A group-specific primer PCR-SBT method and reagents for hla-dqb1 genotyping
A genotyping and specific technology, applied in the direction of DNA / RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of DQB1*02 allele missed detection, allele missed detection, etc., to reduce rejection and improve accuracy Sexuality, the effect of improving the success rate and survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] The content of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the examples.
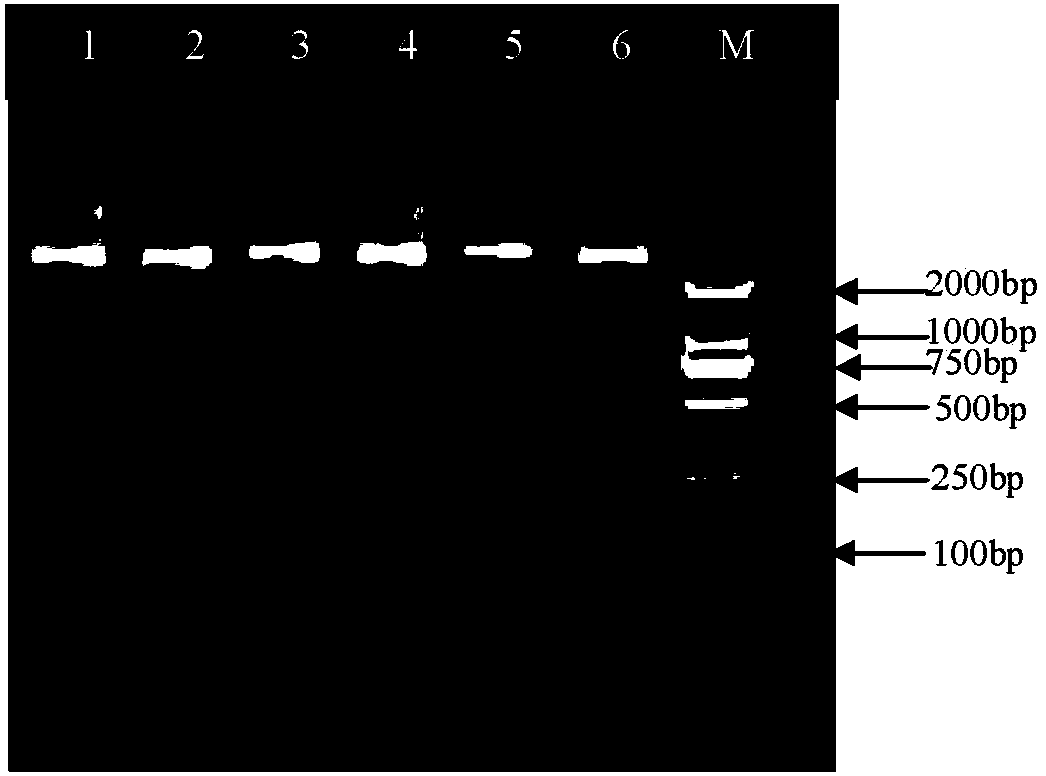
[0053] This implementation specifically takes one specimen for HLA-DQB1 genotyping as an example to describe the content of the present invention in detail. A group-specific primer PCR-SBT method for HLA-DQB1 genotyping used in the present invention specifically includes the following steps:
[0054] 1. Prepare human genomic DNA as a template for PCR amplification in subsequent steps.
[0055] 200 µl of whole blood to be tested was taken, and genomic DNA was extracted according to the instructions of the QuickGene DNA whole blood kit S kit, and the concentration and purity of the genome were determined by a spectrophotometer.
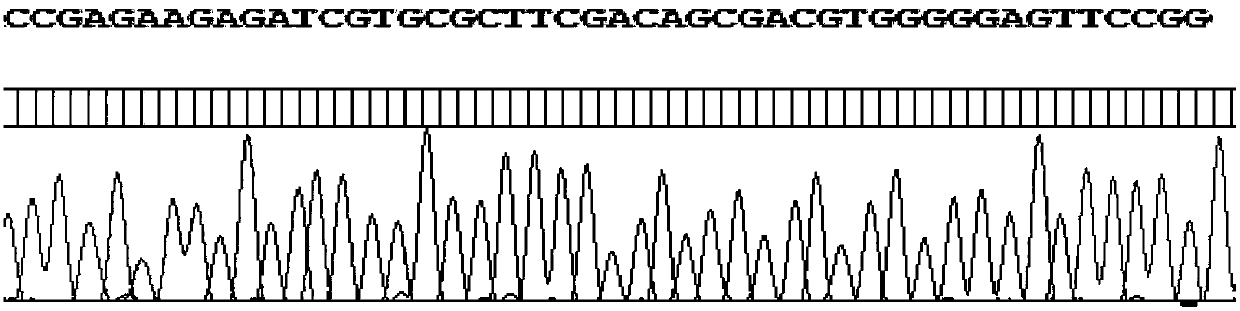
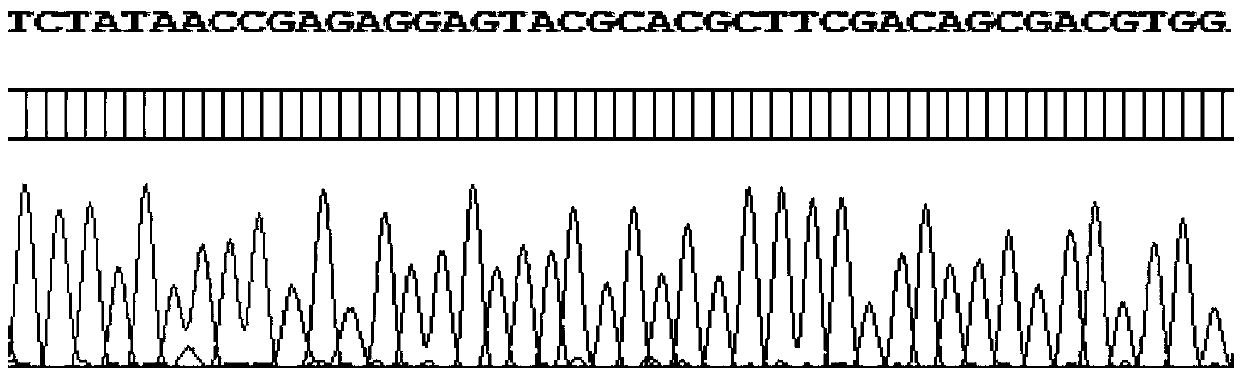
[0056] 2. Synthesize 6 pairs of amplification primers and 4 sequencing primers. For the specific sequence, please refer to the sequence in the content of the invention mentioned above, which will not be repeated. Dilute the amplifica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com