Light field imaging and printing device and thin film with three-dimensional floating images
A printing device and light field imaging technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of weak 3D dynamic sense and inability to realize spatial multiplexing, and achieve the effect of enriching printing modes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
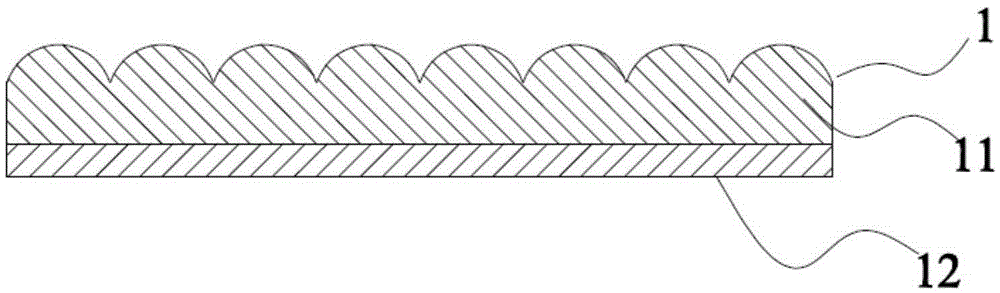
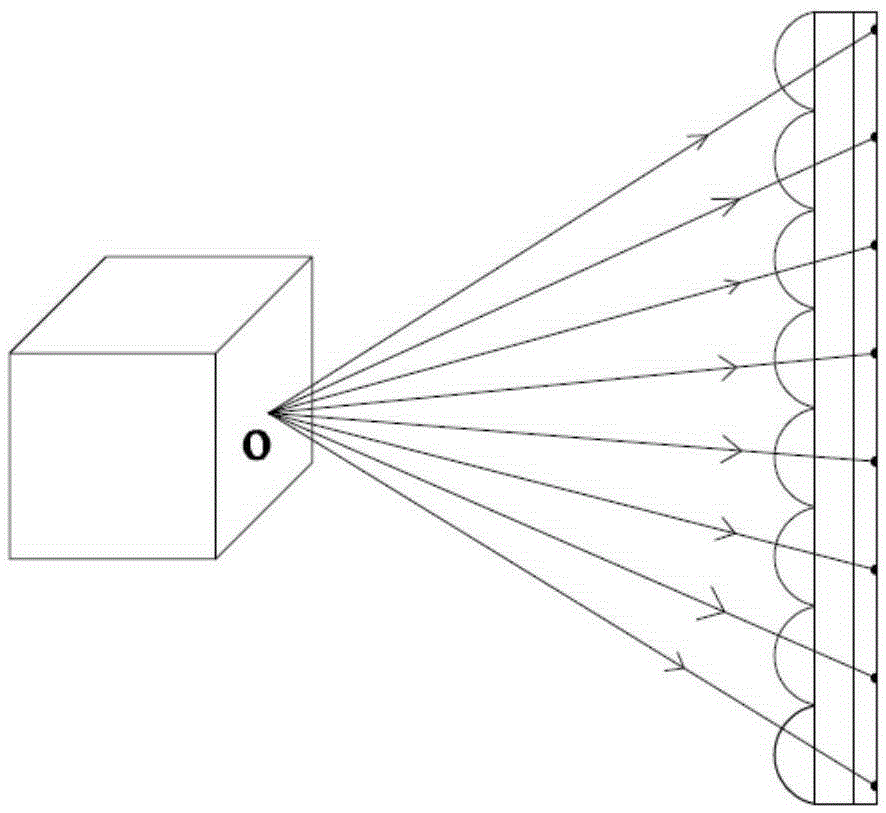
[0071] exist Figure 6 In the light field imaging printing device shown, when printing, the cylindrical lens 4 is fixed to a certain orientation angle, and the computer controls the scanning galvanometer system 3 to keep the laser scanning on the circular arc surface of the cylindrical lens, and obtain the result through the converging lens group 6 The voxel light field is a fan-shaped surface with a fixed orientation angle, and is recorded by the microlens recording material 1 . According to the input 3D model data, the x-y-z platform where the microlens recording material 1 is located is controlled, and the light field recording of the 3D object is realized by horizontal layer-by-layer printing. Since the light field of all voxels of this 3D object is a fan-shaped area with the same orientation angle, the object can only be observed in the collection plane with this orientation angle during reproduction. When the observer changes continuously in this orientation plane Dynam...
Embodiment approach 2
[0073] In Embodiment 1, the voxel light field can be expressed as L1(x, y, z). After completing the 3D light field imaging and printing, rotate the cylindrical lens 4 and repeat the above printing process to input another 3D object light field data L2(x, y, z), when the cylindrical lens 4 is rotated to different orientation angles, the light field data Ln(x, y, z) of different 3D objects are sequentially input. When reproducing, the principle is as described in Embodiment 1. The observer can only observe different 3D printed objects sequentially within the selected orientation angle fan-shaped assembly plane, such as Figure 10 As shown, a cubic model can be observed when at the orientation angle position, and a spherical model can be seen again when the recording material is rotated to the orientation angle. The 3D reproduction with such viewing angle characteristics can allow multiple people to observe different object information from different directions, realizing the mul...
Embodiment approach 3
[0075] As a special example of Embodiment 2, the rotation of the cylindrical lens 4 makes the orientation angle change continuously instead of having a discrete value. Here the rotation frequency of the cylindrical lens 4 should be much lower than the scanning frequency of the scanning galvanometer system 3, to ensure that the scanning galvanometer system 3 can still move the cylindrical lens 4 when the rotation angle is lower than 1 milliarc (ie 1 mrad). At least one complete scanning period is completed on the arc surface of the lens 4 . Assuming that the scanning frequency of the scanning galvanometer system 3 is T1, and the rotation frequency of the cylindrical lens 4 is T2, according to the above conditions, it should be ensured that the time for the cylindrical lens 4 to rotate 1mrad is not less than 1 / T1, so that the relationship T2≤ T1 / (2000π), such as T1=200000Hz, after calculation, the rotation frequency of the cylindrical lens 4 should not be greater than 31Hz. If ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com