Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Reduce braking force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
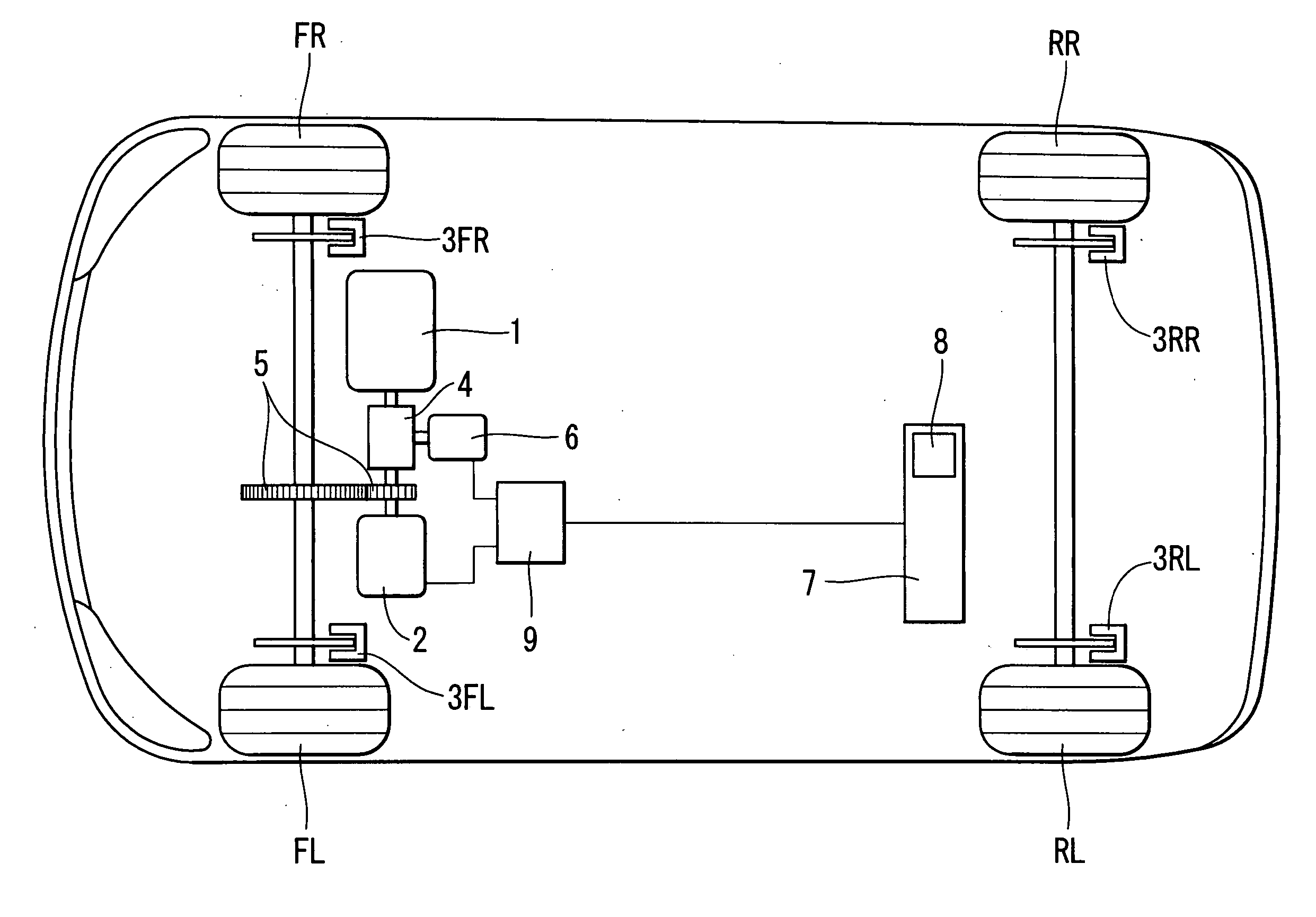
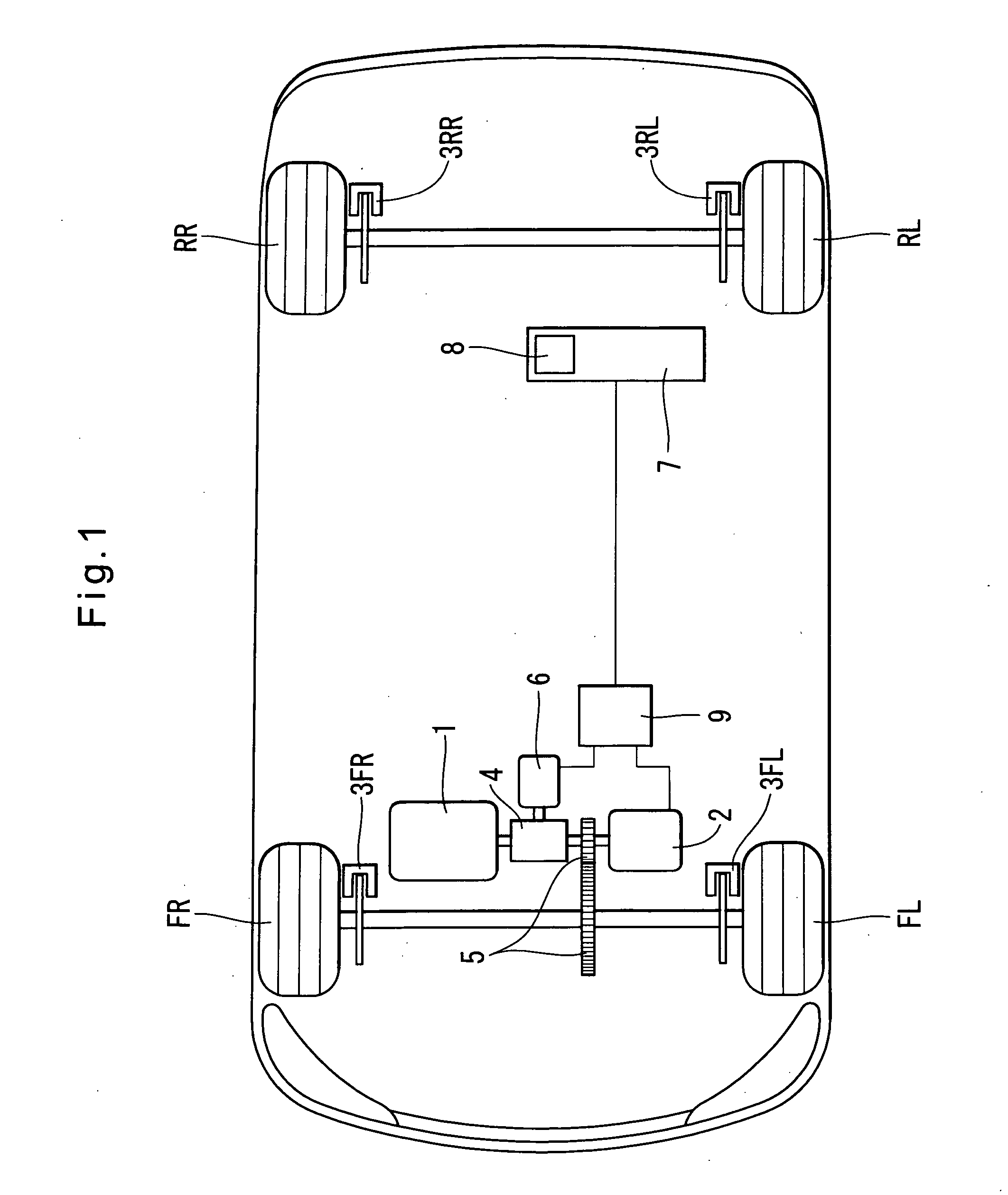
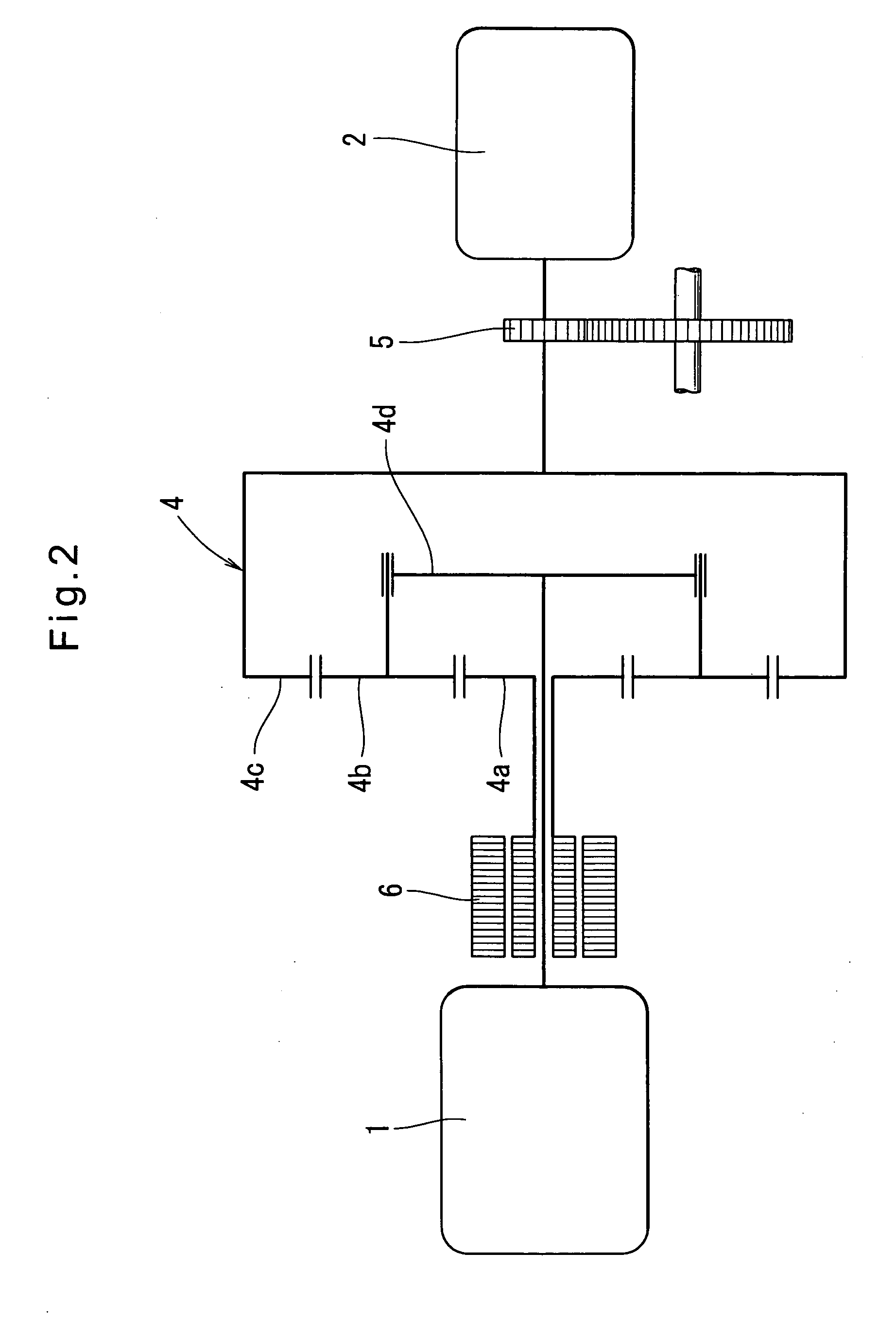
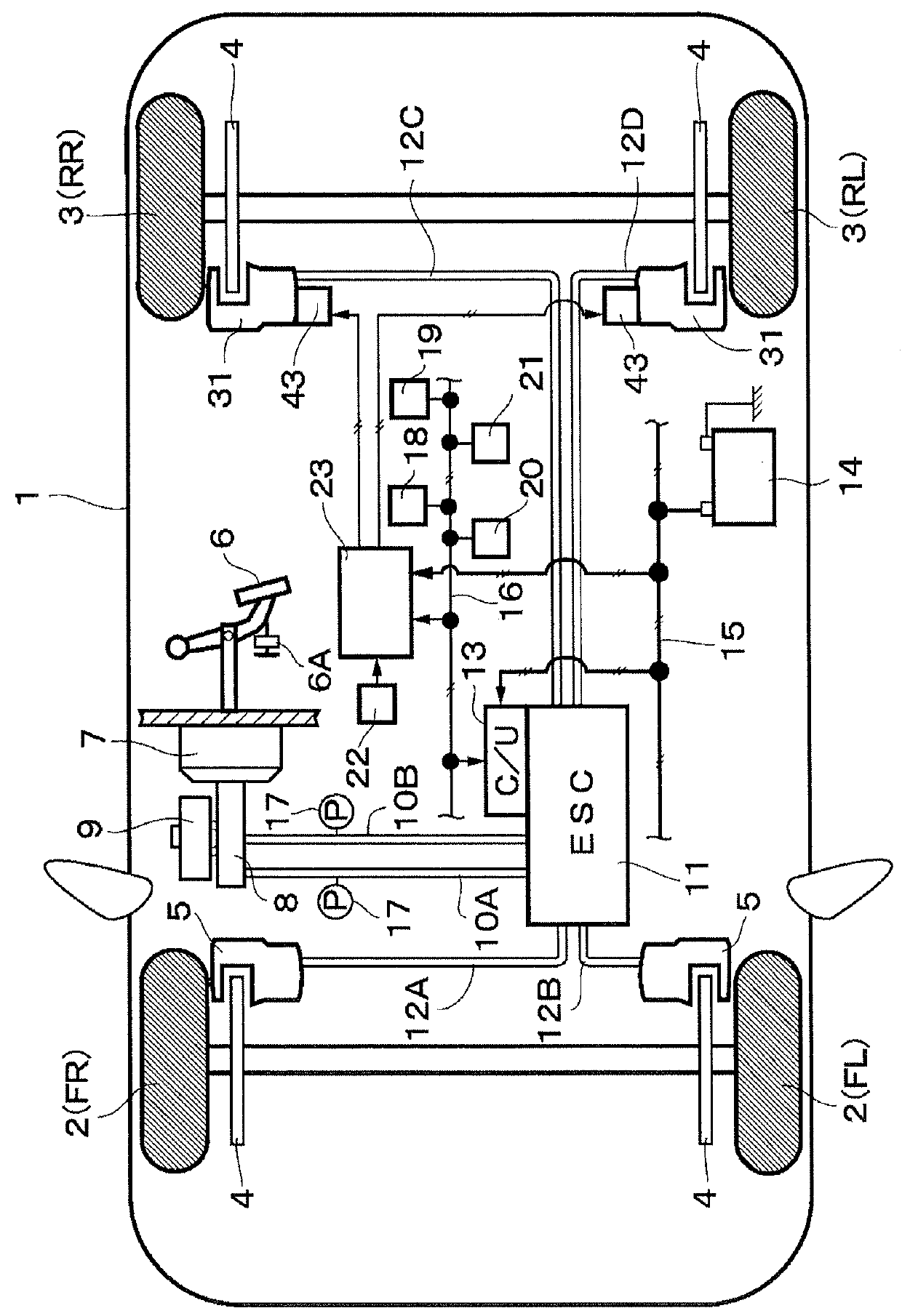
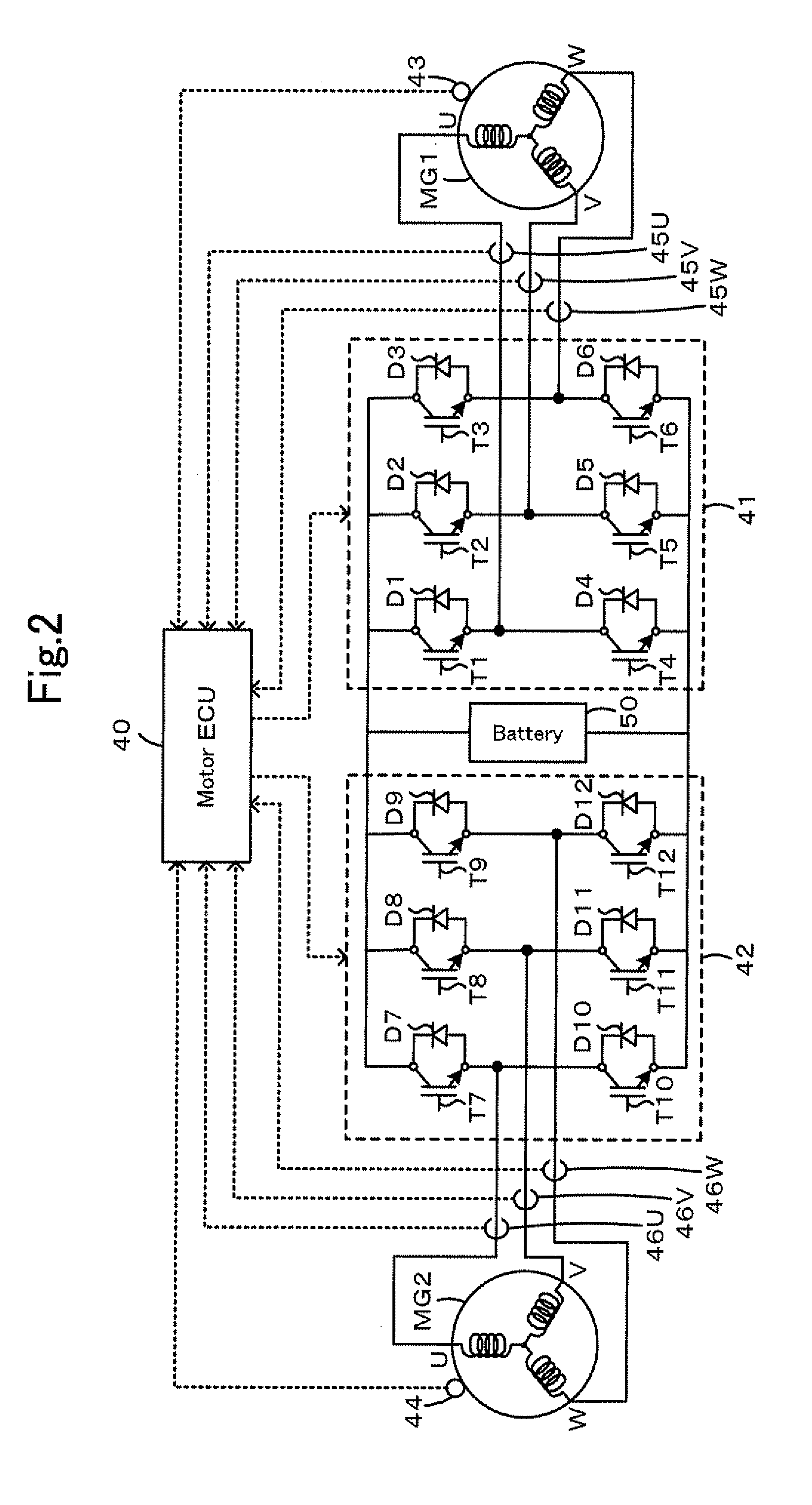
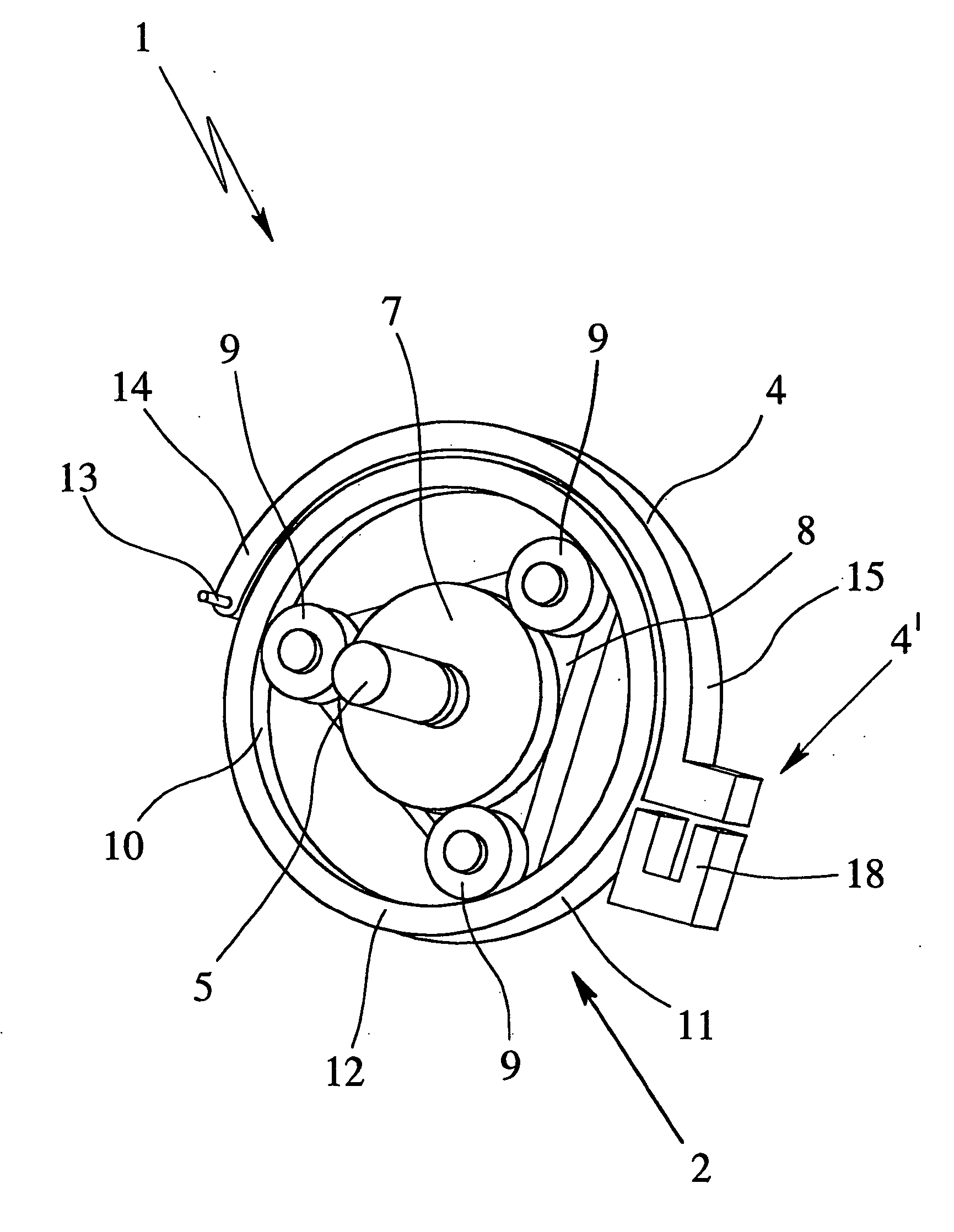
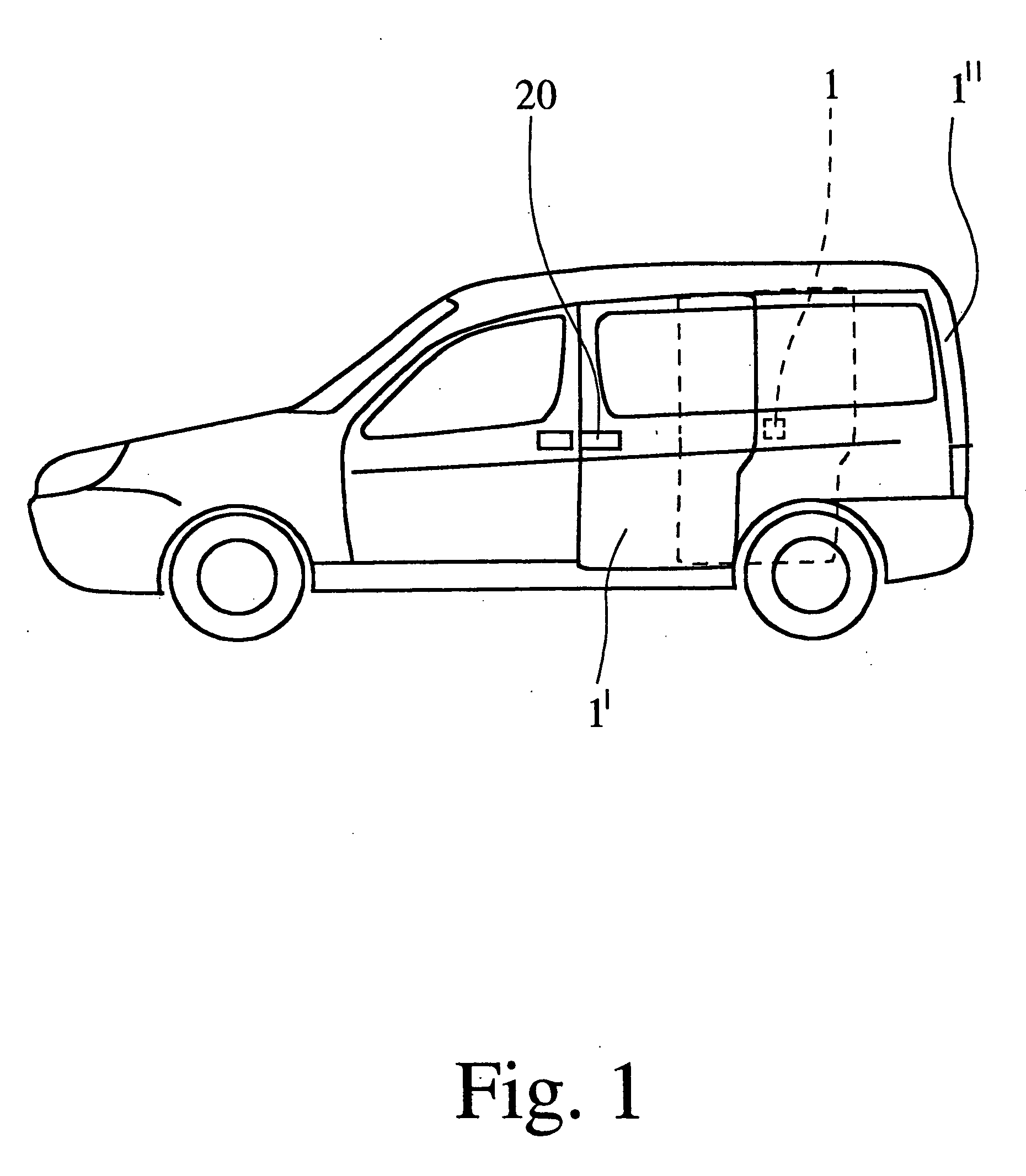
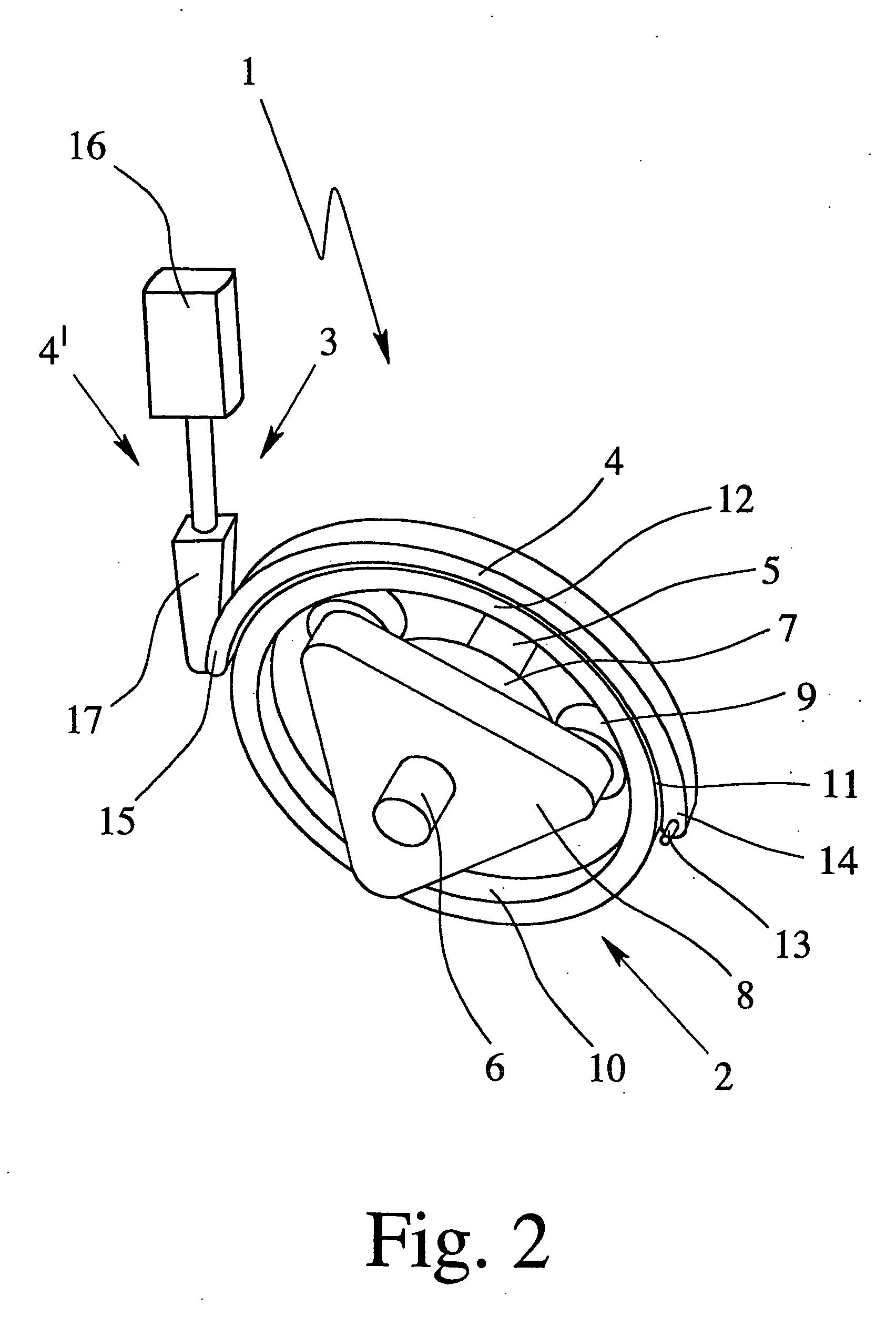
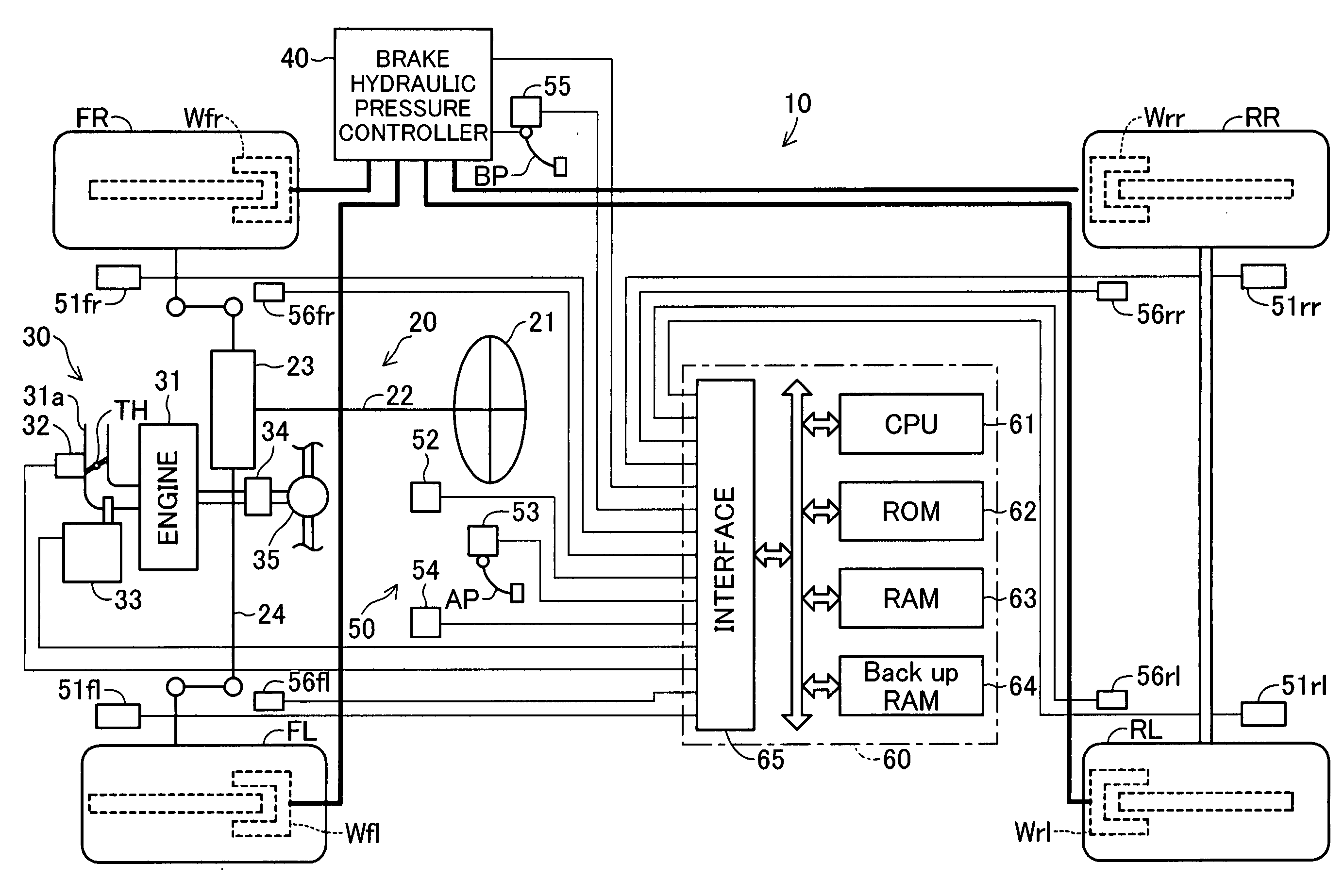
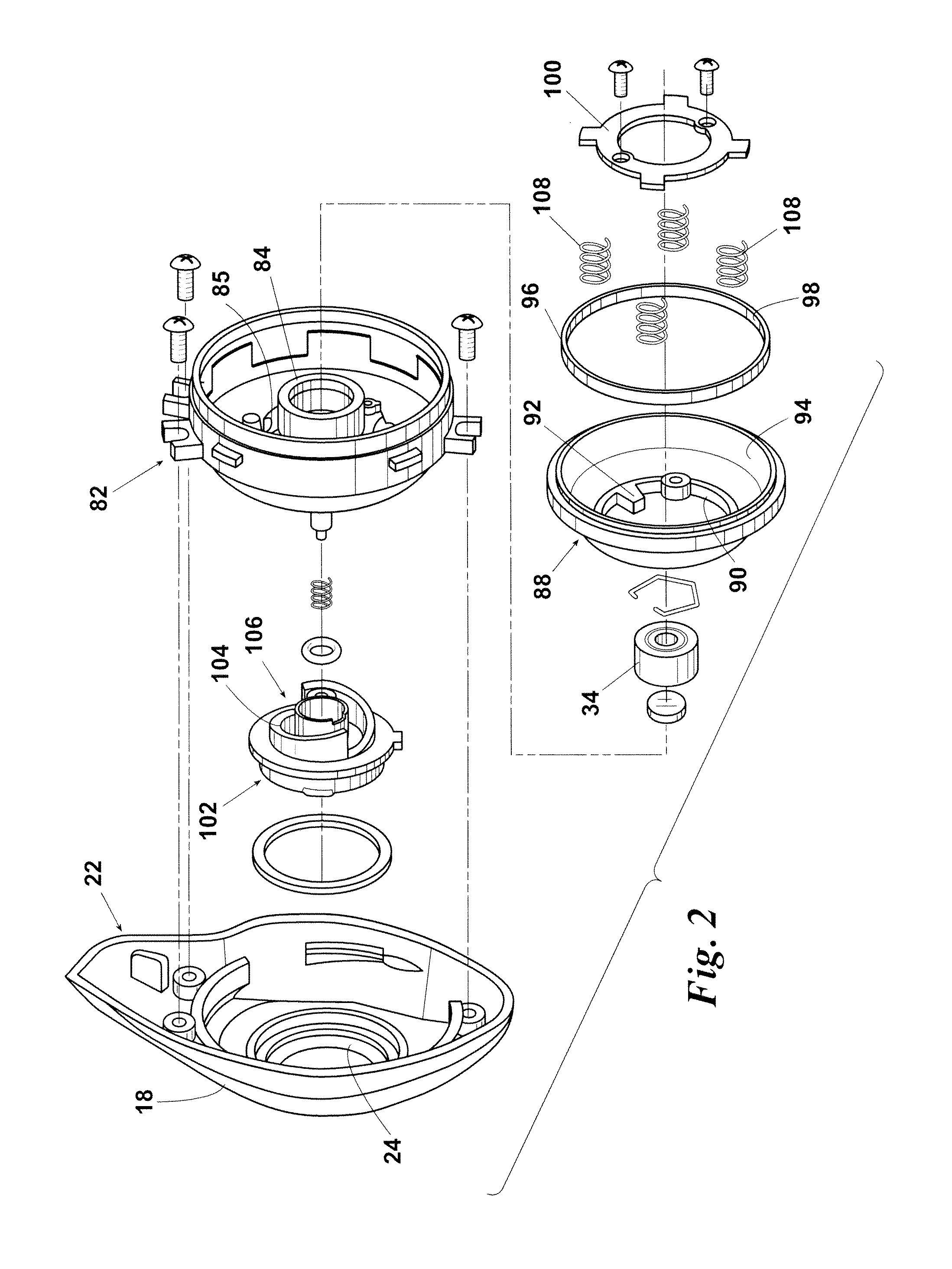
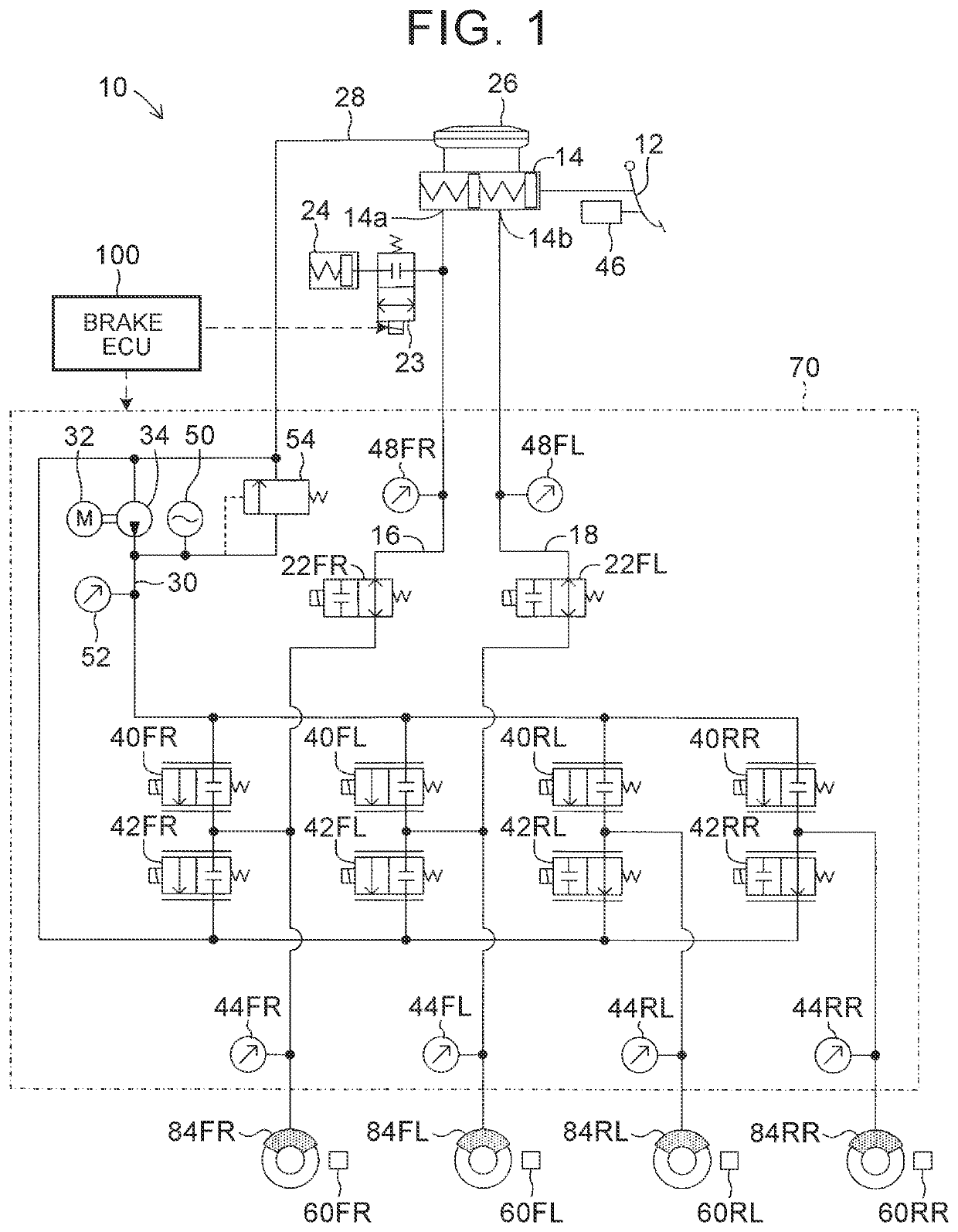
Vehicle brake system
InactiveUS20070046099A1Eliminate locking tendencyReduce braking forceHybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsRegenerative brakeBraking system
An improved vehicle brake system for controlling the frictional braking force and the regenerative braking force to be applied to a wheel of a vehicle. The brake system reduces the regenerative braking force to a predetermined force and keeps the regenerative braking force at the predetermined force before the start of anti-lock control. When the anti-lock control starts, the brake system decreases the regenerative braking force from the predetermined force. With this arrangement, it is possible to quickly eliminate a locking tendency of any wheel of the vehicle, thereby stabilizing the vehicle.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Brake apparatus
ActiveUS20160032995A1Less discomfortSmooth brake release operationBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesPower flowCalipers
A brake apparatus comprising: a caliper having a piston configured to move a brake pad to be pressed on a disc rotor rotating with a wheel; a thrust retaining mechanism located in the caliper to thrust the piston and maintain braking force exerted by the thrust piston; an electric motor mounted on the caliper to operate the thrust retaining mechanism; and a controller configured to apply electric current to the electric motor in response to an application command or a release command, thereby perform control according to the commands, wherein the controller, upon receiving a release command, configured to operate the electric motor to reduce braking force exerted by the piston by performing current maintenance control which continuously applies electric current to the electric motor and switching control which successively switches between a larger and a smaller amount of electric current applied to the electric motor.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Vehicle, control method of vehicle, and driving apparatus
InactiveUS20100152940A1Reduce braking forceEasily obtainedDigital data processing detailsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingThree-phaseSteering angle
