Bidirectional automatic variable-speed motor transmission device
A technology of motor transmission and automatic speed change, applied in the field of machinery, can solve problems such as the loose structure of the two-way automatic speed change motor transmission mechanism, and achieve the effects of improving work stability, reducing distance, and working stably
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
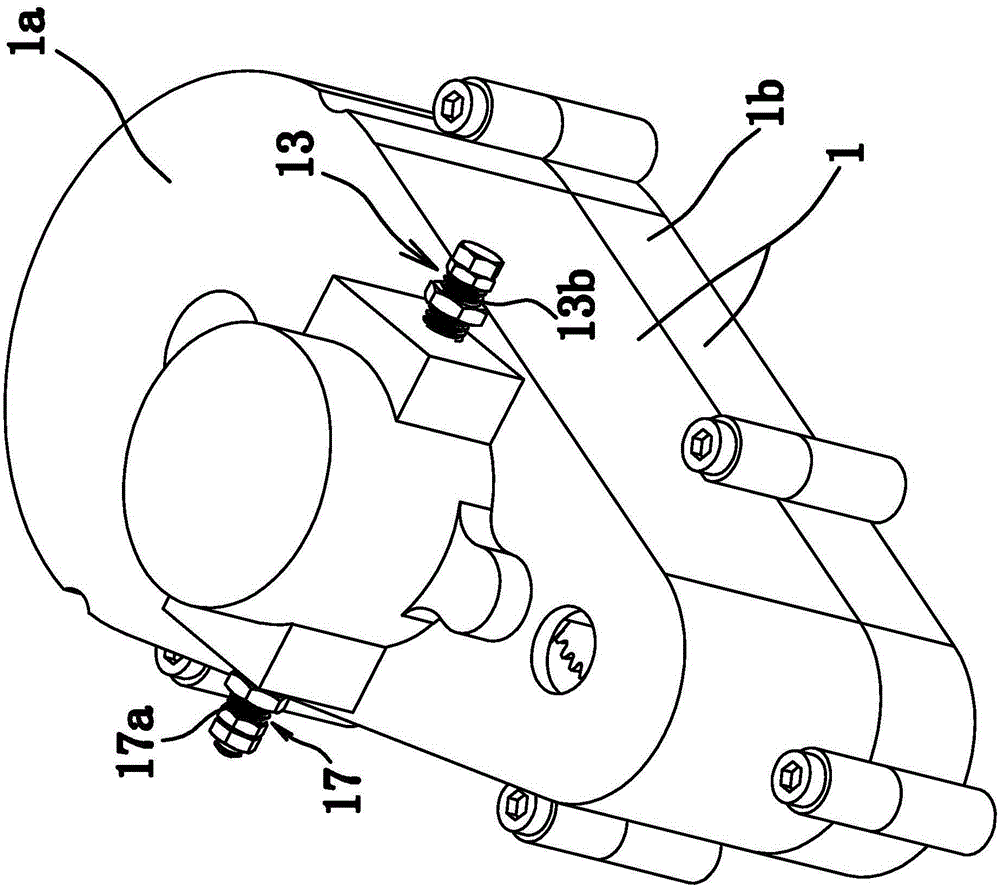
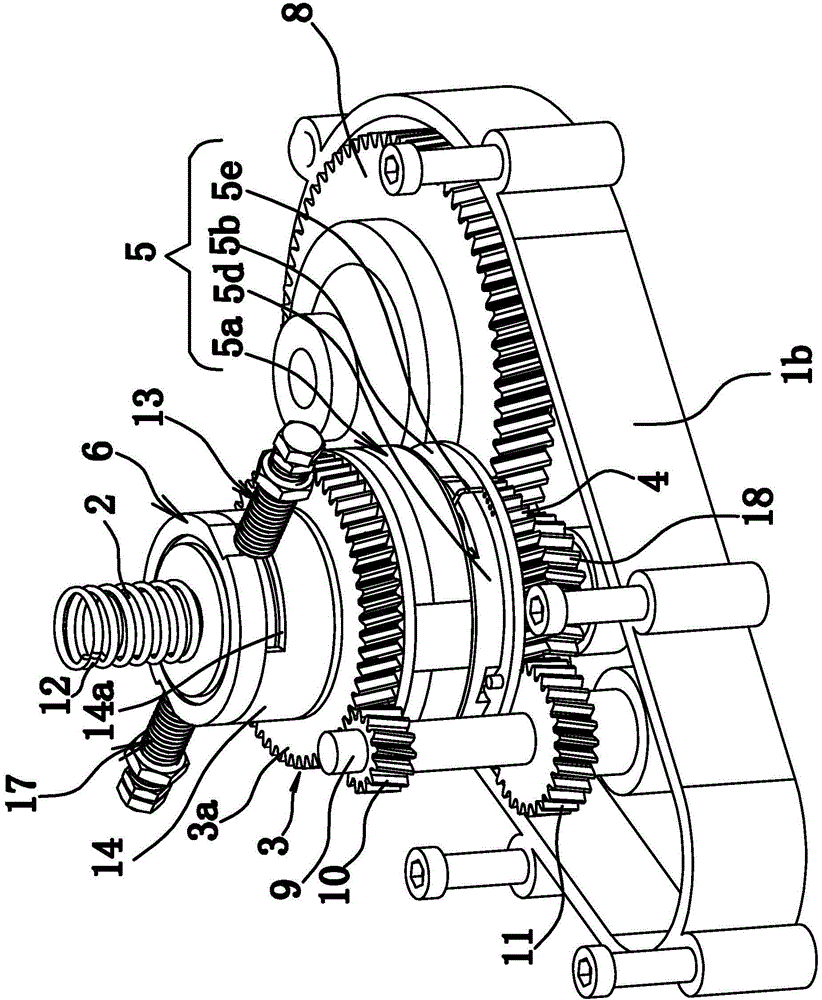
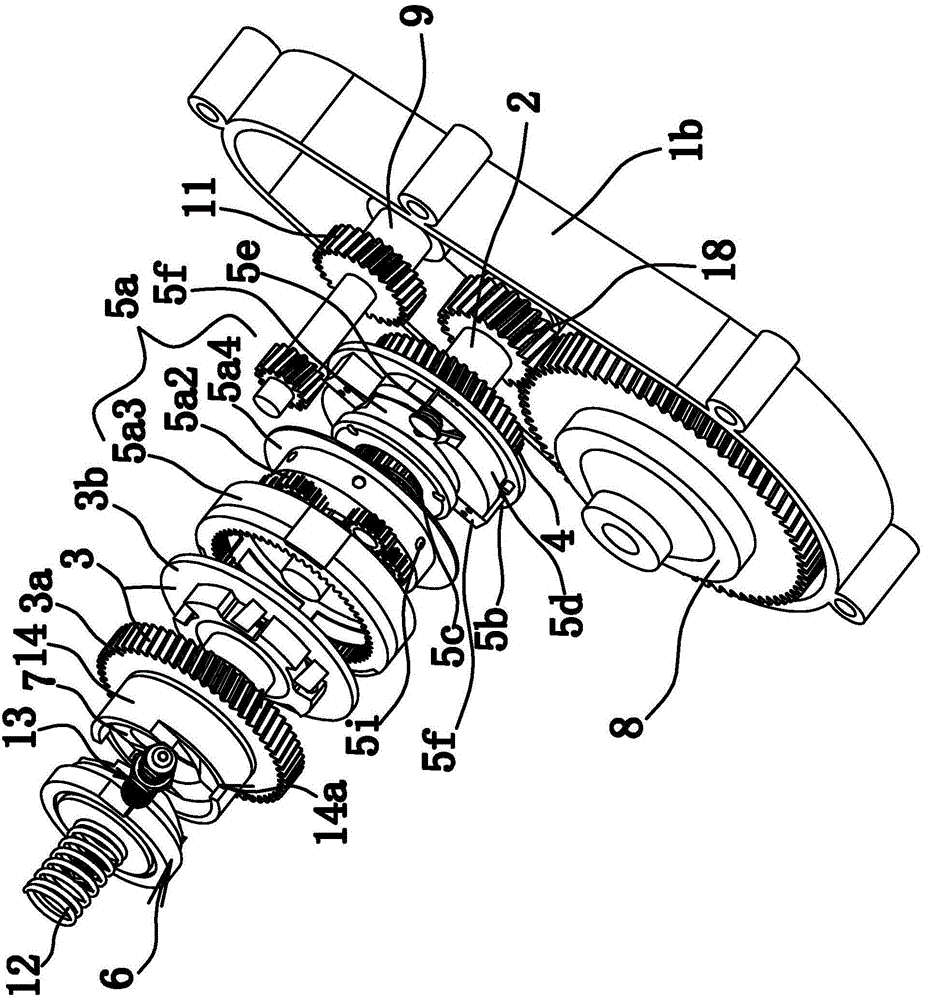
[0075] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, the bidirectional automatic variable speed motor transmission device is composed of a housing 1, a main shaft 2, a one-way device 3, a gear 4, a speed change mechanism 5, a transmission part 6, a connecting part 7, a differential 8 and the like. Wherein, the main shaft 2 is a spline shaft. Such as figure 1 As shown, the housing 1 includes an upper half shell 1a and a lower half shell 1b that are fixedly connected.
[0076] The main shaft 2 is axially fixed in the housing 1; the gear 4 and the main shaft 2 are axially fixed, that is, the gear 4 can rotate circumferentially relative to the main shaft 2; the one-way device 3 is sleeved on the main shaft 2. Wherein, the one-way device 3 includes an outer ring 3 a with outer teeth and an inner ring 3 b fixed to the main shaft 2 . In this embodiment, the one-way device 3 is a roller-type one-way clutch, and the structure between the inner ring 3b and the outer ring 3a is the same as ...
Embodiment 2
