Patents
Literature
74 results about "Packet delay variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
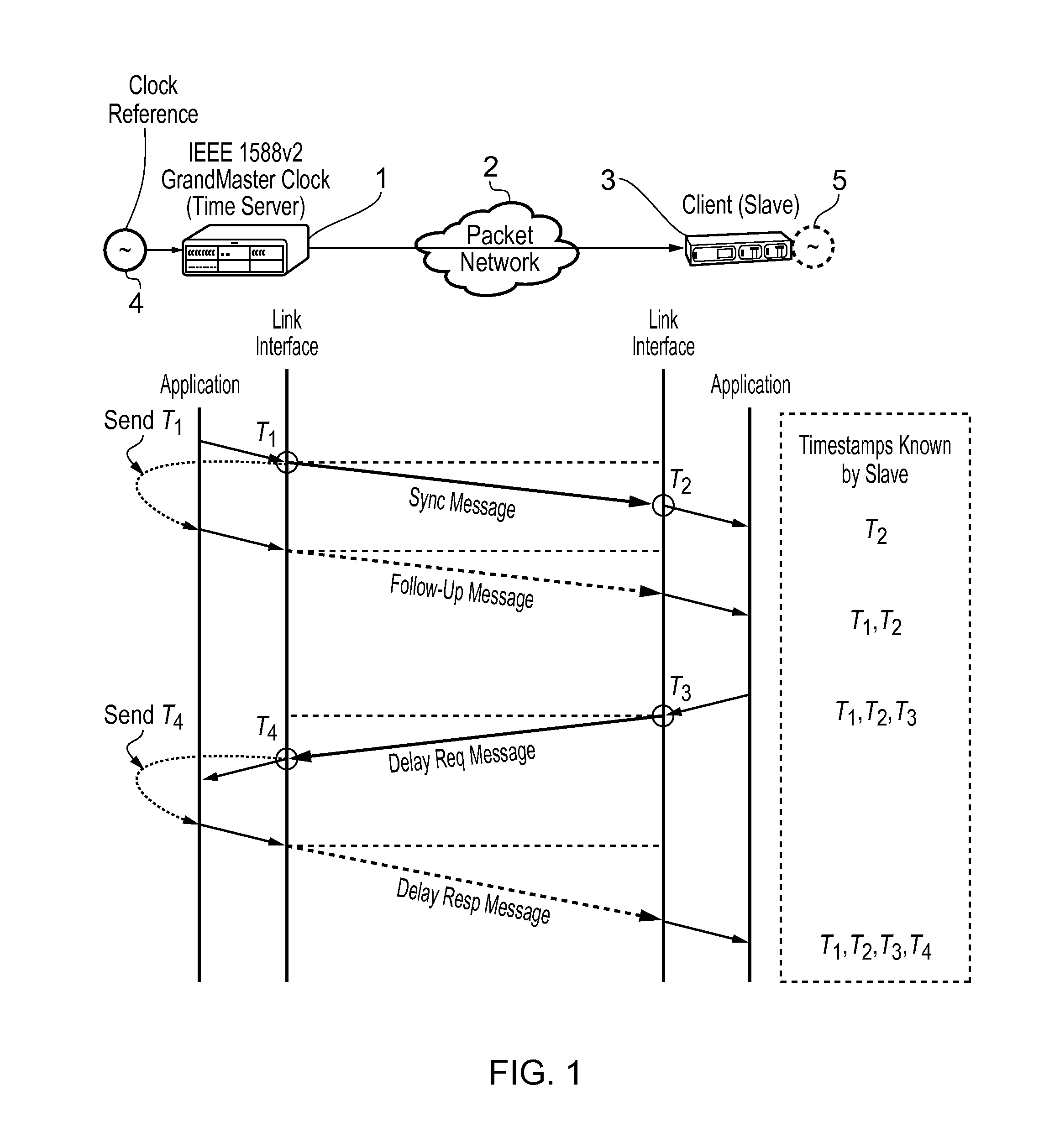
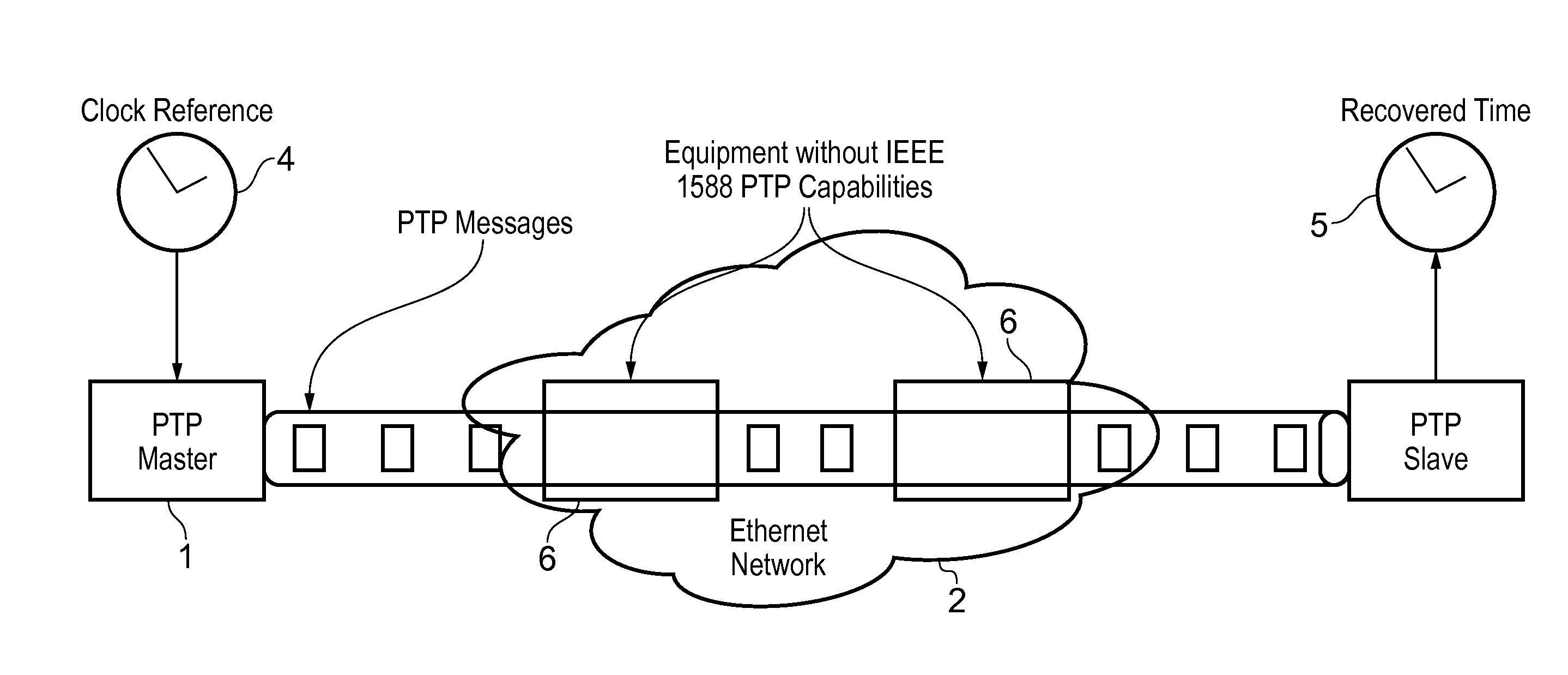
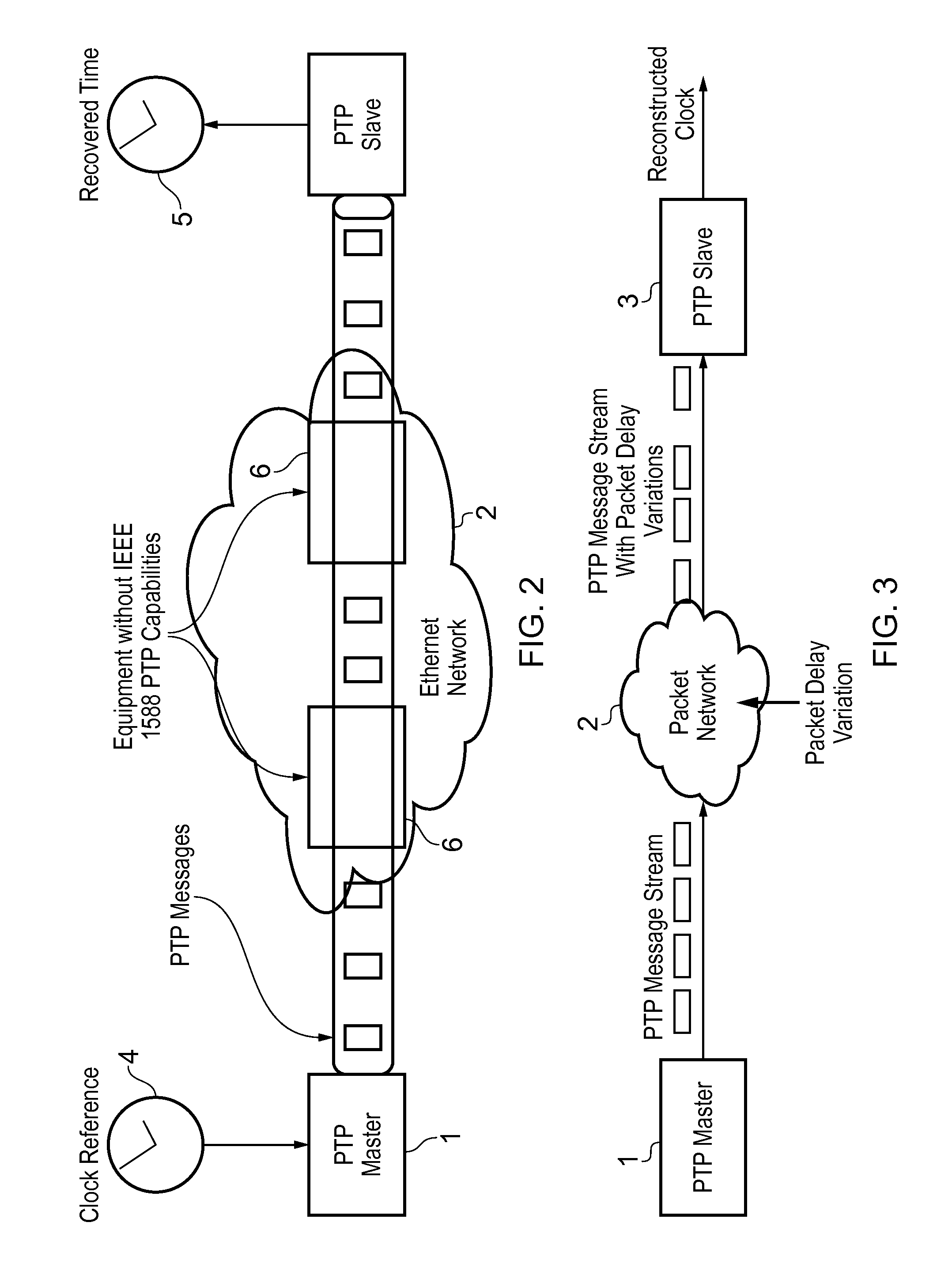
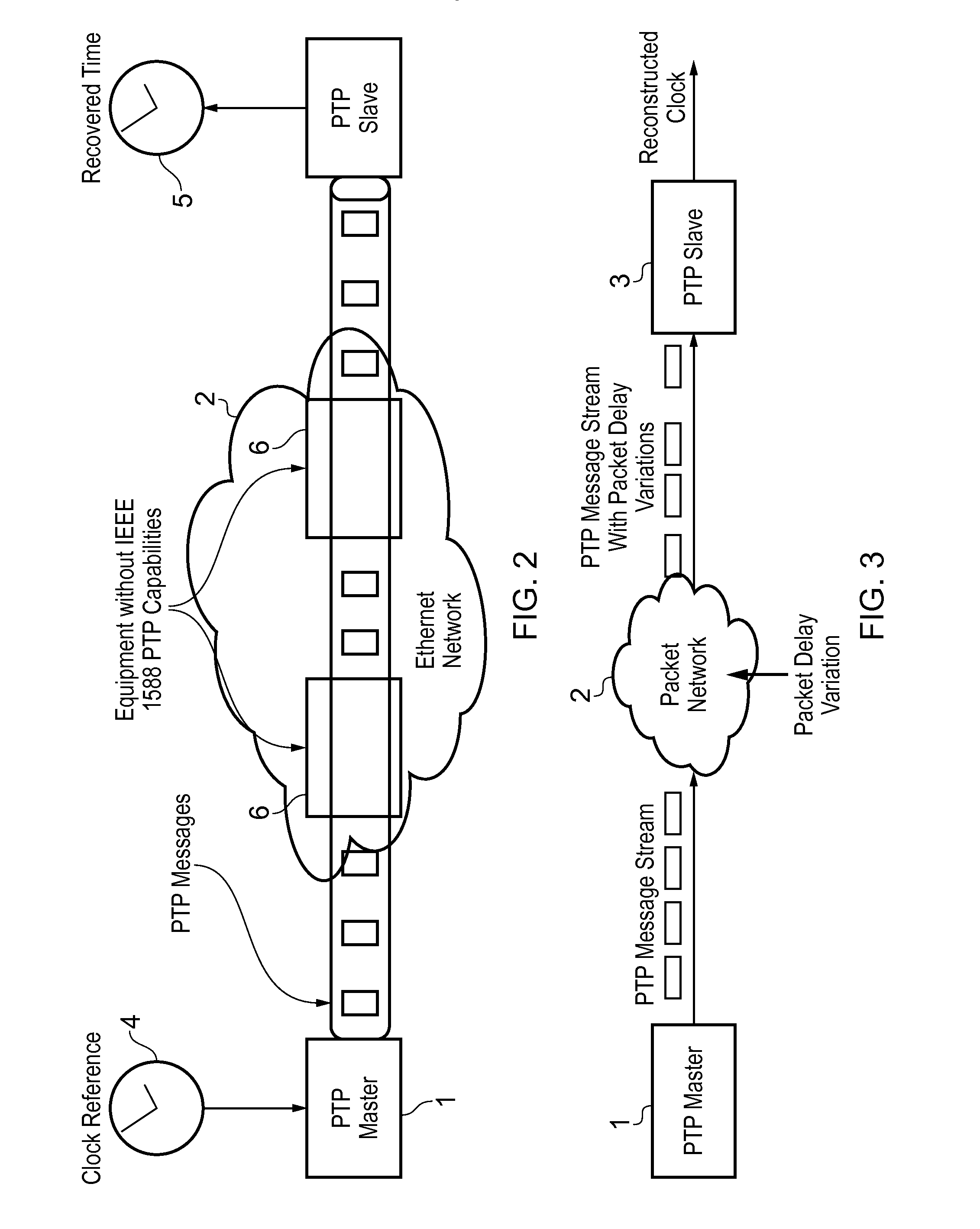
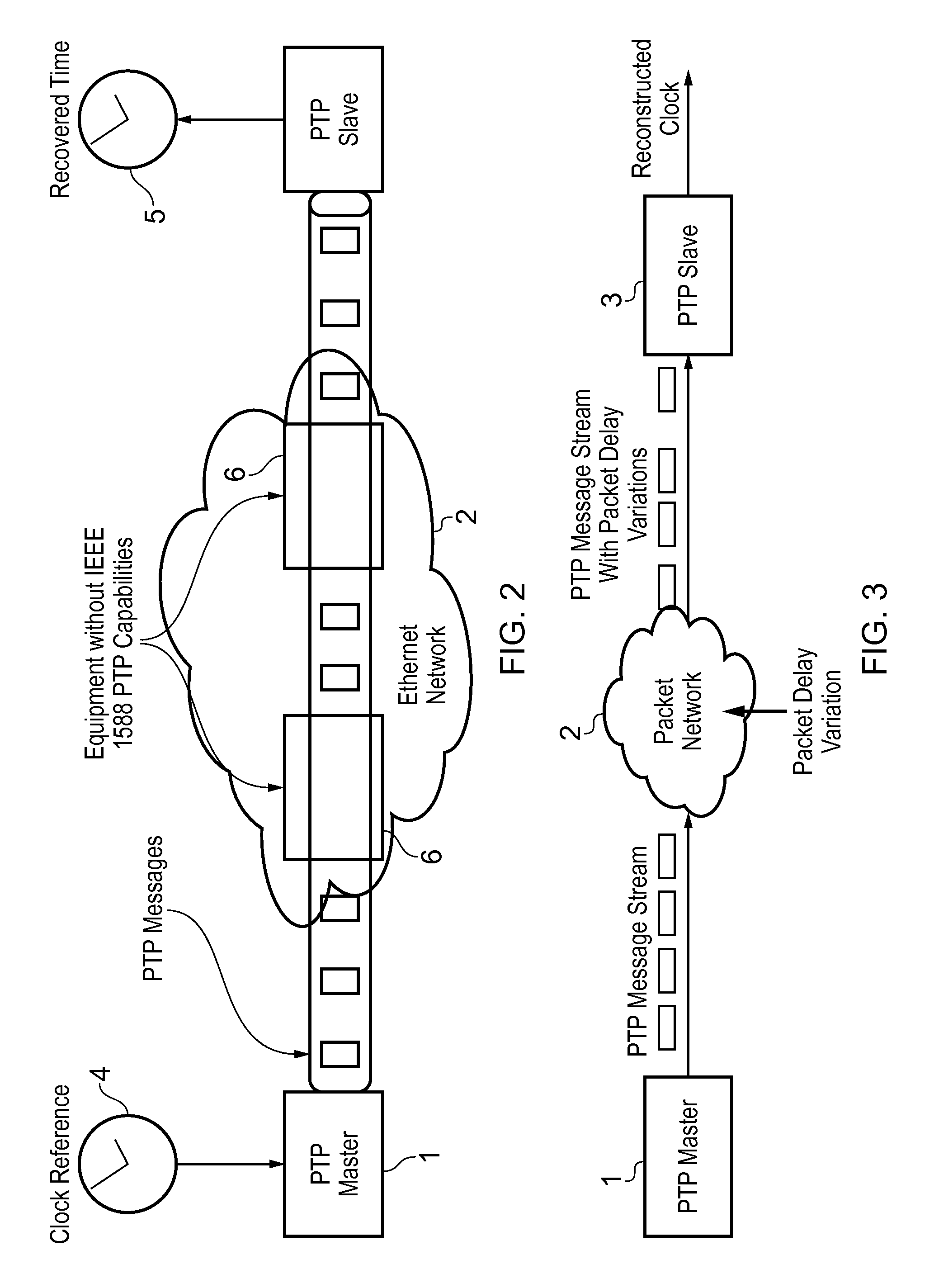
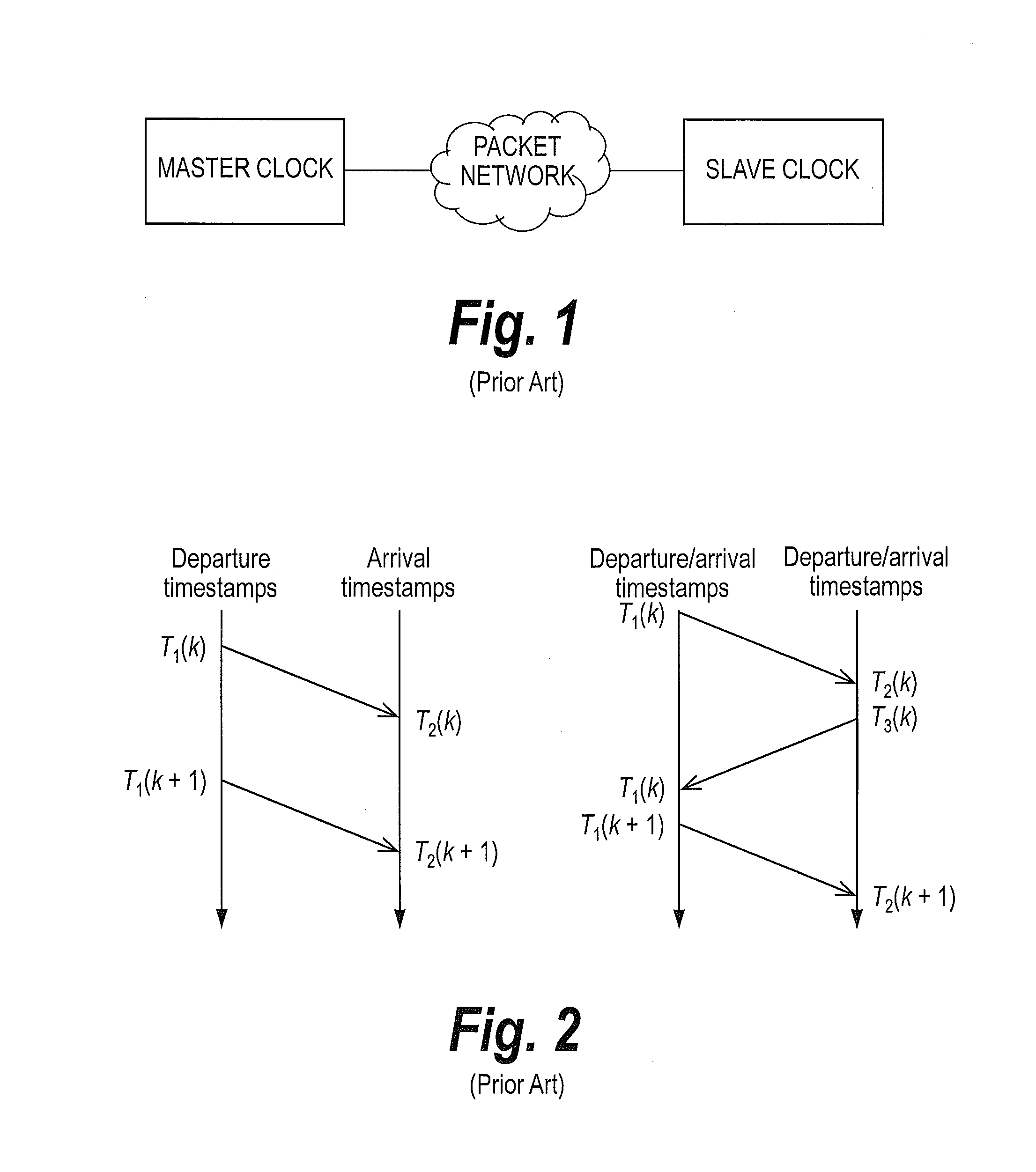
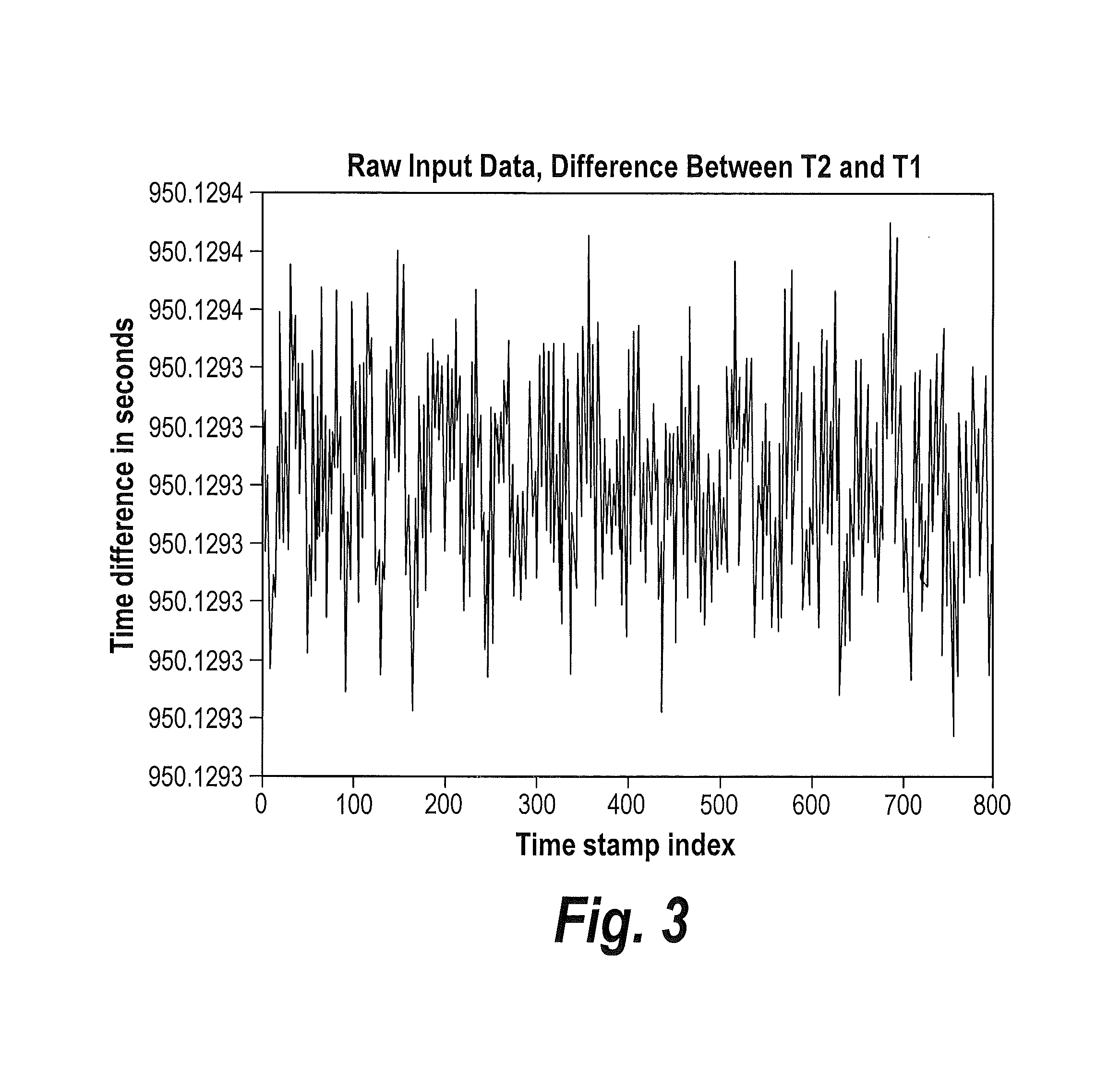
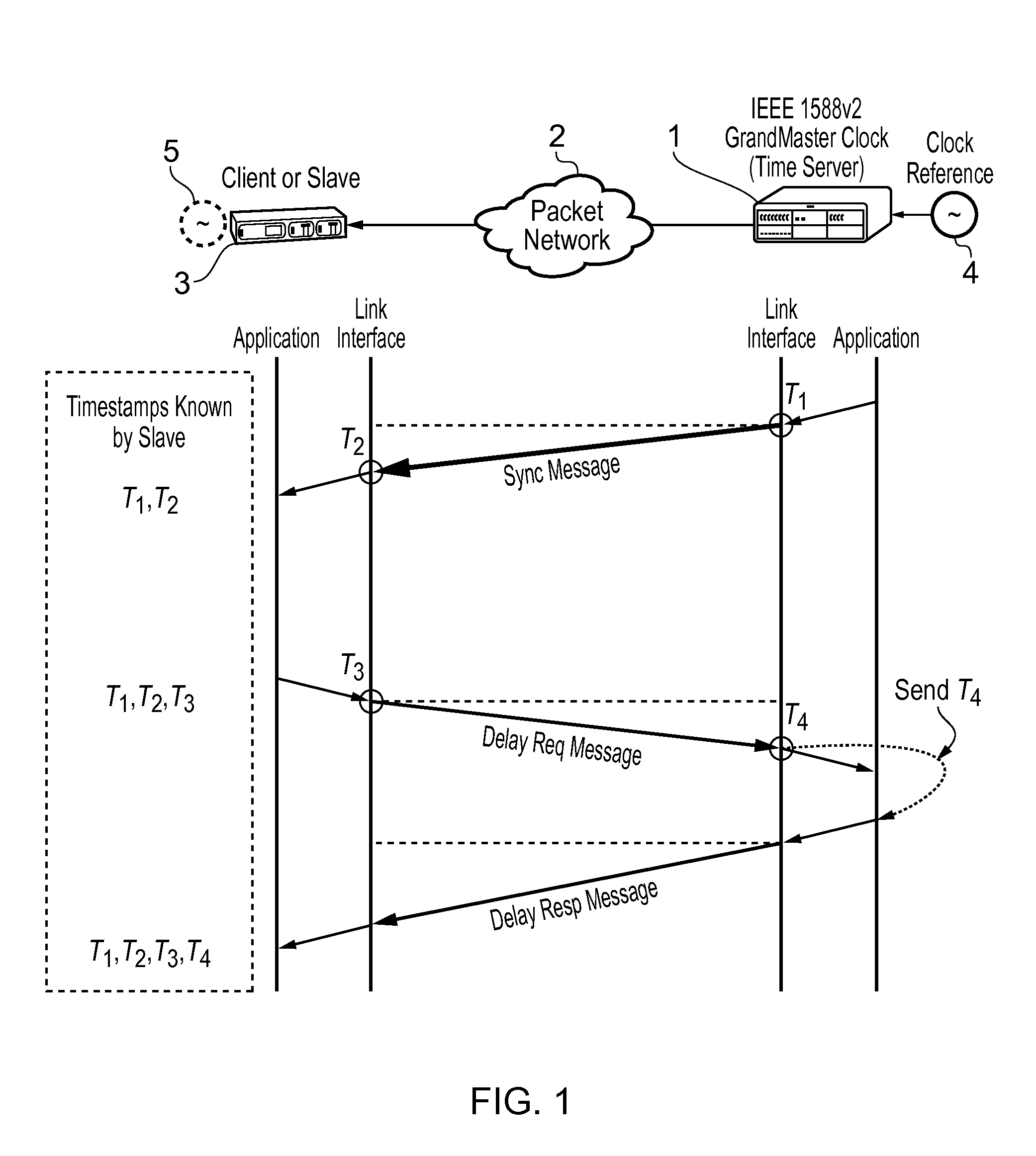
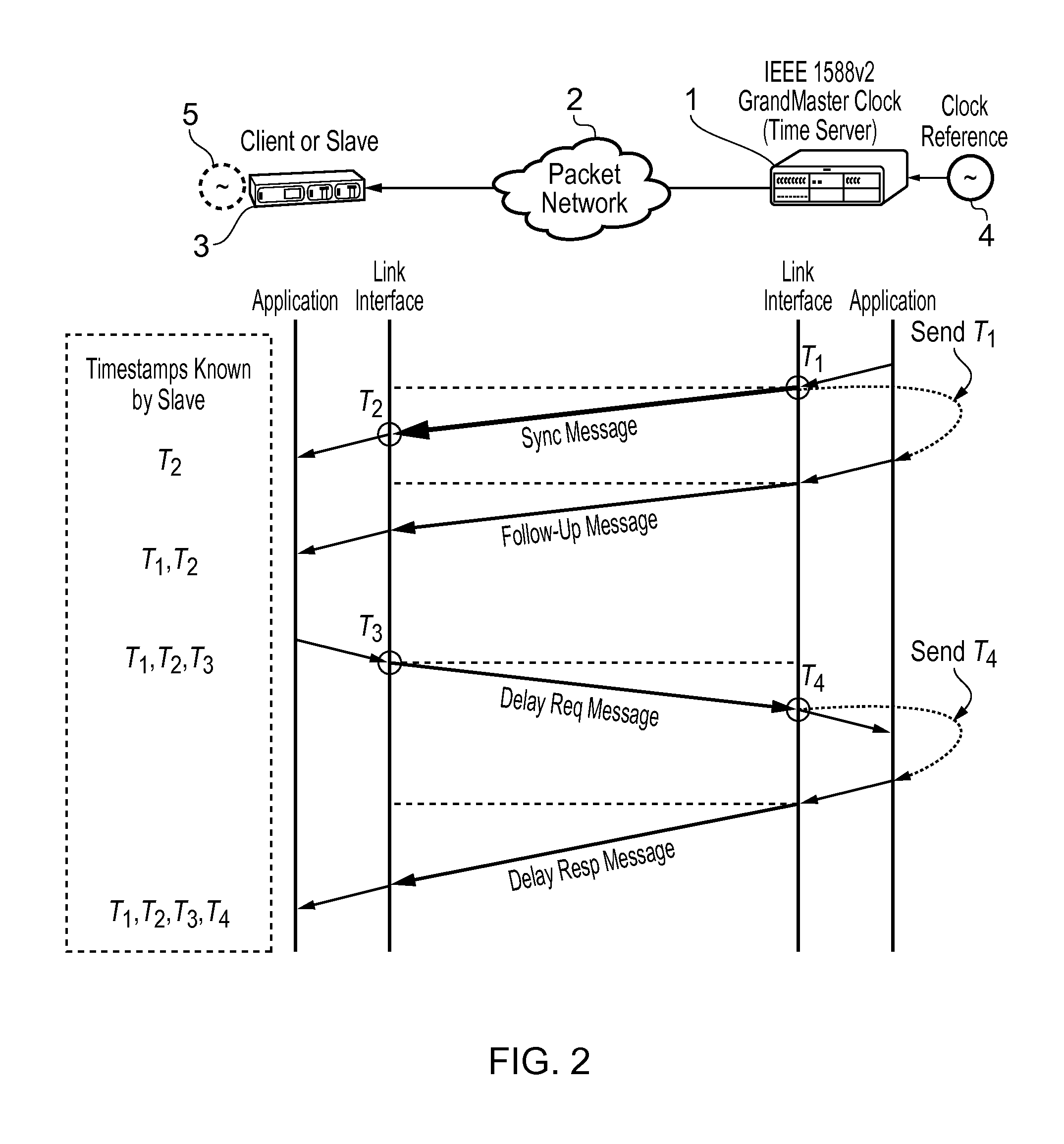
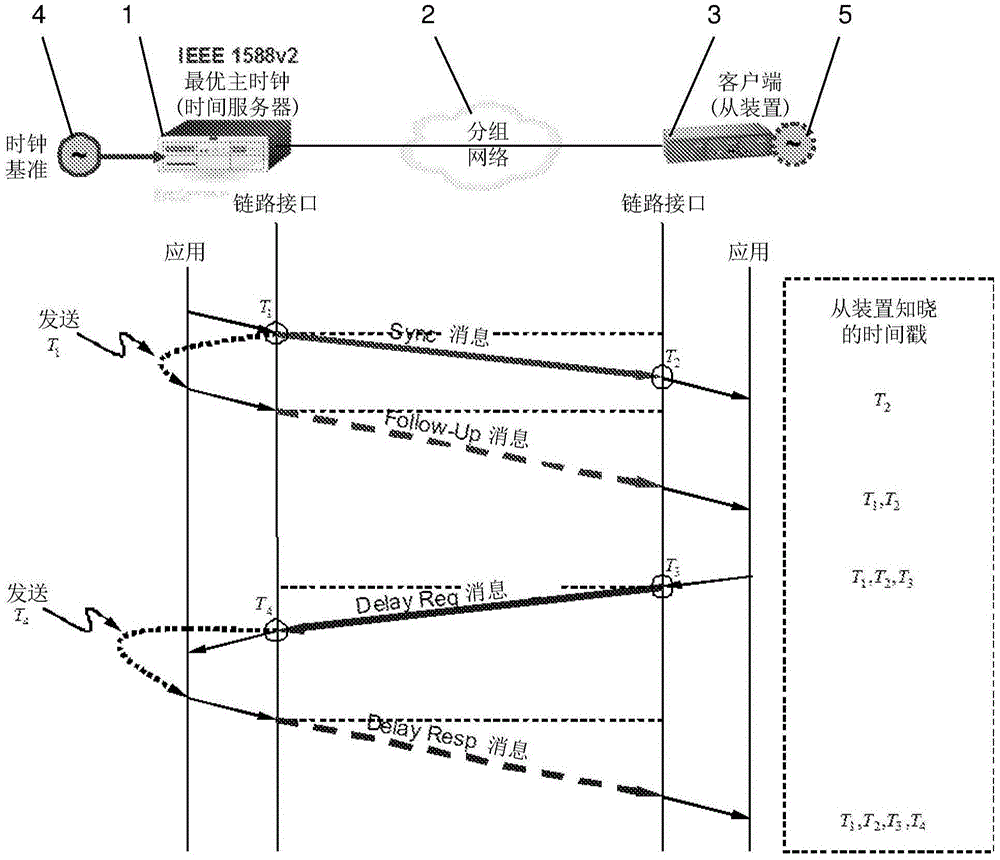
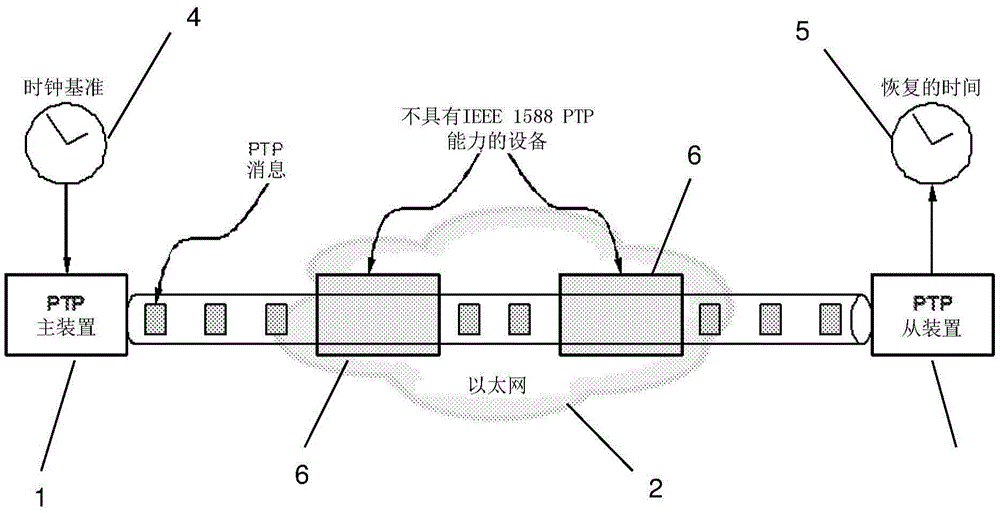
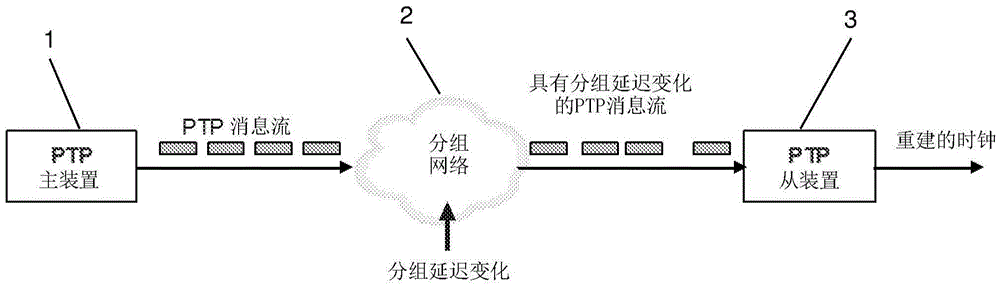
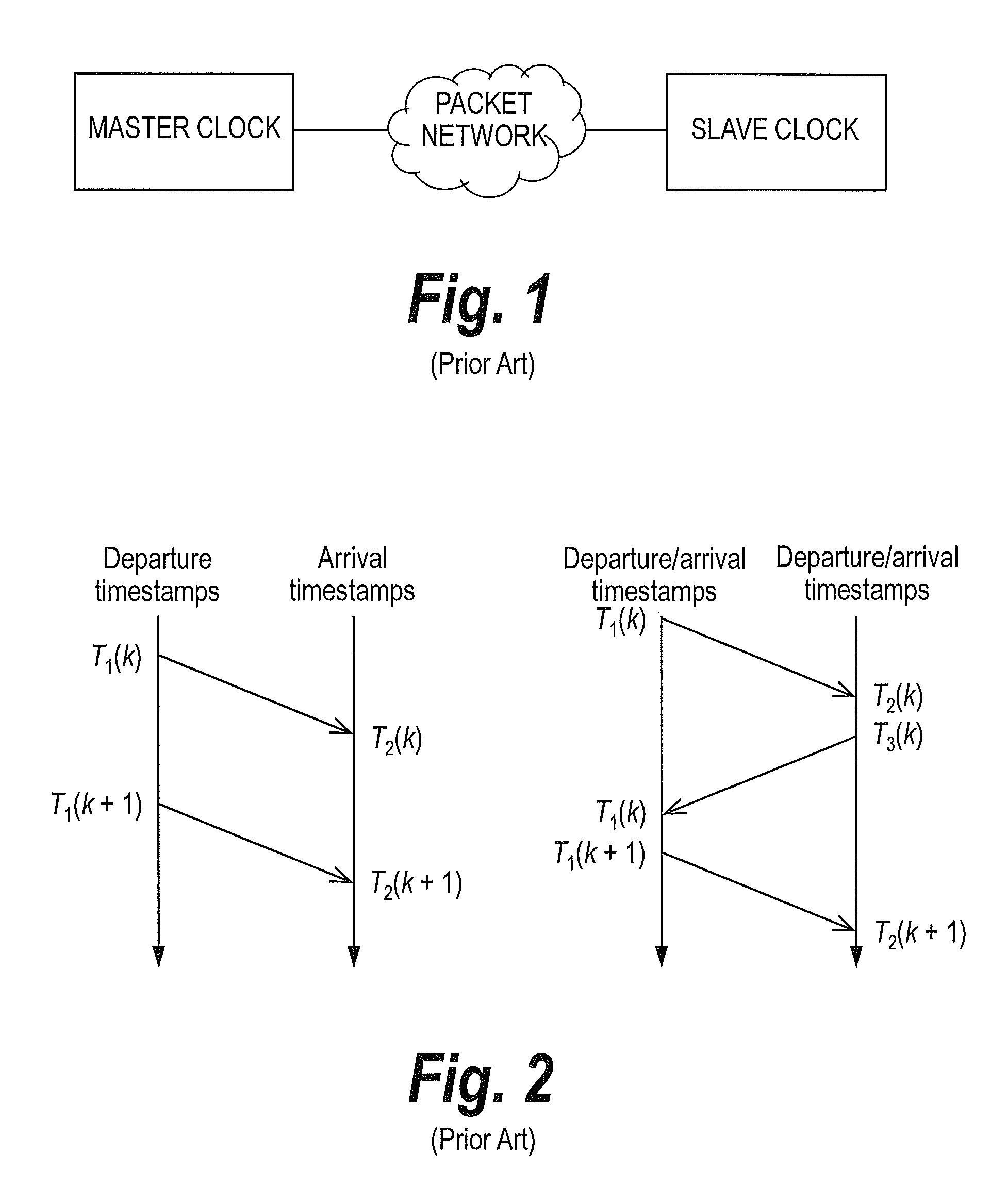
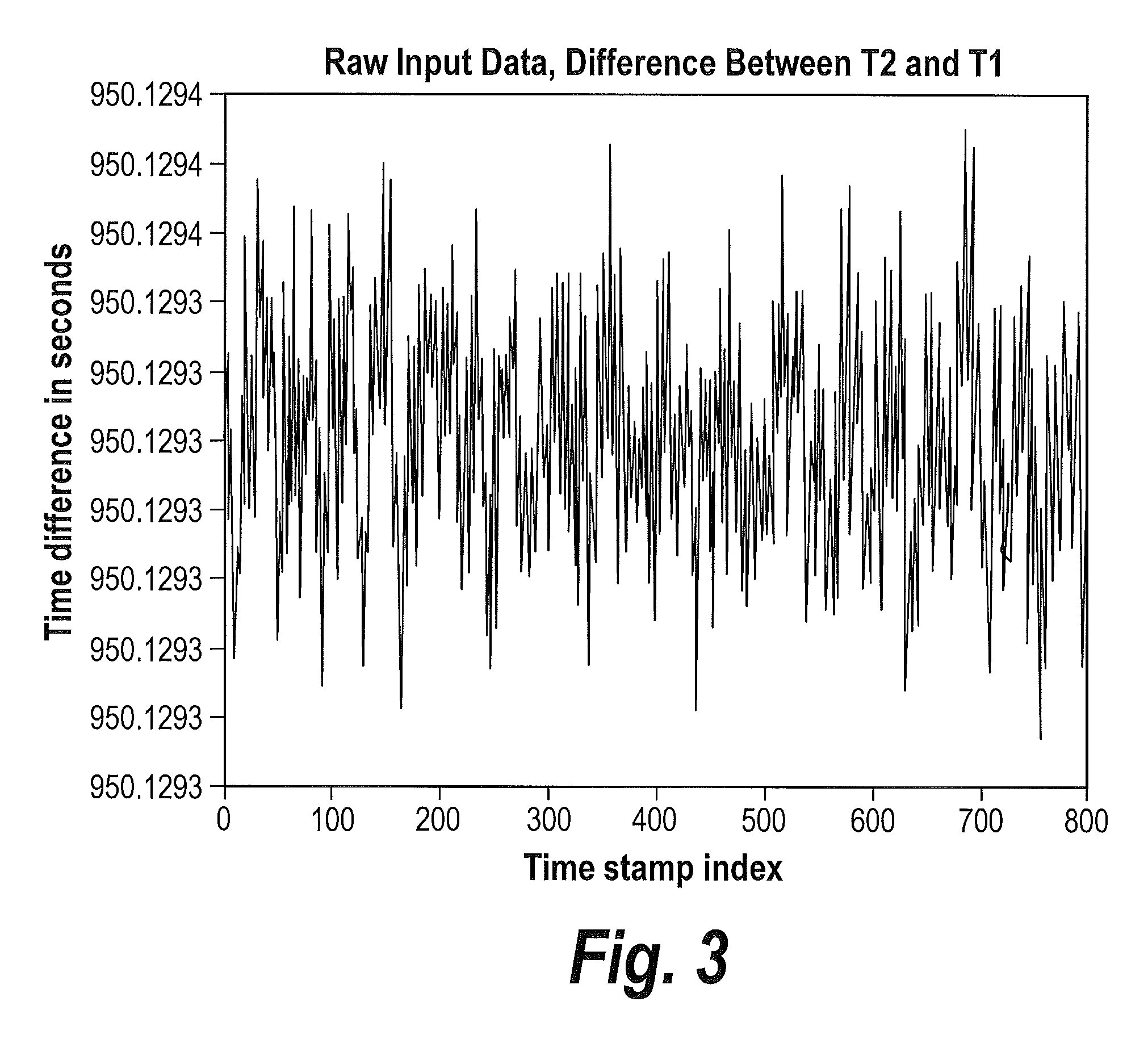
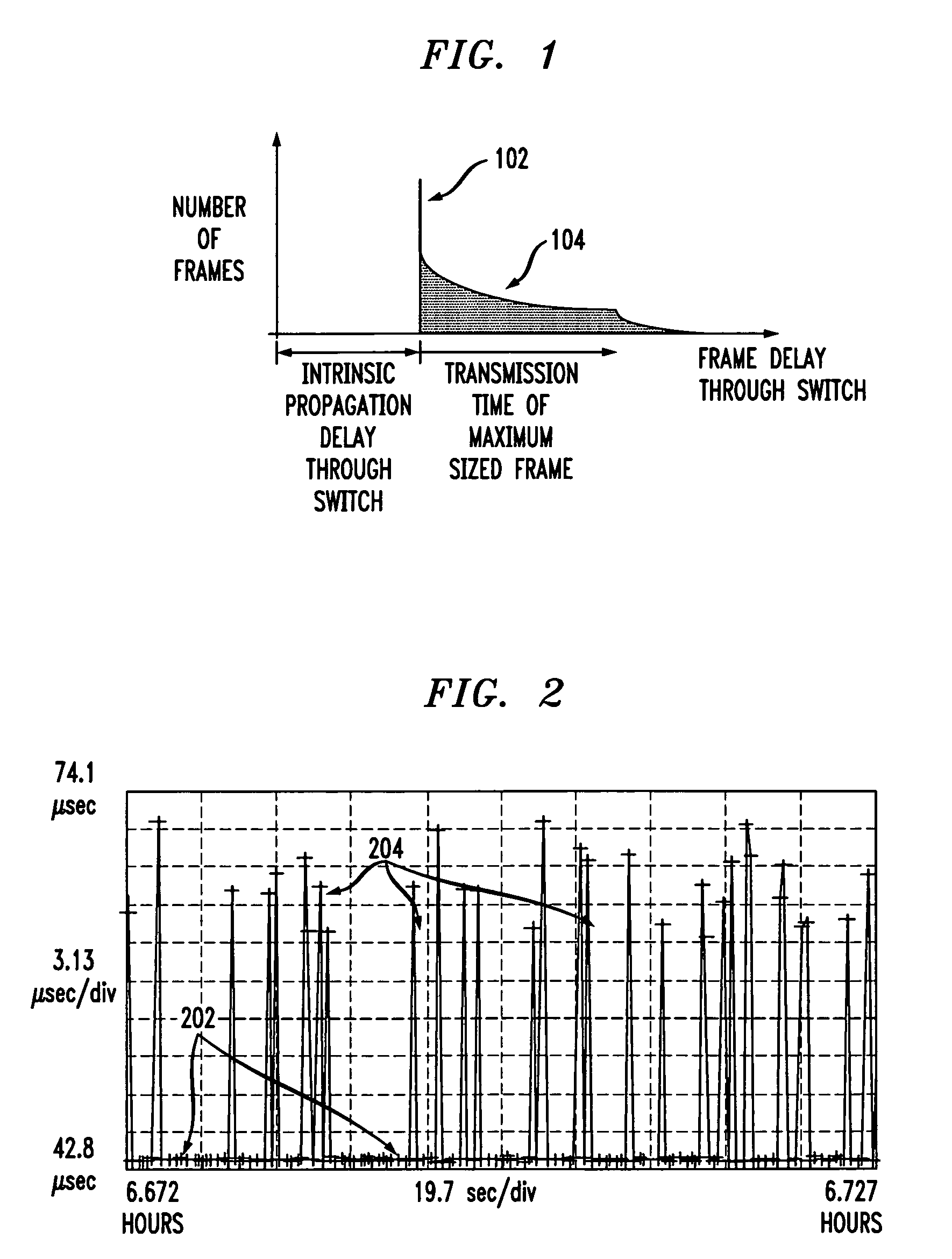
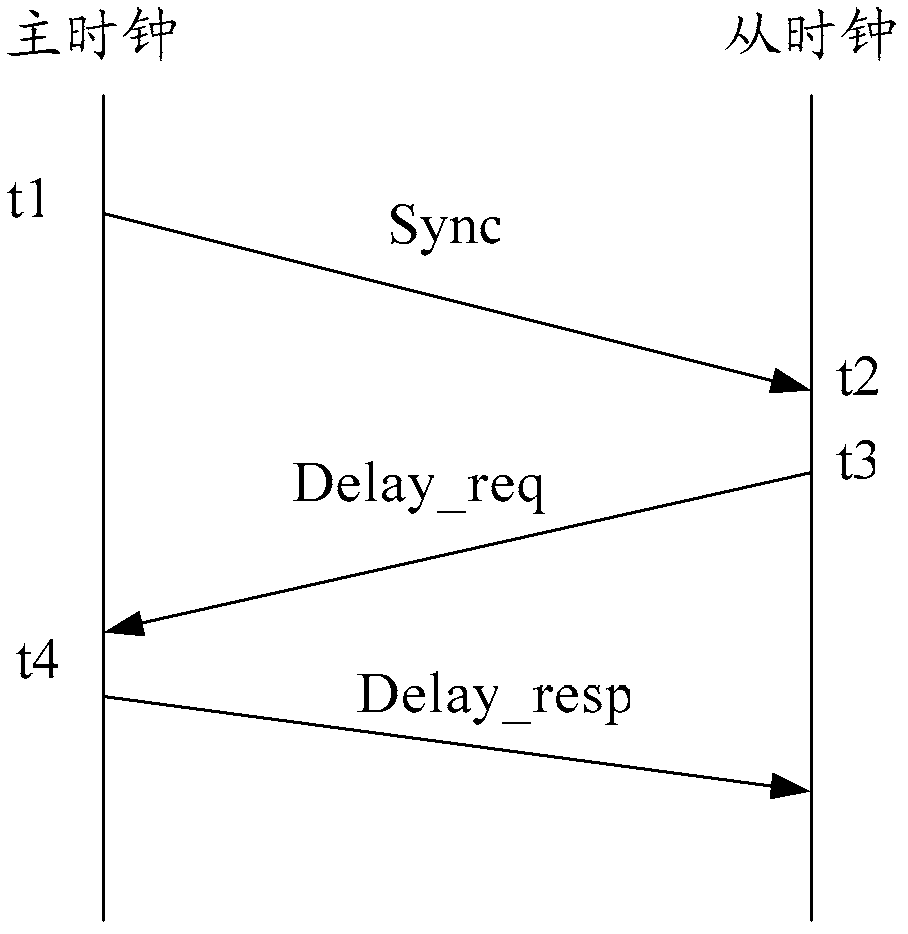
In computer networking, packet delay variation (PDV) is the difference in end-to-end one-way delay between selected packets in a flow with any lost packets being ignored. The effect is sometimes referred to as packet jitter, although the definition is an imprecise fit.
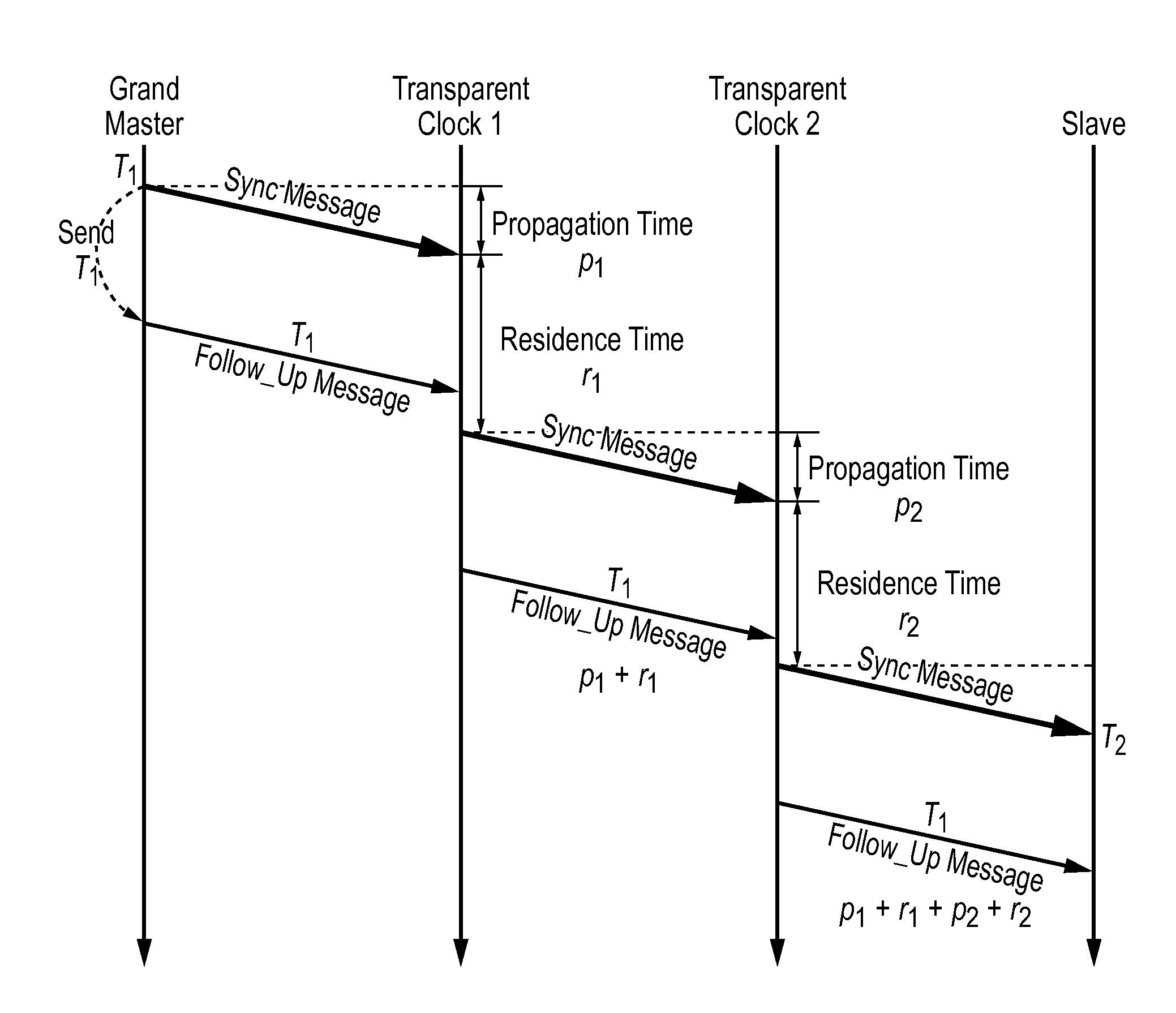
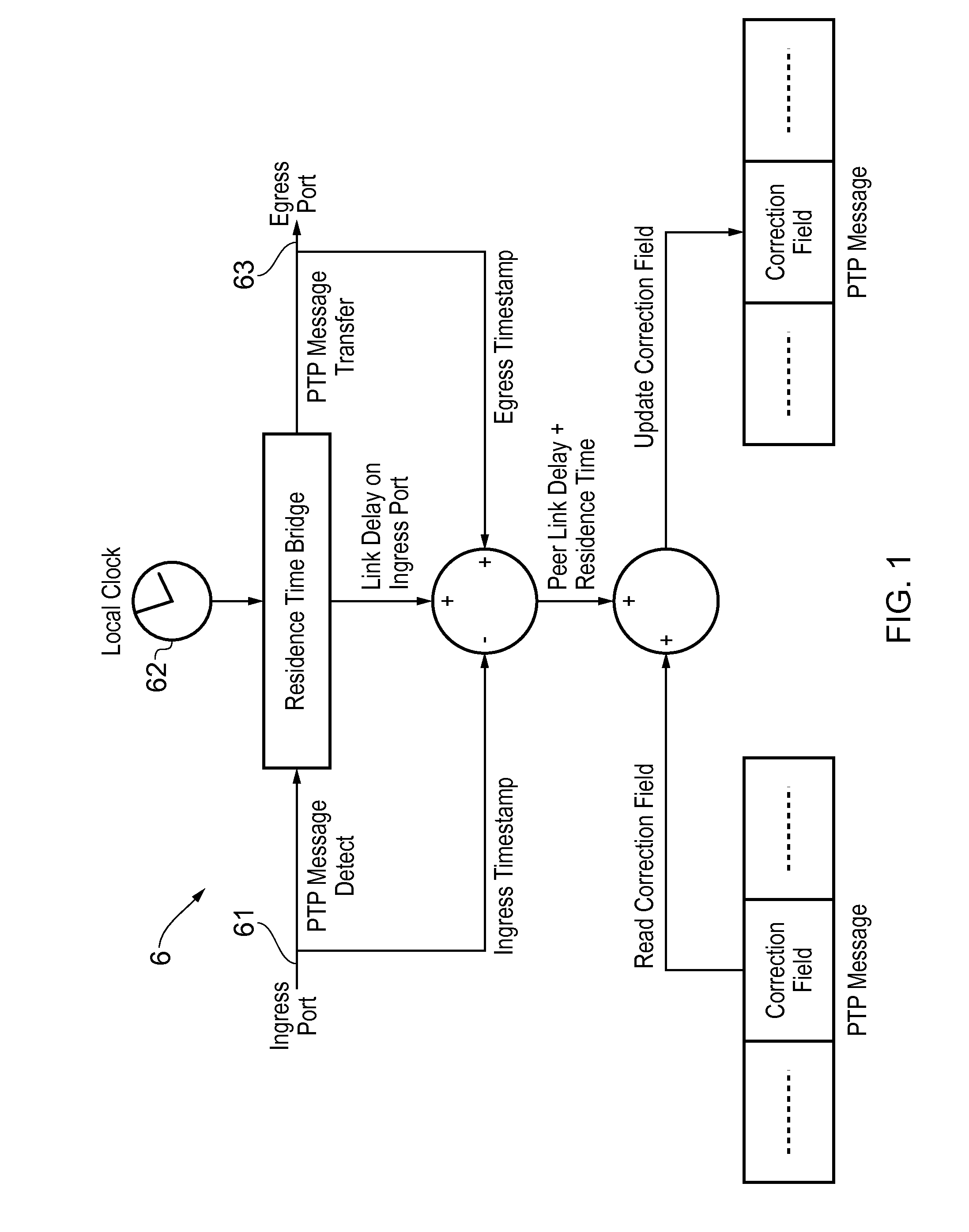
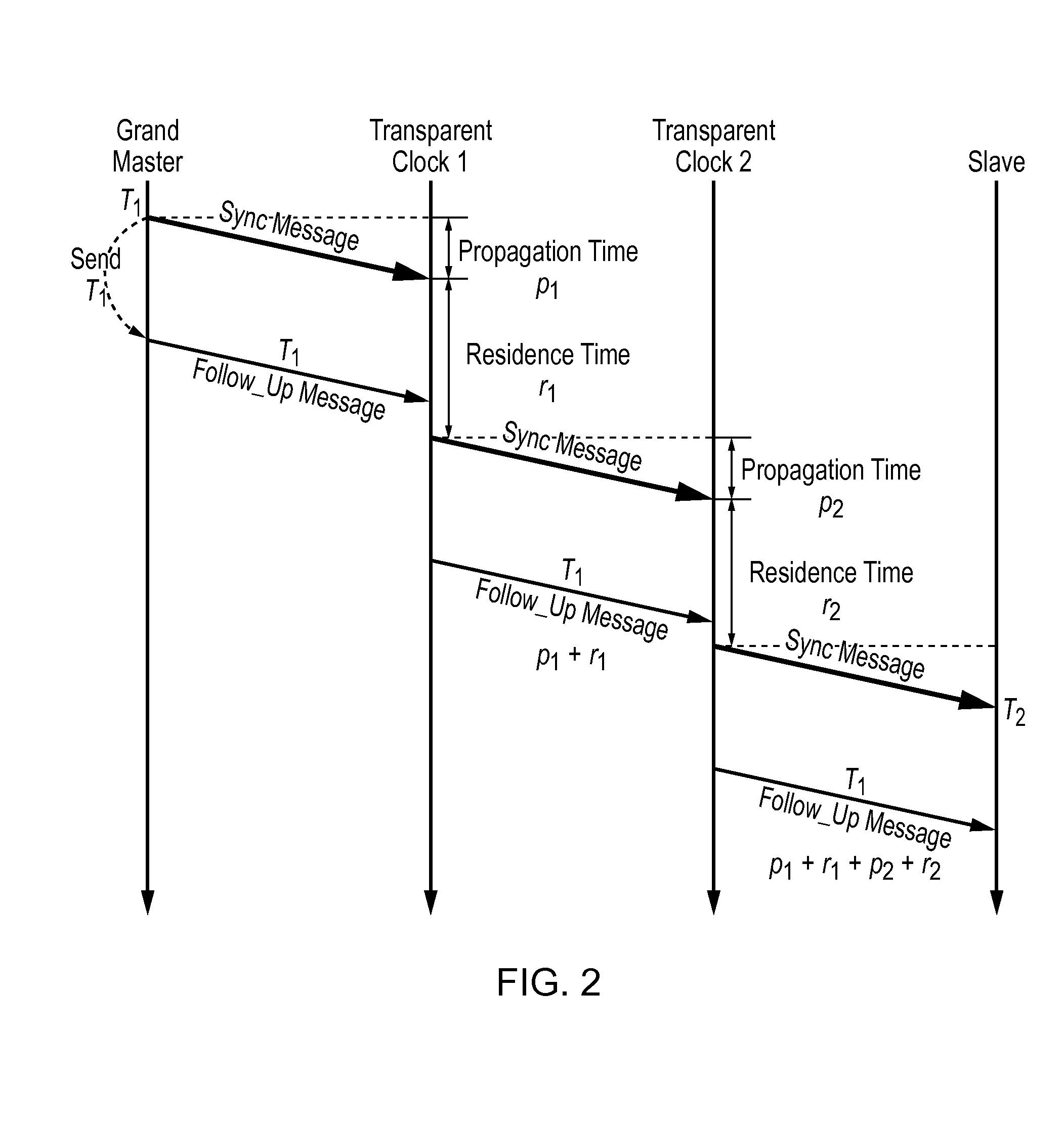
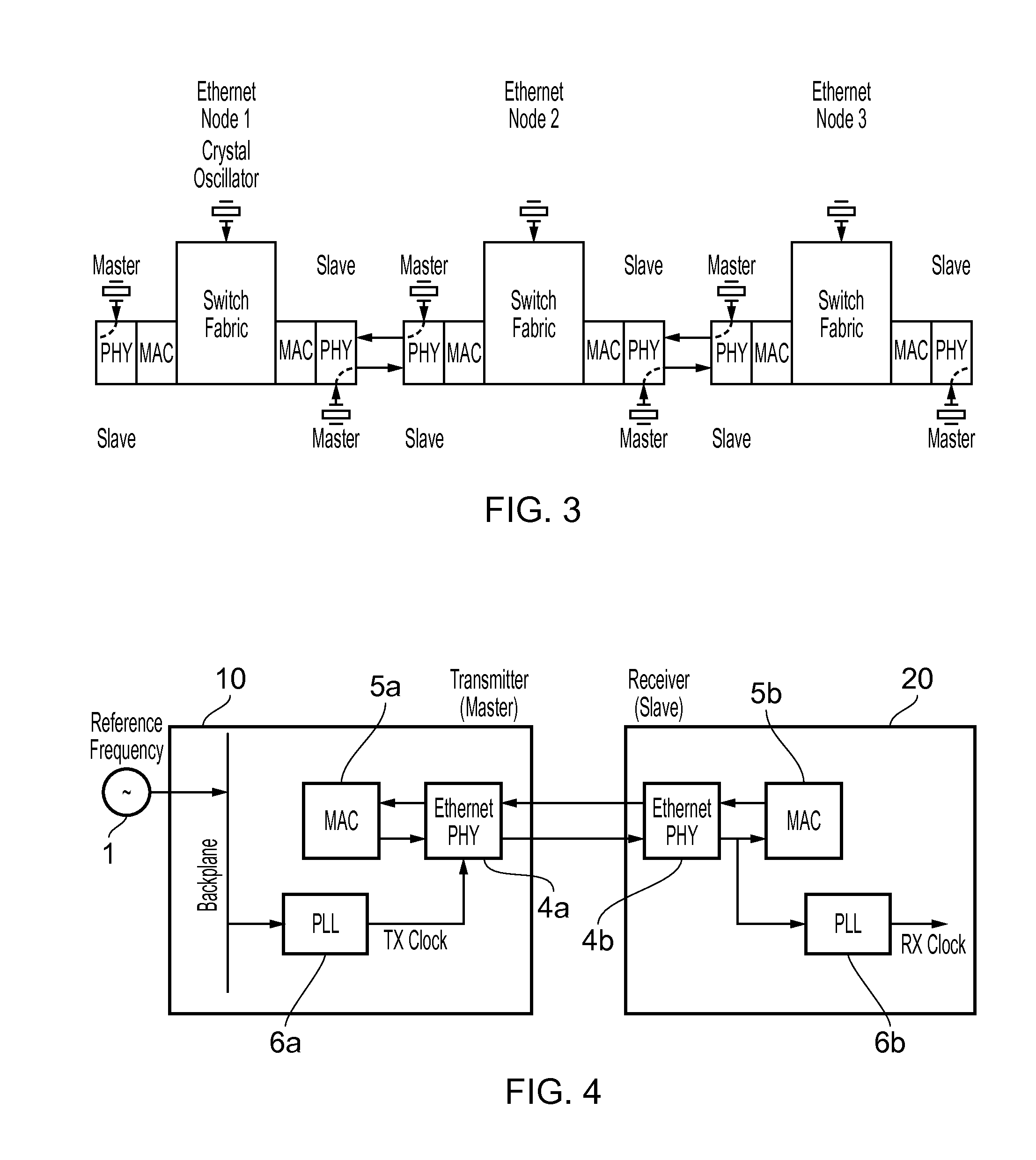
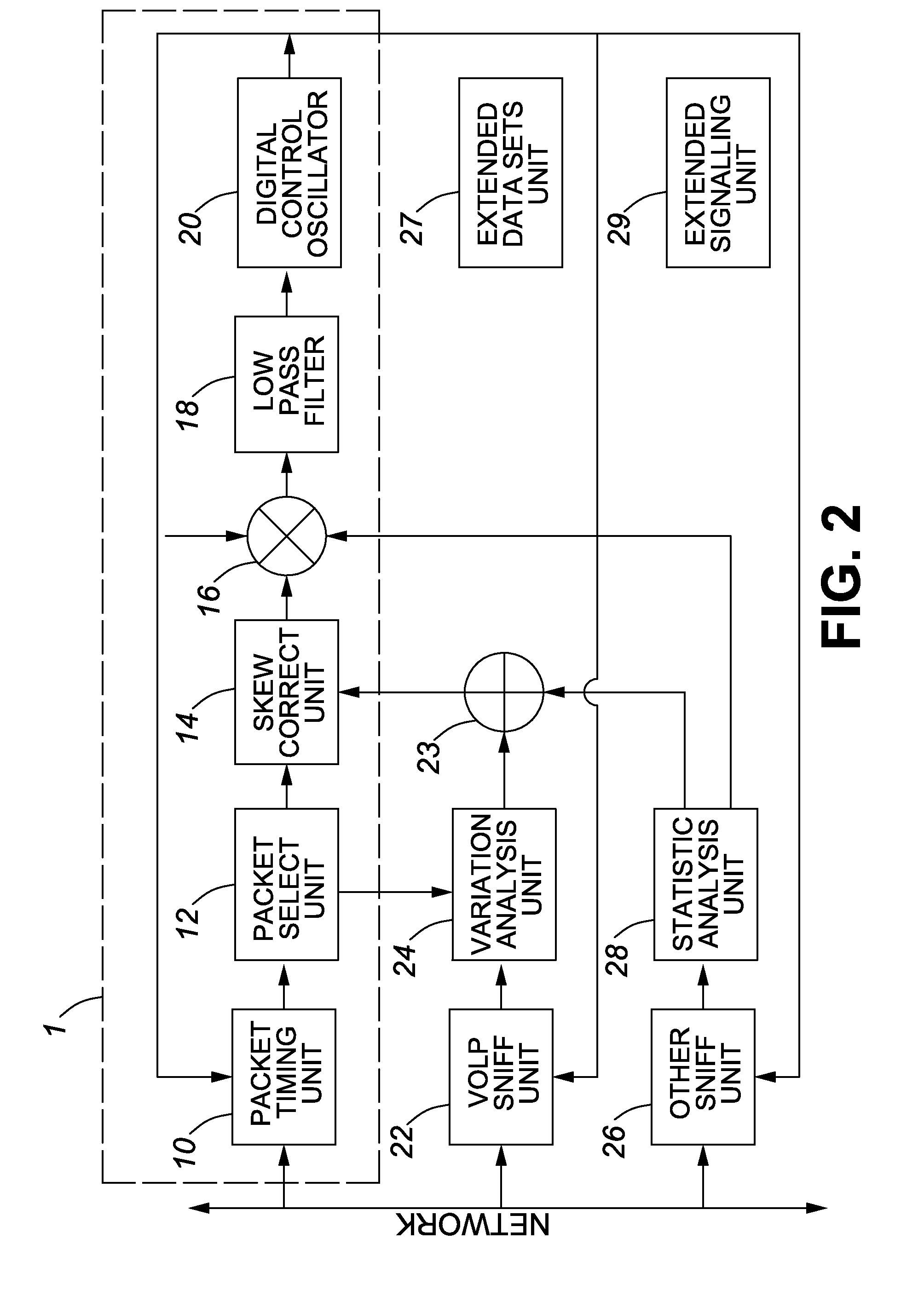
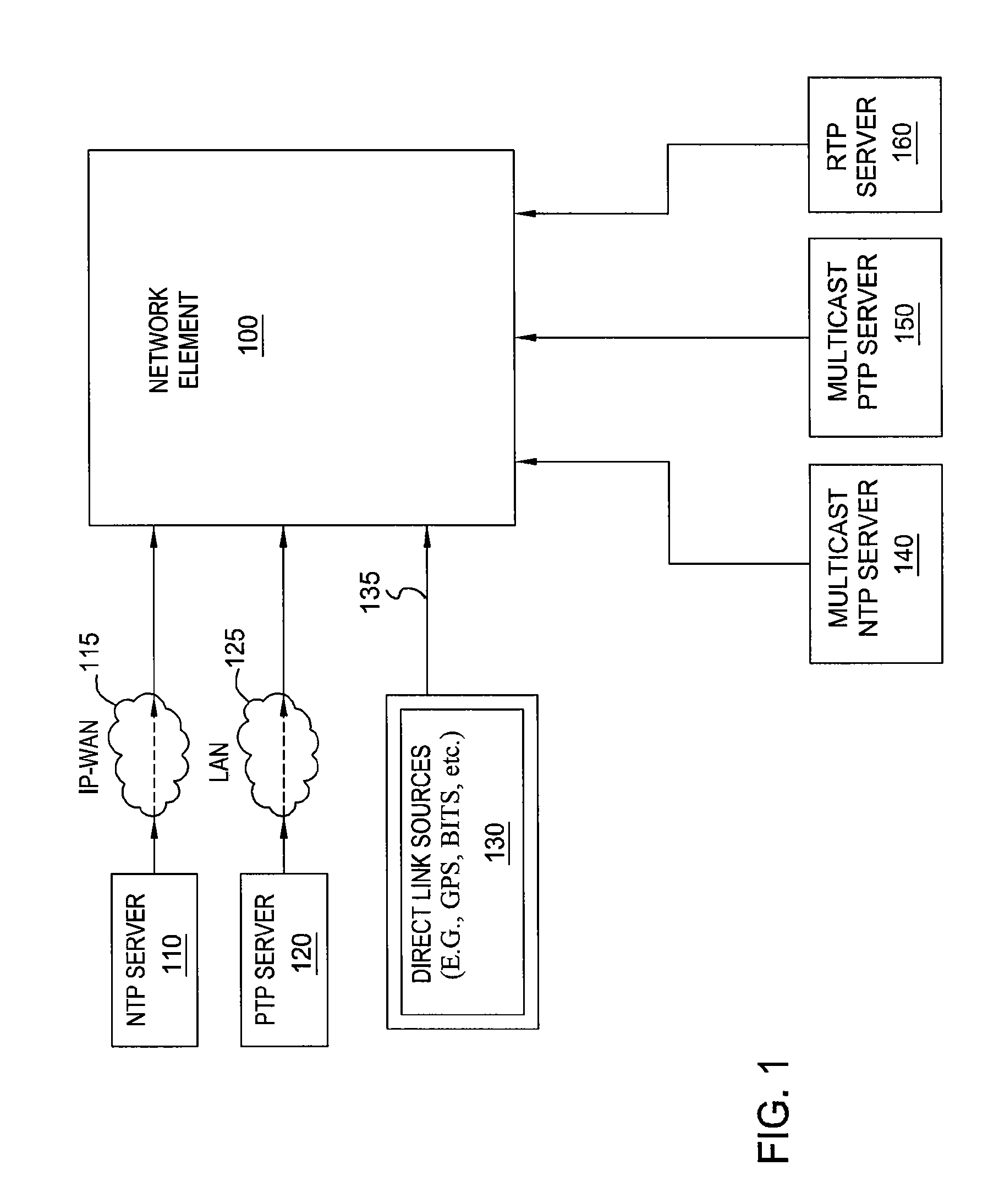
Method and devices for time transfer using peer-to-peer transparent clocks
ActiveUS20160170439A1Generating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple useNetwork linkTime transfer
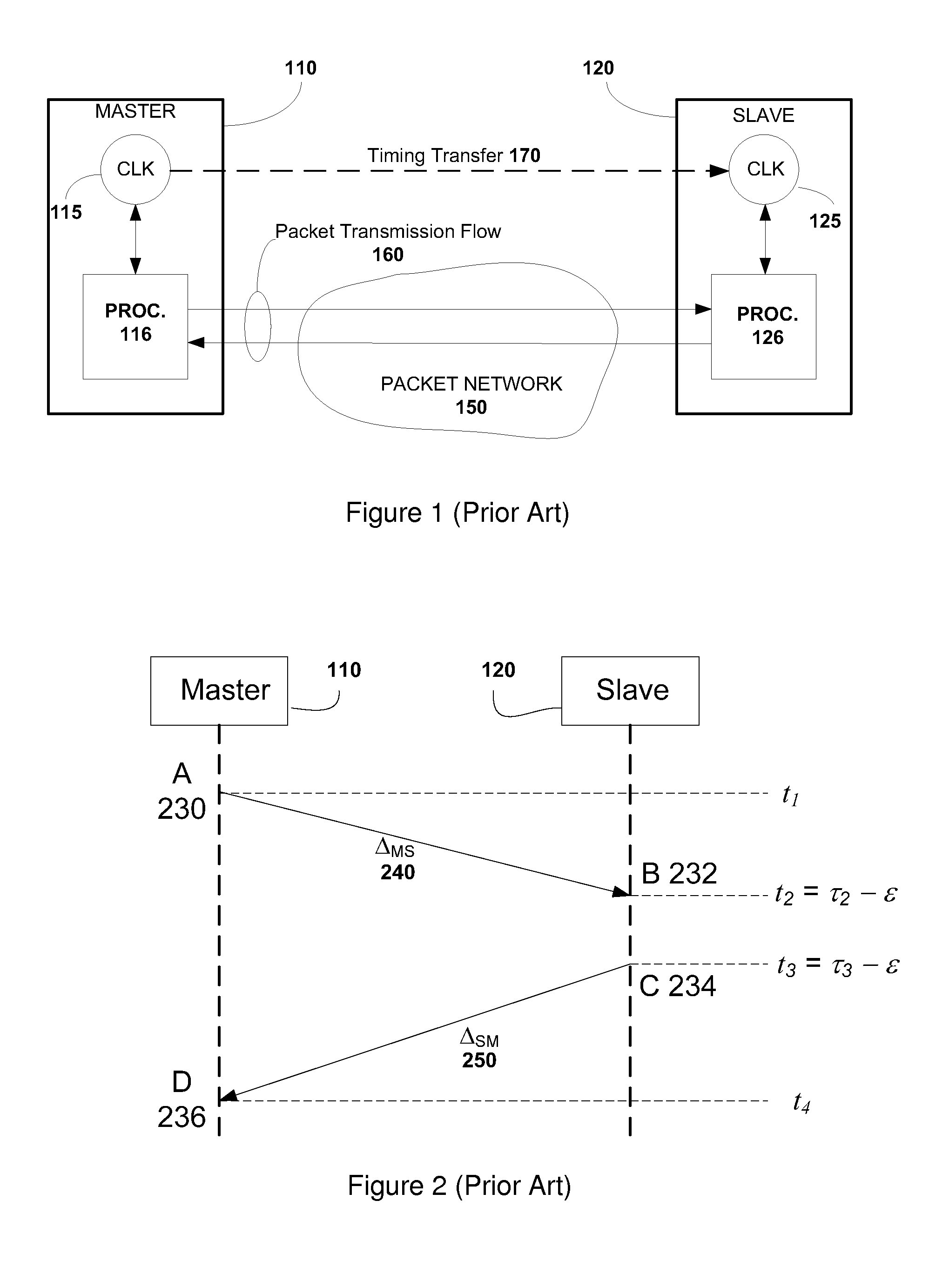
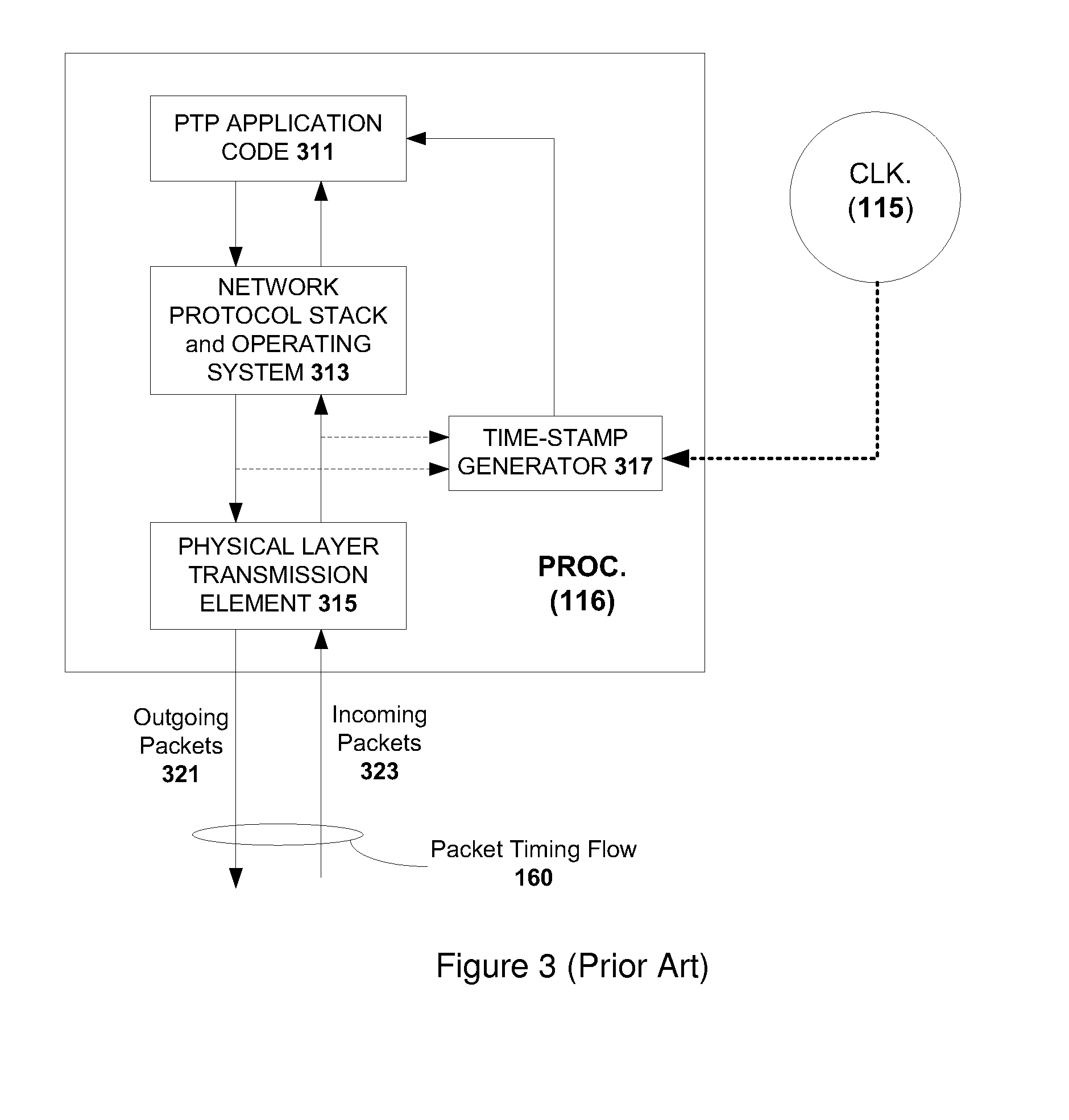
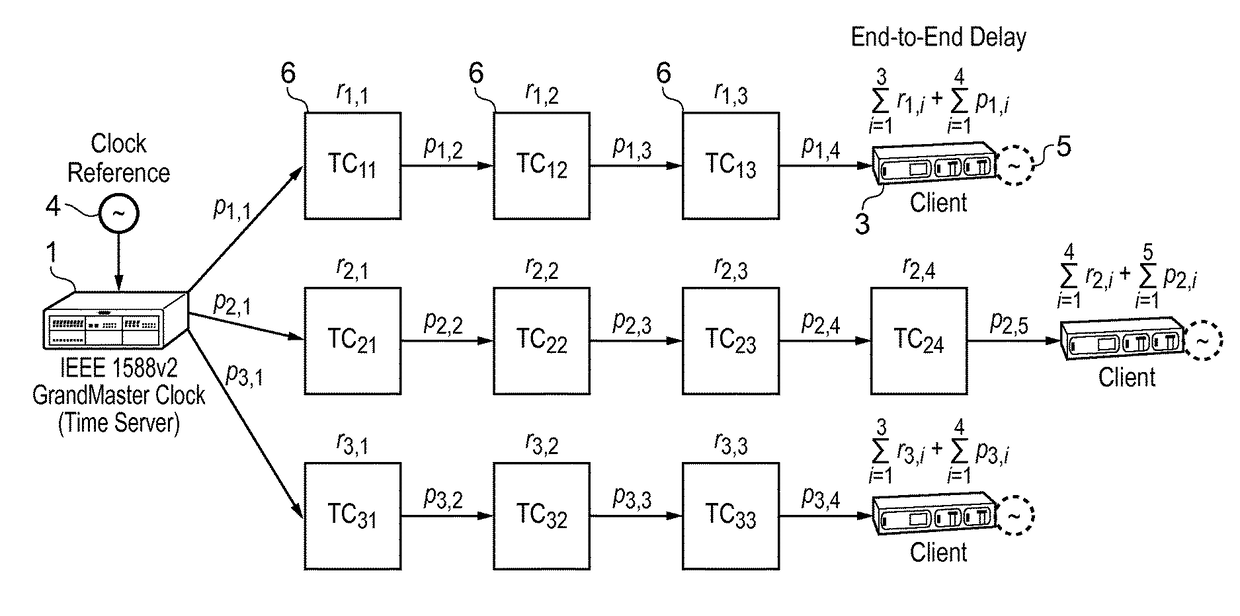
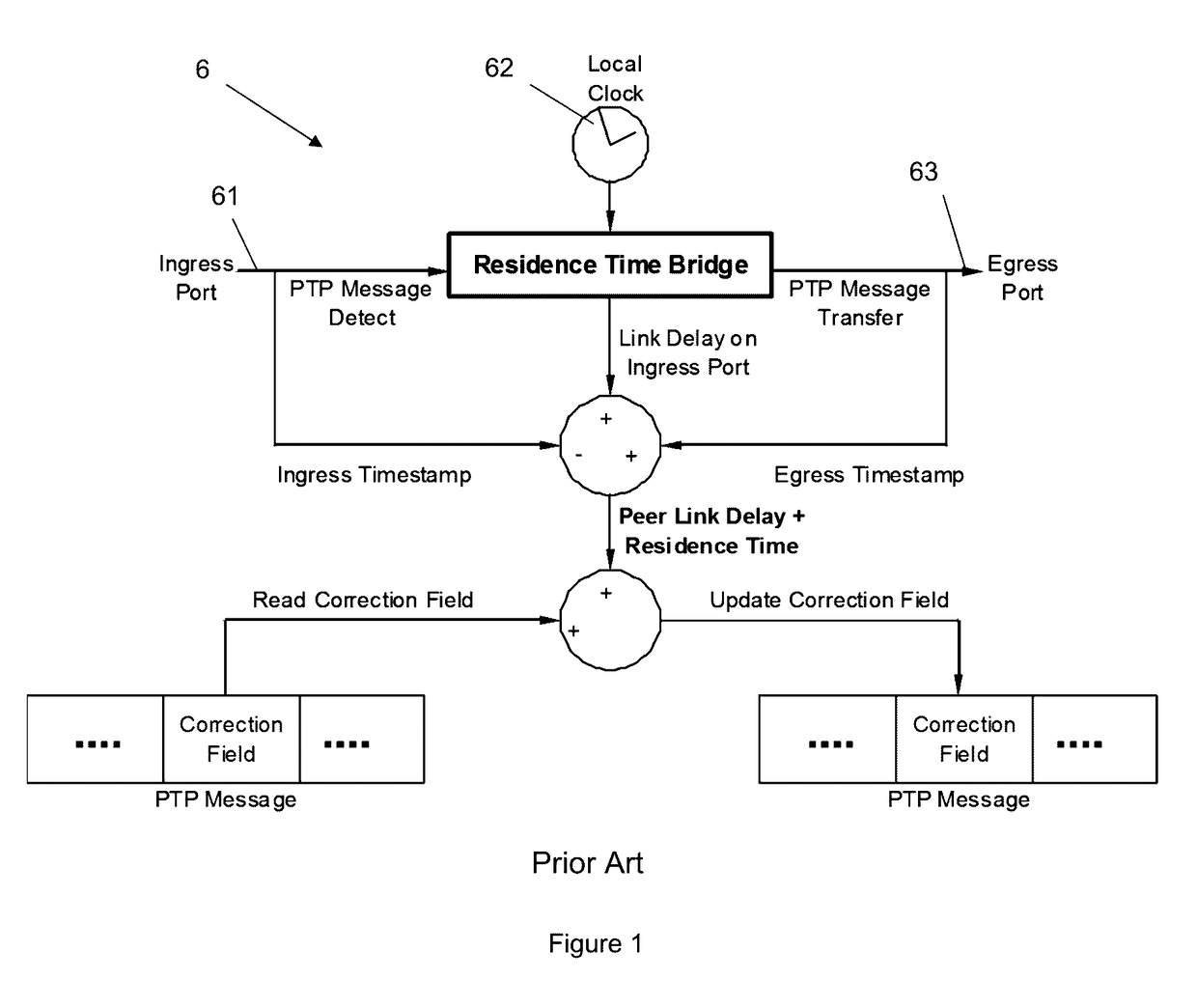
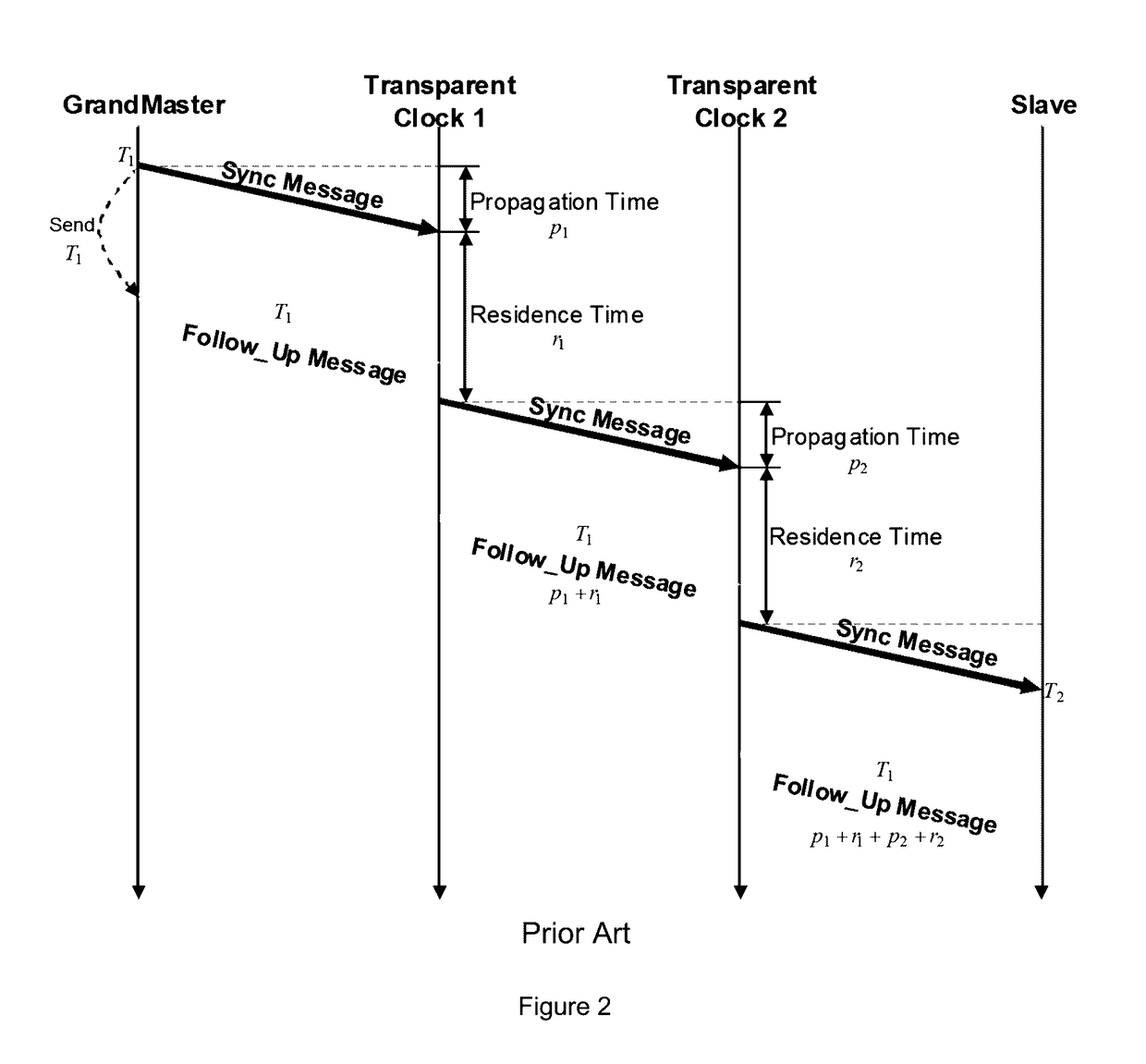
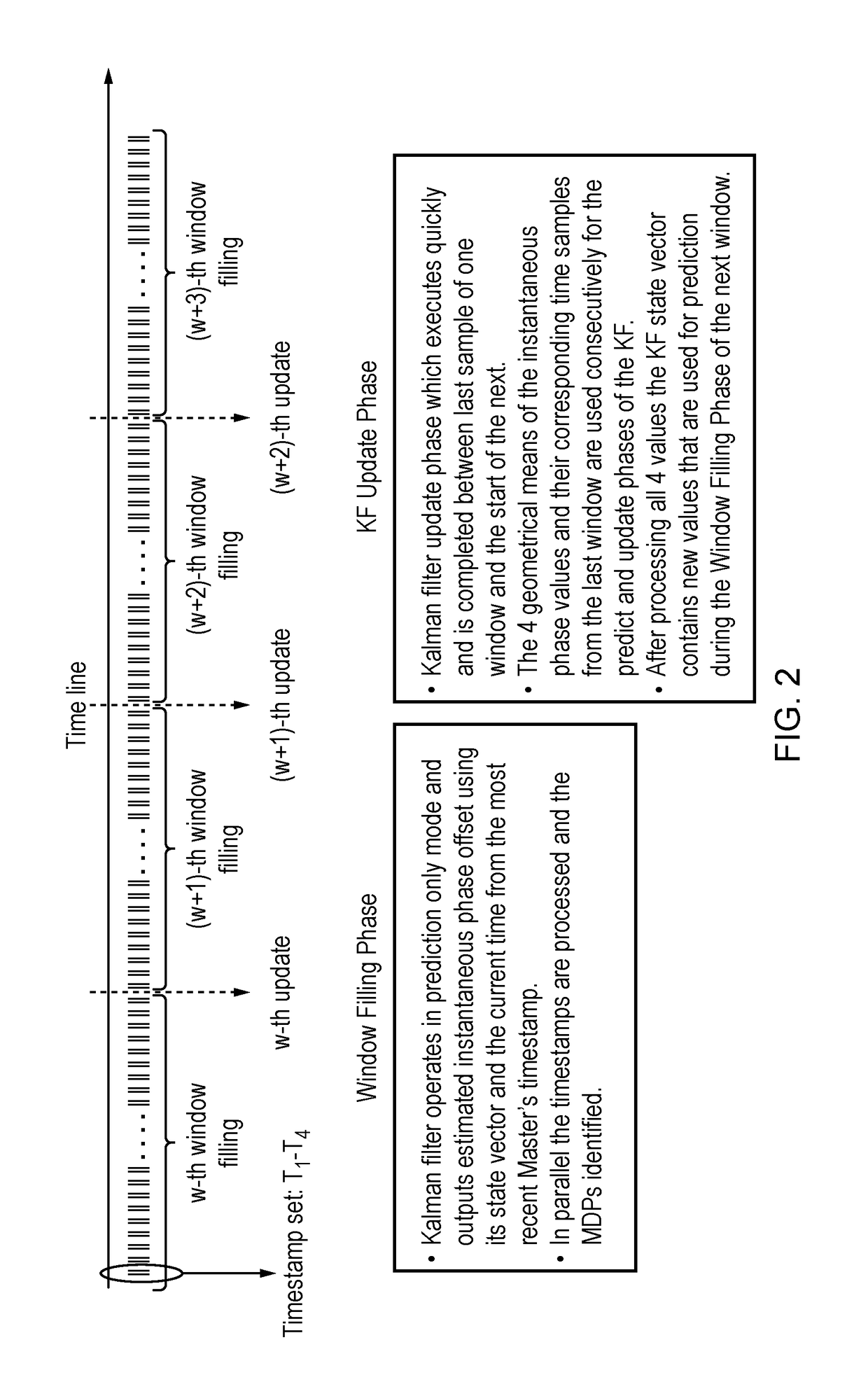
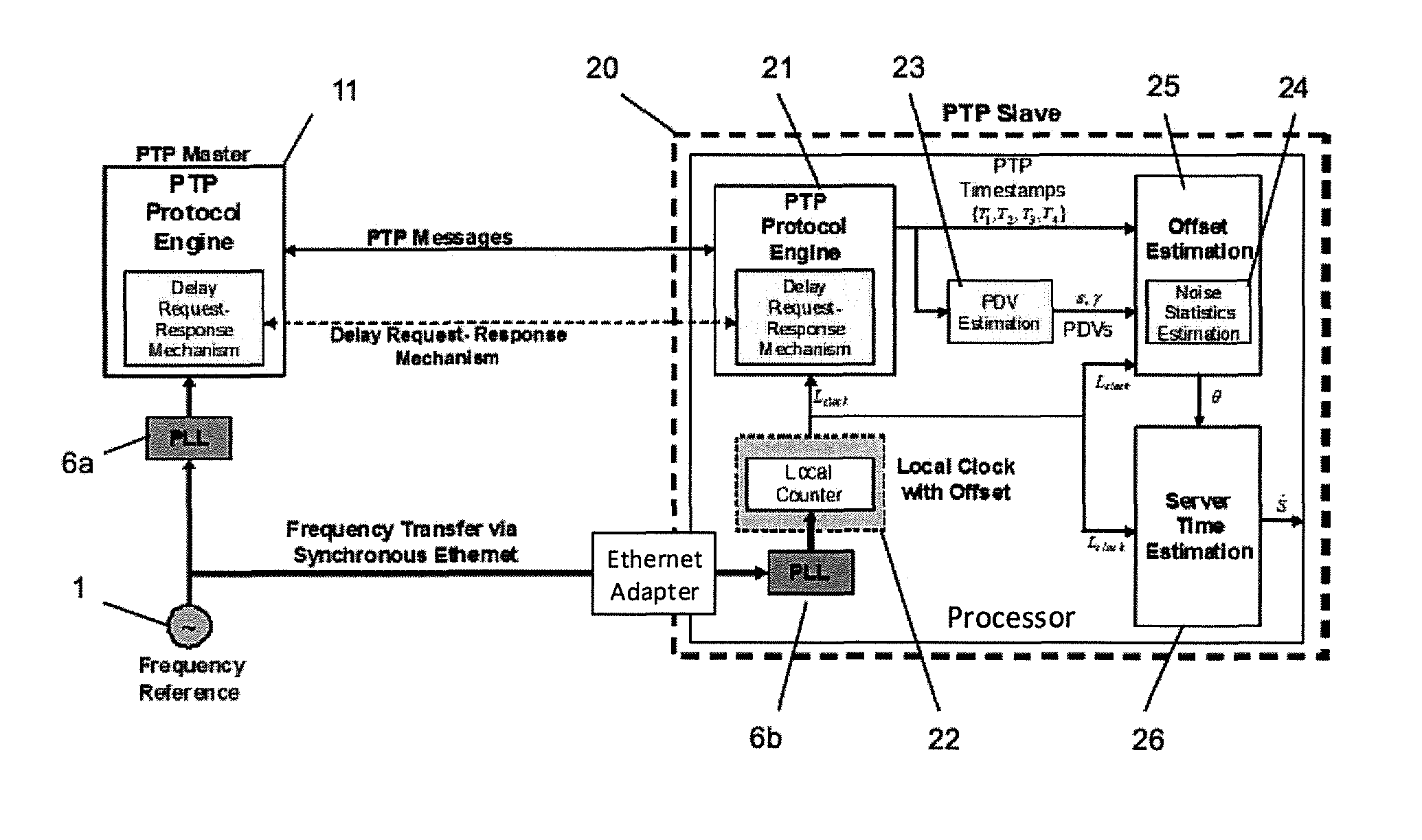