Upon the occurrence of the abnormality that the inverter for driving the motor is in the one-phase short circuited state, this inverter is stopped in the three-phase short circuited state and sets the execution torque by subtracting the counter electromotive force application torque that is applied the driveshaft due to the counter electromotive force generated by rotation of the motor and the steering angle application torque corresponding to the steering angle from the torque demand according to the step-on amount of the accelerator pedal. The engine and the inverter for driving the motor is controlled so that the vehicle is driven with the set execution torque. This enables the driving force output to the driveshaft from the engine and the motor to be in accordance with the torque demand.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
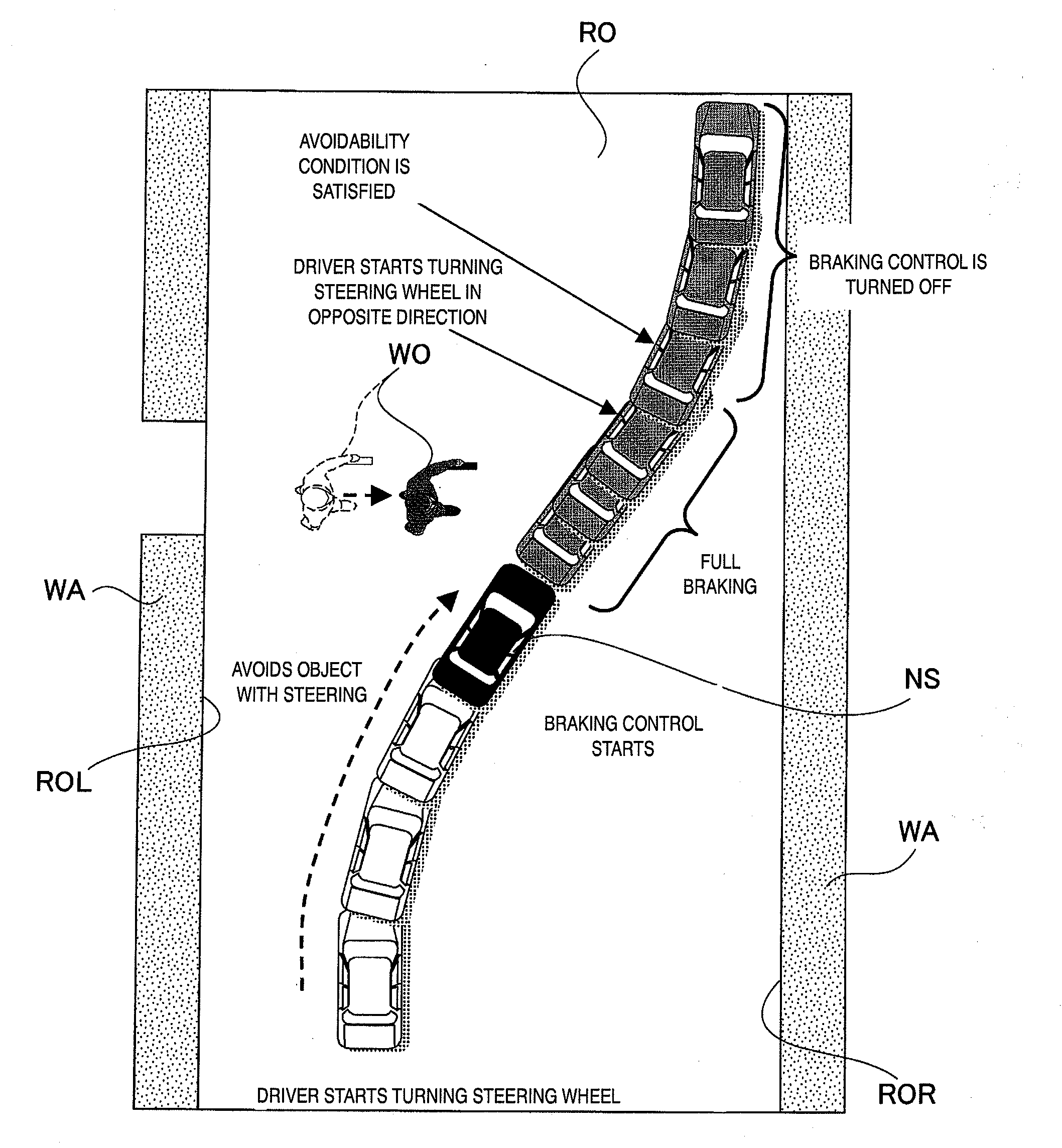
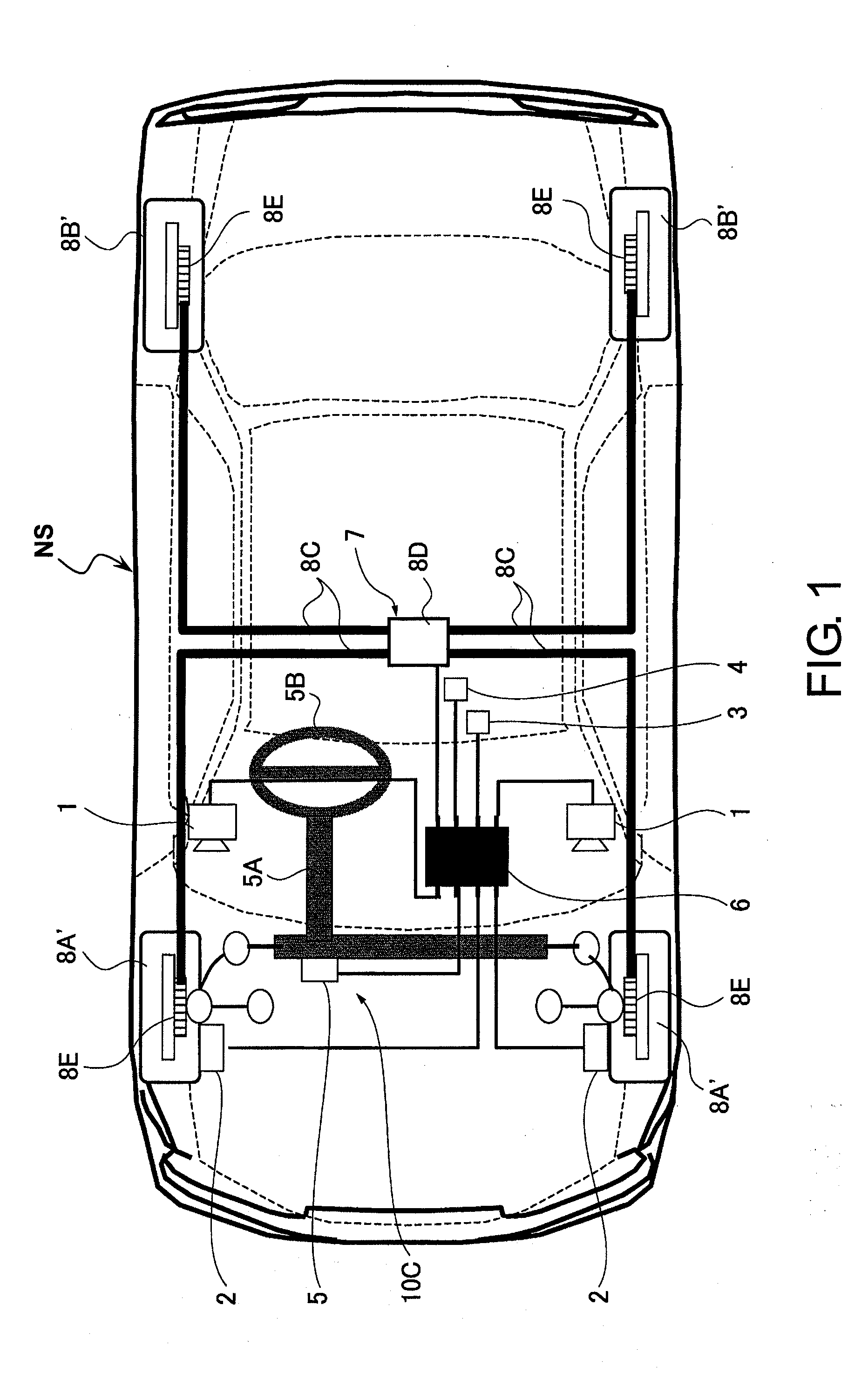
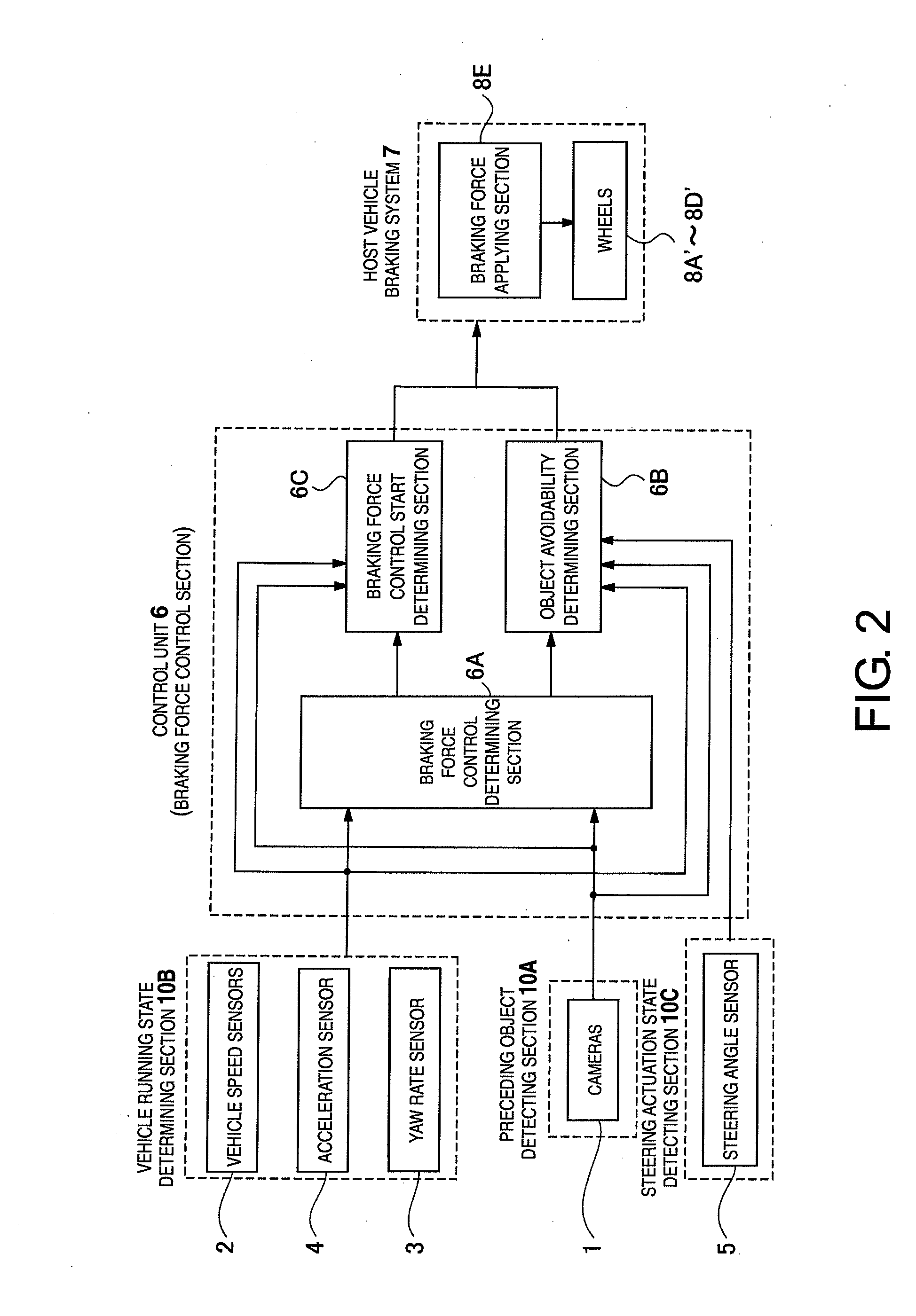
Vehicle brake control system and method
InactiveUS20070294019A1Improve accuracyReduce braking forceAnalogue computers for trafficPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSteering wheelControl system
A vehicle brake control system is provided with a preceding object detecting section, a running condition detection section, a steering actuation state detecting section, a braking force detecting section, a preceding object avoidability determining section and a braking force control section. The preceding object avoidability determining section determines a possibility of avoiding the preceding object by steering and reducing the current braking force acting on the host vehicle based on the position of the preceding object, the running condition of the host vehicle, the braking force applied to the host vehicle and the steering wheel actuation state that are detected. The braking force control section reduces the current braking force applied by the host vehicle braking system when the preceding object avoidability determining section determines that the preceding object can be avoided by steering and reducing the current braking force acting on the host vehicle.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Drive arrangement for a motor vehicle door or hatch which can be moved by a motor
ActiveUS20050277512A1Reduce braking forceImprove securityConstruction fastening devicesToothed gearingsDrive shaftGear wheel
A drive arrangement for a motor vehicle door or hatch which can be moved by a motor with a planet gear and a brake device with a brake. The brake device has a brake drive which is separate from the drive which drives the drive shaft and the brake is able to be moved at least from one of two positions into the other of the two positions by the brake drive. The brake can be an arc-shaped clip pivotally supported by a pivot axle with an inner periphery which is matched to an outer periphery of an element of the planet gear. The brake can be combined with the brake drive as an eddy current brake or can be operated by a further gearing or use of a permanent magnet with which an electromagnet is able to interact.
