Radial turbine rotor blade
A moving blade and radial flow technology, which is applied to the supporting components of the blades, non-variable engines, engine components, etc., can solve the problems of reducing impact loss efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing impact loss and improving turbine efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0072] refer to figure 1 , the first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0073] First, refer to Figure 10A , Figure 10B The variable capacity exhaust turbocharger 3 using the radial turbine 1 will be described. As shown in the figure, a spiral scroll 7 is formed in the turbine housing 5, and a gas outlet passage 9 is formed on the inner peripheral side. In addition, a compressor housing and a turbine housing with a compressor not shown are formed. 5 and the bearing shell 11.
[0074] The turbine rotor 13 is composed of a hub 17 fixed to an end portion of a rotor shaft 15 and a plurality of rotor blades 50 fixed at equal intervals in the circumferential direction on the outer periphery of the hub 17 . Furthermore, a compressor (not shown) is connected to the rotor shaft 15 on the opposite side to the turbine rotor 13 .
[0075] Furthermore, a compressor (not shown) is connected to the opposite side of the rotor shaft 15 . A bearing 21 that supports ...
no. 2 approach
[0091] refer to figure 2 , 3 , and the second embodiment will be described.
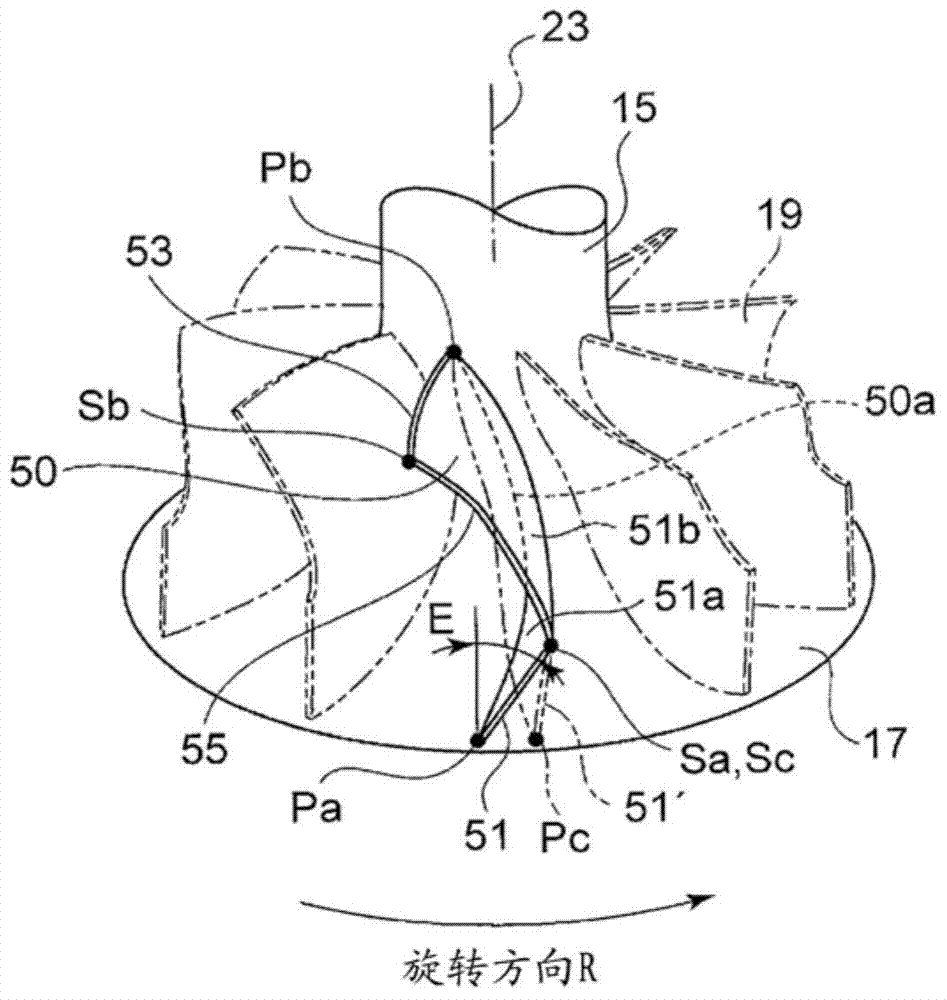
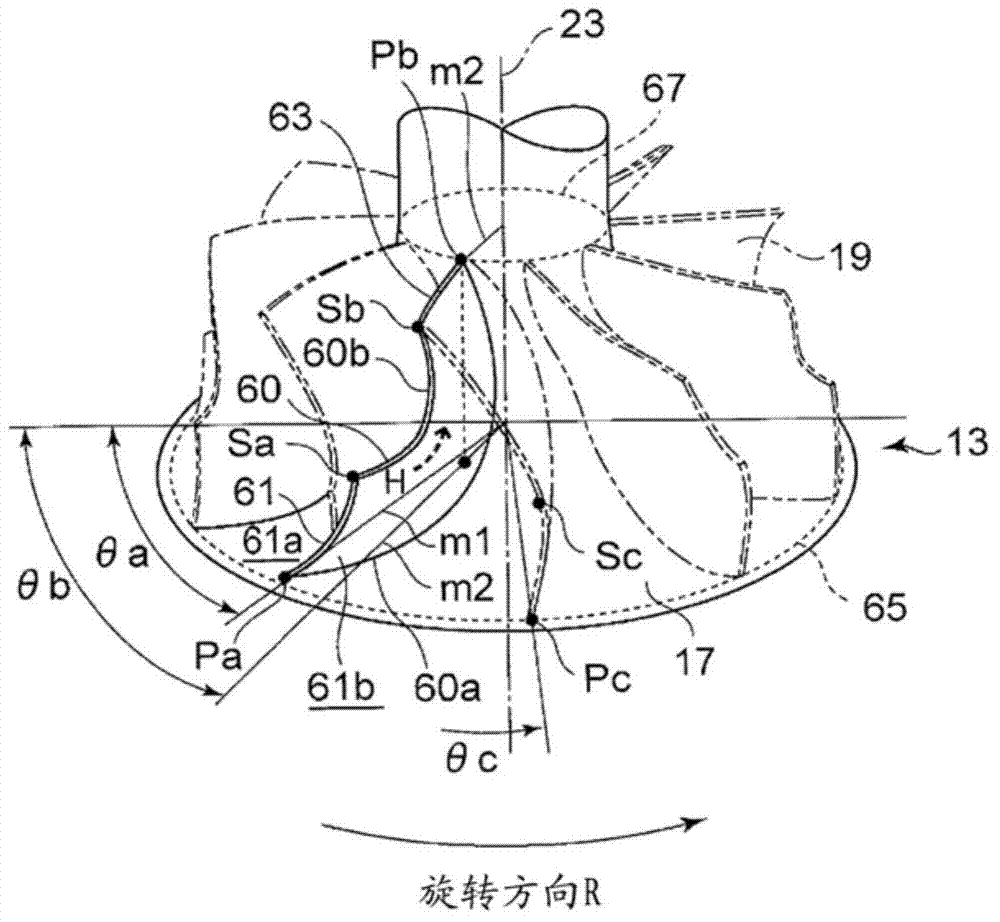
