Method for screening or identifying herbicide-resistant rice via agarose matrix
A herbicide-resistant and agarose-resistant technology, which is applied in the field of crop cultivation, can solve the problems of unapplied screening and identification of unknown genes, many technical links, time-consuming and labor-intensive problems, etc., and is suitable for large-scale screening or identification, with low requirements for experimental conditions. The effect of perfect technical system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
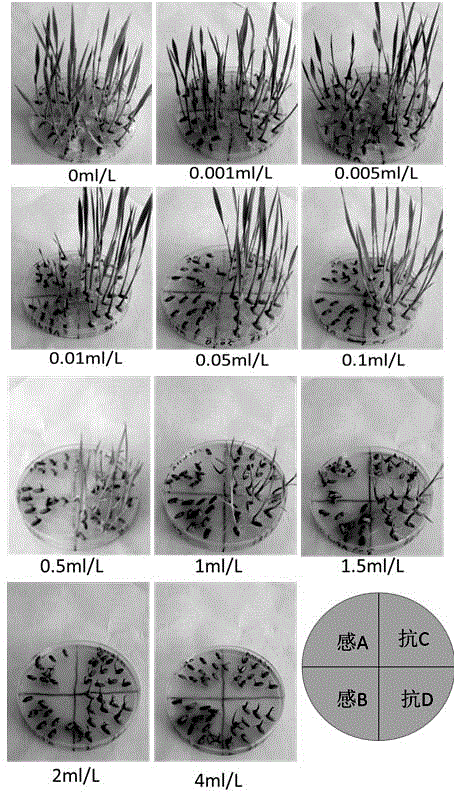
[0034] Using agarose matrix to identify methods for cultivating herbicide-resistant rice:
[0035] (1) The rice seeds to be tested were obtained
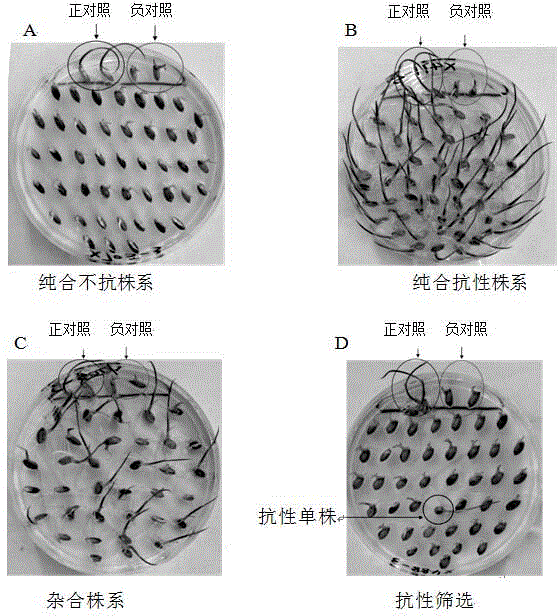
[0036] Imazethapyr-sensitive rice J1 and imazethapyr-insensitive rice Jindao 263 were sowed in the field, Jindao 263 was detasseled at the full flowering stage, and the pollen of J1 was used for hybridization to harvest F1 generation seeds. The F1 generation seeds are planted, and the F2 generation seeds are mixed; the F2 generation plants are planted on a single plant, and the F3 generation seeds are harvested from a single plant.
[0037] (2) Seed soaking and germination
[0038] Put the above 100 seeds harvested from the F3 generation in sulfuric acid paper bags, mark different individual plants, soak them in warm water at 32°C, and place them together with the container in a light incubator at 32°C to keep warm, morning, noon and evening every day. Change the water three times, and sow after 3 days of dew.
[0039] (3) Medium...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The method for screening and cultivating herbicide-resistant rice using agarose matrix:
[0050] (1) The rice seeds to be tested were obtained
[0051] Soak 1kg of Jinjaponica 28 seeds in distilled water for 5 hours, change to 1% EMS solution and soak overnight (about 12 hours), rinse with water for 4 hours, then soak in water at 32°C for overnight cultivation, and sow them in the seedling field on the second day. After growing 4-5 leaves, transplant them to the field, and obtain M1 generation seeds after maturity. Sow all M1 generation seeds, transplant single plants, and harvest M2 generation seeds on a single plant (multiple plants can be harvested in order to reduce workload).
[0052] (2) Seed soaking and germination
[0053] Put the above-mentioned 100 single-plant (or multi-plant mixed) M2 generation seeds in sulfuric acid paper bags, mark them, soak them in warm water at about 32°C, and place them together with the container in a light incubator at 32°C to kee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com