Owner:BROSE SCHLIESSSYSTEME GMBH & CO KG
Motion control apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20070112498A1Increase in roll angle can be preventedReduce the overall heightHand manipulated computer devicesDigital data processing detailsRolloverEngineering
In rollover prevention control, an inner front wheel braking force is generated only in a front wheel located on the radially inner side of a turning locus in a relatively early stage where the absolute value of actual lateral acceleration is between a first value and a second value. When the absolute value becomes greater than the second value, in addition to the inner front wheel braking force, an inner rear wheel braking force is generated in a rear wheel located on the radially inner side of the turning locus. When the absolute value becomes greater than a third value, in addition to the inner rear wheel breaking wheel, an outer wheel braking force is generated in the front wheel located on the radially outer side of the turning locus. Thus, an increase in the roll angle is suppressed, and a desired turning locus tracing performance is maintained satisfactorily.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Vehicle control device
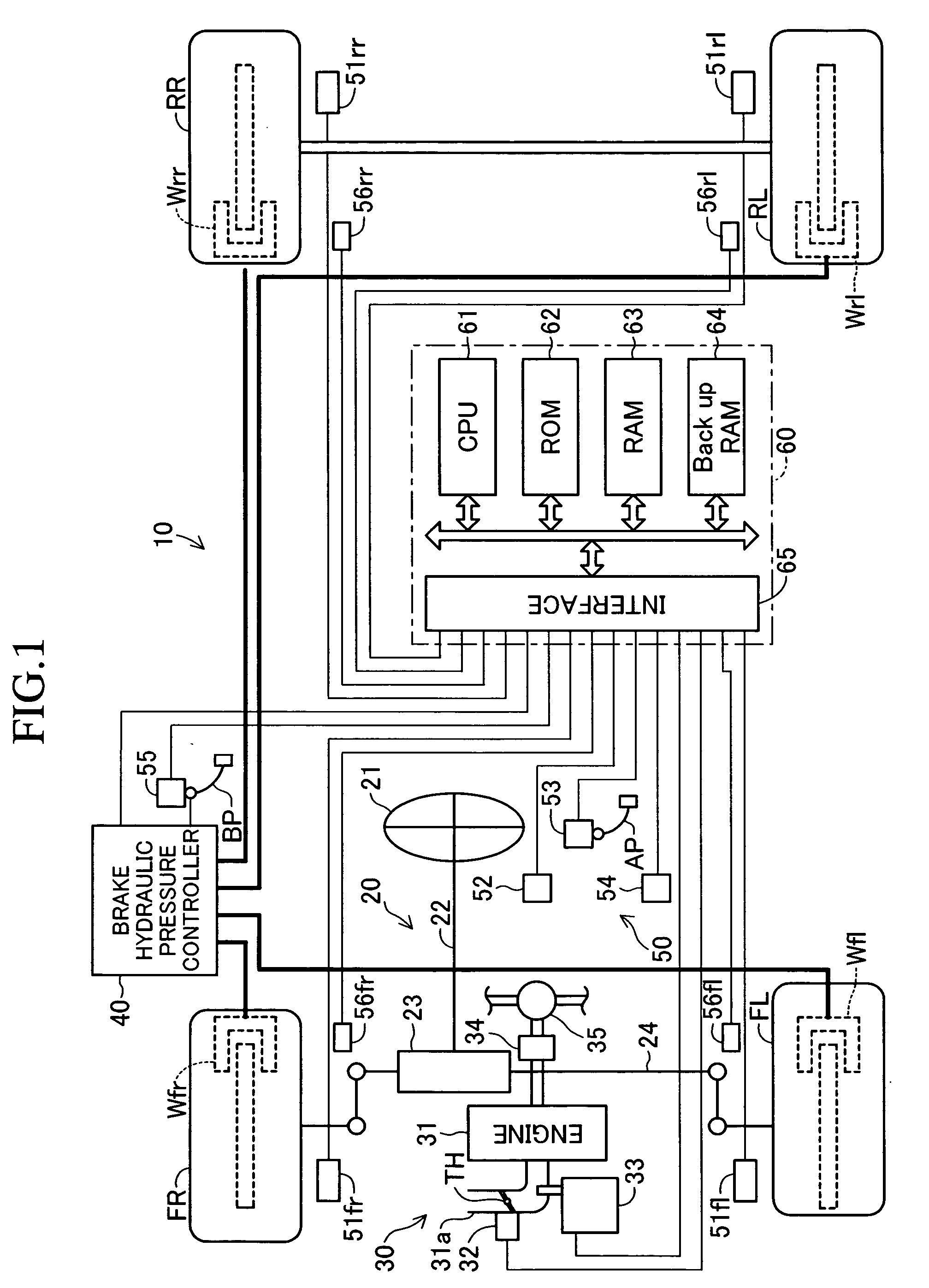
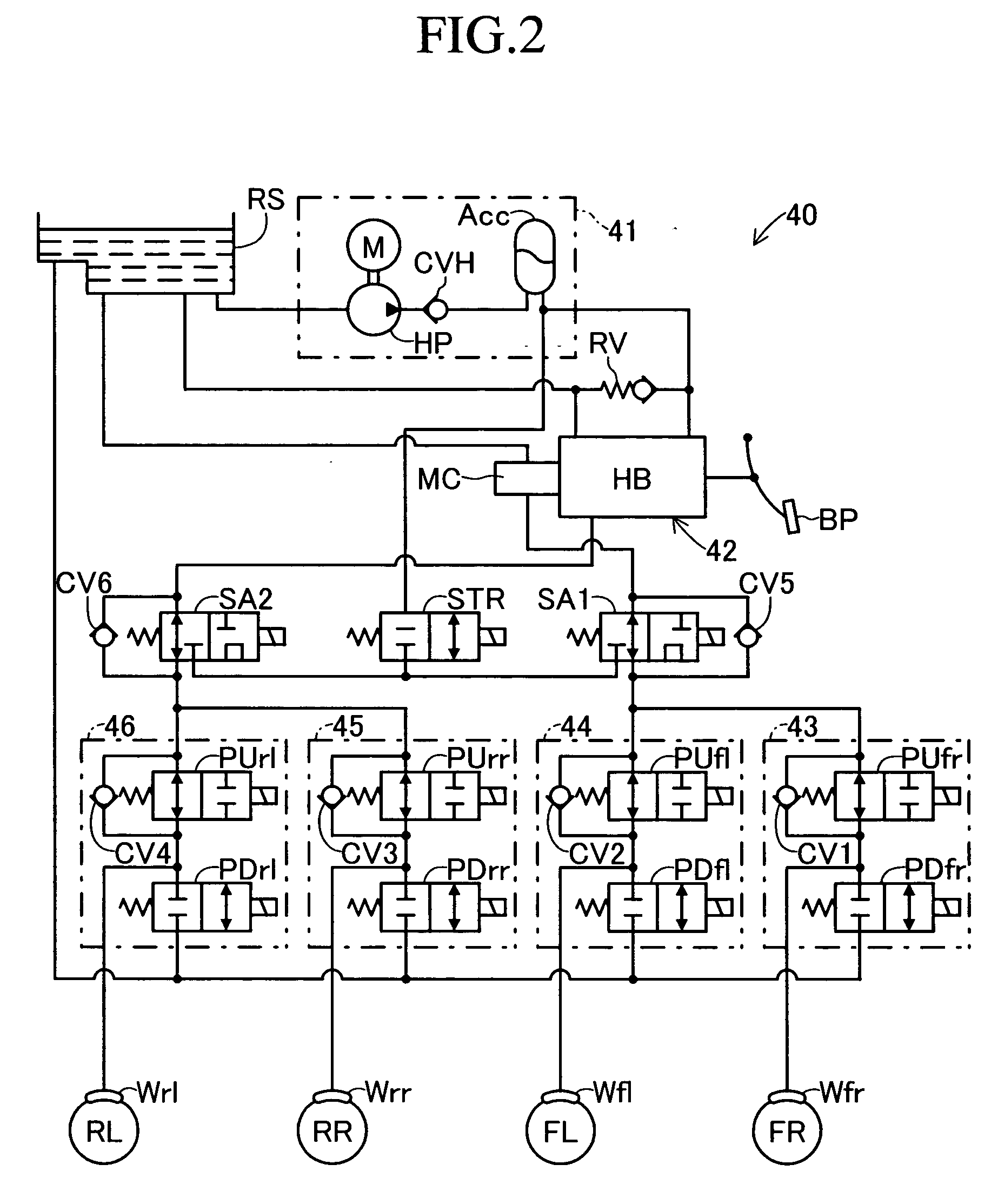
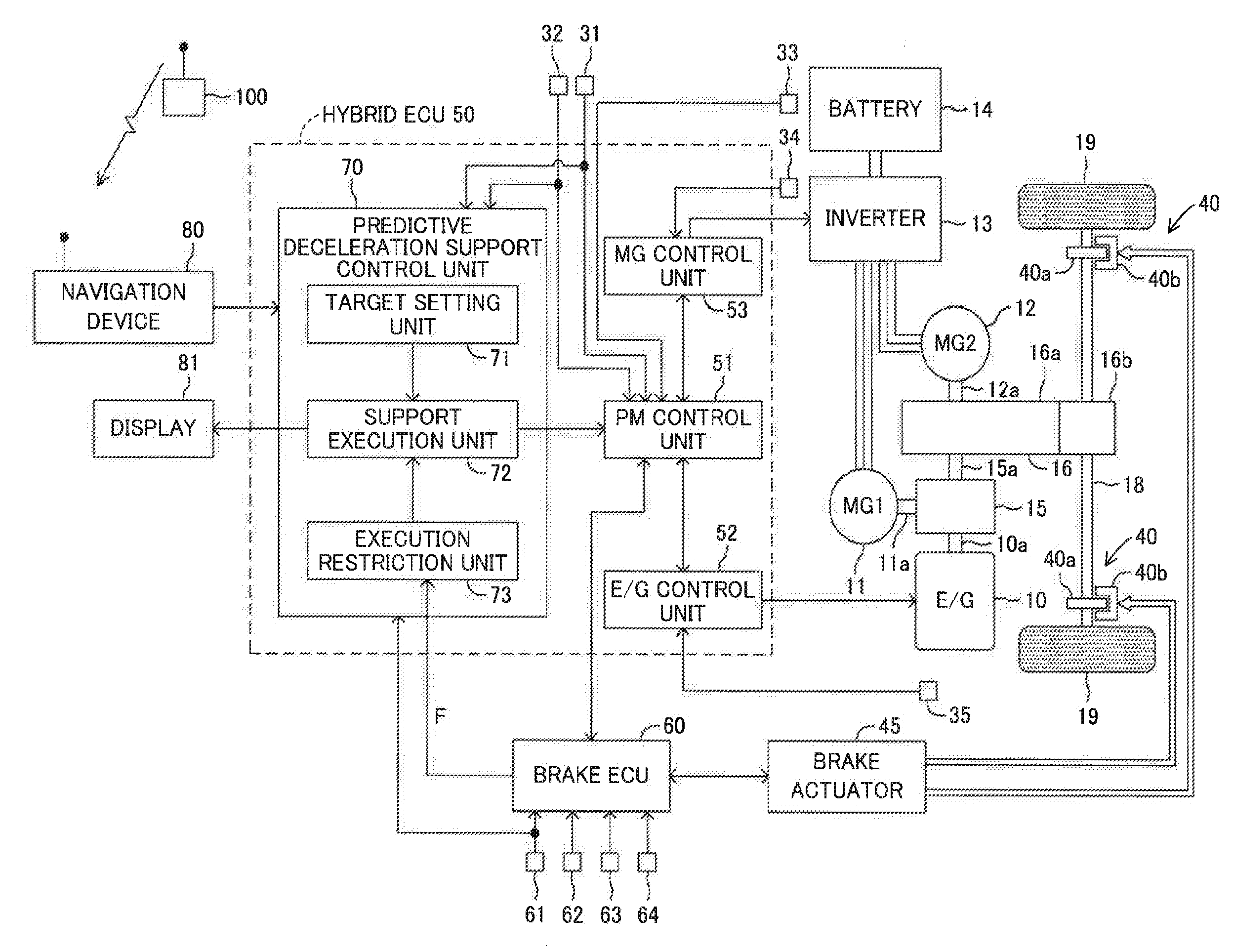
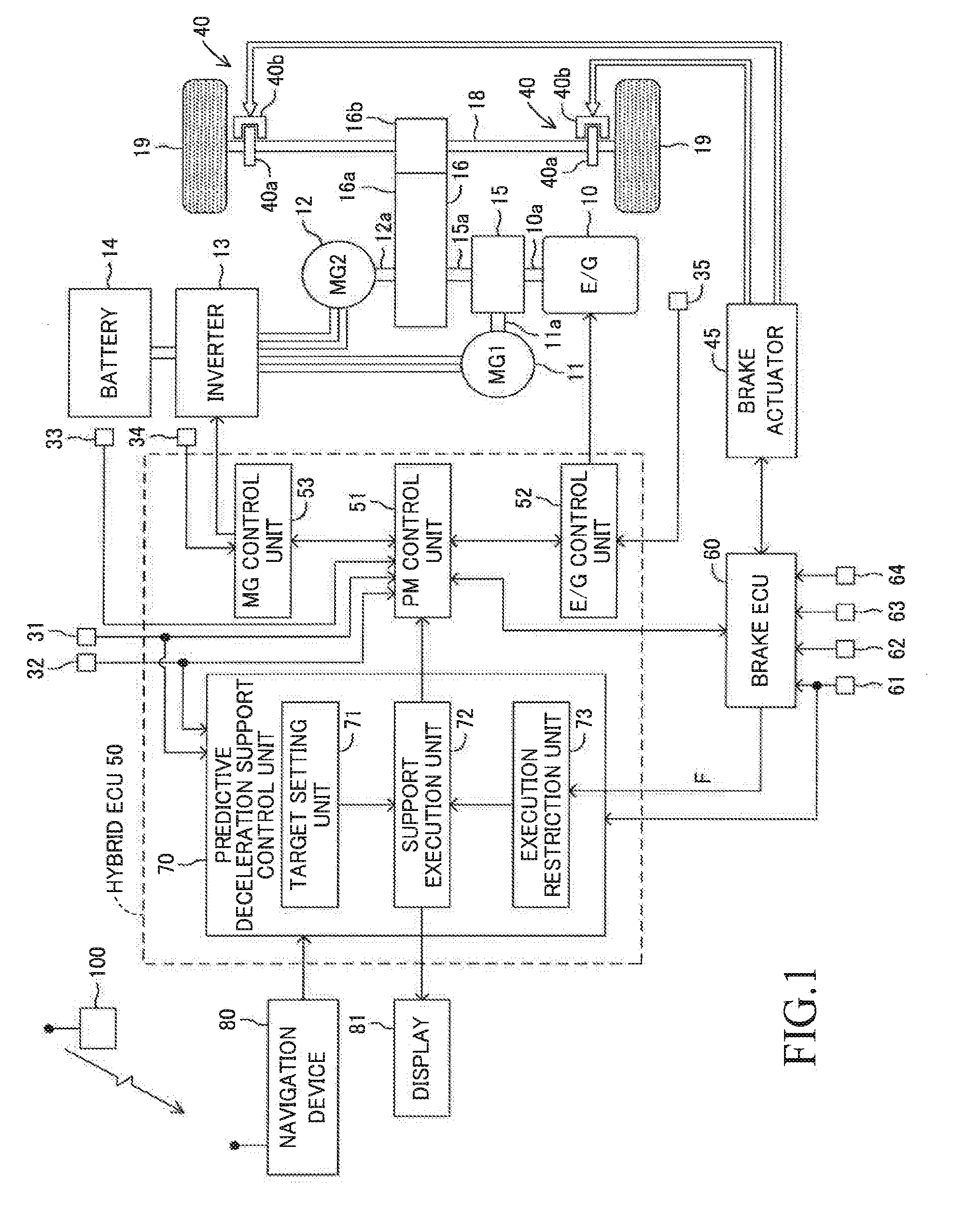
ActiveUS20170015323A1Reduce braking forceIncrease braking powerHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingNormal stateVehicle control
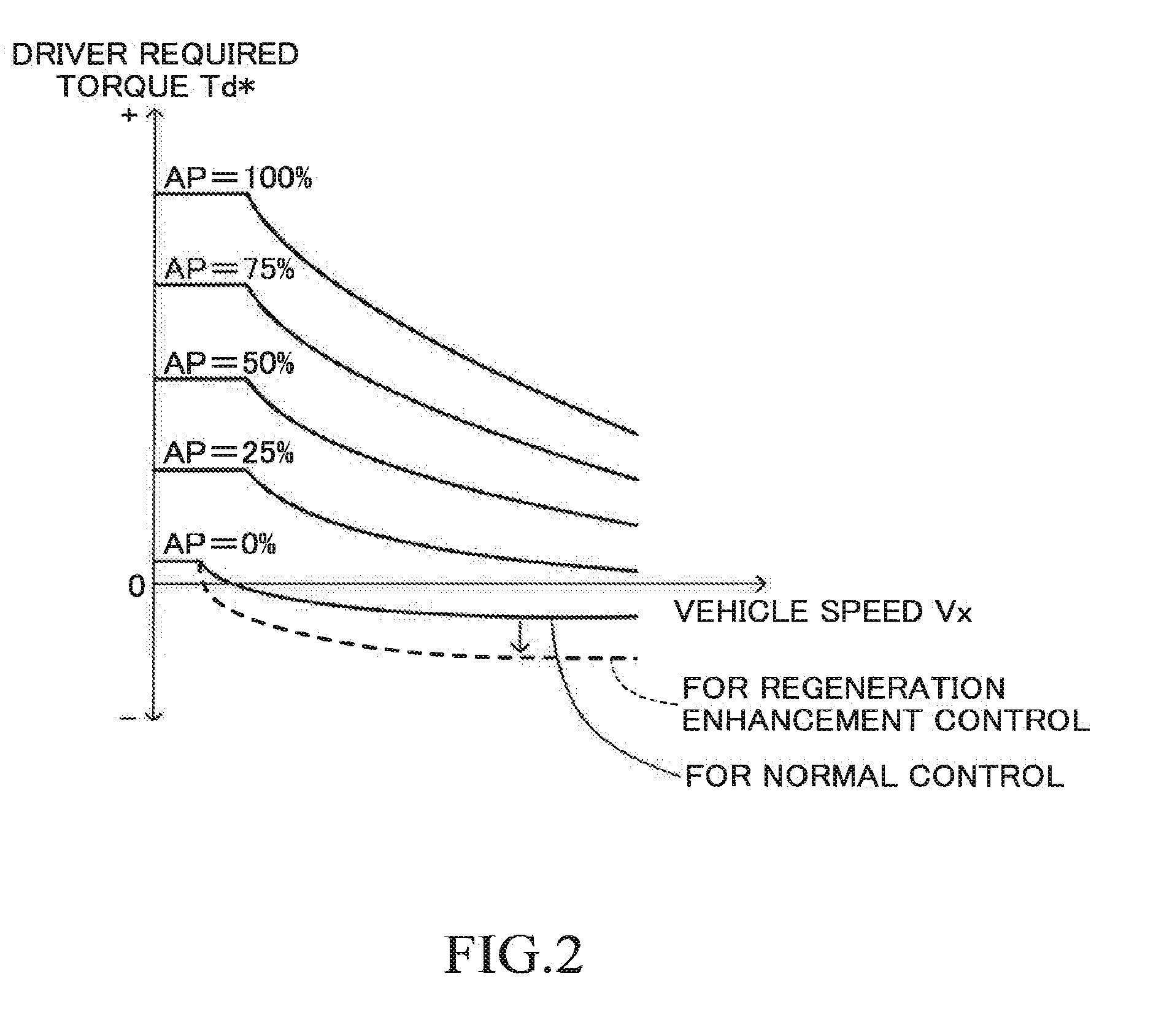
Appropriate vehicle stability control is enabled in a vehicle configured to carry out regeneration enhancement control. A predictive deceleration support control unit is configured to set a position at which the vehicle is predicted to finish deceleration as a target deceleration end position, and guide a driver to release an accelerator pedal so that the deceleration of the vehicle is finished at the target deceleration end position, to thereby carry out regeneration enhancement control under a state in which the accelerator pedal is released so as to generate a larger deceleration than in a normal state. The predictive deceleration support control unit is configured to read a vehicle stability control flag from a brake ECU and stop the regeneration enhancement control when the vehicle stability control is being carried out.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for Controlling a Braking Force of a Vehicle
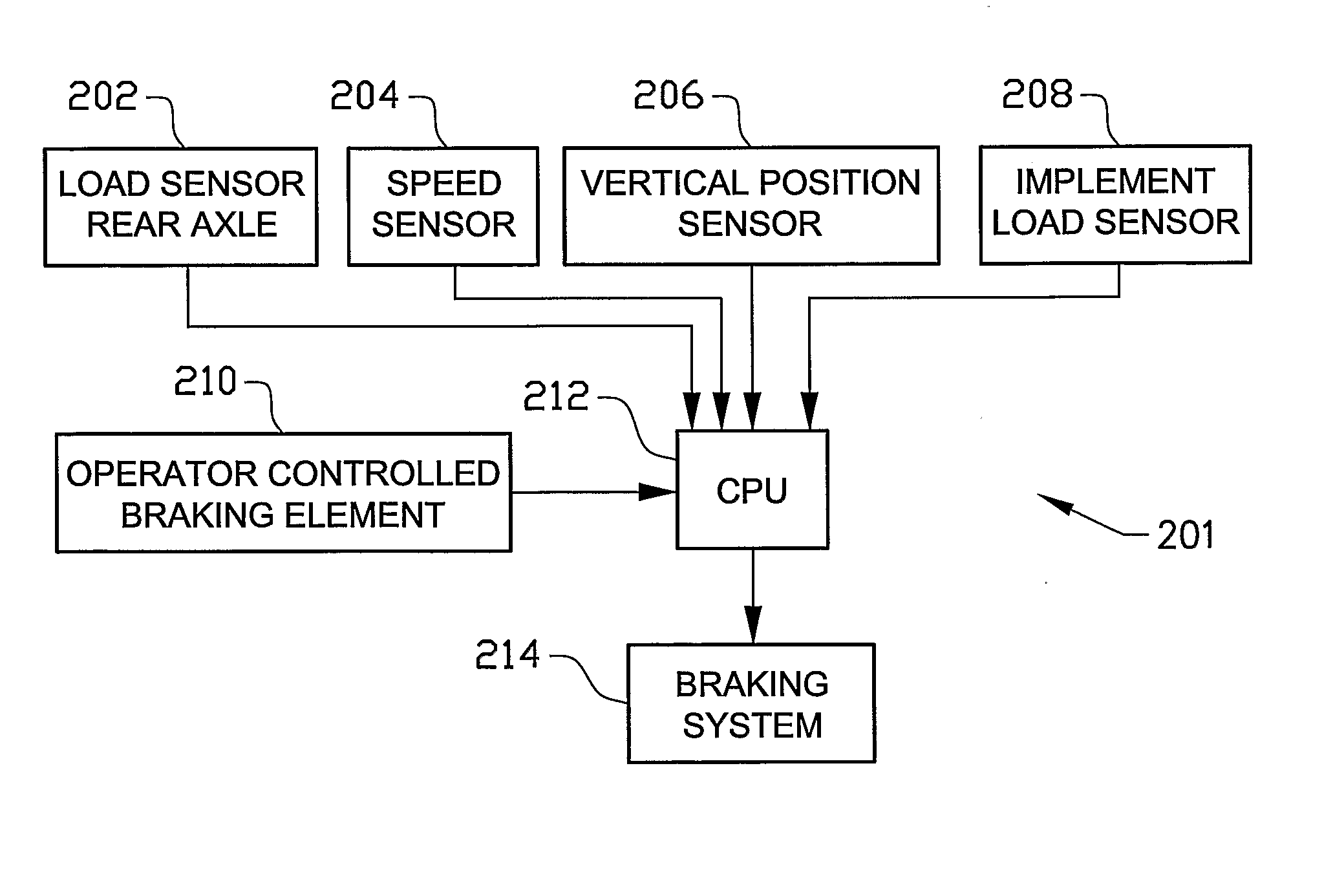
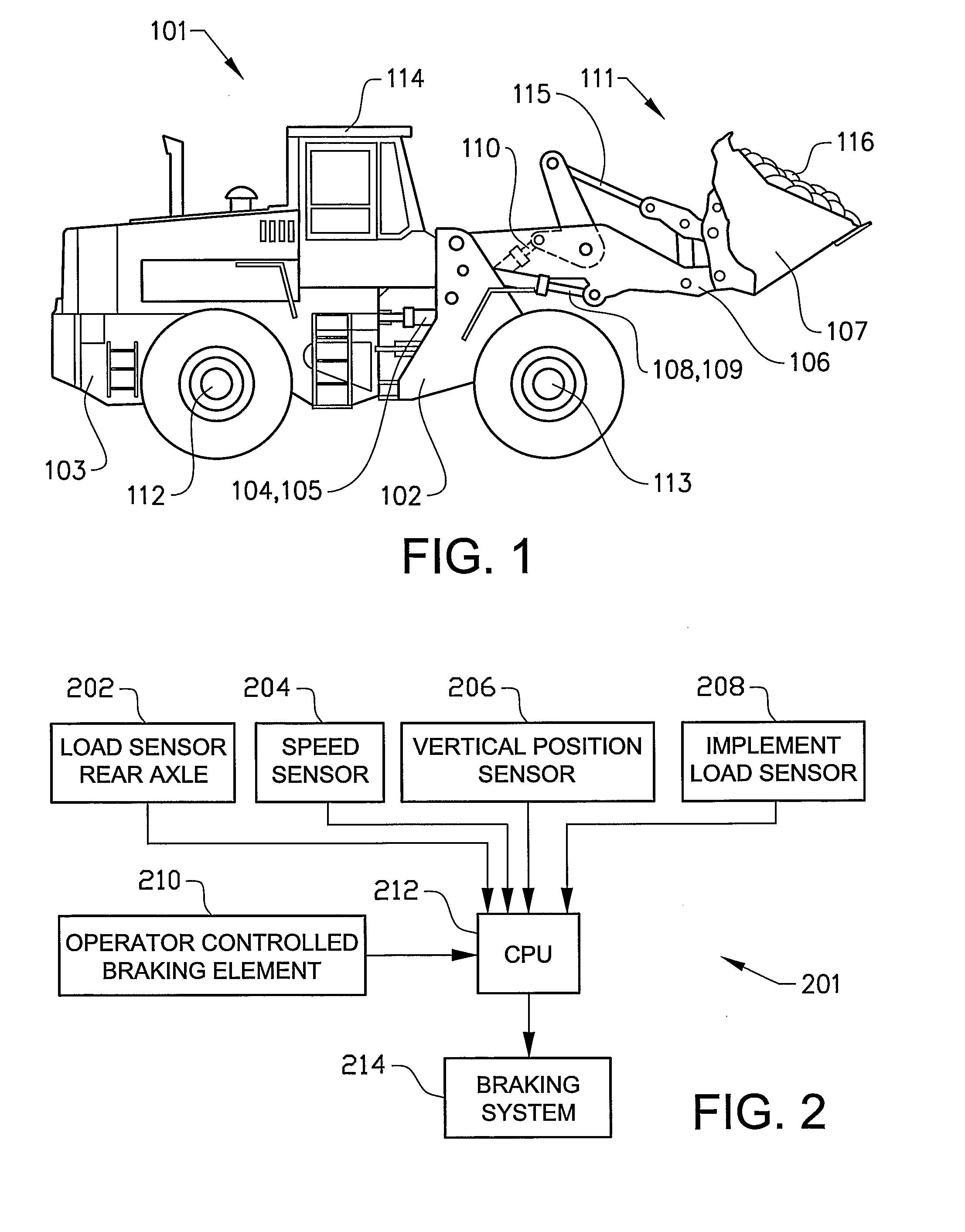
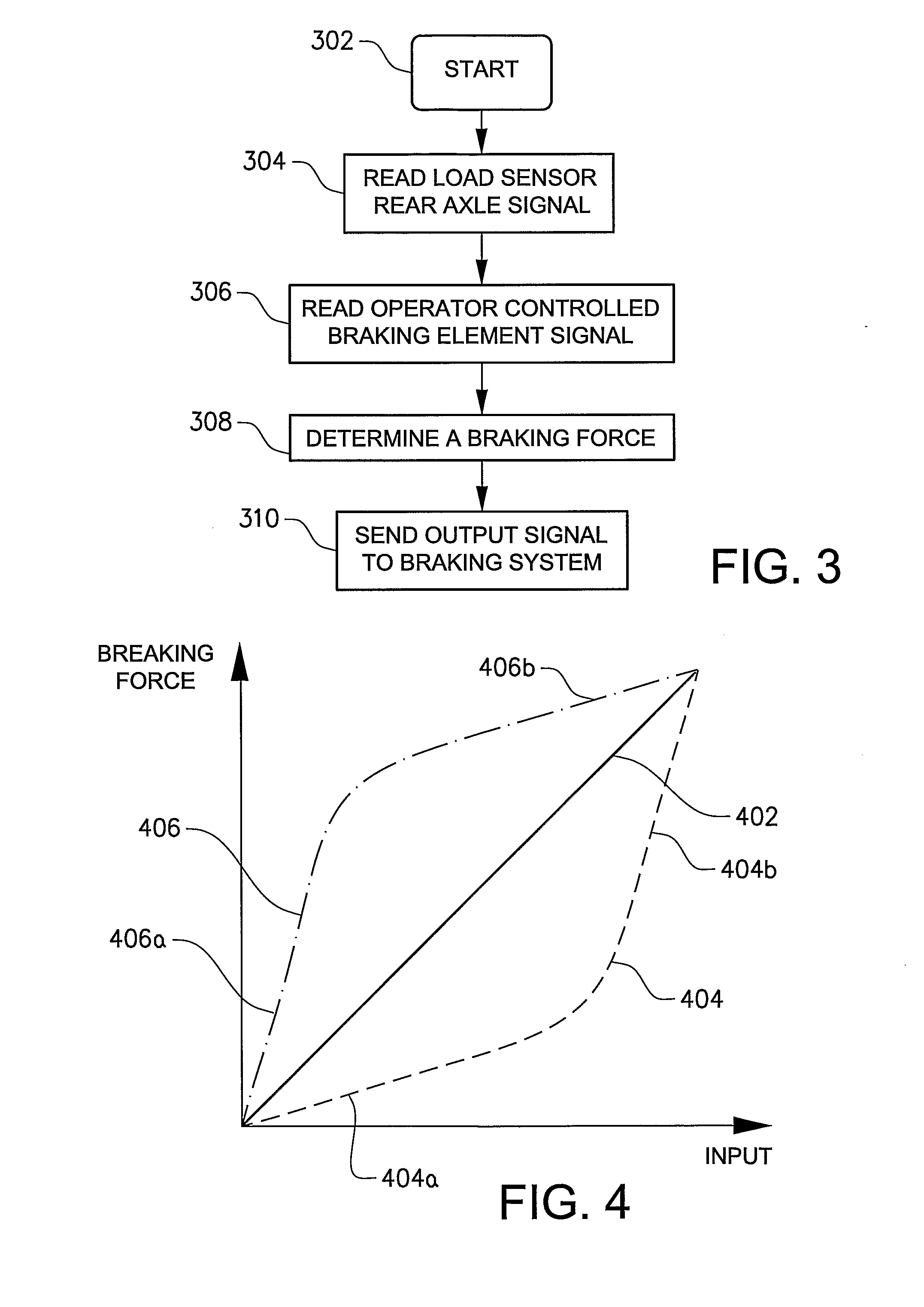
ActiveUS20080262682A1Reduce braking forceEncourages operator confidenceAnalogue computers for trafficSoil-shifting machines/dredgersBrake forceAutomotive engineering
A method and a system are provided for controlling a braking force of a vehicle. The method includes the steps of detecting at least one operating parameter of the vehicle, detecting a position of an operator controlled braking element, determining a magnitude of a braking force on the basis of a detected magnitude of the operating parameter and the detected position of the operator controlled braking element and braking the vehicle according to the determined braking force.