This invention relates to methods and devices for time synchronization. The invention has particular application in the alignment of slave clocks to a master clock and in dealing with packet delay variation and dynamic asymmetries in the network links between them. In embodiments of the invention, the slave clock uses the peer link delay and residence times measured by peer-to-peer transparent clocks to compensate for clock synchronization errors that arise due to variability in message transfer delays. Embodiments provide a simple linear approximation technique and a Kalman filter-based technique for estimating offset and skew of the slave clock.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Method and devices for time and frequency synchronization using a phase locked loop
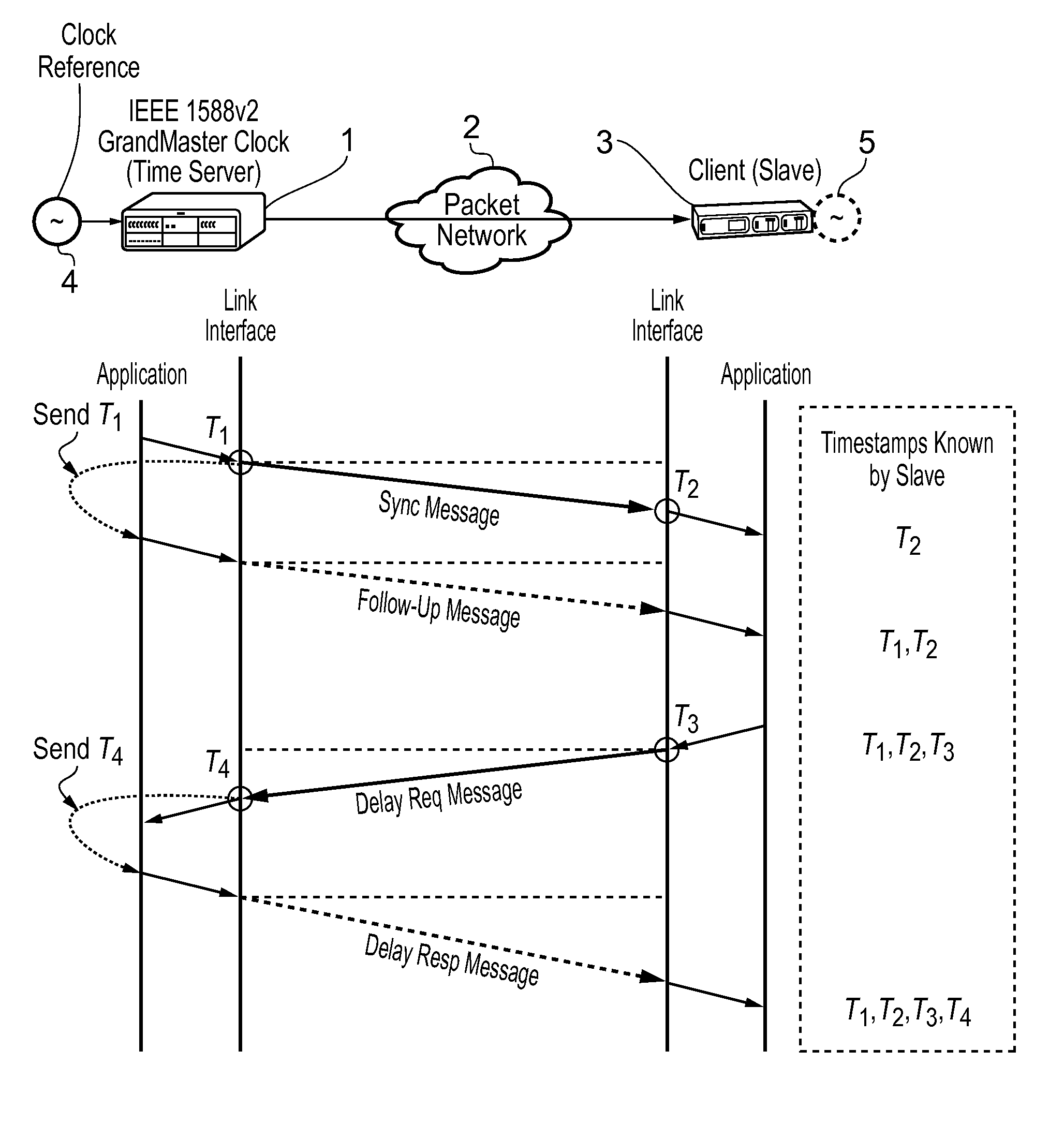
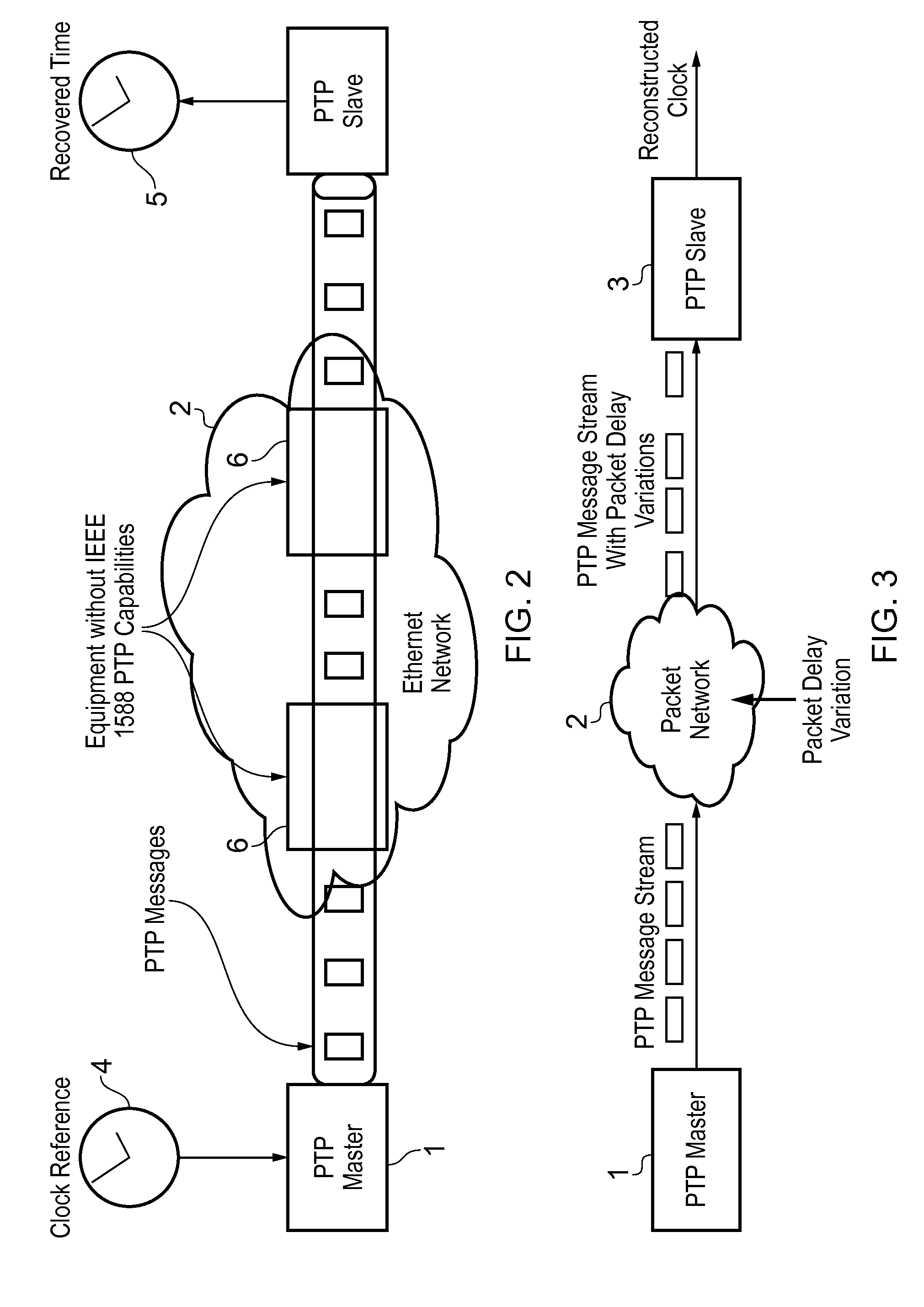
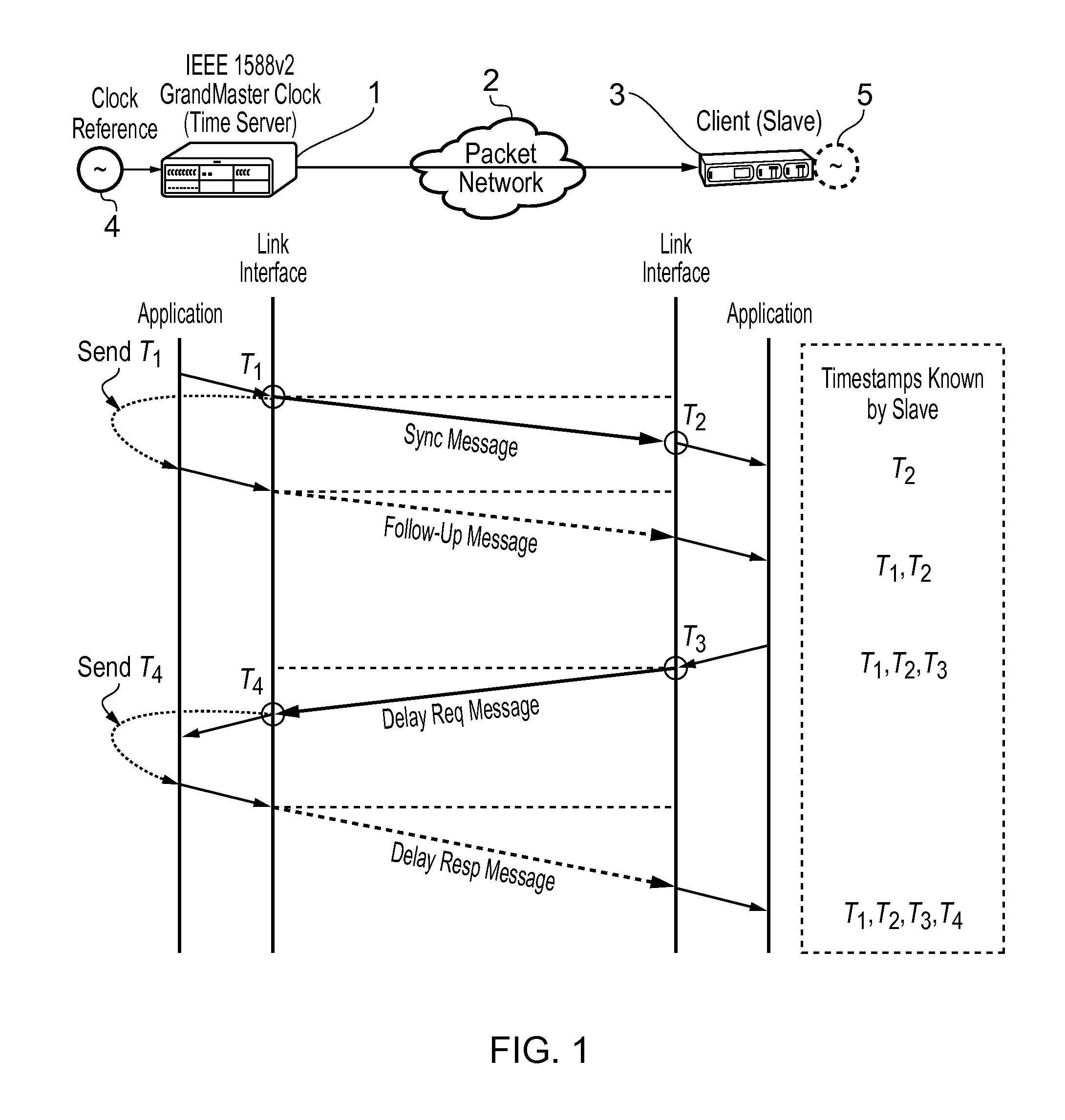
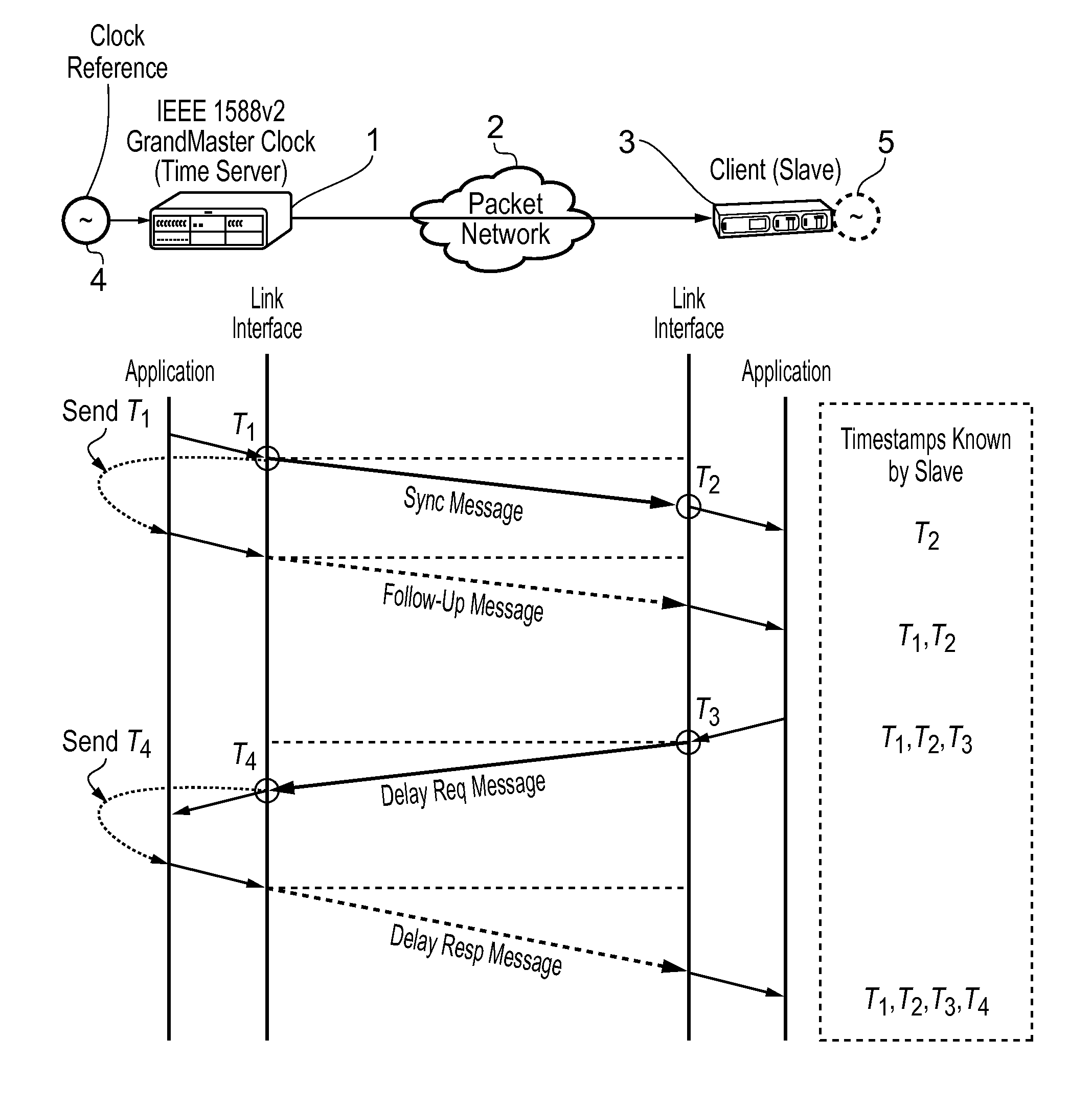
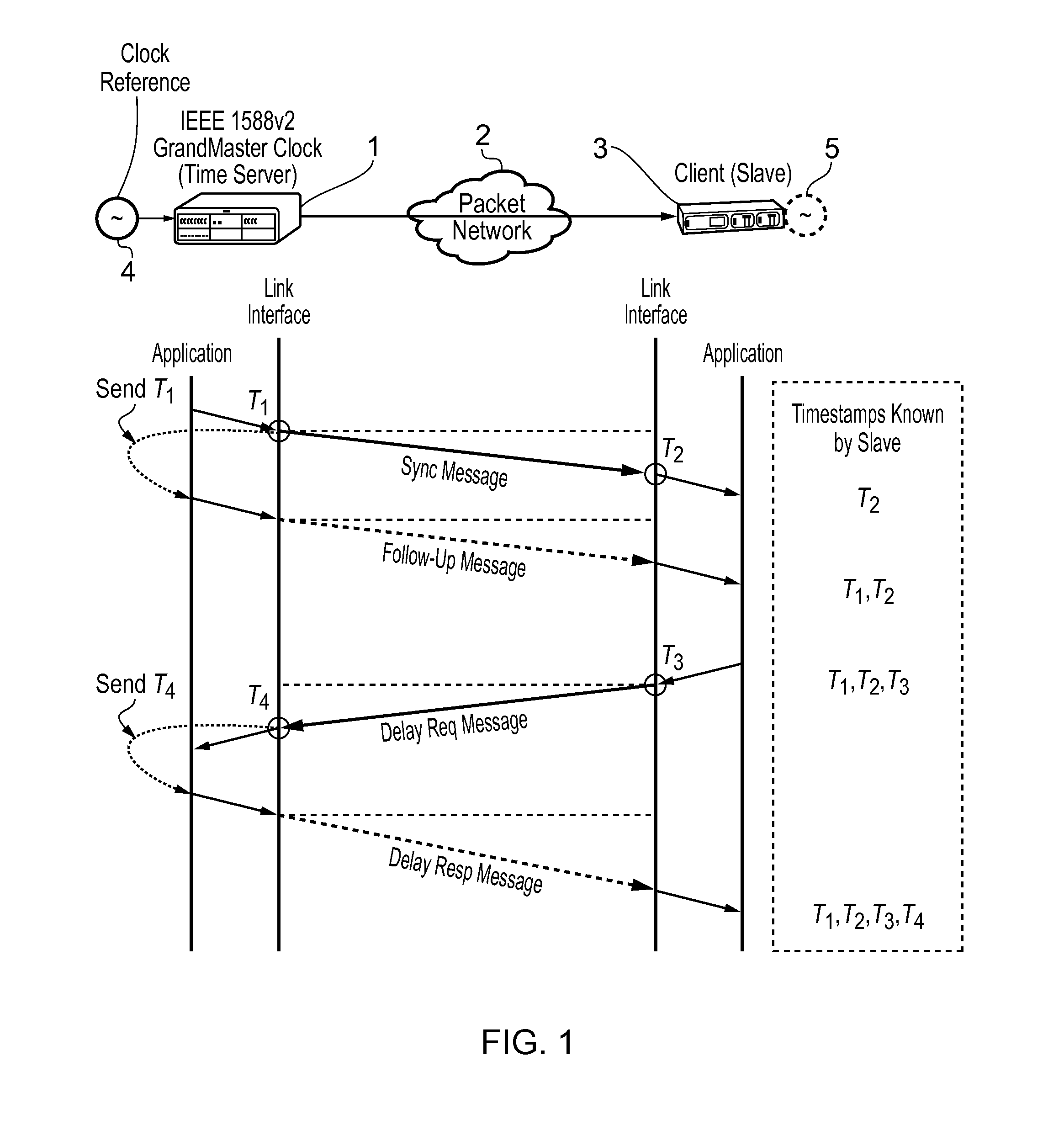
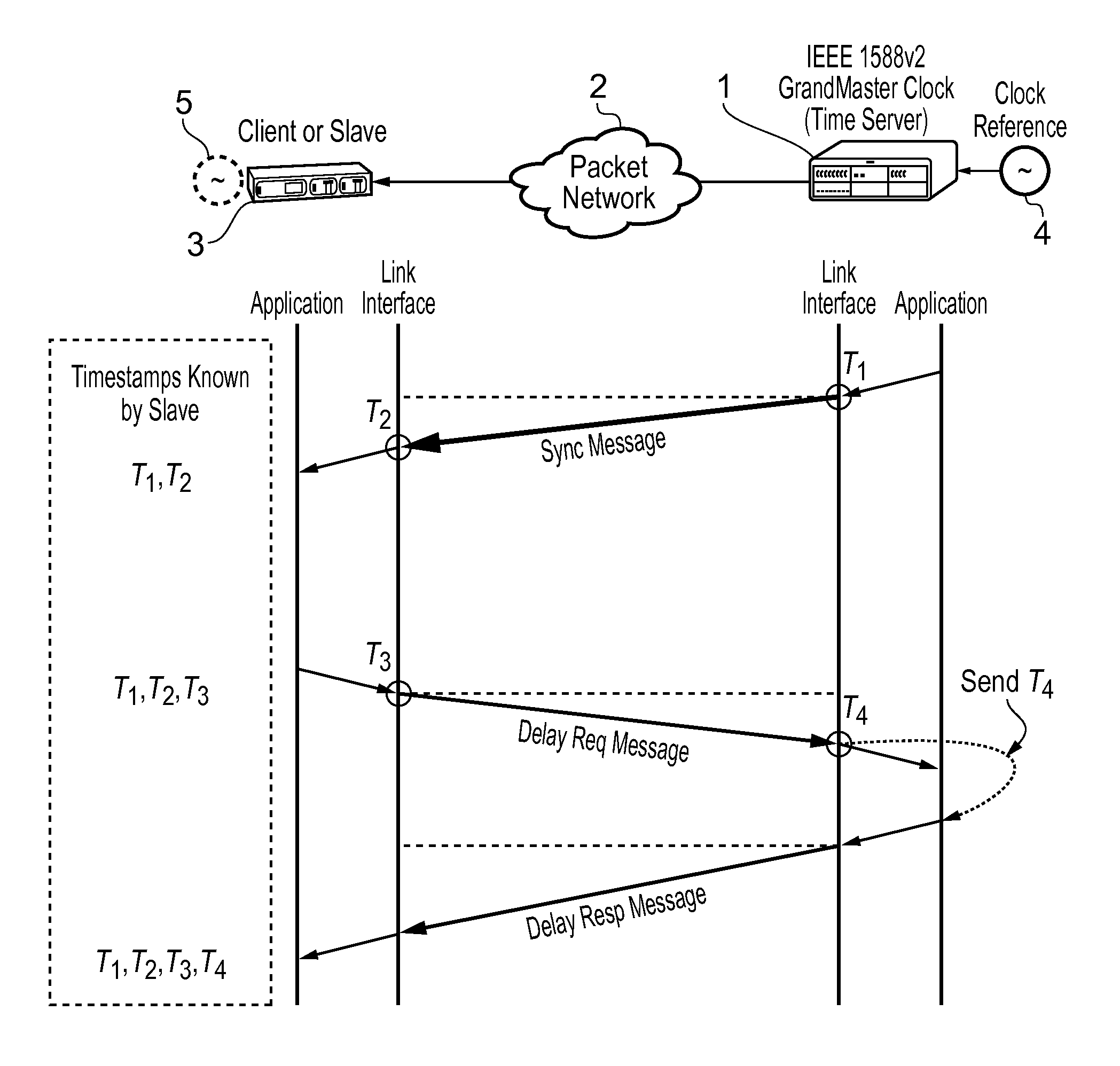
This invention relates to methods and devices for time and frequency synchronization, especially over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). Timing protocol messages are exposed to artifacts in the network such as packet delay variations (PDV) or packet losses. Embodiments of the invention provide a digital phase locked loop (DPLL) based on direct digital synthesis to provide both time and frequency signals for use at the slave (time client). An example of this DPLL in conjunction with a recursive least squares mechanism for clock offset and skew estimation is also provided.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
Method and devices for synchronization
