material can be applied to large-scale integrated circuit lead frames, folding screens and other products, the yield strength of manufactured strips is 650MPa or above, the electric conductivity is 65%IACS or above, and the good high-temperature softening resistance is achieved.
Owner:NINGBO POWERWAY ALLOY PLATE & STRIP CO LTD +1
System display method of original austenite grain boundary of high-carbon high-alloy die steel
InactiveCN107121322AAccurate measurementEasy to implementPreparing sample for investigationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsAustenite grainHigh carbon
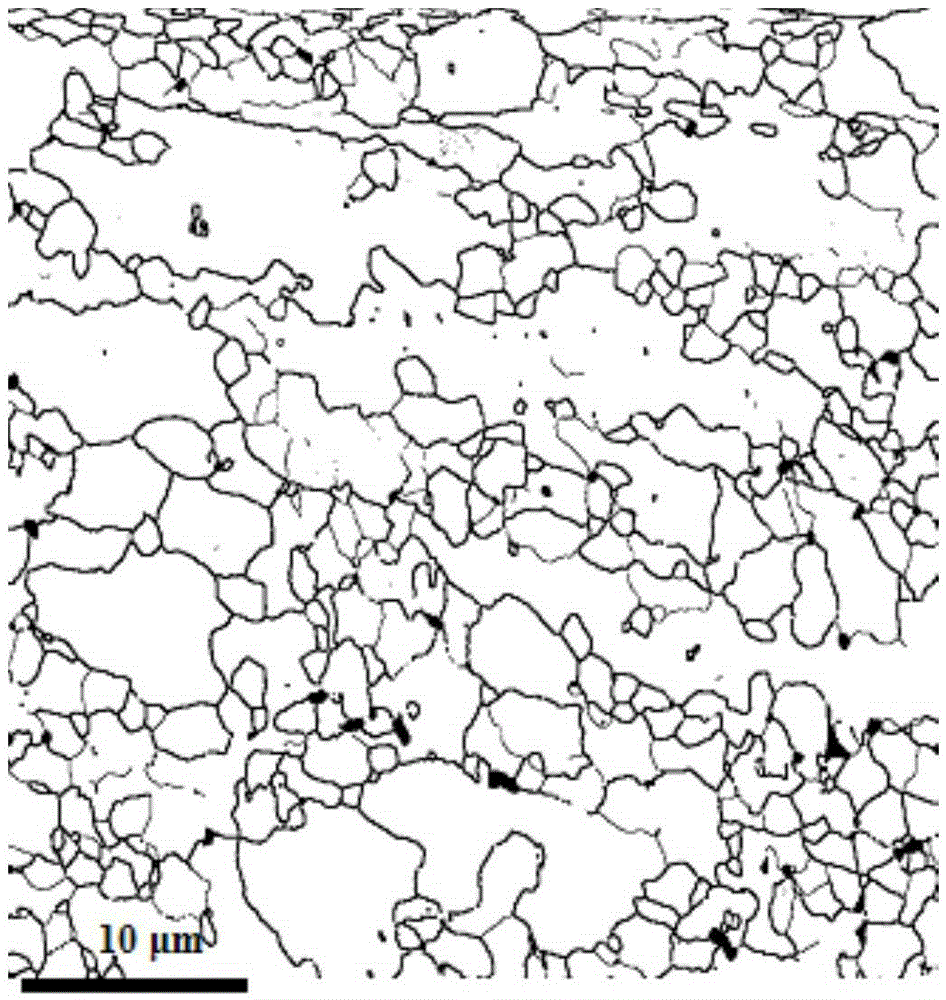
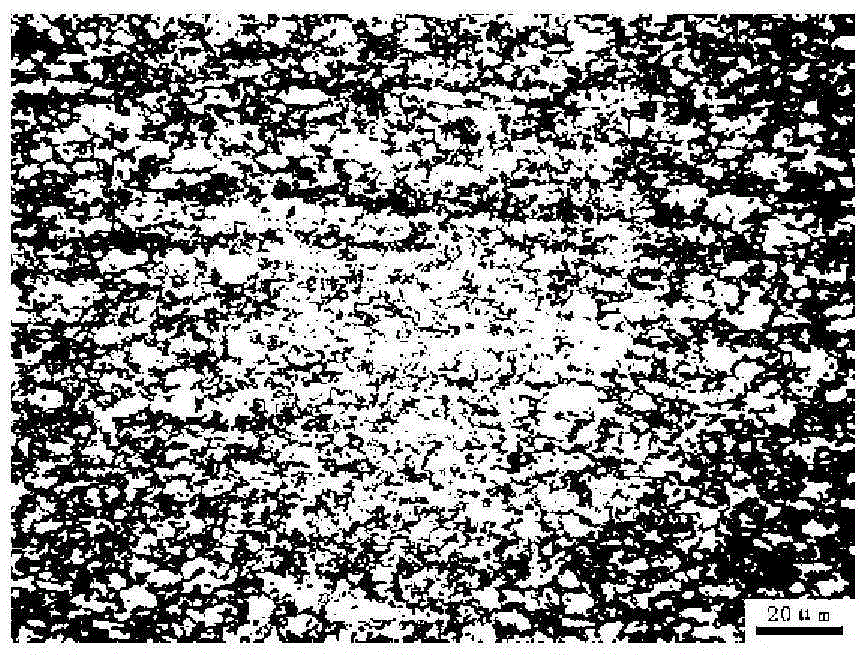
The invention discloses a system display method of an original austenite grain boundary of high-carbon high-alloy die steel. In the method, different corrosive agents are selected according to the heat treatment process of a sample; when the heating temperature exceeds 1100 DEG C, and the heat preservation time exceeds 400 s, a second metallographic etchant is selected and used; on the contrary, when the heating temperature is equal to or lower than 1100 DEG C, and the heat preservation time is within 400 s, a first metallographic etchant is selected and used; the treatment steps are as follows: sample preparation, corrosive agent preparation, sample corrosion and image acquisition. By applying the system display method disclosed by the invention, the grain boundary of the high-carbon high-alloy die steel sample under different heat treatment conditions can be systematically displayed, the original austenite grain size of the high-carbon high-alloy die steel can be clearly distinguished, the technical problem of difficult corrosion resistance and grain boundary display of the high-carbon high-alloy die steel is solved, and the measurement of the grain size and the evaluation of the grain size are greatly facilitated.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Thermomechanical treatment method for aluminium alloy grain refinement
The invention discloses a thermomechanical treatment method for aluminium alloy grain refinement. The method comprises the following steps: insulating an aluminium alloy for 30-60min for 360-460 DEG C, then cooling the aluminium alloy material to room temperature and then carrying out rolling deformation with a rolling deformation amount of 18-30%, then carrying out low-temperature annealing treatment on the pre-deformed aluminium alloy material for 24-168h at 260-290 DEG C, cooling