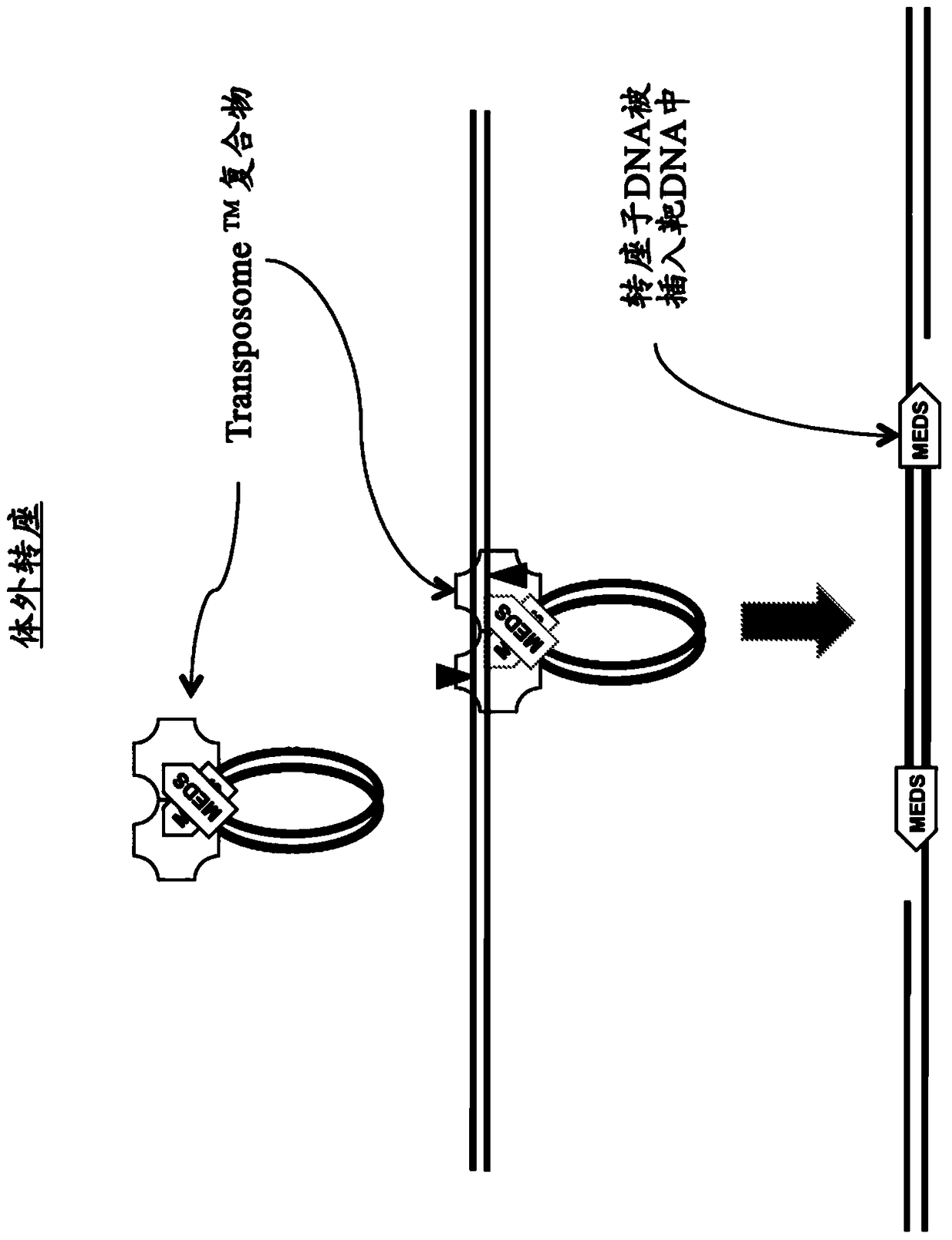
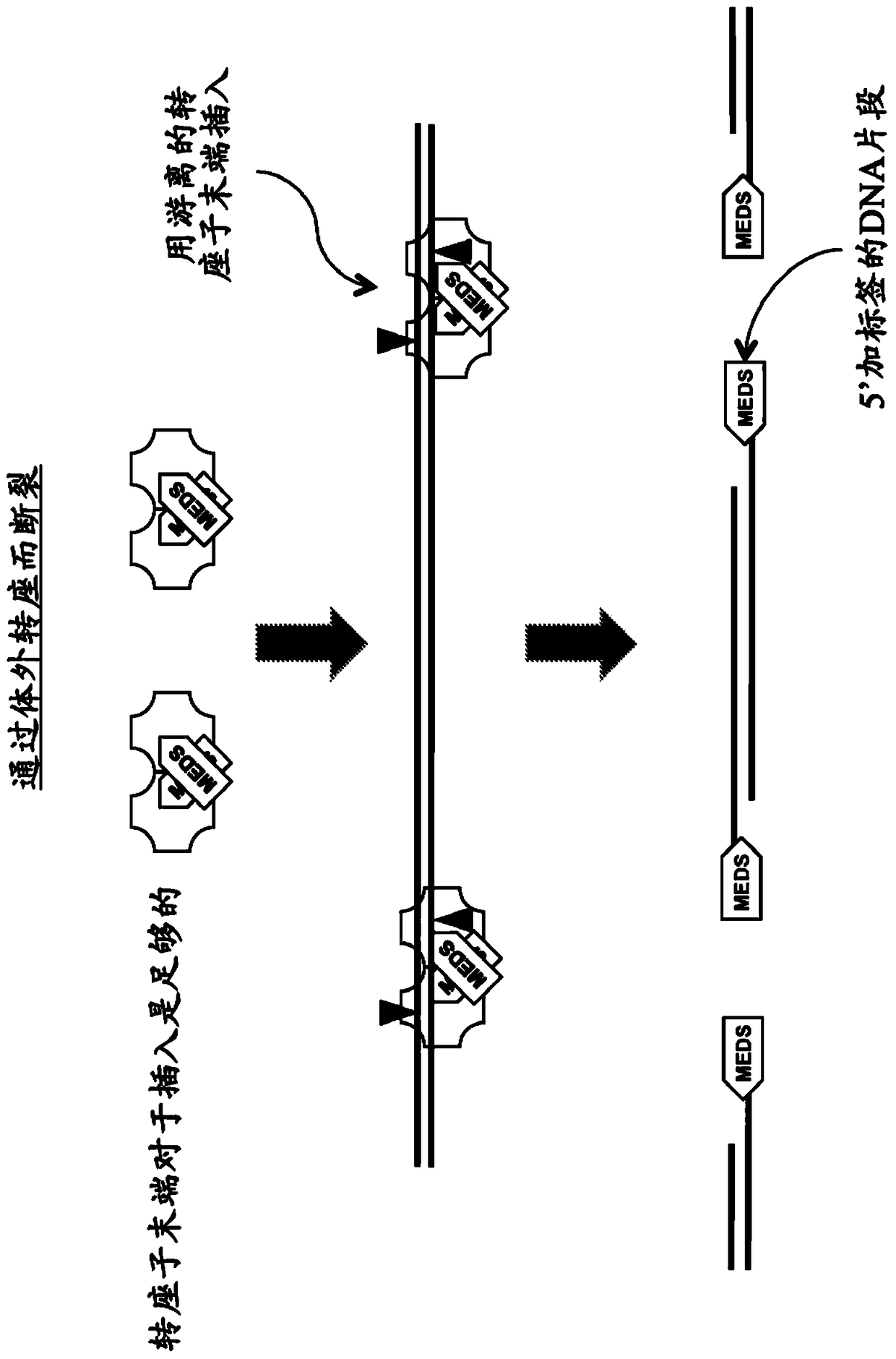
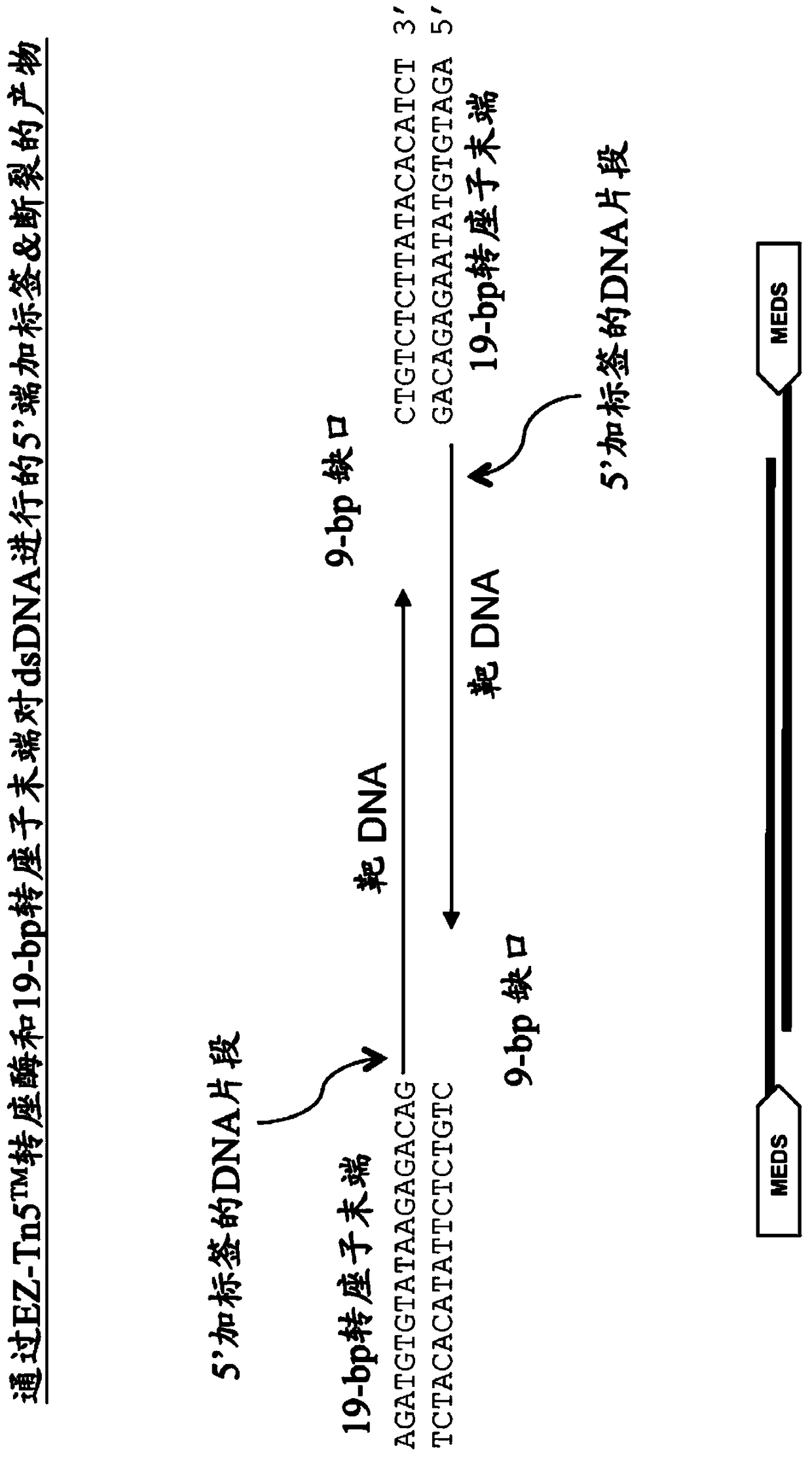
Kits for Modification of Nucleic Acids
A kit and polynucleotide technology, applied in the field of kits for modifying nucleic acids, can solve the problems of cumbersome, difficult procedures, waste of DNA, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0474] Use EZ-Tn5 TM Transposase and EZ-Tn5 TM In vitro transposition-mediated DNA fragmentation and 5' tagging of transposon ends
[0475] Assemble the following reaction mixture:
[0476]
[0477] *In some embodiments, two different pMEDS transposon ends that each additionally display an arbitrary sequence that differs in the corresponding 5' portion of the transferred transposon end, i.e., 5' of the transferred transposon end sequence ( Figure 4 ).
[0478] After mixing, the reactions were incubated at 37°C for 1 hour. Stop the reaction with 10 microliters of stop solution (15% sucrose, 66 mM EDTA, 20 mM TRIS, pH 8.0, 0.1% SDS, 0.9% orange G [Sigma O-7252], and 100 micrograms per milliliter of proteinase K), mix and Heat at 50°C for 10 minutes.