ActiveUS20150092793A1Time-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementReal-time computingSynchronous Ethernet
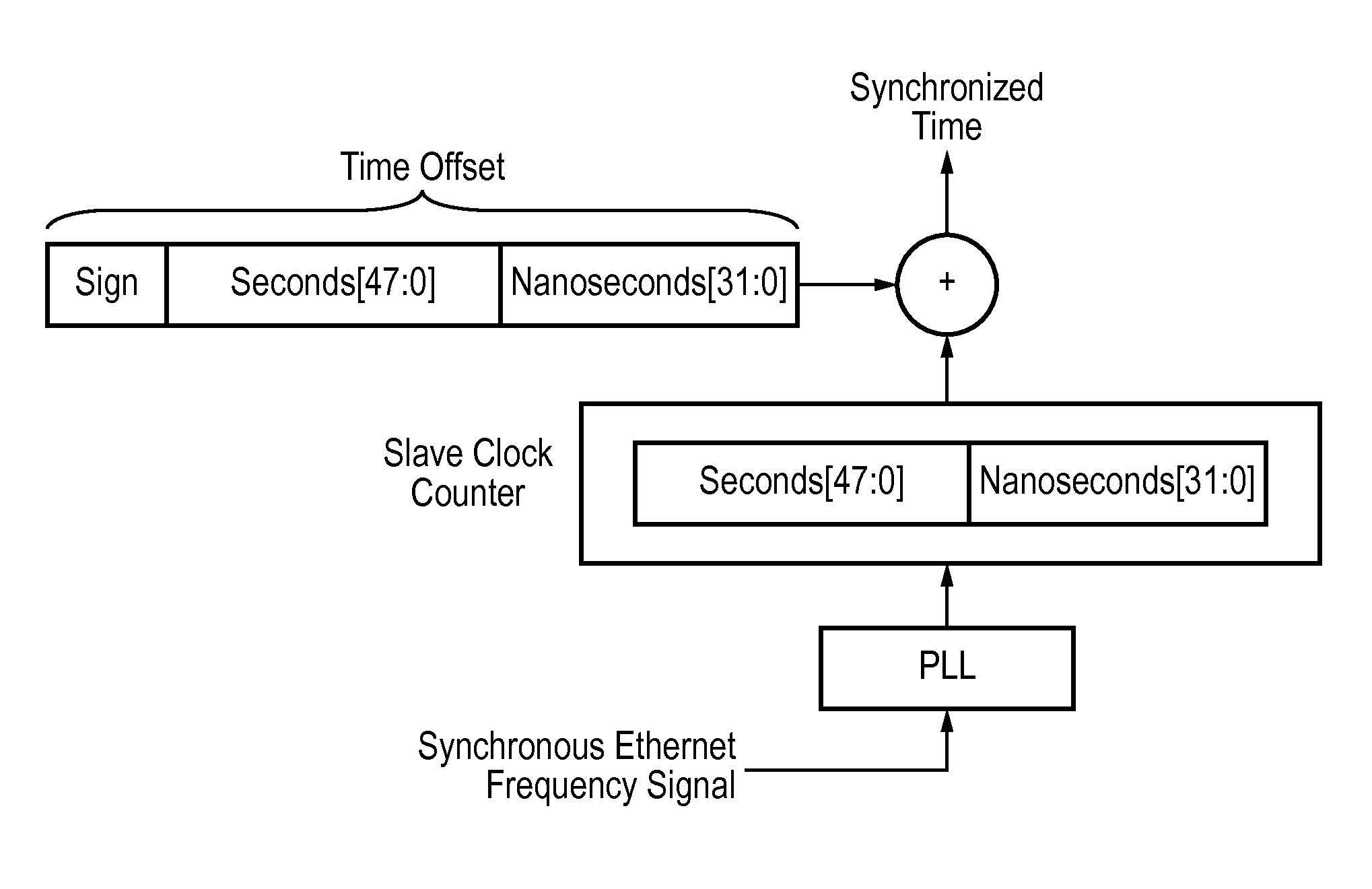
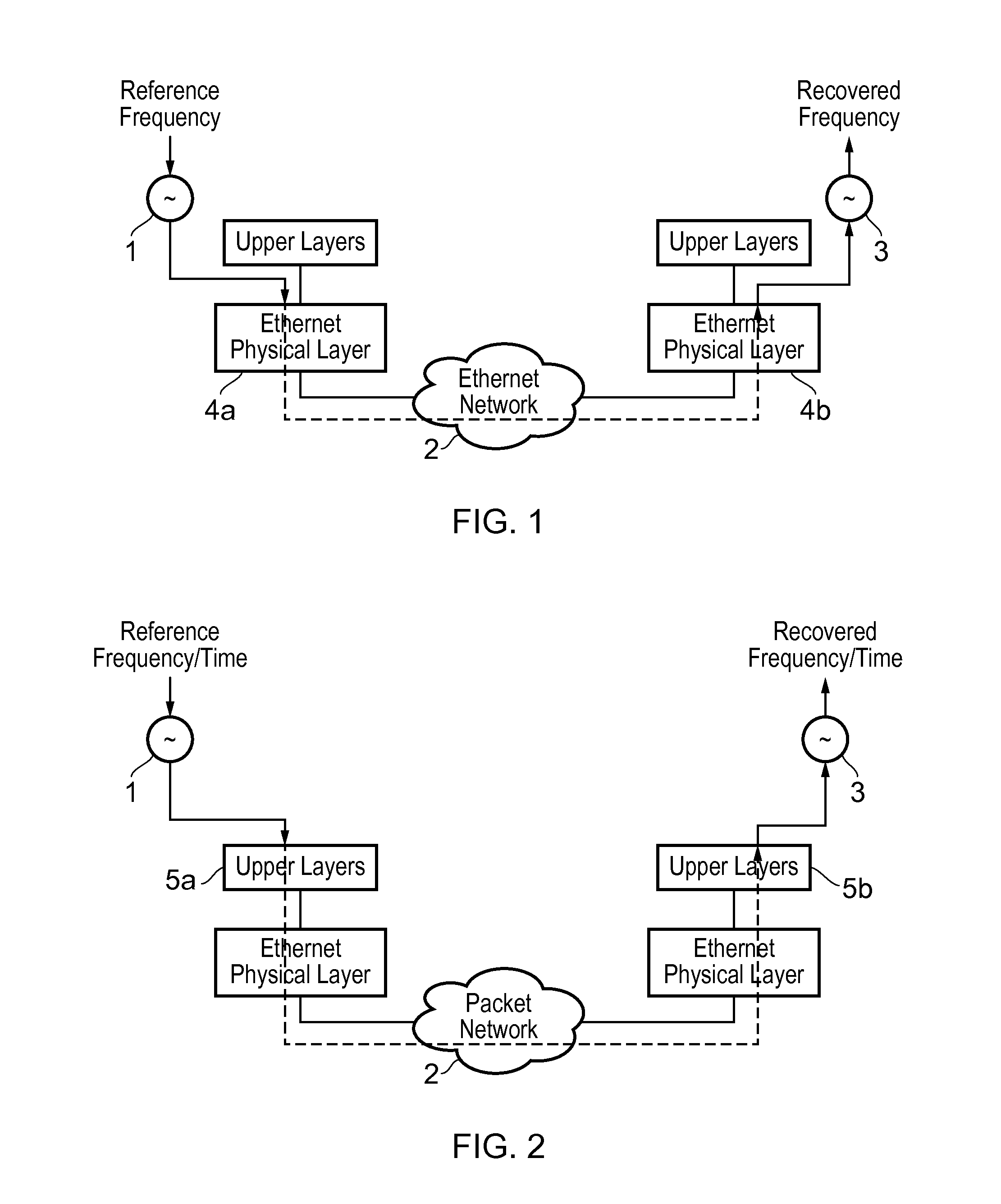
This invention relates to methods and devices for time and frequency synchronization. The invention has particular application where time and frequency synchronization over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is being carried out. The primary challenge in clock distribution over packet networks is the variable transit delays experienced by timing packets, packet delay variations (PDVs). Embodiments of the invention provide a method for time offset alignment with PDV compensation where a synchronized frequency signal is available at a slave device via Synchronous Ethernet and is used to determine the compensation parameters for the PDV.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
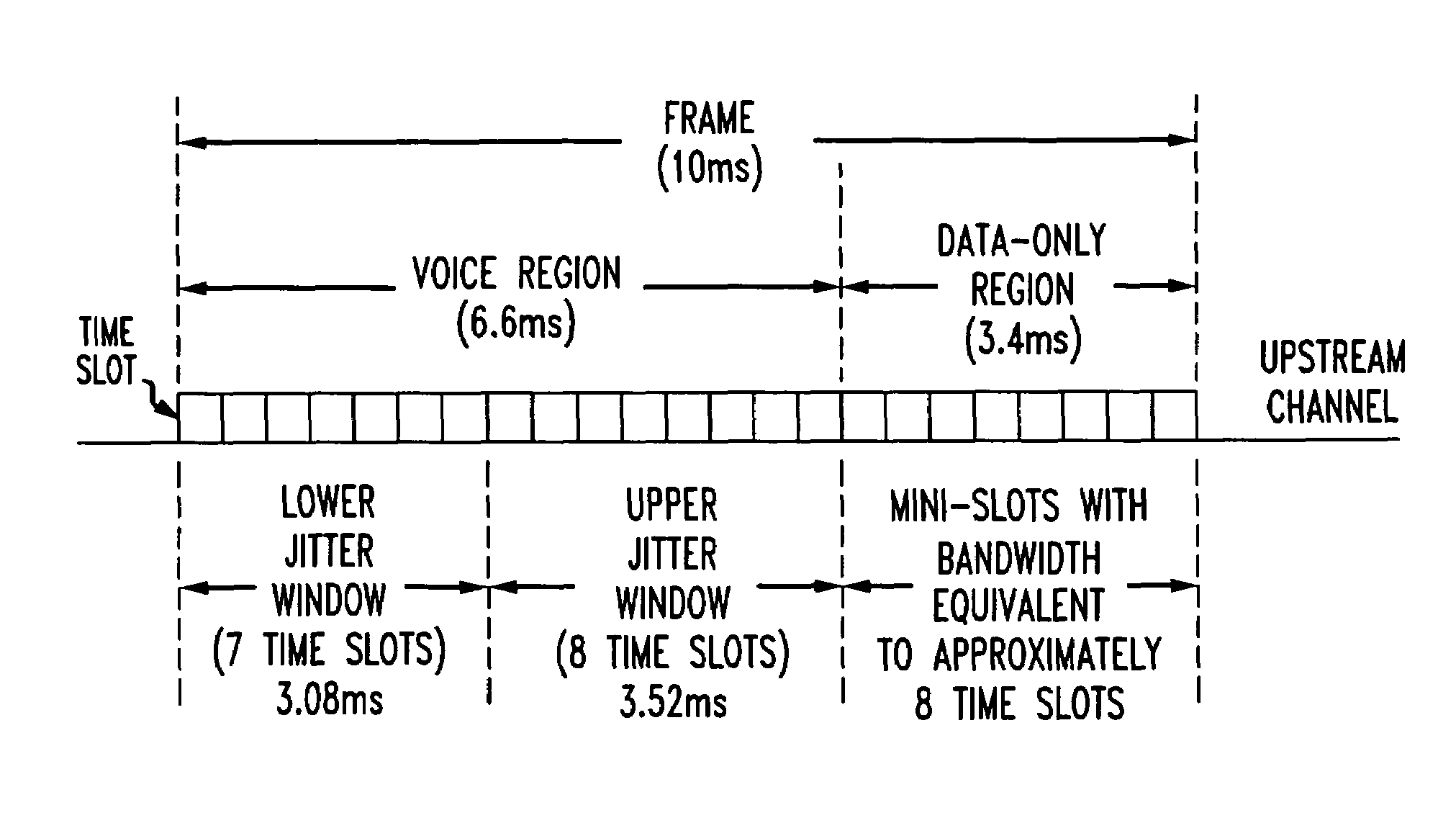
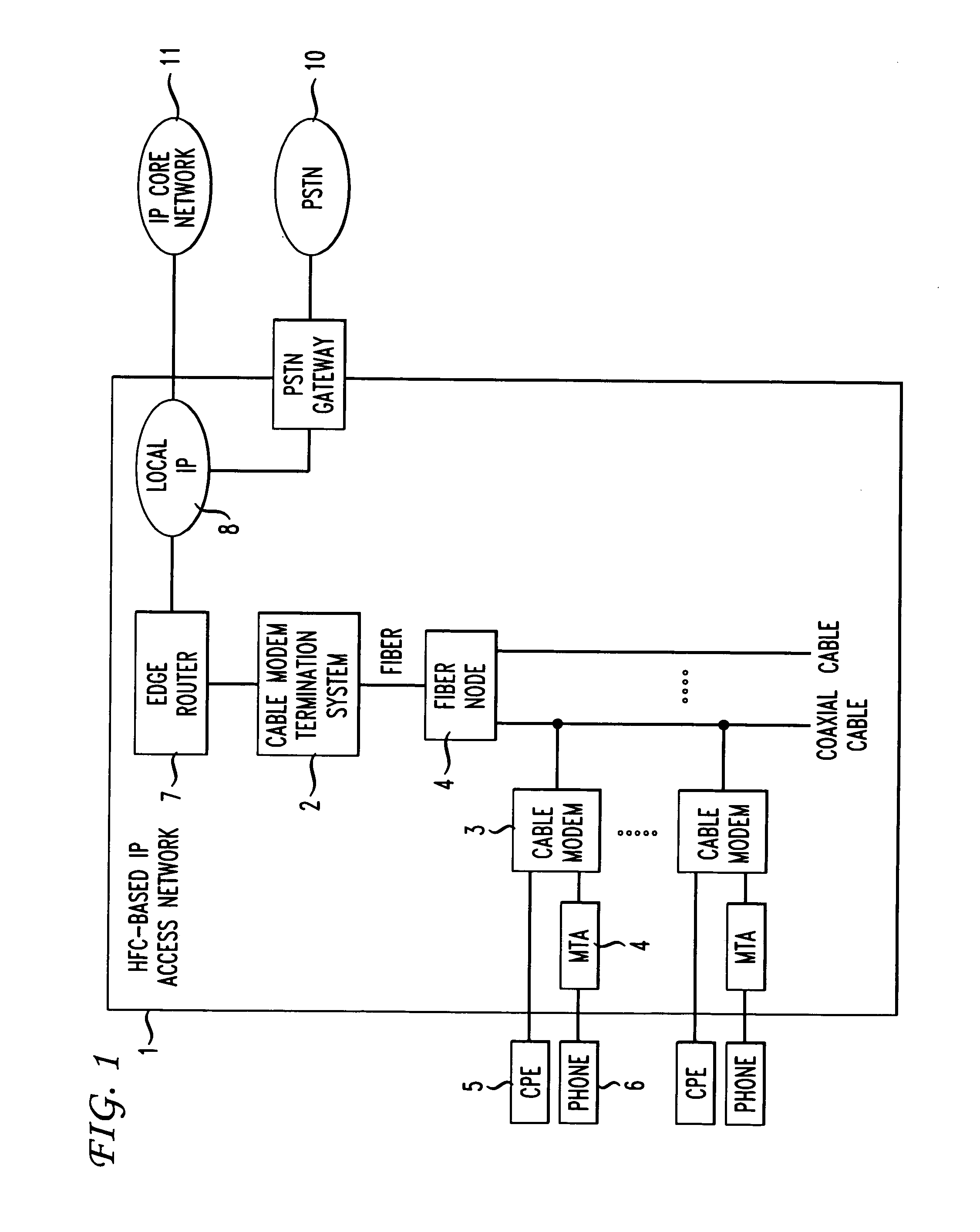
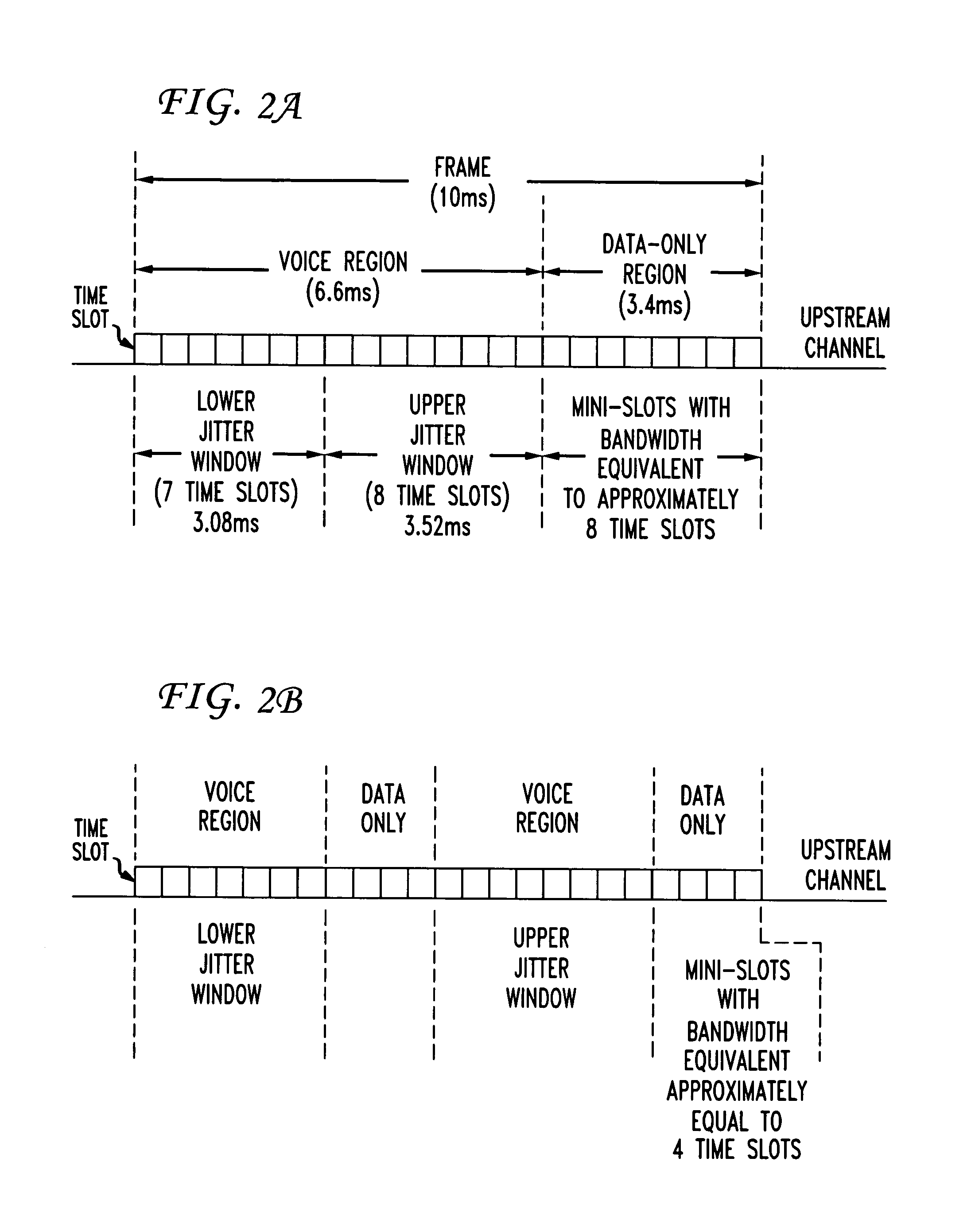
Upstream bandwidth allocation for packet telephony in a shared-media packet-switched access network
InactiveUS7269159B1Minimize jitterCable networksBroadband local area networksModem deviceTime duration
A method and apparatus is provided for allocating bandwidth and reducing jitter in an upstream transmission in a shared-media packet-switched access network with multiple upstream channels offering integrated Internet Protocol voice and high-speed data services. To allow multiple simultaneous CBR (constant-bit-rate) voice connections to be supported by a cable modem, when only a single channel can be accessed at a time, a method to select an upstream channel and assign to each connection a time