Multi-scale debris flow risk evaluation method
An evaluation method and debris flow technology, applied in special data processing applications, structured data retrieval, design optimization/simulation, etc., which can solve the problem that a multi-scale debris flow risk assessment method has not yet been established.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0171] This embodiment 1 is for the risk assessment of Haitong ditch debris flow
[0172] (1.1) "6.23" mudslide
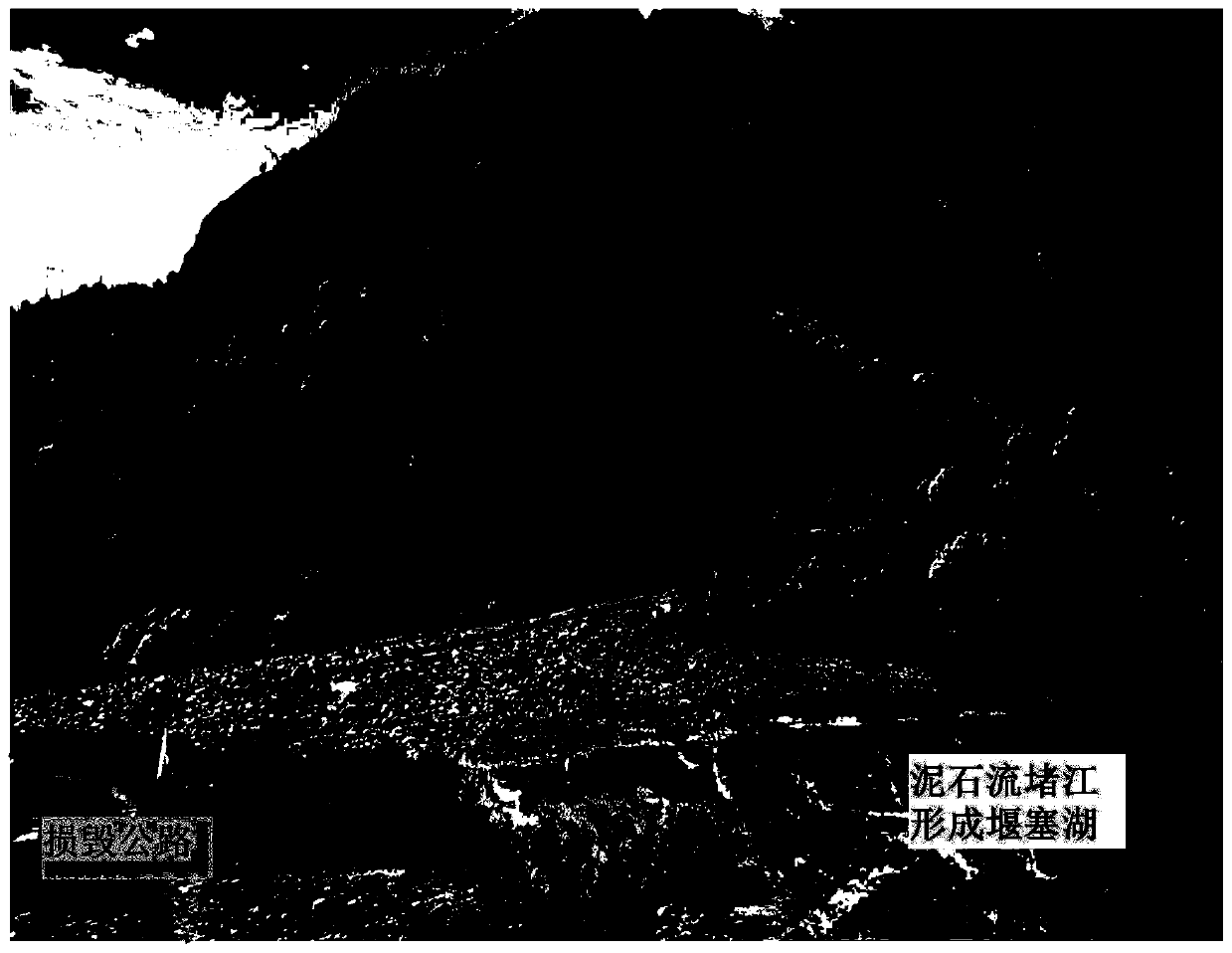
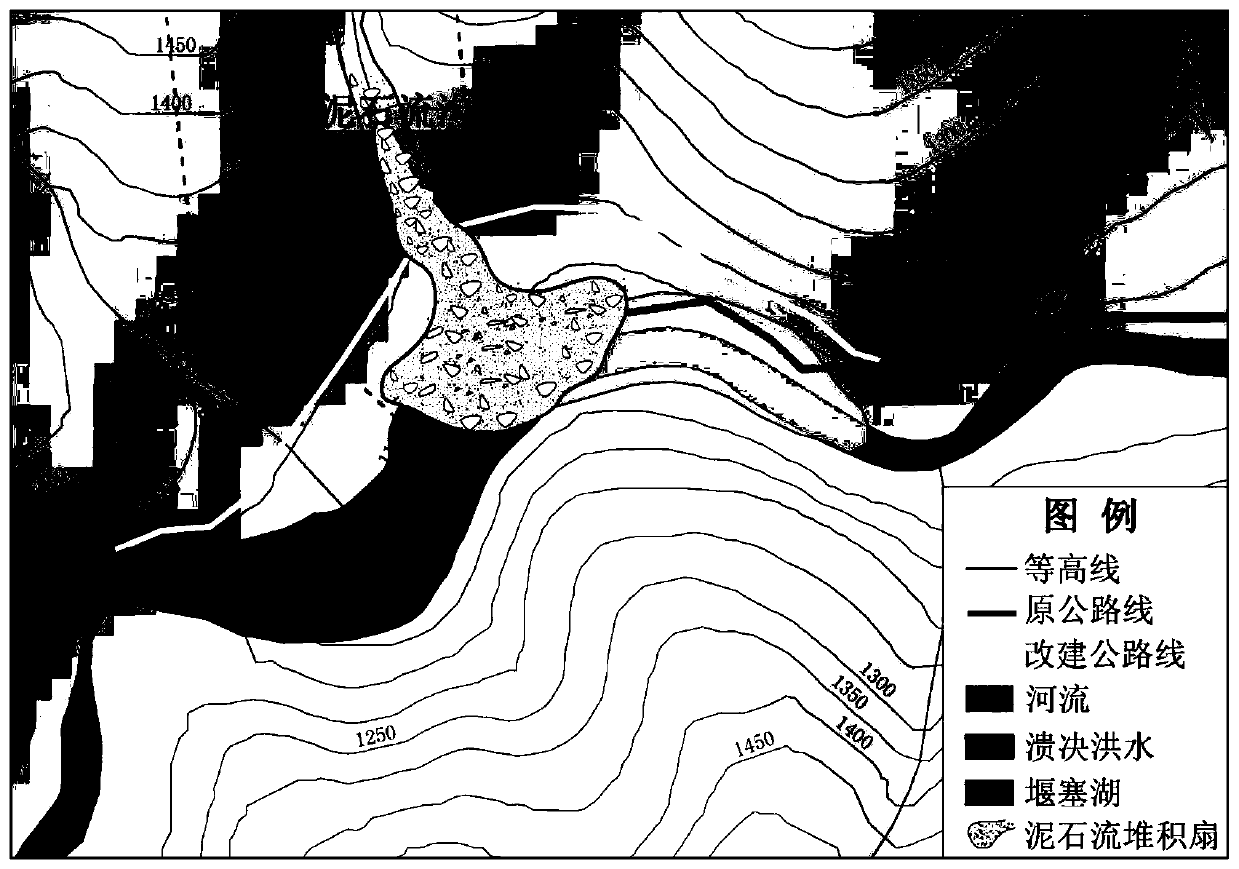
[0173] Affected by continuous heavy rainfall, on June 23, 2012, a large-scale debris flow disaster occurred on the Haitonggou section of the Sichuan-Tibet Highway in Mangkang County, Tibet (K3404 km of the G318 line of the Sichuan-Tibet Highway) ( figure 2 ). The accumulation fan formed by the debris flow is about 100m long, about 210m wide along the river, and has an average thickness of about 7-8m. Debris flow washed away the G318 road foundation by more than 200m, blocking the sea channel and forming a barrier lake ( image 3 ), the backwater of the barrier lake is about 300m, the average width is 60m, the average water depth is 5-6m, and the storage capacity is about 100,000m 3 , causing 160m of roadbed to be submerged, and the deepest part of the highway was 8m of water. In addition, about 500m of road surface was eroded and silted by sand and floods. The...
Embodiment 2
[0228] This example 2 is for the risk assessment of debris flow in the Xiqu River section
[0229] (2.1) Debris flow formation conditions
