Zero-power-consumption switching circuit
A switching circuit and zero-power consumption technology, applied in the field of zero-power switching circuits, can solve the problems of unfavorable equipment, such as the use of handheld devices, cumbersome operation, and large capacitance, and achieve convenient volume and appearance requirements, simple and convenient operation, and material selection volume. small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
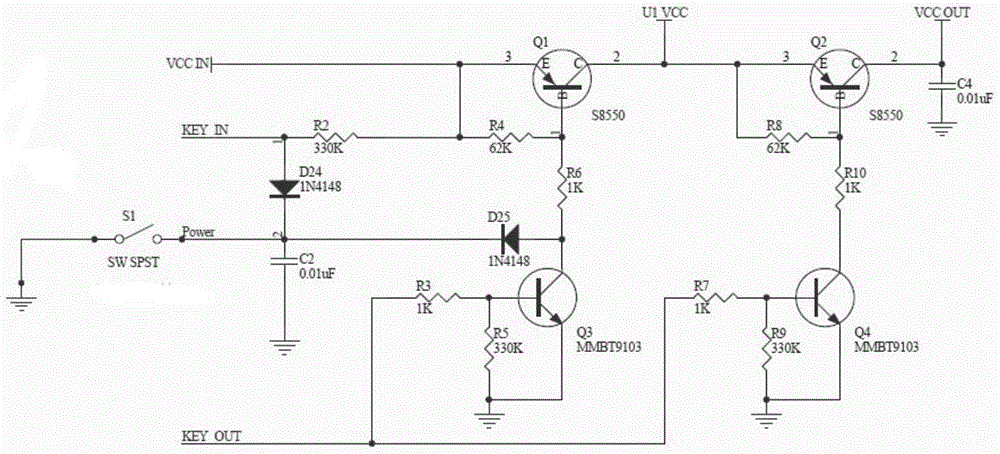
[0023] Such as figure 1 , Figure 4 As shown, a zero power consumption switching circuit includes a first triode Q1, a second triode Q2, a third triode Q3, and a fourth triode Q4, and the first triode Q1 and the second triode The second transistor Q2 is a PNP transistor, the third transistor Q3 and the fourth transistor Q4 are NPN transistors,
[0024] The input terminal VCC IN of the main power supply is connected to the emitter of the first triode Q1, and the fourth resistor R4 which acts as a bias is connected between the input terminal of the main power supply and the base of the first triode Q1. The collector of the transistor Q1 is connected to the emitter of the second triode Q2, and the eighth resistor R8 which acts as a bias is connected between the collector of the first transistor Q1 and the base of the second transistor Q2. The collector of the transistor Q2 is used as the output terminal of the switch circuit;
[0025] The collector of the first triode Q1 is co...
Embodiment 2
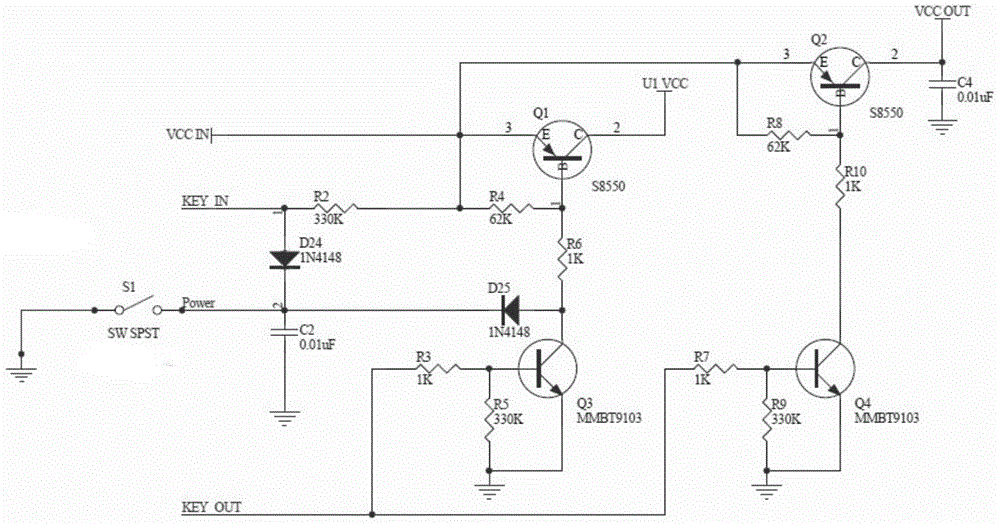
[0039] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the emitter of the second transistor Q2 and the eighth resistor R8 are disconnected from the collector of the first transistor Q1 and directly connected to the input terminal VCC IN of the main power supply. Above, others are consistent with Embodiment 1. This embodiment skips the first triode Q1 by skipping the power-taking position of the output terminal VCC OUT of the switch circuit, and directly takes power from the input terminal VCC IN of the main power supply. If it is large Current working circuits can use this circuit, which minimizes the current consumption on the circuit.
Embodiment 3
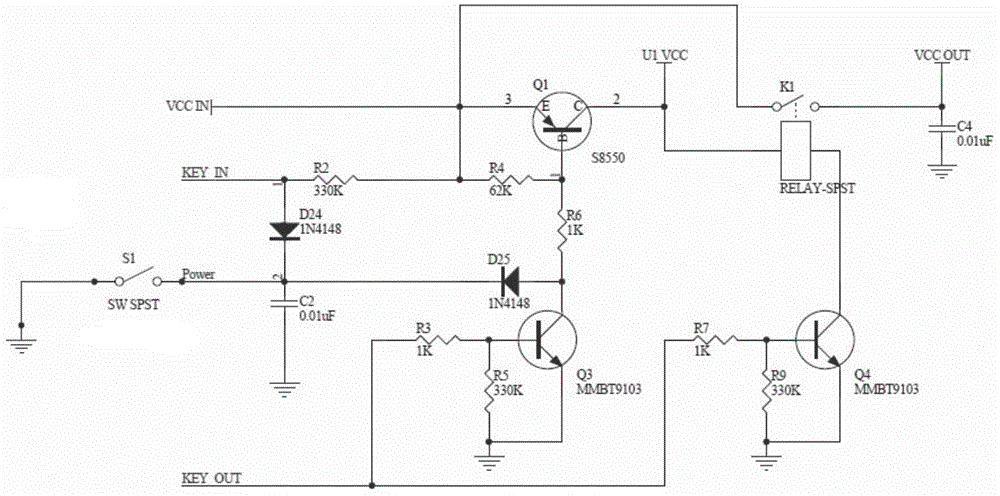
[0041] The difference between this embodiment and the above two embodiments is that the second triode Q2 is replaced by a relay, and the control coil of the relay is connected to the collector of the first triode Q1 and the fourth triode Between the collectors of Q4, the switch K1 controlled by the relay control coil is connected between the input terminal VCCIN of the main power supply and the output terminal VCC OUT of the switch circuit, and the others are consistent with the above-mentioned embodiments. In this embodiment, a relay is used as a circuit for taking power from the system, which can be expanded and used in industrial high-current or high-voltage fields.
[0042] Preferably, the second triode can also be replaced with other controllable electronic components such as field effect transistors or photocouplers, and the control connection methods thereof are well known to those skilled in the art.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com