slot in the upstream channel is provided. Jitter, i.e. packet delay variation, results when packets associated with a voice connection are not received at expected intervals. To maintain jitter within predetermined tolerances, the sequence of mini-slots in an upstream channel is divided into frames. Each frame will have a sequence of voice and data-only regions, and the voice region is divided into non-overlapping jitter windows of generally equal length. Even when an upstream channel change is required, each active voice connection is maintained in one of the jitter windows, thereby limiting jitter to the duration of a jitter window.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Distributed two-step clock
ActiveUS20140269672A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTime transferComputer science
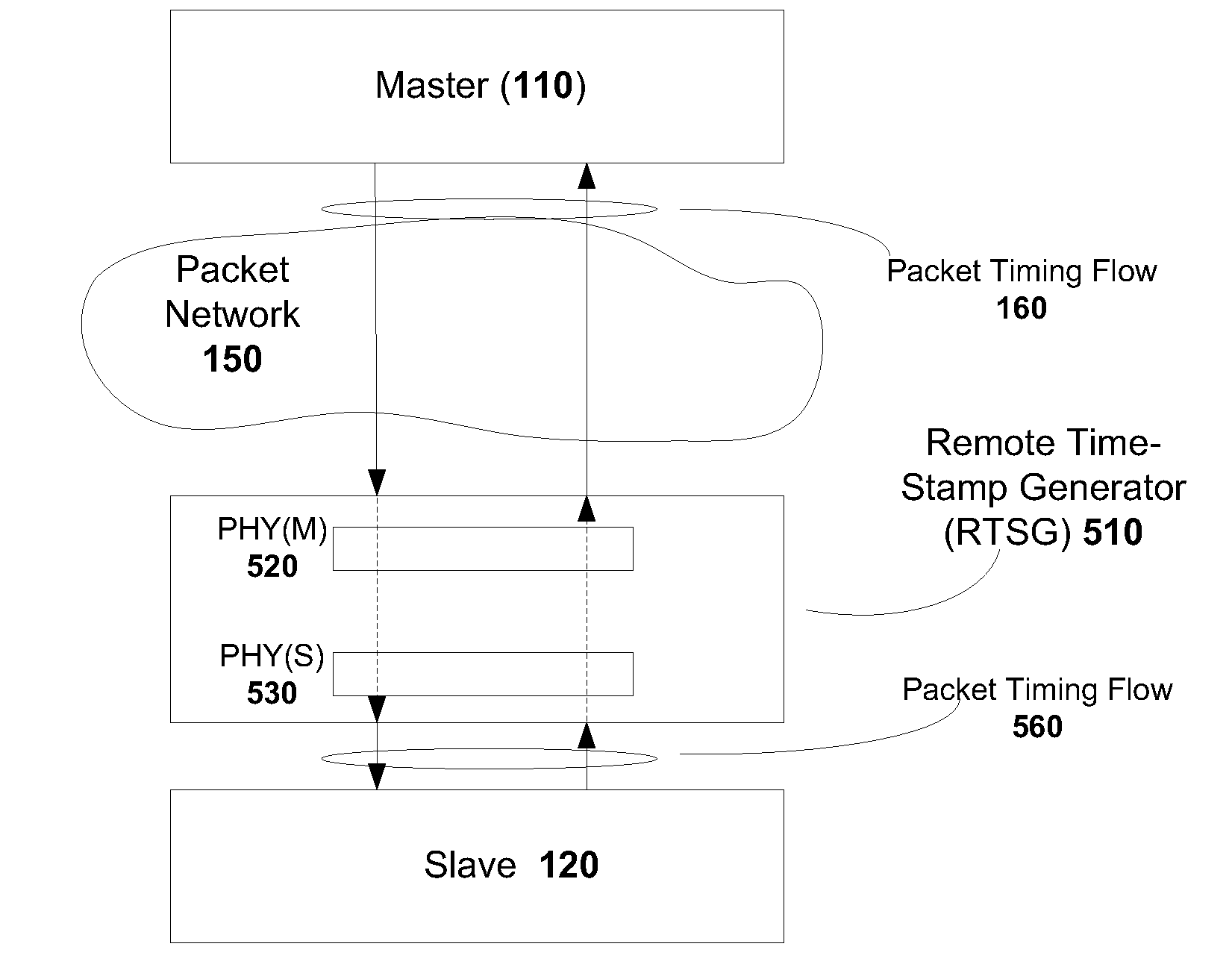
The present invention generally relates to methods and apparatus for precision time transfer wherein the inherent packet delay variation and possible asymmetry introduced in networks is avoided or mitigated. In one embodiment, the timing functions of a master device may be placed closer to a slave device using a Remote Time-Stamp Generator, located in the network between the master and the slave, and whose time reference serves as a proxy for the time reference of the master. Time-of-traversal of packets at the remote time-stamp generator may be used as proxies for the time-of-departure and the time-of-arrival of certain messages at the master. Such proxy times may be used to synchronize the slave with the master, particularly if the master and the Remote Time-Stamp Generator are both synchronized with a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) source.