Owner:VOLVO CONSTR EQUIP
Apparatus and method for placing and tensioning an aerial rope through a traveler of a power line
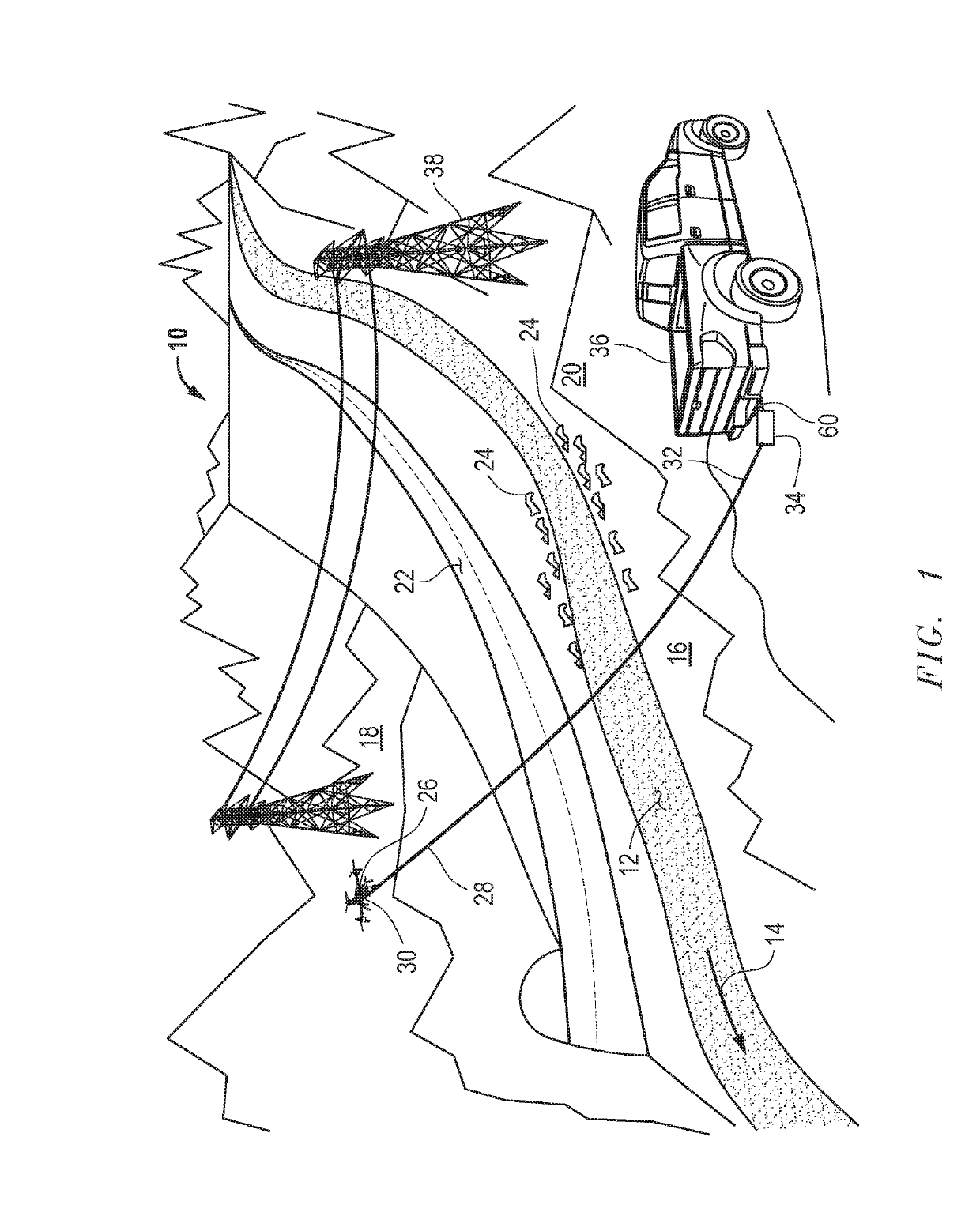
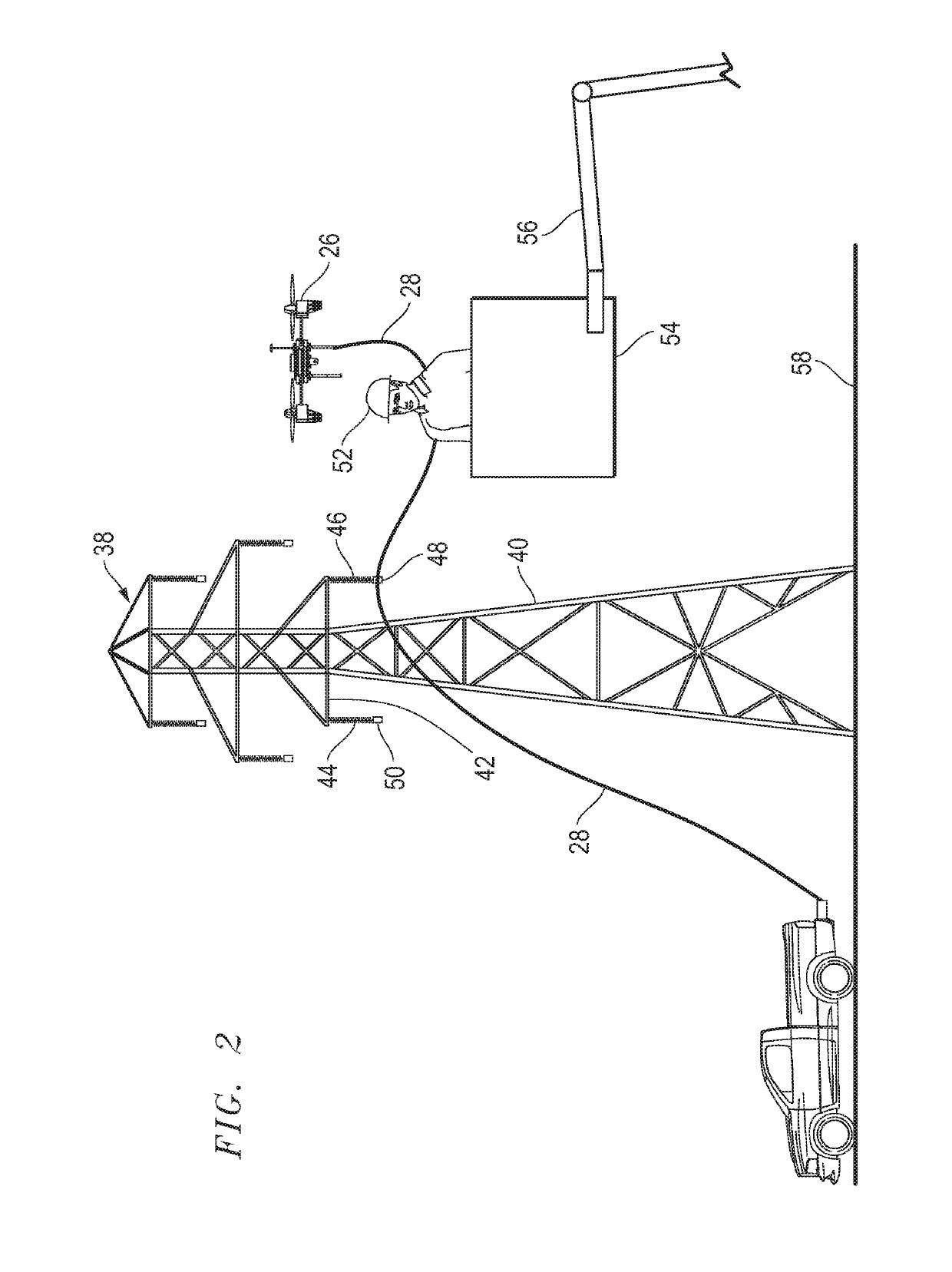
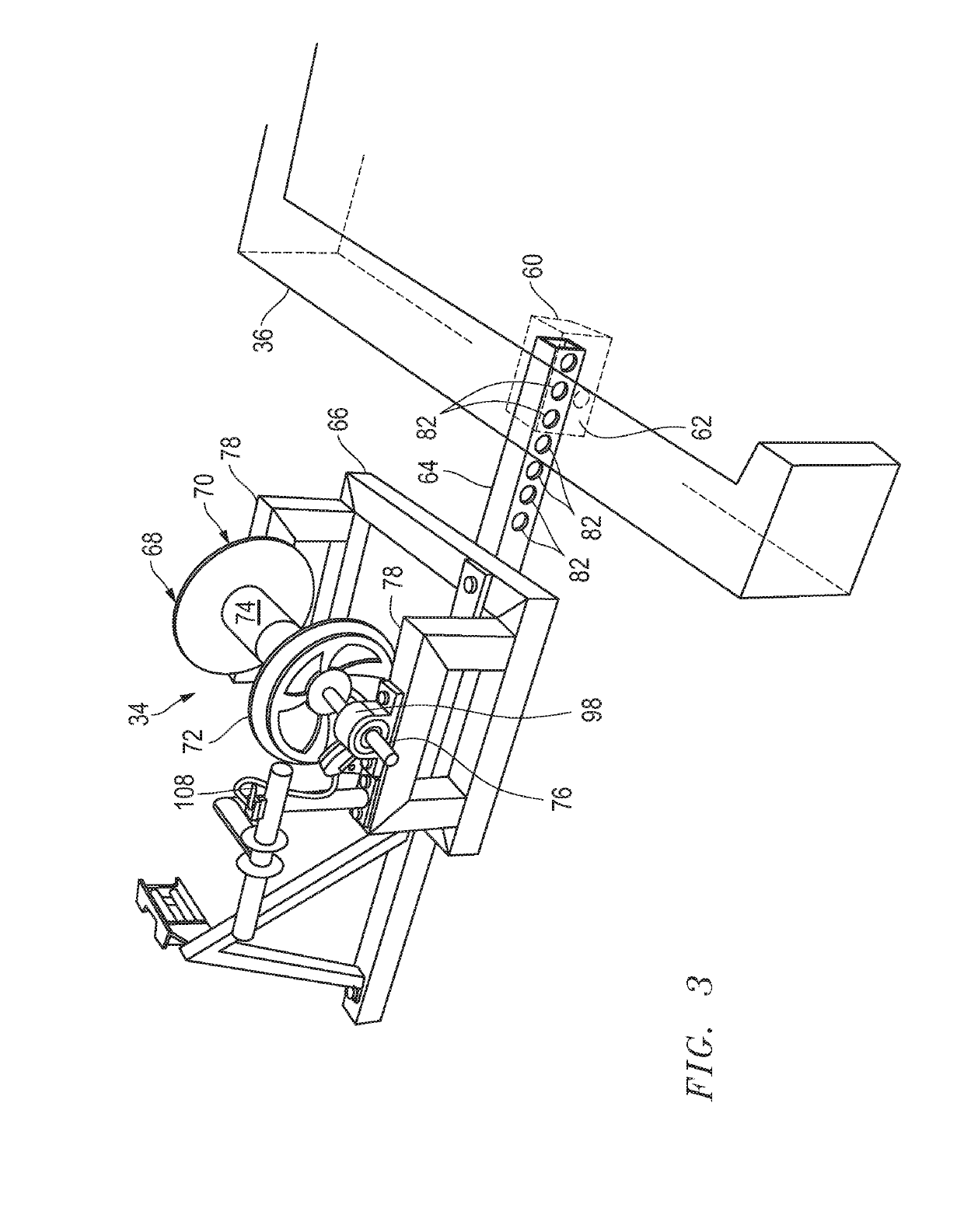
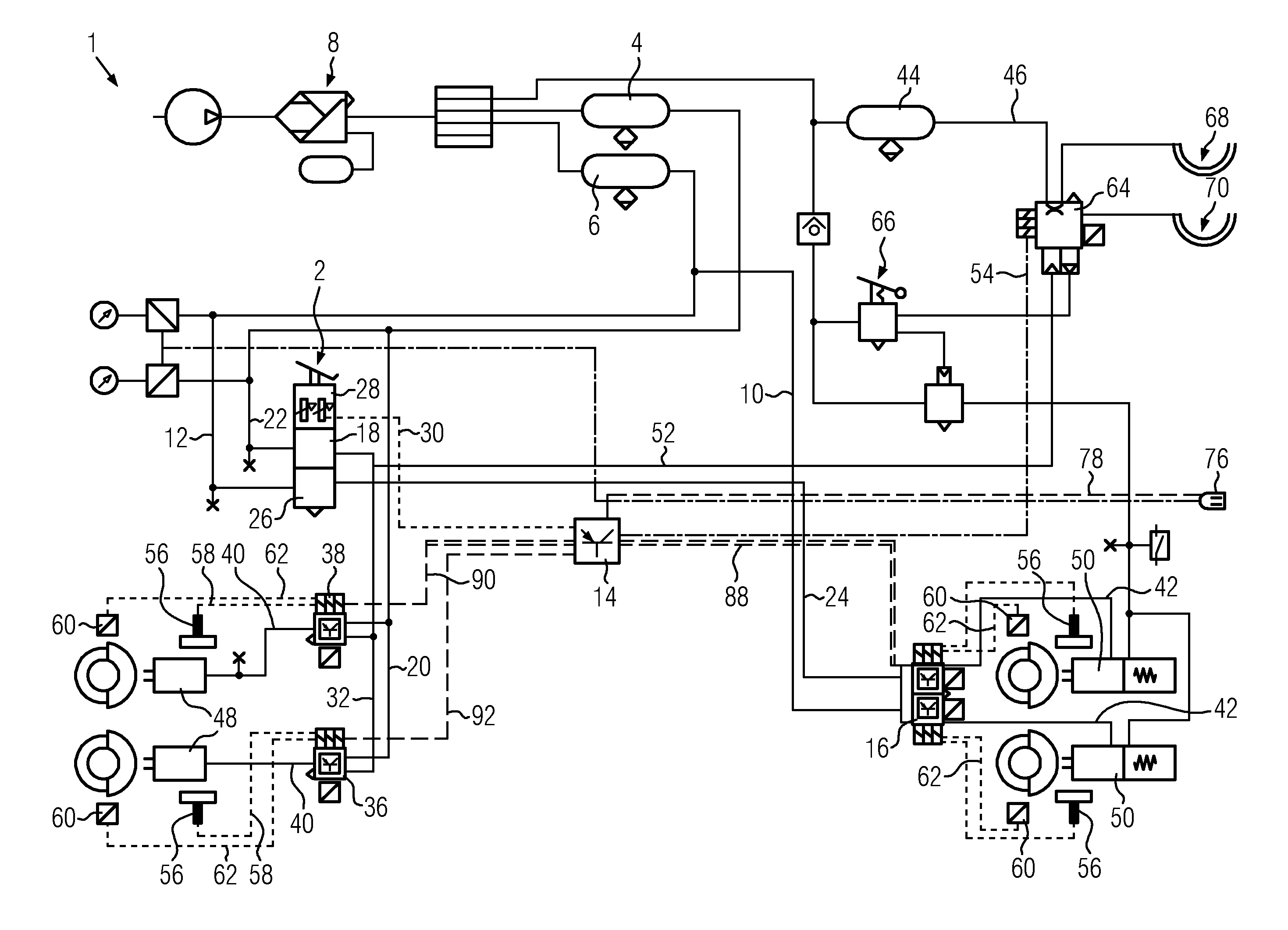
ActiveUS20190218076A1Fast disconnectionReduce tensionUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftEngineeringCalipers
An apparatus for controlling tension in a pulling rope that is attached to a flying, unmanned aerial device or drone may utilize a cylinder around which the rope is wound, a shaft that longitudinally passes through the cylinder, a disc brake rotor that is mounted to the shaft, a brake caliper that is mounted circumferentially at a periphery of the disc brake rotor, and a brake lever that tensions a cable that is attached to, and movable to control movement of, the brake caliper, which may be hydraulic, against surfaces the disc brake rotor. The brake lever may be hand actuated and mounted to a handlebar. A frame may be part of the apparatus and support apparatus components and may have a protruding hitch portion that inserts into a vehicle's receiver hitch. An adjustable pulling rope guide support through which the rope is threaded, mounts to the frame.
Owner:QUANTA ASSOC
Method for braking a traction vehicle-trailer combination with reduced trailer braking force as a function of the response of the abs of the traction vehicle
ActiveUS20160068144A1Undesired swinging out can be avoidedSpend lessDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsTraction unitBraking system
A method and device for braking a traction vehicle-trailer combination with a traction vehicle and at least one trailer, in which a traction controller is provided for a brake system of the traction vehicle, and for a brake system of the at least one trailer, no traction controller is provided or a traction controller is provided for the axles which are present, but with a brake-slip-determining arrangement on fewer axles than the number of axles, in which (a) the trailer brake system is controlled by the traction vehicle brake system, and (b) during a braking it is determined whether there is a risk of the trailer swinging out as to the traction vehicle, or whether such swinging is imminent or is occurring, and (c) the braking force or the braking of the trailer is reduced if it has been determined in (a) that there is a risk of the trailer swinging out, or is imminent or is occurring, and (d) a risk of the trailer swinging out, or imminent or occurring swinging out of the trailer, as to the traction vehicle, is detected according to (a) by the traction controller.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Automatic external adjustable spool braking system
In a fishing reel, in addition to an externally adjustable brake system, an automatic spool brake system adjusts spool braking action dependent upon spool rotation speed to provide brake control for preventing backlash and to achieve better casting distance by reducing spool braking force at low spool rotation speeds. A brake assembly has a plurality of brake shoes and speed adjust shoes and is slidably mounted on a spool shaft. An adjustable brake ring selectively engages the brake shoes to provide a braking action to the spool. A spring is provided for biasing the brake assembly away from the brake. Centrifugal force causes the speed adjust shoes to migrate outwardly in contact with a conical surface. The shoes impart an axial force to the brake assembly for moving the assembly towards the brake ring. At lower speeds, the spring pushes the brake assembly away from the brake ring.
Owner:KIM HYUNKYU +1
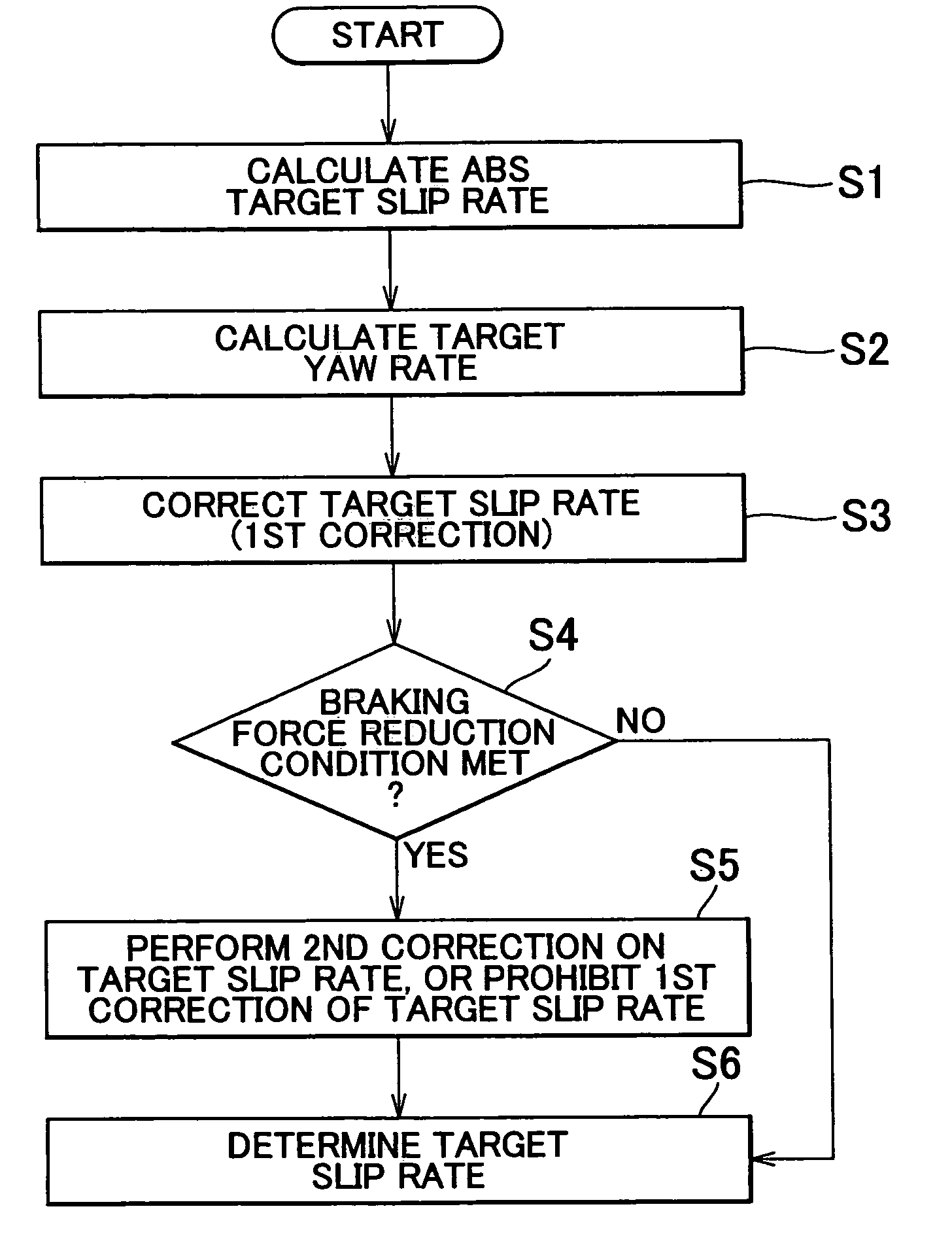
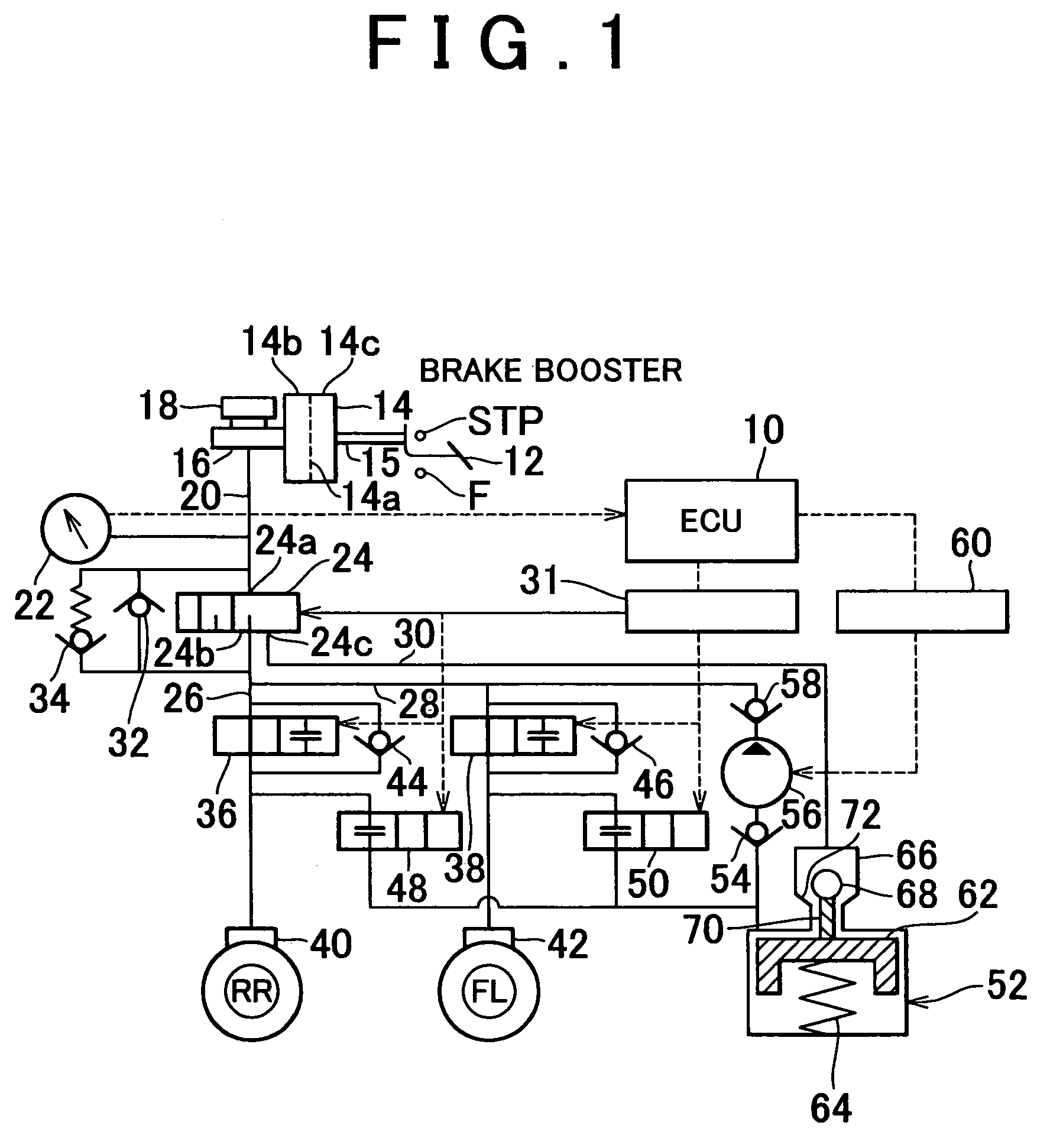
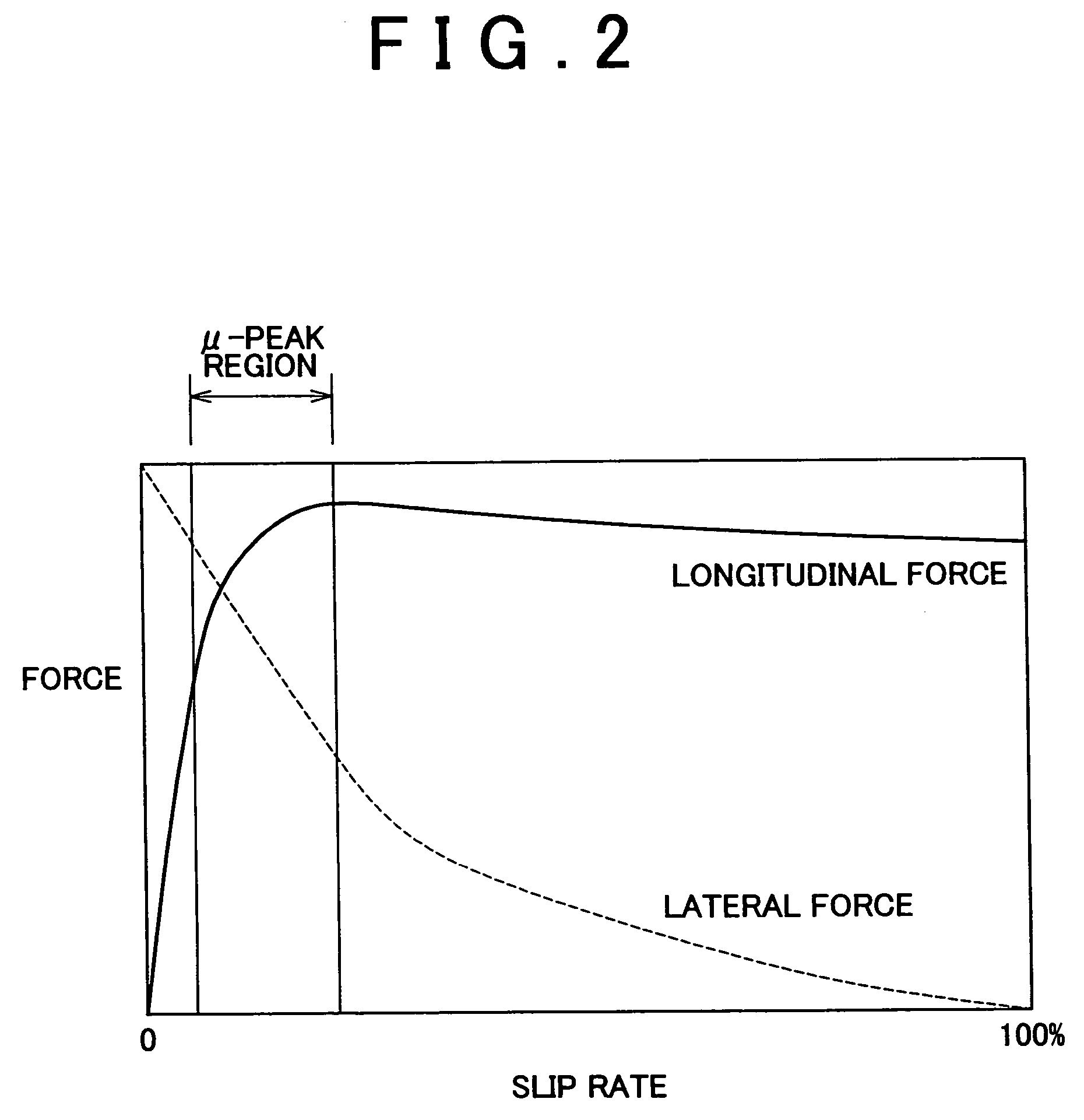
Vehicular brake system and method of controlling same brake system
ActiveUS7168769B2Stabilizing vehicle behaviorReduce braking forceAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsEngineeringControl mode
The brake system of the invention, during the ABS control mode, corrects the target slip rate in accordance with the turning of the vehicle, and determines whether the vehicle is running on a poor surface road. If the vehicle is running on a poor surface road, the system sets a target slip rate that provides a greater longitudinal force than the aforementioned target slip rate.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Method for braking a traction vehicle-trailer combination with reduced trailer braking force as a function of the response of the ABS of the traction vehicle
ActiveUS9809206B2Undesired swinging out can be avoidedSpend lessAutomatic initiationsBraking systemVehicle brake
