Tooth slot structure of high-power-density permanent magnet brushless motor used for space manipulator
A permanent magnet brushless motor, high power density technology, applied in the field of motors, can solve the problem of reducing volume, achieve the effect of reducing the overall length, simple structure, and reduced complex procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
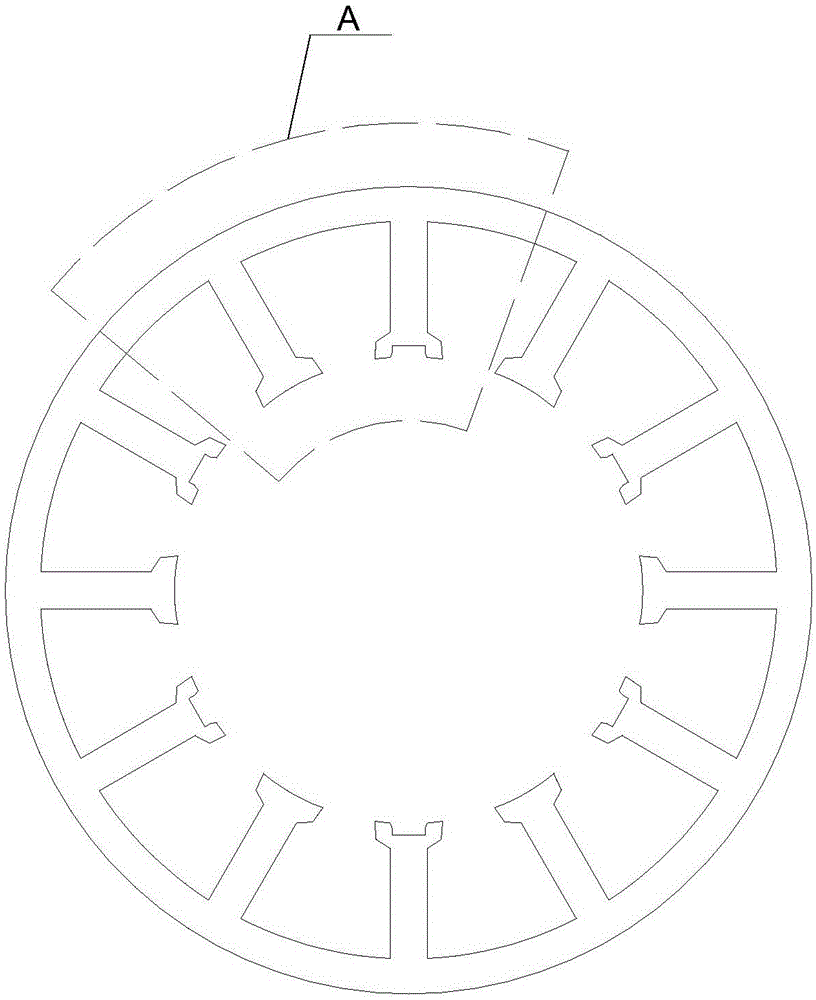
[0012] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 Describe this embodiment, the cogging structure of the high power density permanent magnet brushless motor for the space robot arm described in this embodiment, the inner surface of the stator of the motor is arranged along the circumference of p pairs of stator teeth, and every two adjacent stator teeth Stator tooth slots are formed between the pole shoes, and the stator tooth slots are narrow outside and wide inside; there are Hall element embedded slots at the tooth crowns of the p stator teeth, and the slots face the direction of the center of the circle ; The p stator teeth with Hall element embedded slots are arranged alternately with the remaining p stator teeth;
[0013] p is a positive integer greater than or equal to 2.
[0014] The motor involved in this embodiment includes a stator and a rotor. The stator is arranged outside the rotor. The rotor adopts a hollow disc structure....