Owner:MICROSEMI FREQUENCY & TIME
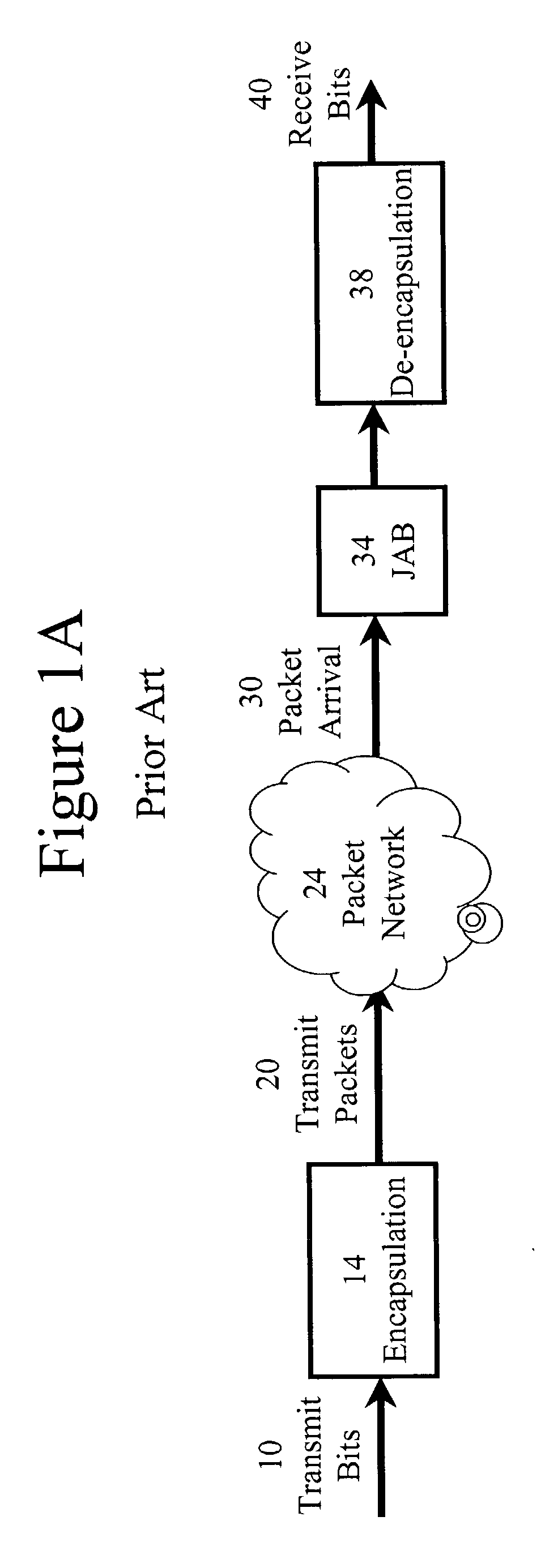
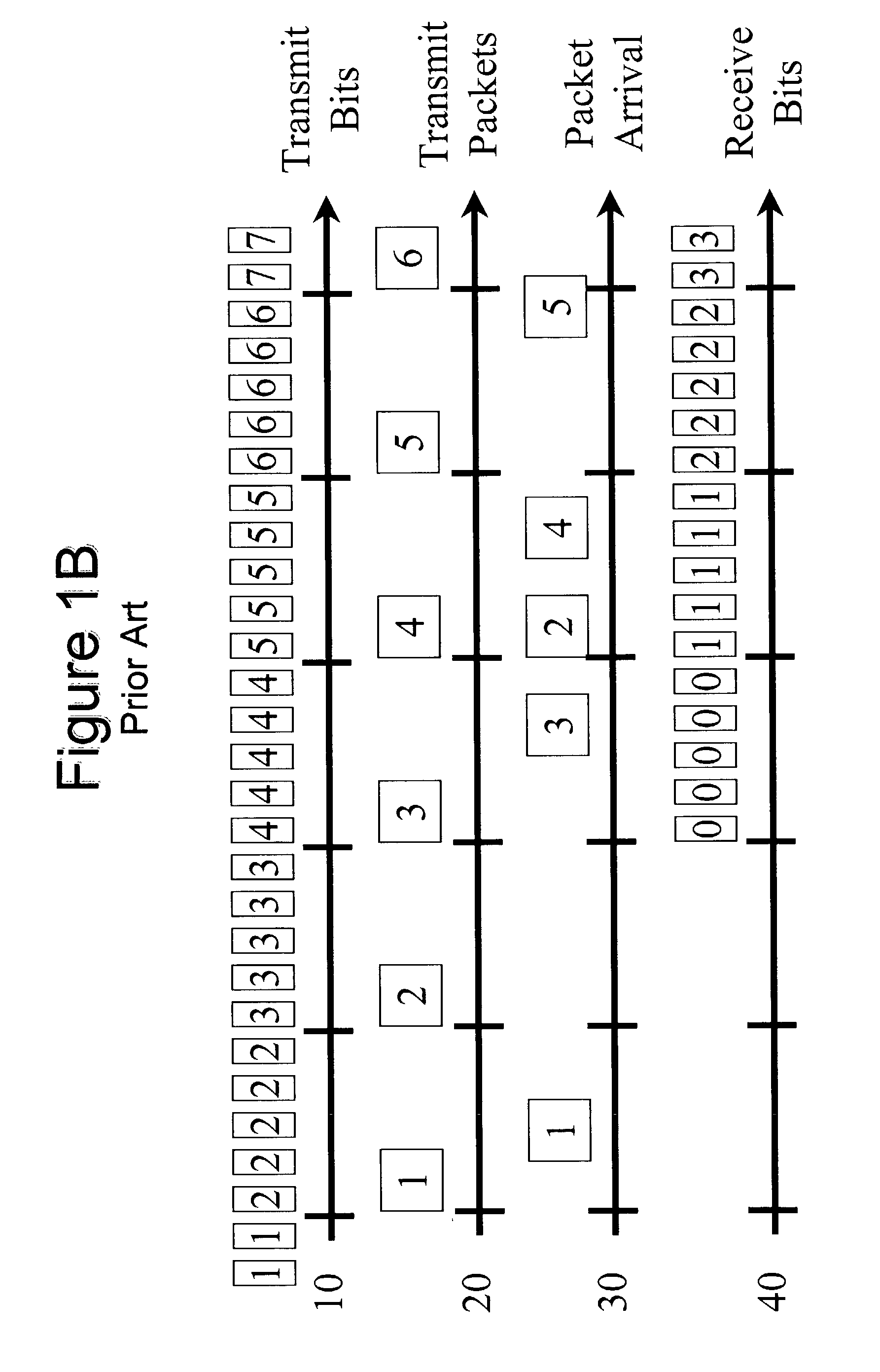
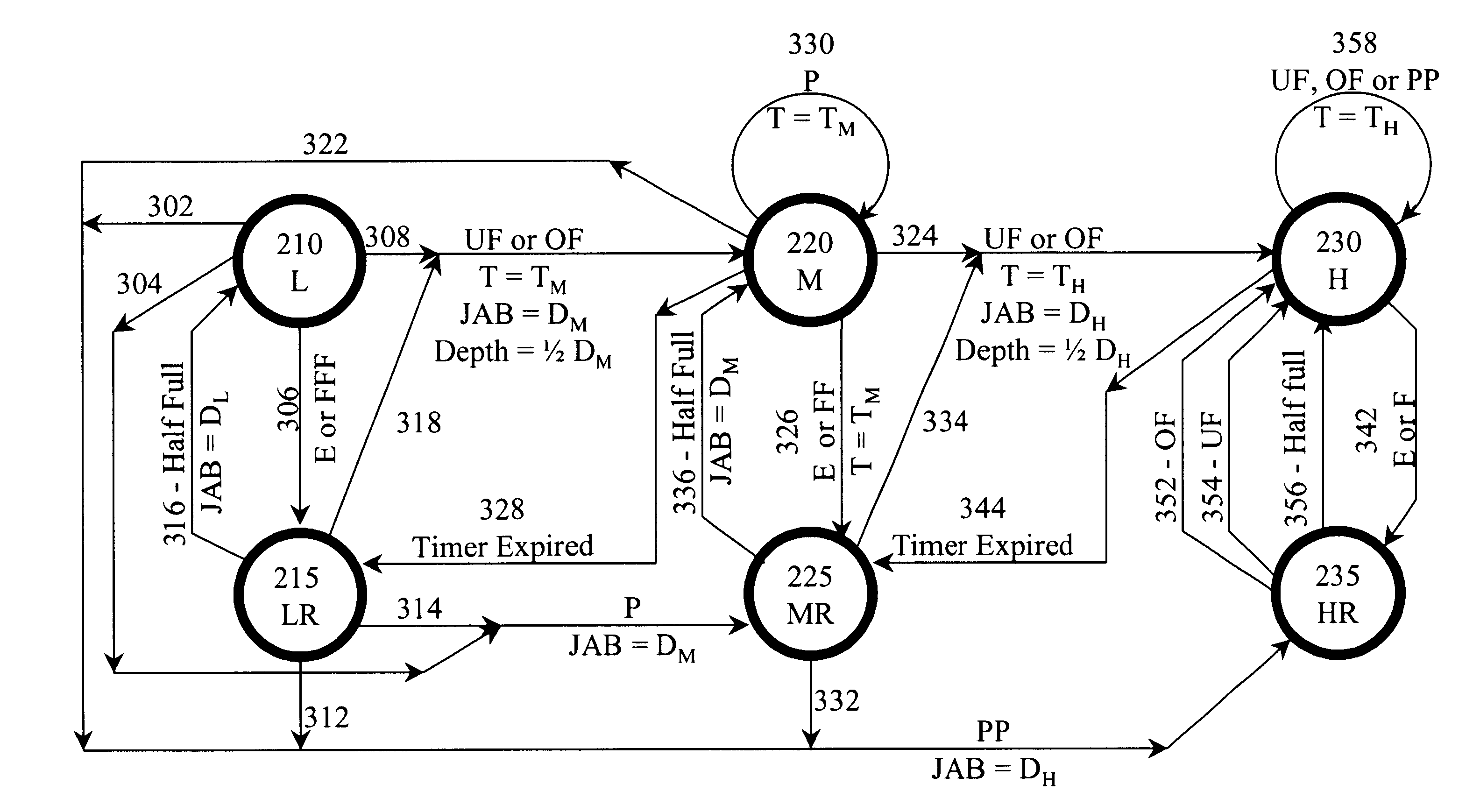
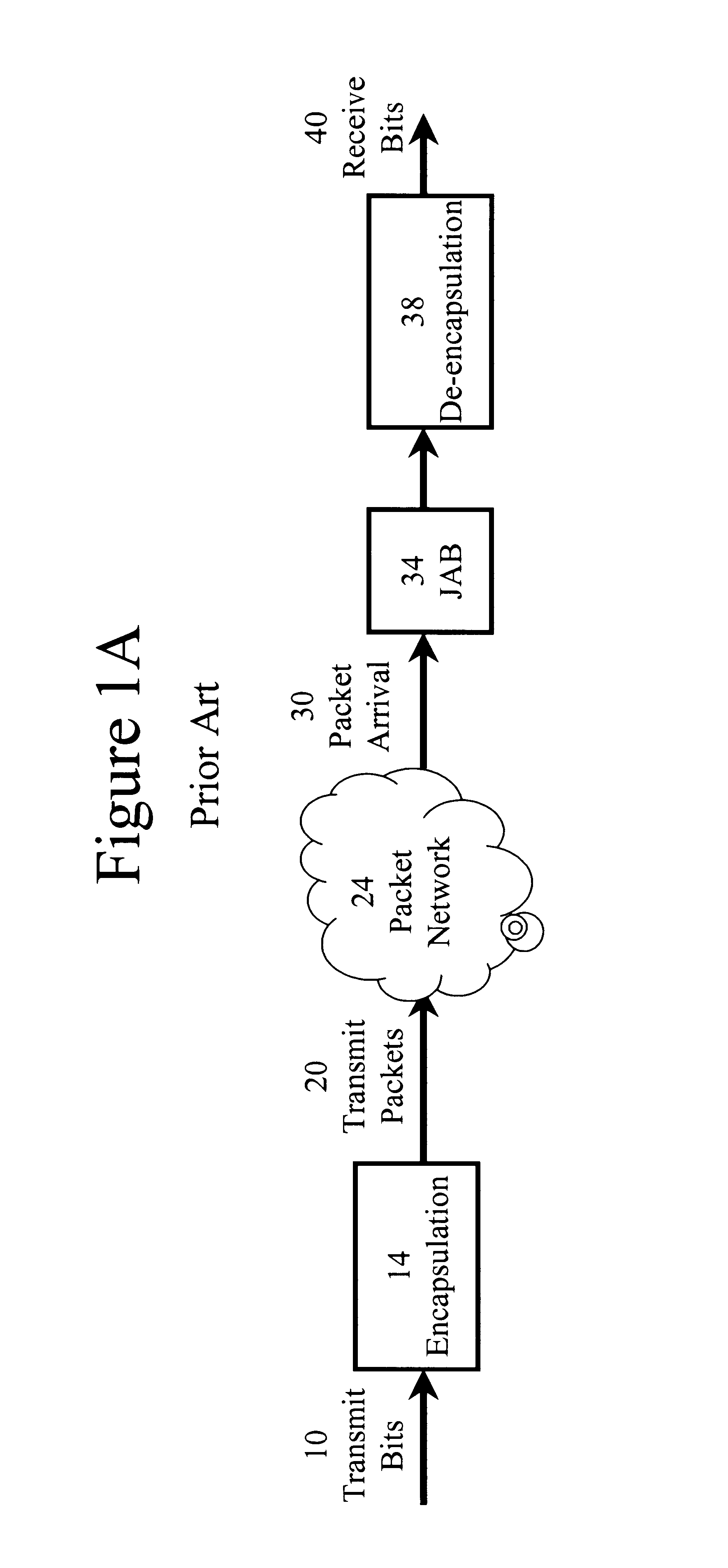
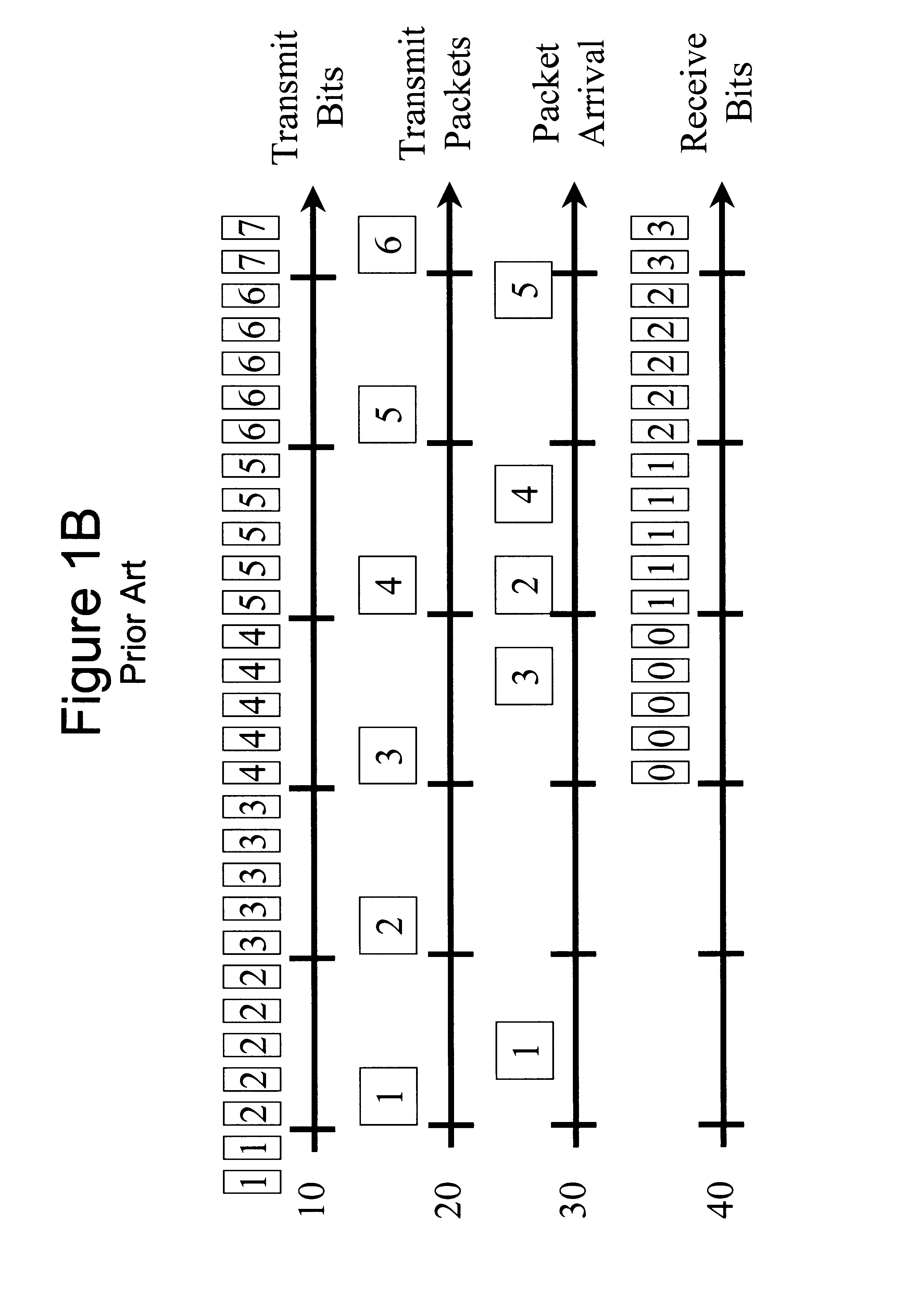
Automatic adjustment of buffer depth for the correction of packet delay variation
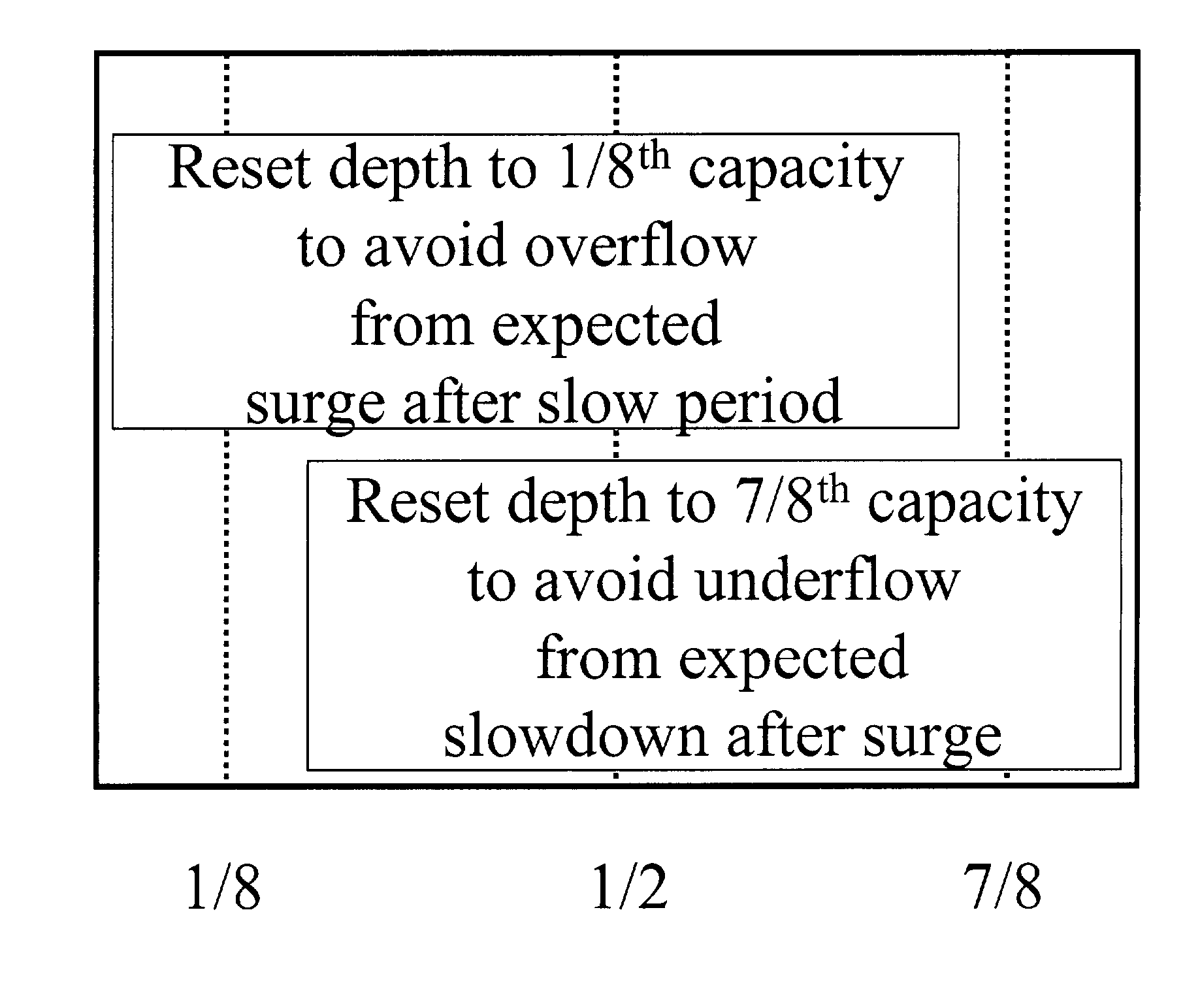
InactiveUS20030086372A1Special service provision for substationError preventionNetwork conditionsReal-time computing
The size of a Jitter Absorption Buffer (JAB) is automatically changed in response to changes in network conditions. The JAB size is changed based on the fullness of the JAB and the recent variations in JAB depth. Automatic adjustment allows for a balance of providing adequate correction for Packet Delay Variation (PDV) while avoiding unnecessary increases in Absolute Packet Delay (APD) from the prolonged use of an oversized JAB. This abstract is provided as a tool for those searching for patents, and not as a limitation on the scope of the claims.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Method and devices for synchronization using linear programming
This invention relates to methods and devices for synchronization using linear programming, especially over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). Timing protocol messages are exposed to artifacts in the network such as packet delay variations (PDV) or packet losses. Embodiments of the invention provide a two-dimensional linear programming technique for estimating clock offset and skew, particularly from two-way exchange of timing messages between a master and a slave device. Some embodiments include a skew and offset adjustable free-running counter for regenerating the master time and frequency at the slave device.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
Method and devices for time and frequency synchronization
This invention relates to methods and devices for time and frequency synchronization, especially over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). Timing protocol messages are exposed to artifacts in the network such as packet delay variations (PDV) or packet losses. Embodiments of the invention provide a recursive least squares mechanism for clock offset and skew estimation. A major potential advantage of such estimation is that it does not require knowledge of the statistics of the measurement noise and process noise. An implementation using a digital phase locked loop based on direct digital synthesis to provide both time and frequency signals for use at the slave (time client) is also provided.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH & RES KUSTAR +2
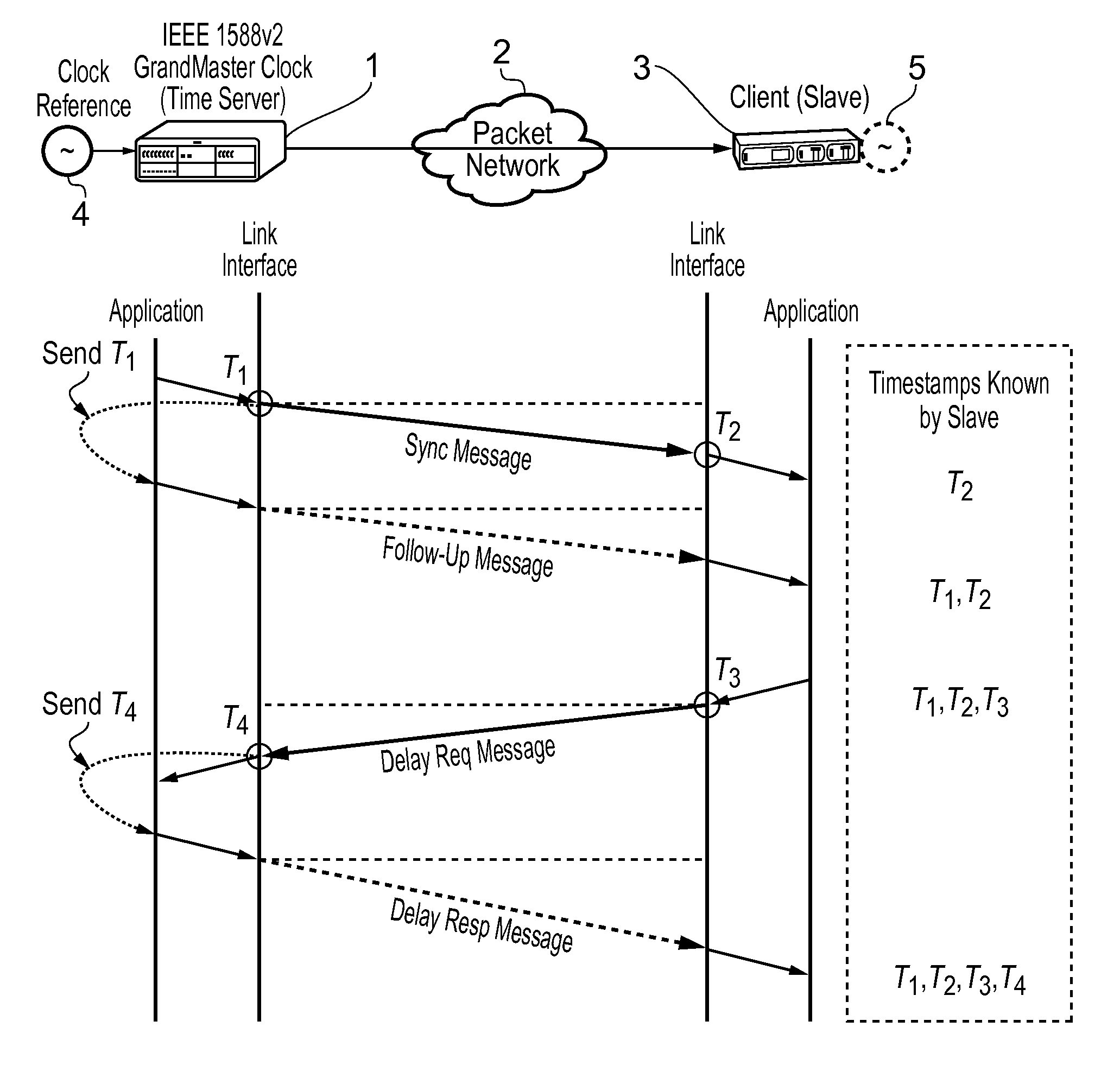
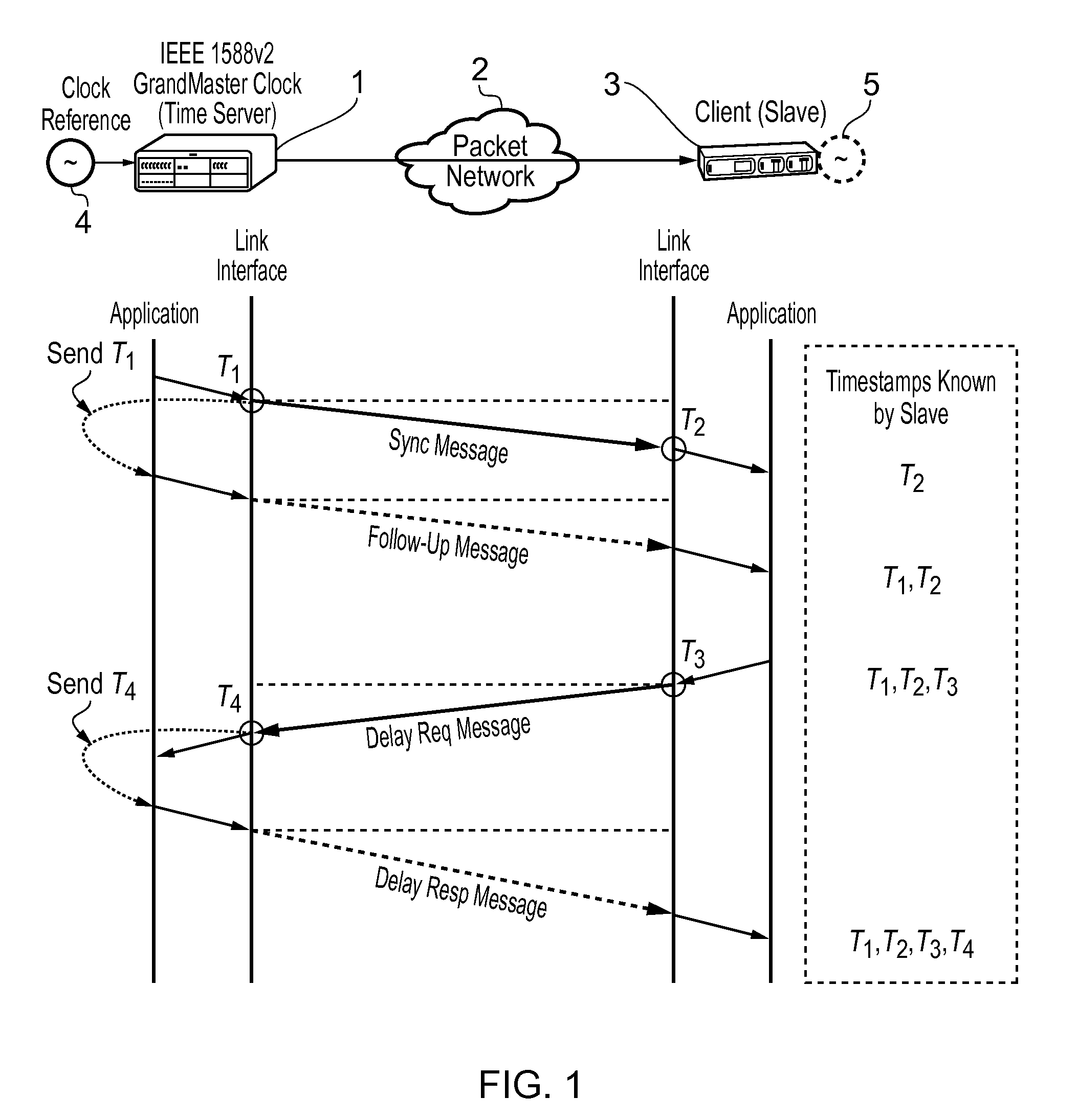
Automatic management of timestamp-based synchronisation protocols
A method for automatic management of a timestamp-based synchronization protocol within a packet-based network to synchronize a slave within a synchronization topology including a plurality of masters, the slave clock being locked to a master clock at an initialization time, said method comprising an assessment step of end-to-end packet delay variation on the basis of the slave clock accuracy, over a plurality of (slave, path, master) combinations, each path linking the slave to a master.