A method and device for braking a traction vehicle-trailer combination with a traction vehicle and at least one trailer, in which a traction controller is provided for a brake system of the traction vehicle, and for a brake system of the at least one trailer, no traction controller is provided or a traction controller is provided for the axles which are present, but with a brake-slip-determining arrangement on fewer axles than the number of axles, in which (a) the trailer brake system is controlled by the traction vehicle brake system, and (b) during a braking it is determined whether there is a risk of the trailer swinging out as to the traction vehicle, or whether such swinging is imminent or is occurring, and (c) the braking force or the braking of the trailer is reduced if it has been determined in (a) that there is a risk of the trailer swinging out, or is imminent or is occurring, and (d) a risk of the trailer swinging out, or imminent or occurring swinging out of the trailer, as to the traction vehicle, is detected according to (a) by the traction controller.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
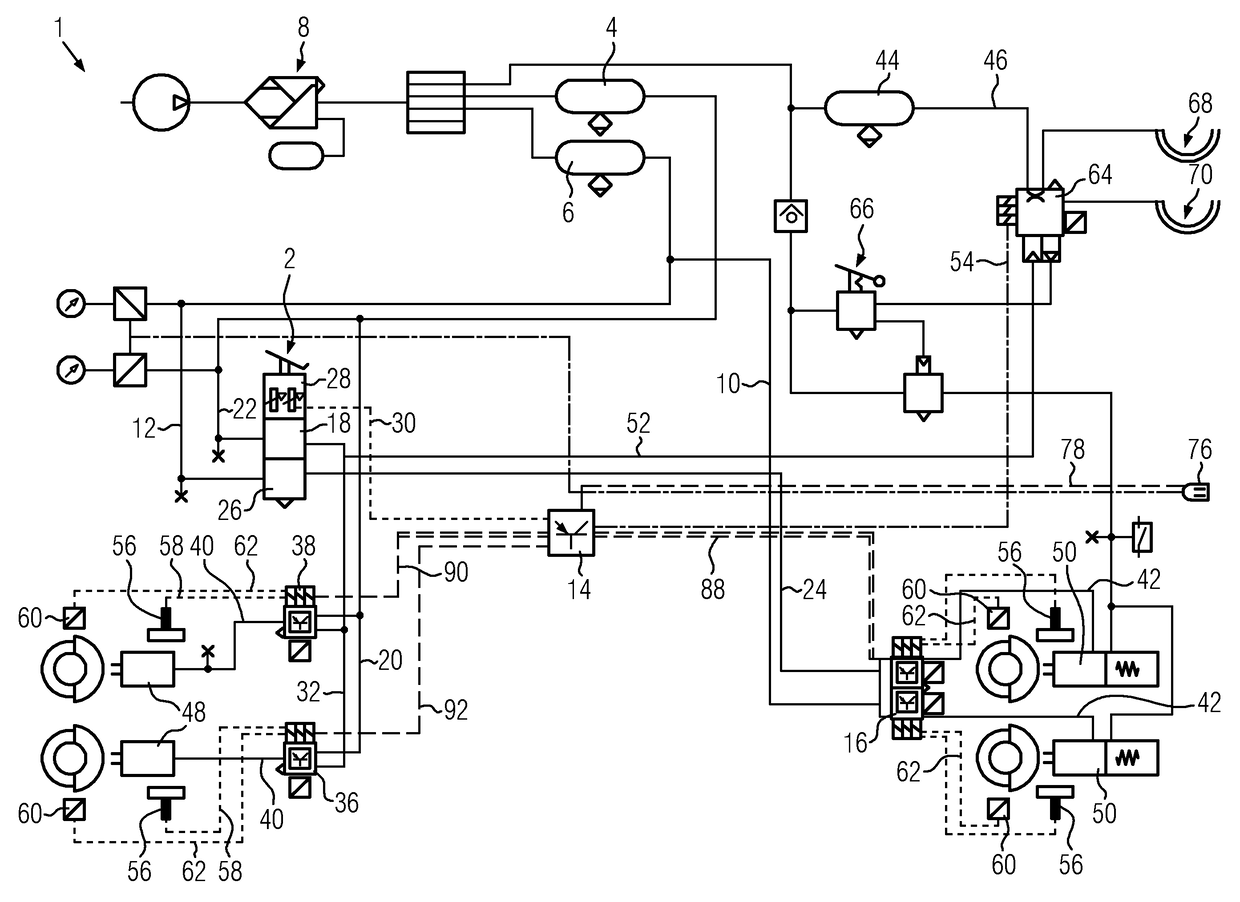
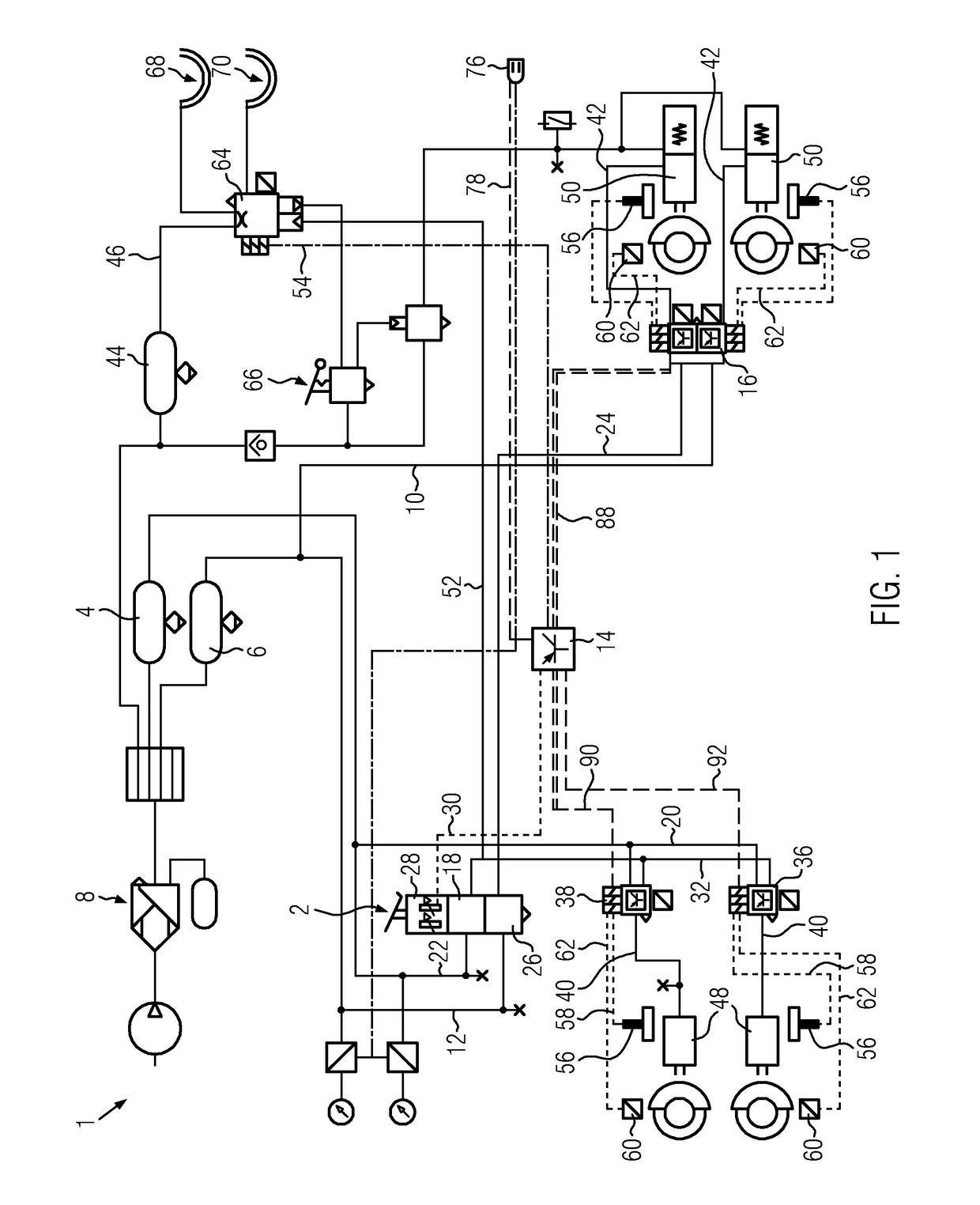
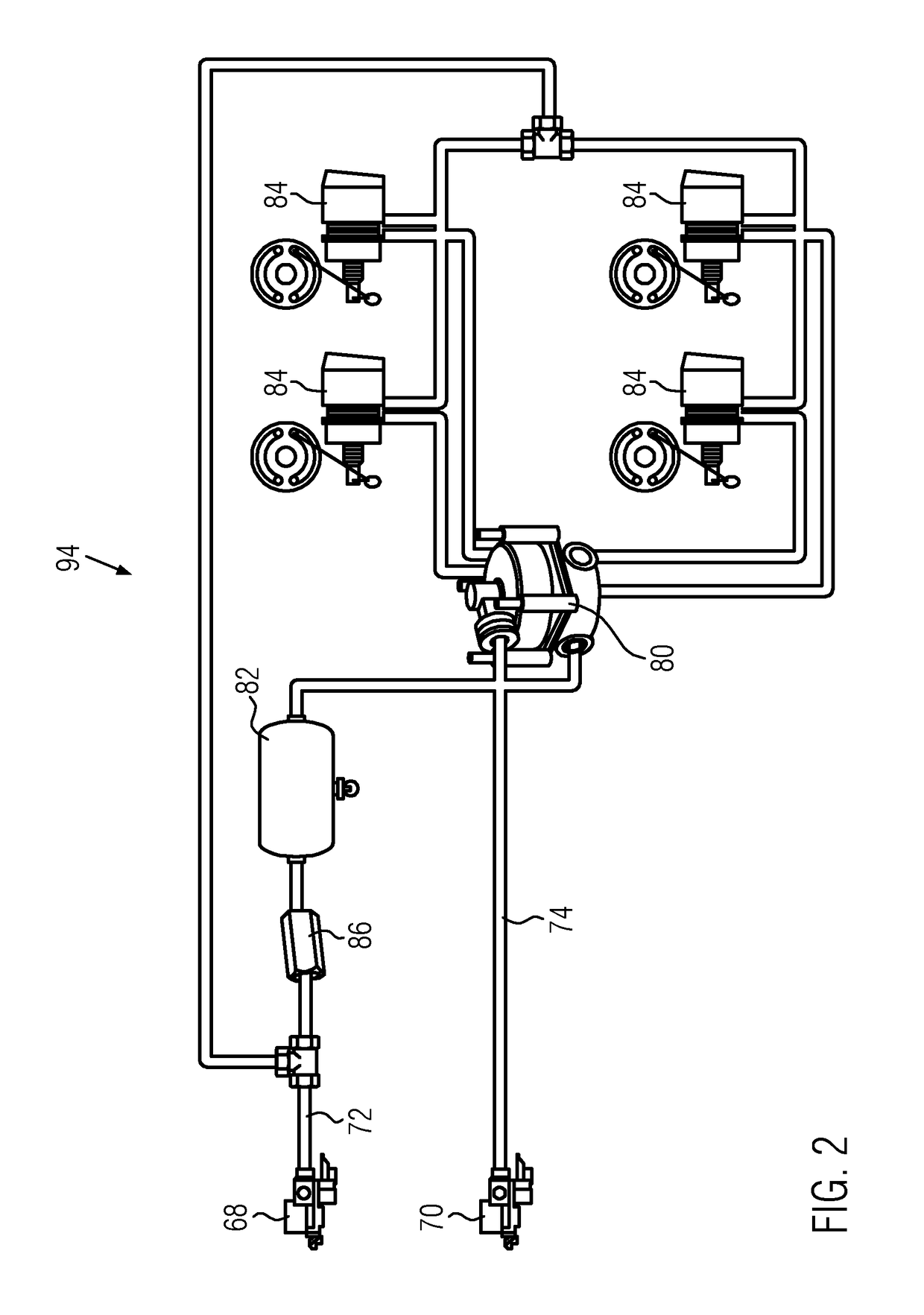
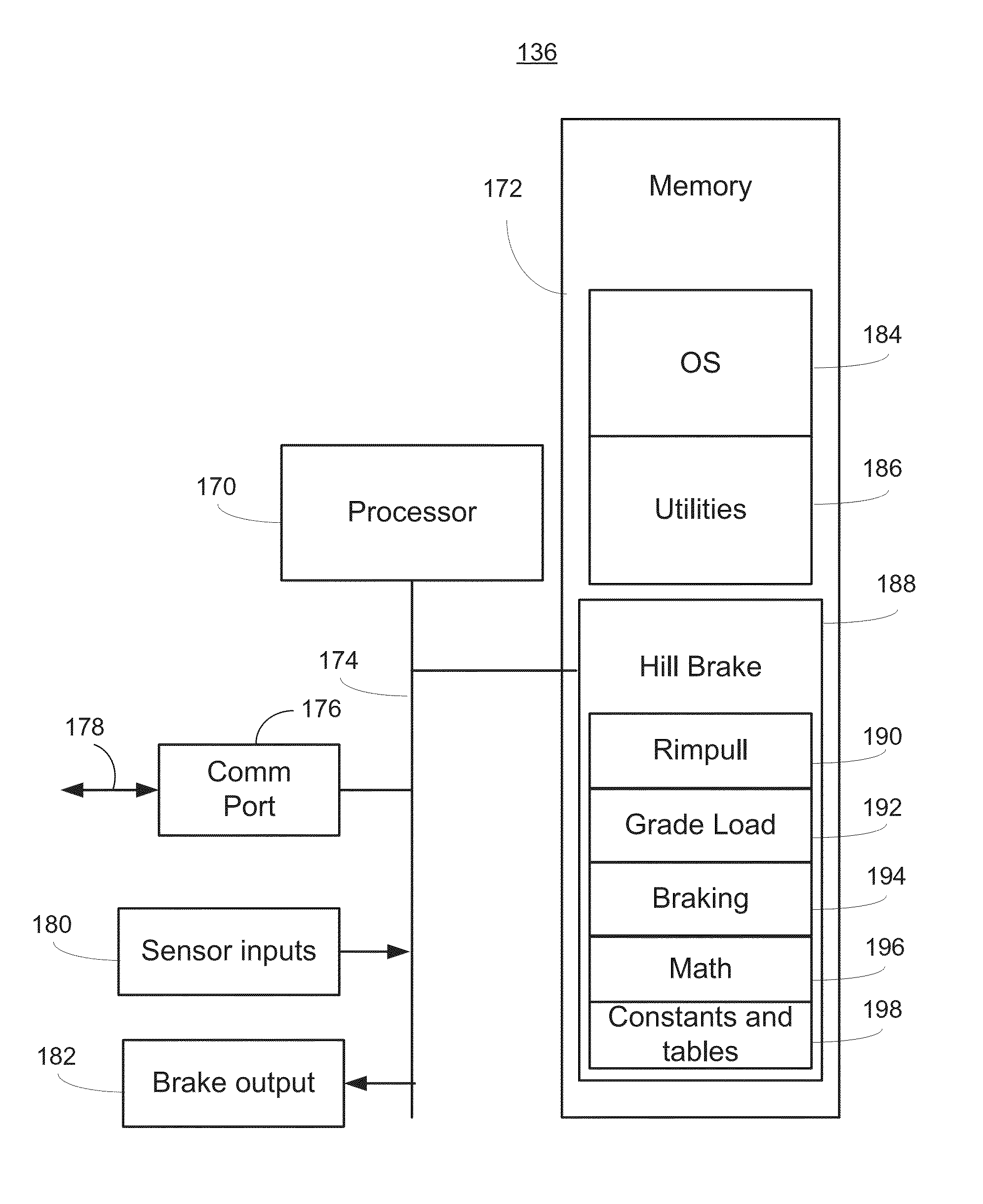
Hill Start in a Vehicle
InactiveUS20140249729A1Reduce braking forceReduce forceAnalogue computers for trafficAutomatic initiationsDrivetrainGravitational force
A hill brake system in a vehicle uses a controller to determine when a number of conditions, such as being stopped on an incline, are met and then automatically applies a braking force at least equal to a calculated grade load, that is, gravitational force. Using drive train measurements and known drivetrain characteristics, a rimpull force is calculated after release of an operator-controlled brake and the automatically applied braking force is reduced corresponding to the rimpull force generated by the drivetrain. The automatically applied braking force is released when any of several conditions are met including uphill motion of the vehicle or expiration of a timeout timer.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Theft Prevention Using Existing ABS Sensors
InactiveUS20130249683A1Reduce braking forceLoss of controlAnti-theft devicesAutomotive engineeringAugmentation system
The automobile theft prevention system proposed in this invention detects motion by using the existing wheel rotational sensors that are part of the anti lock braking and stability augmentation systems present in most automobiles, without the requirement of any additional hardware specific to the theft prevention system.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Vehicle travel assistance system
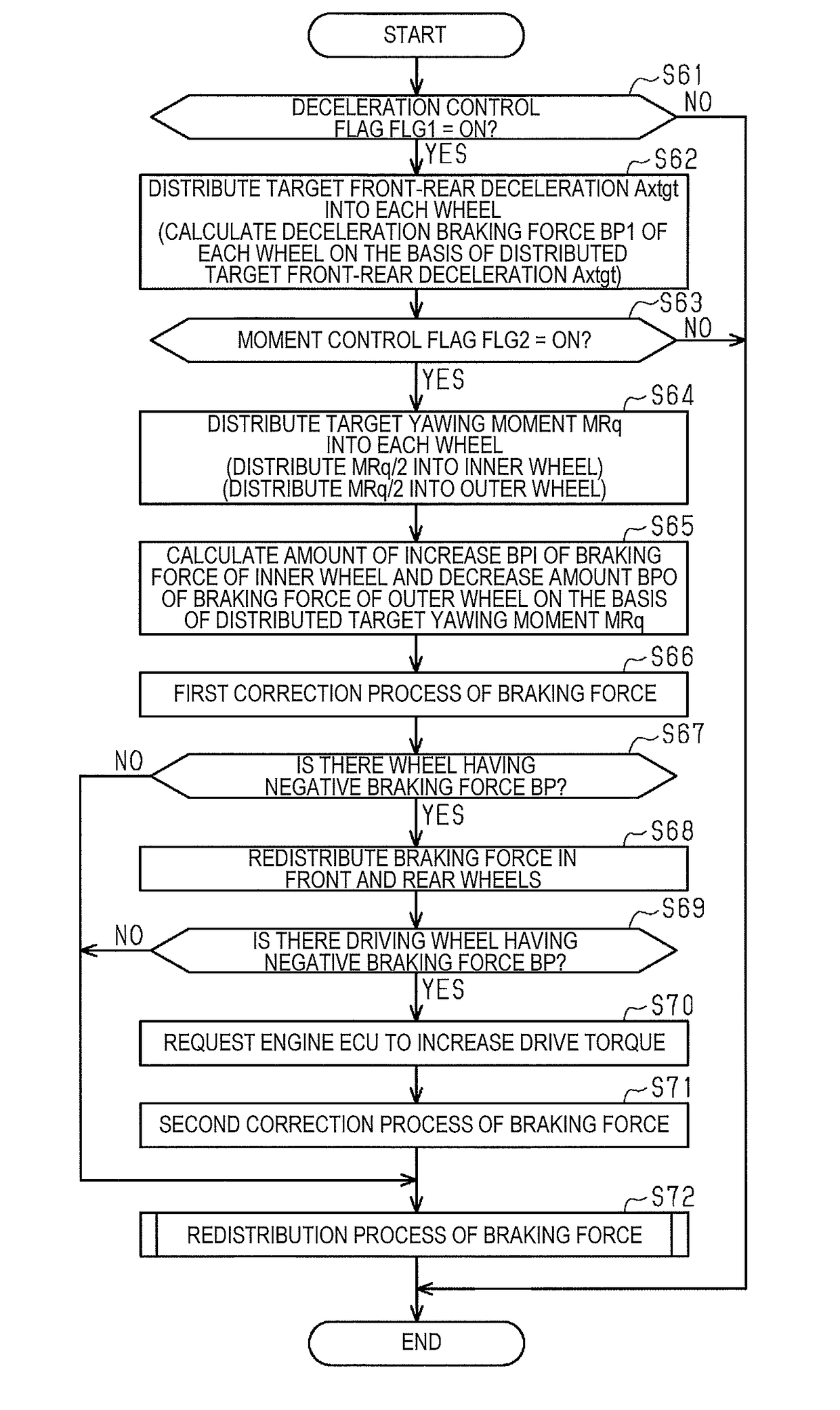
ActiveUS20180281763A1Inhibit deteriorationLesser outer forceAutomatic initiationsEngineeringAuxiliary system
A vehicle travel assistance system includes distributing half of target yawing moment to inner wheels and distributing the rest to outer wheels; increasing the amount of increase in the braking force of the inner wheels as the target yawing moment distributed to the inner wheels increases, and increasing the amount of decrease in the braking force of the outer wheels as the target yawing moment distributed to the outer wheels increases; and causing the braking force of the inner wheels to increase according to the amount of increase in the braking force of the inner wheels, and causing the braking force of the outer wheels to decrease according to the amount of decrease in the braking force of the outer wheels.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Remote brake release mechanism for an elevator machine
InactiveUSRE38835E1Reduce braking forceLimited and controlled movementElevatorsBuilding liftsMechanical engineeringBrake force
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
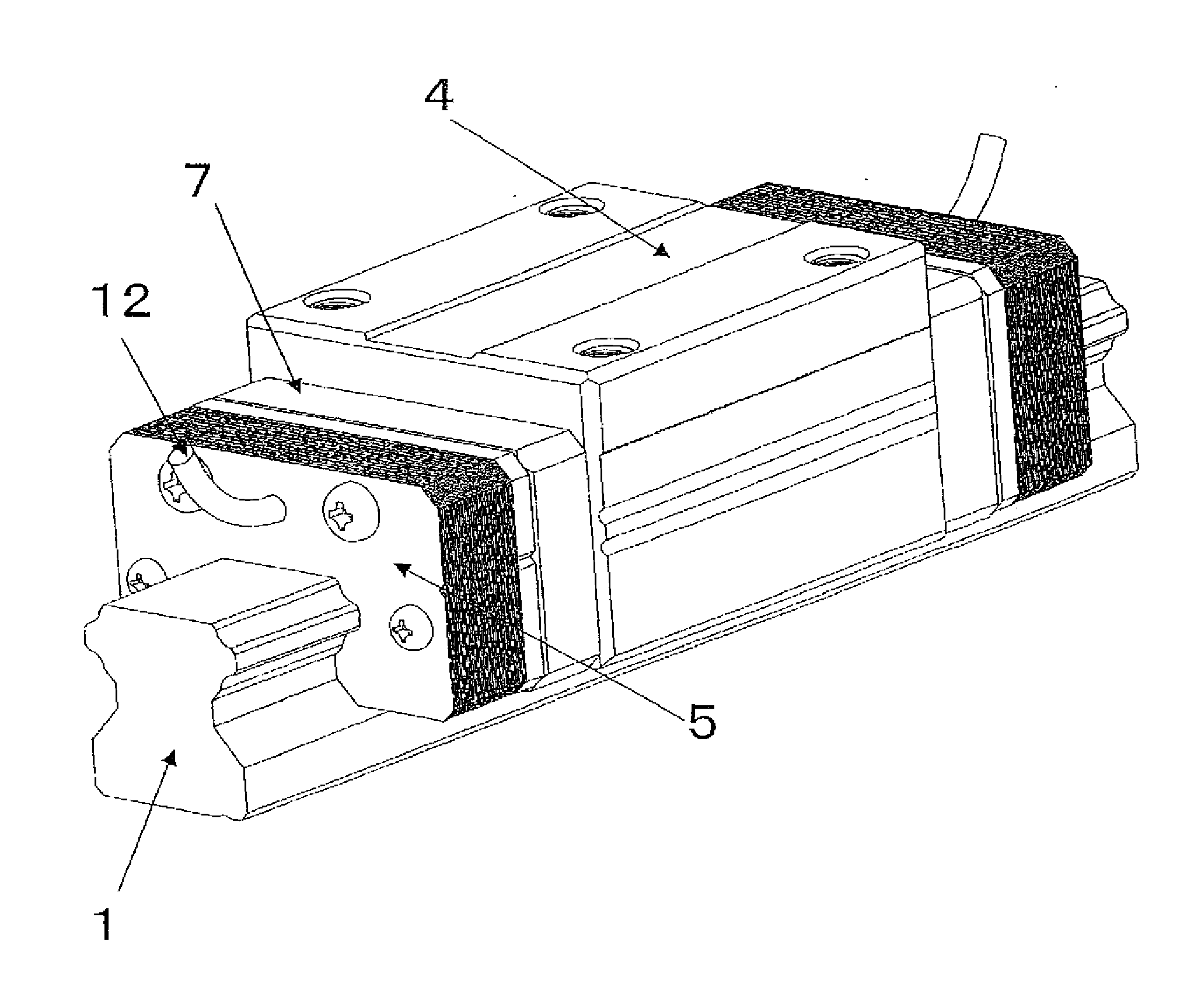
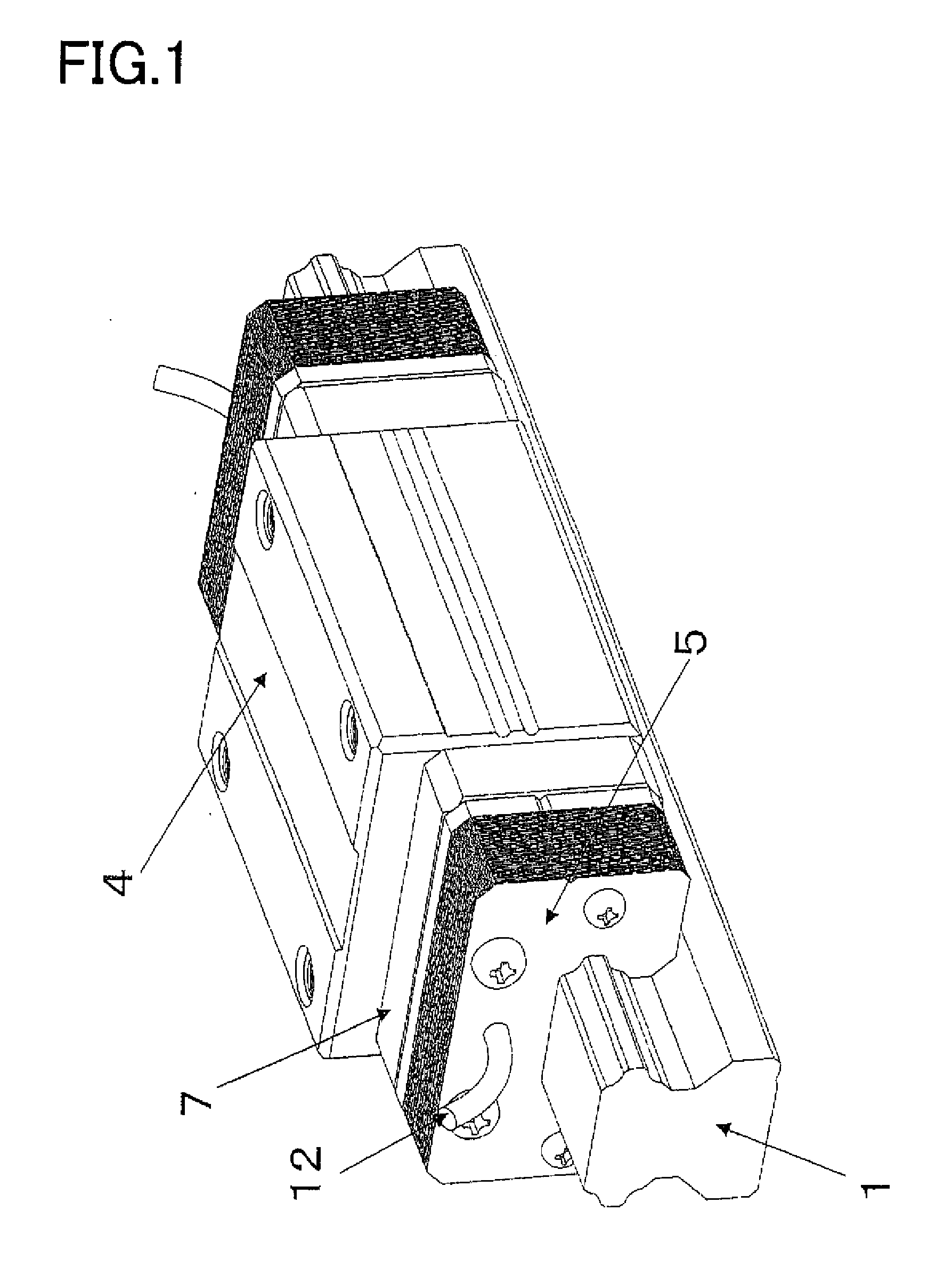
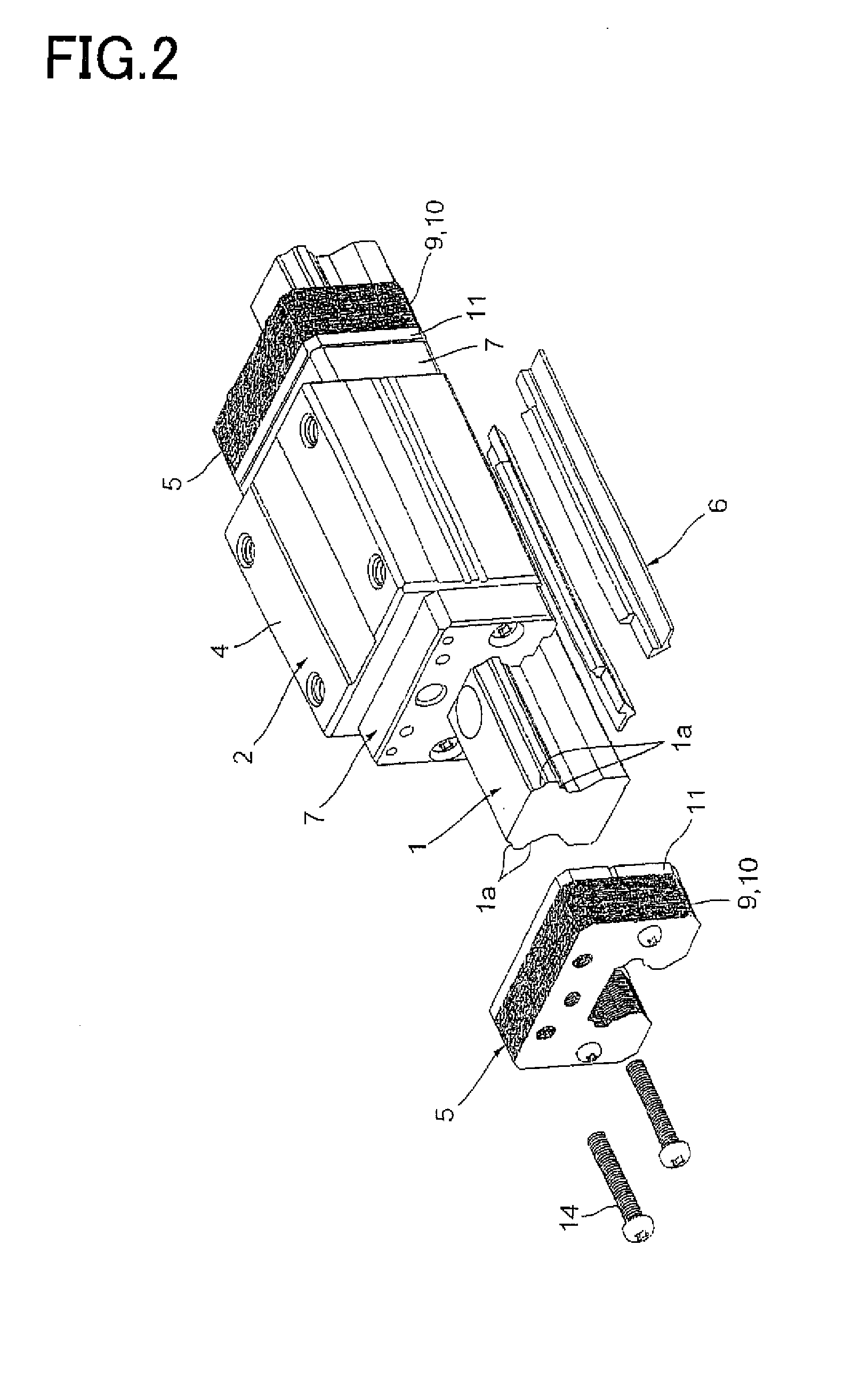
Motion guide device, table apparatus, and damping method for motion guide device
InactiveUS20090161996A1Reduce braking forceBraking force can be made to suppressLinear bearingsBearing componentsEngineeringViscosity
A motion guide device that has a novel damping structure different from the conventional damping structure is provided. The present invention comprises a raceway member (1) having a rolling-element rolling part (1a); a moving member (2) having a loaded rolling-element rolling part (2a) facing the rolling-element rolling part (1a) and being allowed to make a linear or curved movement relatively to the raceway member (1); and a plurality of rolling elements (3) intervening between the rolling-element rolling part (1a) of the raceway member (1) and the loaded rolling-element rolling part (2a) of the moving part (2). A gap (16) between the raceway member (1) and the moving member (2) is filled with a layer of oil contacting the raceway member (1) and the moving member (2). Viscosity resistance of the oil is utilized to apply a braking force to the moving member (2) or the raceway member (1) in proportion to a speed.
