Cache optimization method and system for resisting continuous variable-domain name prefix attack
A cache optimization and domain name change technology, applied in transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as poor stability, forged data packets, and large overall impact, and achieve the effects of ensuring stability, saving space, and ensuring real-time performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047] The system of the present invention runs as a plug-in of a cache domain name server. The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings and specific embodiments.
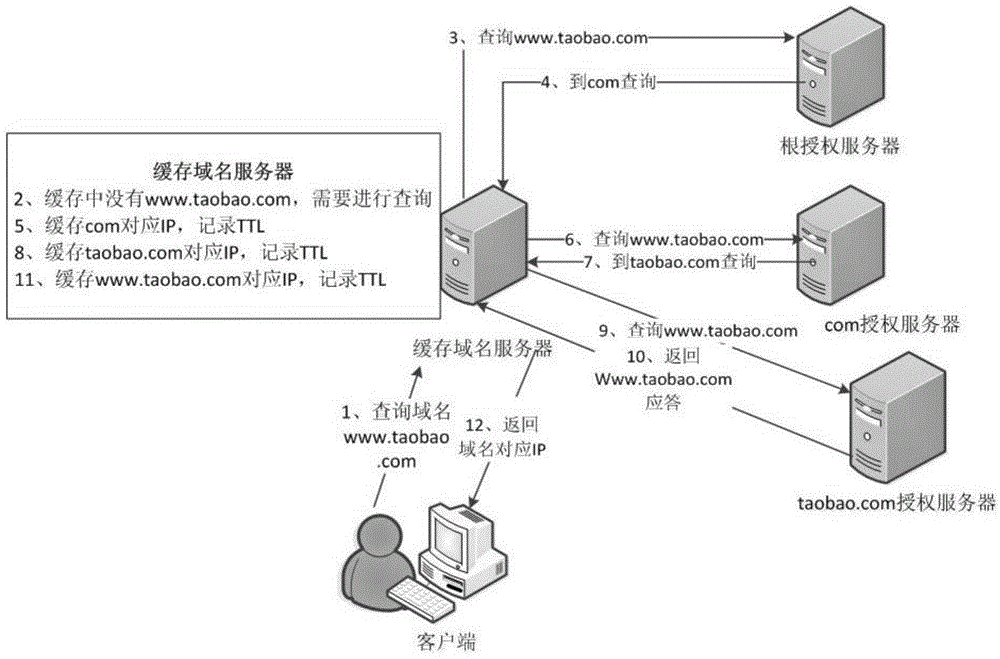
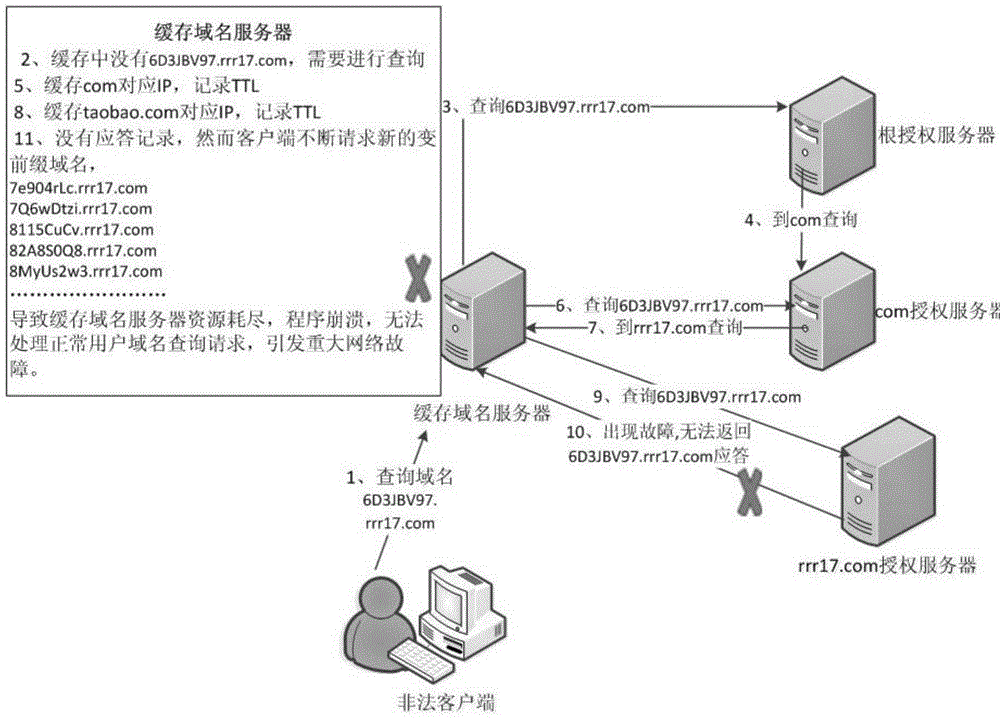
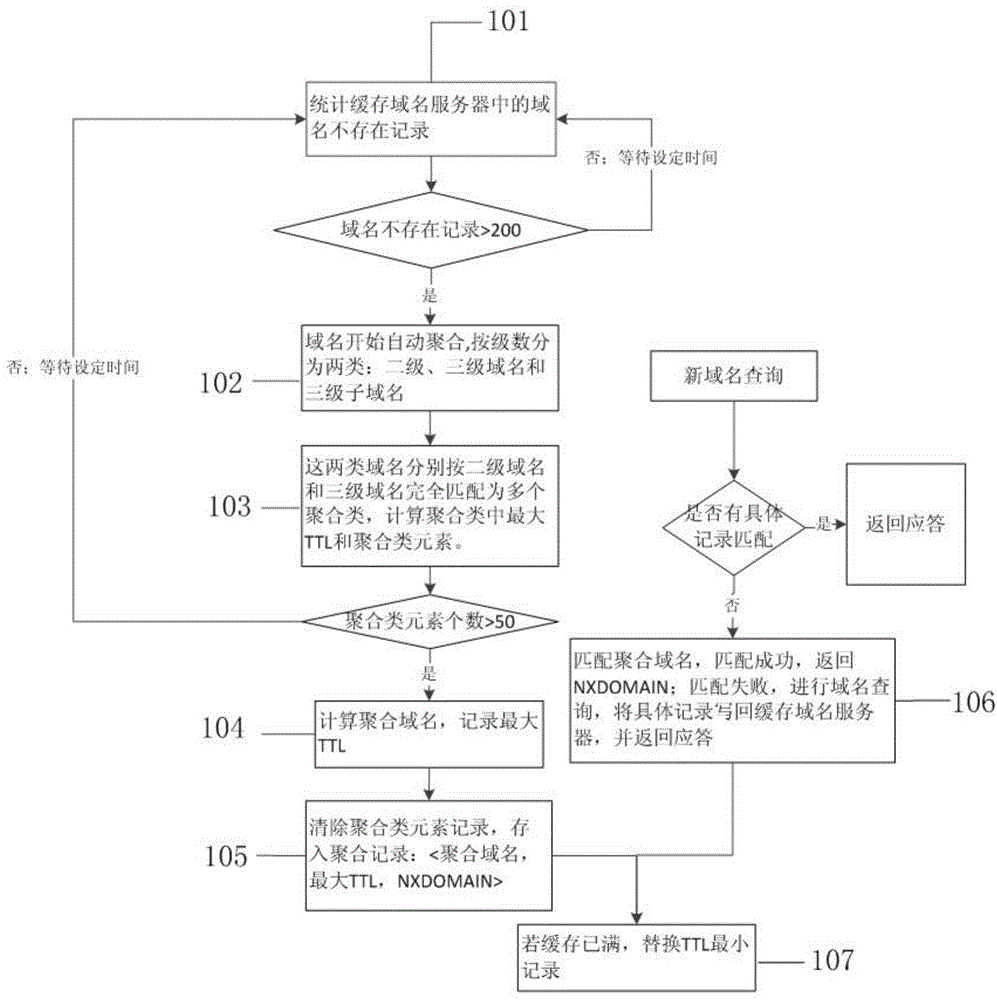
[0048] Such as image 3 As shown, a cache optimization method for caching domain name servers to resist the continuous variable domain name prefix attack, the method includes the following steps:
[0049] Step 101): Build a currently popular bind9.0 cache domain name server on the virtual machine, and optimize the cache of the bind9.0 cache domain name server. First, in order to conduct experiments, there must be a data set that matches reality. We use the second-level domain name (rrr17.com) and third-level domain name (1.499aa.com) of the website being upgraded to randomly generate 100,000 invalid variable prefix third-level domain names (*.rrr17.coms) and 100,000 invalid variable prefixes. Prefix the fourth-level domain name (*.1.499aa.com), from which 300 domain names are r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com