Owner:RPX CORP
Automatic adjustment of buffer depth for the correction of packet delay variation
The size of a Jitter Absorption Buffer (JAB) is automatically changed in response to changes in network conditions. The JAB size is changed based on the fullness of the JAB and the recent variations in JAB depth. Automatic adjustment allows for a balance of providing adequate correction for Packet Delay Variation (PDV) while avoiding unnecessary increases in Absolute Packet Delay (APD) from the prolonged use of an oversized JAB. This abstract is provided as a tool for those searching for patents, and not as a limitation on the scope of the claims.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Method and devices for synchronization using linear programming
This invention relates to methods and devices for synchronization using linear programming, especially over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). Timing protocol messages are exposed to artifacts in the network such as packet delay variations (PDV) or packet losses. Embodiments of the invention provide a two-dimensional linear programming technique for estimating clock offset and skew, particularly from two-way exchange of timing messages between a master and a slave device. Some embodiments include a skew and offset adjustable free-running counter for regenerating the master time and frequency at the slave device.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
Method and devices for time transfer using peer-to-peer transparent clocks
This invention relates to methods and devices for time synchronization. The invention has particular application in the alignment of slave clocks to a master clock and in dealing with packet delay variation and dynamic asymmetries in the network links between them. In embodiments of the invention, the slave clock uses the peer link delay and residence times measured by peer-to-peer transparent clocks to compensate for clock synchronization errors that arise due to variability in message transfer delays. Embodiments provide a simple linear approximation technique and a Kalman filter-based technique for estimating offset and skew of the slave clock.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Methods of performing time-of-day synchronization in packet processing networks
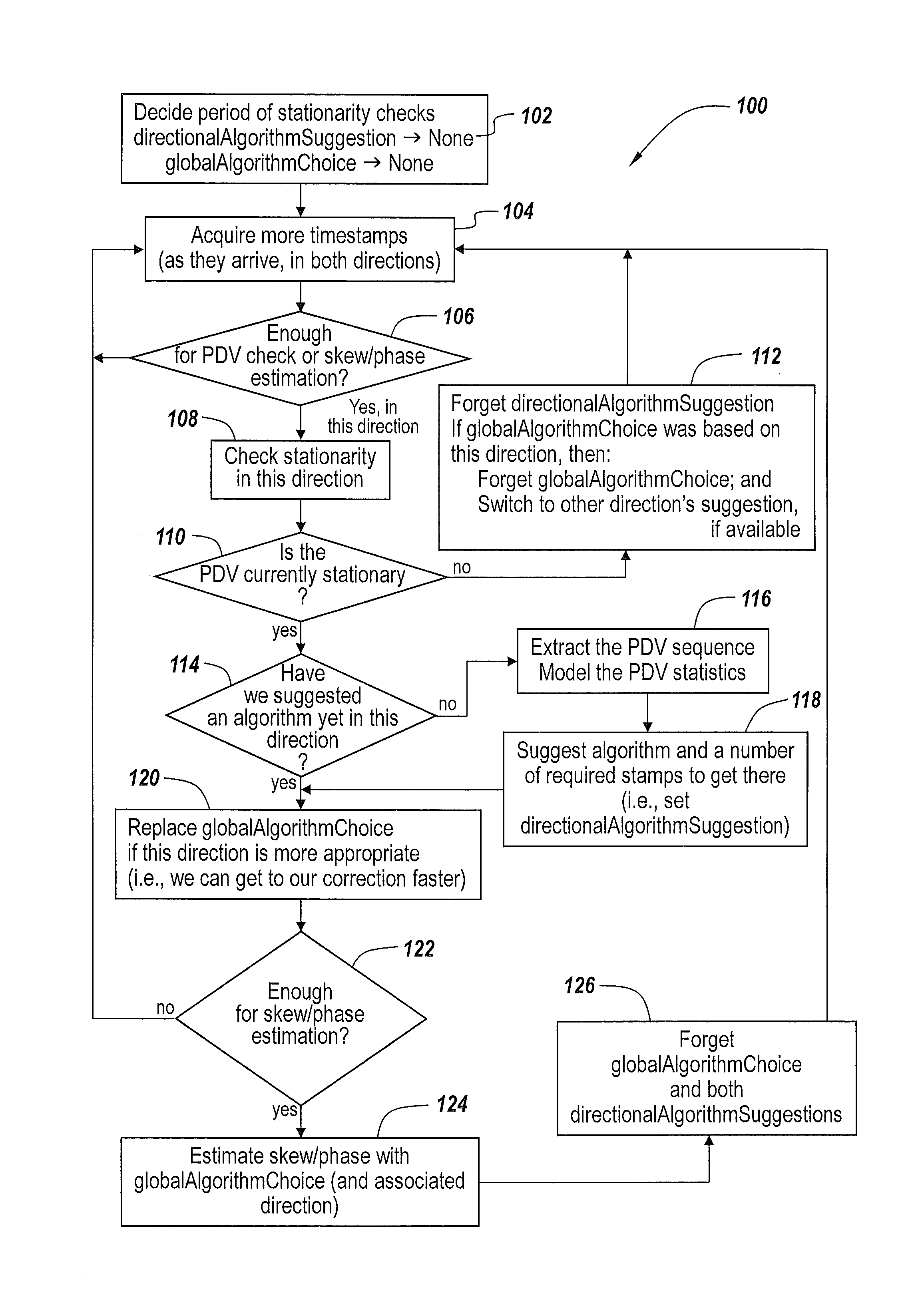
Methods of performing time-of-day synchronization in a packet processing network include accumulating timestamps transmitted in packets between master and slave devices, which are synchronized to respective master and slave clocks and separated from each other by the packet processing network. Operations are also performed to determine whether first timestamps accumulated in a first direction across the packet network demonstrate that a first packet delay variation (PDV) sequence observed from the first timestamps is stationary. A phase offset between the master and slave clocks is then adjusted using a time-of-day (ToD) estimation algorithm. This adjusting can include evaluating a location-dependent statistic of the first PDV sequence.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Method and devices for packet selection
This invention relates to packet selection techniques that can be used in conjunction with a clock recovery mechanism to mitigate the effects of packet delay variation on timing messages exchanged over a packet network, particularly when seeking to synchronize the time of a clock in a slave device to that of a master clock. The packet selection techniques can assist in reducing the noise in the recovered clock signal at the slave device, allowing recovery to a higher quality. Embodiments of the invention provide techniques based on extracting timing packets that create a constant interval between the arrival of selected packets at the slave device and on extracting timing packets which are closest to making the interval between arrival of the selected packets equal to the interval between the departure of the packets.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Method and devices for time and frequency synchronization using a phase locked loop
This invention relates to methods and devices for time and frequency synchronization, especially over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). Timing protocol messages are exposed to artifacts in the network such as packet delay variations (PDV) or packet losses. Embodiments of the invention provide a digital phase locked loop (DPLL) based on direct digital synthesis to provide both time and frequency signals for use at the slave (time client). An example of this DPLL in conjunction with a recursive least squares mechanism for clock offset and skew estimation is also provided.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
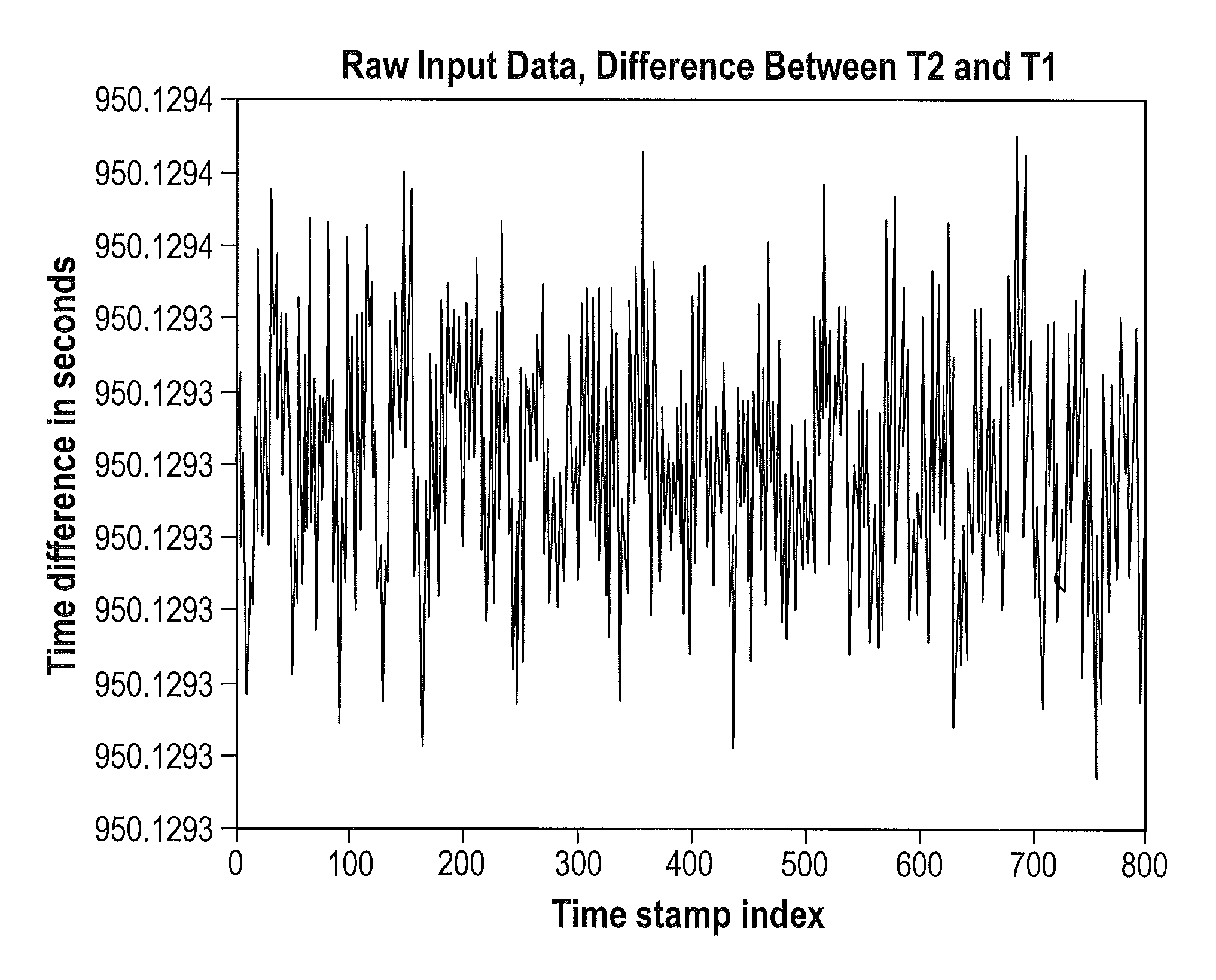
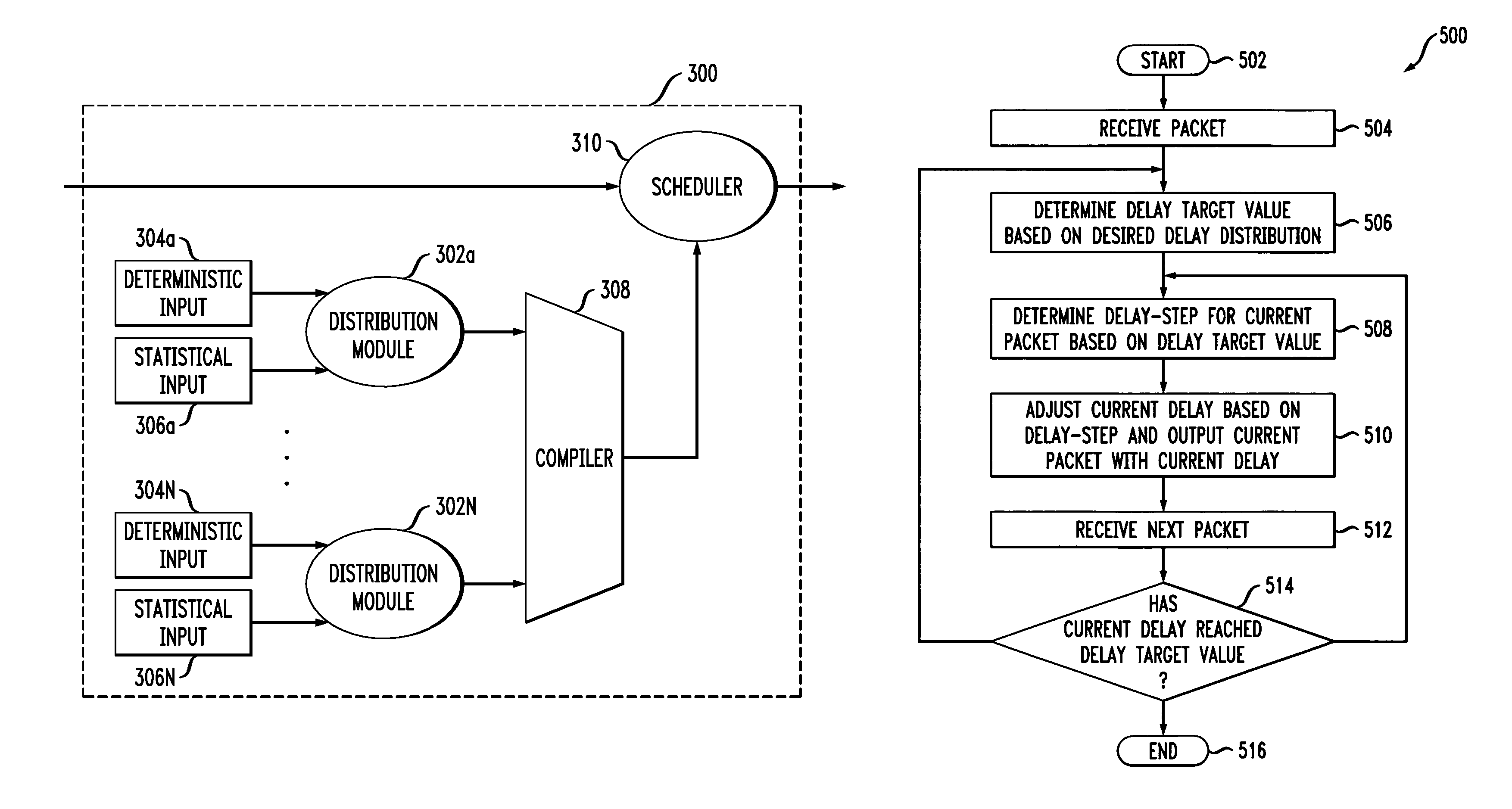
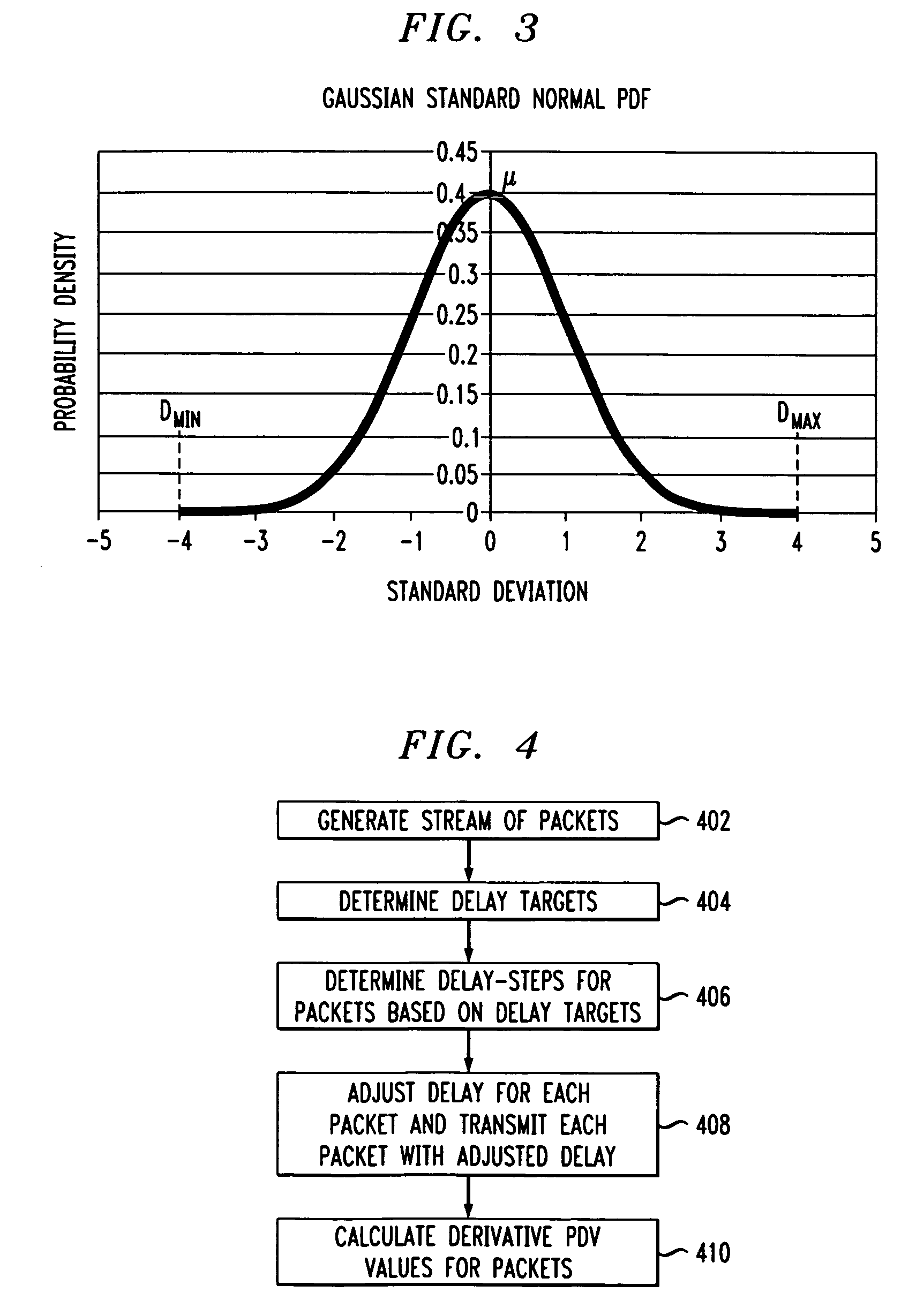
Simulating packet delay variation using step-target delay method
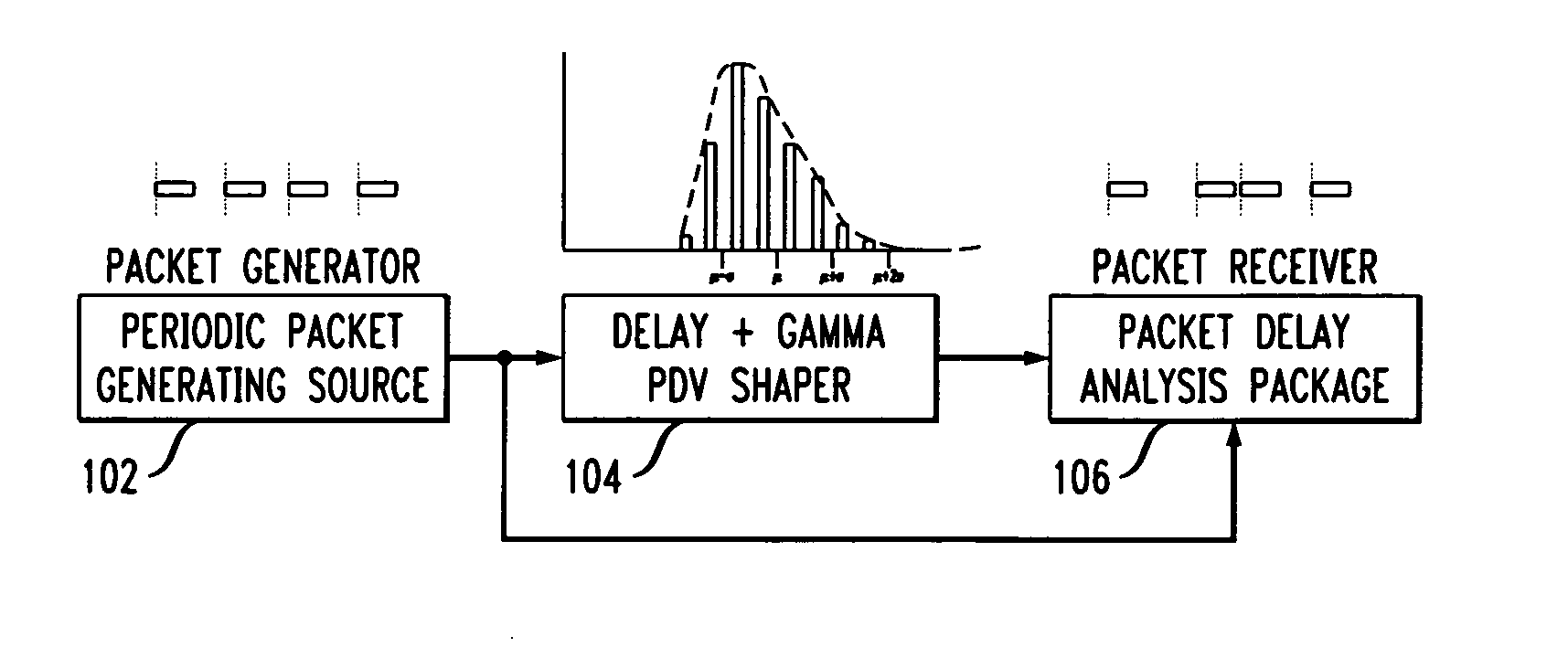
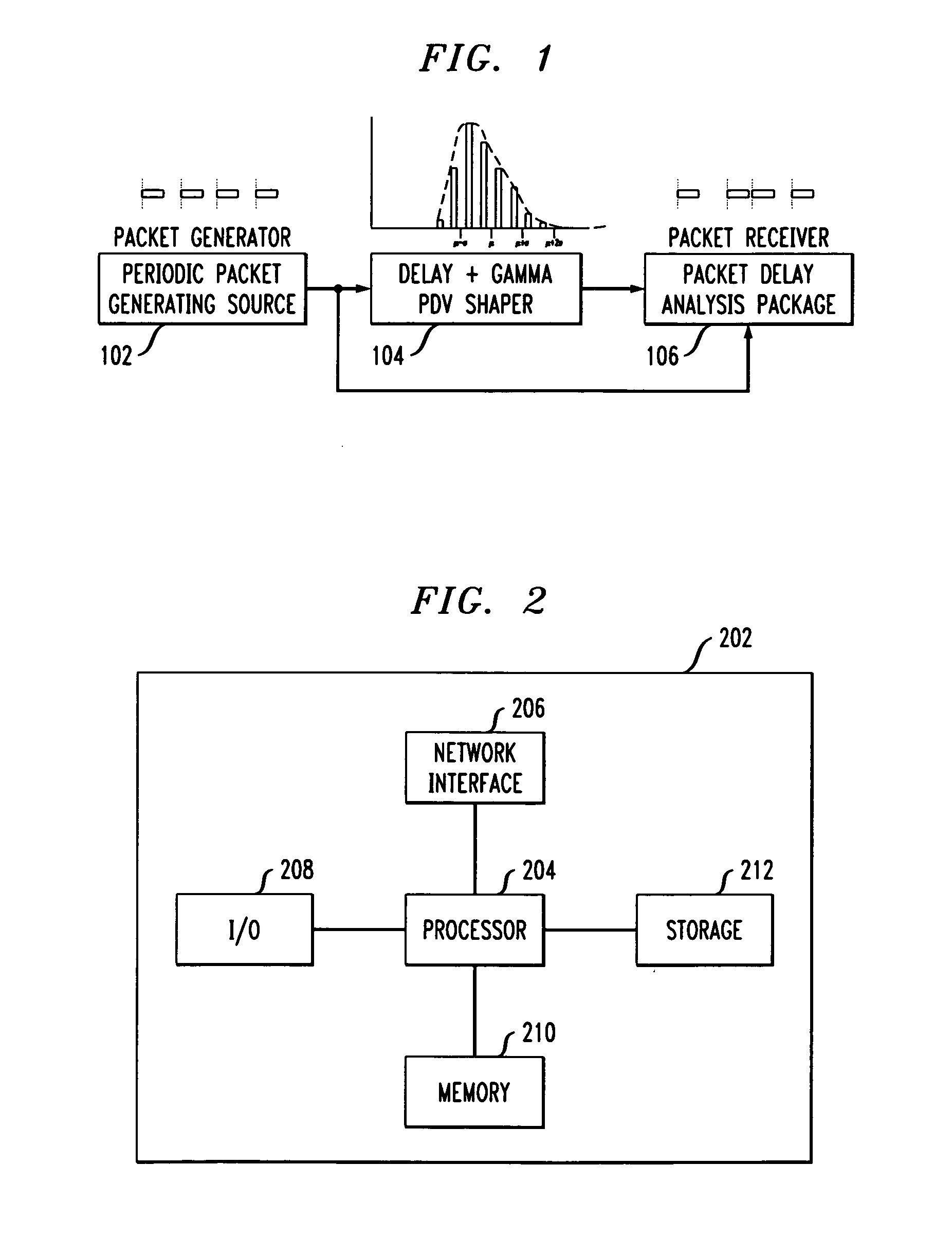
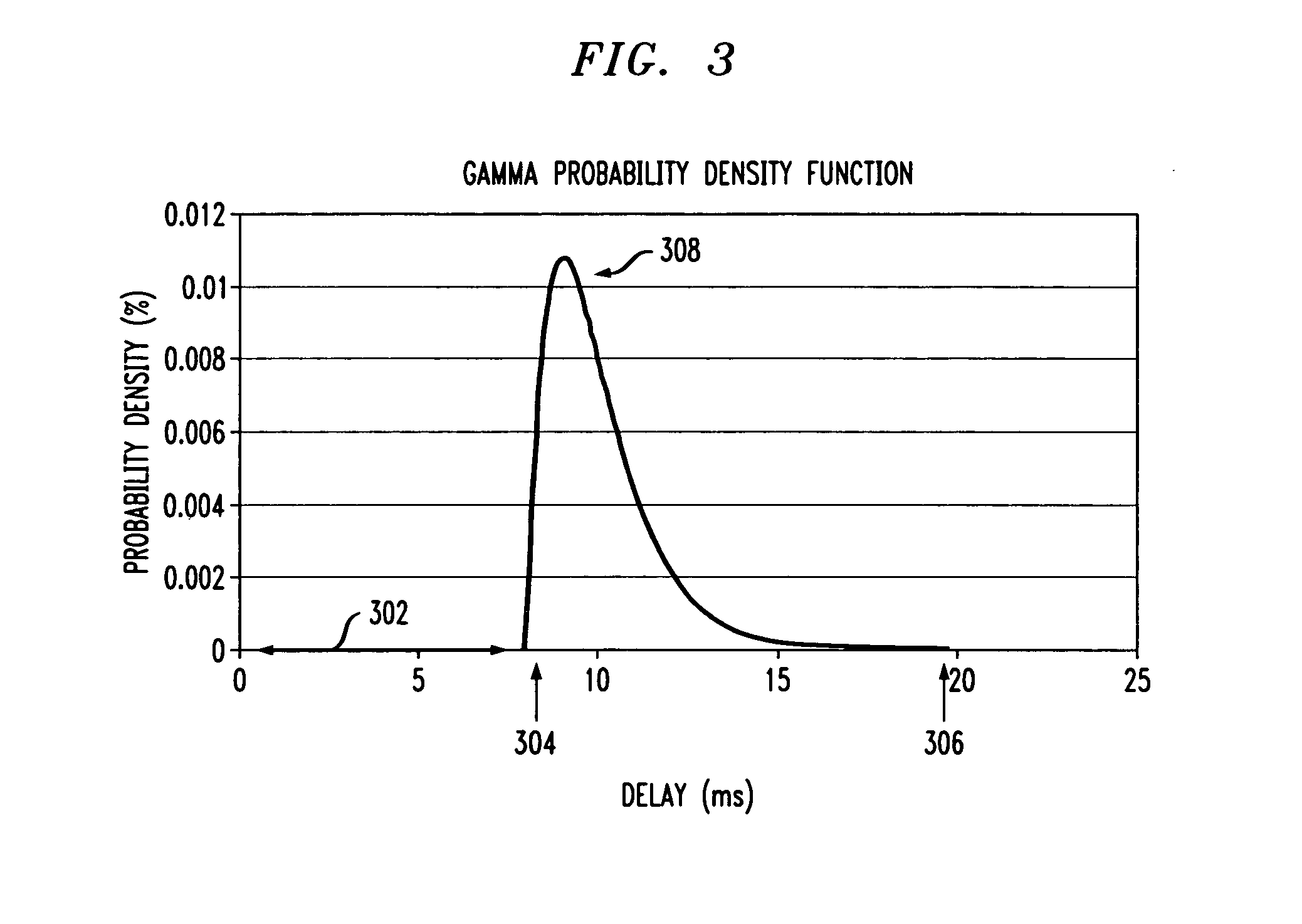
A method and system for simulating packet delay variation (PDV) is disclosed. The delay-step method for simulating PDV determines a delay for each packet is a stream of packets generated at a regular interval. Delay target values are randomly selected based on a statistical distribution, such as a Gamma distribution, which models a desired PDV. Delay-steps are determined for each packet based on the delay target values. The delay-steps can be fixed or variable sized steps which are used to adjust the delay of sequential packets. Each of the packets is then transmitted with the delay determined for that packet.