the aluminium alloy material subjected to the low-temperature annealing to room temperature and then carrying out rolling deformation with a total rolling deformation amount of 80-96%, and finally carrying out recrystallization annealing on the rolled-formed aluminium alloy for 0.5-24h at 260-310 DEG C. The structural state of an aluminium alloy plate treated by the method disclosed by the invention is uniform and fine isometric crystals, thus 1-2[mu]m fine-grain structural state is realized; and moreover, the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristic of no limits on machining equipment, and dimensions of machined workpieces.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Thermal ageing assessment method of cast austenitic stainless steel of CPR1000 nuclear power plant
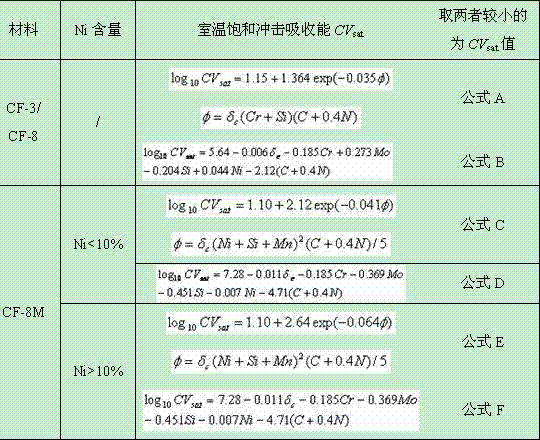
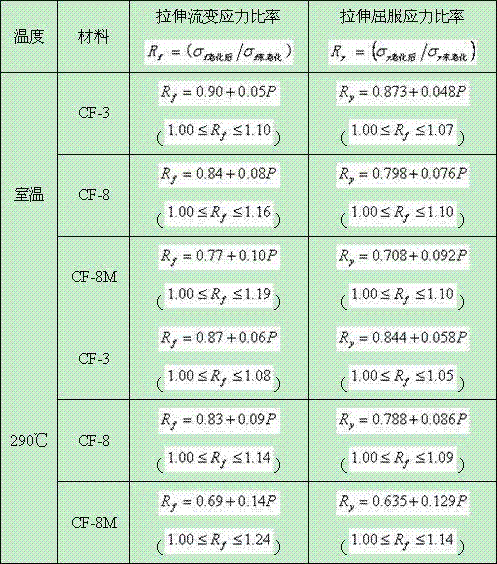
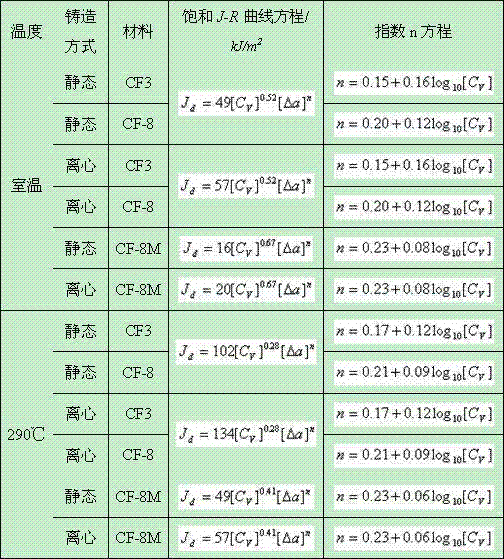
InactiveCN104777280ASolve the problem that the fracture toughness cannot be judgedImprove securityTesting metalsThermal ageingCrazing
The invention relates to a thermal ageing assessment method of cast austenitic stainless steel of a CPR1000 nuclear power plant. The method comprises the following steps: (a) analyzing the elements of the austenitic stainless steel, and calculating the equivalent chromium content Creq and ferrite content deltac; (b) checking the casting manner and the material mark of the austenitic stainless steel; (c) calculating indoor-temperature Charp impact absorption energy Cv; (d) calculating a breaking tenacity value J1C and a breaking tenacity value Jd when the crack depth is 2.5mm; (e) determining the thermal ageing state of the austenite austenitic stainless steel according to the calculated indoor-temperature Charp impact absorption energy Cv, the breaking tenacity value J1C and the breaking tenacity value Jd when the crack depth is 2.5mm. The thermal ageing sensitivity and the thermal ageing state of the austenitic stainless steel can be assessed and judged by testing the mass content of the specific elements in the austenitic stainless steel based on the casting manner and the material mark; as a result, the problem that the breaking tenacity of the stainless steel cannot be judged in the operation process of the corresponding equipment / part of the CPR1000 nuclear power plant is solved, and a key way is provided for improving the safety of the power plant.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +2
