Managing method for free block of Java card
A management method and technology of free blocks, applied in data processing applications, instruments, payment architecture, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency and long transaction time, and achieve the effect of improving execution efficiency and improving operation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] The storage method of the free block information table is as follows:
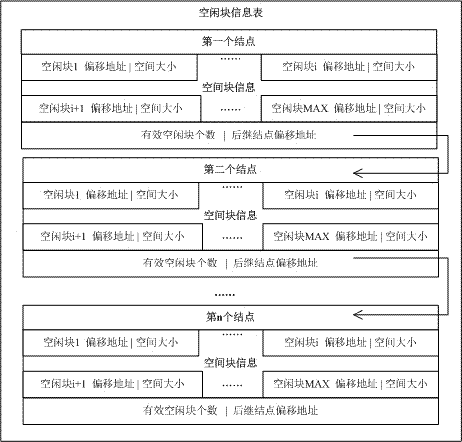
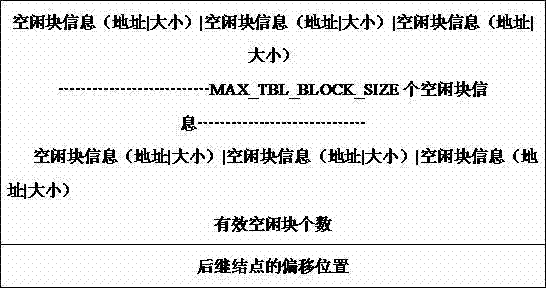
[0074] (1) The free block information table adopts a chain storage structure. When the free block information stored by a node reaches the maximum number of MAX_TBL_BLOCK_SIZE, a successor node is created and the address of the successor node is written into the information of the current node; each node The node consists of three parts: free block information, the number of free blocks, and the address of the successor node. The free block information consists of two parts: address and size, as shown in Table 1:
[0075] Table 1 Structure of free block information table
[0076]
[0077] (2) The storage space occupied by each node of the free block information table is the same size. If the CPU word length of the Java card chip is X bits, the storage space size of each node is MAX_TBL_BLOCK_SIZE×2X+X+X bytes;
[0078] (3) Allocate space from the EEPROM for the first node of the free block infor...
Embodiment 2
[0080] A Java card free block management method, assuming that the size of the application space is E2P_SIZE, the optimal size block matching algorithm comprises the following steps:
[0081] (1) Traverse each node in the free block information table in turn;
[0082] (2) Traverse the free block information in the current node based on the binary search algorithm:
[0083] ① Determine the start block number B_NO:
[0084] A. Obtain the number of valid blocks BLOCK_Number stored in the current node;
[0085] B. Calculate the middle block number NO (the first middle block number is NO=(1+BLOCK_Number) / 2), and get the middle block size BLOCK_Size;
[0086] C. If BLOCK_Size=E2P_SIZE, the search is successful and the algorithm is executed;
[0087] D. If BLOCK_Size>E2P_SIZE, you need to continue to calculate the serial number of the middle block on the left, and obtain the new block size BLOCK_Size’, if BLOCK_Size’≤E2P_SIZE, record the current block number as the starting block;...
Embodiment 3
[0097] A kind of Java card free block management method, set release block space first address as B_Address, tail address is E_Address, and block merging and sorting algorithm comprises the steps:
[0098] (1) Traverse each node in the free block information table in turn;
[0099] (2) Traverse the free block information in the current node:
[0100] ①If E_Address=start address of the current block:
[0101] A. If the merging status FLAG is true, that is, the starting address of the released block is the end address of a free block, and a merging has already been performed, then further merging will be performed, adding the size of the last merged block information to the current block size, and modifying the current block information The address of the address is 0, which means an invalid address;
[0102] B. If the merging state FLAG is false, then save the current block information for backup, add the size of the current block information to the size of the released block...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com