Droop control method of DC converter with function of secondary adjustment of adaptive impedance
A DC converter and secondary regulation technology, which is applied in parallel operation of DC power supplies, can solve the problems of low steady-state and dynamic current sharing accuracy and poor drooping current sharing effect of parallel DC converters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
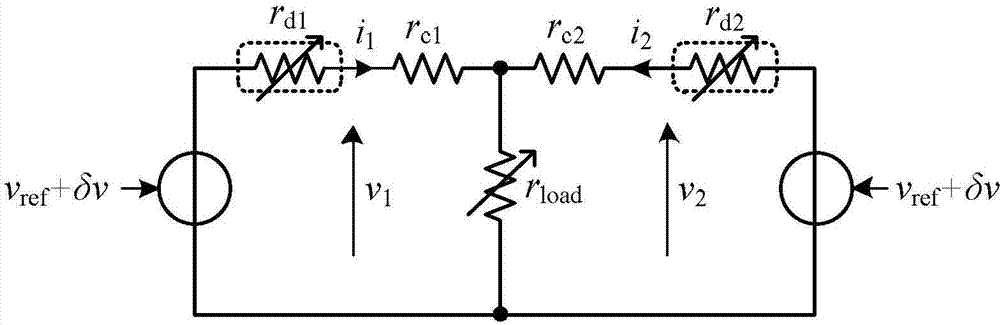
[0038] Specific implementation mode one: refer to Figure 4 Specifically illustrate the present embodiment, the DC converter droop control method with adaptive impedance secondary adjustment described in the present embodiment, it comprises the following steps: secondary control adjustment step and droop control step;
[0039] The secondary control adjustment steps are:
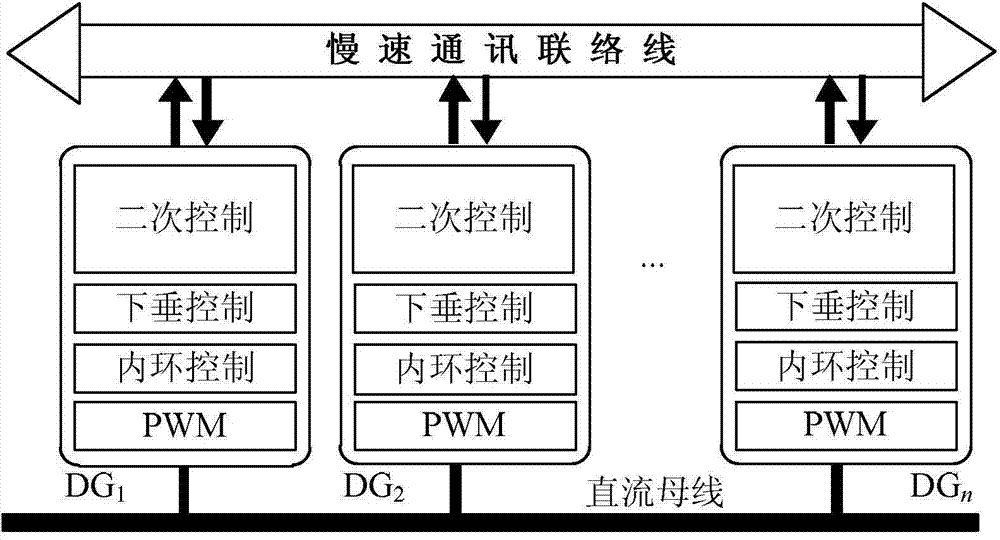
[0040] The output voltage, current and droop coefficient of each converter in the DC distributed power supply system are collected through the slow communication line, and then the average output voltage v of the converter in the system is calculated respectively avg , the average amount of output current i avg and the average amount of droop coefficient r avg ;
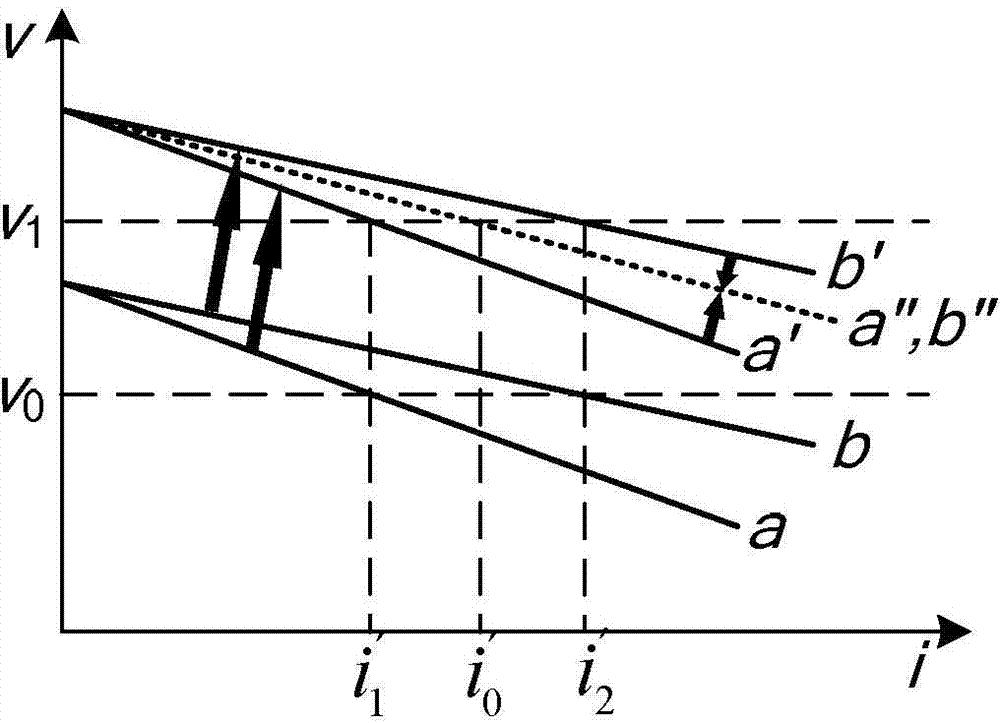
[0041] The average output voltage v avg and bus voltage given value v ref After making a difference, the average voltage adjustment is performed on the obtained difference Δv to obtain the drooping curve translation amount δv;
[0042] The avera...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0071] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of the DC converter droop control method with adaptive impedance secondary adjustment described in specific embodiment 1. In this embodiment, before all steps, the following steps are carried out :
[0072] Step 1: Keep the output voltage of the converter at a given reference value;
[0073] Step 2: Design the given value of the droop coefficient according to the converter capacity, quantity and allowable range of the bus voltage;
[0074] Step 3: Build a system slow communication network, so that each converter can send its own voltage, current and droop coefficient to other converters, and at the same time receive information such as voltage, current and droop coefficient of other online converters.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0075] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is to further explain the droop control method of DC converter with adaptive impedance secondary adjustment described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the DC converter droop control method is also Including inner loop control steps, the steps are as follows:
[0076] The given reference of the voltage outer ring and the output voltage v of the nth converter DGn The difference is sent to the voltage control loop, and the voltage control loop outputs the fourth intermediate variable V 4 ;
[0077] The fourth intermediate variable V 4 and the current i flowing through the boost converter diode D o The difference is sent to the current control loop, and the signal output by the current control loop passes through the PWM generator to drive the switching tube of the boost converter.
[0078] The function of the inner loop control is to adjust the output voltage of the boost converter to be stable near a given reference value.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com