Ultrasonic inspection technology of large-size austenitic stainless steel forge pieces and application of ultrasonic inspection technology
InactiveCN105806951AQuality assuranceAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesReference testLongitudinal wave
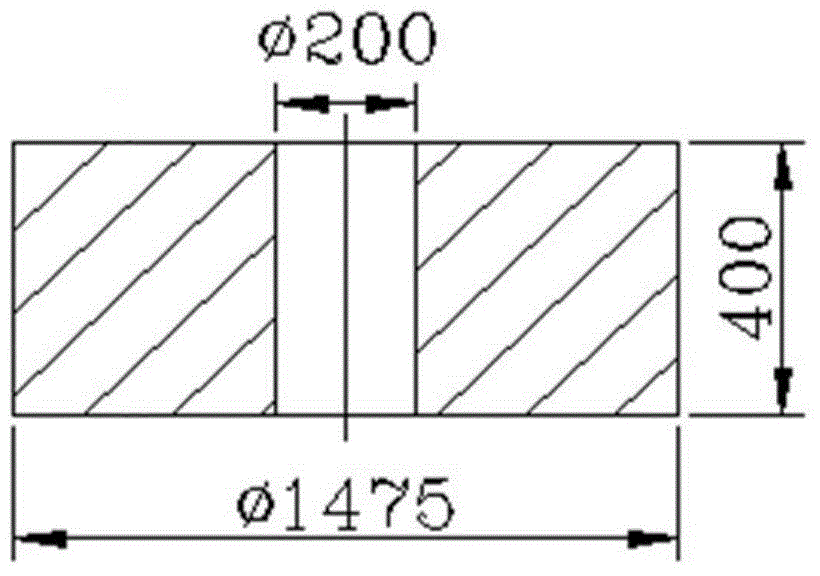
The invention discloses an ultrasonic inspection technology of large-size austenitic stainless steel forge pieces and application of the ultrasonic inspection technology, and belongs to the technical field of nondestructive testing in an equipment manufacturing industry. An ultrasonic inspection procedure of large-size thick-wall austenitic stainless steel forge pieces is formulated through selecting angles and frequency of a longitudinal wave angle probe, selecting a tapered wedge manufacturing material, designing a reference test block and the like; the technology is applied to the large-size austenitic stainless steel forge pieces with the section thickness of more than or equal to 600mm, and particularly can meet quality requirements on the austenitic stainless steel forge pieces of a nuclear power station primary loop.
Owner:SHENYANG BLOWER WORKS GRP NUCLEAR PUMP
High-uniformity tin-phosphor bronze strip preparation process
The invention belongs to the technical field of bronze strip manufacturing, and particularly relates to a high-uniformity tin-phosphor bronze strip preparation process. The high-uniformity tin-phosphor bronze strip preparation process comprises the following steps of S1, smelting, S2, casting, S3, milling, S4, homogenizing heat treatment, S5, cold rough rolling, S6, intermediate annealing, S7, cold intermediate rolling, S8, cold finish rolling, and S9, finished product annealing. According to the technical scheme, the smelting process can improve the component and structure uniformity of a casting blank, the gas content in melt can be effectively reduced, meanwhile, the components in a smelting furnace are uniformly distributed, and the burnout rate of alloy elements is low; and in the subsequent processing process, microsegregation forms such as intragranular segregation and grain boundary segregation can be eliminated by promoting the high-temperature diffusion process, a recrystallization structure is controlled and residual stress is reduced through a combined deformation heat treatment process, the microsegregation and stress distribution uniformity of the alloy is further improved, so that a tin-phosphor bronze strip with good structure and performance uniformity is obtained.
