Method for harvesting microalgae
A technology of microalgae and harvesting trays, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as difficult operation, low sedimentation rate, unfavorable separation of clear liquid, etc., and achieve simple and efficient methods High, high sedimentation rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] This example is used to illustrate the method for harvesting microalgae of the present invention.
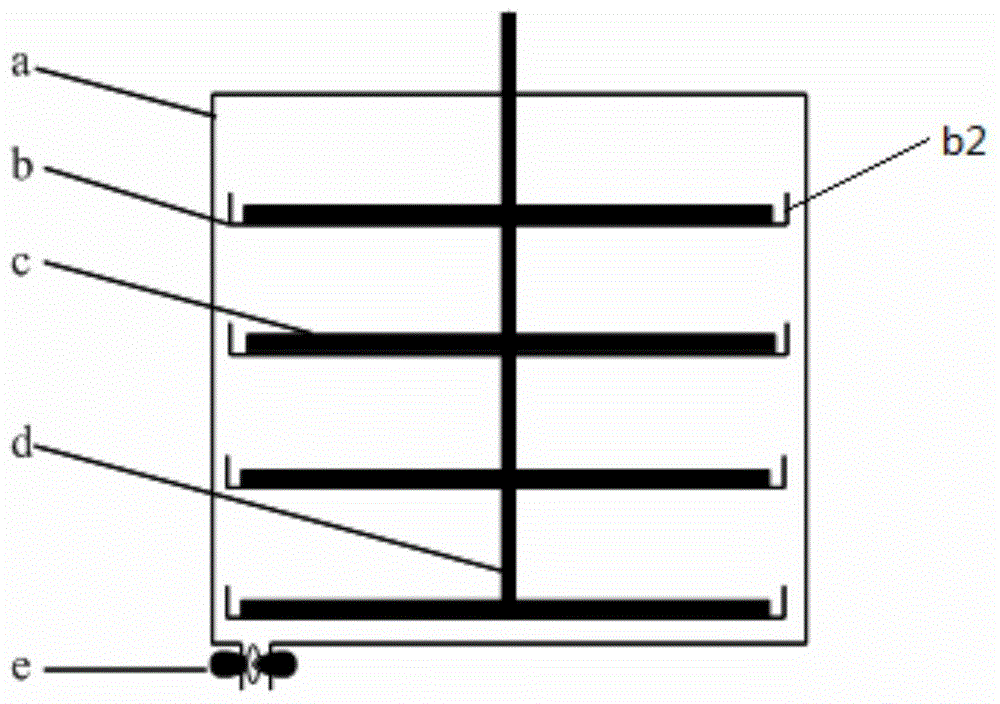
[0056] The chlorella algae liquid (cultivated with BG11 medium, OD 680 2.1) transport to the sedimentation harvester a, and fill the sedimentation harvester a, adjust the pH=8, the temperature is 25 ° C, and settle in the dark for 24 hours. After the sedimentation, the separated water (that is, the clear liquid after the sedimentation , the same below) OD 680 0.2, the sedimentation rate reaches 90%. Then open the water outlet e, slowly release the separated water, the settled algae mud stays on the settling recovery tray b and the bottom of the settling recovery device a, and the rotating shaft d passes the scraper to settle the algae mud on the settling recovery tray b Scrape off the bottom of the sedimentation collector a, and collect the algae mud at the bottom of the sedimentation collector a.
Embodiment 2
[0058] This example is used to illustrate the method for harvesting microalgae of the present invention.
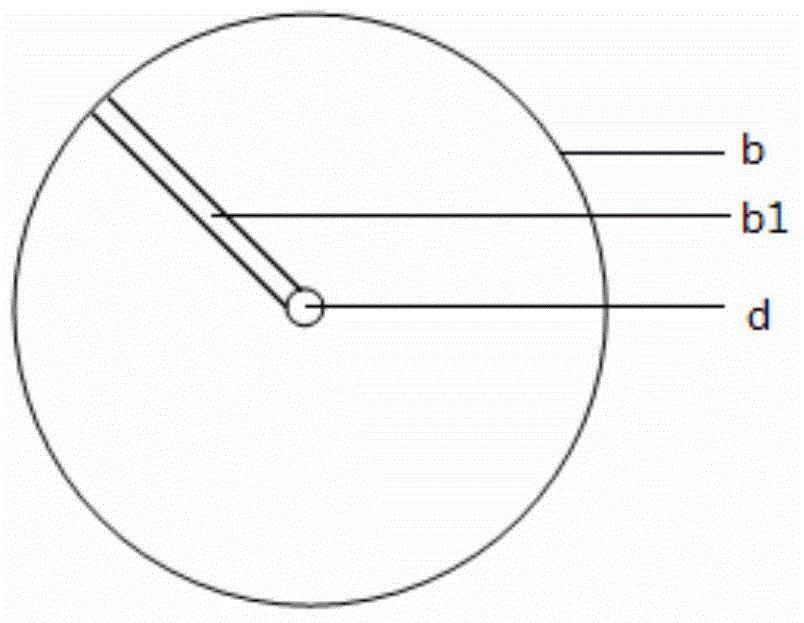
[0059] The chlorella algae liquid (cultivated with BG11 medium, OD 680 7.8) transport to the sedimentation collector a, and fill the sedimentation collector a, adjust the pH = 9, the temperature is 30 ° C, and settle in the dark for 24 hours. After the sedimentation, the separated water OD 680 is 0.45, and the sedimentation rate reaches 94%. Then the settling recovery tray b is taken out from the settling recovery tray a, and the rotating shaft d scrapes off the algal mud settled on the settling recovery tray b through a scraper and leaves the settling recovery tray b through the structure b1, and collects it, and then opens The water outlet e slowly releases the separated water, and collects the algae mud at the bottom of the settlement collector a.
Embodiment 3
[0061] This example is used to illustrate the method for harvesting microalgae of the present invention.
[0062] The chlorella algae liquid (cultivated with BG11 medium, OD 680 3.6) Transport to the sedimentation harvester a, and fill the sedimentation harvester a, adjust the pH=8.5, the temperature is 35°C, and settle in the dark for 24 hours. After the sedimentation, the separated water OD 680 is 0.33, and the sedimentation rate reaches 91%. Then open the water outlet e, slowly release the separated water, the settled algae mud stays on the settling recovery tray b and the bottom of the settling recovery device a, and the rotating shaft d passes the scraper to settle the algae mud on the settling recovery tray b Scrape off the bottom of the sedimentation collector a, and collect the algae mud at the bottom of the sedimentation collector a.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| sedimentation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| sedimentation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| sedimentation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com