Method for switching different carrier wave ratios in frequency-division synchronous modulation
A technology of segmental synchronous modulation and carrier ratio, applied in control systems, control generators, vector control systems, etc., can solve problems such as torque pulsation, switching phase deviation in different frequency bands, motor current, torque and speed disturbance, etc. Achieve the effect of improving speed regulation performance, reducing peak current and torque ripple, and reasonable conception
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
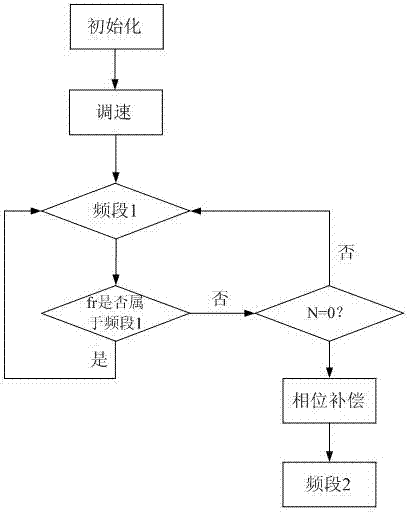
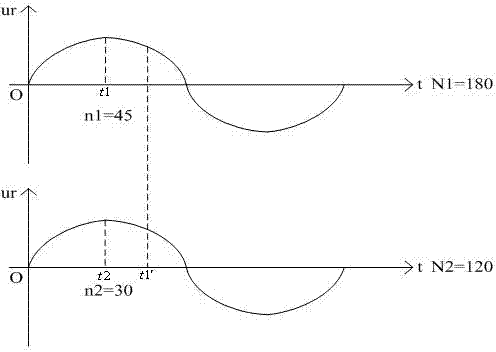
[0015] like figure 1 As shown, the method for switching between different carrier ratios in the segmented synchronous modulation of the present invention specifically adopts at least two or more frequency bands and sets the number of sampling points as N. When the speed of the asynchronous motor changes and the frequency signal changes, it enters the first One frequency band, the first frequency band corresponds to a certain carrier ratio and modulation degree, observe the state of the motor running in the first frequency band, when the frequency changes, judge whether it belongs to the first frequency band, if it belongs to the first frequency band, return to the first The state of the frequency band is running. If it does not belong to the first frequency band, then judge whether the sampling point N is equal to 0 at this time. If the sampling point N is equal to 0, then enter the second frequency band after a certain phase compensation. If N is not equal to 0 , then return ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com