Method and devices for time and frequency synchronization using a phase locked loop
A digital phase-locked loop, time technology, used in synchronization devices, automatic power control, multiplexing communication, etc., can solve problems such as clock signal deterioration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0080] Development of basic clock models and measurement and processing models
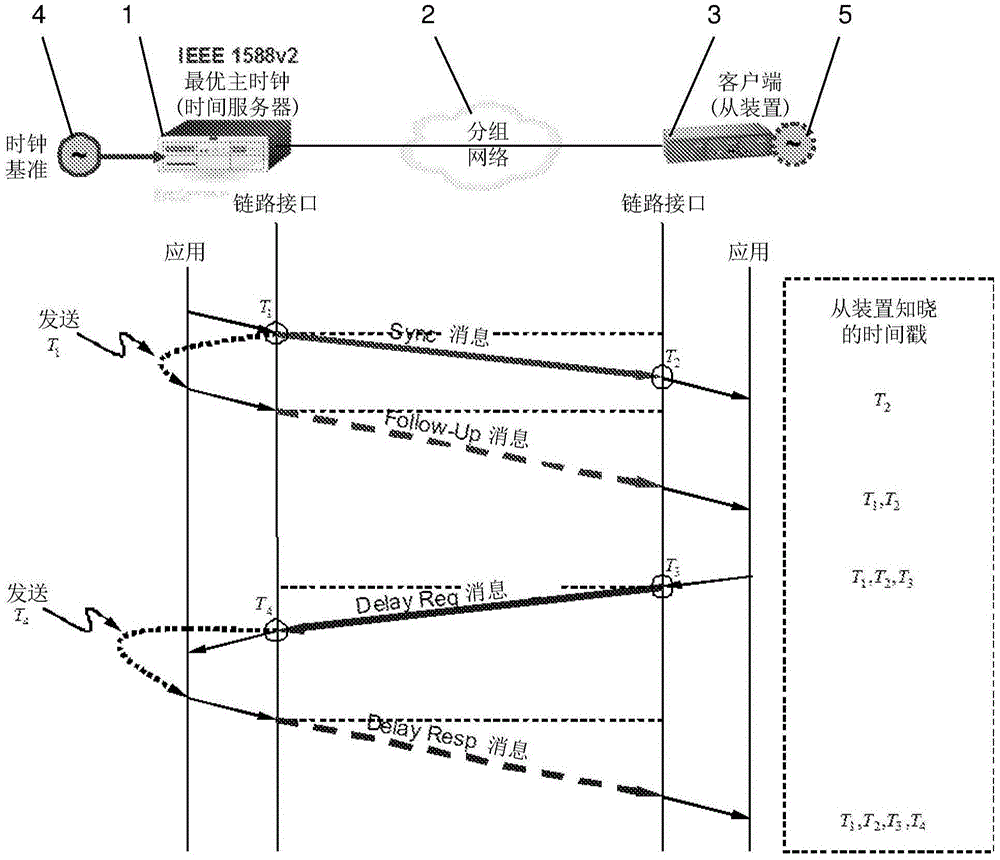
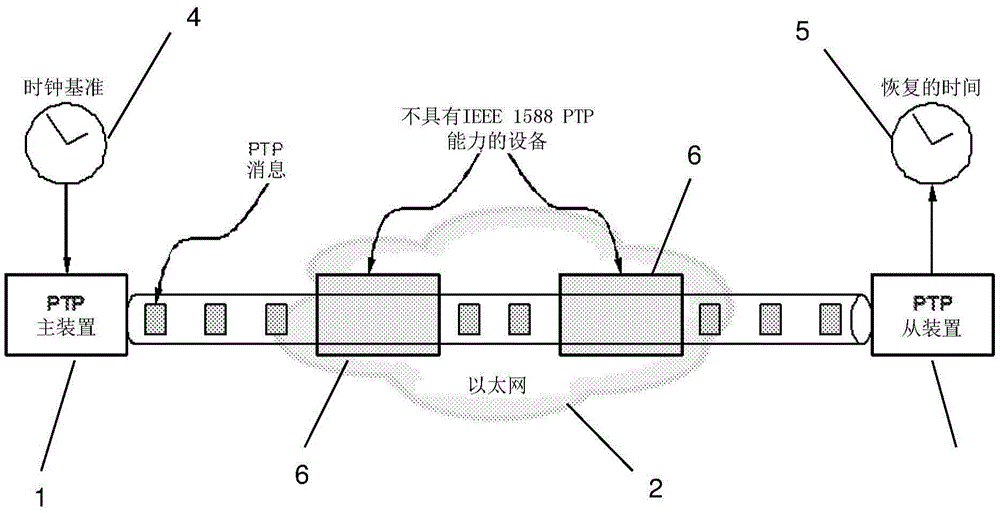
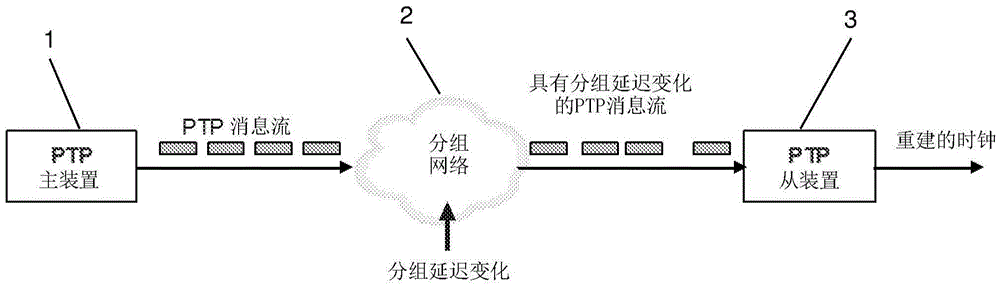
[0081] Consider the time server (master) clock S and the time client (slave) clock C separately. The difference or offset of clock C relative to S at time t≥0 is θ(t)=(S(t)−C(t)). t is used to indicate real or reference (ideal) time. Frequency is the rate at which a clock advances, and the frequency of S at time t is s'(t). Skew α is defined as the normalized frequency difference between a clock and another clock. Generalized clock skew and skew equations can then be defined for synchronization problems. Assuming at any particular moment, an instantaneous diagram of the relationship between a master (server) clock with timeline S(t) and a slave (client) clock with timeline C(t) can be given by Figure 5 is described by the known simple skewed clock model shown, and is described by the following equation,
[0082] S(t)=(1+α)C(t)+θ, (1)
[0083] Among them, the normalized α is a very small quan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com