Owner:INTEL CORP
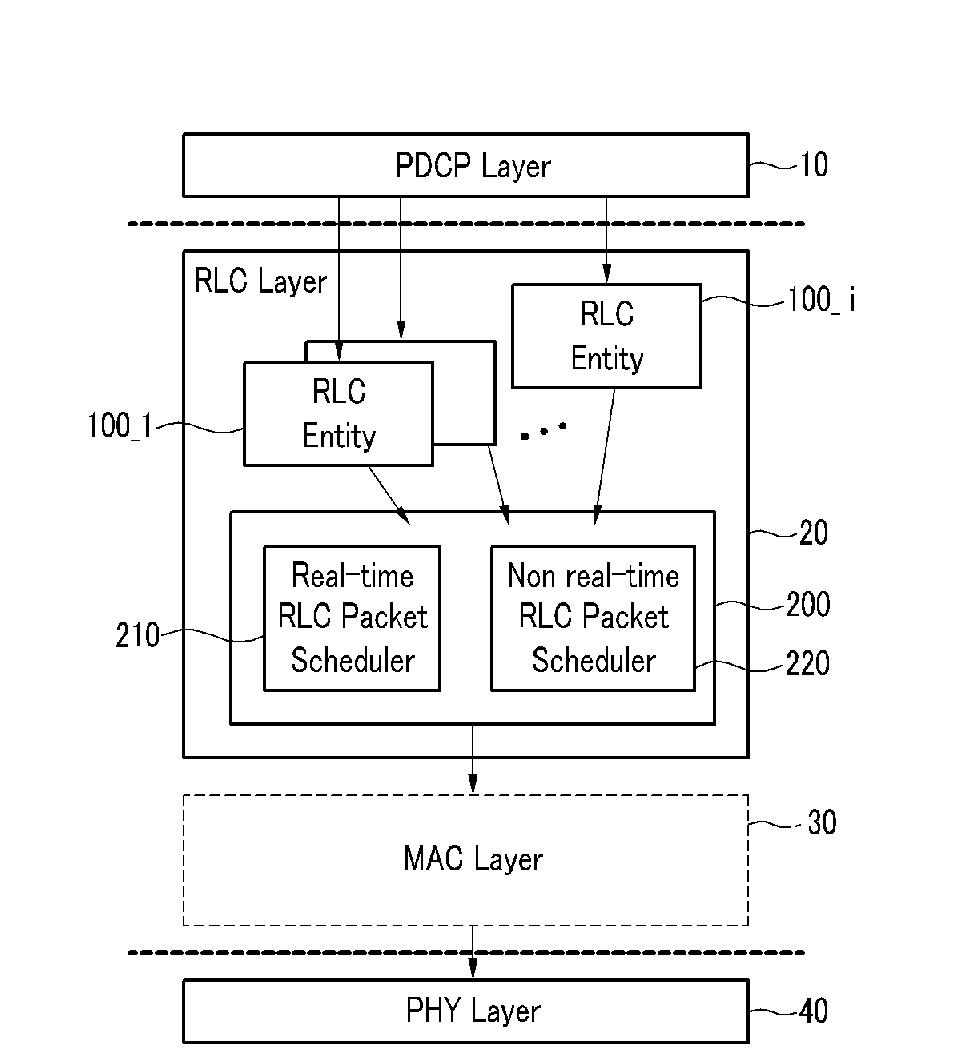
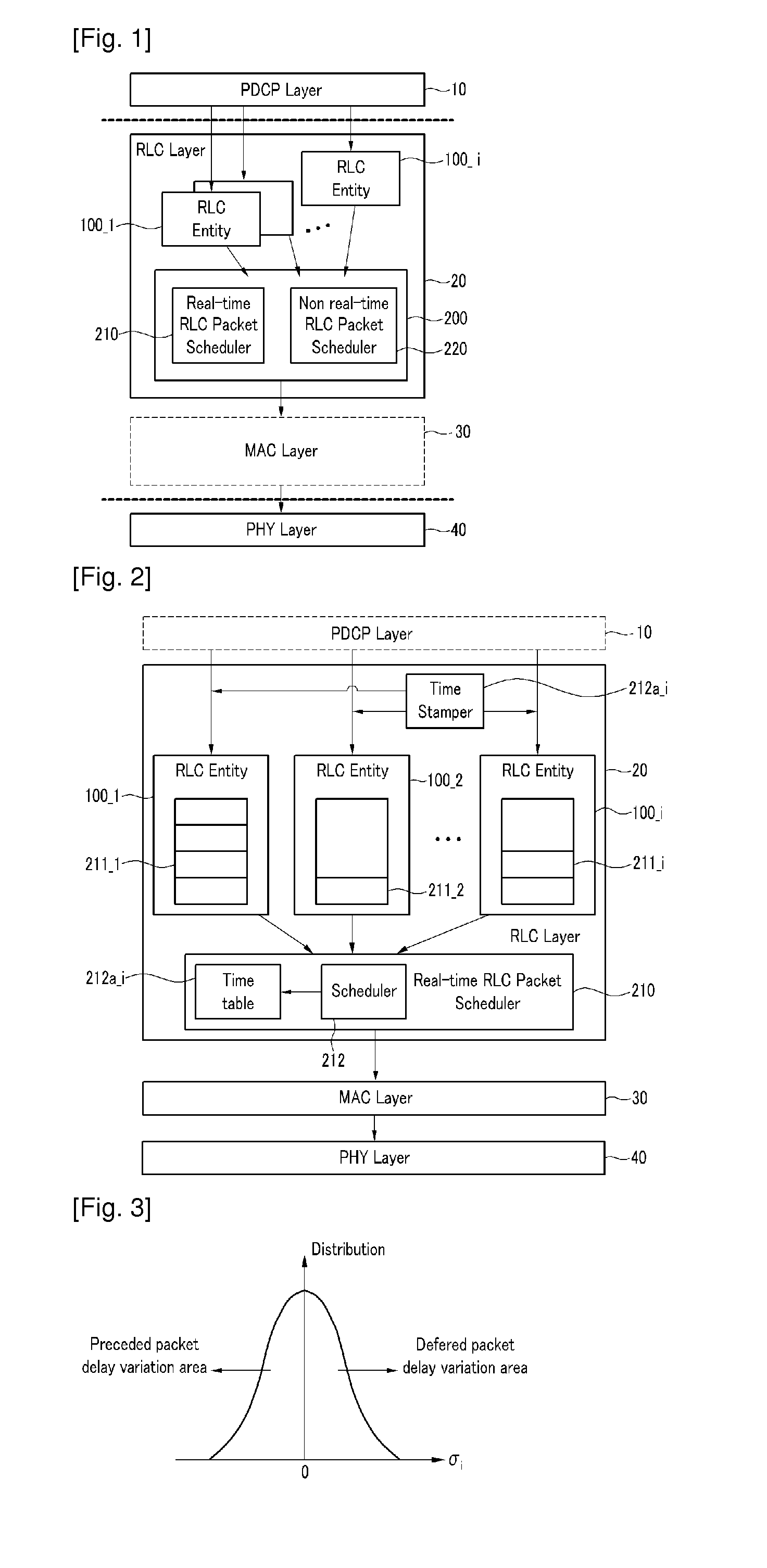
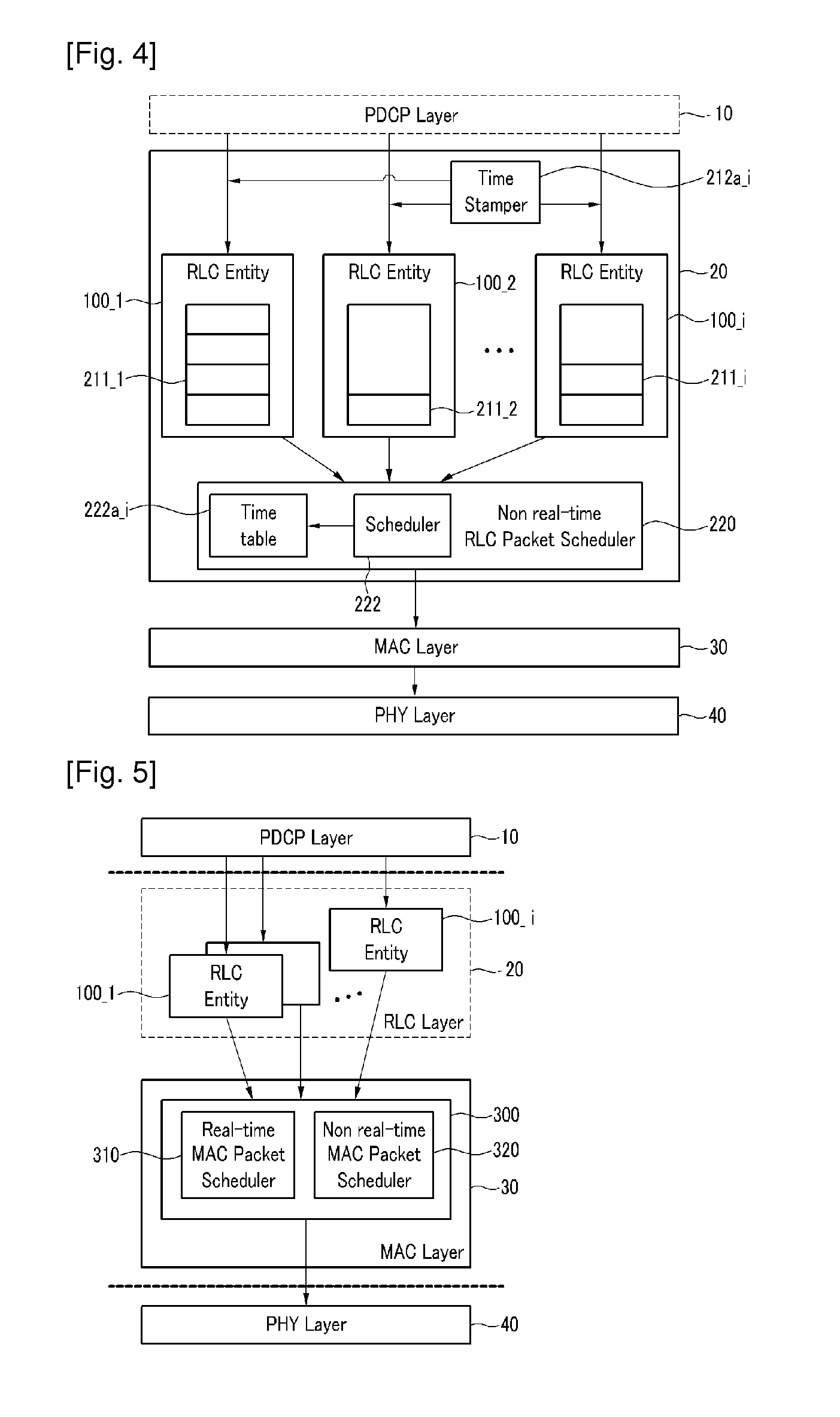
Packet scheduler and packet scheduling method
InactiveUS20100002632A1Improve user satisfactionImprove satisfactionNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationPacket delay variationDistributed computing
A method for scheduling packets from a plurality of radio bearers by a scheduler of a first layer includes calculating a virtual scheduling time for the radio bearers by using a packet delay variation of the radio bearers, and transmitting the packet of the radio bearer having the greatest virtual scheduling time from among the plurality of radio bearers to a second layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Methods of packet-based synchronization in non-stationary network environments
Methods of packet-based synchronization in non-stationary network environments can include accumulating timestamps transmitted in packets between master and slave devices that are separated from each other by a packet network. Operations are also performed to determine whether first timestamps accumulated in a first direction across the packet network demonstrate that a first packet delay variation (PDV) sequence observed from the first timestamps is stationary. Thereafter, estimates of at least one of frequency skew and phase offset between the master and slave clocks are acquired using a first algorithm, from the first timestamps accumulated in the first direction. These operations of determining further include determining whether second timestamps accumulated in a second direction demonstrate that a second packet delay variation (PDV) sequence observed from the second timestamps is stationary.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
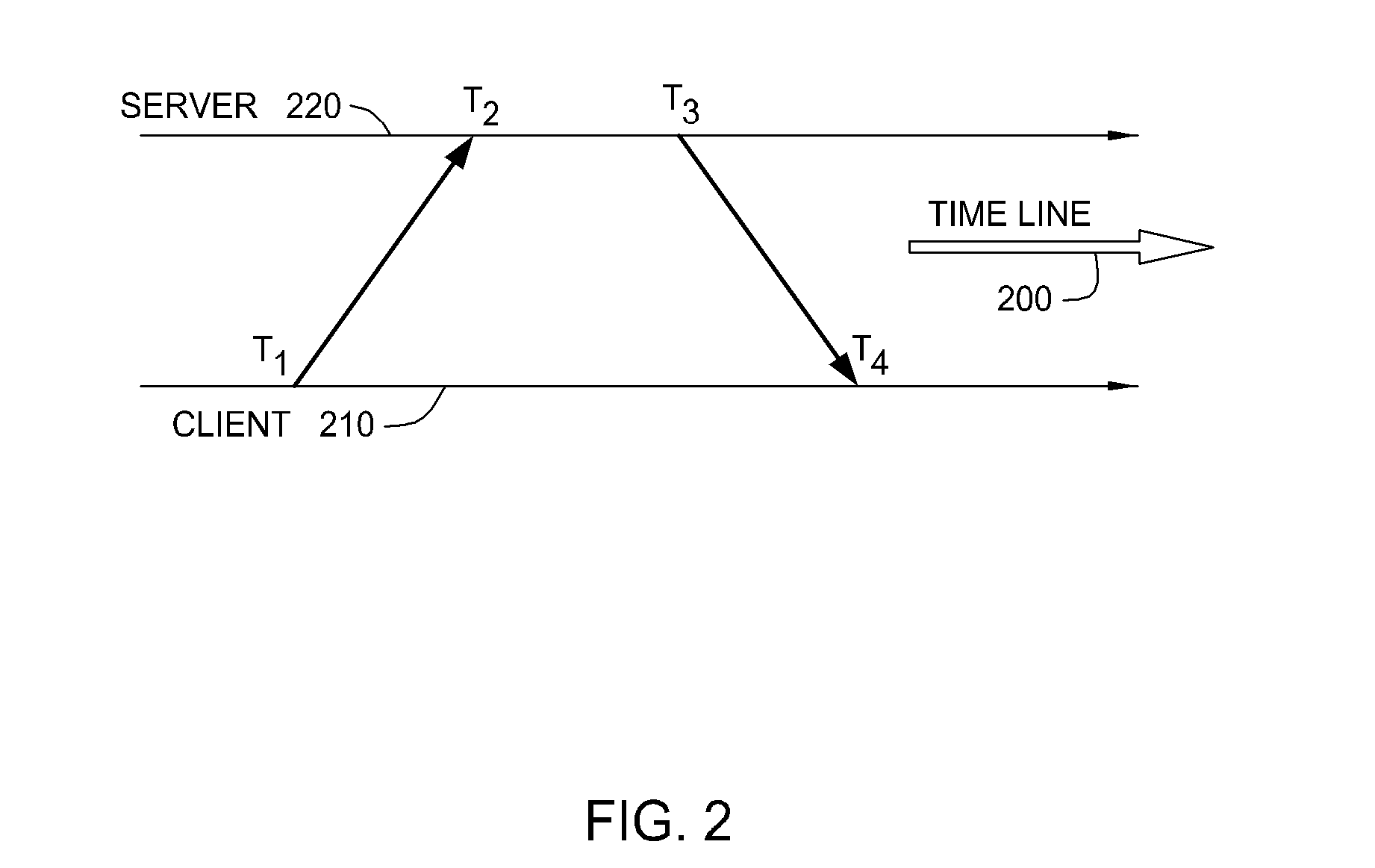
Method of adjusting a local clock in asynchronous packet networks
ActiveUS20130308660A1Reduce congestionAccurate timingTime-division multiplexTransmissionArrival timeLatency distribution
In a computer-implemented method of adjusting a local clock at a receiver in a packet network, the local clock is generated by a phase locked loop locked to a master clock with the aid of time-stamped timing packets arriving over the network from the master clock with a packet delay distribution about a nominal delay. The timing packets are filtered to adjust for the packet delay distribution. A control input for the phase locked loop is derived from the timing packets. The amount of skew in the packet delay distribution about the nominal delay is determined, and the arrival times of timing packets are then selectively modified to correct for the amount of skew in the packet delay variation distribution prior to filtering the timing packets.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
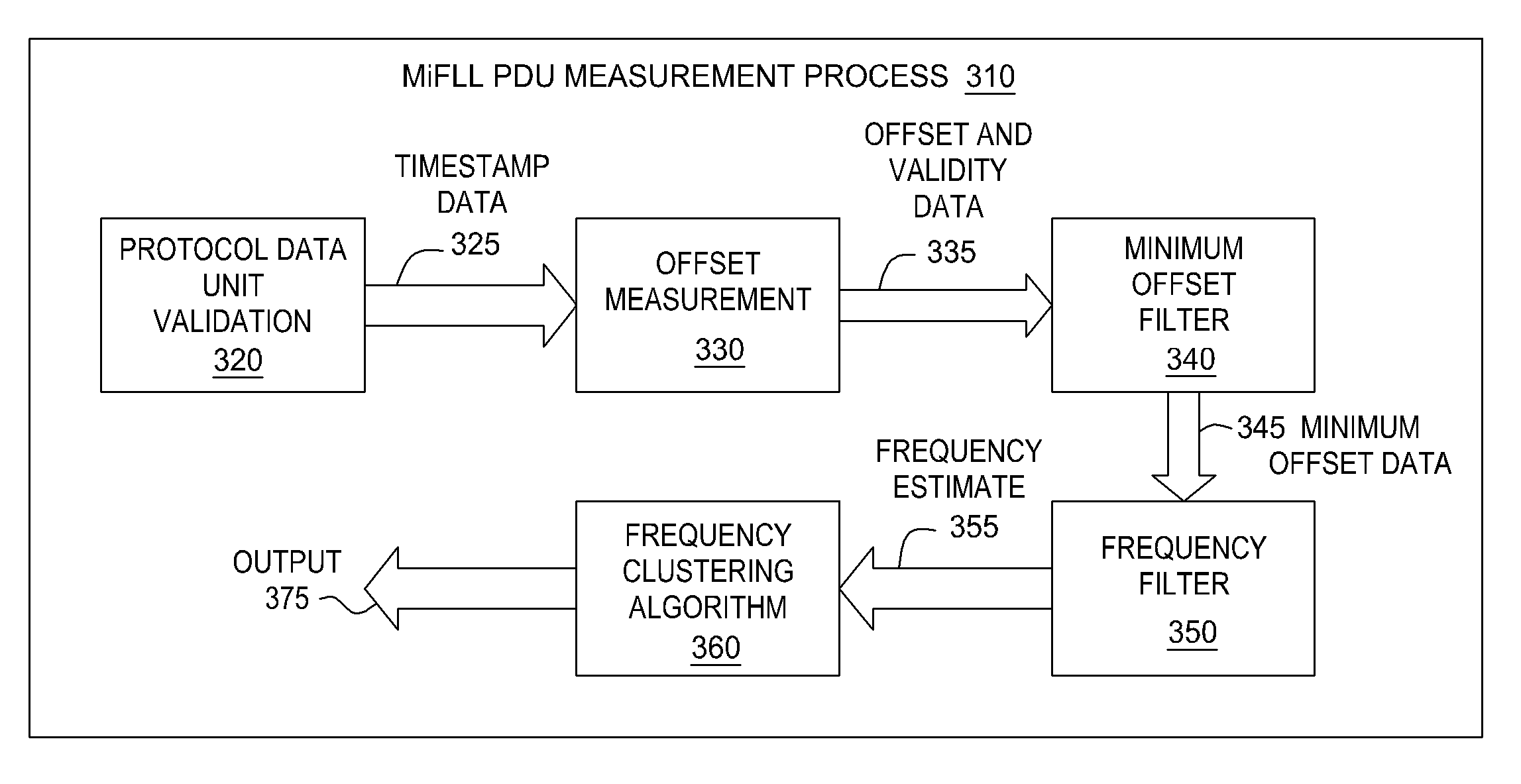
Enhanced clock control in packet networks
ActiveUS8064484B2Improve stabilityLow costTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationFrequency filteringQuality control
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a method for autonomously validating the time and frequency data obtained from multiple sources, and generating a suitable estimate of the frequency difference between the client clock and the source. The method includes the steps of protocol data unit validation, offset measurement, minimum offset filtering, and frequency filtering. With these steps, the negative effects of packet delay variation may be mitigated and a frequency estimate is determined for the source in question, together with an associated validity status. Consequently, quality control of the local clock is achieved in packet networks at significantly reduced cost and decreased level of complexity relative to prior art approaches.
Owner:MICROSEMI FREQUENCY & TIME
Method and apparatus for simulating packet delay variation of a multi-switch network
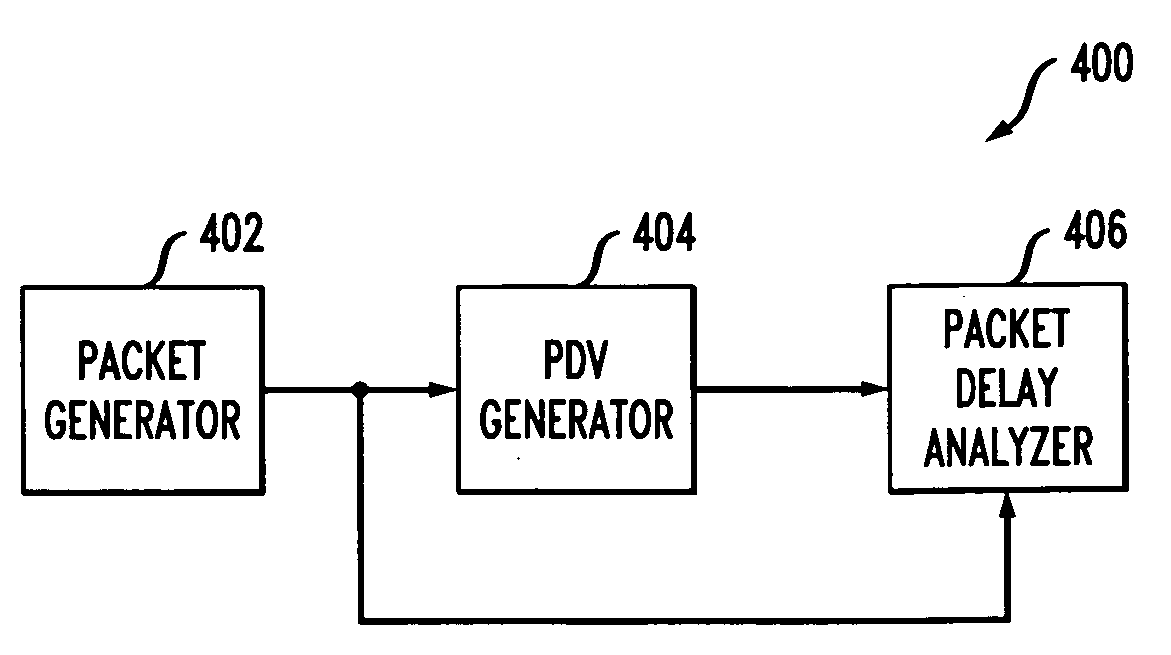
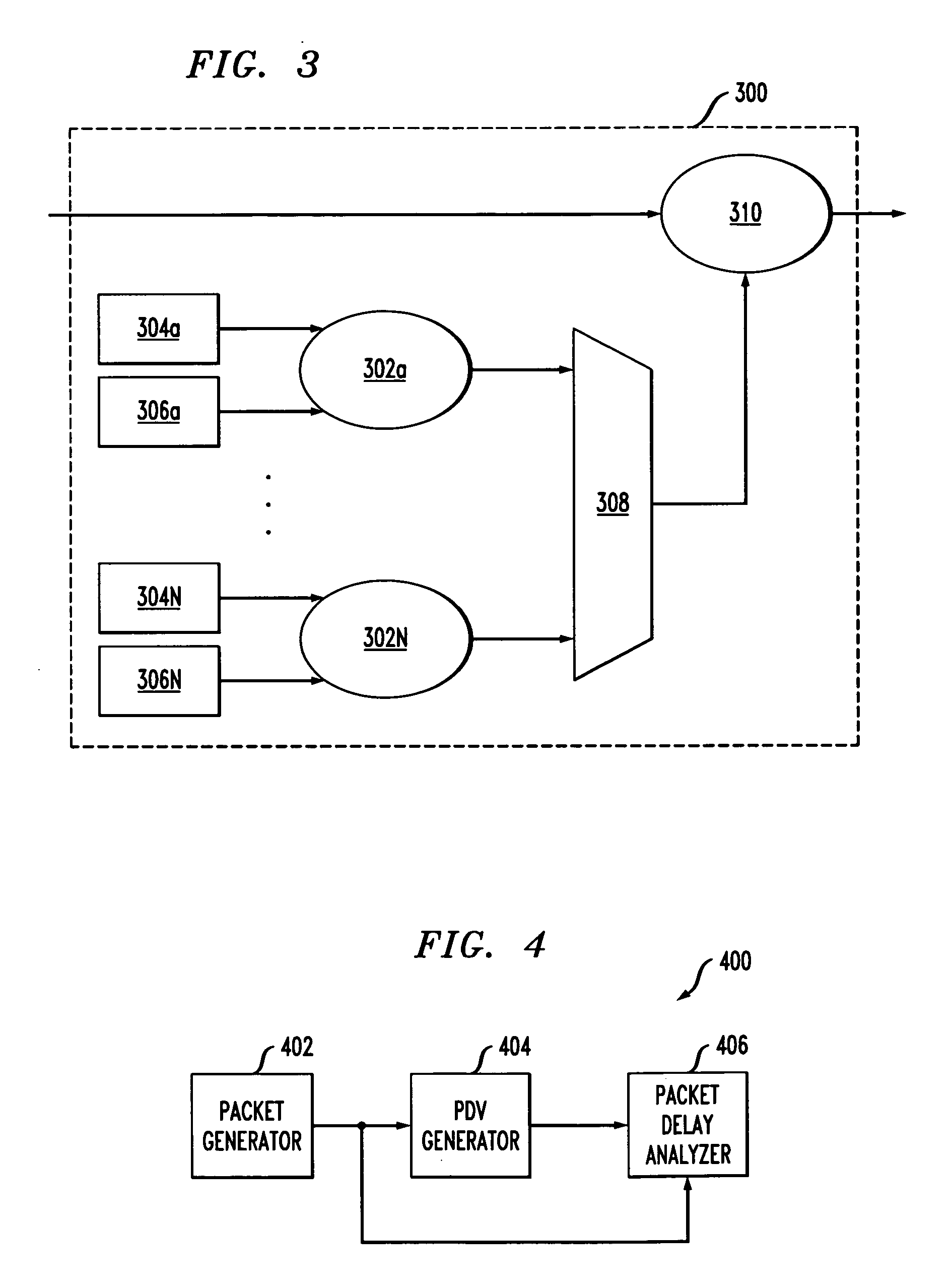
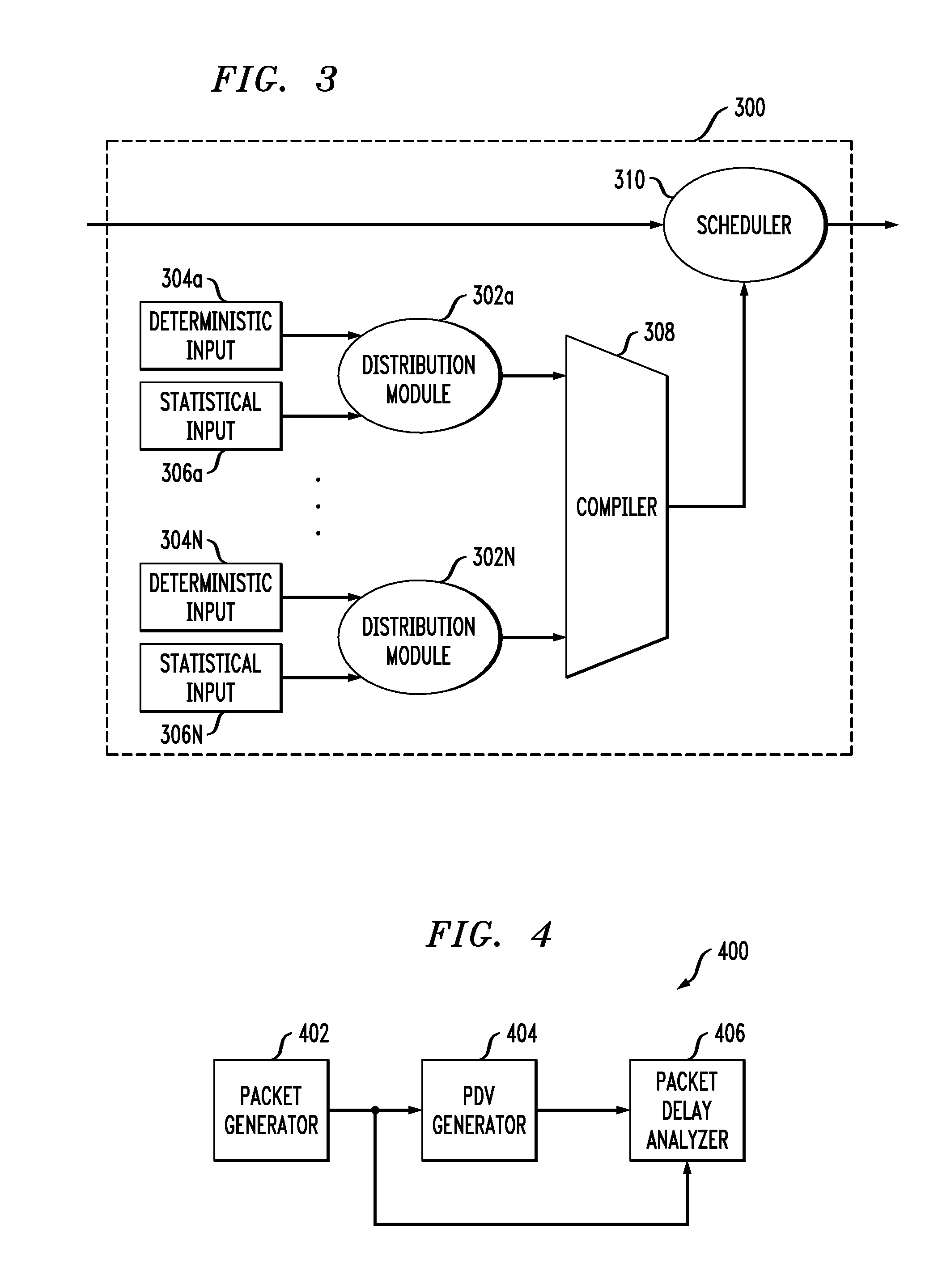
InactiveUS20090259445A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusVoltage-current phase angleTotal delayPacket generator
A packet delay variation simulation system has a packet generator, a packet delay variation generator, and a packet delay analyzer to analyze delayed packets. The packet delay variation generator has multiple delay distribution modules that use both a deterministic delay process and a statistical delay process packet for determining a packet's delay. The packet delay variation generator may utilize different probability density functions to describe various portions of measured packet data. That is, measured packet delay information is analyzed and information from this analysis is used to construct a total delay model for a network. The delay may include a pre-determined deterministic delay offset as well as one or more variable statistical delay offsets.
