Manufacturing method of oxide semiconductor thin film transistor array substrate
A technology of oxide semiconductors and thin film transistors, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, and photolithography on patterned surfaces, etc. It can solve problems such as rising production costs and complex manufacturing processes, and achieve improved performance and low process temperature. , The effect of streamlining the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
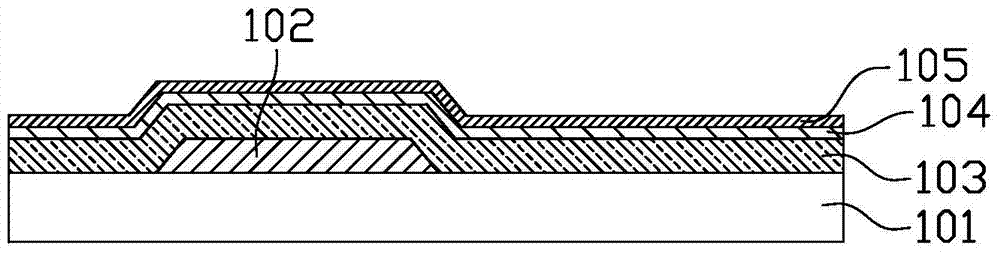
[0045] Figure 1 to Figure 8 It is a schematic cross-sectional view of the manufacturing process of the oxide semiconductor thin film transistor array substrate in the first embodiment of the present invention, and the manufacturing method includes:
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, firstly, a gate 102 is formed on a base substrate 101 . Specifically, the base substrate 101 is, for example, a transparent glass substrate, and the gate 102 can be fabricated and formed on the base substrate 101 through a photolithography process. The photolithography process mainly includes film layer deposition, photoresist coating, exposure, development, and etching. , Photoresist removal and other processes are well known to those skilled in the art and will not be repeated here.
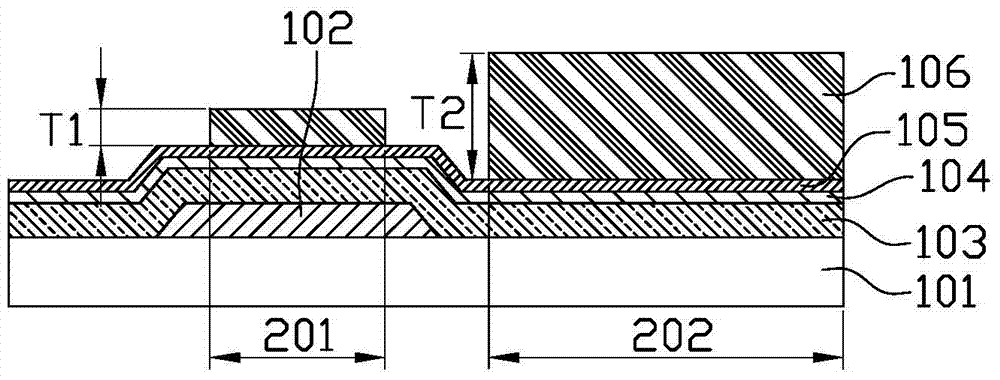
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, a gate insulating layer 103 , an oxide semiconductor layer 104 , and a pixel electrode layer 105 are sequentially deposited on the gate 102 to form. The material of the gate ...
no. 2 example
[0071] Figure 9 to Figure 11 It is the second embodiment of the present invention, which differs from the first embodiment in that its TFT device adopts an etch barrier structure, that is, the oxide semiconductor layer 104 and the source electrode in the active layer region 201 are compared with the first embodiment. 111 . An etch stopper layer (ESL) 115 is added between the drain electrodes 112 to protect the semiconductor channel of the active layer from being damaged by the etching process of the source-drain metal layer. The process before forming the etching stopper layer 115 in this embodiment is common to that of the first embodiment, please refer to the description of the corresponding process in the first embodiment and Figure 1 to Figure 6 .
[0072] Before the etching stopper layer 115 is formed, it is preferable to perform etching damage repair treatment on the oxide semiconductor layer 104 as the active layer, such as adding O2 plasma treatment, N2O plasma trea...
no. 3 example
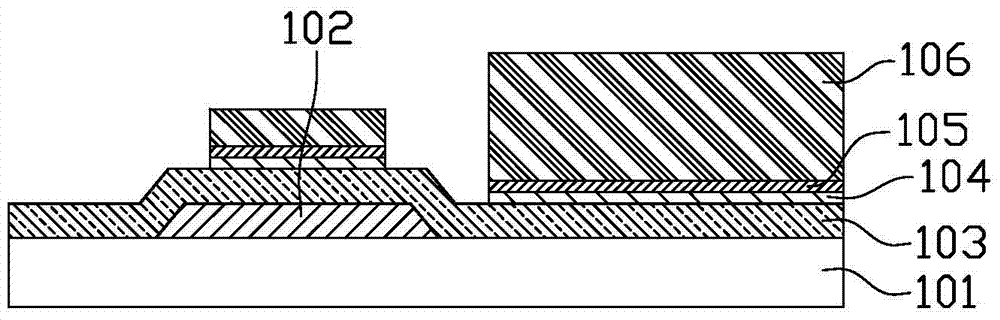
[0079] Figure 12 to Figure 18 It is the third embodiment of the present invention, which differs from the first embodiment in the half-exposure process of the photoresist 106 coated on the pixel electrode layer 105 and the structure on the active layer.
[0080] Such as Figure 12 As shown, when the photoresist 106 is half-exposed, the half-exposed area is changed from the entire active layer area 201 to the TFT back channel area, that is, only the TFT back channel area is half-exposed, which is equivalent to reducing the half-exposure area. In other words, the active layer region 201 can be divided into three sub-regions: the middle, the left and the right. The middle region corresponds to the TFT back channel region. In this embodiment, only the active layer region 201 located in the middle The photoresist 106 on the active layer region 201 is half-exposed, and the photoresist 106 on both sides (left and right) of the active layer region 201 is normally exposed (fully exp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com