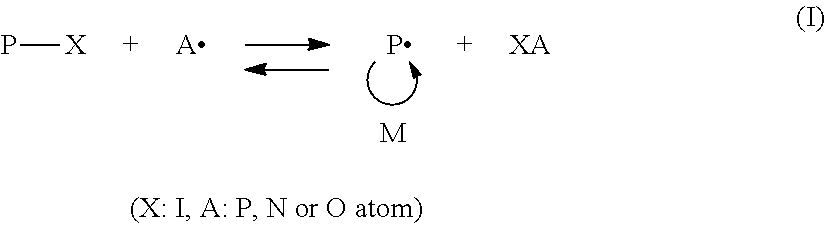Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Easily obtained" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
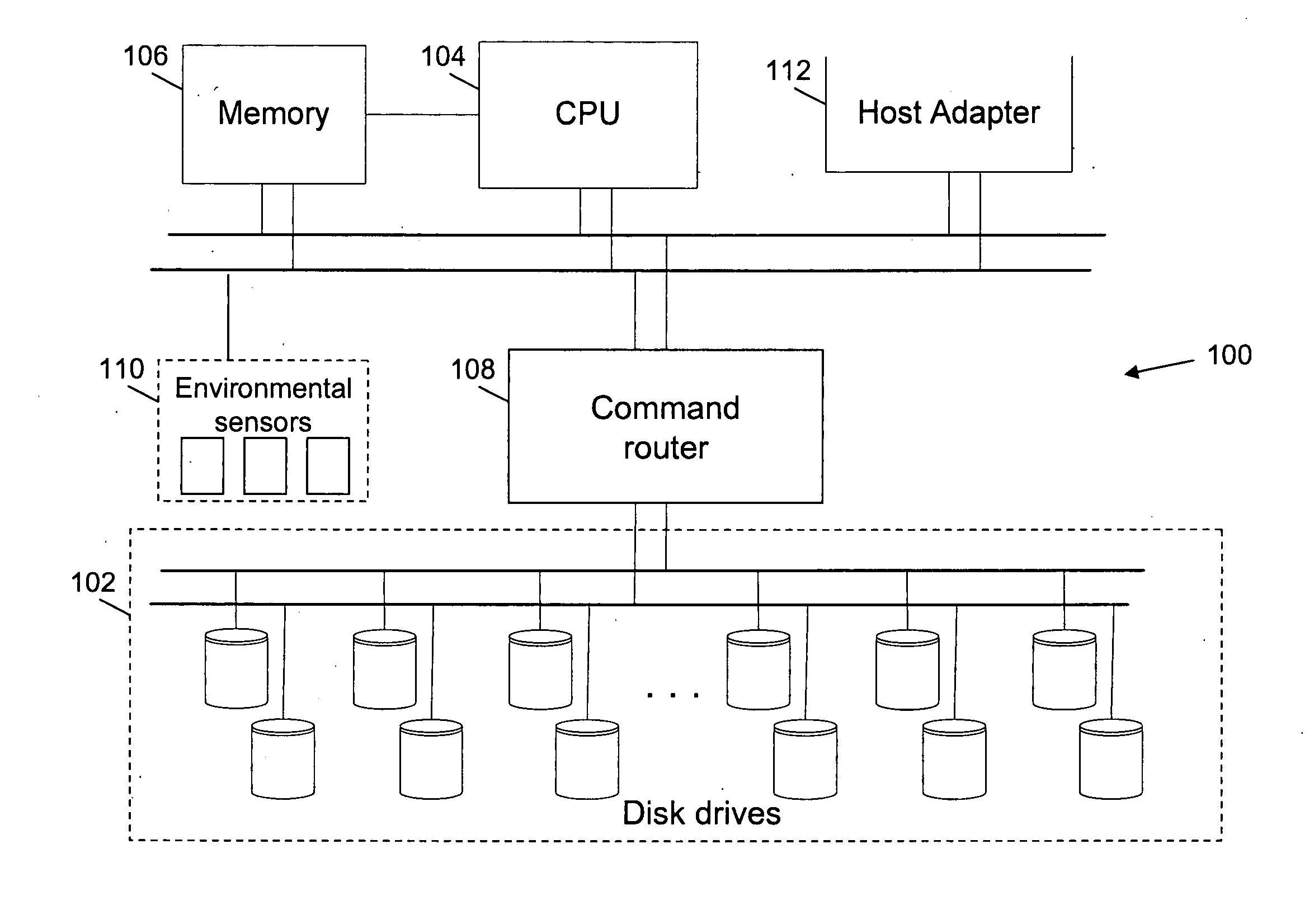
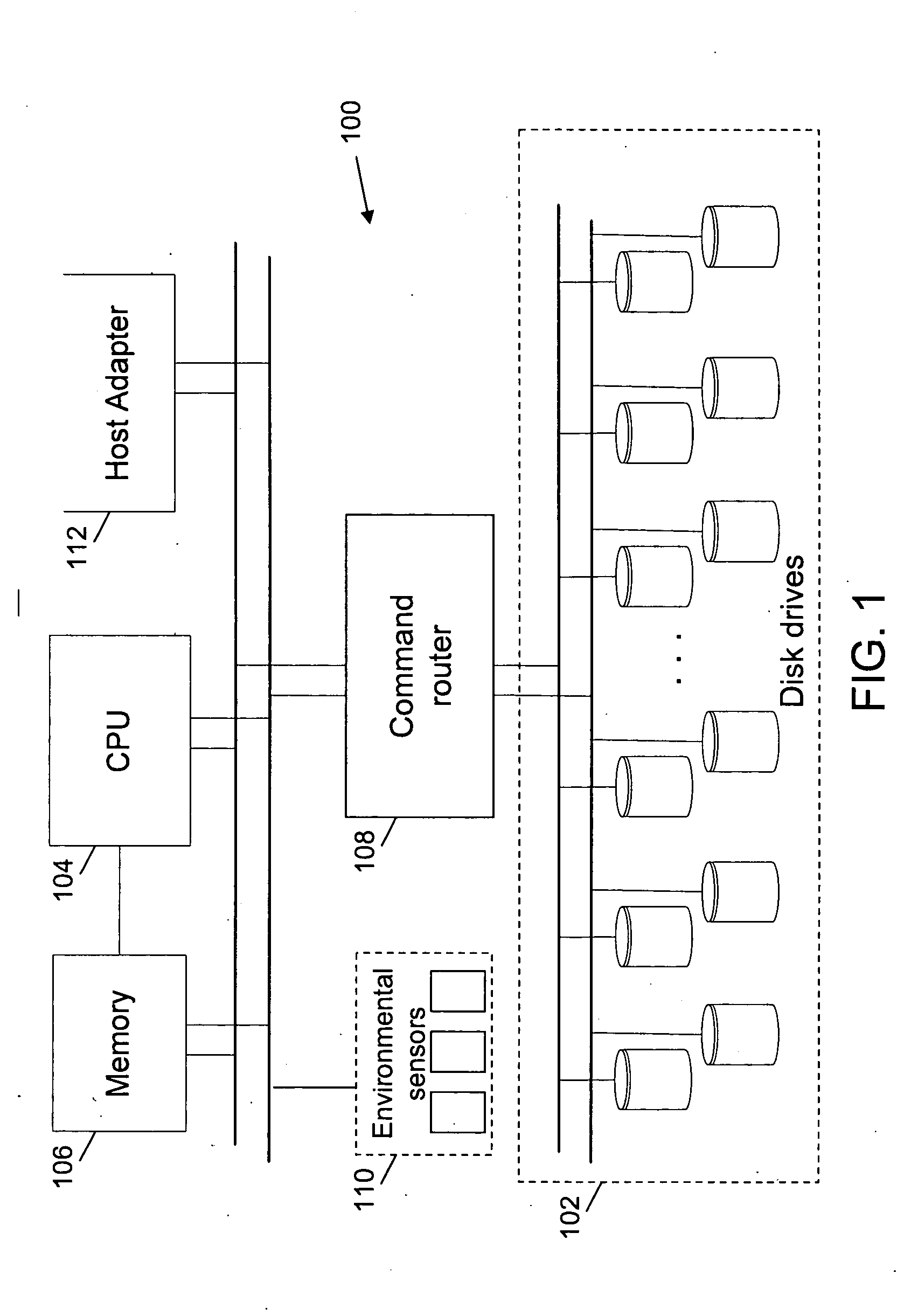
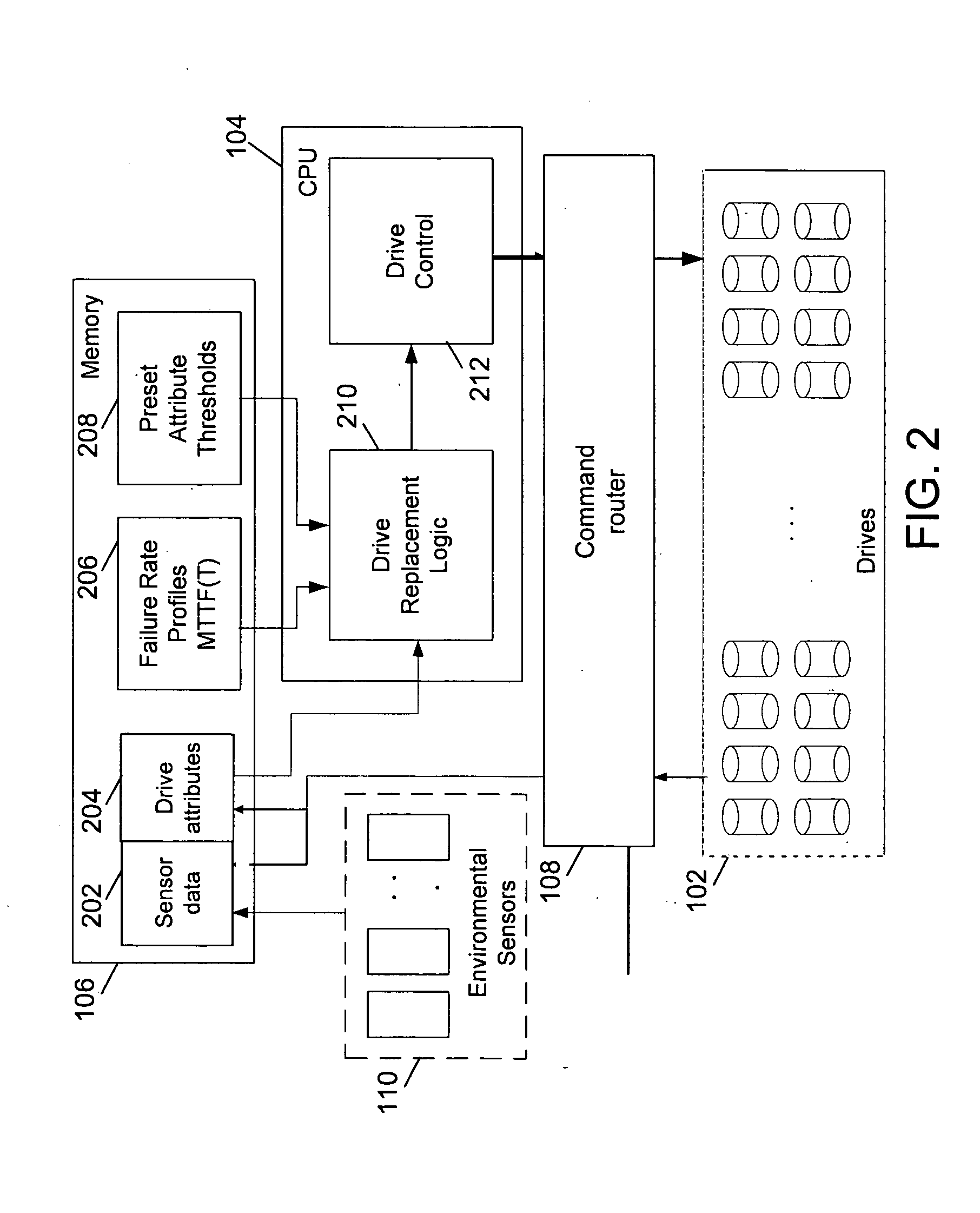
Method and system for proactive drive replacement for high availability storage systems
ActiveUS20050060618A1Avoid failureEasily obtainedRecord information storageReliability/availability analysisHigh availabilityEarly onset
Methods for preventing the failure of disk drives in storage systems are disclosed. A system and a computer program product for preventing the failure are also disclosed. Factors relating to the aging or early onset of errors in a disk drive are monitored. These factors are then compared to thresholds. In case the thresholds are exceeded, an indication for the replacement of the disk drive is given. Sudden rises in the factors are also used to indicate the impeding failure of disk drives.
Owner:COPAN SYST INC +1
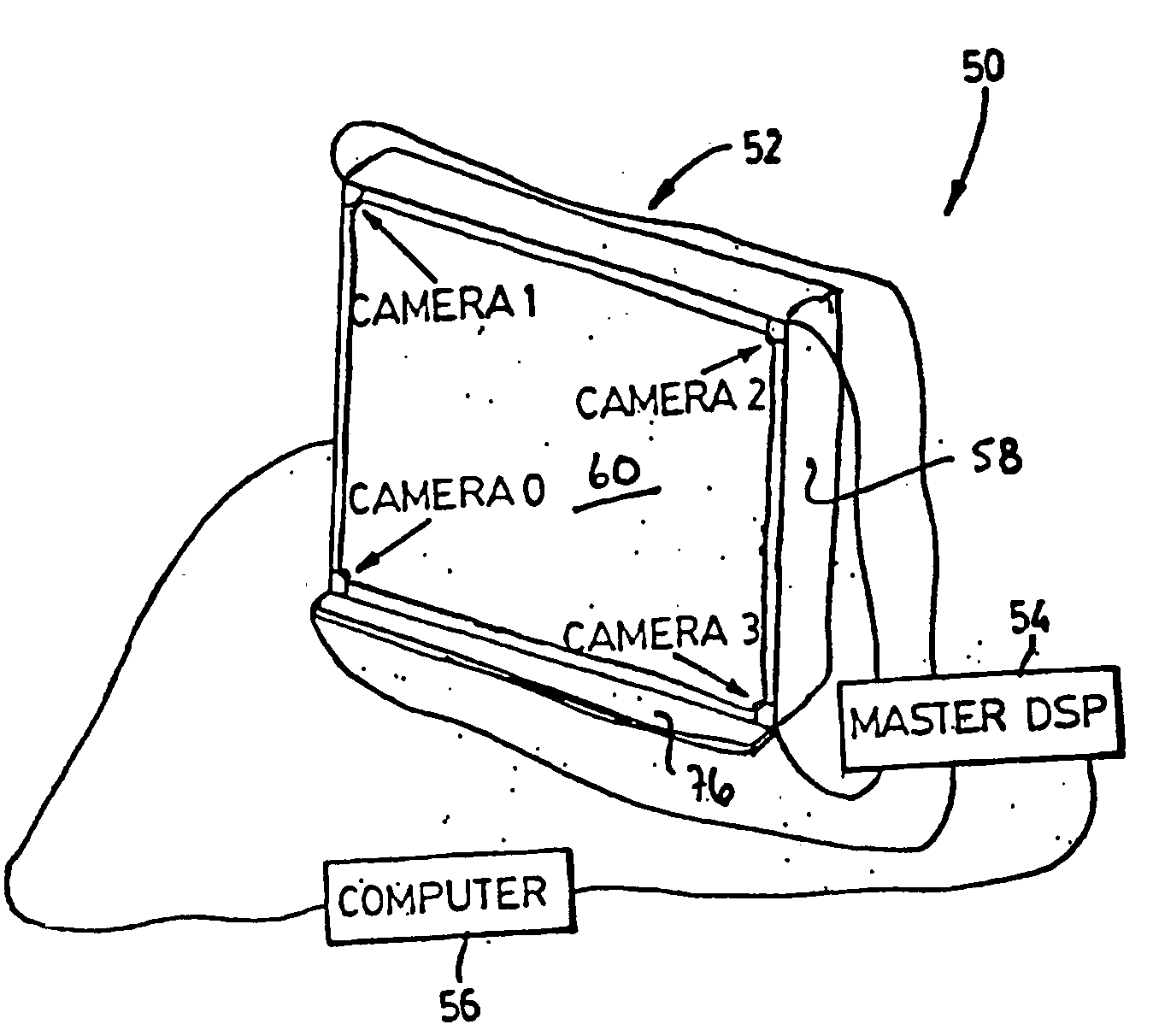
Apparatus for detecting a pointer within a region of interest
ActiveUS20050178953A1Easily obtainedLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansCounting objects on conveyorsRegion of interestLight source
An apparatus for detecting a pointer within a region of interest includes at least one pair of imaging devices. The imaging devices have overlapping fields of view encompassing the region of interest. At least one light source provides illumination across the region of interest and is within the field of view of at least one of the imaging device. A filter is associated with the at least one imaging device whose field of view sees the light source. The filter blocks light projected by the light source to inhibit the imaging device from being blinded by the projected light.