Owner:THK CO LTD
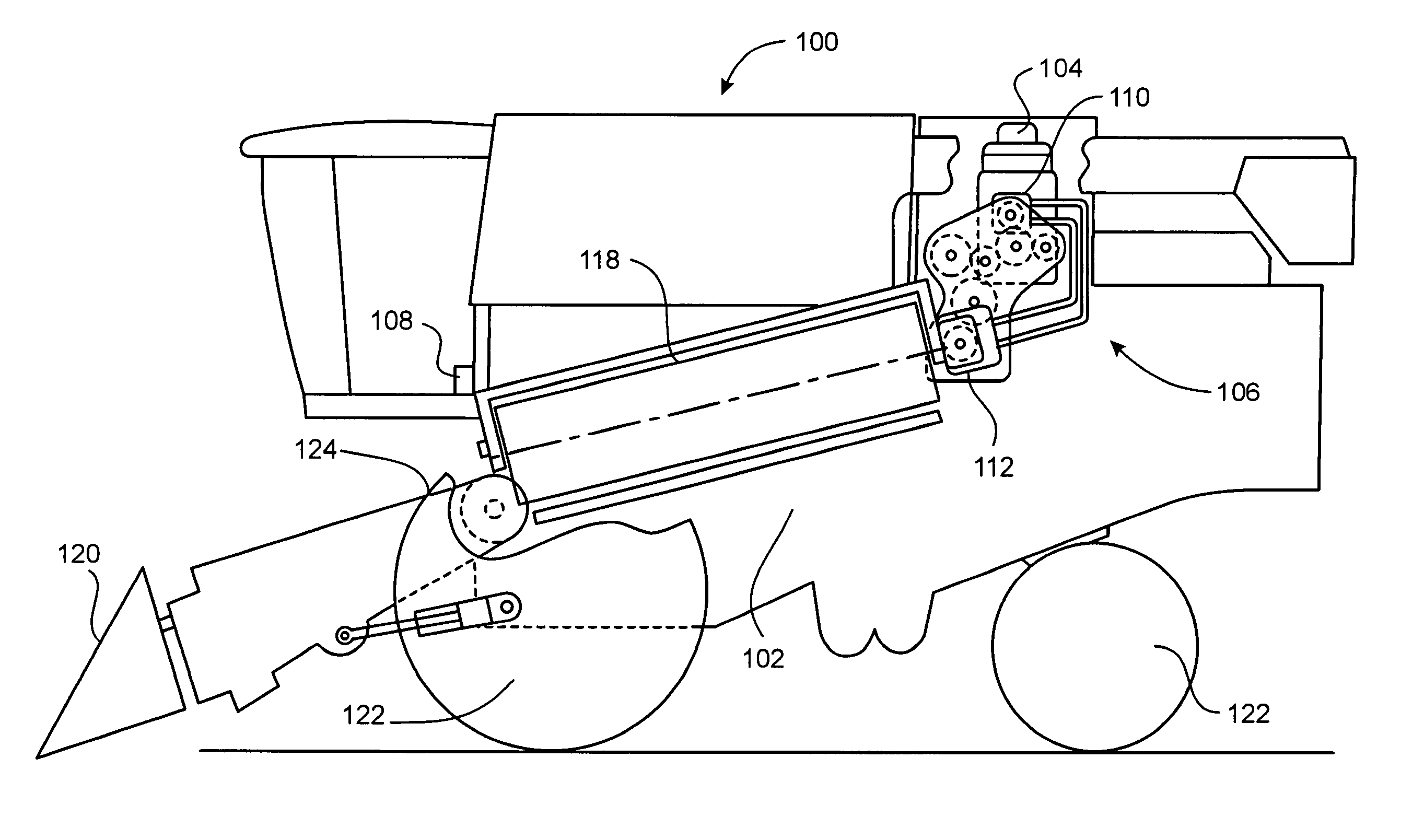
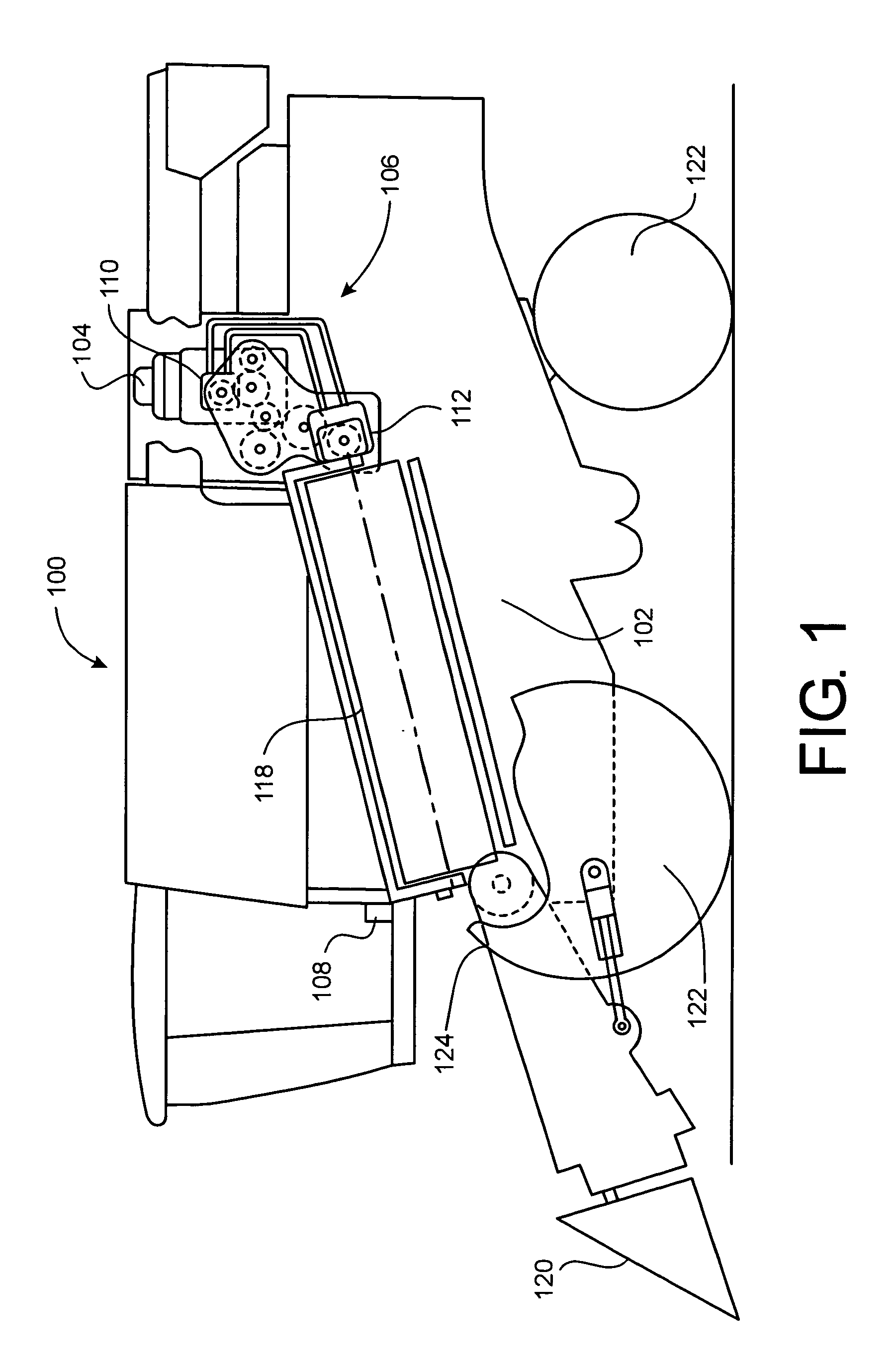
Active combine rotor deceleration
ActiveUS20060178177A1Reduce braking forceReduce forceMowersToothed gearingsCombine harvesterControl system
A system and method for actively decelerating a combine rotor is provided. The system includes an electronic control system configured to disengage the combine rotor from an engine, to brake the combine rotor at a first deceleration rate for a first time interval, and to subsequently brake the combine rotor at another deceleration rate until the rotor is stopped.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P
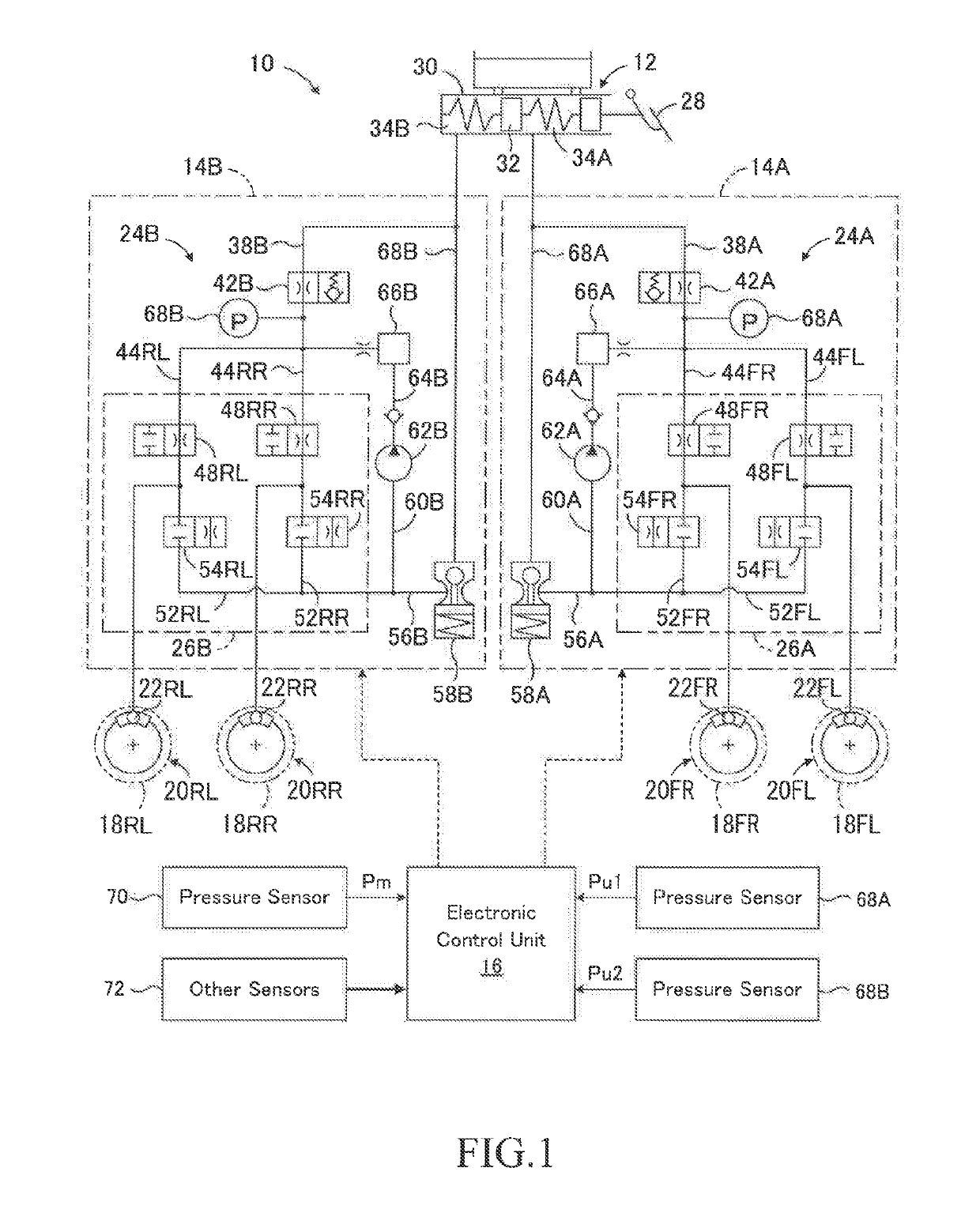
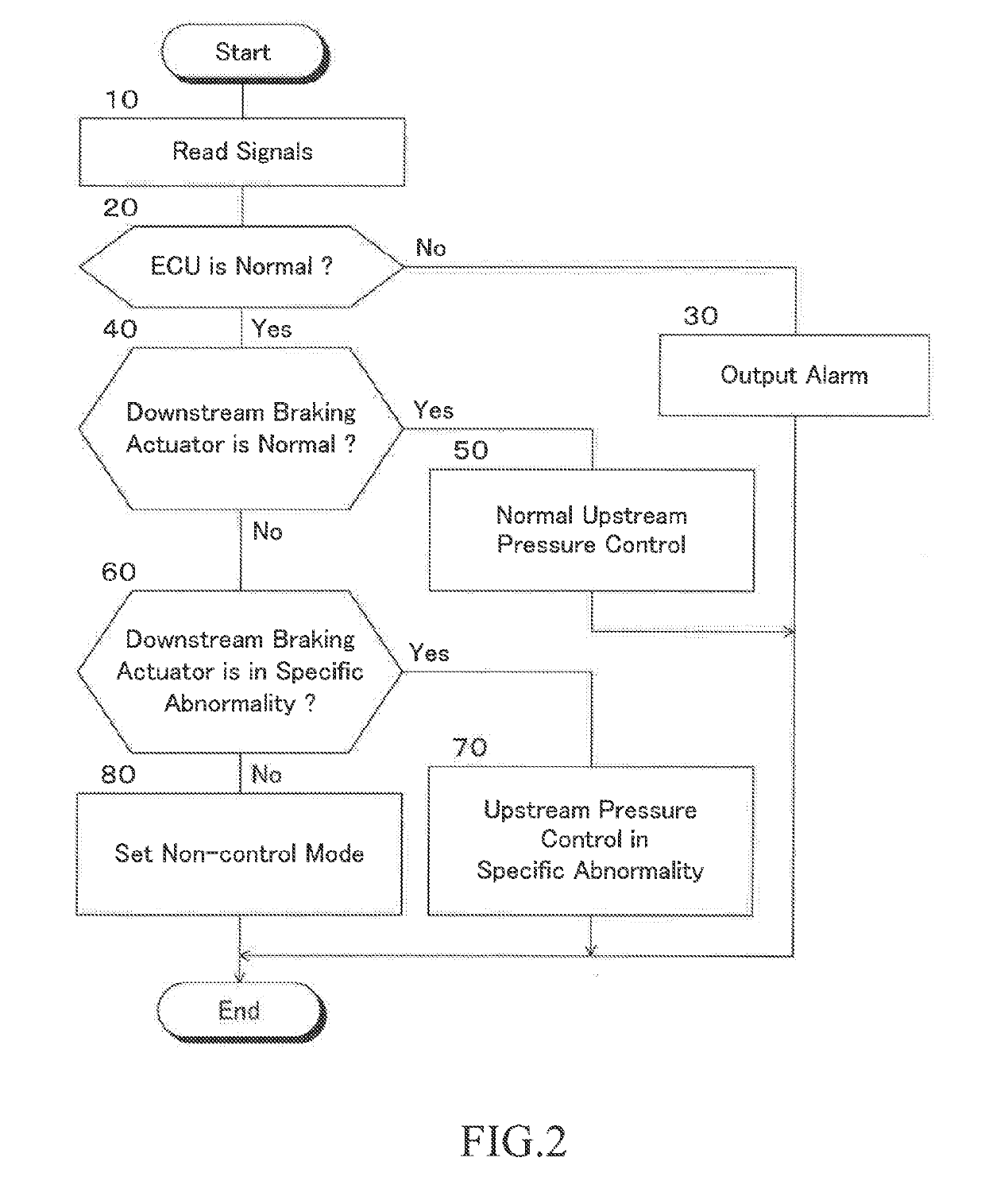
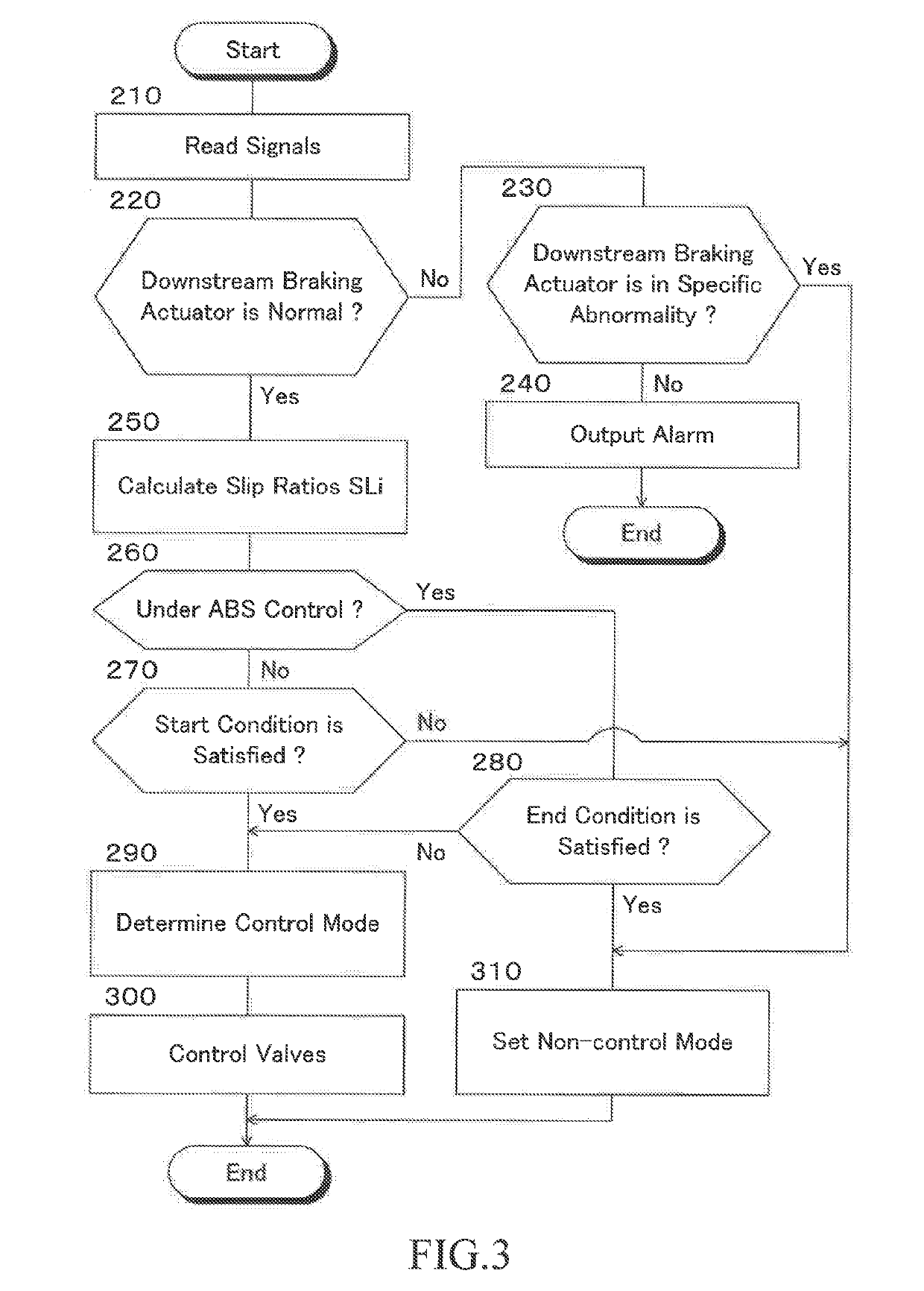
Braking force control apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20190106091A1Reduce braking forceReduce the possibilityHybrid vehiclesBrake control systemsPressure decreaseActuator
A braking force control apparatus is provided which has a first system including a first upstream braking actuator and a first downstream braking actuator, a second system including a second upstream braking actuator and a second downstream braking actuator, and a control unit. When the downstream braking actuator is abnormal and the upstream pressure can be supplied to braking force generating devices, but a braking pressure of any one of the wheels cannot be normally controlled, the control unit select the pressure increasing side control mode out of the front wheel control modes as a first prescribed control mode, select the pressure decreasing side control mode out of the rear wheel control modes as a second prescribed control mode, and to control the first and second upstream pressures in the first and second prescribed control modes.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Medium supply device and image forming apparatus
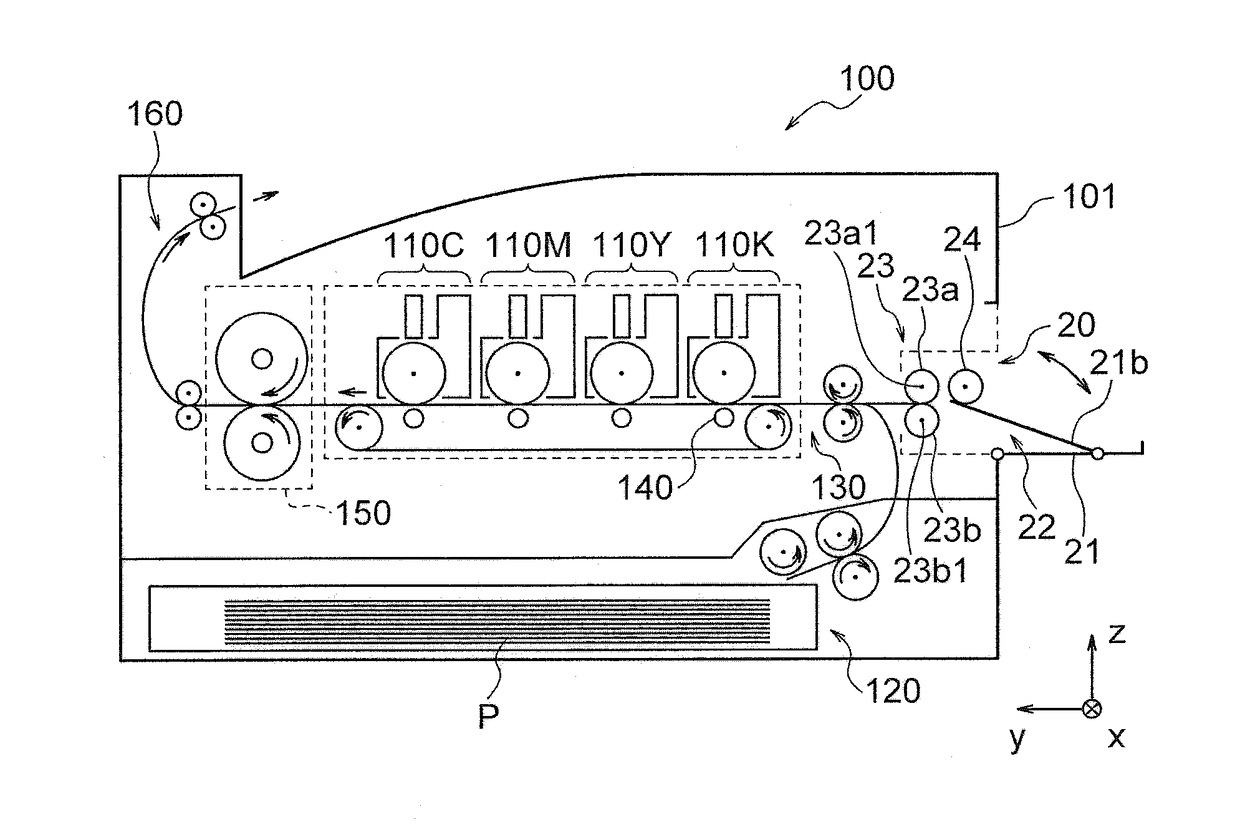
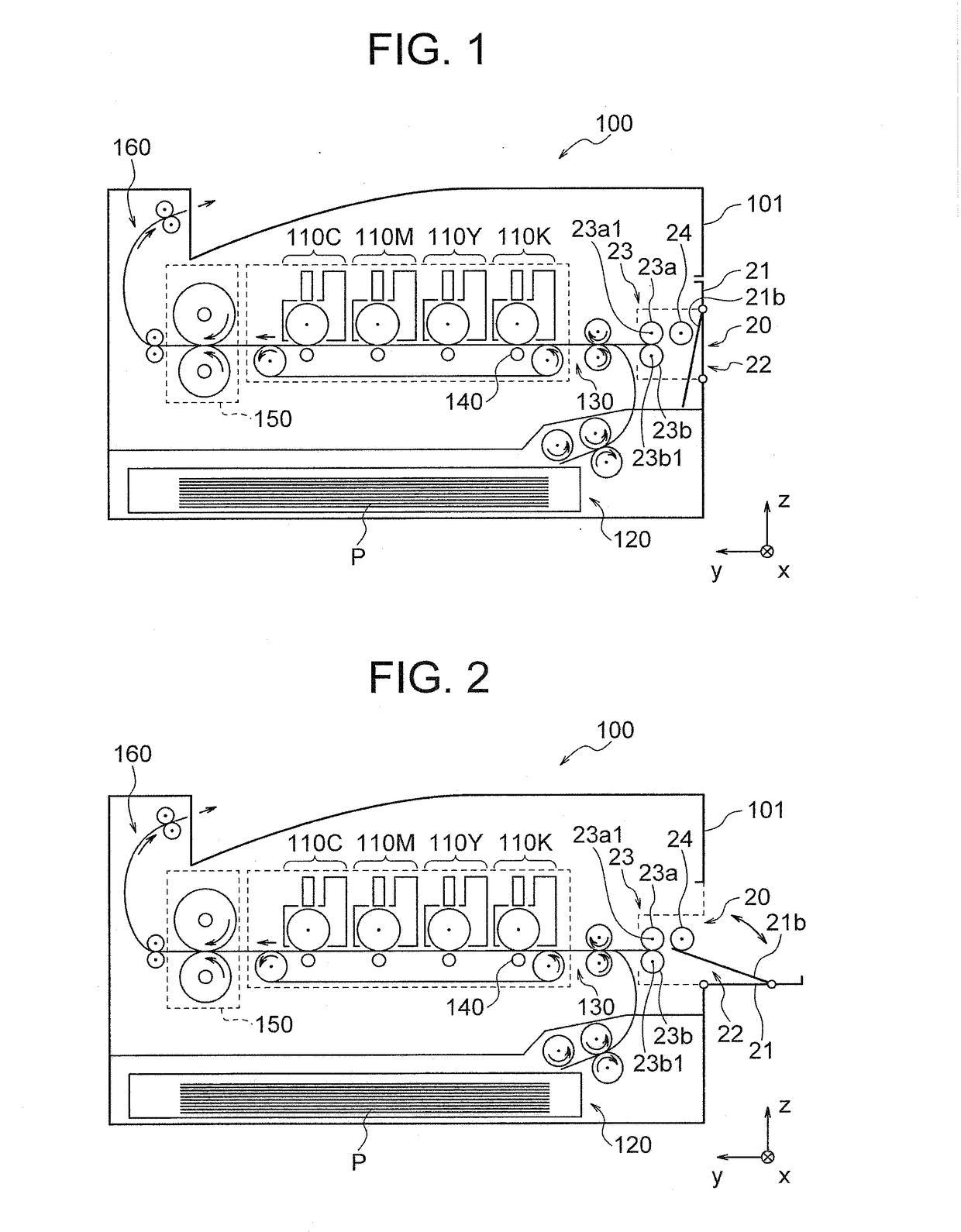
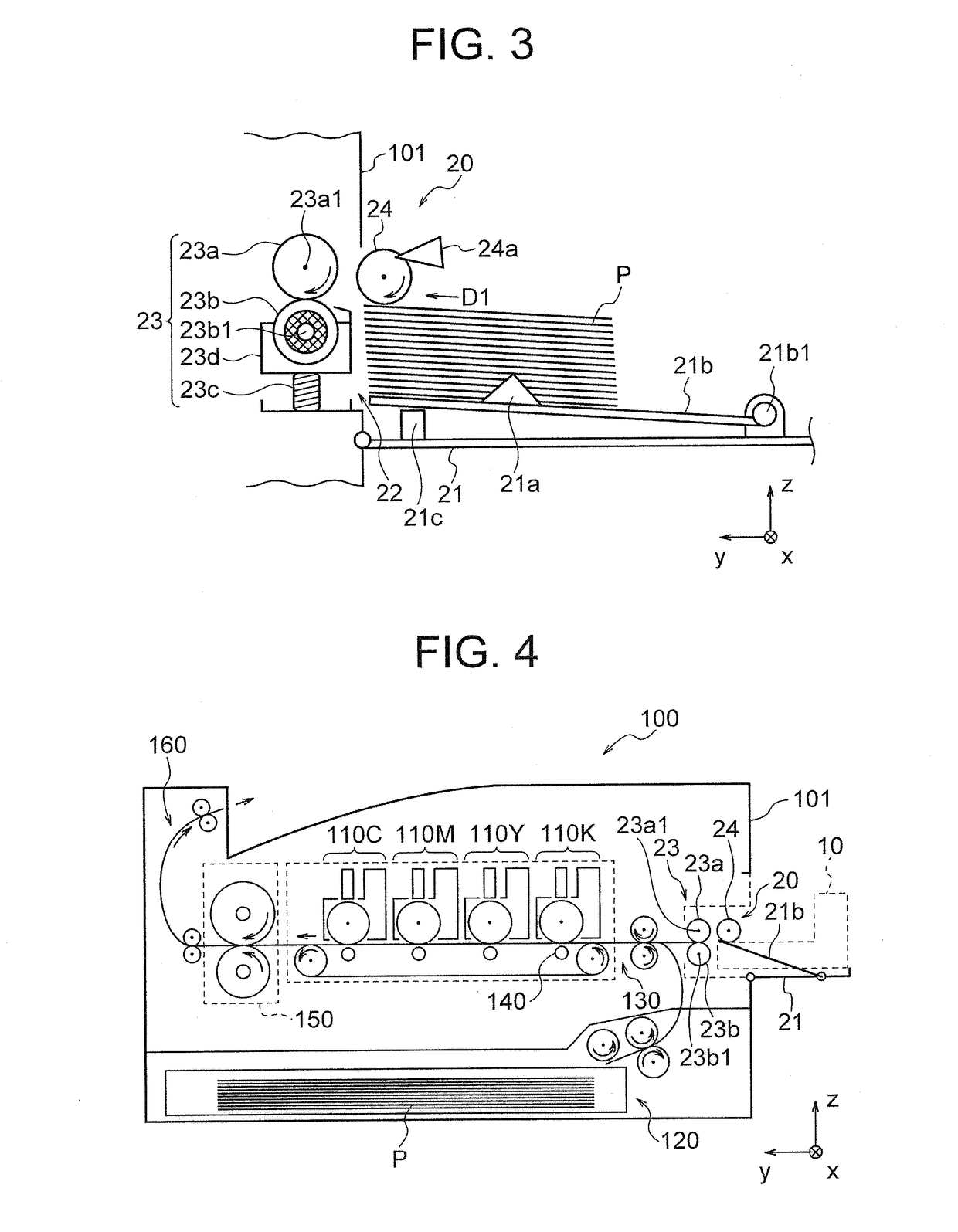
ActiveUS20170368843A1Reduce braking forceReduce generationElectrographic process apparatusOther printing apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Provided is an apparatus that can reduce a braking force of a medium separating mechanism to thereby reduce occurrence of paper jams only by attaching a medium supply device to an image forming apparatus body. The medium supply device is configured to be attached to an image forming apparatus body including a medium separating mechanism, and includes a medium conveying mechanism that supplies a recording medium from stacked recording media to a predetermined position, and first mechanism that reduces a braking force generated in the medium separating mechanism.