[0479] DNA was analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis in TAE buffer. DNA was separated into size fractions using LMP agarose. The gel was stained with SYBR Gold and DNA was visualized with non-UV light. The gel shee...
Embodiment 2
[0482] Using different EZ-Tn5 TM Size range of 5'-tagged DNA fragment transposition products by Tn5 transposase concentration.
[0483] Add Tn5 hyperactive EZ-Tn5 at a concentration of 90 units per microliter TM Transposase (EPICENTRE) was diluted to final concentrations of 45, 22.5, 11.3 and 9 units per microliter. Combine two microliters of each concentration of enzyme with 1 microgram of phage T7D111 target DNA (with a size of approximately 39 Kbp) and 1 micromole of pMEDS transposon ends in TA buffer in a final reaction mixture volume of 50 microliters at 37 °C. Incubate for 1 hour.
[0484] The reaction was stopped with 10 microliters of stop solution containing 15% sucrose, 66 mM EDTA, 20 mM Tris / HCl pH 8.0, 0.1% SDS, 0.9% Orange G and 100 micrograms per milliliter of proteinase K. After mixing and incubation at 50 °C for 10 min, 10 microliter aliquots were run on a 1% agarose gel in TAE buffer at 100 volts for 1 h. Gels were stained with SYBR Gold and photographed ...
Embodiment 3
[0487] Size range of transposition products of 5'-tagged DNA fragments using different concentrations of pMEDS transposon ends.
[0488] use T 10 E. 1 Buffer 25 micromolar stocks of pMEDS transposon ends were serially diluted 2-fold, 4-fold and 8-fold. Then, 2 μl of each transposon-end dilution and no transposon-end control in a buffer containing 1×TA buffer, 1 μg of phage T7D111 target DNA, and 0.4 units / μl of hyperactive Incubate the 50 μl reaction with Tn5 transposase for 1 hr.
[0489] Reactions were terminated as described in Example 2 and samples were analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis.
[0490] A 4-fold dilution of the 25 uM stock to give a final concentration of 0.25 micromolar pMEDS transposon ends in the reaction mixture produced good fragmentation of the target DNA and was probably the most efficient in terms of use of pMEDS transposon ends. At this concentration, most of the phage T7D111 target DNA was fragmented into DNA that migrated on the gel in siz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com