[0097] The structure and principle of the second embodiment are basically the same as those of the first embodiment, except that the limiter 13 includes a limiter 13a that is against the end surface of the stop edge 6c1 close to the outer ring 3a and a limiter 13a that can be driven Electromagnet 1 that translates toward or away from the main shaft 2, and electromagnet 1 is fixed to the housing 1; the coupling mechanism does not include a retreat structure, and other parts of the coupling mechanism are the same as in Embodiment 1; the separation mechanism does not include an advancing structure, And the other parts of the separation mechanism are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0099] The structure and principle of this third embodiment are basically the same as that of the first embodiment, except that the guide assembly includes a guide portion 7a, an inclined surface 7a1 facing the transmission part 6, and a protruding part on the end surface of the transmission part 6. Straight rod-shaped support portion. When the guide part 2 6a is plugged into the socket, the support part abuts against the inclined surface 1 7a1. When the rotating shaft 9 rotates clockwise, the supporting part moves along the inclined surface 7a1, so that the rotation of the connecting part 7 is converted into the axial movement of the transmission part 6, and drives the abutting part to overcome the elastic force of the compression spring 12 and protrude out of the socket. Make the connecting piece 7 and the transmission piece 6 in the disengaged state. By setting the guide assembly as the inclined surface 7a1 on the guide part 7a and the support part on the transmission part...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com