In-situ regeneration method of solid polymer electrolyte water electrolyzer
A solid polymer, in-situ regeneration technology, applied in the electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of heavy workload, achieve low cost, improve regeneration efficiency, and restore performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
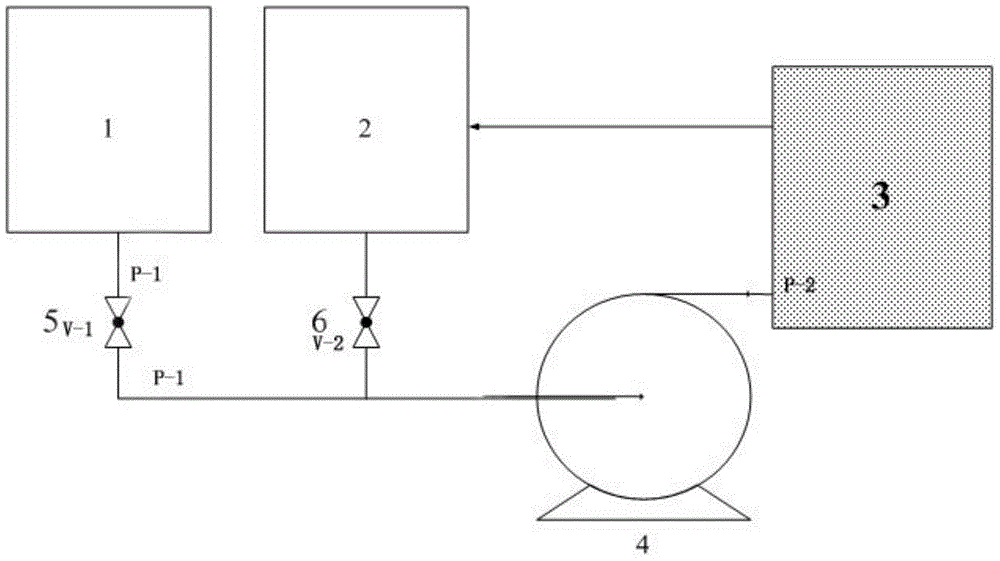
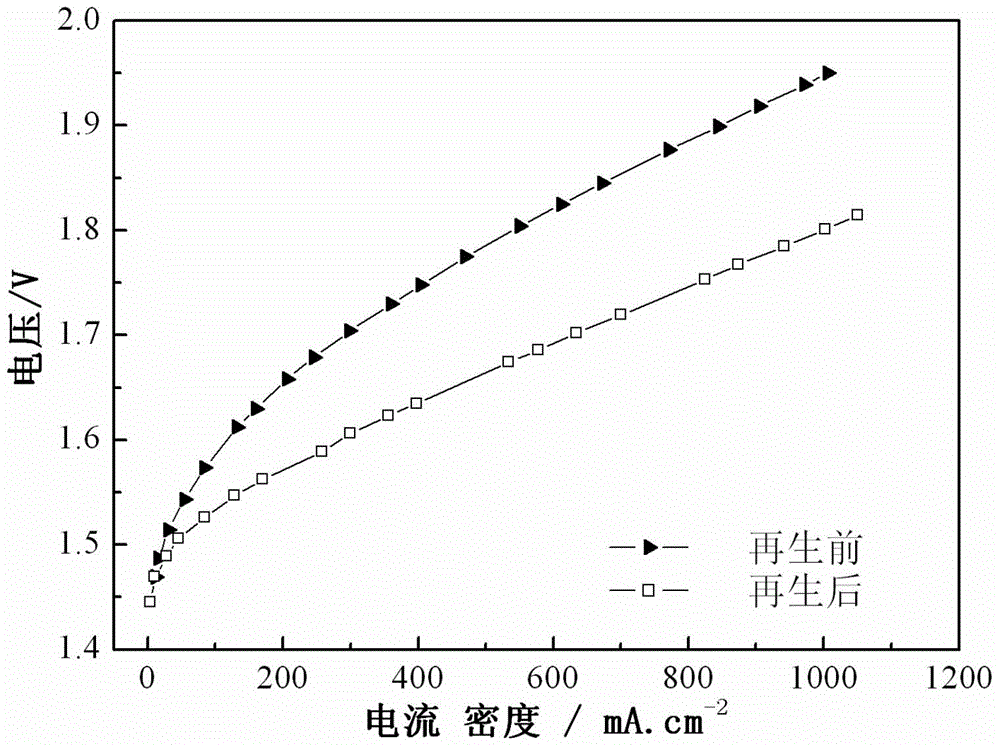
[0023] Embodiment 1 adopts the water pump circulation cleaning mode, at first 4MH 2 o 2 Pass the solution into the anode of the SPE water electrolysis cell for 7 hours, then clean the anode and cathode of the electrolysis cell with pure water for 8 hours, repeat the above steps 5 times, then measure the performance of the electrolysis cell after regeneration, and compare the V-I curves before and after regeneration, as shown in figure 2 As shown, the electrolytic cell is at 500mAcm before regeneration -2 The voltage of the battery is 1.77V, and it is 1.65V after regeneration, and the performance of the electrolytic cell is improved by 120mV, so this method can restore the performance of the electrolytic cell to a large extent.
