Quick comparing and positioning method for gene sequence segments on reference genome
A reference genome and gene sequence technology, applied in the field of rapid comparison and positioning of gene sequence fragments on the reference genome, can solve the problems of accelerating the data analysis process, consuming large computing resources and time, and achieving low time complexity and low time complexity Accuracy and high positioning efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Hereinafter, taking CNV analysis (CopyNumberVariation analysis / copy number variation analysis) through rapid sequence alignment as an example, the method for rapid alignment and positioning of gene sequence fragments on the reference genome of the present invention will be further described.
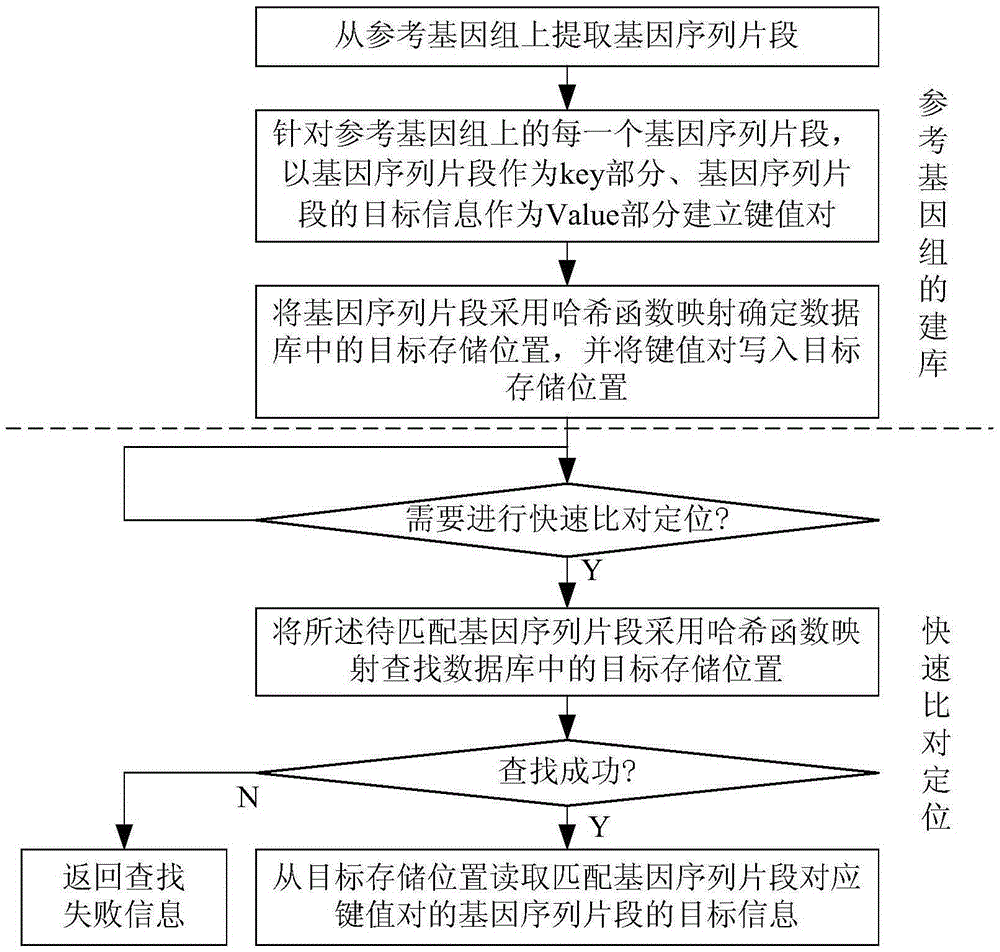
[0042] Such as figure 1As shown, the steps of the method for rapid alignment and positioning of gene sequence fragments on the reference genome in this embodiment include:
[0043] 1) Extract gene sequence fragments from the reference genome;
[0044] 2) For each gene sequence fragment on the reference genome, use the gene sequence fragment as the key part and the target information of the gene sequence fragment as the Value part to establish a key-value pair, and use the hash function mapping to determine the target storage in the database for the gene sequence fragment location, and write the key-value pair into the target storage location, and finally complete the library cons...
Embodiment 2
[0085] In addition to CNV analysis, the rapid alignment and positioning method of gene sequence fragments on the reference genome of the present invention can also be used for bacterial species identification. In this embodiment, the reference genome is a cross-species reference genome, and when step 2) is used to build a reference genome, the reference genome is downloaded from the NCBIRefSeq database (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / refseq / ) The human reference genome and all bacterial and viral genome sequences. Use the gem-mappability software to calculate the mappability map of the reference sequence 31mer (human, bacteria, virus), and select the unique sequence fragment with a mappability of 1; in the NCBI species taxonomy database (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / taxonomy) to download detailed taxonomic information for species. For each gene sequence fragment on the reference genome, the key-value pair is established with the gene sequence fragment as the key part and the tar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com