Method for shortening the time of testing the cycle life of lithium ion batteries
A lithium-ion battery, cycle life technology, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring devices, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve the problems of market preemption, loss of opportunities, and dragging down the time to market of new products, achieving high accuracy, speeding up evaluation, The effect of speeding up time to market
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
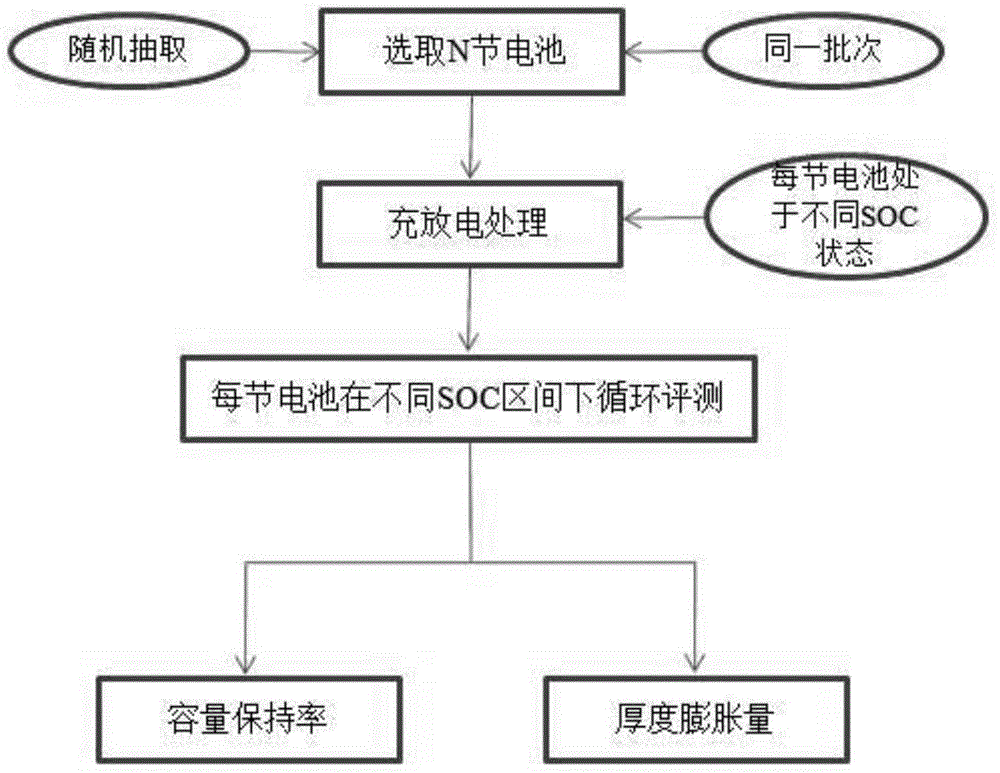
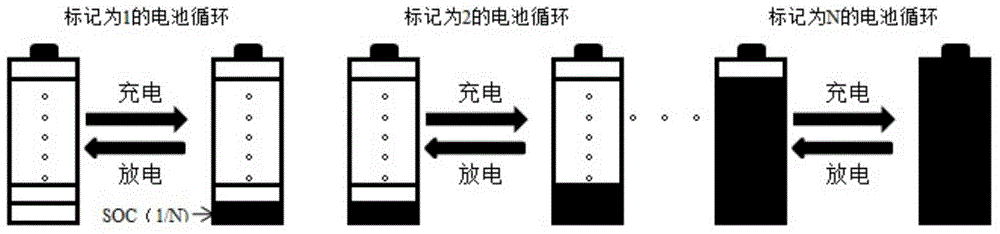
[0031] (1) Select 4 batteries and mark them as 1, 2, 3, 4 respectively;
[0032] (2) After the battery in the above step (1) is charged and discharged, each battery is in a different SOC state, and the cycle life of each battery is evaluated in a different SOC interval, and the battery marked as 1, Cycle between SOC0%~SOC25%, the charge cut-off voltage is 3.85V, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.00V; the battery marked 2 cycles between SOC25%~SOC50%, the charge cut-off voltage is 3.90V, and the discharge cut-off condition is 3.67V; the battery marked 3 cycles between SOC50%~SOC75%, the charge cut-off voltage is 4.01V, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.75V; the battery marked 4 cycles between SOC75%~SOC100%, the charge cut-off condition : Voltage 4.20V, current 100mA, discharge cut-off voltage 3.88V;
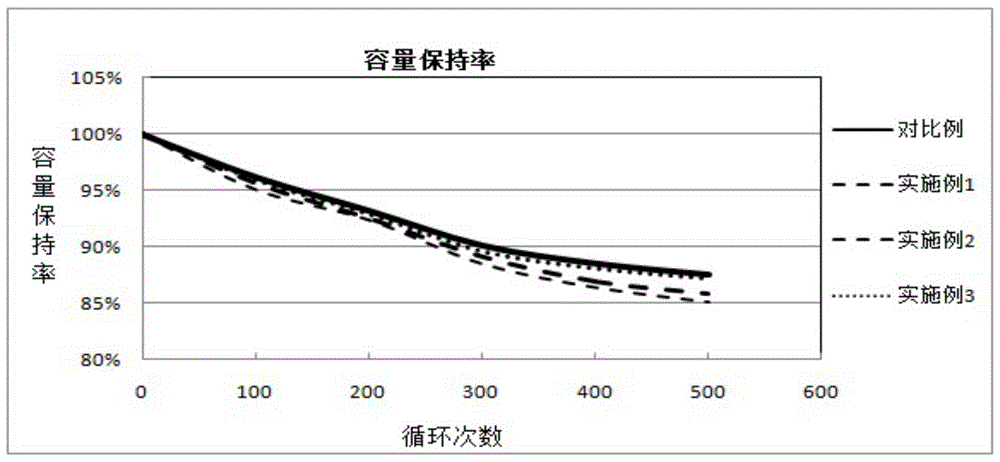
[0033](3) Table 2: The test conditions for the cycle life of the 4 batteries in the implementation case 1;
[0034]
[0035] (4) The cycle time of the batteries ma...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Select 6 batteries, marked as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 respectively;
