Optical Signal Modulation Format Recognition Method Based on Spectral Features
A modulation format and identification method technology, applied in the field of optical fiber communication, can solve the problems of limited rate, high power consumption, limited working band, etc., and achieve the effects of wide working band, large signal transmission damage tolerance, and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
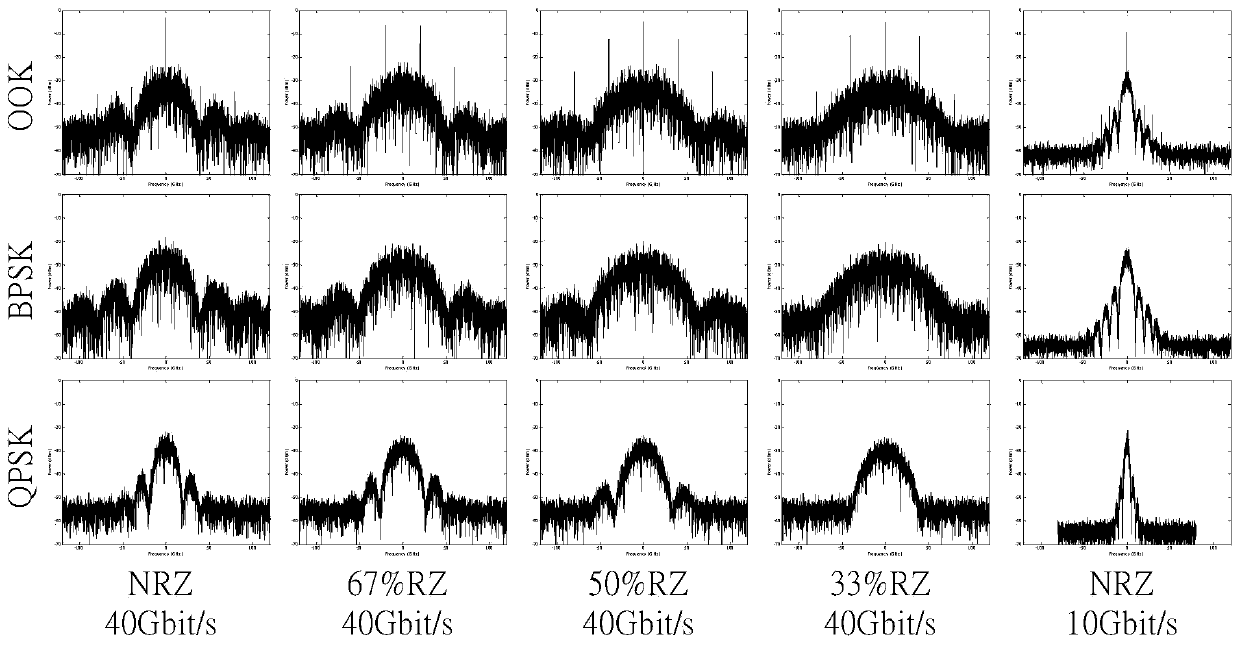
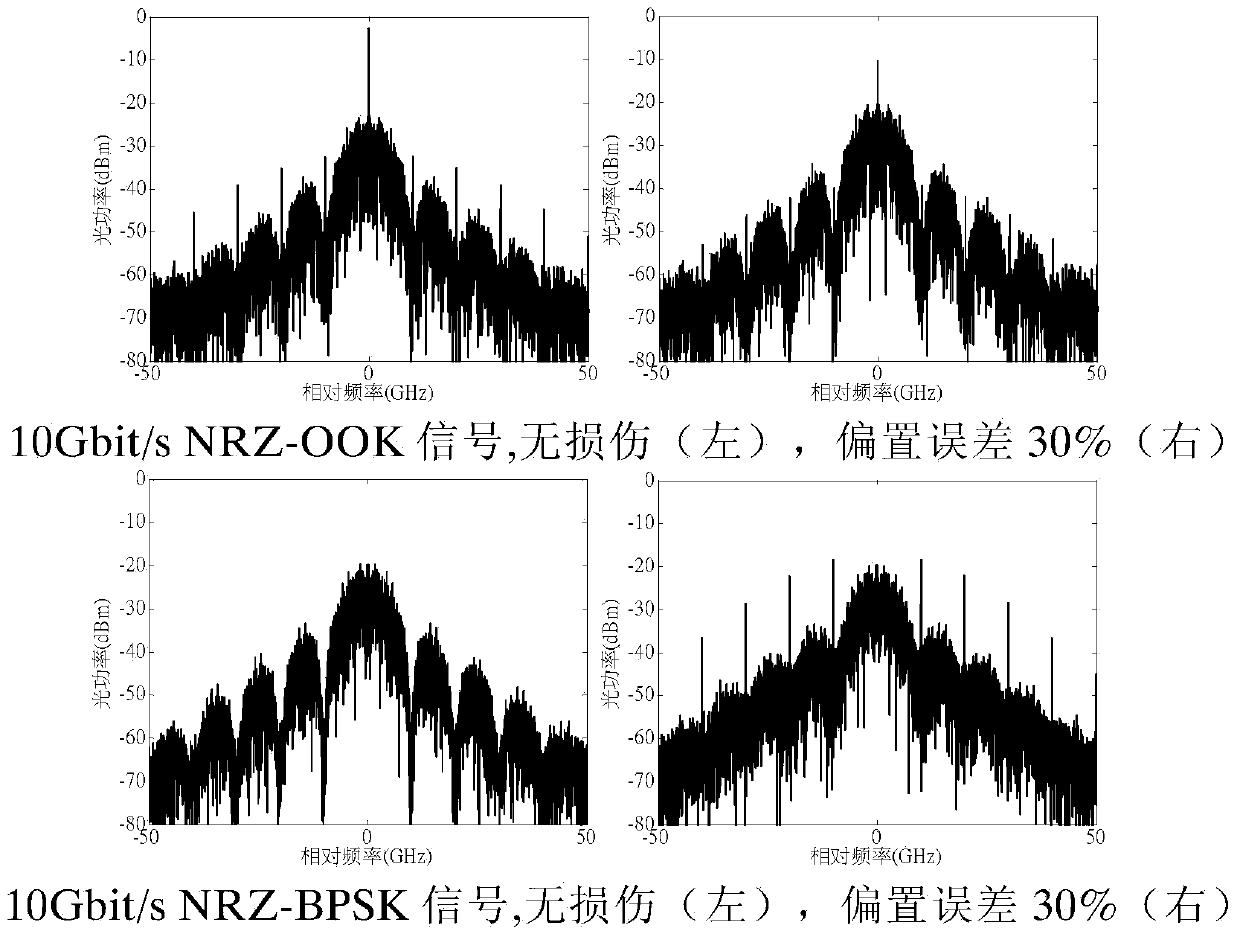
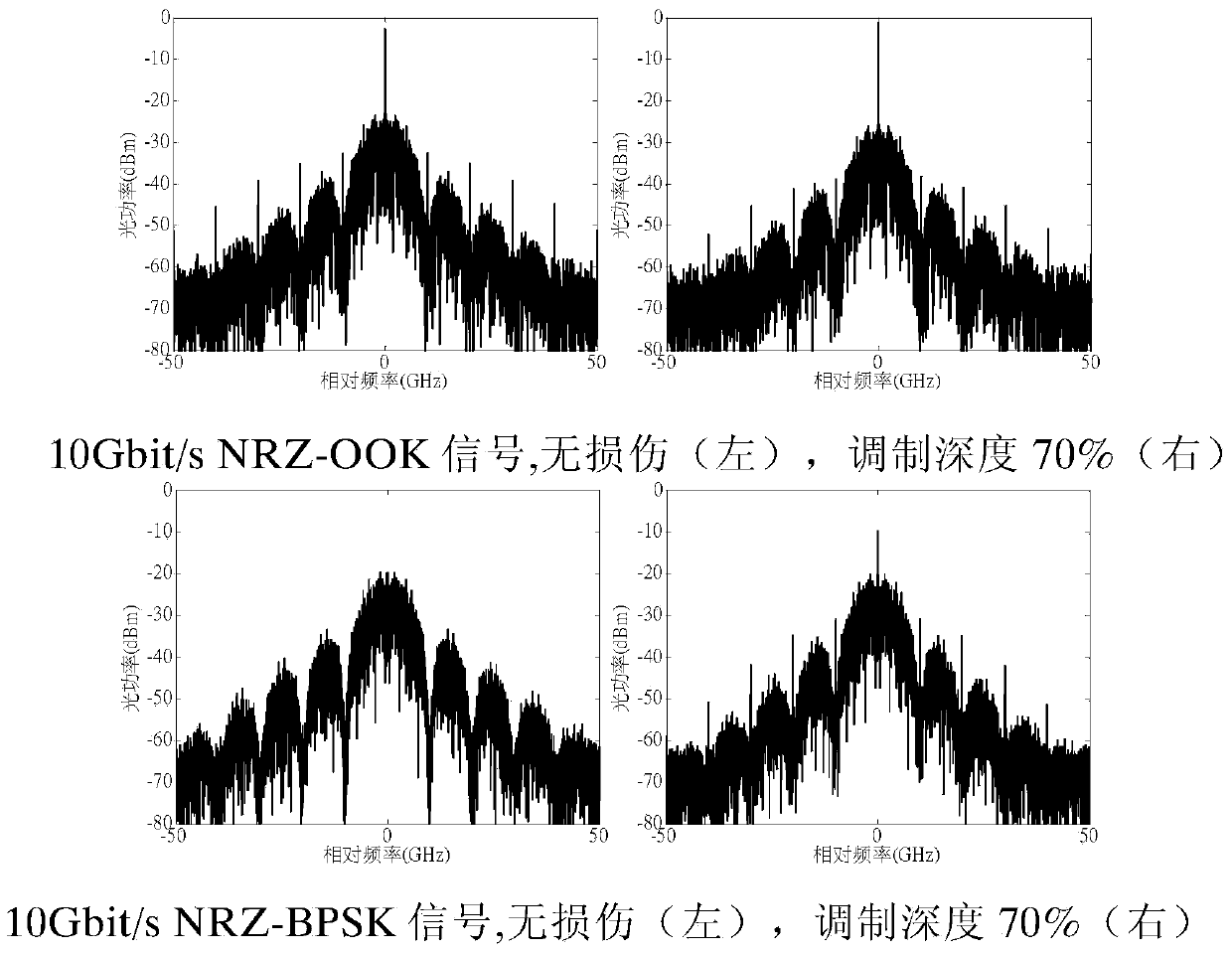
[0023] For optical signals with different modulation formats and rates, there are certain differences in their spectra, such as figure 1 shown. The spectrum of the OOK signal has obvious line spectrum, and the frequency interval between the line spectrum is proportional to the bit rate of the signal, and there is no line spectrum at the carrier frequency of the spectrum of 67% RZ-OOK signal due to carrier suppression; for the same For a baud rate-format combined signal, different duty ratios lead to different broadening of the main lobe of the spectrum. The smaller the duty ratio, the larger the width of the main lobe; while BPSK and QPSK signals with the same duty ratio and bit rate have the same shape, However, because the number of bits carried by each symbol of the two is different, the actual baud rate is different. Since the spectral broadening is proportional to the baud rate, there is a big difference between the two spectral broadening. The same bit rate and duty cycl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com