Hot processing technique for restraining martensite phase transformation during austenitic stainless steel deformation
A technology of austenitic stainless steel and martensitic transformation, applied in the field of metal heat treatment, it can solve the problems of increased cracking tendency, decreased toughness, instability, etc., to reduce the degree of work hardening, reduce the cracking tendency, and reduce the driving force. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
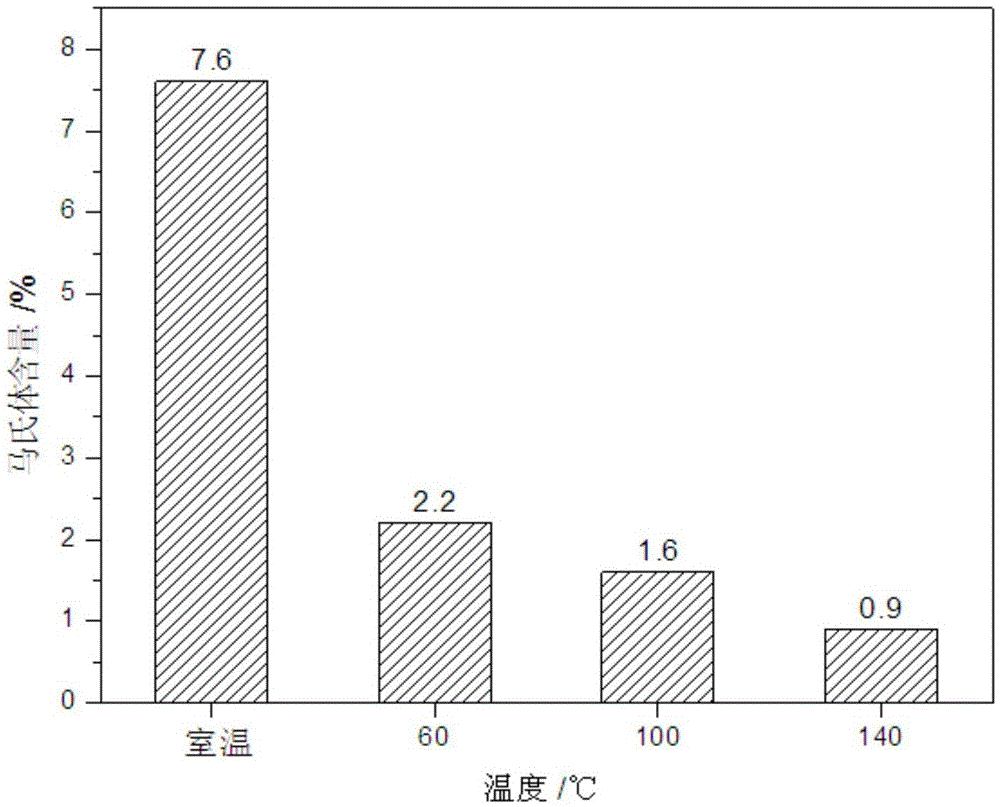
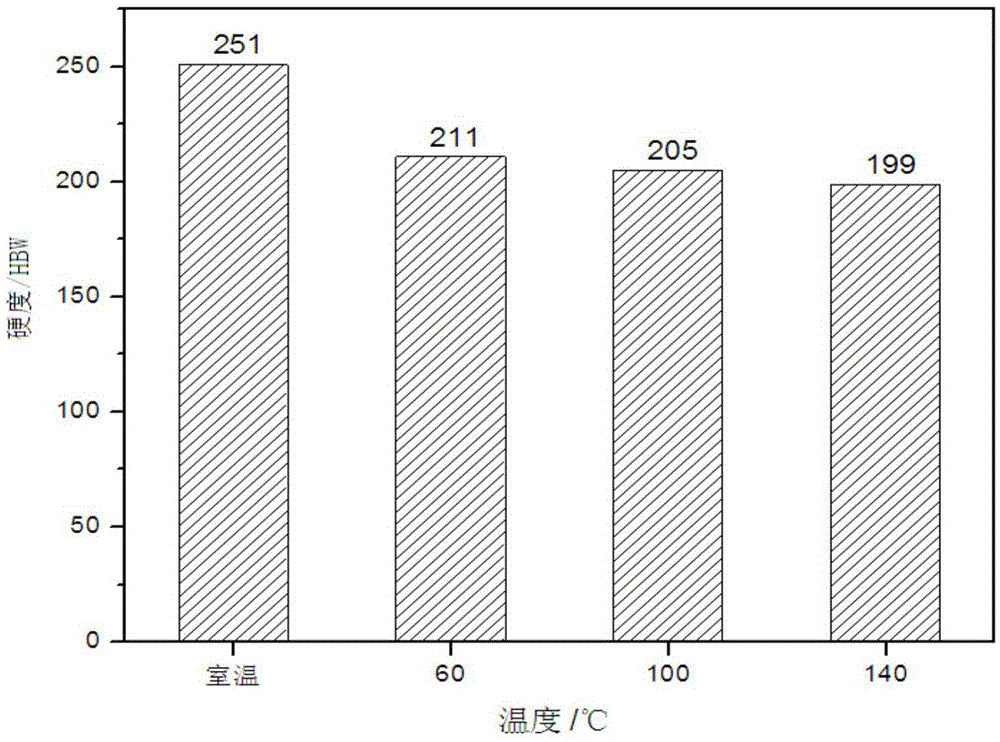
[0018] (1) Cut the stainless steel plate into a sample of 25×200mm.
[0019] (2) Mark the original gauge length on the sample, and the original gauge length is 150mm.
[0020] (3) Put the sample into the heating furnace, turn on the power, start timing when the furnace temperature reaches 140°C, and keep warm for 10 minutes.
[0021] (4) Immediately after the heat preservation is over, the sample is stretched on a stretching machine until the original gauge length is stretched to 163.5mm (9% stretch).
[0022] (5) After the sample is cooled, grind the surface of the sample with 240#~1200# SiC sandpaper successively.
[0023] (6) Carry out martensite content measurement and hardness test.
Embodiment 2
[0025] (1) Cut the stainless steel plate into a sample of 25×200mm.
[0026] (2) Mark the original gauge length on the sample, and the original gauge length is 150mm.
[0027] (3) Put the sample into the heating furnace, turn on the power, start timing when the furnace temperature reaches 100°C, and keep warm for 10 minutes.
[0028] (4) Immediately after the heat preservation is over, the sample is stretched on a stretching machine until the original gauge length is stretched to 163.5mm (9% stretch).
[0029] (5) After the sample is cooled, grind the surface of the sample with 240#~1200# SiC sandpaper successively.
[0030] (6) Carry out martensite content measurement and hardness test.
Embodiment 3
[0032] (1) Cut the stainless steel plate into a sample of 25×200mm.
[0033] (2) Mark the original gauge length on the sample, and the original gauge length is 150mm.
[0034] (3) Put the sample into the heating furnace, turn on the power, start timing when the furnace temperature reaches 60°C, and keep warm for 10 minutes.
[0035] (4) Immediately after the heat preservation is over, the sample is stretched on a stretching machine until the original gauge length is stretched to 163.5mm (9% stretch).
[0036] (5) After the sample is cooled, grind the surface of the sample with 240#~1200# SiC sandpaper successively.
[0037] (6) Carry out martensite content measurement and hardness test.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com