[0039] (2) After the battery in the above step (1) is charged and discharged, each battery is in a different SOC state, and the cycle life of each battery is evaluated in a different SOC interval, and the battery marked as 1, Cycle between SOC0%~SOC(1 / 6), the charge cut-off voltage is 3.81V, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.00V; the battery marked 2 cycles between SOC(1 / 6)~SOC(1 / 3) , the charge cut-off voltage is 3.87V, and the discharge cut-off condition is 3.65V; the battery marked with 3 circulates between SOC(1 / 3)~SOC50%, the charge cut-off voltage is 3.92V, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.69V; marked as The battery of 4 cycles between SOC50%~SOC(2 / 3), the charge cut-off voltage is 3.98, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.75V; the battery marked 5 is between SOC(2 / 3)~SOC(5 / 6). cycle, the charge cut-off voltage is 4.10V, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.80V; the battery marked ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) Select 10 batteries, marked as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10;
[0047] (2) After the battery in the above step (1) is charged and discharged, each battery is in a different SOC state, and the cycle life of each battery is evaluated in a different SOC range, at SOC0%~SOC10% cycle between, the charge cut-off voltage is 3.76V, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.00V; the battery marked 2 cycles between SOC10%~SOC20%, the charge cut-off voltage is 3.83V, and the discharge cut-off condition is 3.61V; marked 3 The battery cycled between SOC20%~SOC30%, the charge cut-off voltage is 3.87V, the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.66V; the battery marked 4 cycles between SOC30%~SOC40%, the charge cut-off voltage is 3.89V, The voltage is 3.68V; the battery marked with 5 cycles between SOC40% and SOC50%, the charge cut-off voltage is 3.91V, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 3.70V; the battery marked with 6 cycles between SOC50% and SOC60%. The cut-off voltage is 3.96V, and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com