Owner:中铜华中铜业有限公司
Ultrahigh strength open section hot roll forming process and device
ActiveCN102974683AAvoid deformationHigh dimensional accuracyShaping toolsRoom temperatureRoll forming
The invention relates to an ultrahigh strength open section hot roll forming process and an ultrahigh strength open section hot roll forming device. The ultrahigh strength open section hot roll forming process comprises the following steps of: 1, uncoiling and cutting; 2, forming, i.e. transferring a sheet metal into roll forming equipment and preforming the sheet metal into a semifinished product open section under the condition of room temperature; 3, heating, i.e. heating the section to a temperature of 800 to 1,100 DEG C and preserving heat for 2min to 6min; and 4, stamping and sizing, i.e. rapidly transferring the section into a stamping die to carry out shaping and cooling, totally coating the section with a shaping die, loading the shaping die by 3 to 10 stamping racks, utilizing the die to shape the semifinished product open section into a finished product of which the size accords with the requirements after loading the shaping die, and when shaping, filling a circulating cooling medium in a passage below the surface of the die, utilizing the temperature difference of the die and the section to quench the high temperature section and cooling the open section in a pressure maintaining state to enable a microstructure of the section to be rapidly transformed from an austenite structure at a high temperature into a martensitic structure at normal temperature from an austenite structure at a high temperature so as to obtain a high strength section.
Owner:BAOSTEEL METAL
Copper alloy material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a copper alloy material and a method thereof. The high-thermal-stability copper alloy consists of the following components: 0.30-0.80 wt.% of Cr, 0.04-0.20 wt.% of Zr, 0.05-0.15 wt.% of Ti, impurities contained in pure copper, and the balance Cu. The preparation method of the alloy includes several steps: upward drawing continuous casting, cold drawing, solid solution, colddrawing, aging, and cold drawing. Trace elements Cr and Zr with little influence on the electrical conductivity of the copper alloy and a Ti element with significant influence on the strength of thealloy are selectively added. The addition of the Ti element is combined with deformation heat treatment, so the coherent precipitated phase can be stabilized, the nucleation of a bcc-Cr phase in the aging process is inhibited, the material always has the microstructure characteristics of an fcc-Cr phase coherently precipitated with a matrix, and excellent comprehensive properties can be obtained.In the premise of guaranteeing slight reduction of the electrical conductivity of the copper alloy, the mechanical properties of the alloy are greatly improved, the tensile strength reaches 630-730 MPa, the electrical conductivity reaches 65-85% IACS, and the softening temperature is still remained at 610-660 DEG C.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Twin-roll strip casting-rolling production process for superaustenitic stainless steel
The invention relates to a twin-roll strip casting-rolling production process for superaustenitic stainless steel. The twin-roll strip casting-rolling production process comprises the following steps: (1) hoisting and swinging molten steel with qualified components to a ladle turret; (2) injecting the molten steel into a tundish; (3) carrying out twin-roll casting-rolling; (4) carrying out strip billet hot-rolling; (5) carrying out strip steel cooling and head-tail removal; and (6) carrying out strip steel coiling. According to the twin-roll strip casting-rolling production process disclosed by the invention, a superaustenitic stainless steel strip is directly produced through the twin-roll casting-rolling, so that the hot-rolling procedure is simplified, and the surface layer cracking and layering cracking of superaustenitic stainless steel during hot-rolling in the prior art are avoided. Production for strips with thin gauges of 1.0-3.5mm is realized through the combination of the twin-roll casting-rolling and the hot-rolling, and qualified raw materials are provided for the subsequent cold-rolling process, so that energy consumption is reduced while the production flow is shortened.
Owner:JIUQUAN IRON & STEEL GRP
Heating, spinning and thickening method for annular outer edge of round plate
The invention discloses a heating, spinning and thickening method for the annular outer edge of a round plate. The method comprises the step of heating the annular outer edge of the round plate and the step of carrying out spinning, thickening and integral forming on the annular outer edge of the round plate. In the heating step, a heating spray gun is used for heating the annular outer edge of the round plate in the whole forming process, and the temperature of the annular outer edge of the round plate is kept above the austenite transformation temperature; in the spinning, thickening and integral forming step, a spinning wheel with an annular rolling groove is used for performing radial feeding and extruding on the annular outer edge of the round plate, and therefore single-pass and large-thickening-ratio thickening can be achieved; and the heating spray gun and the spinning wheel are matched with each other so as to constantly thicken the heated annular outer edge of the round plate. By means of cooperation of the heating step and the spinning and thickening step, the metal plasticity is improved, metal flowing is facilitated, and the gradual thickening of the annular edge is achieved while a round plate is heated. The tonnage of a spinning machine needed by forming is small, a spinning wheel die is simple, large pressure machines or forging dies are not needed, and the manufacturing cost is reduced.