Owner:SMART TECH INC (CA)
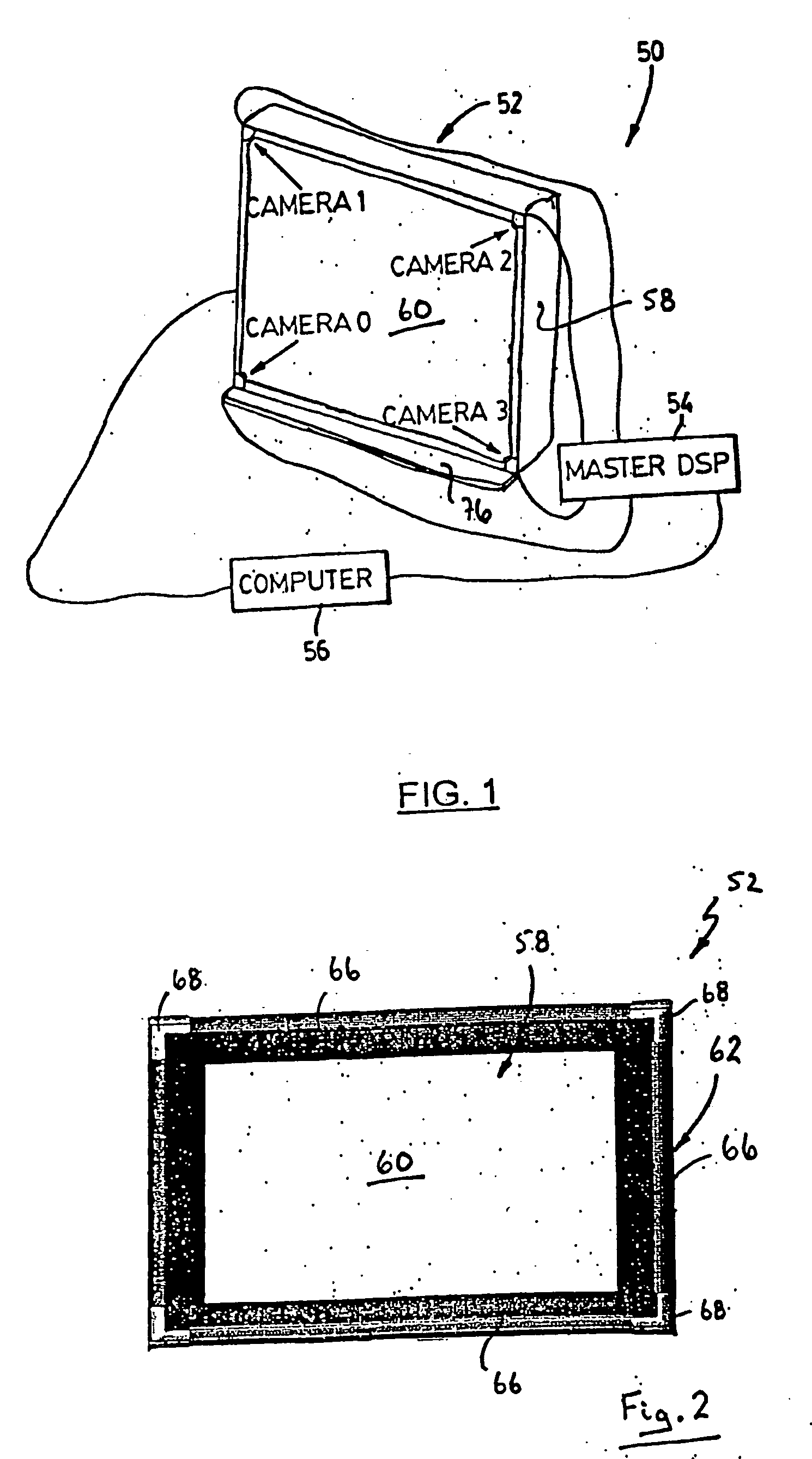
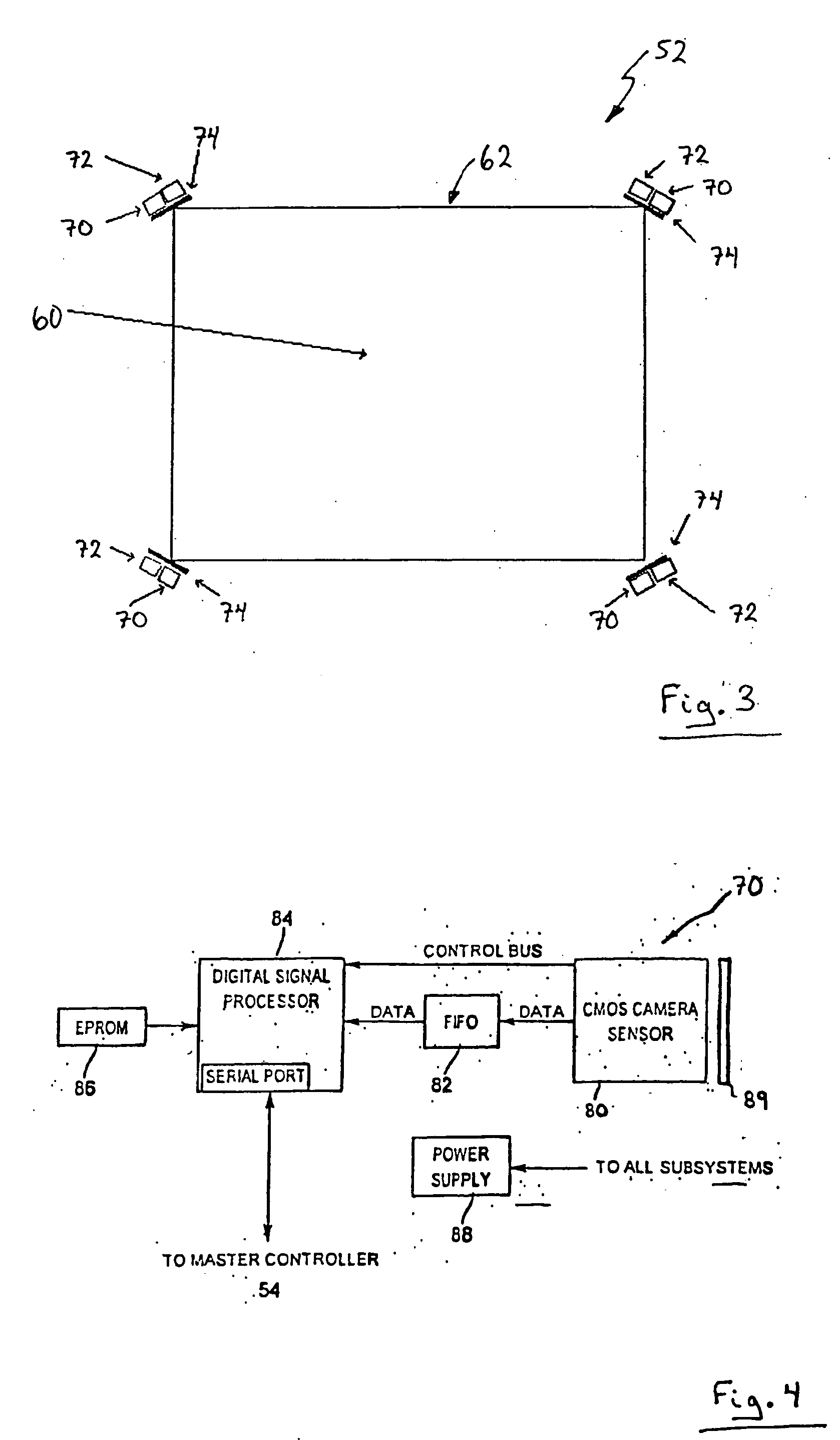
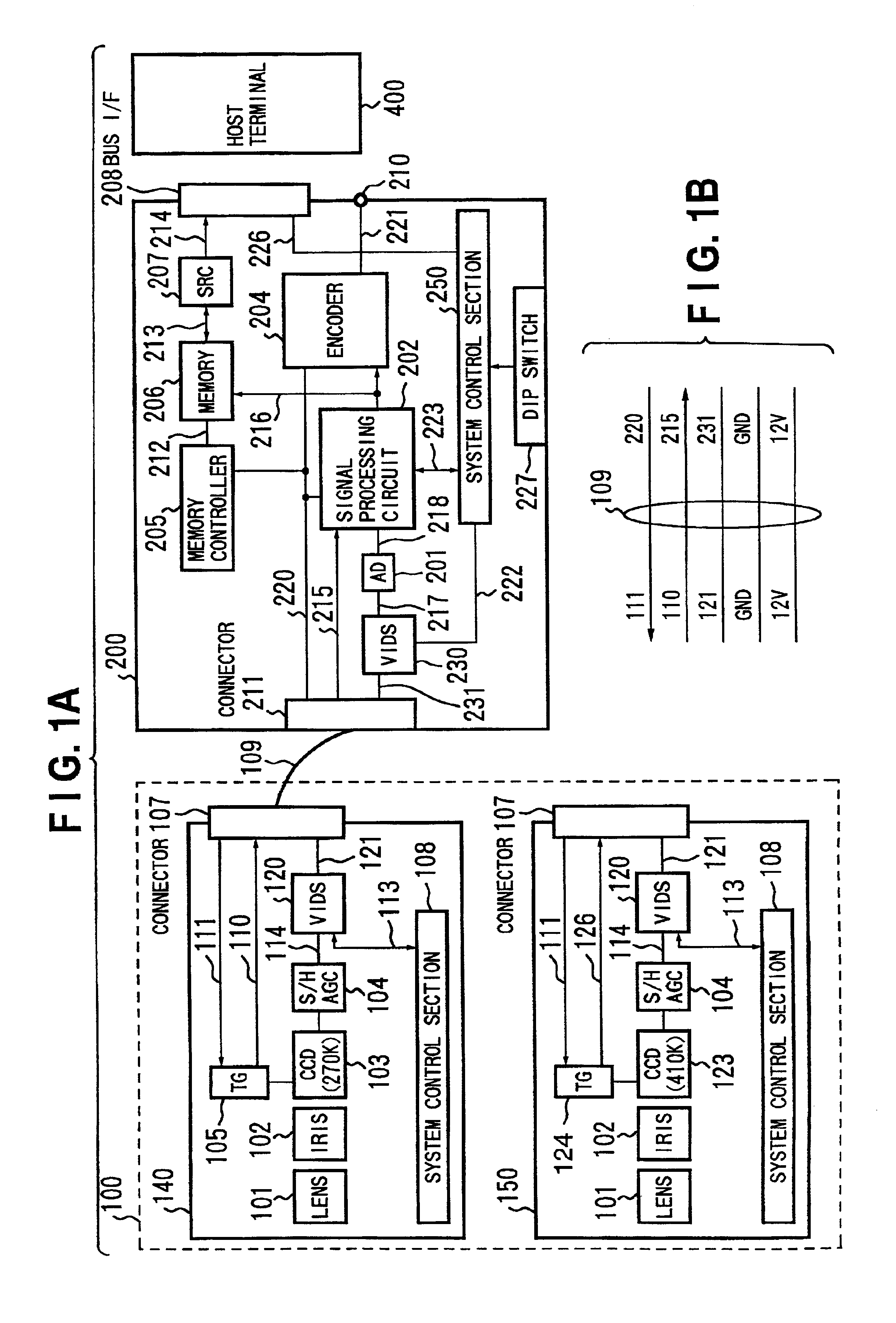
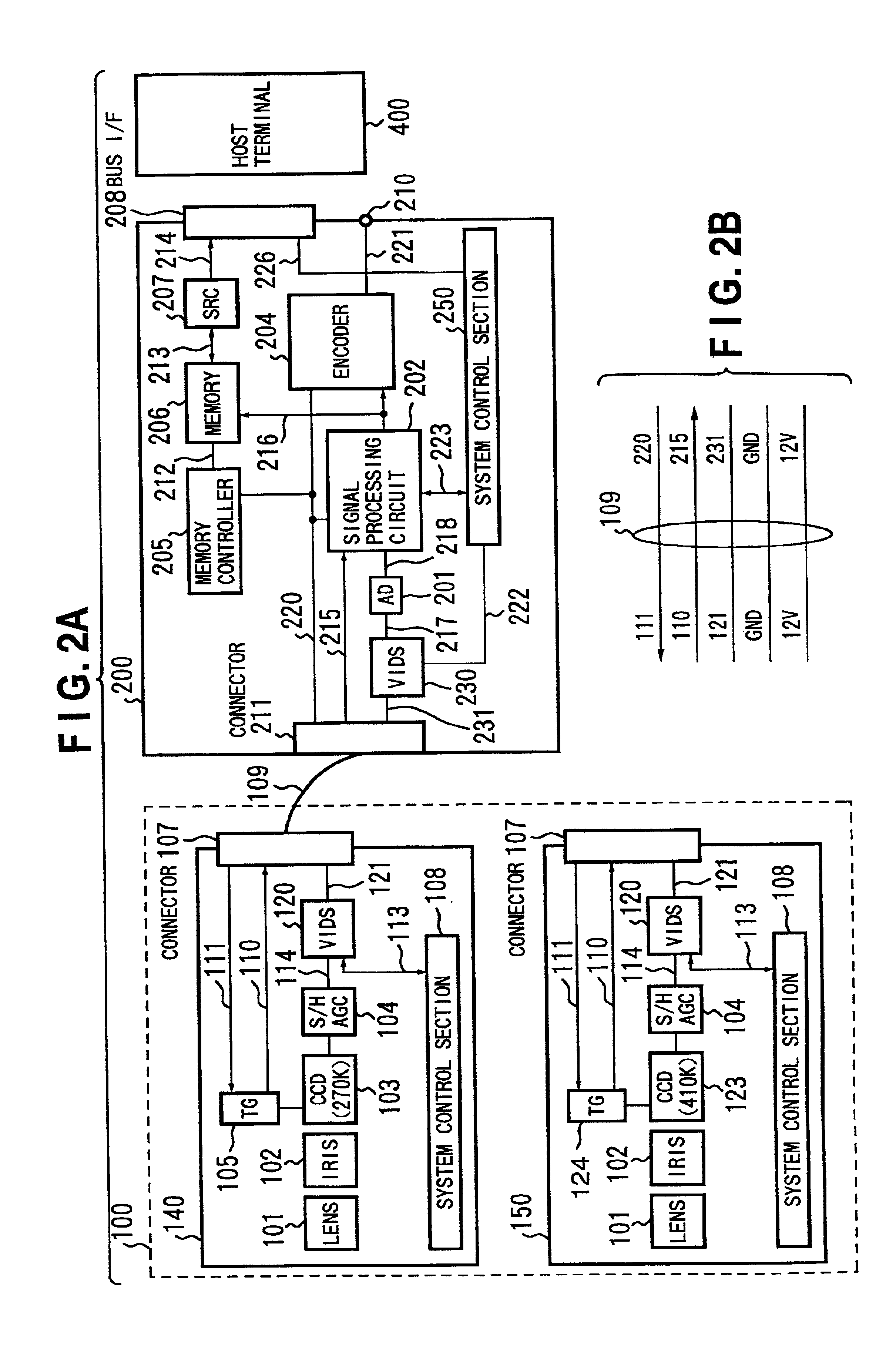
Video input apparatus and image pickup system including the apparatus
InactiveUS6965400B1Accurate operationEasily obtainedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSignal onImage signal
A video input apparatus and image pickup system having a camera section having a camera unit, and a video processing section for processing an image signal from the camera section so as to supply to a host terminal. The camera section outputs a multiplexed signal on which synchronizing signals of an image signal are multiplexed on the image signal, to the video processing section through a cable. The video processing section separates the image signal and the synchronizing signals from the multiplexed signal and processes the image signal to output a video signal. The camera unit in the camera section is exchangeable, and the video processing section detects the type of the camera unit based on the separated synchronizing signals and processes the image signal in accordance with the detected type of the camera unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Curable composition and method for temporal fixation of structural member using the same
ActiveUS20100012263A1High adhesive strengthEasily obtainedLamination ancillary operationsPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesSolventTemperature-responsive polymer
To provide a method for temporarily fixing an optical member for processing, and a curable composition useful for such a method.A curable composition comprising (A) a polyfunctional (meth)acrylate, (B) a monofunctional (meth)acrylate, (C) a photopolymerization initiator, and (D) a polar solvent. The curable composition may further contain (G) a temperature-responsive polymer and / or a copolymer of a temperature-responsive polymer, or (H) a granular material. The method for temporarily fixing a member, comprises temporarily fixing the member by means of such a curable composition, processing the temporarily fixed member, and immersing the processed member in warm water of from 30 to 90° C., thereby to remove a cured resin of the curable composition.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