Embodiment 2
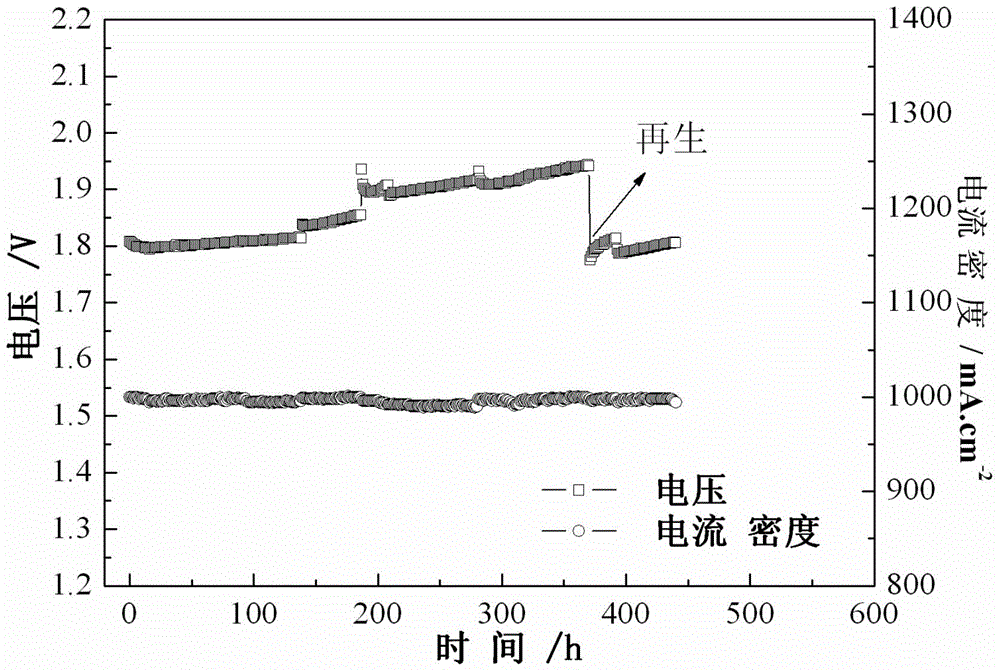
[0025] Embodiment 2 adopts the siphon static cleaning method, passes 4.5M hydrochloric acid aqueous solution into the anode and cathode of the SPE water electrolysis cell, soaks the SPE water electrolysis cell for 24 hours, repeats 4 times; then cleans with pure water for 8 hours, repeats 5 times. Then proceed to the electrolytic cell life experiment, such as image 3 shown, constant current density 1000mAcm -2 Running, the voltage is reduced from 1.95V to 1.75V, and the performance is basically stable until 450h, which shows that this method can restore the performance of the electrolytic cell to a large extent.
[0026] The above examples illustrate that the regeneration method of the present invention can prolong the life of the SPE water electrolysis cell, reduce the operating cost of the SPE water electrolysis cell, and is of great significance for promoting the marketization process of the SPE electrolysis cell.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com