Owner:HUBEI LIOHO TIANLUN MACHINERY +1
Deformation heat treatment method for toughening high-performance deformation rare-earth magnesium alloy
The invention relates to a deformation heat treatment method for toughening high-performance deformation rare-earth magnesium alloy, and belongs to the technical field of the alloy. The method comprises the following steps that 1) homogenizing heat treatment is performed; 2) pre-annealing heat treatment before deformation is performed, wherein pre-aging treatment is performed on an ingot blank needing to be extruded to deform at an extrusion temperature for 0.1h to 9h; 3) reverse extrusion deformation treatment is performed, wherein extrusion deformation treatment is performed on the pre-agedsample, the extrusion temperature is 400 DEG C to 450 DEG C, the extrusion ratio is 10:1 to 20:1, and the extrusion speed is 1 mm / s; and 4) aging heat treatment is performed, wherein T6 aging heat treatment is performed on the sample obtained after extrusion deformation. According to the deformation heat treatment method, the purposes that the toughness of the alloy can be obviously enhanced whilethe high strength is kept can be achieved, and the problem that the deformed magnesium alloy is high in strength and low in toughness is solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
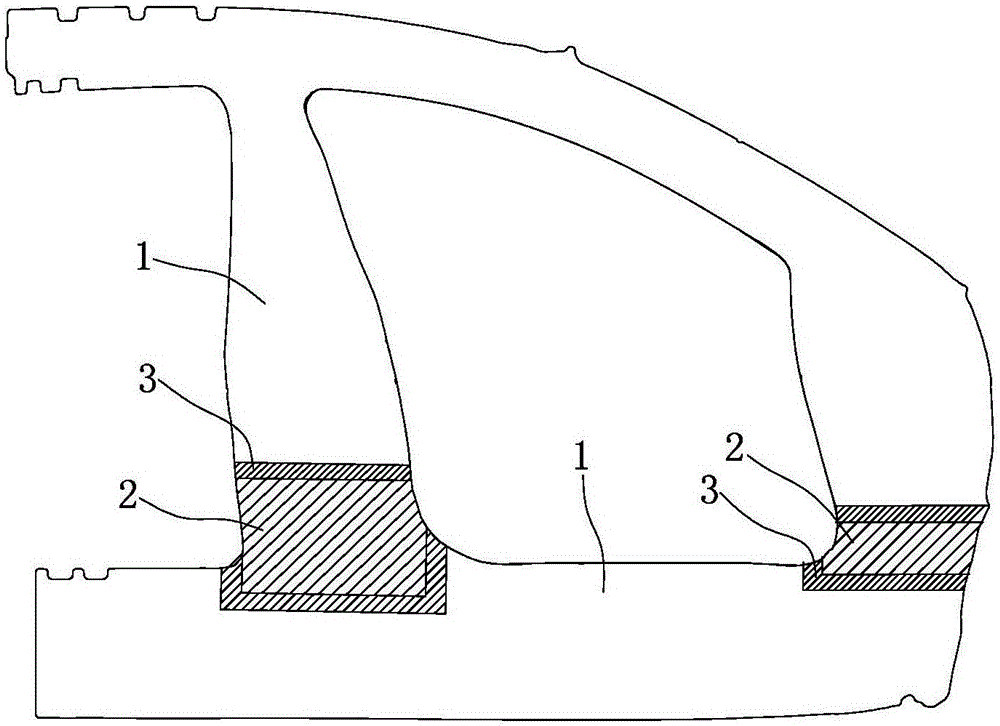
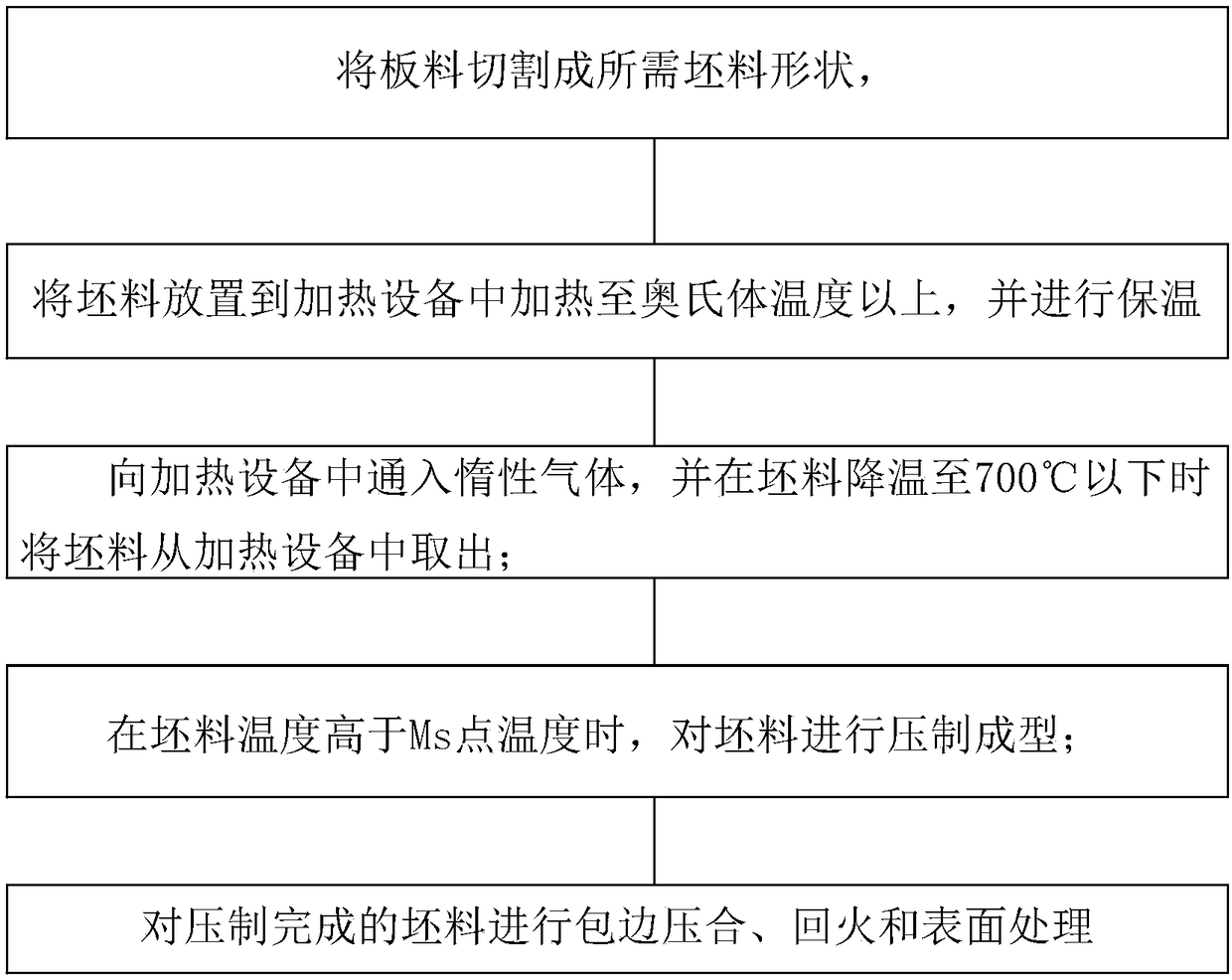
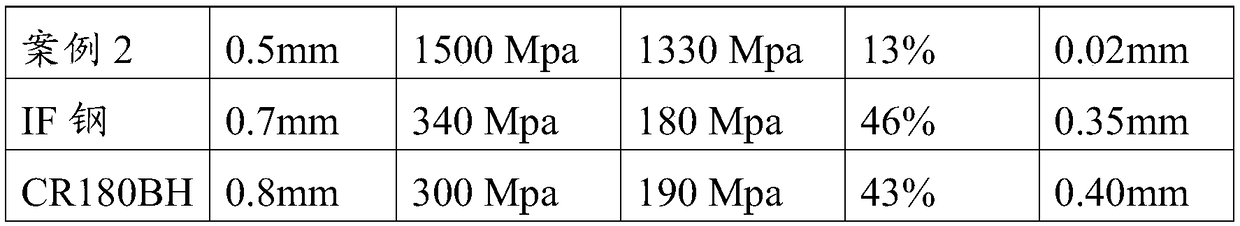
High-strength steel car outer covering part assembly and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength steel car outer covering part assembly and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the steps that a plate is cut into a needed blank shape, whereinthe plate is made from spring steel or medium manganese steel, and the plate is subjected to cold rolling treatment or cold rolling annealing acid pickling treatment; the blank is placed in heating equipment to be heated to austenitic temperature or above, and heat preservation is carried out; inert gas is introduced into the heating equipment, and the blank is taken out of the heating equipmentwhen the temperature of the blank is reduced to be below 700 DEG C; when the temperature of the blank is higher than the temperature of the point Ms, the blank is