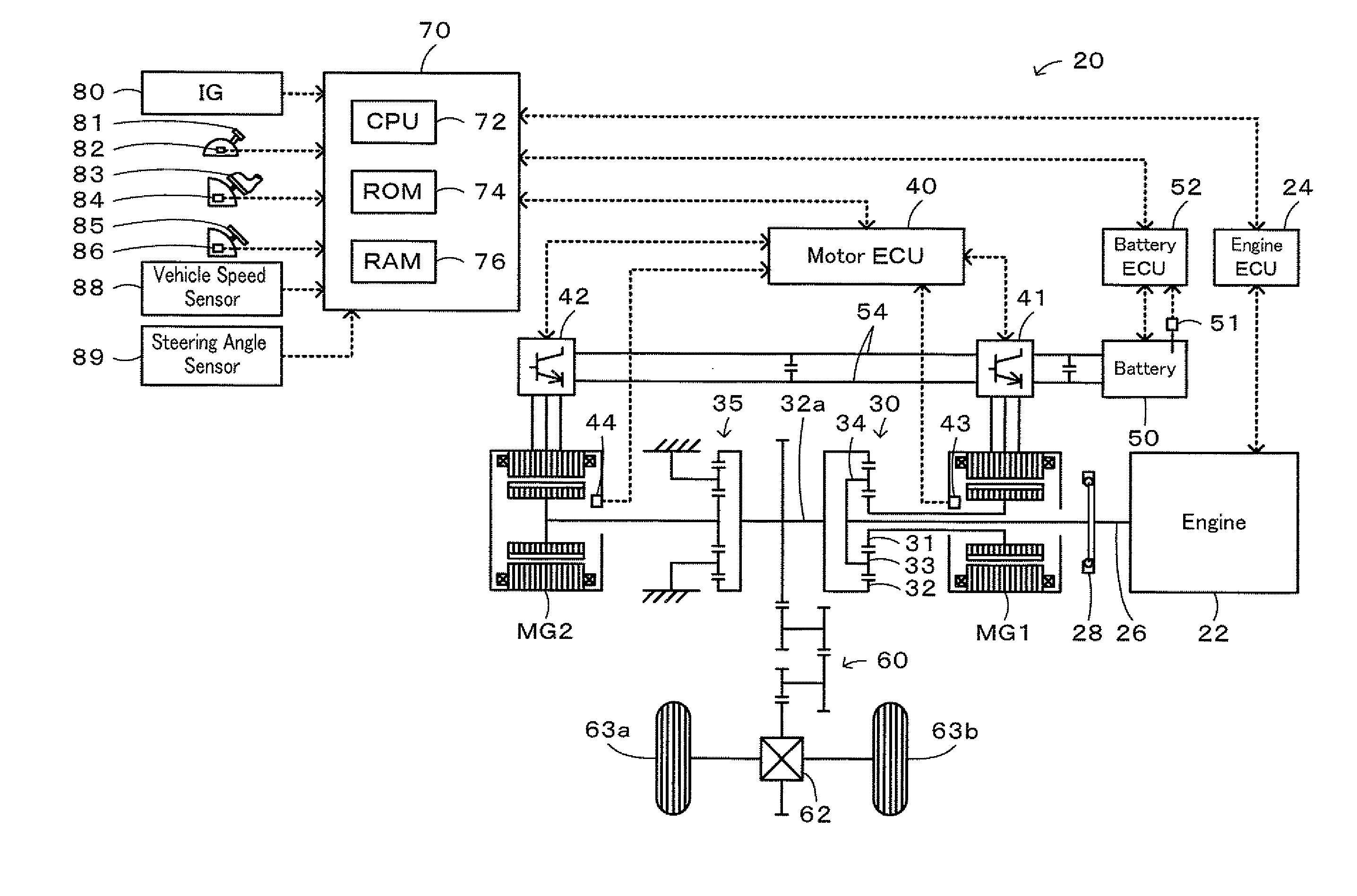
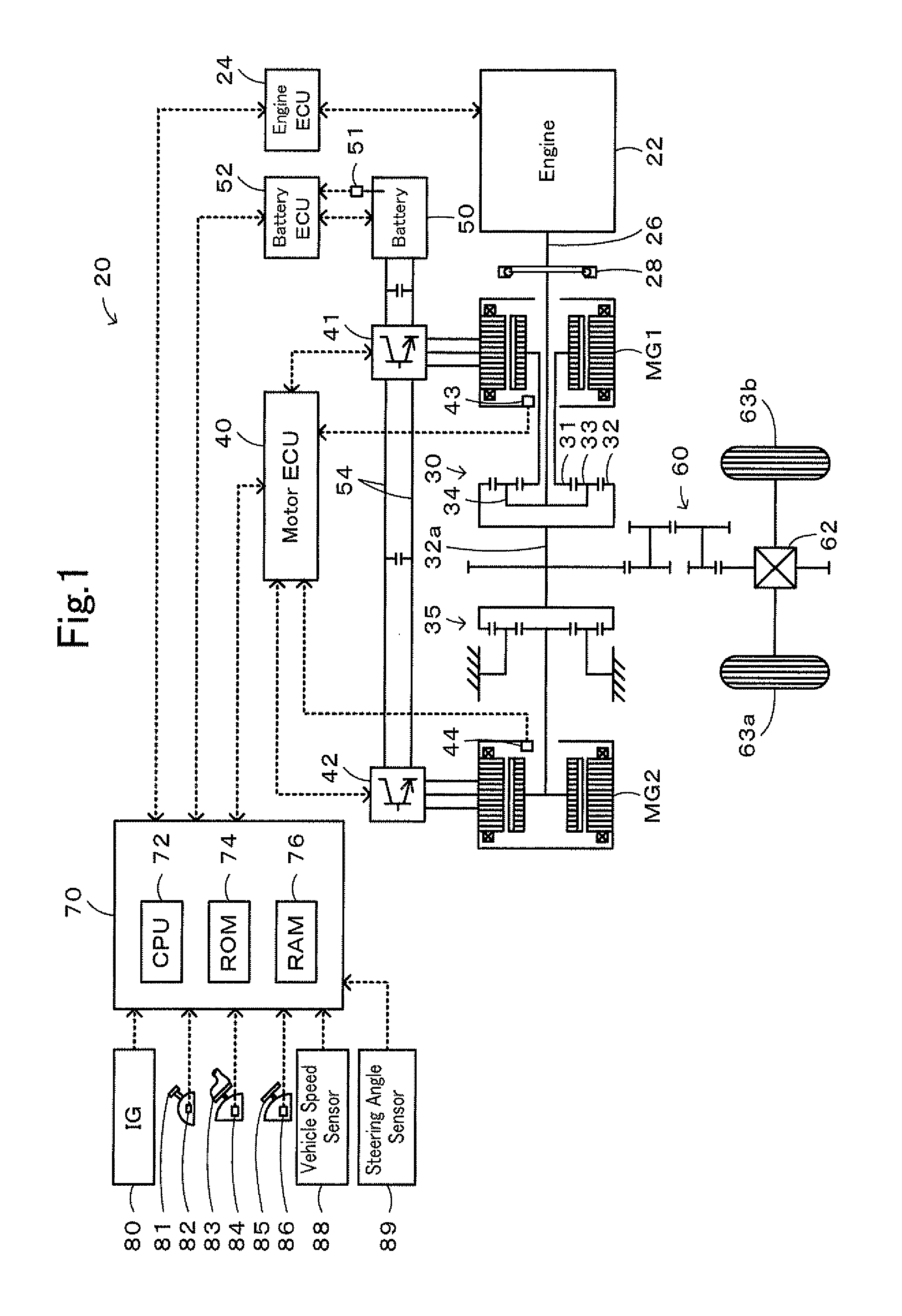
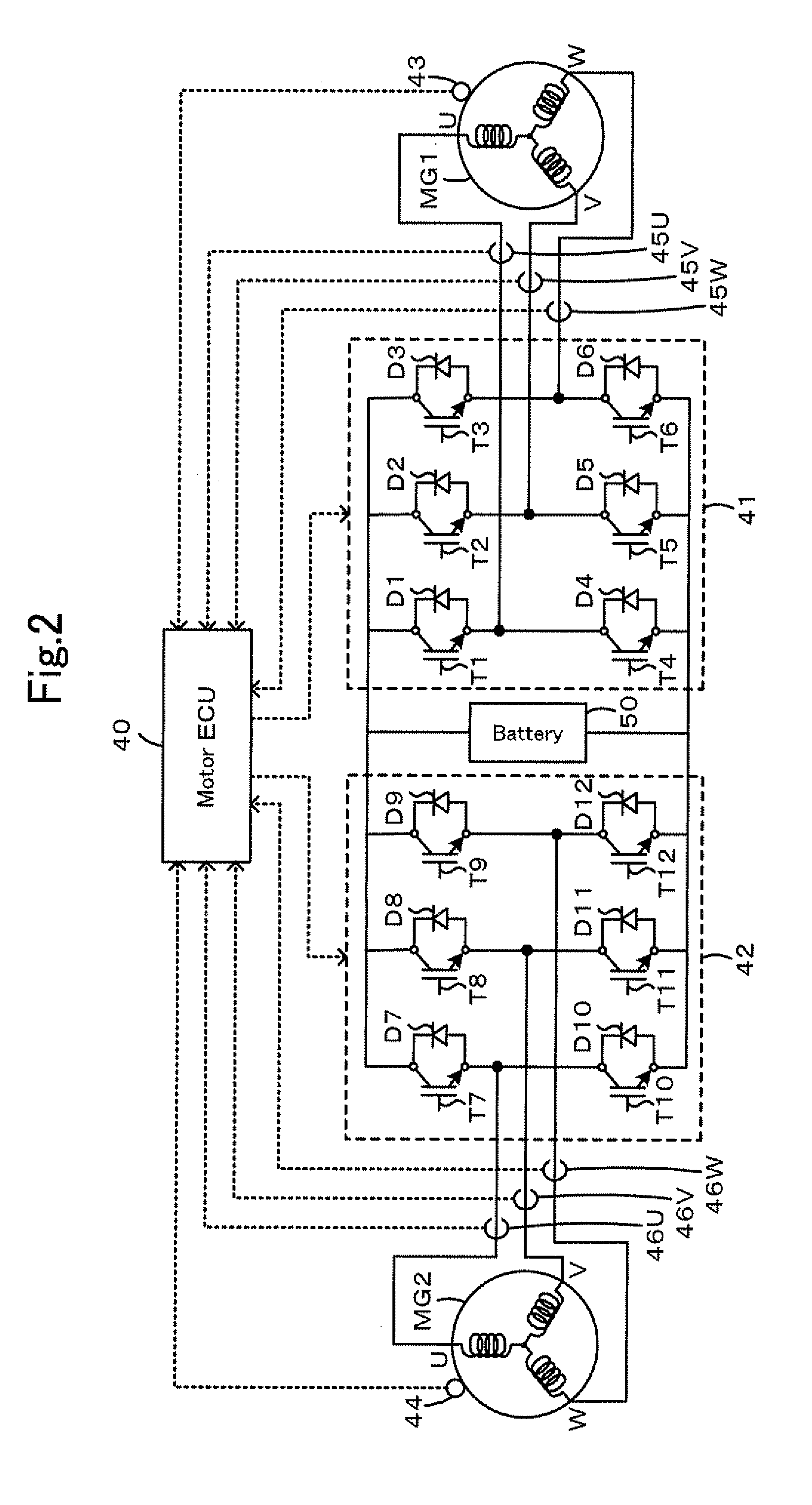
Vehicle, control method of vehicle, and driving apparatus
InactiveUS20100152940A1Reduce braking forceEasily obtainedDigital data processing detailsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingThree-phaseSteering angle
Upon the occurrence of the abnormality that the inverter for driving the motor is in the one-phase short circuited state, this inverter is stopped in the three-phase short circuited state and sets the execution torque by subtracting the counter electromotive force application torque that is applied the driveshaft due to the counter electromotive force generated by rotation of the motor and the steering angle application torque corresponding to the steering angle from the torque demand according to the step-on amount of the accelerator pedal. The engine and the inverter for driving the motor is controlled so that the vehicle is driven with the set execution torque. This enables the driving force output to the driveshaft from the engine and the motor to be in accordance with the torque demand.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
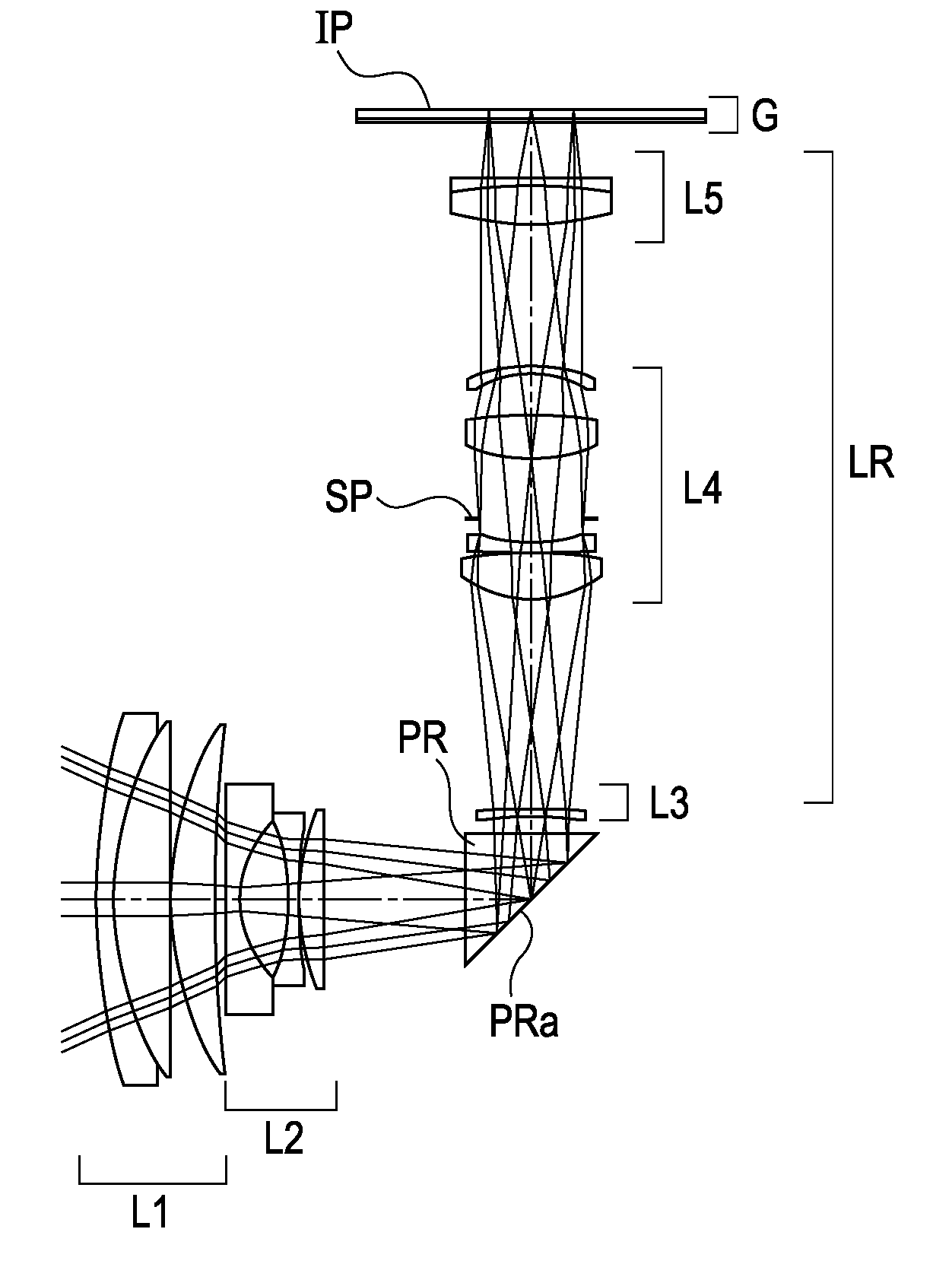
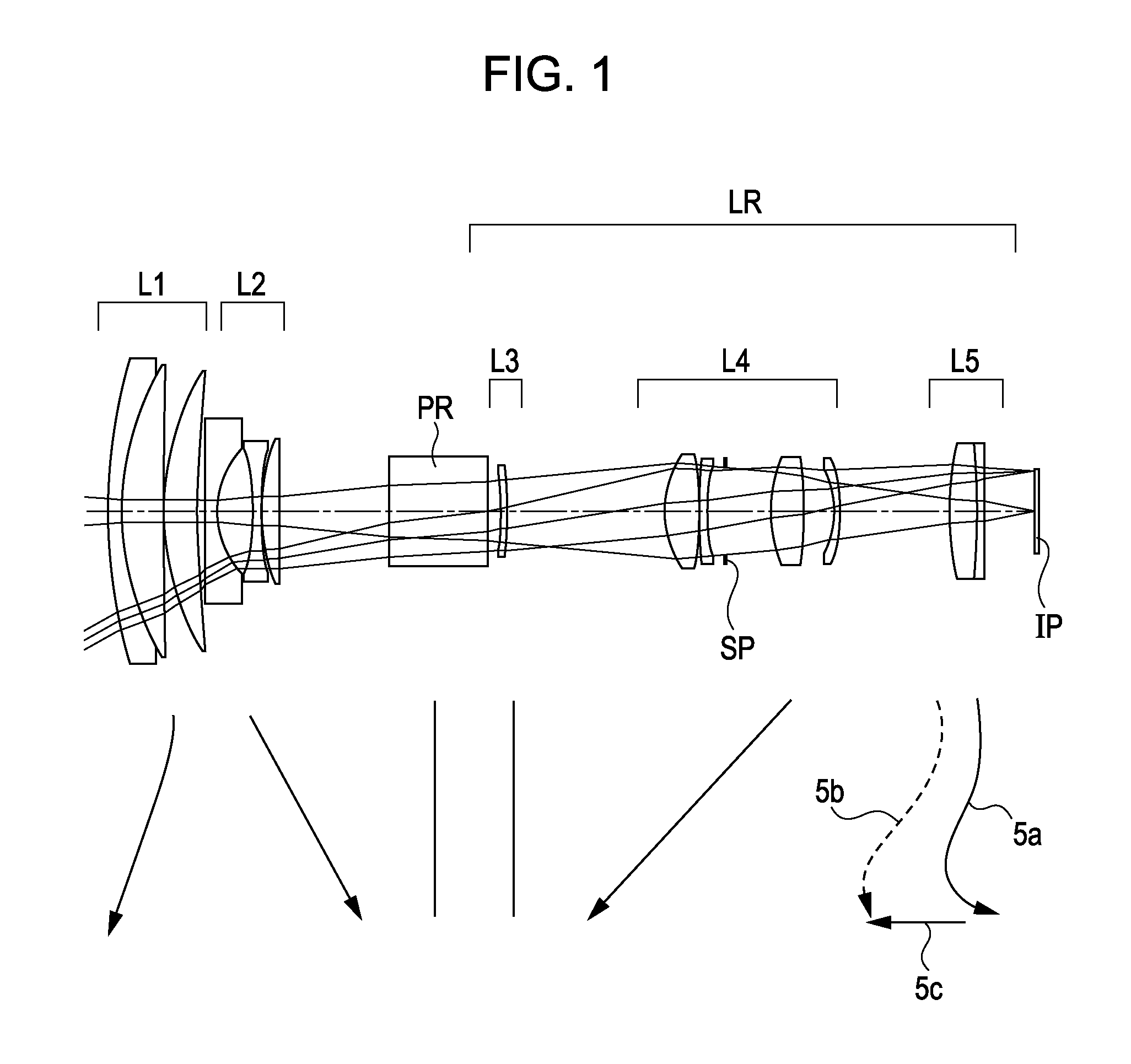
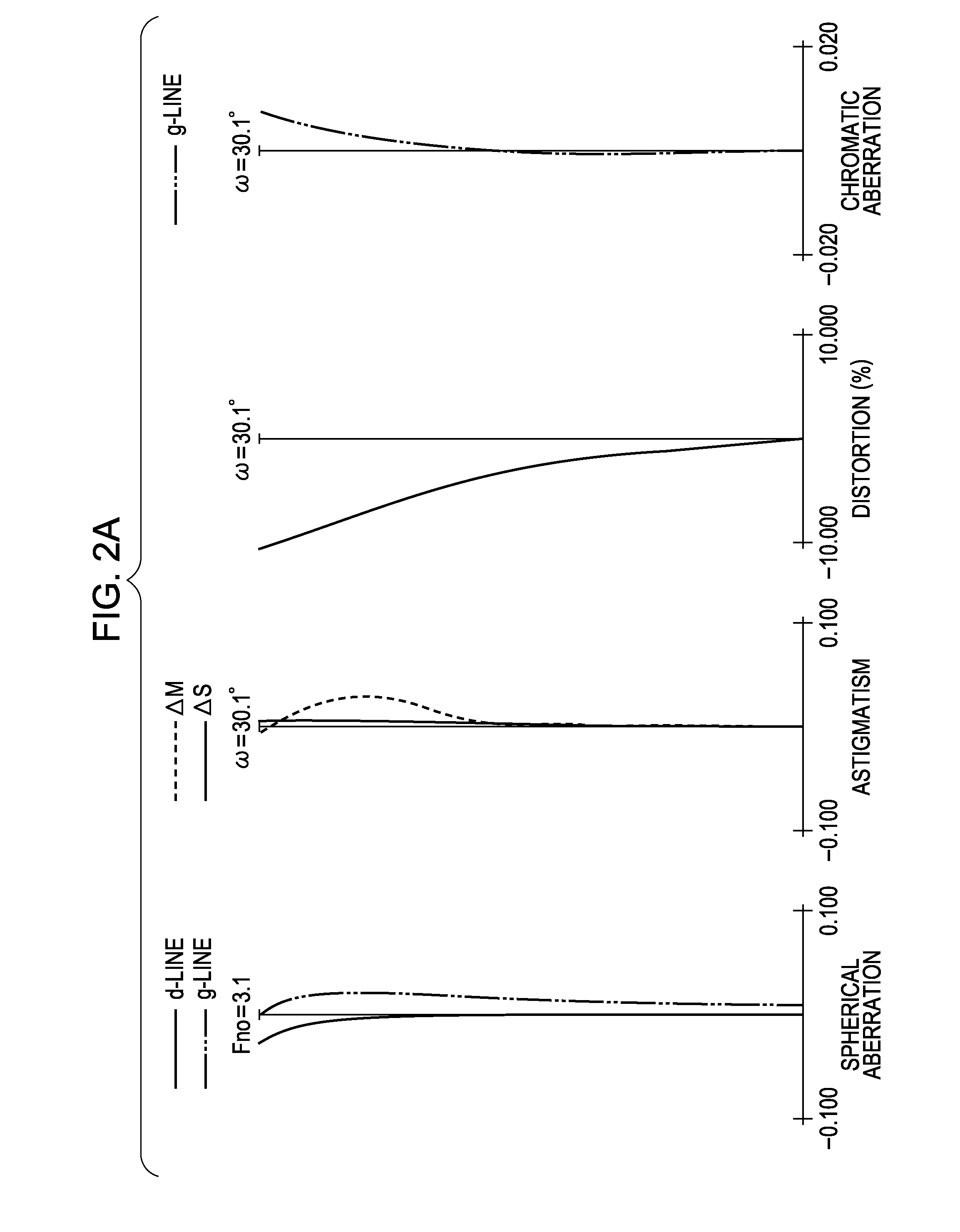
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus including the same
A zoom lens includes, in order from an object side to an image side, first and second lens units respectively having positive and negative refractive powers, a reflecting prism for bending an optical path, and a rear lens group including lens units. At least the first and second lens units move for zooming. During retraction into