Owner:OKI DATA CORP
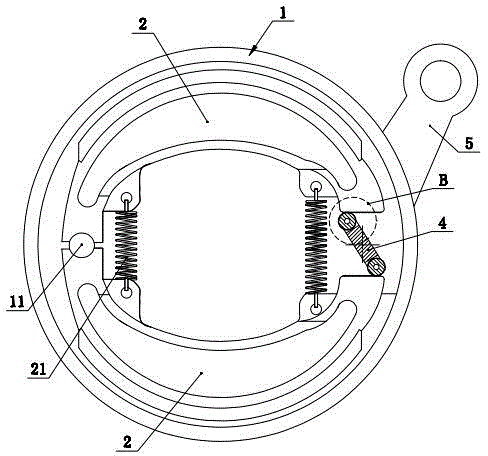
Drum brake
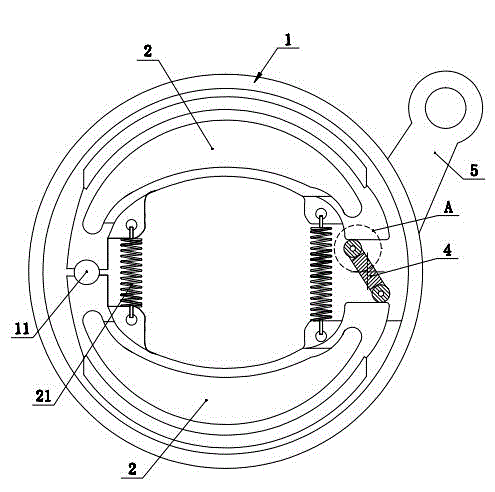
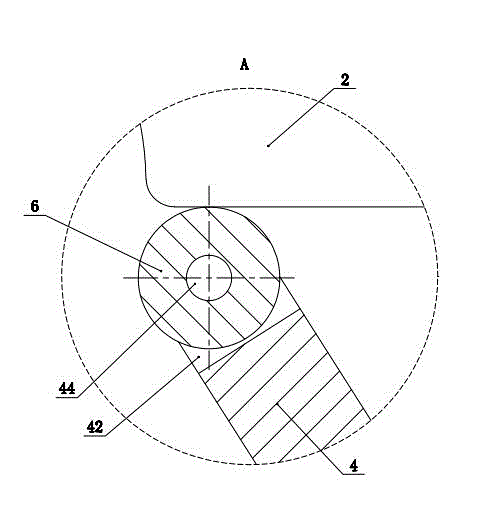
ActiveCN104653662AAchieving Rolling FrictionReduce wearBraking membersDrum brakesRolling resistanceEngineering
The invention discloses a drum brake which comprises a shell, a brake cam shaft and two brake shoes, wherein the two brake shoes are arranged in the shell; the outer end, which is positioned outside the shell, of the brake cam shaft is in driving connection with a brake arm which drives the brake cam shaft to rotate; the inner end, which is positioned inside the shell, of the brake cam shaft is provided with a rectangular block which is defined by two long edges and two short edges; certain ends of the two brake shoes are articulated with the shell, and the other ends of the two brake shoes are expansion brake ends; the rectangular block is positioned between the expansion brake ends of the two brake shoes; the side surfaces of two short edges of the rectangular block are respectively provided with one groove; two sides of the grooves respectively penetrate through the side surfaces of two long edges of the rectangular block; rolling pieces which form rolling friction with the corresponding end surfaces of the brake shoes are movably arranged in the grooves. According to the adopted structure, rolling friction is adopted, so that abrasion can be effectively reduced, and the brake driving force is correspondingly and greatly reduced; furthermore, the rolling pieces capable of realizing rolling friction are simple in structure and convenient to assemble and disassemble.
Owner:朱启东
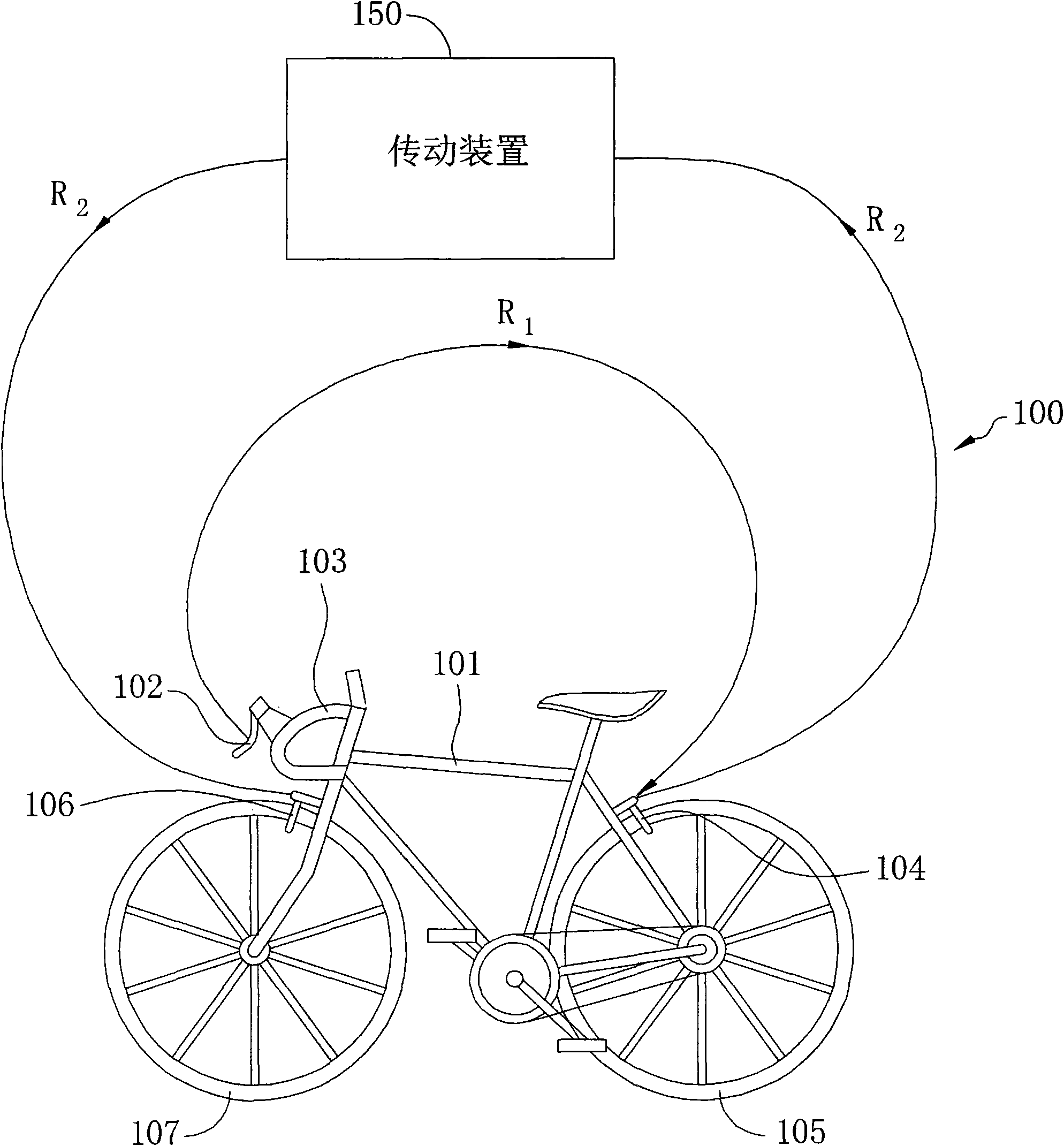
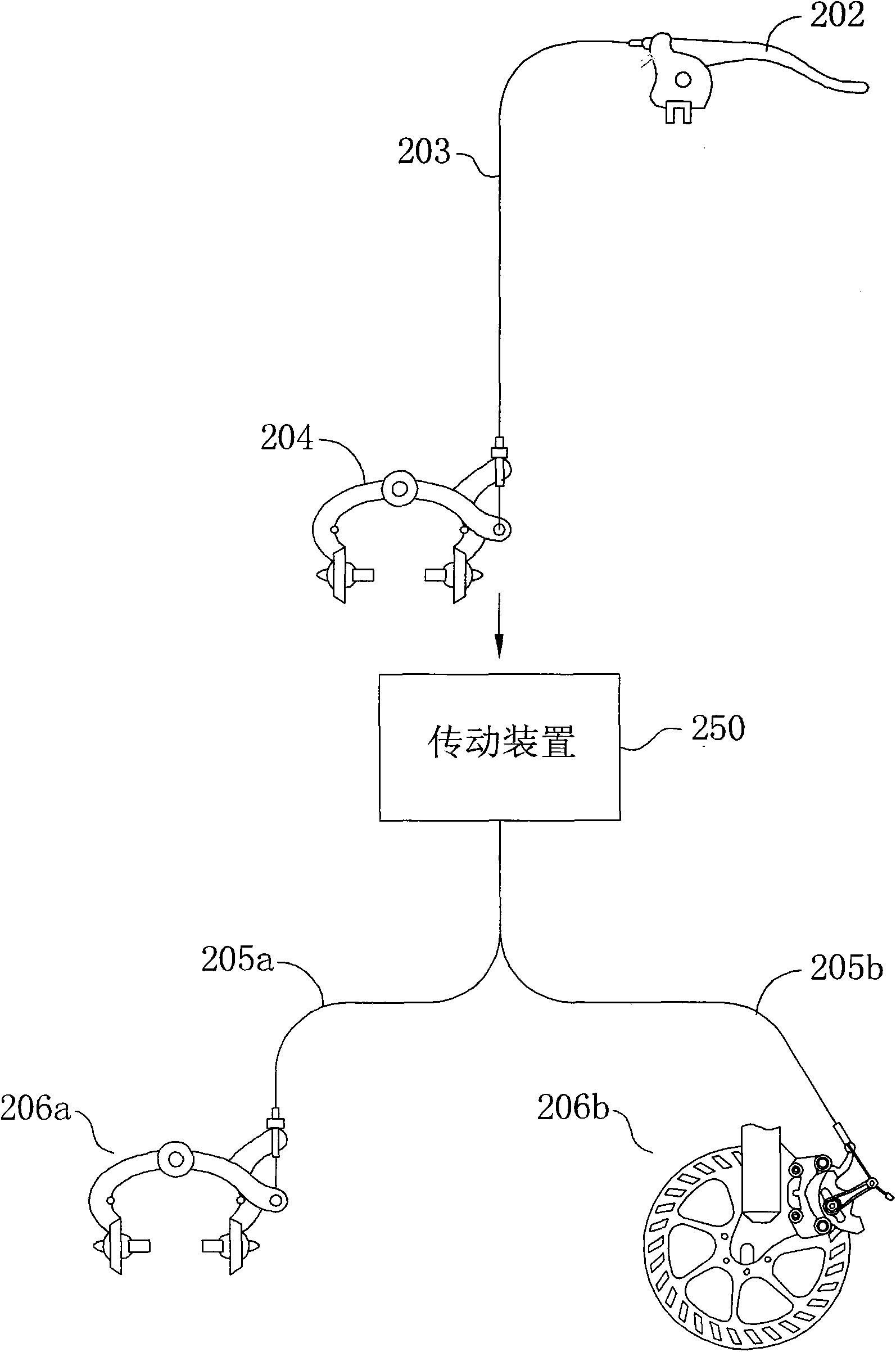
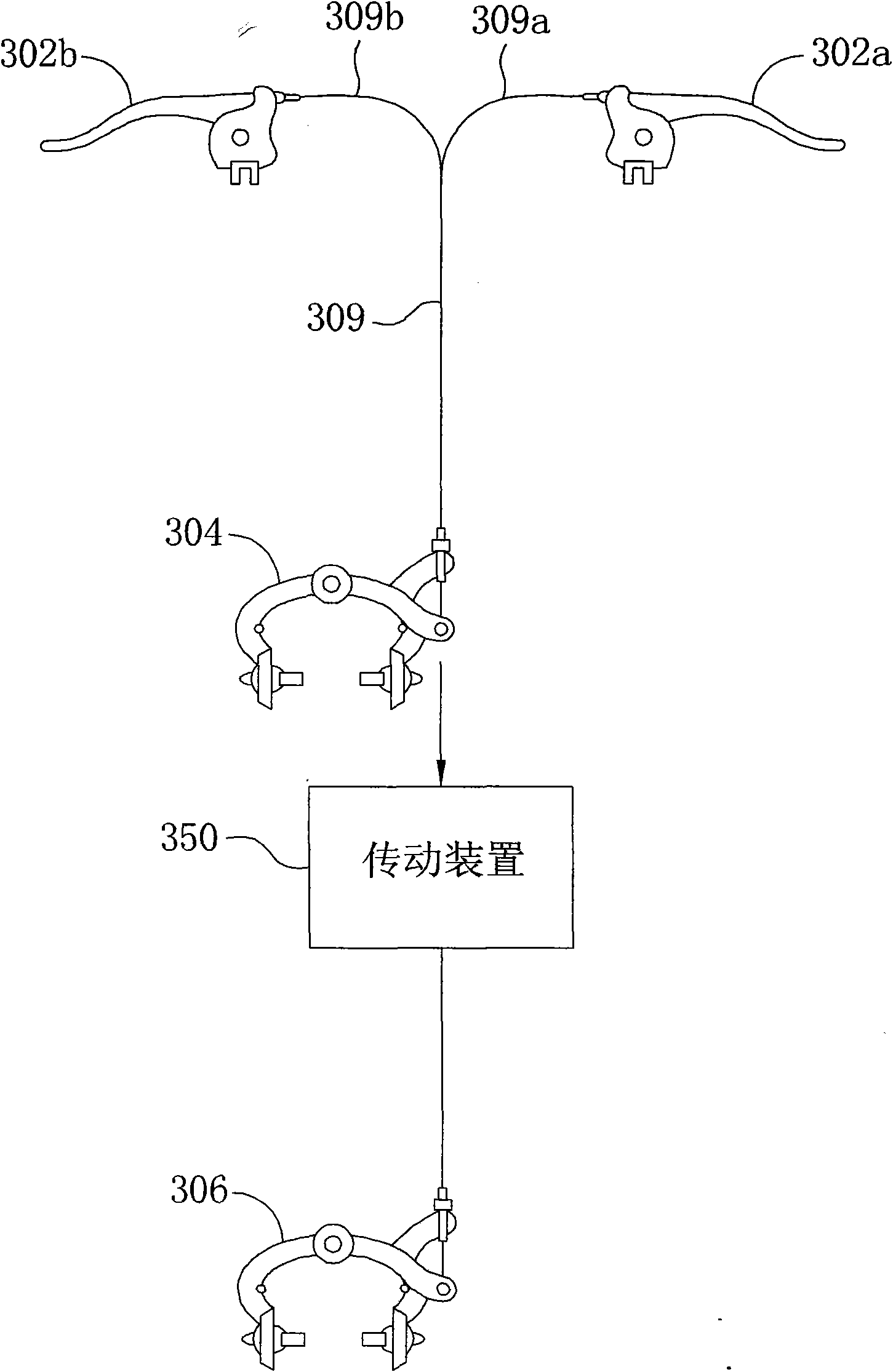
Brake system and method and two-wheeled vehicle using the same
InactiveCN101643105AAdjust brake forceReduce slippageBraking action transmissionCycle brakesBraking systemBrake force
In the specification and drawing a new brake system and a two-wheeled vehicle using the same are described. The new brake system includes a first brake to apply a first brake force on a first wheel ofa vehicle and transfers the first brake force to physically actuate a second brake to brake a second wheel of the vehicle. A transmission device is disclosed to transfer the first brake force to actuate the second brake.