subjected to compression moulding; and the blank subjected to compression moulding is subjected to edge covering press fit, tempering and surface treatment. According to the high-strength steel car outer covering part assembly and the manufacturing method thereof, the high-strength spring steel or medium manganese steel is adopted as the car outer covering part assembly, the tensile strength ranges from 1,000 Mpa to 2,300 Mpa, the yield strength ranges from 1,000 Mpa to 1,500 Mpa, and the yield ratio ranges from 0.7 to 0.9; and the anti-dent performance is excellent, and meanwhile the thickness of the outer covering part can be reduced by 20% to 30%.
Owner:SUZHOU PRESSLER ADVANCED FORMING TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
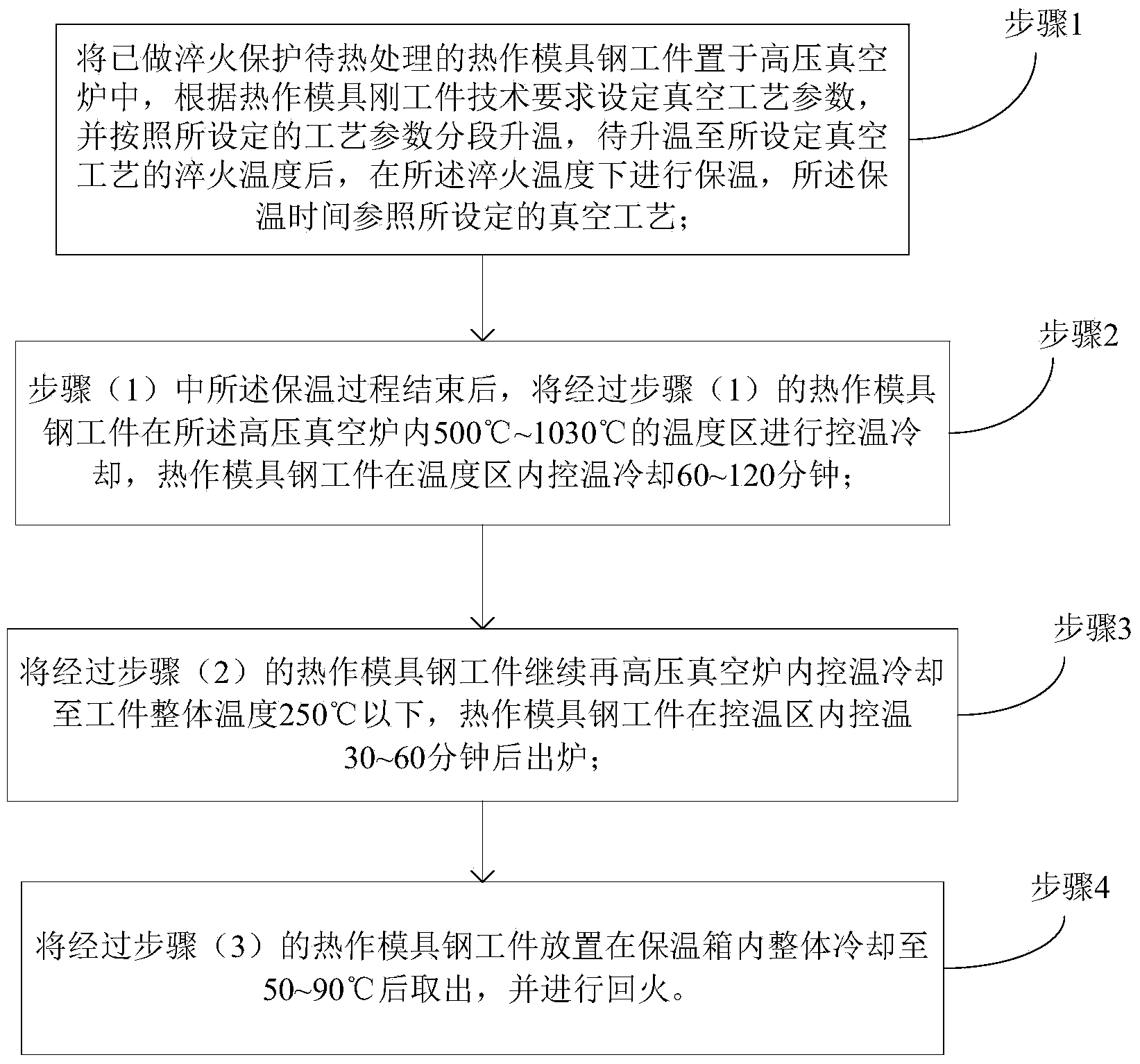
Quenching method for hot work die steel
The invention discloses a quenching method for hot work die steel. According to the method, after protection is carried out according to the shape and size of a hot working die, a hot work die steel workpiece is treated in the manner of segmented temperature-controlled cooling under the condition of a temperature above martensite initiating transformation temperature; control of temperature in a high-pressure vacuum furnace is realized by using computer analog technology, the law of changing of the rotating speed of a fan with a temperature field in the furnace is controlled to realize automatic adjusting, so temperature changes of the die in the furnace is controlled. The quenching method for hot work die steel provided by the invention fully reduces temperature difference between and thermal stress on the surface of the hot work die steel workpiece and a core material, enables influence of thermal stress on quenching deformation to be greatly weakened when a hot work die steel material transforms from an austenite structure state to a martensite structure state, reduces cracking risks of the hot work die by changing cooling rates during quenching and allows a high impact toughness value to be obtained.
Owner:FOSHAN SUMMIT NIKKA MOLD & METAL PROD CO LTD