a storage state, the prism moves to a position different from a position in an image taking state, and at least a part of the first and second lens units is retracted into a space formed by movement of the prism. Thicknesses of the first and second lens units, a moving amount of the first lens unit during zooming from a wide angle end to a telephoto end, a focal length of the first lens unit, and a focal length of the entire zoom lens at the telephoto end are set properly.
Owner:CANON KK
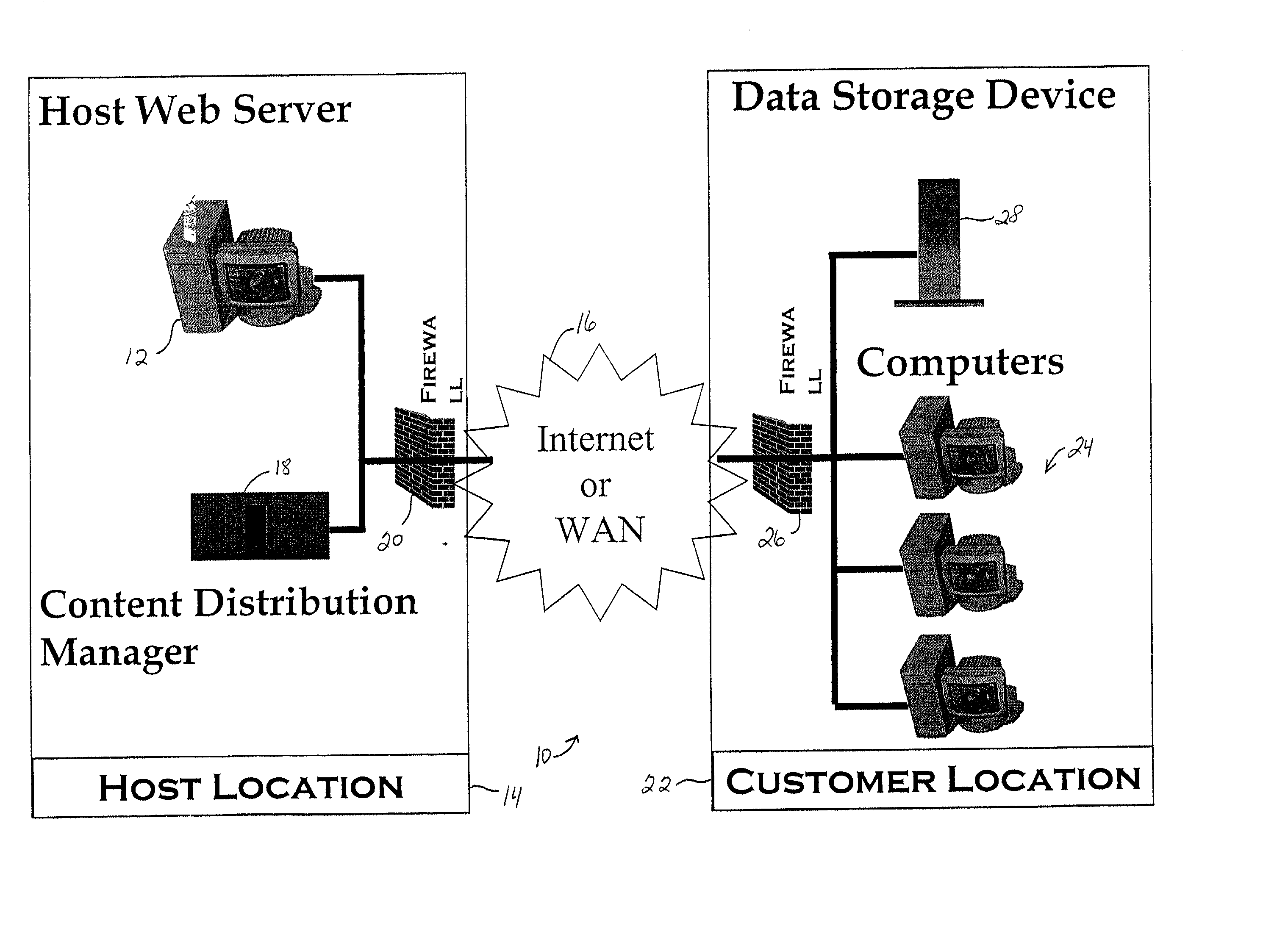
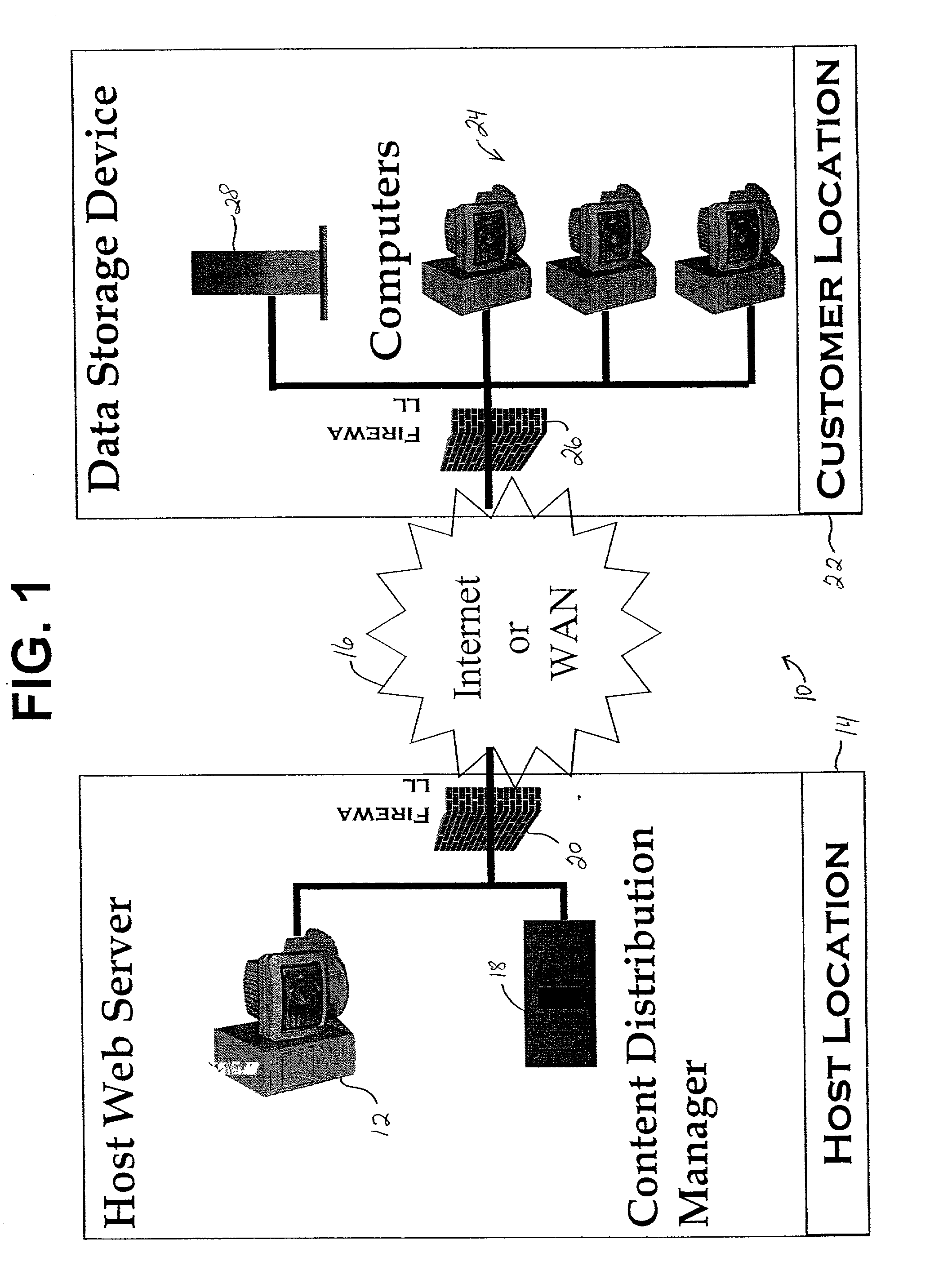
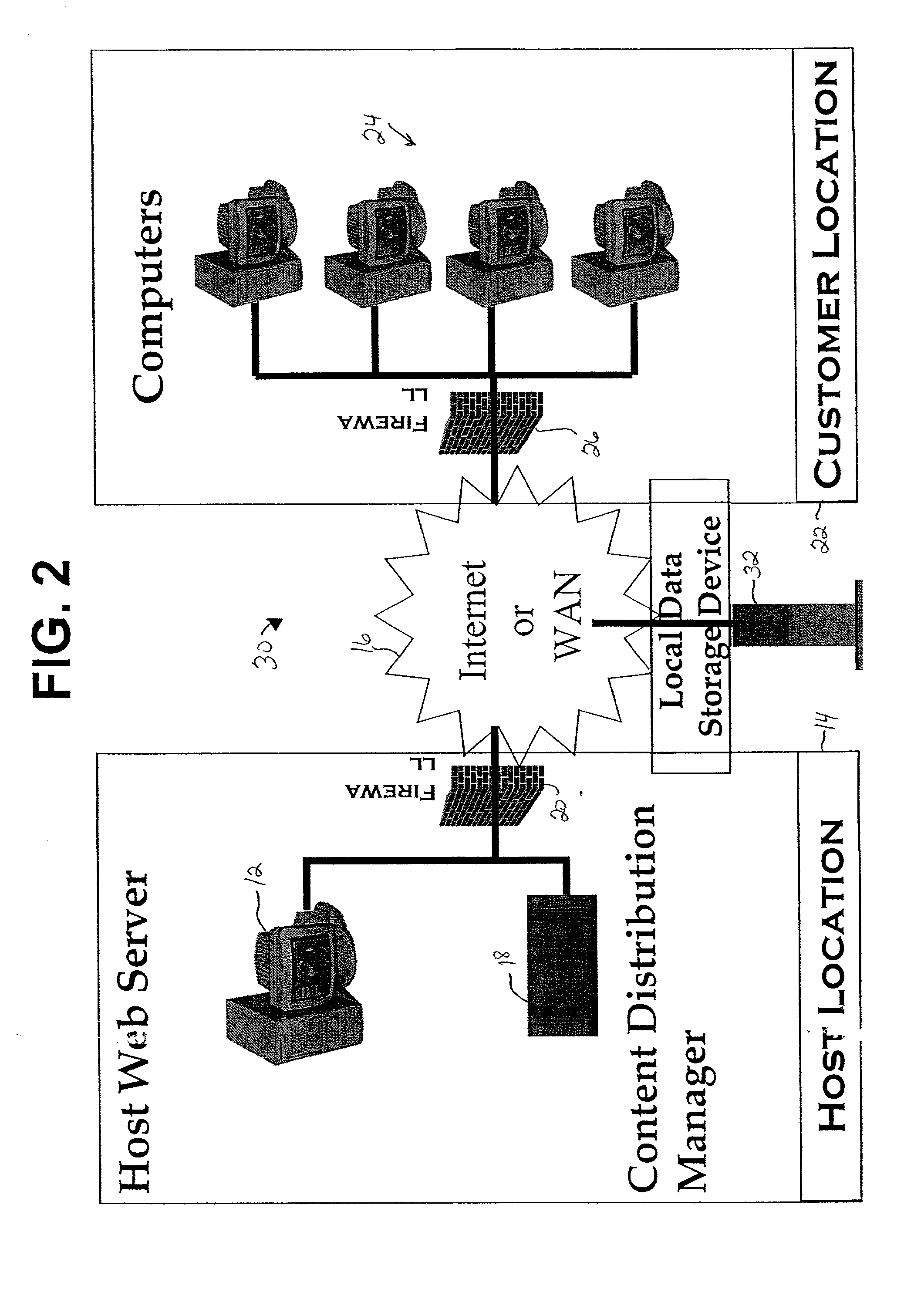
Internet based tutorial system for electronic assembly systems
InactiveUS20020127531A1Costly downtimeEasily obtainedElectrical appliancesMechanical appliancesElectronicsElectronic assemblies
A tutorial software program provides information about the operation of an electronics assembly machine and a computer software interface used to operate the electronics assembly machine. A host transmits the tutorial program over a network, such as the Internet, to a computer at a customer's location. The information provided by the tutorial software program includes pictures representing the computer software interface, text that provides information about the electronics assembly machine and the computer software interface, audio that provides information about the electronics assembly machine, and video that shows the electronics assembly machine in use. Systems and methods for providing the tutorial program are also provided. The tutorial program allows a customer to instruct employees how to fully operate the electronics assembly machine without having to train employees on the machine itself, which could result in costly downtime of the machine.
Owner:COOKSON PROCESS TECH
Semiconductor substrate with stacked oxide and SOI layers with a molten or epitaxial layer formed on an edge of the stacked layers
InactiveUS6872979B2Easily obtainedSuppressed increase in production costTransistorPolycrystalline material growthOxideSemiconductor