Owner:INTEL CORP
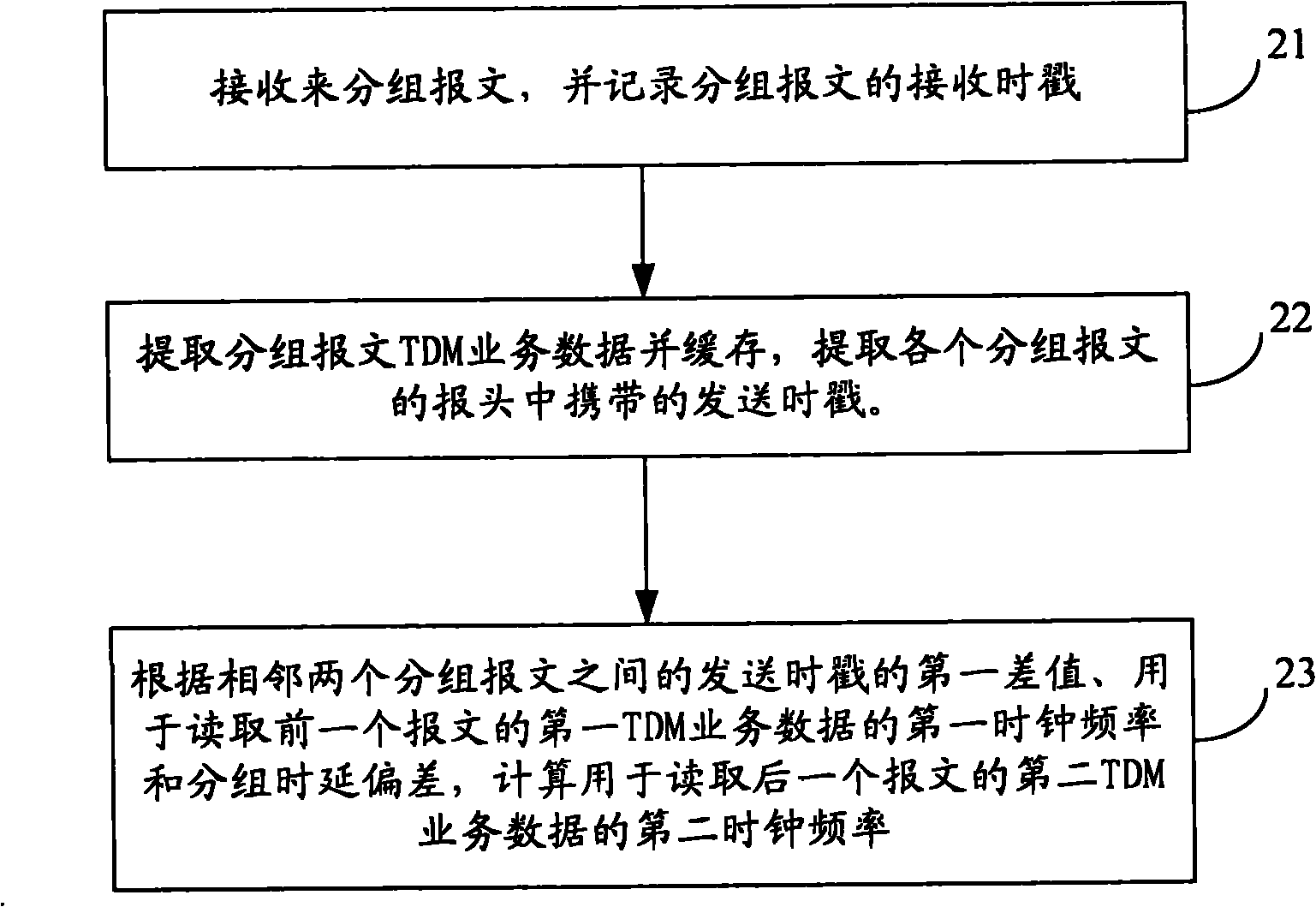
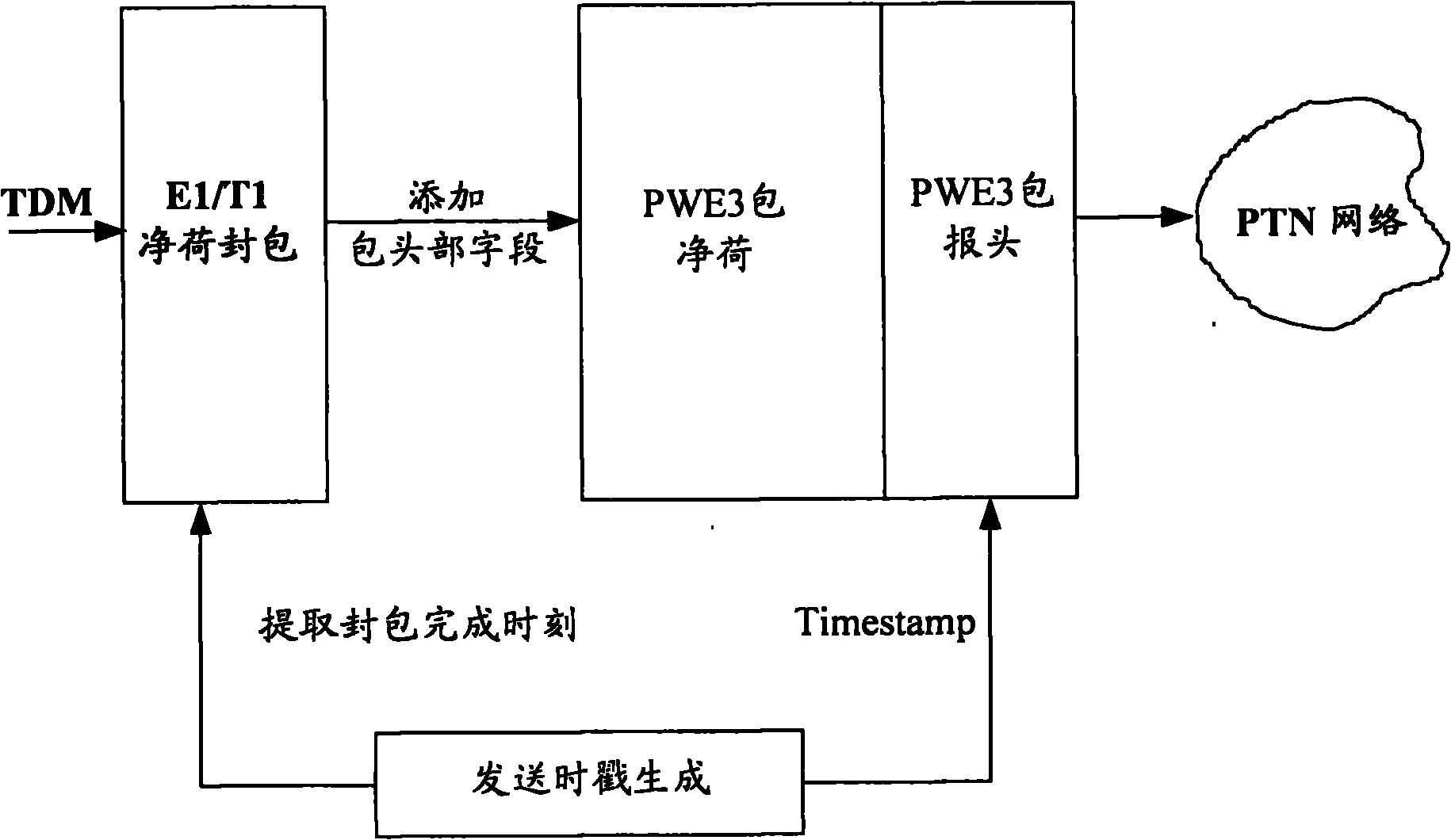
Timestamp-based clock recovery method and device
ActiveCN102340365AReduce adverse effectsTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementRecovery methodTimestamp
The invention provides a timestamp-based clock recovery method and a timestamp-based clock recovery device. The method comprises that: a receiver receives a packet message encapsulated with time division multiplexing (TDM) service data from a packet transport network, and records a receiving timestamp of the packet message; and the receiver calculates and updates the clock frequency of the receiver according to a transmission time difference between two adjacent packet messages and a packet delay variation of the transmission of the packet messages in the packet transport network. By the method and the device, sudden changes in the frequency of a transmitter can be tracked, and the transmission frequency of the transmitter can be rapidly locked.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for simulating packet delay variation of a multi-switch network
InactiveUS8094686B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusVoltage-current phase angleTotal delayPacket generator
A packet delay variation simulation system has a packet generator, a packet delay variation generator, and a packet delay analyzer to analyze delayed packets. The packet delay variation generator has multiple delay distribution modules that use both a deterministic delay process and a statistical delay process packet for determining a packet's delay. The packet delay variation generator may utilize different probability density functions to describe various portions of measured packet data. That is, measured packet delay information is analyzed and information from this analysis is used to construct a total delay model for a network. The delay may include a pre-determined deterministic delay offset as well as one or more variable statistical delay offsets.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and devices for frequency distribution
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Methods and systems for determining optimal packets
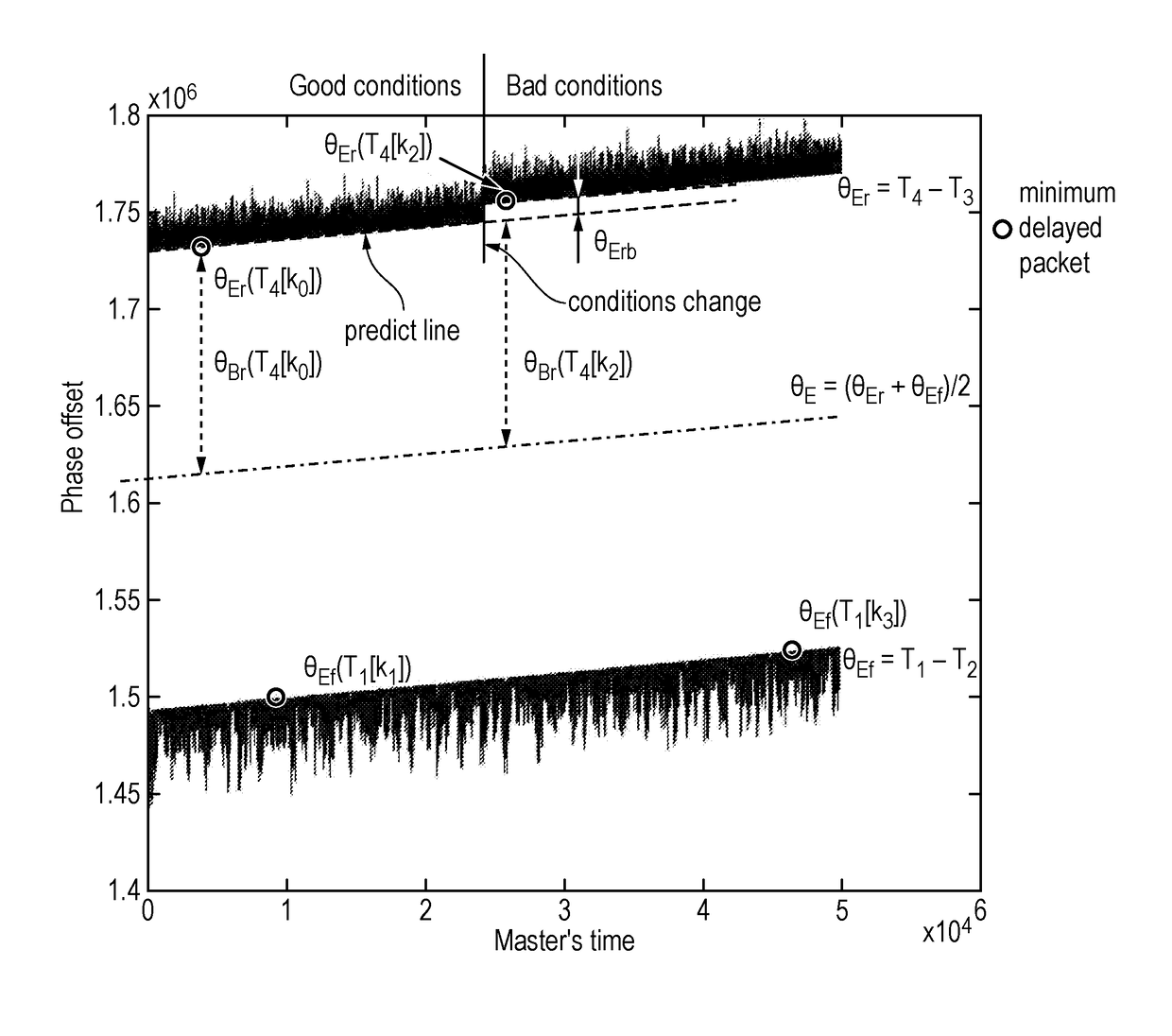
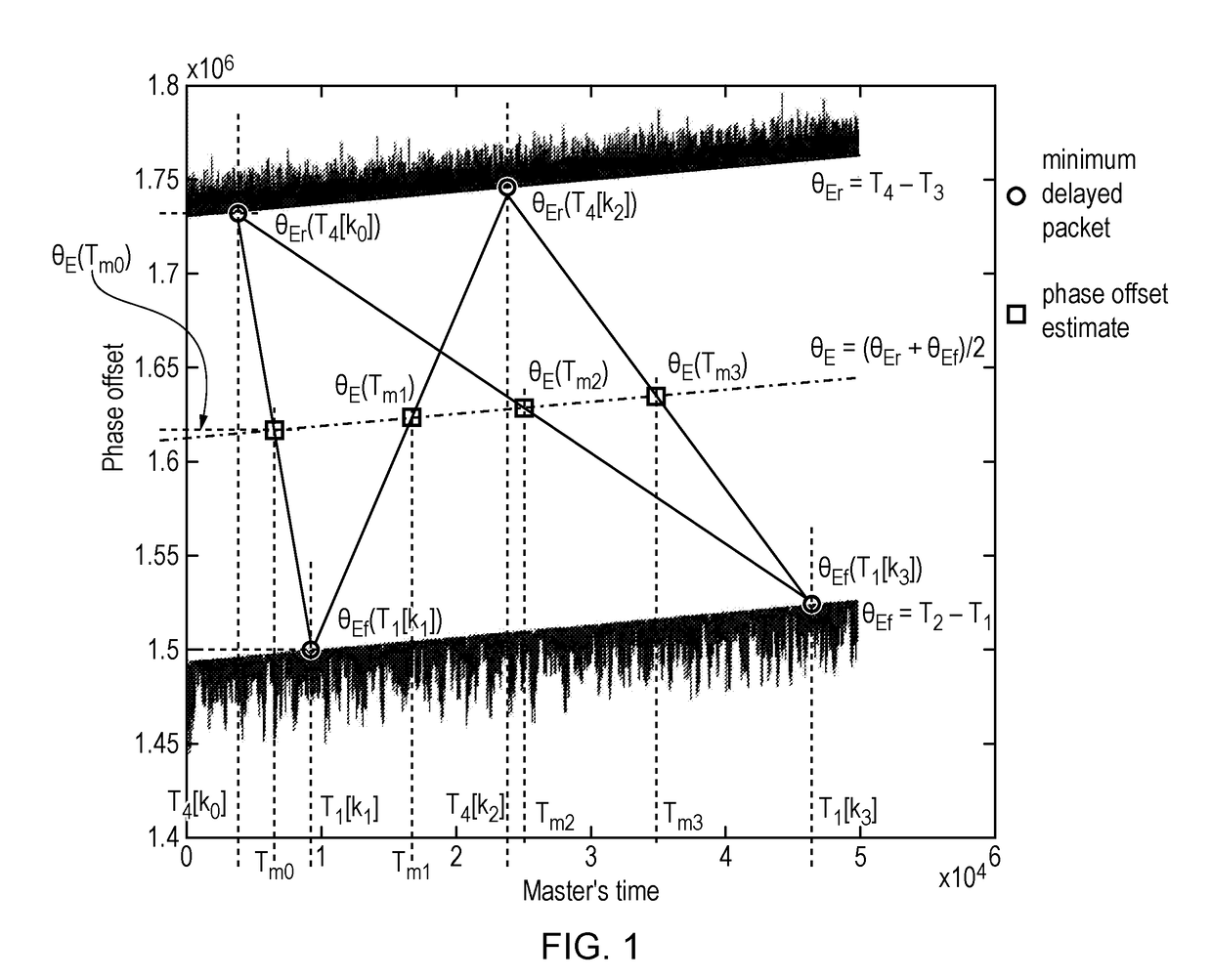
This invention relates to timing message selection techniques that can be used in conjunction with a clock recovery mechanism to mitigate the effects of packet delay variation on timing messages exchanged over a packet network, particularly when seeking to synchronize the time of a clock in a slave device to that of a master clock. The selection techniques allow the identification of optimal or minimally-delayed timing messages which can subsequently be used in timing synchronisation. Embodiments of the invention provide techniques which identify optimal timing messages in both forward and reverse directions which are then processed to form composite timing messages which are used in a frequency estimation algorithm. Timing messages selected by the methods of the invention are particularly useful in phase synchronization between the master and slave clocks.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH & RES KUSTAR +2
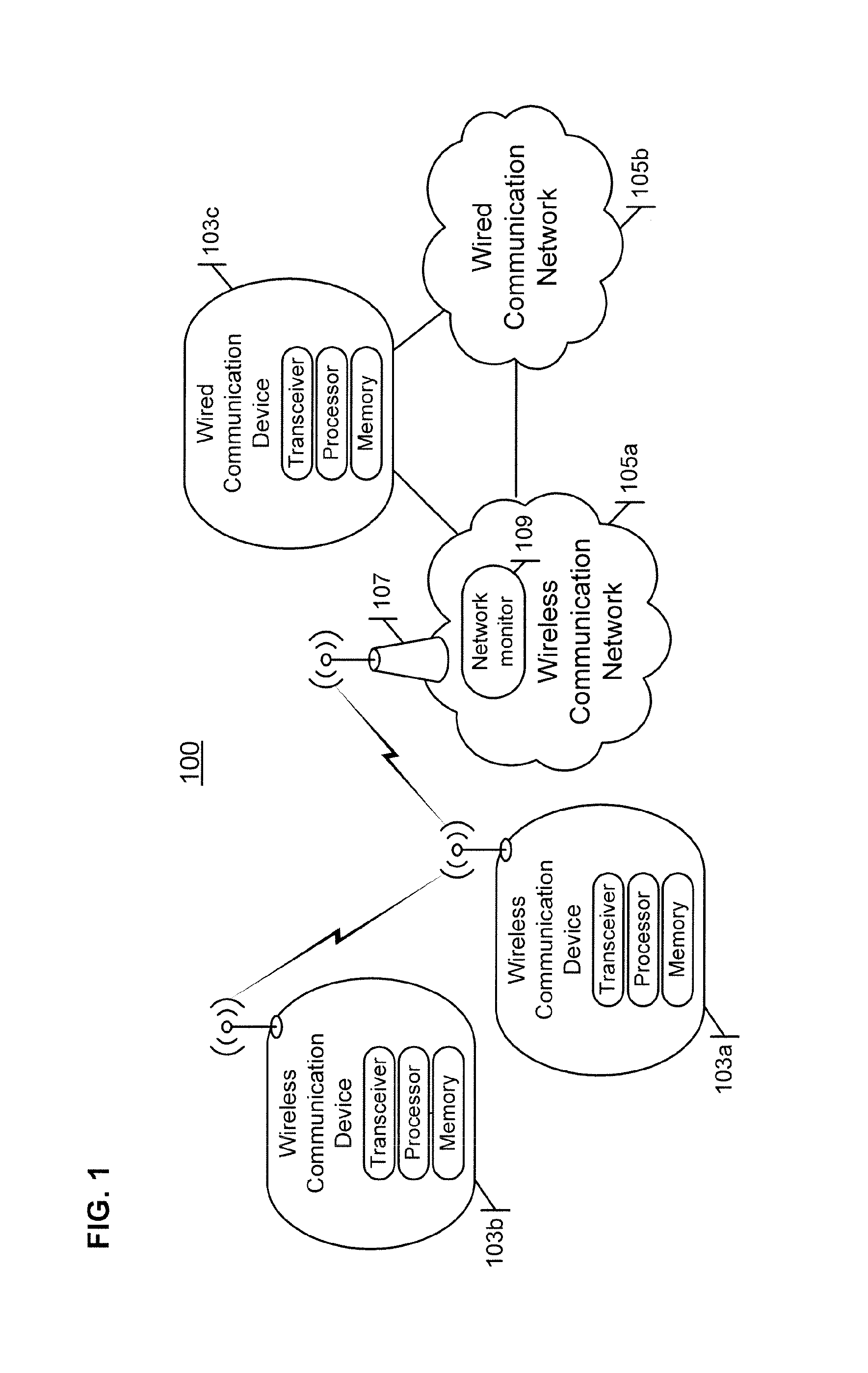
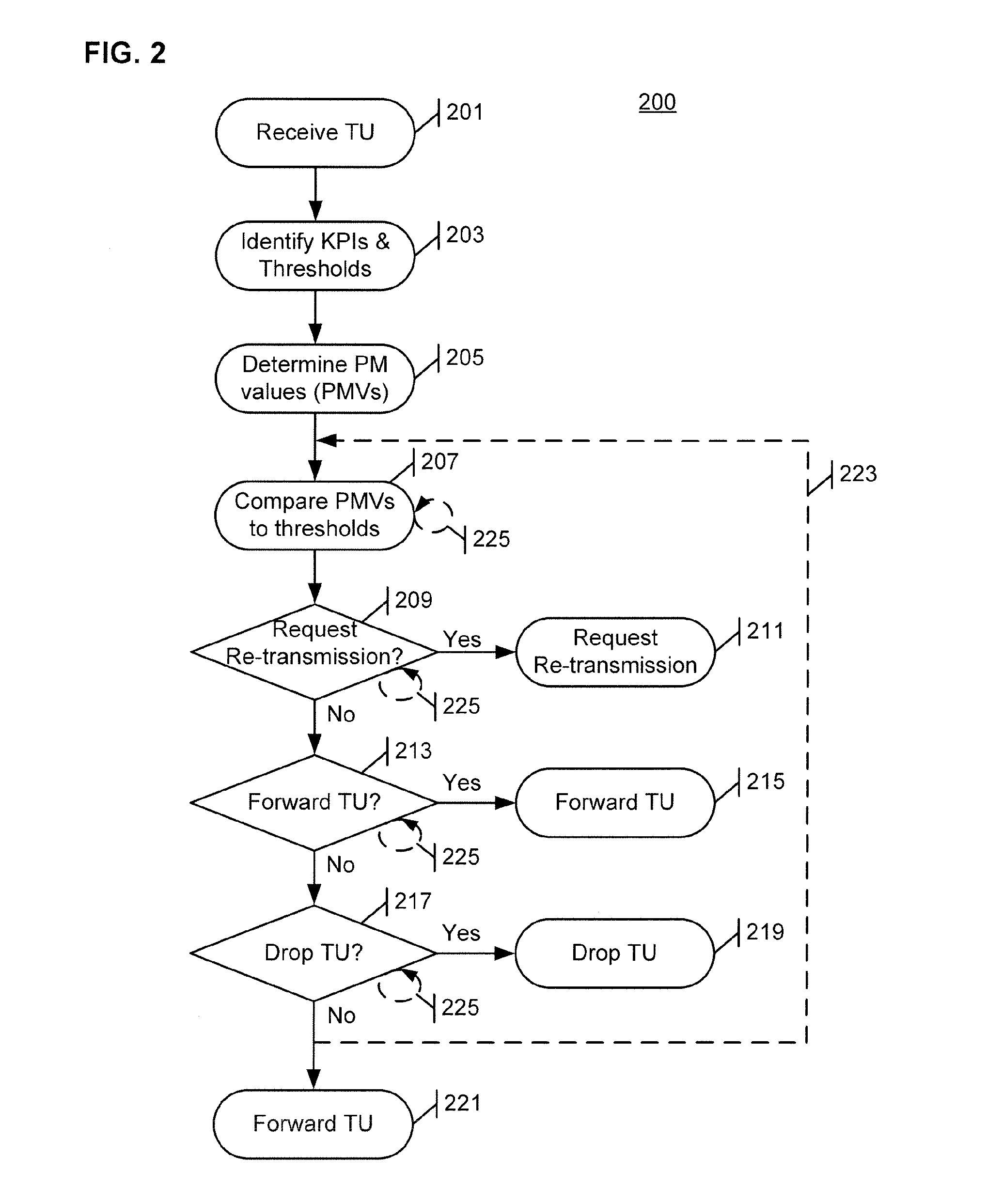
System and method for improving information carrying capacity by controlling re-transmissions
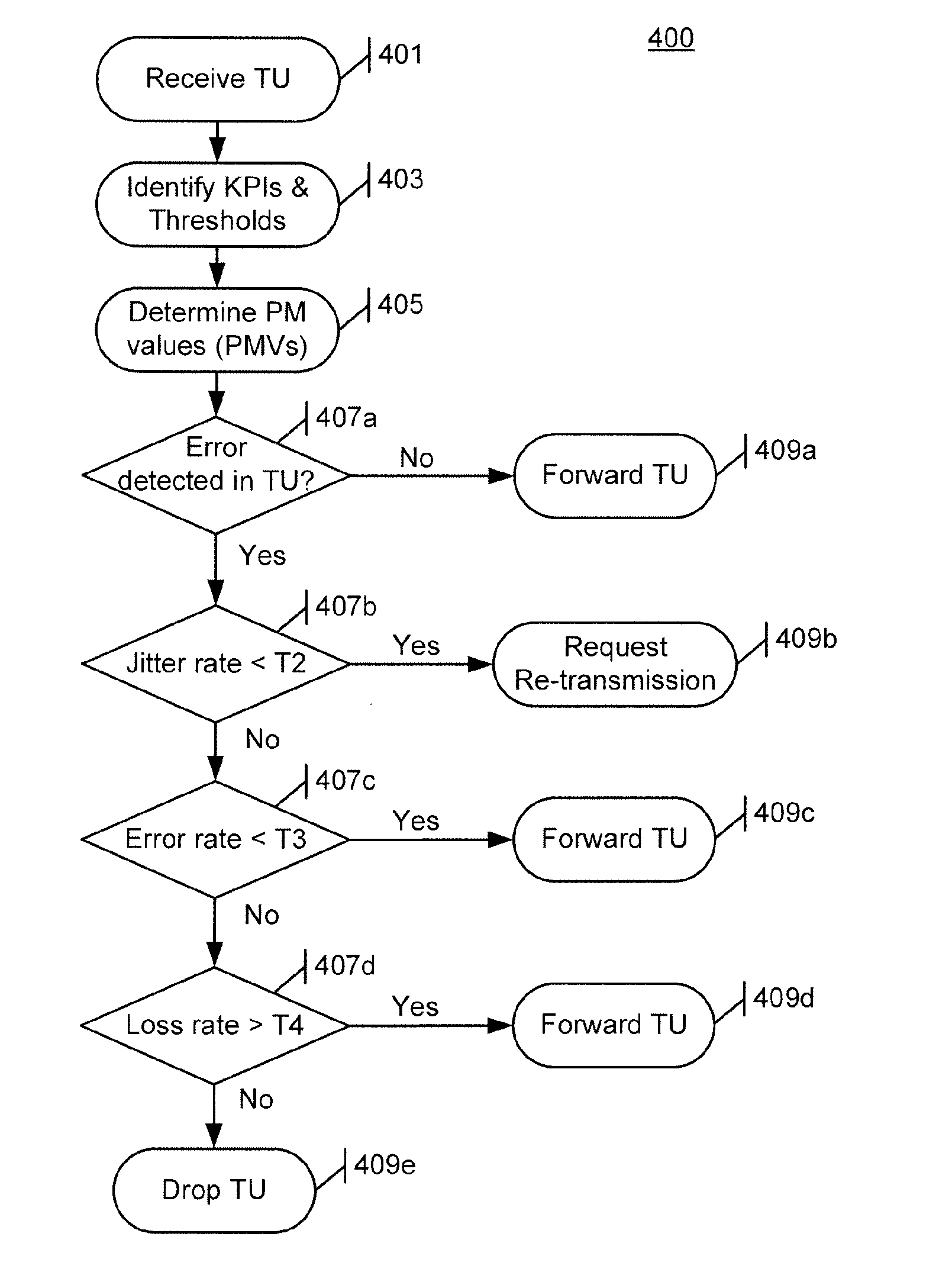
ActiveUS20140119212A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsQuality of serviceCarrying capacity
The re-transmission of transmission units (TUs) received in a communication device over a communication link is controlled to improve the information carrying capacity of the link. A received TU has an associated service characteristic indicative of a quality of service (QOS) for the TU. The service characteristic is associated with a select set of key performance indicators (KPIs), such as measures of packet error, packet delay, packet delay variation, and / or packet loss experienced by TUs on the communication link. Upon receipt of a TU, the performance of the communication link is evaluated with respect to each KPI in the select set to obtain a corresponding measurement value, and the measurement values are compared to corresponding threshold values. Upon determining that a determined performance value does not satisfy a corresponding threshold value for a KPI in the select set, re-transmission of the TU is requested.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC +1
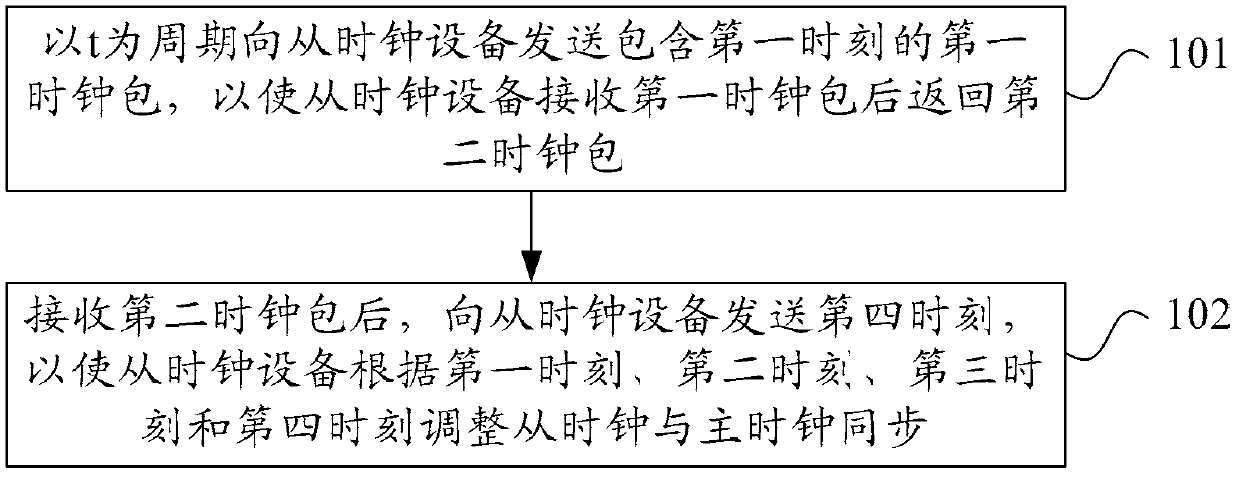
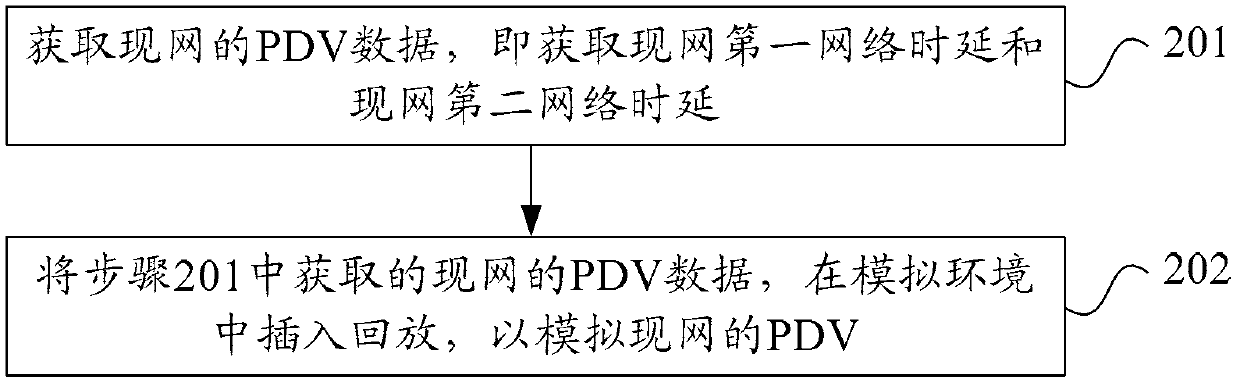
Method and apparatus for simulating packet delay variation in current network
ActiveCN102171966ARealize feasibility verificationSynchronising arrangementSlave clockReal-time computing
Embodiments of the invention provide a method and an apparatus for simulating Packet Delay Variation (PDV) in a current network. The method includes: a first clock packet including a first time is transmitted, with the period of t, to a slave clock device, so that the slave clock device returns a second clock packet after receiving the first clock packet, wherein the first time is a difference value between the time for transmitting the first clock packet and a first network delay in the current network, the time when the slave clock device receives the first clock packet is a second time, and the time when the slave clock device transmits the second clock packet is a third time; after the second clock packet is received, a fourth time is transmitted to the slave clock device, so that theslave clock device adjusts, according to the first time, the second time, the third time and the fourth time, the slave clock to synchronize with a master clock, wherein the fourth time is a sum of the time when the second clock packet is received and a second network delay in the current network. The embodiments of the invention achieve simulating the PDV procedure in the current network, can perform a PDV test for the current network in a simulation environment, and achieve the feasibility validation for clock algorithms in the current network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
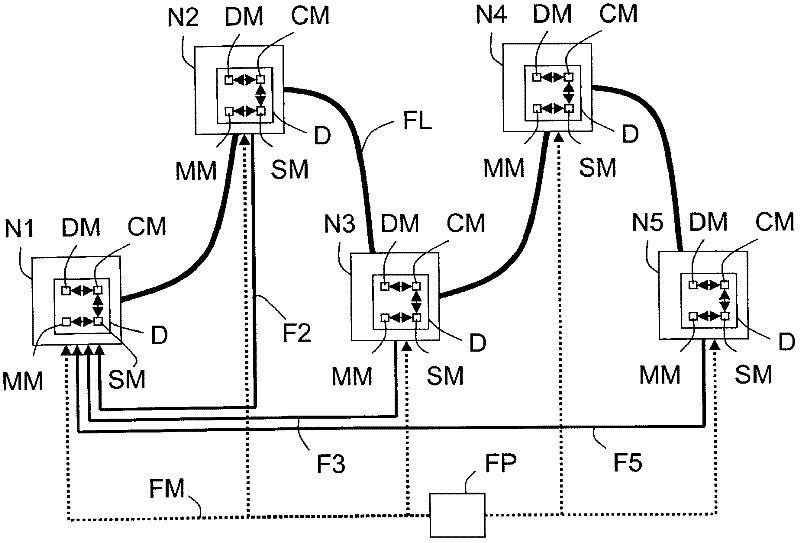
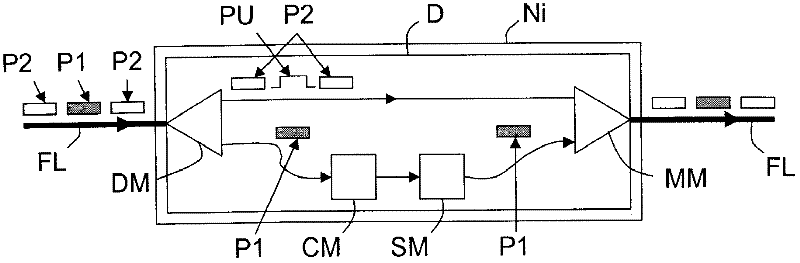
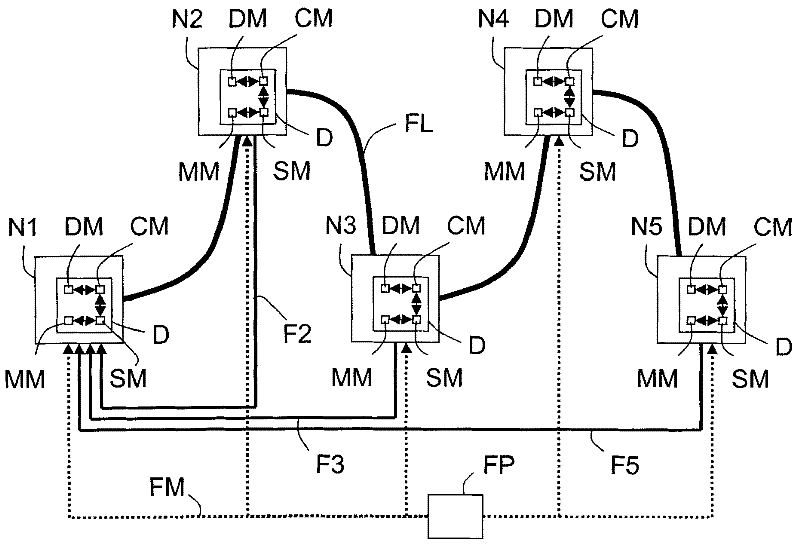
Method for processing distributed data having a chosen type for synchronizing communication nodes of a data packet network, and associated device
InactiveCN102349251ATime-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTime informationComputer science
A method is intended for processing distributed data of a chosen type in a data packet network comprising communication nodes (N1-N5). This method comprises the steps of: - receiving a plurality of packets, comprising data of the chosen type and sent at regular time intervals by a source communication node (N1), - assessing a packet delay variation of each of these received packets, - selecting a subset of these received packets according to their respective assessed packet delay variations, and - synchronizing a destination communication node (N5) of the data packet network by means of timing information derived from the selected subset.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and devices for synchronization
This invention relates to methods and devices for time and frequency synchronization. The invention has particular application where time and frequency synchronization over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is being carried out. The primary challenge in clock distribution over packet networks is the variable transit delays experienced by timing packets, packet delay variations (PDVs). Embodiments of the invention provide a method for time offset alignment with PDV compensation where a synchronized frequency signal is available at a slave device via Synchronous Ethernet and is used to determine the compensation parameters for the PDV.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
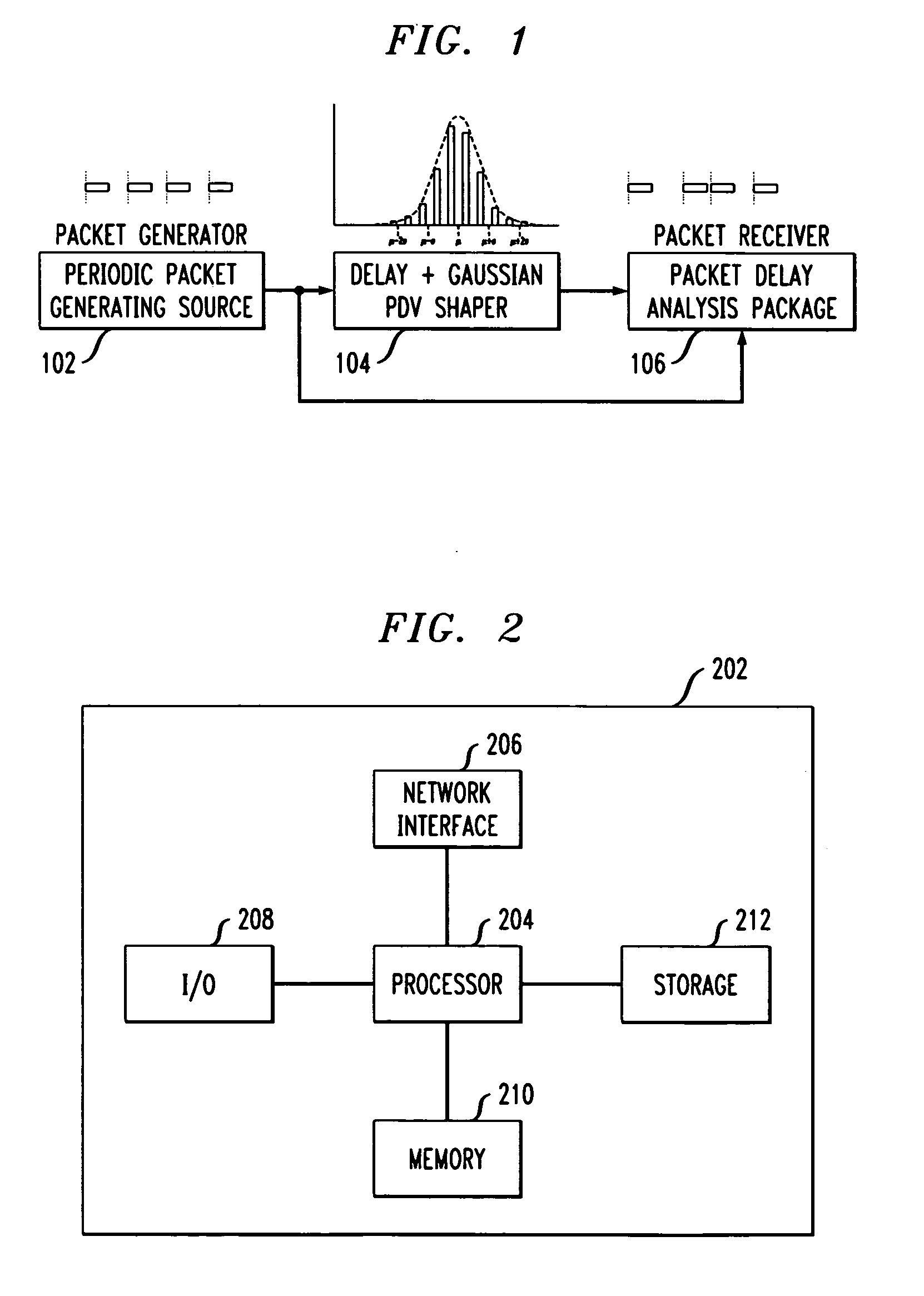
Derivative packet delay variation as a metric for packet timing recovery stress testing
A method and system for analyzing simulated packet delay variation (PDV) using derivative PDV is disclosed. The delay-step method for simulating PDV determines a delay for each packet in a stream of packets generated at a regular interval. Delay target values are randomly selected based on a statistical distribution, such as a Gaussian distribution. Delay-steps are determined for each packet based on the delay target values. The delay-steps can be fixed or variable sized steps which are used to adjust the delay of sequential packets. PDV is generated by delaying each of the packets with the delay determined for that packet. The derivative PDV is calculated to evaluate a delay rate of change on a packet-by-packet basis. The derivative PDV can be used as a metric to specify stresses for adaptive packet timing recovery stress testing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com