High-specific-modulus aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-specific-modulus aluminum alloy. The alloy is prepared from, by mass, 2%-4% of Li, 1%-7% of Mn, 0.05%-0.3% of Zr, 0.0%-0.3% of Ti, 0.0%-0.3% of Sc and the balance of Al. Li and Mn are necessary elements for improving the modulus of the aluminum alloy, and Zr, Ti and Sc are grain control elements. The preparation method comprises the following steps of weighing the components according to a designed aluminum alloy component proportion, smelting in a vacuum smelting furnace, casting, molding, and carrying out thermal deformation to form a bar or a plate. The aluminum alloy with high modulus and high specific modulus is prepared by adopting a smelting casting and deformation heat treatment method and controlling the contents of alloy elements (Li and Mn) with increased modulus and the grain control elements Zr, Ti and Sc. An aluminum-manganese-lithium alloy with modulus higher than that of the existing aluminum alloy is prepared, the preparation process is simple, and the alloy can be used as a light structural material with high specific stiffness.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
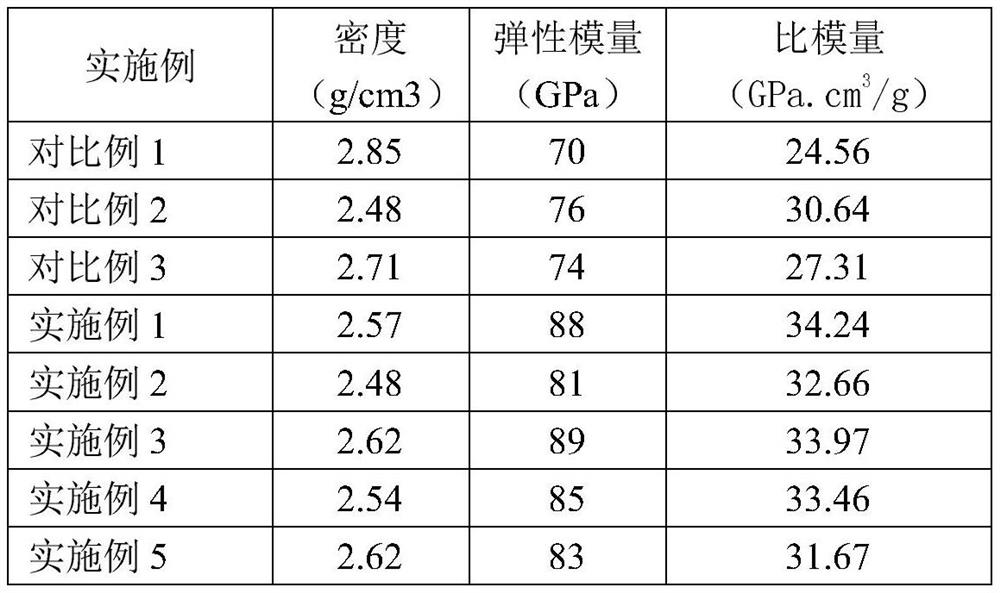
Austenitic stainless steel accurate steel strip performance prediction model and cold rolling process planning thereof
ActiveCN101320031BImprove pass rateSimplify the formulation processRoll mill control devicesTesting metalsProcess designMaterials science
The invention relates to a performance predicting model of an austenite stainless steel precise belt and a precision cold rolling process design thereof, which are characterized in that the stainless steel cold rolling board performance prediction model which is constructed through artificial neural network technology (such as Plexi neural network development environmental software) mainly comprises a data storing memory base, a computer artificial intelligent network, a final deformation degree predication module and a final deformation degree prediction value judging module. The model can implement the calculation of multivariate function according to all factors influencing the chemical properties of products, including chemical components, and the like, and implement the correction training on the performance prediction module according to collected production data to give the most appropriate final deformation degree. With the final deformation degree prediction value given by the prediction