Non-invasive method for prediction of opioid-analgesia and opioid-blood-concentrations
An opioid, blood drug concentration technology, applied in the field of medical treatment such as pain therapy equipment, can solve problems such as undetermined
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0060] material method
[0061] subjects
[0062] Sixteen volunteers (aged 19-36 years, all within ±10% of their normal body weight, 8 males) participated in this double-blind, randomized, single-session study. Subjects were determined to be healthy by examining medical history, current physiological status and routine clinical laboratory tests and abstained from prescription / over-the-counter drugs, alcohol and food 30 days, 24 hours and 6 hours before the experiment, respectively. Effect measures and clinical effects were assessed in this order: visual acuity (duration: 5 min), clinical indices (1 min), pupil size and response to light stimulation (5 min), analgesic effect and accompanying tracking performance assessment (20 min). Non-redundant supplementary data for this study to existing analyzes are published in ( Another case in (Oertel et al., 2001) and (Oertel et al., 2012b).
[0063] medication
[0064] Remifentanil ( Provided via GlaxoWellcome GmbH & Co., Hambu...
Embodiment I
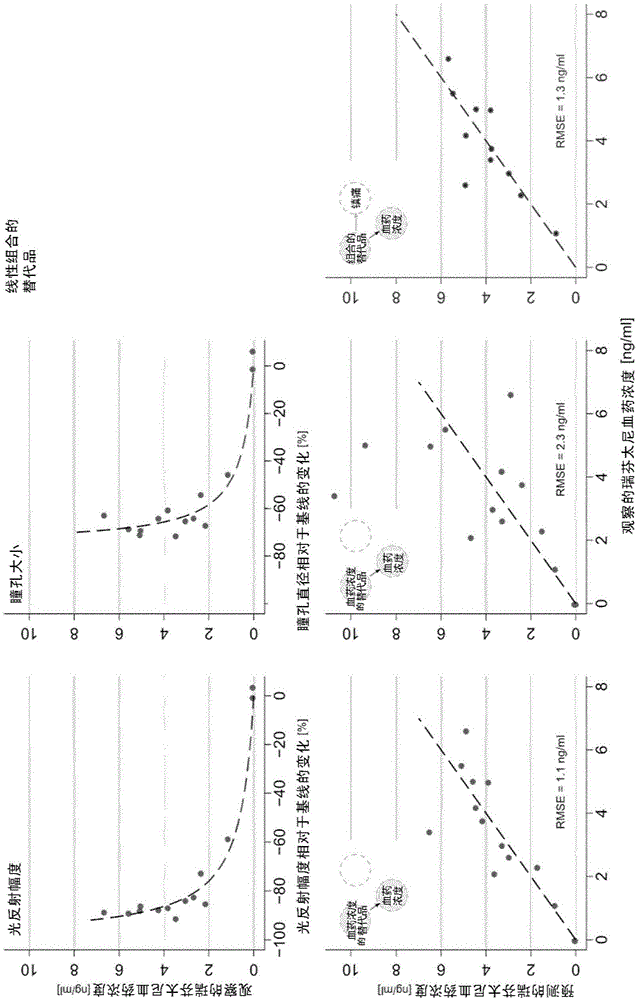
[0078] Embodiment 1: the prediction of substitute to remifentanil blood drug concentration
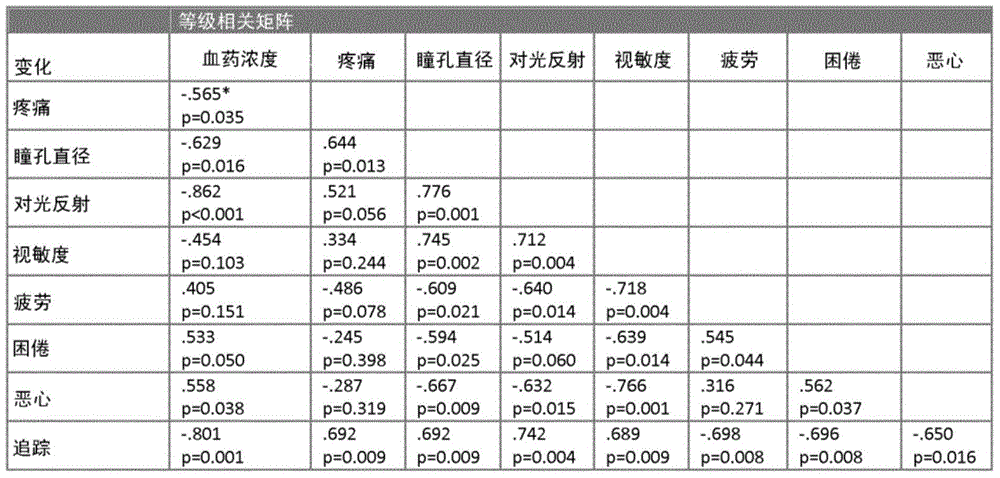
[0079] Data were derived from 14 subjects with three dropouts (at target concentrations of 1.8, 2.4 and 6 ng / ml) and only one replacement (1.8 ng / ml). Two subjects withdrew early from the trial, one because of anxiety that began shortly after the remifentanil infusion, and the other because of excessive vomiting and nausea. The third dropout was a medical decision to stop the remifentanil infusion due to bradycardia.