A semiconductor substrate that prevents formation of particles from an edge part of the substrate. The substrate contains an on-substrate oxide film and an SOI layer stacked on the oxide film. A molten layer is formed on the edge part of the on-substrate oxide film and the SOI layer by mixing the SOI layer and the on-substrate oxide film to cover the edge part. An epitaxial layer may also be formed on the edge part of the on-substrate oxide film and the SOI layer to cover the edge part.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Image editing apparatus and method
ActiveUS8311393B2Easily obtainedEasy to getTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersImaging dataImage editing
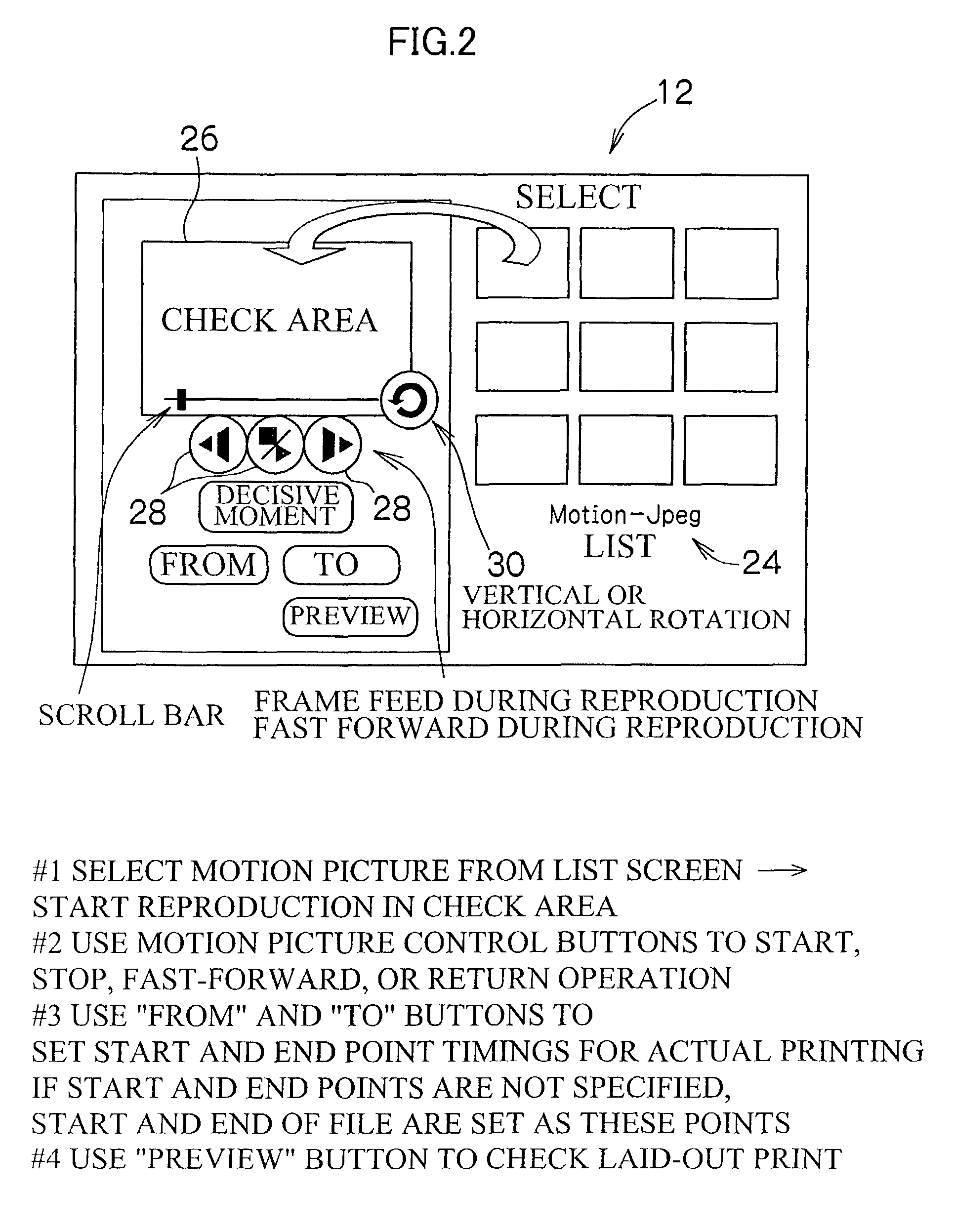
The motion picture image print apparatus extracts a plurality of frames from recorded motion picture data for printing, the apparatus enabling the range of loaded images to be determined from images reproduced on a screen, not from the results of measurement of time, thus allowing a desired print to be more easily obtained. An operator reads motion picture image data recorded on a recording medium. The operator then sets a layout of a print output and the number of image frames in the print output to display a list of motion picture image files on a list screen, thereby selecting motion picture image file to be printed. The operator then depresses a motion picture control button to reproduce the selected motion picture image file in the check area. While viewing the reproduced images, the operator sets at least either a print starting image or a print ending image by depressing a “From” button or a “To” button, respectively. Thus, images corresponding to a predetermined number of frames are extracted from the set range of images at equal intervals. The extracted images are edited so as to be arranged in the set layout and are then printed.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Prism for projection optical system and optical system having same