specific Embodiment approach 2
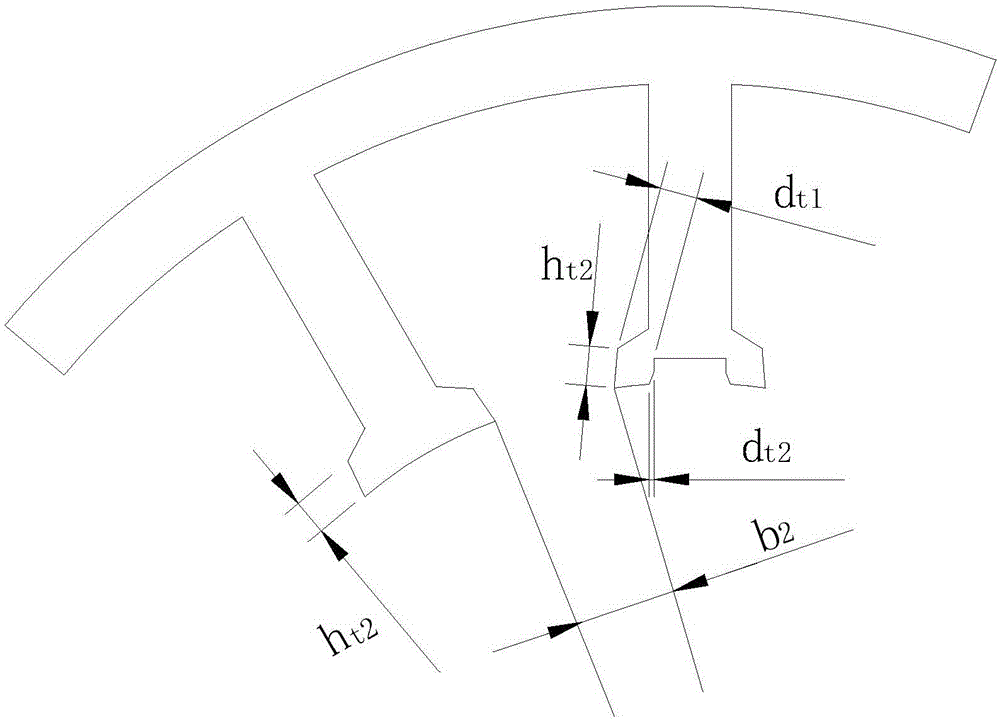
[0017] Embodiment 2: In this embodiment, Embodiment 1 is further described. The Hall element embedding groove is in the shape of a bell mouth, and the outer edge of the groove is the position of the horn opening.
[0018] Increase the width of the notch, i.e. increase d t1 , so that the opening width at the outer edge of the notch becomes larger, forming a bell mouth shape, so as to prevent the saturation of the magnetic circuit, make the magnetic density distribution as uniform as possible, and reduce the harmonic component in the current.
specific Embodiment approach 3
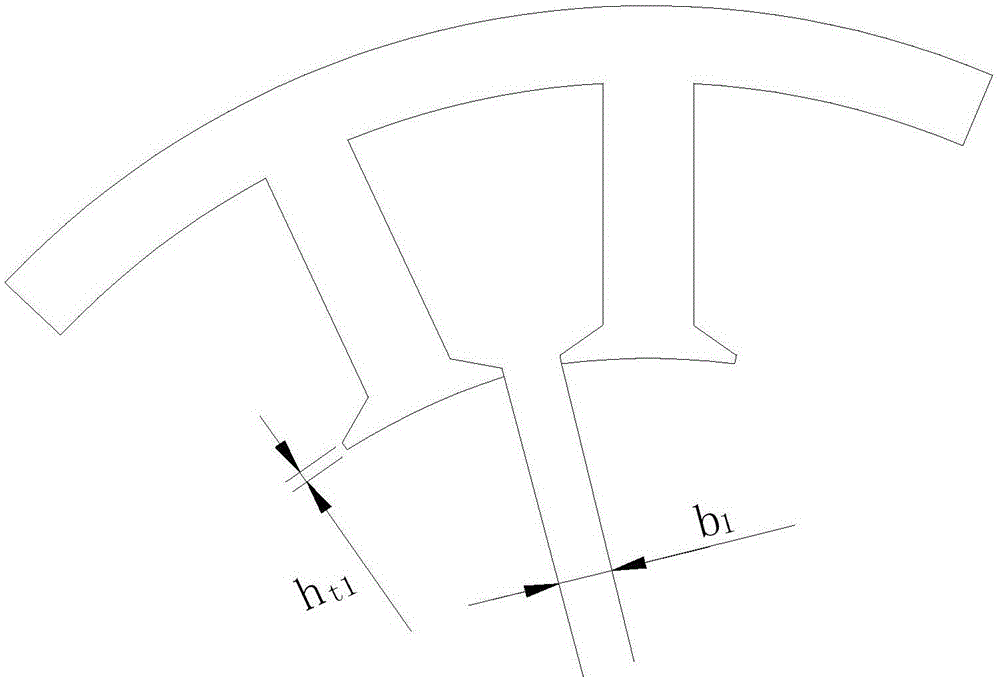
[0019] Embodiment 3: In this embodiment, Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 is further described. The ratio of the radial thickness of the notches of the stator teeth to the radial height of the stator teeth is 0.2-0.3.
[0020] figure 1 The stator tooth structure of a conventional motor is shown, and the radial thickness of the stator slots is b 1 , accounting for 0.1 to 0.15 of the radial height of the stator teeth, and the radial thickness h of the stator tooth notch in this embodiment t2 It is thicker than the radial thickness of the slot of the stator tooth of the traditional motor, so as to better insert the Hall element.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com