Owner:CONCEPTUALIZED ENG
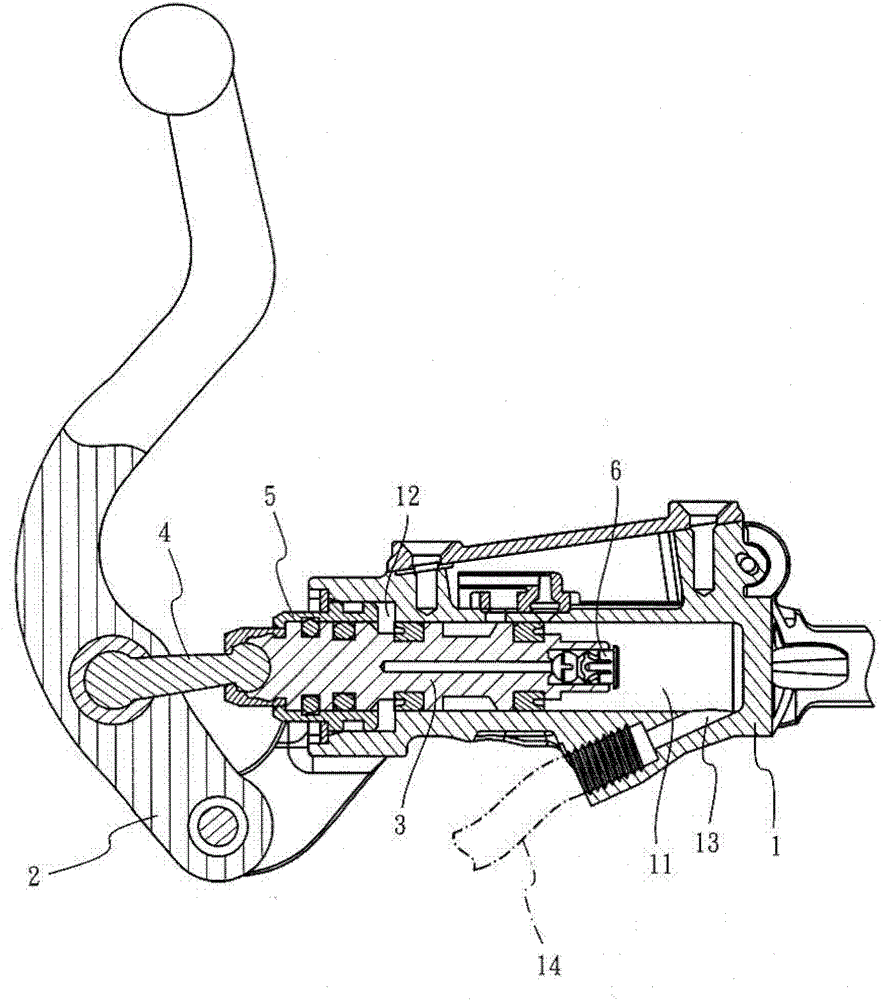
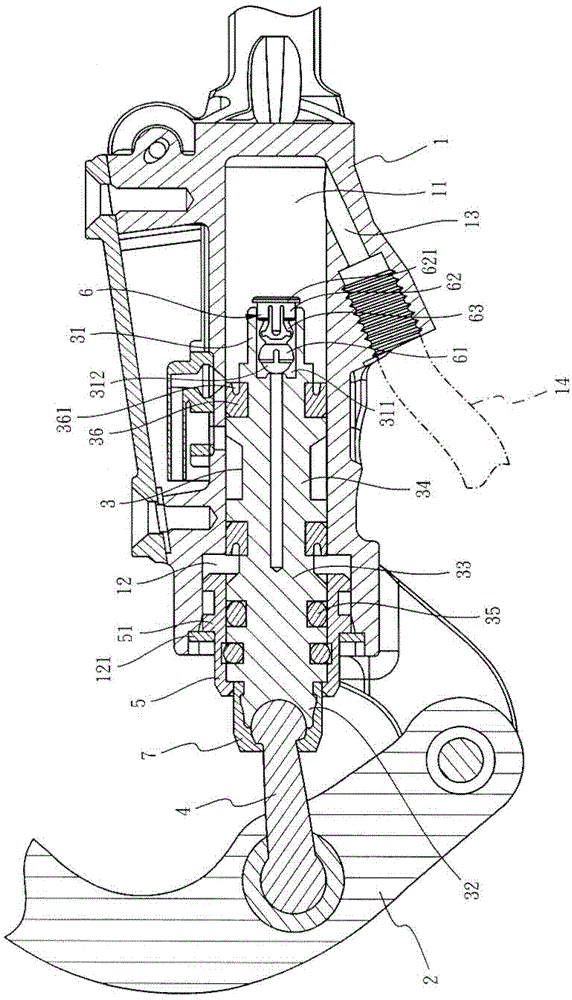
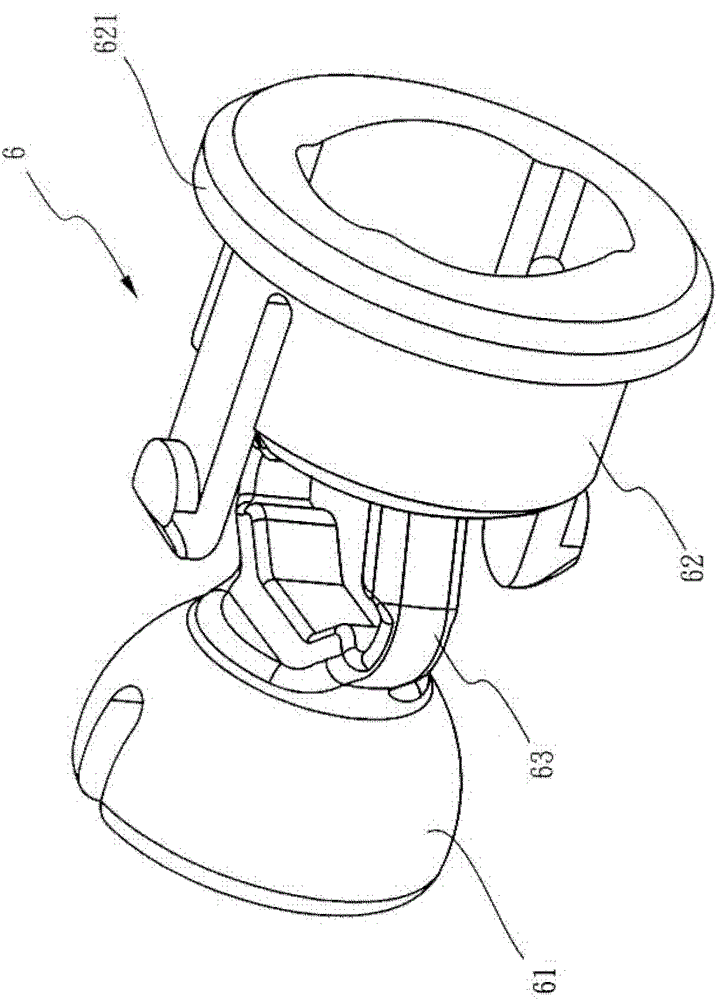
Hydraulic brake sealing device
InactiveCN103373429BAvoid accidentsReduce braking forceCycle brakesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A hydraulic brake sealing device comprises an oil pressure seat, a brake handle, an oil pressure rod, a connecting rod, a sliding pipe sleeve and an elastic member, wherein the oil pressure seat is provided with an oil pressure chamber and an assembling chamber communicated with the oil pressure chamber; one end of the brake handle is pivoted with the oil pressure seat and is correspondingly assembled at the outside of the assembling chamber; the oil pressure rod is assembled to the oil pressure chamber and the assembling chamber movably; a working head located in the oil pressure chamber, an assembling head located at the outside of the assembling chamber, a first sealing section and a second sealing section both connected to the assembling head and the working head in sequence are arranged at one end of the oil pressure rod; two ends of the connecting rod are assembled to the brake handle and the assembling head of the oil pressure rod respectively; the sliding pipe sleeve is arranged in the assembling chamber in a sliding manner and is fixedly sleeved to the first sealing section; the elastic member comprises an assembling part arranged on the working head, an actuating part and two deformation sections connected between the assembling part and the actuating part. When a driver brakes suddenly, the hydraulic brake sealing device can retard braking force and avoids accidents caused by the sudden brake such as deadlock and slipping of wheels relative to the ground surface.
Owner:ASHIMA LTD
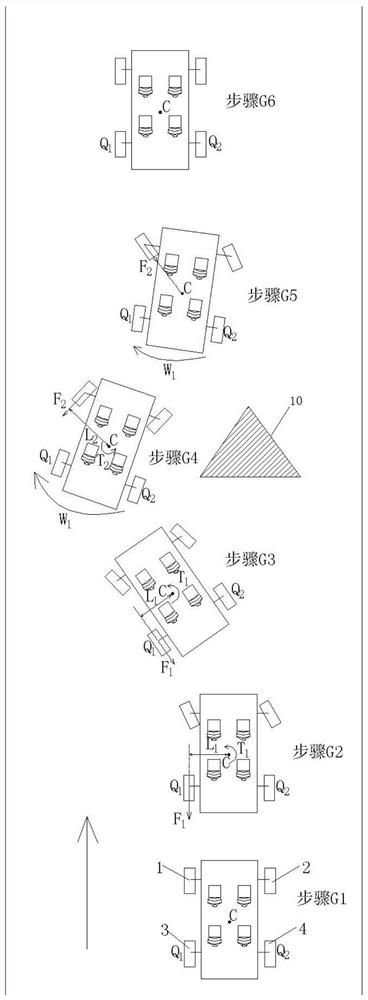
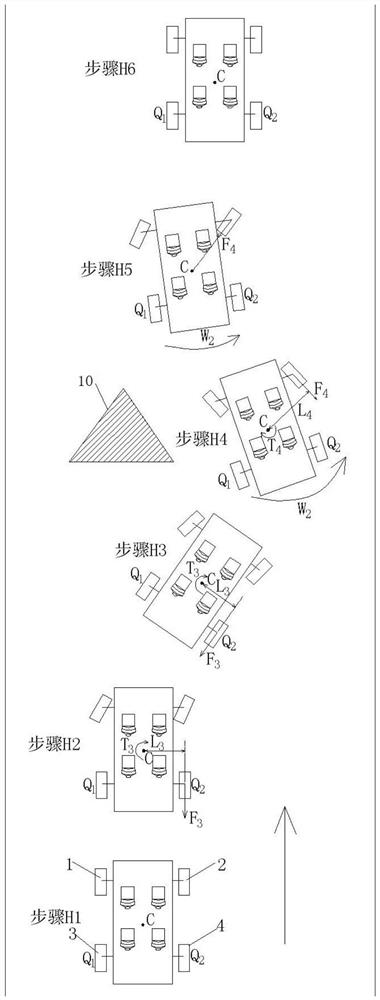
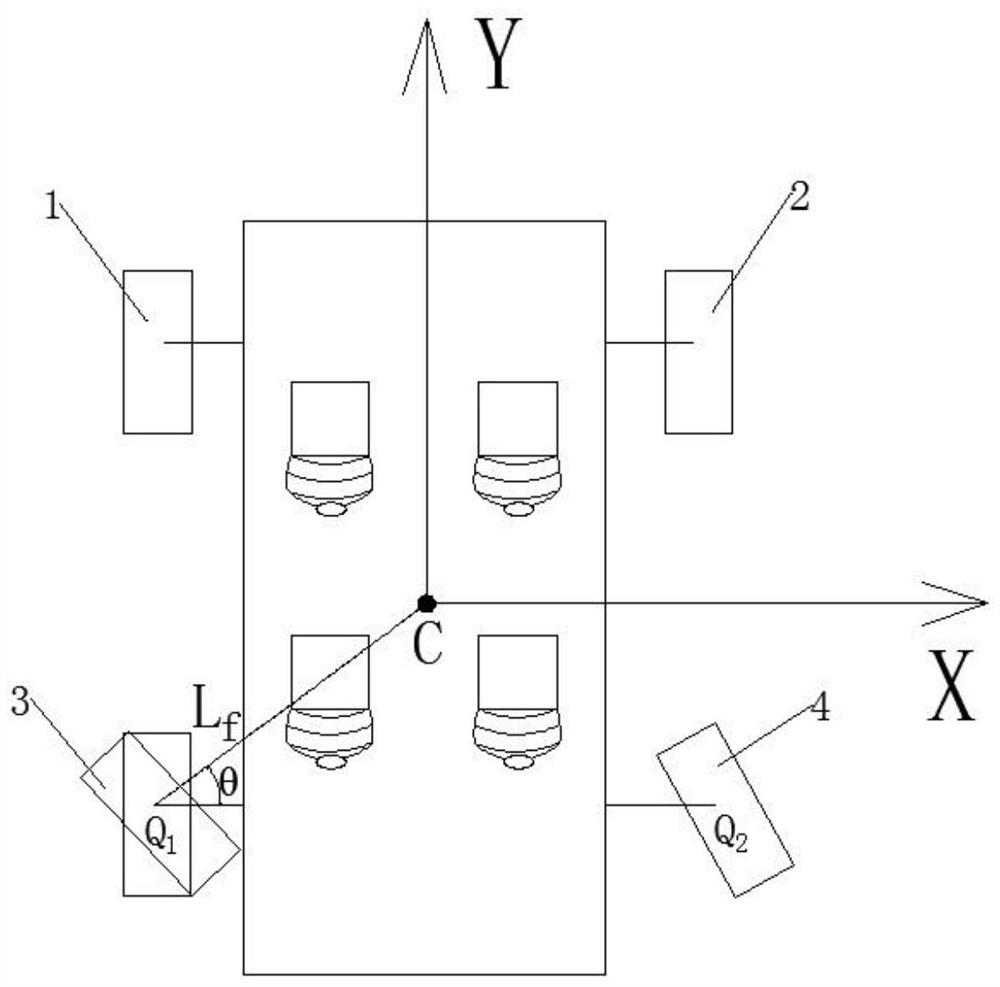
Rear-wheel-steering-based ESP enhanced control method for rear-drive vehicle
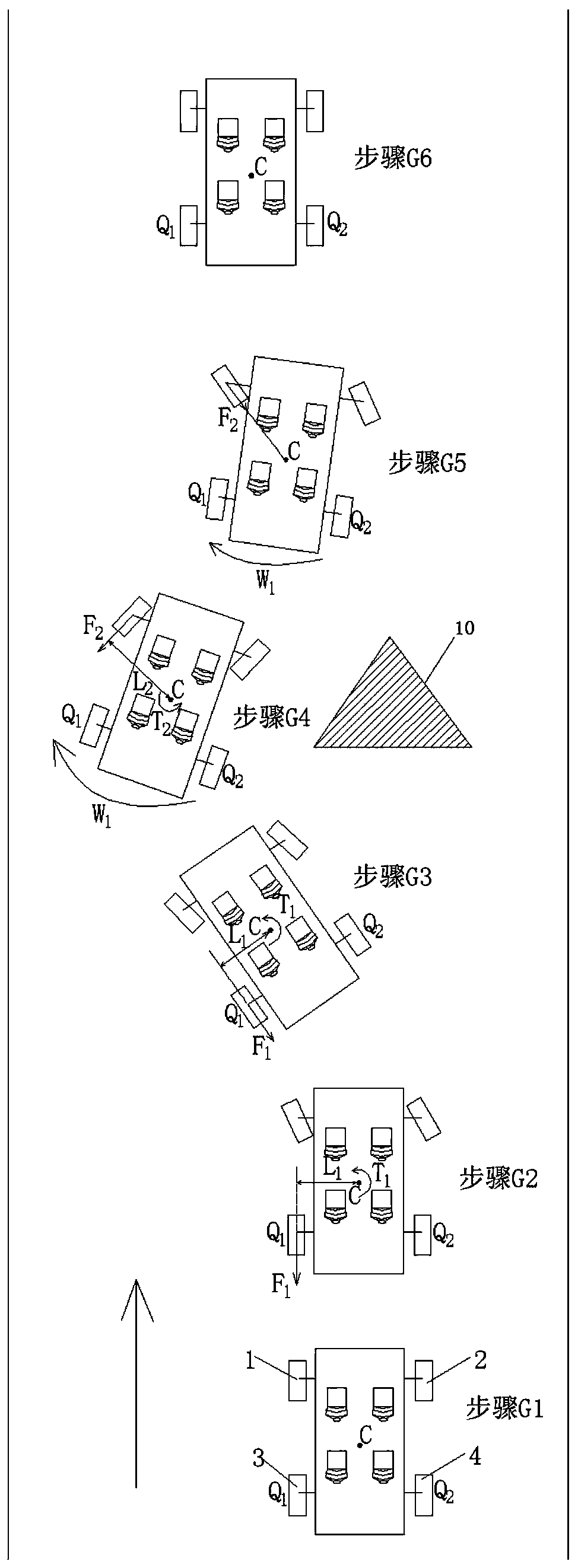
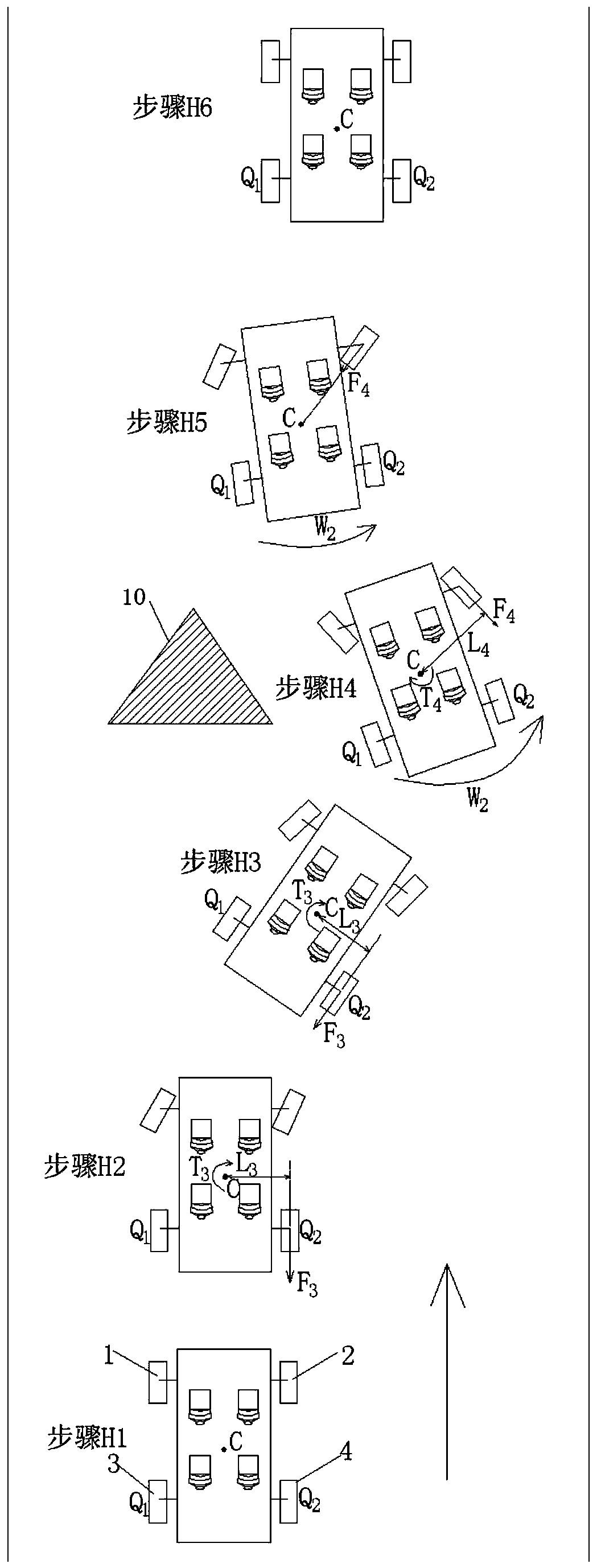
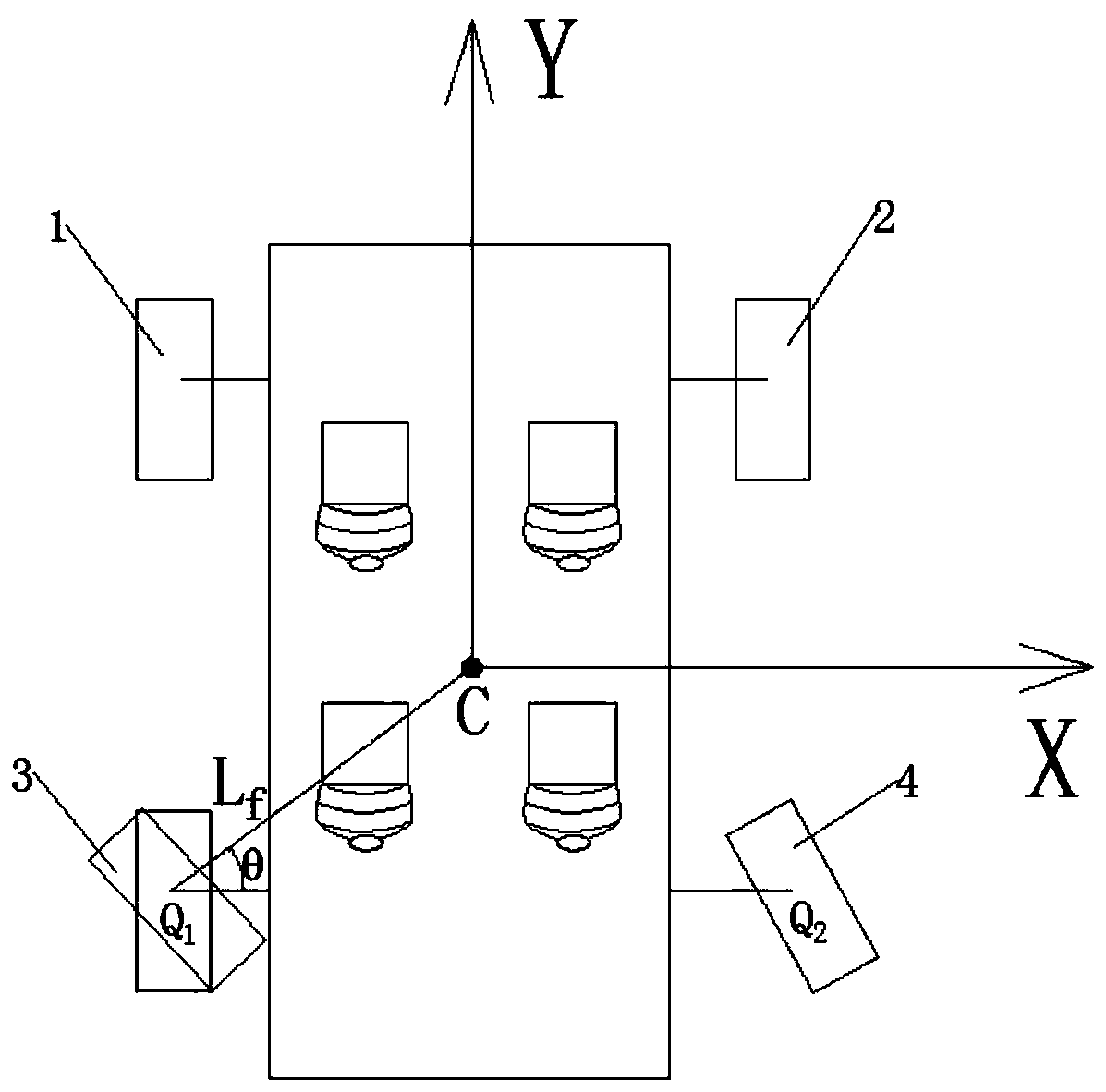
The invention discloses a rear-wheel-steering-based ESP enhanced control method for a rear-drive vehicle. The control method comprises a control process for performing left deflection obstacle avoidance and a control process for performing right deflection obstacle avoidance on a vehicle in linear driving. In the process of obstacle avoidance through the control method, the distance between the Zaxis and the center Q1 of a left rear wheel serves as a force arm Lf or the distance between the Z axis and the center Q2 of a right rear wheel serves as a force arm Lr, so that the force arm Lf or Lrkeeps the maximum value all the time in the process of torque control through the resultant force of the acting force of the rear wheels. When the same control torque is needed, the braking force resultant force applied to the rear wheels can be reduced, and particularly, the effect can be achieved under the road surface conditions with low ground adhesion coefficients, such as wet and slippery or iced road surfaces; and under the condition that the same acting force resultant force is applied to the rear wheels, larger control torque can be generated on the Z axis, and a vehicle head can quickly steer to avoid colliding with obstacles when the vehicle avoids the front obstacles.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Braking force control apparatus
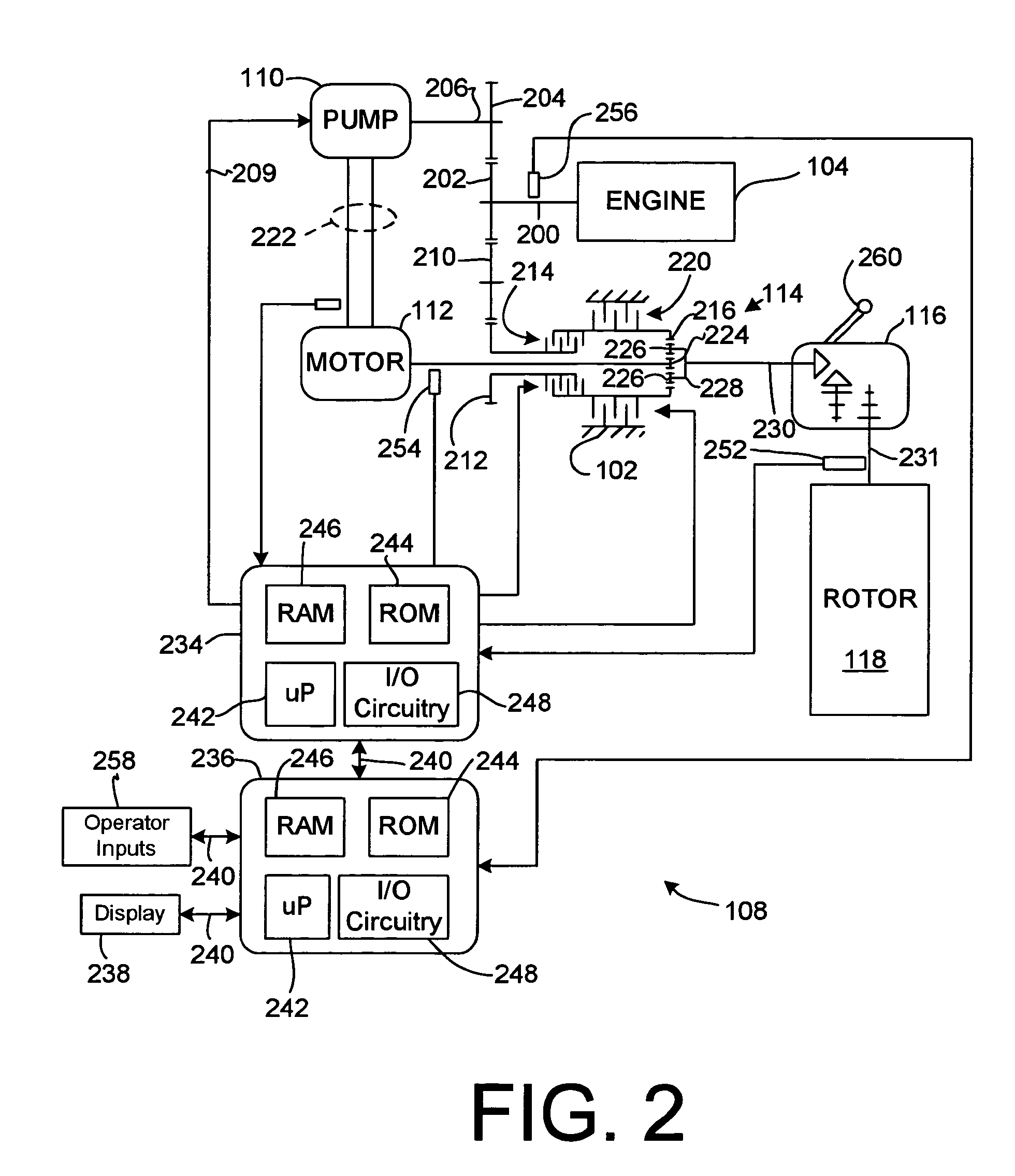
ActiveUS11400899B2Reduce braking forceReduce the possibilityBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionPhysicsElectrical control
A braking force control apparatus includes a fluid pressure generation mechanism, a braking mechanism and an electric control unit. The fluid pressure generation mechanism causes a braking mechanism to generate a required fluid pressure. The braking mechanism applies a braking force depending on the required fluid pressure to each of wheels through the pressing of a braking member against a rotating rotary member due to the required fluid pressure. The electronic control unit performs, when the required fluid pressure is generated and a vehicle state shifts from a running state to a stopped state at a first time point, stop-time boost control to boost the required fluid pressure at and after the first time point.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Apparatus and method for placing and tensioning an aerial, rope through a traveler of a power line
ActiveUS11254551B2Fast disconnectionReduce tensionUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftUncrewed vehicleControl theory
An apparatus for controlling tension in a pulling rope that is attached to a flying, unmanned aerial device or drone may utilize a cylinder around which the rope is wound, a shaft that longitudinally passes through the cylinder, a disc brake rotor that is mounted to the shaft, a brake caliper that is mounted circumferentially at a periphery of the disc brake rotor, and a brake lever that tensions a cable that is attached to, and movable to control movement of, the brake caliper, which may be hydraulic, against surfaces the disc brake rotor. The brake lever may be hand actuated and mounted to a handlebar. A frame may be part of the apparatus and support apparatus components and may have a protruding hitch portion that inserts into a vehicle's receiver hitch. An adjustable pulling rope guide support through which the rope is threaded, mounts to the frame.
Owner:QUANTA ASSOC
Tractor hoist with speed adjusted by super capacitance set storage type generator
InactiveCN101382047BAvoid damageReduce braking forceDrilling rodsDrilling casingsCapacitanceDrivetrain
The present invention relates to a super capacitance assembly energy storage type electric motor speed regulation tractor hoist. The tractor hoist consists of a three-phase alternating-current supply air switch, a charge power supply module, a capacitance assembly energy accumulator, a DC speed regulation module, a control panel, a main electric motor, a clutch, a gear shifting box, a power drive system, a winch clutch, a winch, an auxiliary brake clutch, an exceeding type clutch, an auxiliary brake DC motor, a charger, an energy accumulator, a bottom car system, a hydraulic system and a derrick system. The input and output ends of the three-phase alternating-current supply air switch are connected with an external power supply and the charge power supply module respectively; the charge power supply module, the capacitance assembly energy accumulator, the DC speed regulation module and the main electric motor are connected sequentially; the main electric motor is connected with the winch through the clutch, the gear shifting box and the power drive system in order; and an auxiliary brake system consisting of the auxiliary brake clutch, the exceeding type clutch and the auxiliary brake DC motor is arranged on the other end of the winch in order. The tractor hoist which has a reasonable design and reliable work can save energy, reduce energy consumption, and avoid damages on an electric network caused by a pulse power supply due to discontinuous power utilization.
Owner:盘锦禹帝科技实业有限公司
Vehicle control apparatus
PendingUS20210276521A1Reduce braking forceReduce forceBraking systemsChange controlMechanical engineering
A vehicle control apparatus executes a wheel speed change control to control speeds of first road wheels and a second road wheel to a lower limit wheel speed or more when braking forces are applied to the first and second road wheels, and at least one of the speeds of the first and second road wheels becomes lower than the lower limit wheel speed. A vehicle speed change control executes a first increase-decrease control which alternately executes a first increase control to increase braking forces applied to the first road wheels together and a first decrease control to decrease the braking forces applied to the first road wheels together and (ii) a second increase-decrease control which increases and decreases the braking force applied to the second road wheel.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
ESP Enhanced Control Method for Rear-drive Vehicle Based on Rear-wheel Steering
The invention discloses an ESP enhanced control method for a rear-wheel drive vehicle based on rear wheel steering, including a control method for how to avoid obstacles by left deflection and a control method for obstacle avoidance by right deflection when the vehicle is running straight; In the process of obstacles, align the Z axis with the left rear wheel center Q 1 The distance as the moment arm L f Or align the Z axis with the right rear wheel center Q 2 The distance as the moment arm L r , so that the moment arm L f or L r Always maintain the maximum value during the torque control process using the resultant force of the rear wheels; when the same control torque is required, it is beneficial to reduce the resultant braking force applied to the rear wheels, especially on wet or icy roads It works on road conditions with a low ground adhesion coefficient; when the same force is applied to the rear wheels, it can generate a greater control torque on the Z axis, which is conducive to the car's front speed when avoiding obstacles in front of it. Steer to avoid hitting obstacles.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com