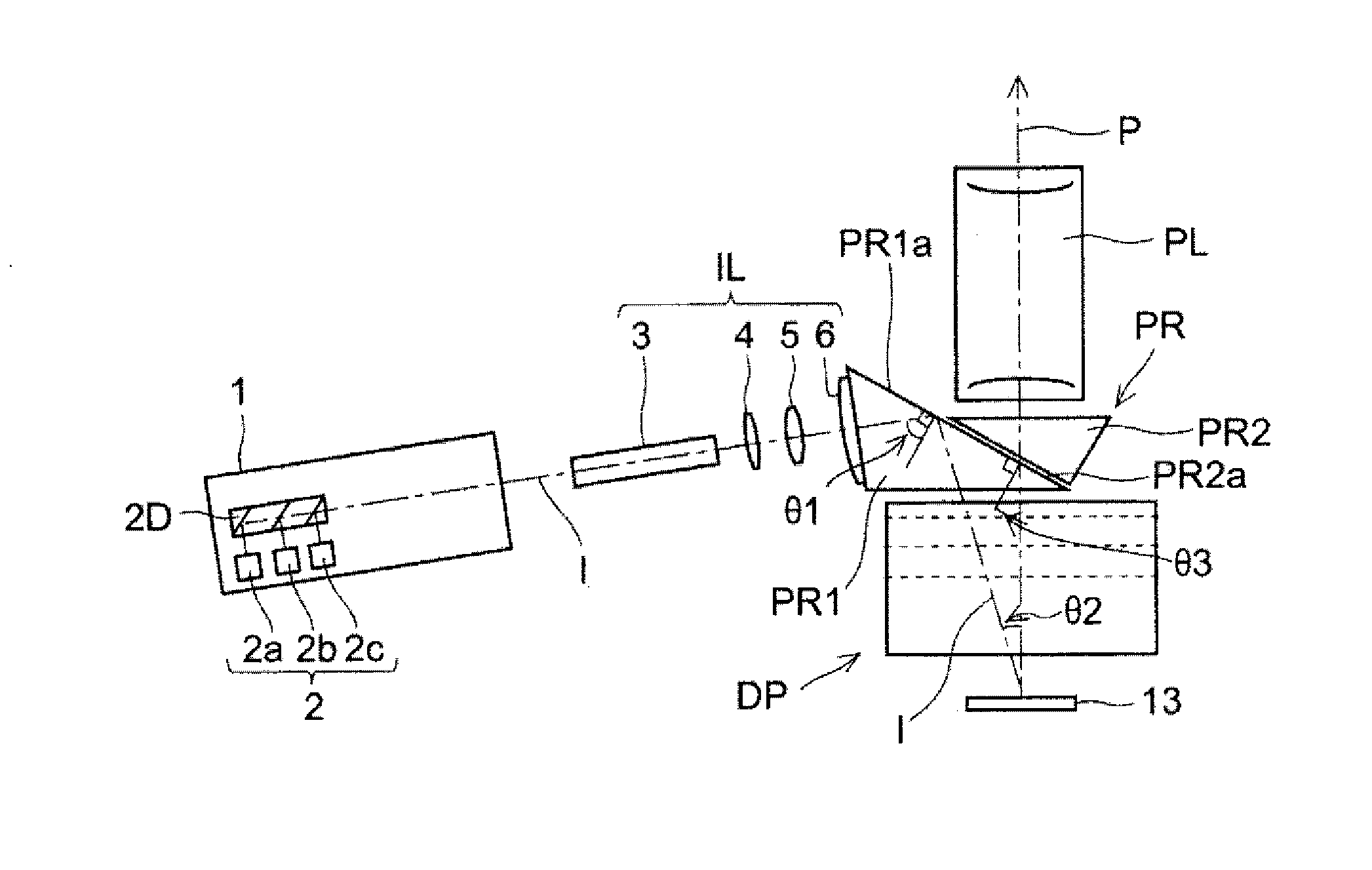
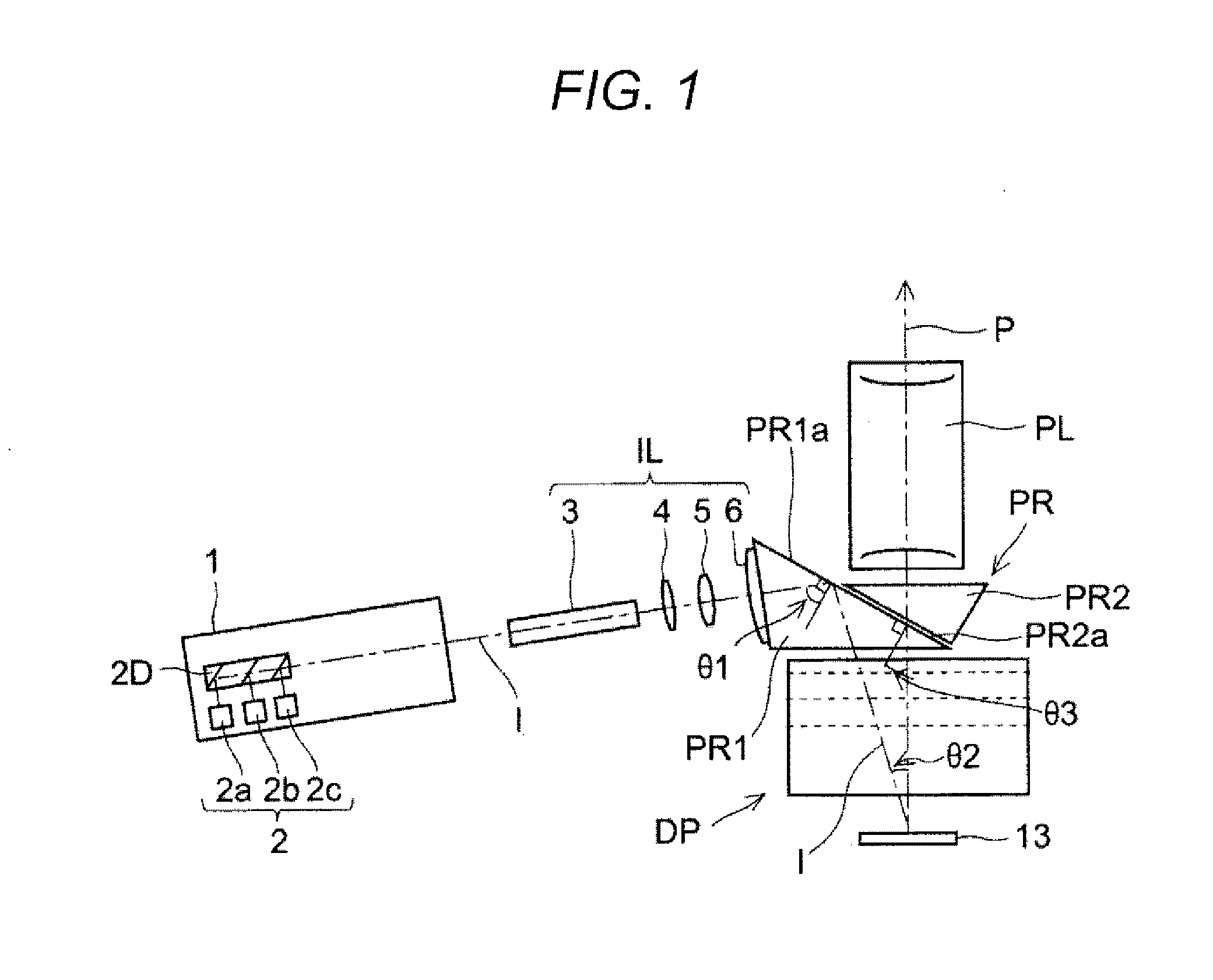
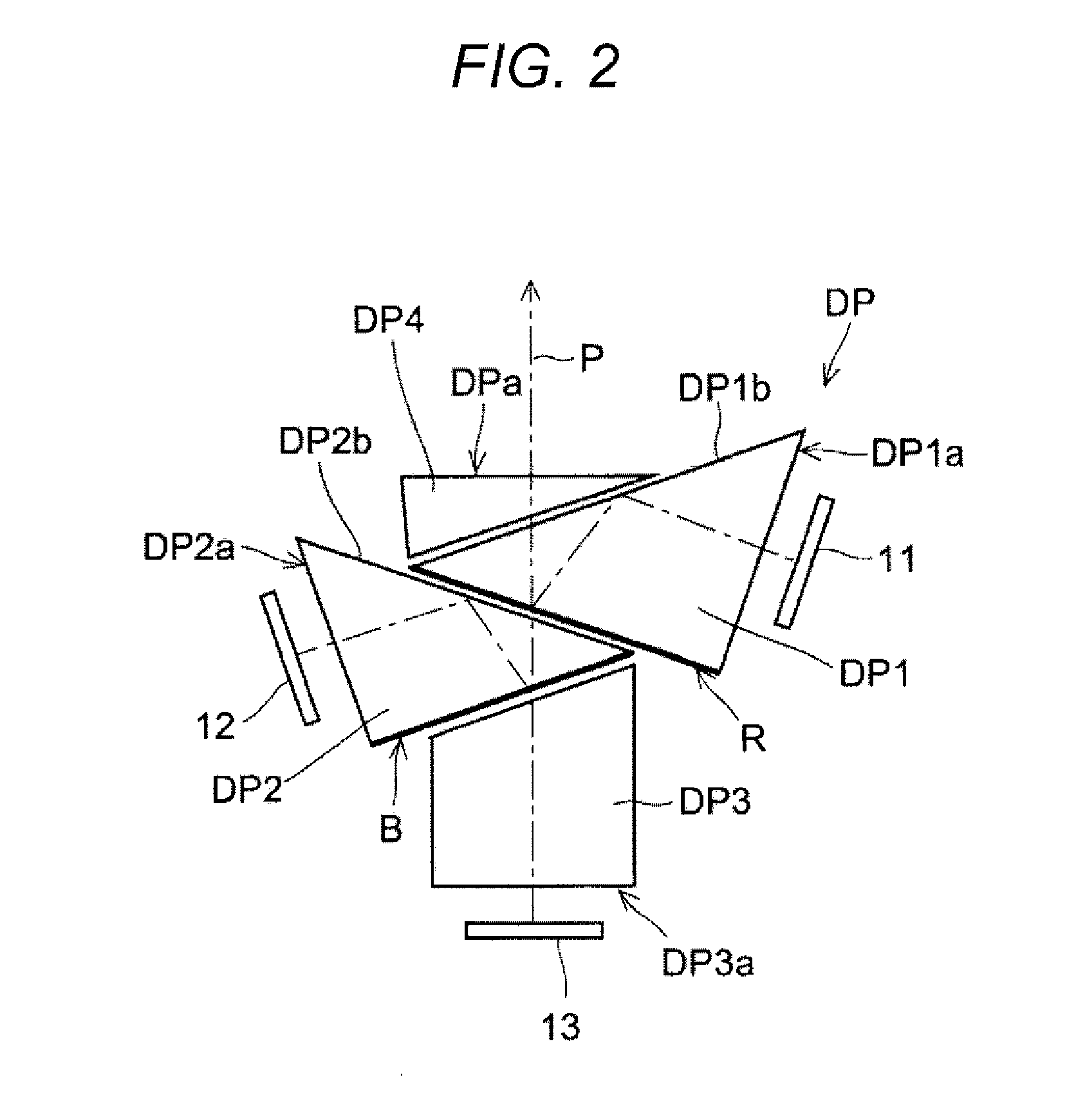
A prism for a projection optical system included in a projector including an illumination light source, an illumination optical system, and a projection optical system, includes: a first surface that totally reflects a beam of one of the illumination light and the projection light and transmits a beam of the other; and a second surface that is opposed to the first surface with an air gap therebetween and transmits a beam passing through the first surface, wherein the first surface has an antireflective film having an average reflectivity of a s-polarized reflectivity and a p-polarized reflectivity at a center angle of a transmitted beam of 2% or lower in three wavelength ranges including a first wavelength range of blue, a second wavelength range of green, and a third wavelength range of red.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
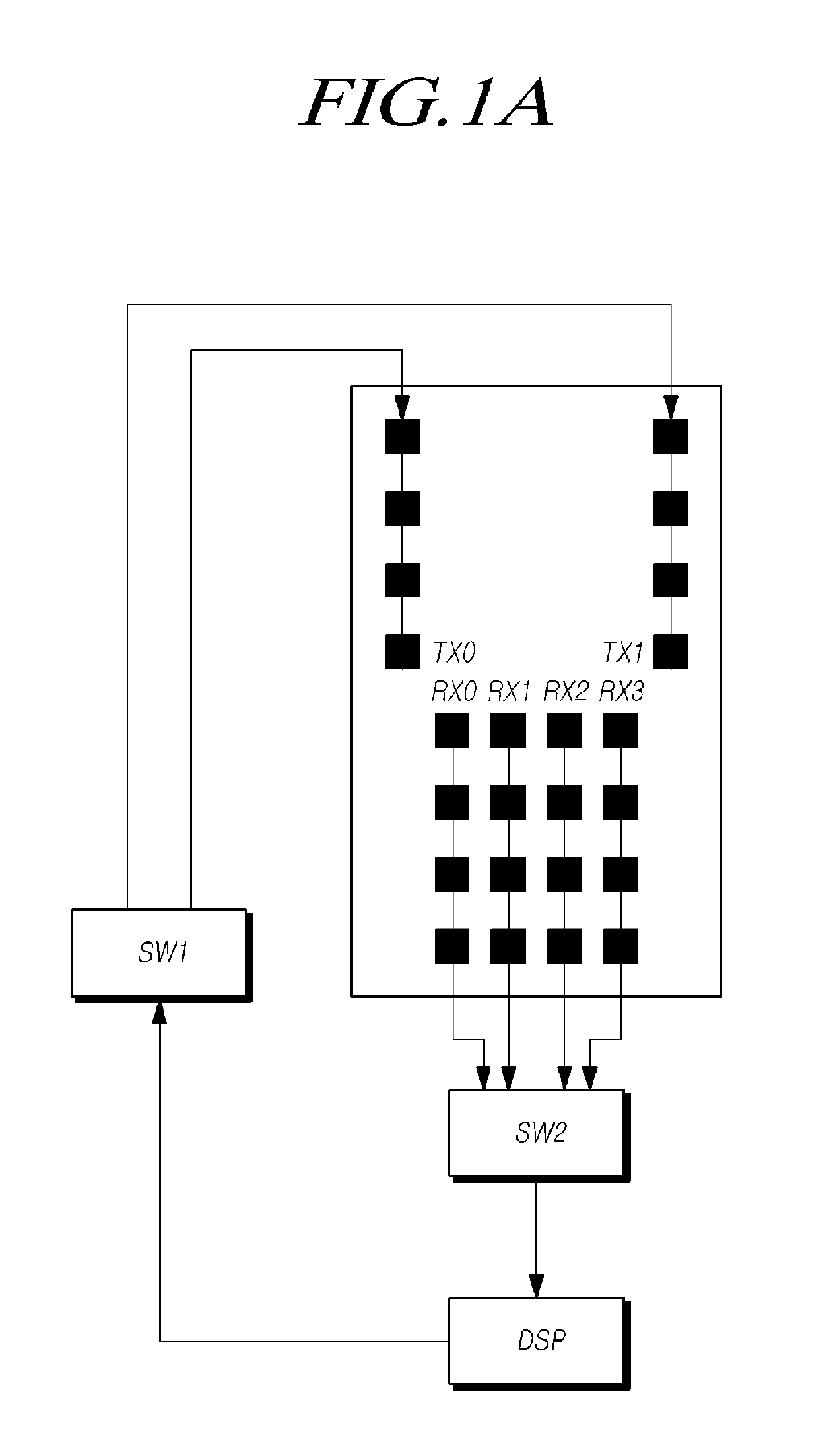
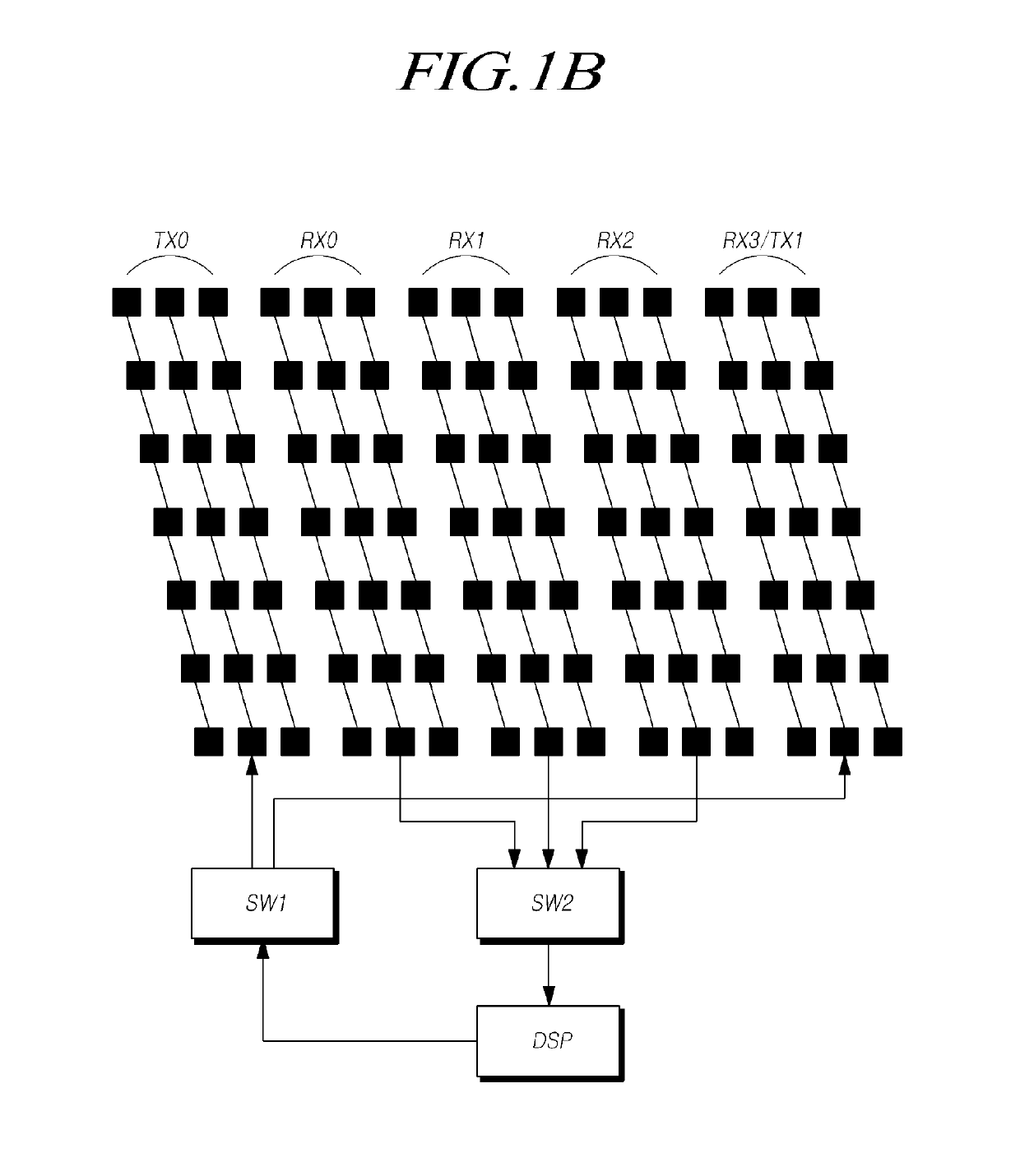
Radar apparatus and antenna apparatus therefor
PendingUS20190310358A1Easily obtainedAvoid interferenceIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna detailsPhysicsVertical distance
The present provides a radar apparatus and an antenna apparatus for the radar apparatus. Two transmission antennas disposed on both sides of the transmission antenna set may be arranged apart from each other by a predetermined vertical distance in a first direction perpendicular to the ground, and the four receiving antennas may be disposed apart from each other by a predetermined horizontal distance, so that the vertical information and the horizontal information of the object can be easily obtained in the long range detection mode and the short range detection mode.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Electrode for Hydrogen Generation, Method for Manufacturing the Same and Electrolysis Method Using the Same