[0230] The Xiqu River Basin is located in the Hengduan Mountains in eastern Tibet. It is a first-class tributary of the Jinsha River. The main river is 123km long and the drainage area is 2776km 2 . The elevation of the estuary is 2455m, the elevation of the highest point of the basin is 5095m, and the relative elevation difference is more than 2640m. The overall terrain of the Xiqu River Basin is high in the northwest and low in the southeast, and the valleys in the basin are "V" shaped high mountains and deep canyons. The topography of this section of Zongla Mountain is steeper; to the east of the Xiqu River Power Station, the river cuts smaller and the slope of the terrain becomes gentler. The average slope of the watershed is above 20°, especially in the upper part of the valley and the source of the gully, which is mostly 35-45°, a...
Embodiment 3
[0258] This embodiment 3 is aimed at the assessment of the risk of debris flow on the Sichuan-Tibet Highway (G318 line)
[0259] (3.1) Factor quantization processing
[0260]Fully considering the availability of data, the research scale and the requirements of evaluation accuracy, GIS data processing is carried out in the form of grids, and the size of each grid is 25m×25m. Use the 1:50,000 DEM data of the study area, combined with the surface analysis tool in the ArcGIS platform to extract slope and surface relief; use the 1:250,000 geological map to extract geological information such as stratum, lithology, and fractures in the study area; the internal friction angle of rocks The cohesion and cohesion are determined according to the lithological characteristics of the formation and the rock shear strength index value in the rock mechanics parameter manual; A long period of time and well-developed rock block joints and fissures are classified as strong weathering; rock forma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com