Method for identifying squids or highly processed product varieties thereof by virtue of fluorescent quantitative PCR
A fluorescent quantitative and product variety technology, applied in the field of fluorescent quantitative PCR detection, can solve the problems of low cost, messy sequencing results, affecting polymorphism of enzyme fragments, etc., and achieve the effect of short detection time, easy operation and good specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Embodiment 1, adopt above-mentioned fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method to the squid frozen product (such as frozen squid ring, frozen squid carcass) species identification of buying randomly on the market, comprise carrying out the following steps:
[0090] ①. Genomic DNA extraction from the squid sample to be tested; Axygen Genomic DNA Mini-Extraction Kit was used to extract sample DNA and store at -20°C.
[0091] ②. Design of primers and probes for specific identification of common squid;
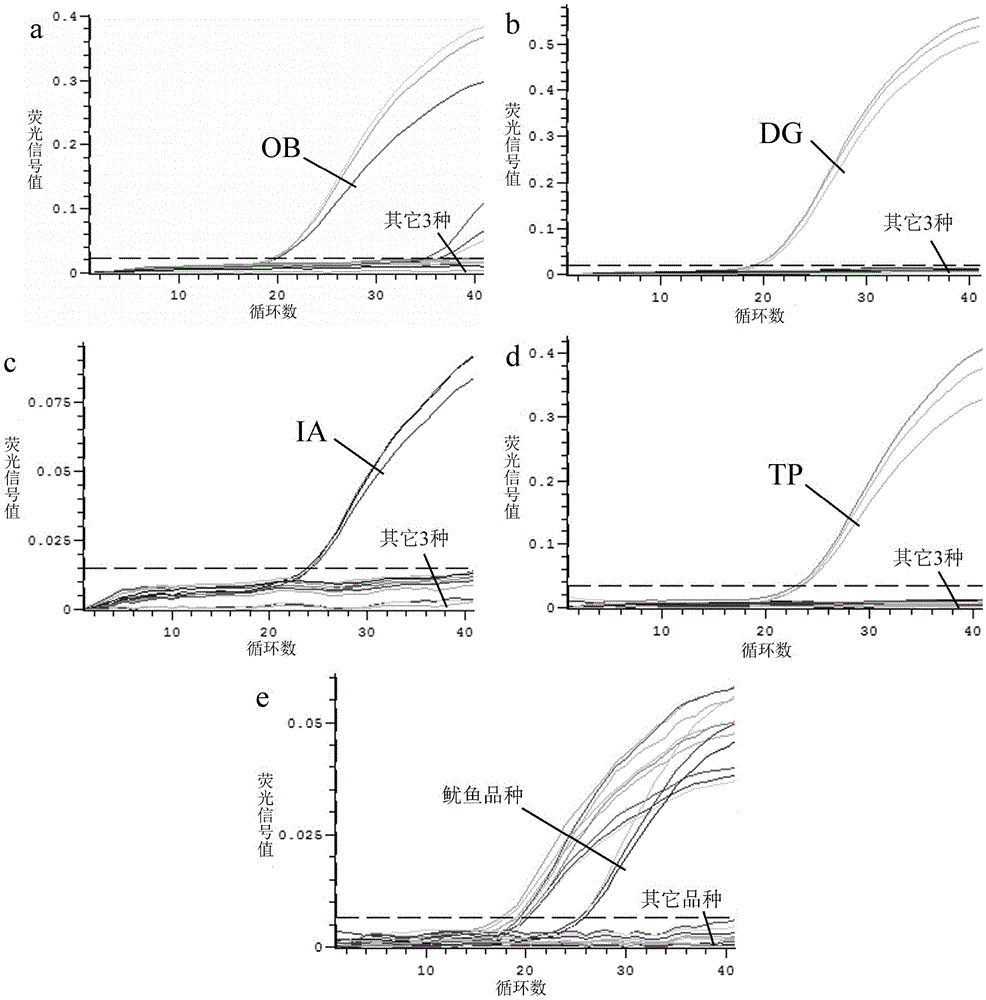
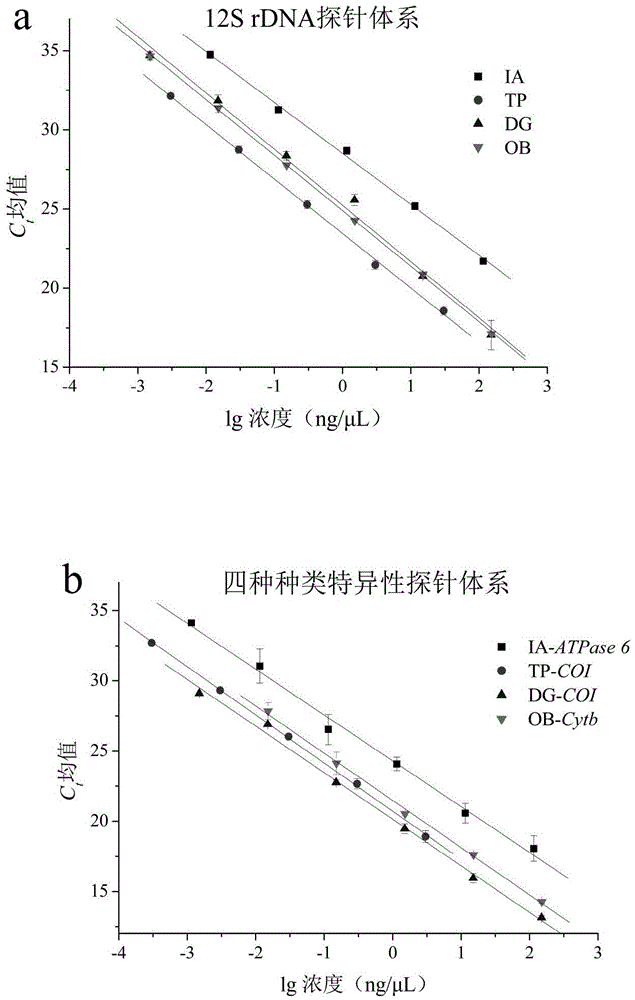
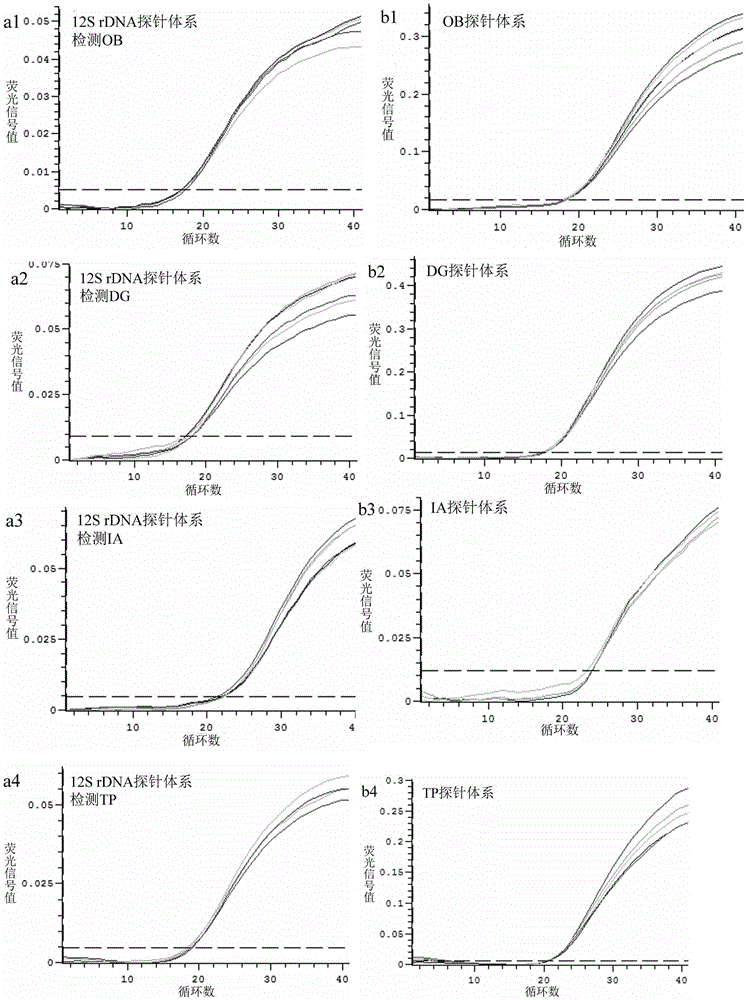
[0092] The 4 common squid are: North Pacific squid (Ommastrephesbartramii), Peruvian squid (Dosidicusgigas), Argentine squid (Illexargentinus) and Japanese sea squid (Todarodespacificus);
[0093] Specifically as described in Table 1.
[0094] ③. Fluorescence quantitative PCR amplification system setting;
[0095] Using genomic DNA as an amplification template, the above-mentioned specific primers and probes are used for real-time fluorescent PCR detection.
[0096] ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Embodiment 2, adopt above-mentioned fluorescent quantitative PCR detection method to carry out kind identification to the canned squid food that buys randomly on the market:
[0113] The canned food labeled as canned squid or canned squid was randomly purchased from the market, and the sample DNA was extracted with TAKARA Meat DNA Extraction Reagent (Cat#9178) and stored at -20°C. The species were identified by fluorescent quantitative PCR. If there is no amplification curve for the 12S rDNA detection gene of the Squididae or C t If the value is ≥ 34, the determination result is negative, and it can be determined that the canned fish sample does not contain fish components of the family Scutellaria; C t If the value is less than 34, it can be determined that the sample result is positive, that is to say, it is determined that the sample contains fish components of the family Scutellaria. If the specificity system tests of the four common squids have no amplification c...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Embodiment 3, adopt above-mentioned fluorescent quantitative PCR detection method to carry out species identification to the deep-processed squid food that buys randomly on the market:
[0120] Randomly purchased from the market marked as squid shreds, squid slices and products containing squid in the product ingredients, TAKARA meat product DNA extraction reagent (Cat#9178) was used to extract sample DNA, and stored at -20 °C. The species were identified by fluorescent quantitative PCR. If there is no amplification curve for the 12S rDNA detection gene of the Squididae or C t If the value is ≥ 34, the judgment result is negative, and it can be judged that the deep-processed product does not contain fish components of the family Scutellaria; C t If the value is less than 34, it can be determined that the sample result is positive, that is to say, it is determined that the sample contains fish components of the family Scutellaria. If there is no amplification curve in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com