ActiveUS20080029396A1Easily obtainedLow hydrogen overvoltage performanceElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentIonChemistry
The present invention provides an electrode for hydrogen generation of which the hydrogen overvoltage is sufficiently low and which is not affected by poisoning due to iron ions, and furthermore, of which the durability is superior because during operations and stop-and-start control, the hydrogen overvoltage does not rise and exfoliation of the supported material does not occur. The present invention also provides a method for manufacturing the aforementioned hydrogen generation electrode and an electrolysis method using the electrode for hydrogen generation as a cathode. An electrode for hydrogen generation is used in which a platinum alloy including platinum and one metal selected from the group consisting of nickel, cobalt, copper, silver, and iron, or an amorphous material of a transition metal element and platinum is supported on a conductive base material. This electrode is obtained by coating a metal compound solution including one selected from the group consisting of nickel, cobalt, copper, silver, and iron, and a platinum compound solution which forms an ammine complex; drying; thermally decomposing at a temperature in a range from more than 200° C. to 700° C. or less; and then subjecting to a reduction processing.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Surface acoustic wave filter
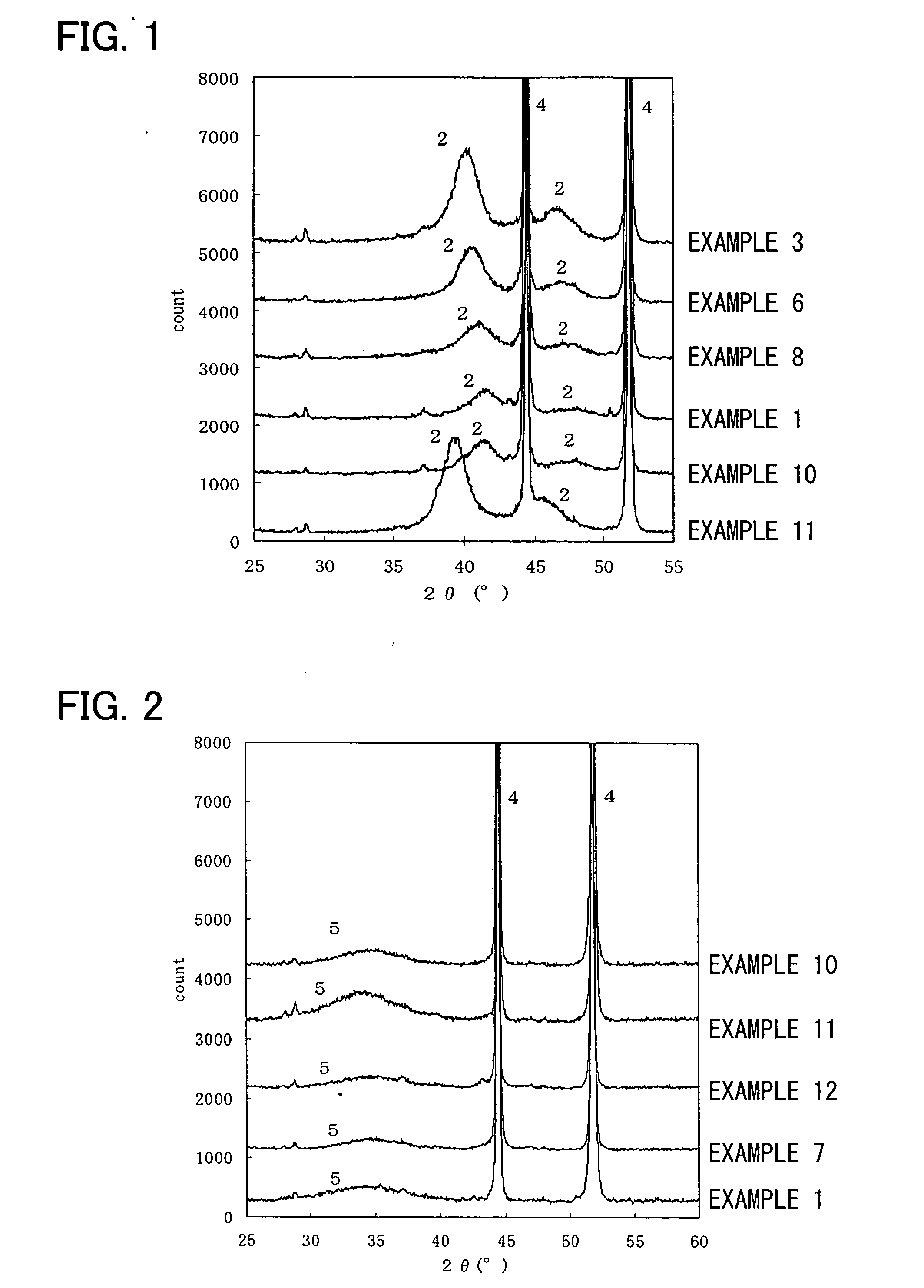
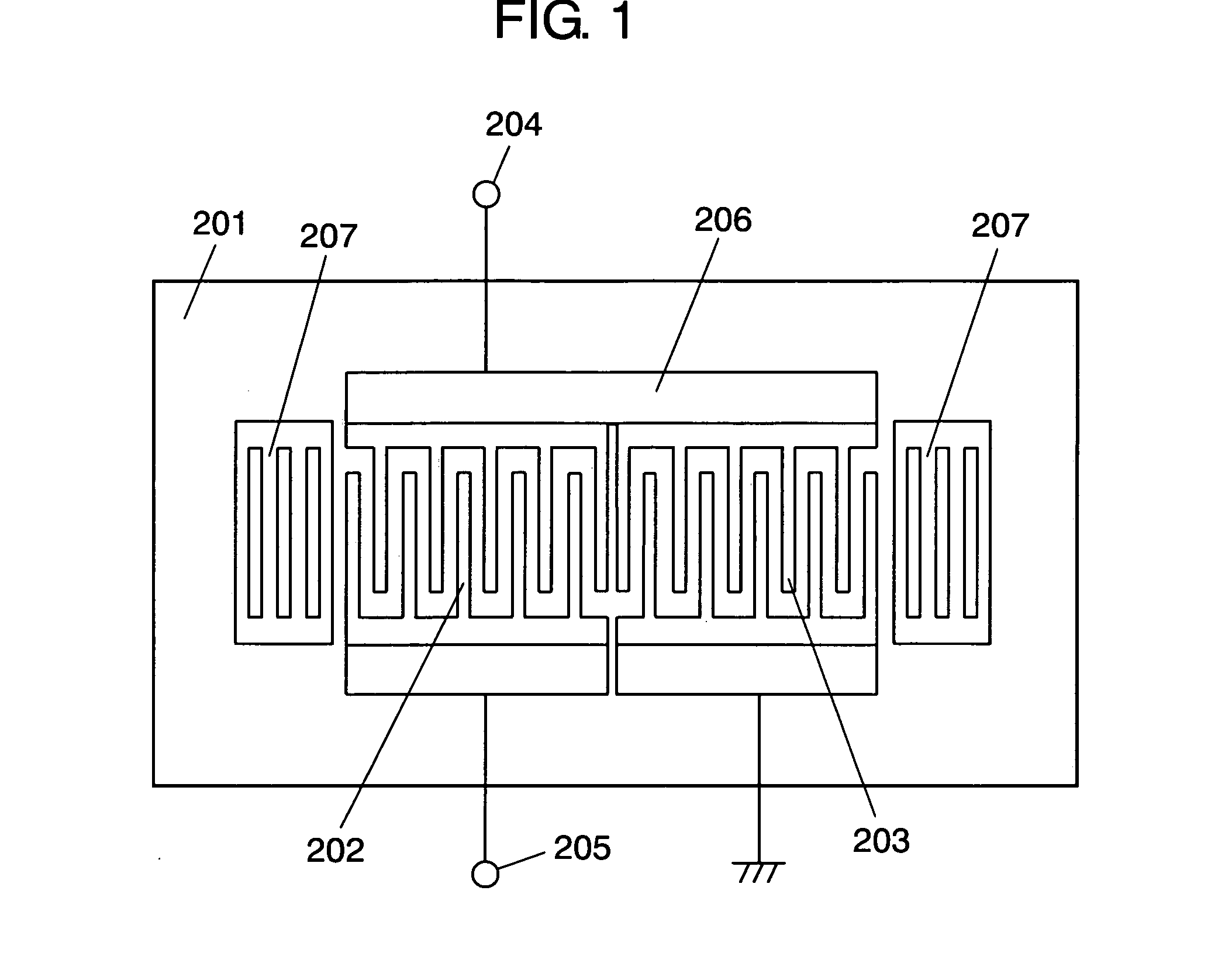
ActiveUS20070069837A1Easily obtainedIncrease degree of freedomImpedence networksResonatorEngineering
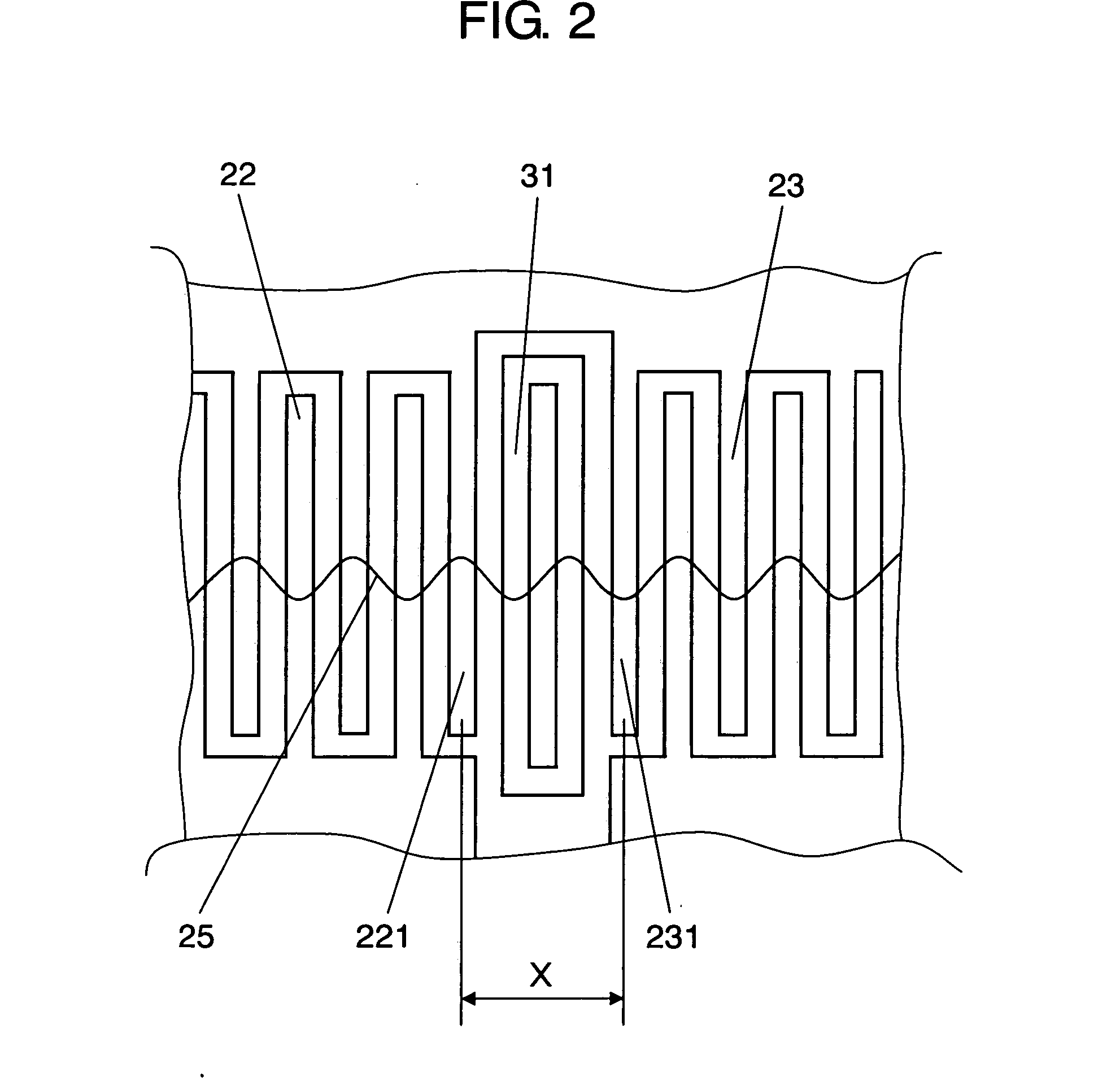
It is configured by forming first IDT (202) and second IDT (203) on piezoelectric substrate (201), and first IDT (202) is arranged between one terminal (204) of input / output terminals and other terminal (205) of the input / output terminals, i.e., serially to a signal path, and second IDT (203) is arranged in parallel to a signal path from a portion between one terminal (204) of the input / output terminals and first IDT (202). First IDT (202) and second IDT (203) are arranged in proximity to each other on the same propagation path of surface acoustic waves which are excited by respective resonators.