model applied, the precision cold rolling process design of the austenite stainless steel precise belt can be implemented conveniently with high efficiency and good effect. High quality austenite stainless steel precise belt finished products can be produced, the mechanical performance error of which is less than Vickers hardness of positive / negative eight units.
Owner:SHANGHAI STAL PRECISION STAINLESS STEEL
Method for improving strength and conductivity of smelted and cast Cu-Cr-Nb alloy
InactiveCN112695219ARealize direct castingHigh strengthTemperature control deviceFoundry mouldsMetal moldUltimate tensile strength
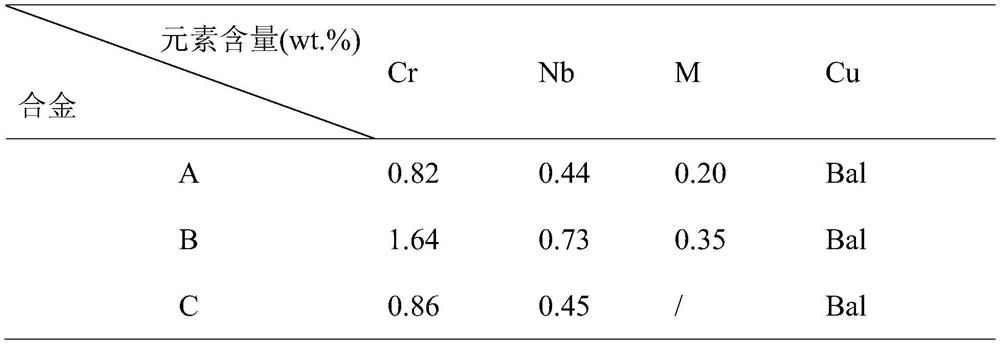
The invention relates to a method for improving strength and conductivity of a smelted and cast Cu-Cr-Nb alloy, and belongs to the field of copper alloy materials. The alloy is mainly prepared from Cu, Cr, Nb and M, the proportion of Cr is 0.5-2.5 wt.%, the proportion of Nb is 0.1-1.0 wt.%, the proportion of M is 0.1-0.50 wt.%, and the balance is copper. The M is composed of at least four elements of RE, Ag, B, P, Si, Ca, Li, Mg, Ti, Fe, Zr and Mn, and the RE is selected from at least one of Ce, La, Y, Pr, Nd, Sm, Sc, Gd and Dy. According to the method, the microalloying element M is added into the alloy, and the large-size high-strength high-conductivity Cu-Cr-Nb-M alloy which is fine in structure and uniform in component is prepared through smelting, casting and thermomechanical treatment. A metal mold is used as an inner mold and surrounds a cooling pipe, a sand mold is used as a special combined mold of an outer mold, and the melt solidification rate is increased through cooling water. By means of the combined action of M microalloying, rapid solidification and thermomechanical treatment, the structure of the alloy is regulated and controlled, the performance of the alloy is improved, a multi-scale multi-phase, fine-grain, sub-grain and dislocation entangled microstructure is obtained, direct casting forming of the large-size Cu-Cr-Nb alloy is achieved, and synchronous improvement and good matching of the strength and the electric conductivity are achieved. The process is simple, the production cost is low and the application prospect is good.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com