[0080] Table 1 : Nonparametric Spearman rank correlation matrix for opioid effect measures (n=14; percent change in effect measure from baseline that served as the basis for this nonparametric correlation analysis). Correlation coefficients ρ are given with respective p-values.
[0081]
[0082] *: Significant nonparametric rank correlations from this table do not imply that pain can be predicted from plasma concentrations using a linear relationship between arteria...
Embodiment II
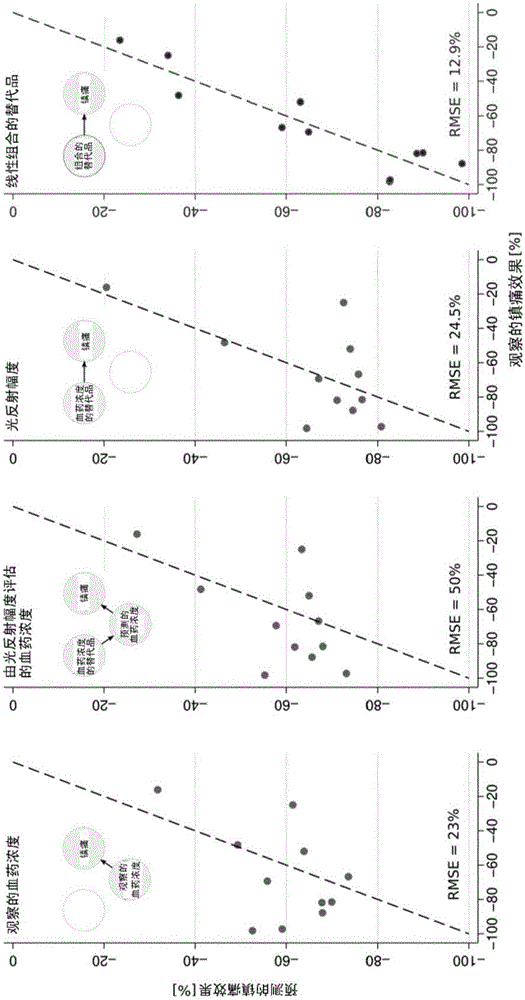
[0085] Example II: Prediction of Analgesia by Surrogates
[0086] In the second part of the analysis, the use of surrogates to predict more clinically relevant remifentanil effects, particularly analgesia, was analyzed. Two subjects at zero concentration and subjects with hyperalgesia (23% increase in pain score from 25 to 30.7 mm VAS at a steady state plasma concentration of 2.1 ng / ml, target 1.8 ng / ml) formed a separate cluster and exclude them. Prediction of analgesic effect based on observed plasma concentrations of remifentanil (E max = -100% and EC 50 = 2.4 ng / ml; again, these values have been obtained using the standard inverse model: EC 50 The estimated standard error of 4, E max not significantly different from the value -100% and thus determined, and R 2 0.274) provides an RMSE of 23%. E. max In the model, the observed concentration was replaced by the predicted concentration based on the magnitude of the pupillary light reflex, and the resulting RMSE was 50...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com