[0092] The first embodiment is characterized in that the shape of the leading edge 51 is formed by the inclination of the straight line connecting the leading edge shroud position Sc and the leading edge hub position Pa. In contrast, the second embodiment is characterized in that The positional relationship between the leading edge 61 side and the trailing edge 63 side on the hub joint line 60 a indicating the connection position of the rotor blade 60 to the upper surface of the hub 17 is also specified.
[0093] like figure 2 As shown, the line segment m1 connecting the leading edge hub position Pa on the leading edge hub circle 65 and the rotation centerline 23 of the moving blade 60 is more than the line segment m1 connecting the trailing edge hub position Pb on the trailing edge hub circle 67 and the The line segment m2 connecting the rotation centerlines 23 is located on the front side of t...
no. 3 approach
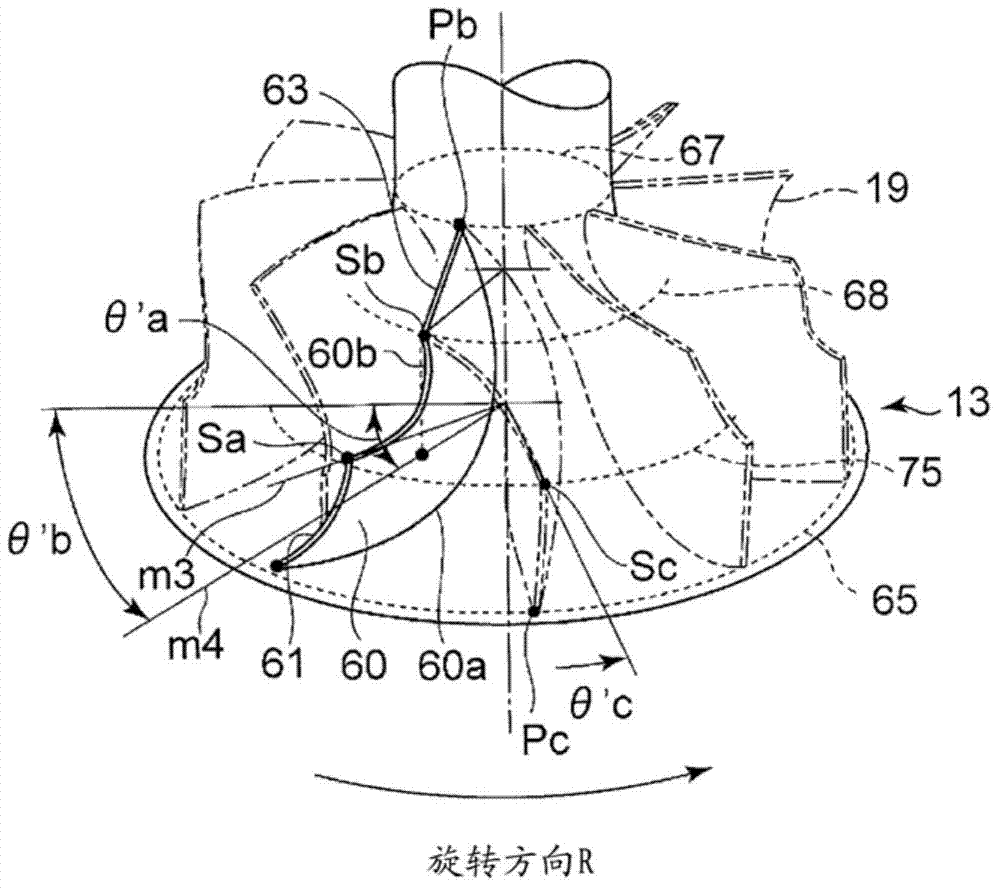
[0105] A third embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 4 .
[0106] The third embodiment is characterized in that the shape of the front edges 51 , 61 of the rotor blade 50 of the first embodiment or the rotor blade 60 of the second embodiment is formed into a substantially linear shape.
[0107] As shown in FIG. 4 , a line segment connecting the leading edge shroud positions Sa, Sc and the leading edge hub position Pa is formed in a substantially linear shape.
[0108] As described above, by forming the rotor blades 50 and 60 in a linear shape, the load in the blade height direction becomes uniform, and the generation of unnecessary secondary flows can be suppressed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com