Technical method for identifying whether oriental fruit flies are irradiated or not
A tangerine fruit fly, irradiation technology, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, devices for capturing or killing insects, etc., can solve problems such as unseen research reports
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Effects of Irradiating Bacteralis dorsalis Eggs and Instar Larvae on Phenoloxidase Activity
[0036] The effects of γ-ray irradiation on Bacteralis dorsalis eggs and instar larvae on the phenoloxidase activity were determined, and the results are shown in Table 1, Table 2, and Table 3.
[0037] Table 1 Phenoloxidase (OD 420 value) Enzyme activity
[0038]
[0039] Note: The data in the table are mean ± standard error. Different letters after the data in the same column indicate a difference (DMRT) at the p=0.05 level; the same in the following table.
[0040] It can be seen from Table 1 that the activity of phenol oxidase in the larvae of normal Bactrocera dorsalis increases gradually with age, and the enzyme activity increases significantly on the 4th day of the larvae. The enzyme activity of the 24-hour hatched larvae of the irradiated B. dorsalis eggs was lower than that of the control, and the enzyme activity decreased more significantly with the dos...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Effect of Example 2 on the activity of superoxide dismutase after irradiation of Bactrocera dorsalis eggs and larvae of each age
[0047] The effects of irradiation on the superoxide dismutase activity of Bactrocera dorsalis eggs and instar larvae were measured, and the results are shown in Table 4-6.
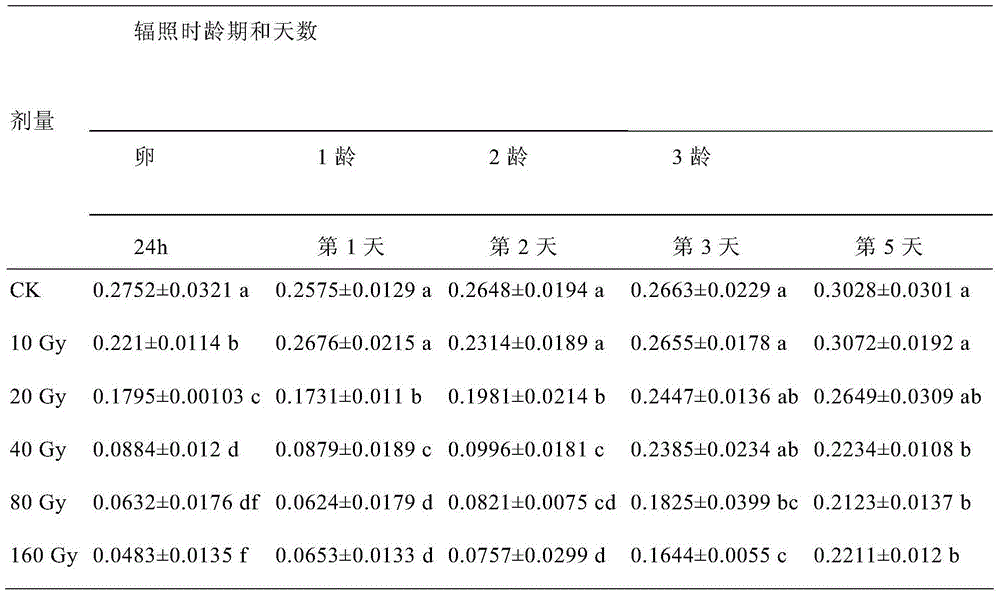
[0048] Table 4 The effect of γ-ray irradiation on the eggs of Bacteralis dorsalis for 24 hours on the activity of superoxide dismutase (OD value) in the 2-7 day old larvae
[0049]
[0050] It can be seen from Table 4 that the superoxide dismutase enzyme activity in normal Bactrocera dorsalis larvae gradually increased with age, and the enzyme activity increased significantly on the third day of larvae. The activity of superoxide dismutase in the hatched larvae of Bacteralis dorsalis eggs irradiated for 24 hours was lower than that of the control, and the enzyme activity decreased more significantly with the increase of dose, but the enzyme activity gradually recovere...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3 Effects of Irradiating Bacteralis dorsalis Eggs and Instar Larvae on Acetylcholinesterase Activity
[0059] The effects of irradiation on Bacteralis dorsalis eggs and larvae of various instars on the activity of acetylcholinesterase were measured, and the results are shown in Table 7-9.
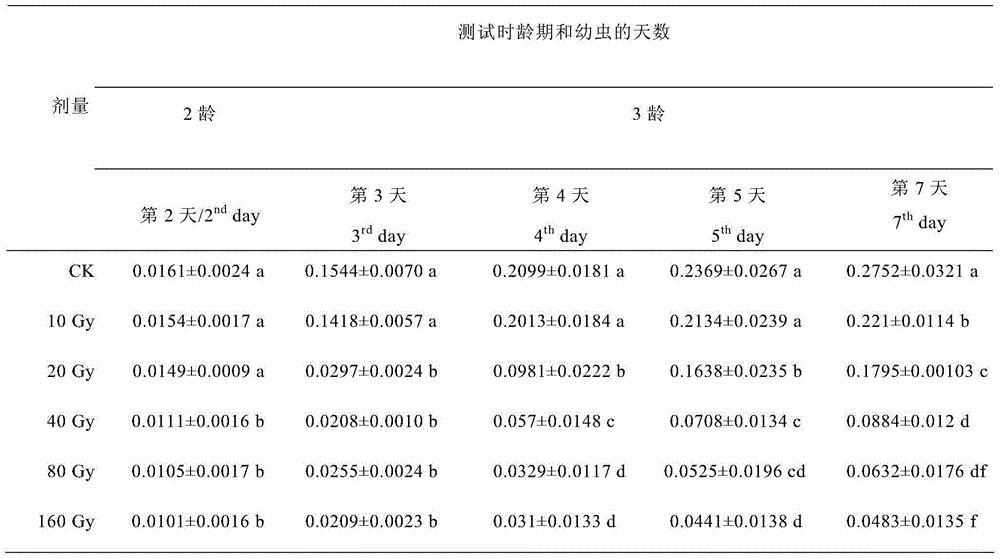
[0060] Table 7 Effects of γ-ray irradiation on Bacteralis dorsalis eggs for 24 hours on the activity of acetylcholinesterase (OD value) in 2-7 days old larvae
[0061]
[0062] It can be seen from Table 7 that the activity of acetylcholinesterase in normal Bactrocera dorsalis larvae increases gradually with age, and the enzyme activity of the larvae increases significantly on the 7th day. The changes of acetylcholinesterase activity in the hatched larvae of Bactrocera dorsalis eggs after 24 hours of irradiation were more complicated, and the enzyme activity of the 2nd instar larvae was higher than that of the control. The lower the dose, the higher the OD value of the enzy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com