Pilot frequency dynamic allocation method of multi-cell large-scale MIMO system
A technology of pilot frequency allocation and dynamic allocation, applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, network planning, space transmit diversity, etc., which can solve the problem of not fully considering the difference between cell edge users and cell non-edge users, and it is difficult to distinguish cell edge users. In order to improve the accuracy of channel estimation, reduce pilot pollution, and improve equality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
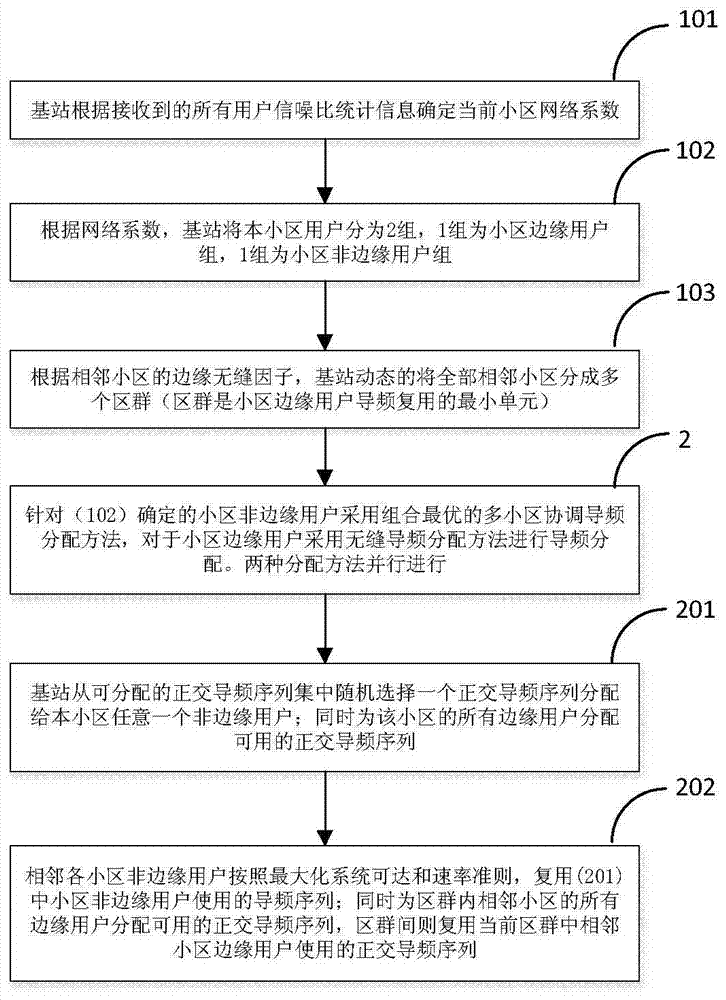
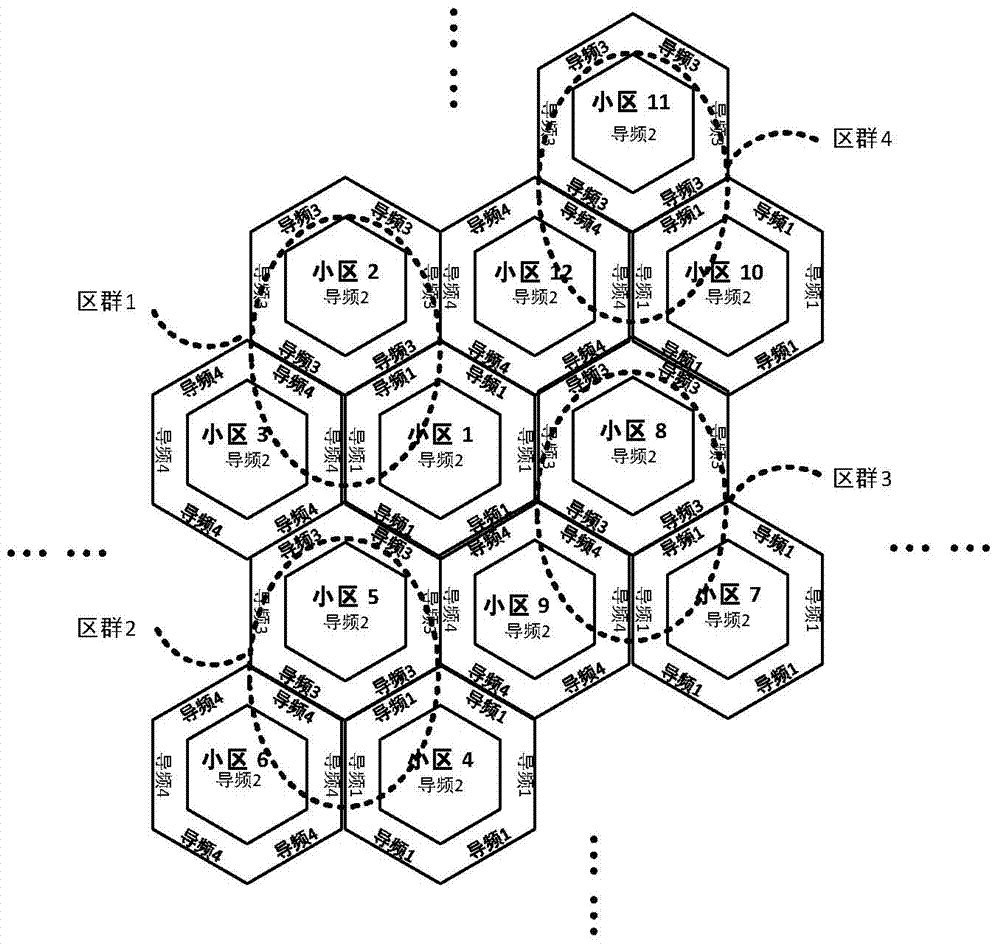
[0023] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the drawings:
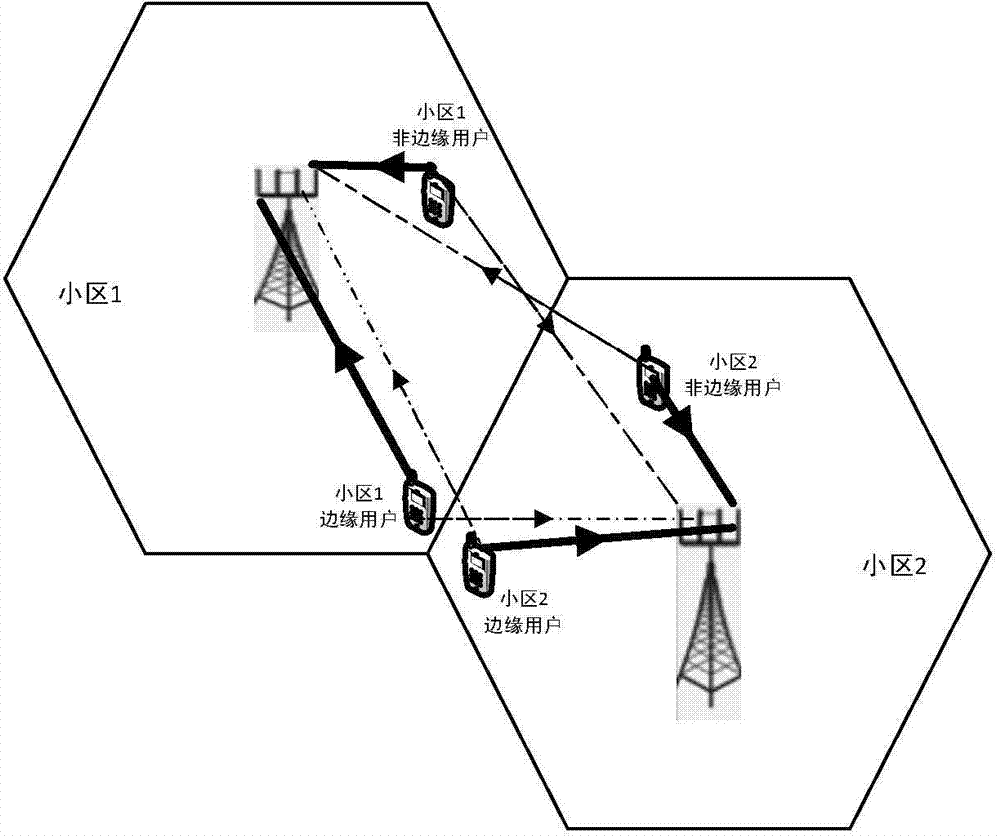
[0024] figure 1 It is the basic model of multi-cell massive MIMO system. There are a total of L cells in a multi-cell massive MIMO system. There are M antennas at the base station, which serve k at the same time. j A single antenna user, the number of base station antennas is far greater than the number of users served by the base station at the same time, namely k j Where H jl Represents the channel matrix composed of uplink channels between the base station in cell j and all users in cell l, Represents the additive Gaussian noise received by the base station in cell j, S l ={S l1 ,S l2 ,...,S lτ } Represents a training sequence of length τ. The base station obtains the estimated value of the channel vector of each user according to the received training signal: Represents the estimated value of the uplink channel between user k in cell j and base station in cell j, which obeys t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com