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Method for producing nanotube material and nanotube material
InactiveUS7592039B2Easily obtainedHigh purityMaterial nanotechnologyEnvelopes/bags making machineryMaterials sciencePorous substrate
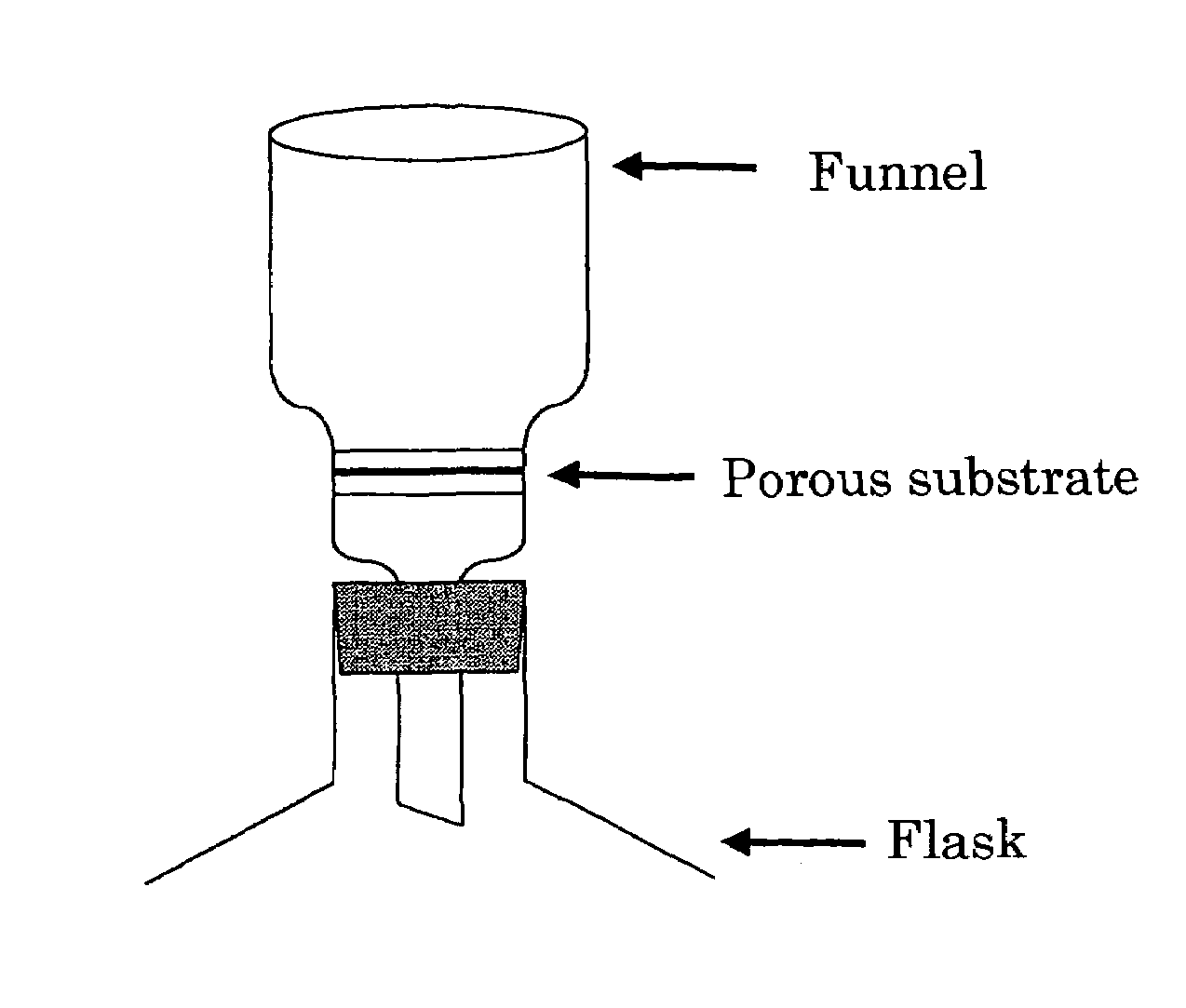
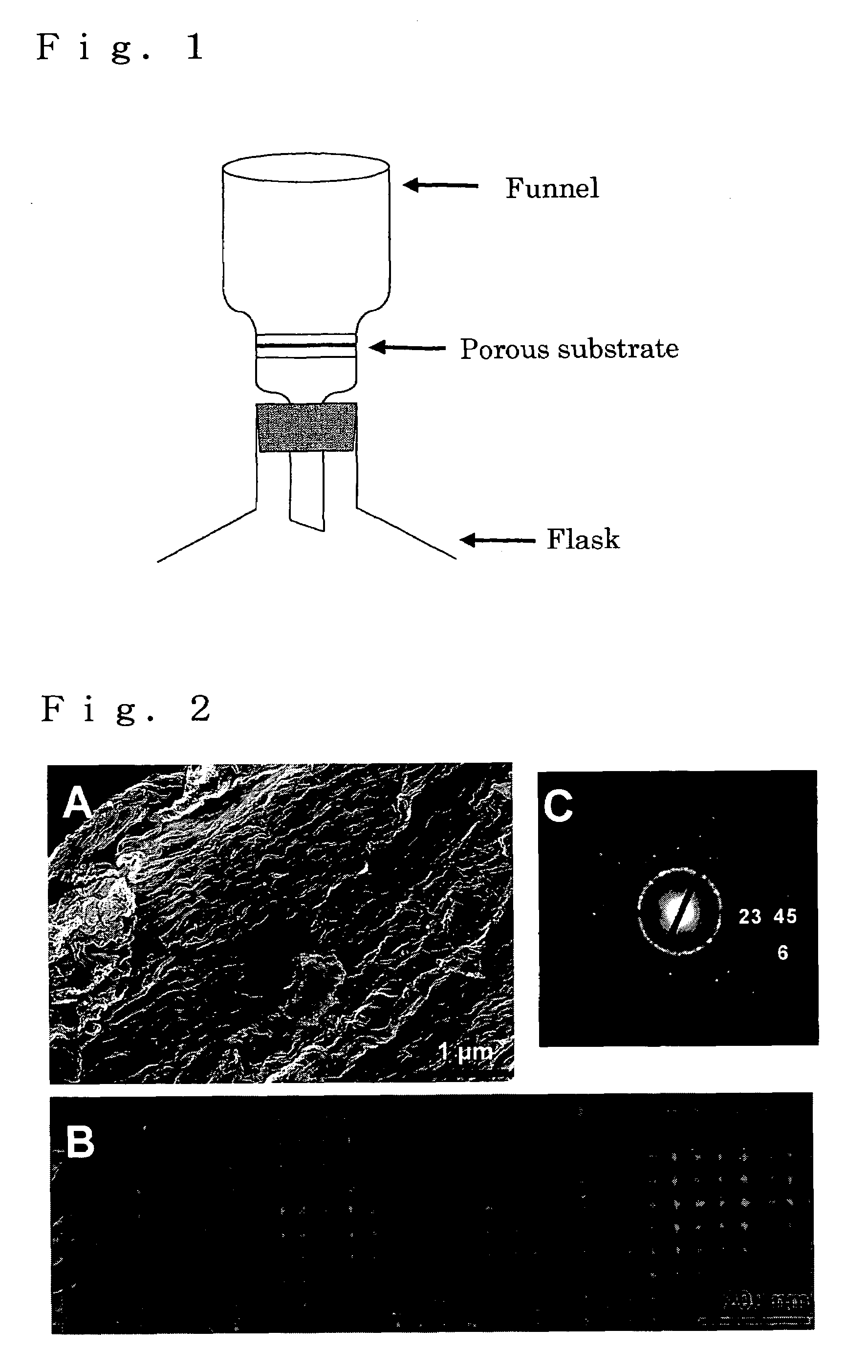
There are provided a method capable of mass-producing a nanotube material easily with low costs, and a nanotube material. The method of the present invention for producing a nanotube material has at least forming a metal oxide thin film or an organic / metal oxide composite thin film on an inner wall of a porous substrate and removing the porous substrate. The nanotube material of the invention has a structure provided from a body comprising a metal oxide thin film or an organic / metal oxide composite thin film formed on an inner wall of the porous substrate, from which a portion corresponding to the porous substrate is removed.
Owner:RIKEN
Coating for humidity indicator, method for production of the coating, and humidity indicator using the coating
ActiveUS20090124497A1Easy to handleEasily obtainedMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAblative recordingEmulsionSolid-state
Disclosed is a humidity indicator which contains no heavy metal and has good visibility of a color change that occurs when the humidity is increased. The humidity indicator can be produced by applying an aqueous coating comprising a leuco dye, an acidic compound which is in a solid state at ambient temperature, a deliquescent substance and an aqueous resin emulsion onto a substrate such as a resin film, a nonwoven fabric or a paper, and heating and drying the resulting product.
Owner:KYODO INSATU KK KYODO PRINTING CO LTD
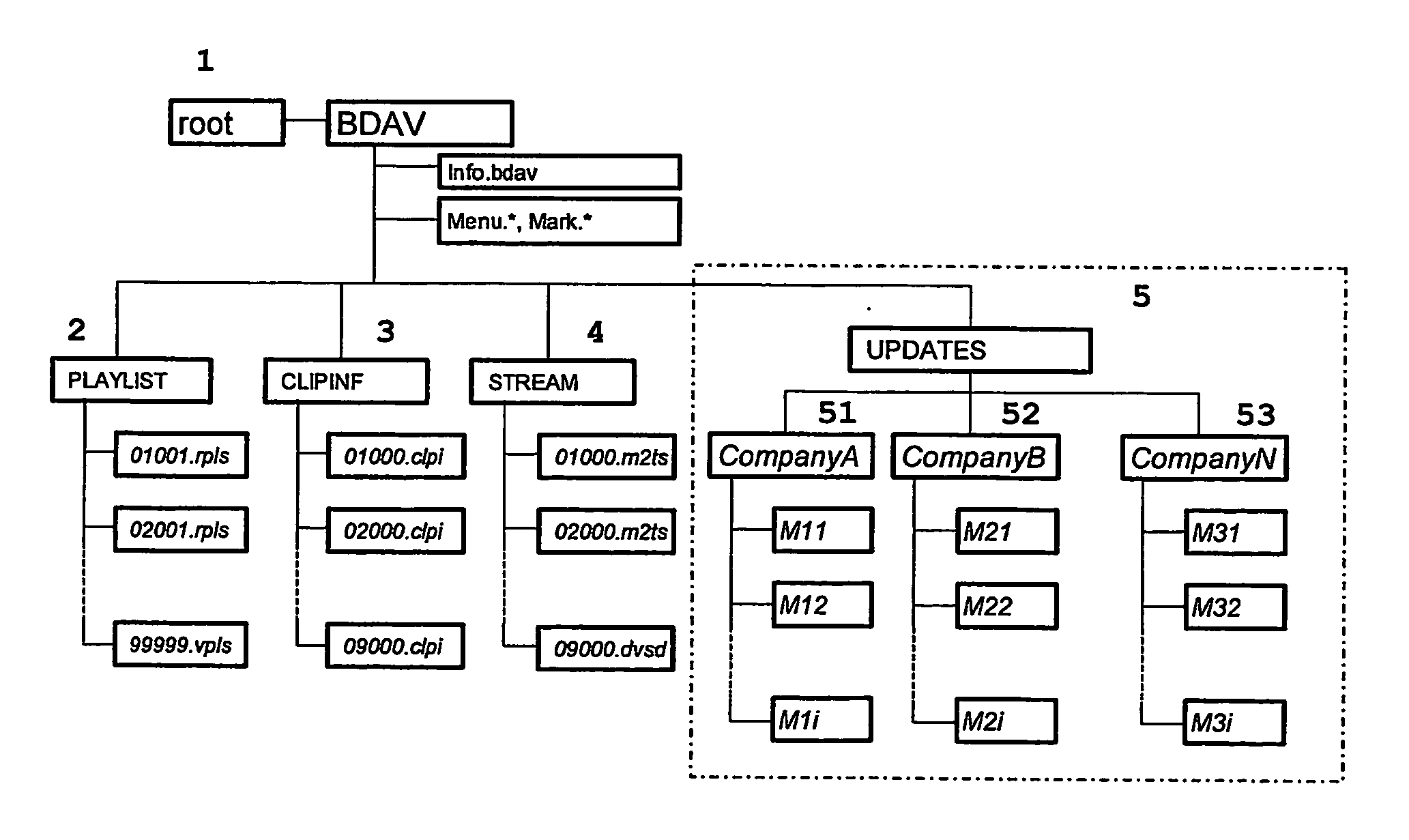
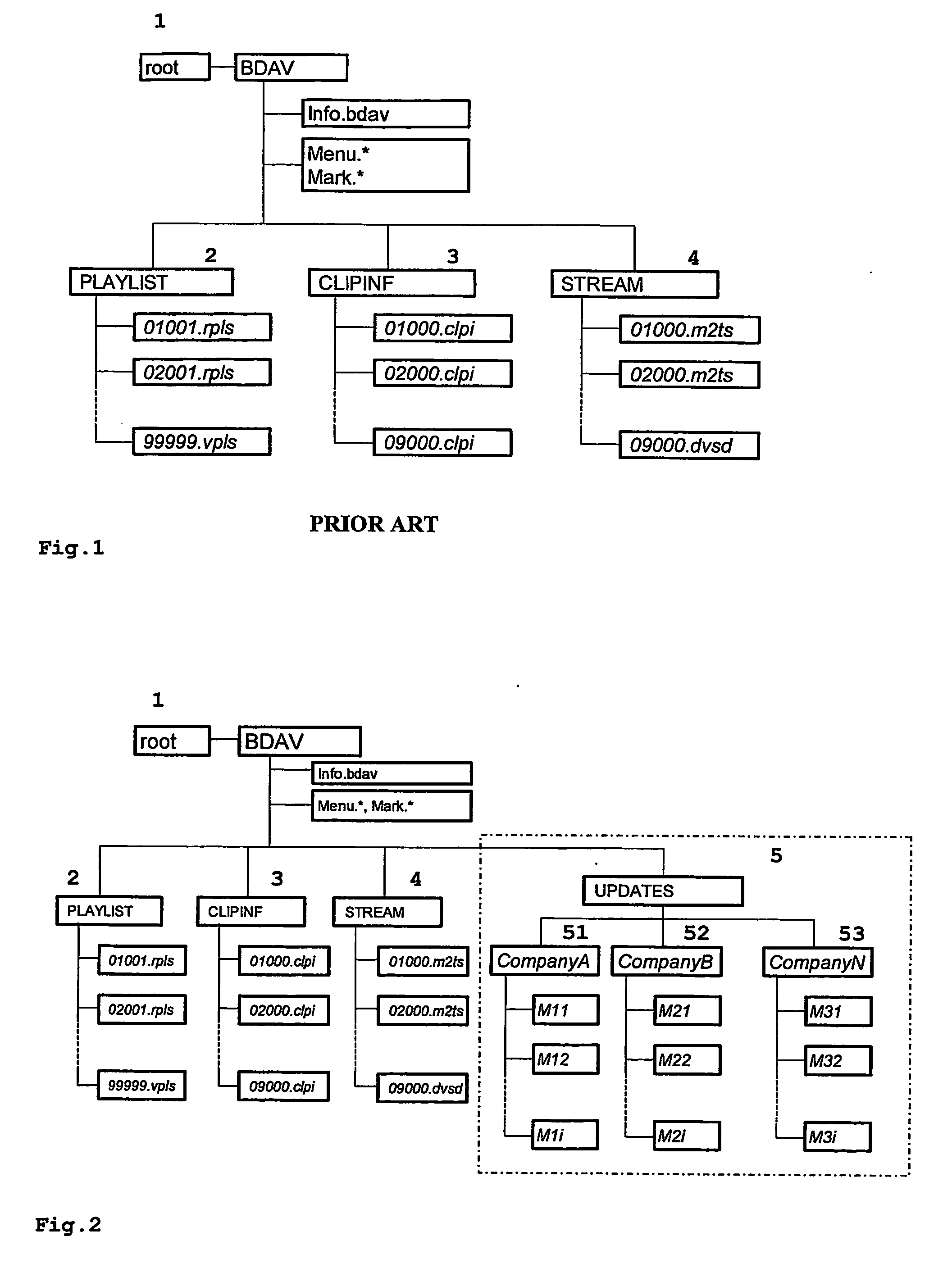
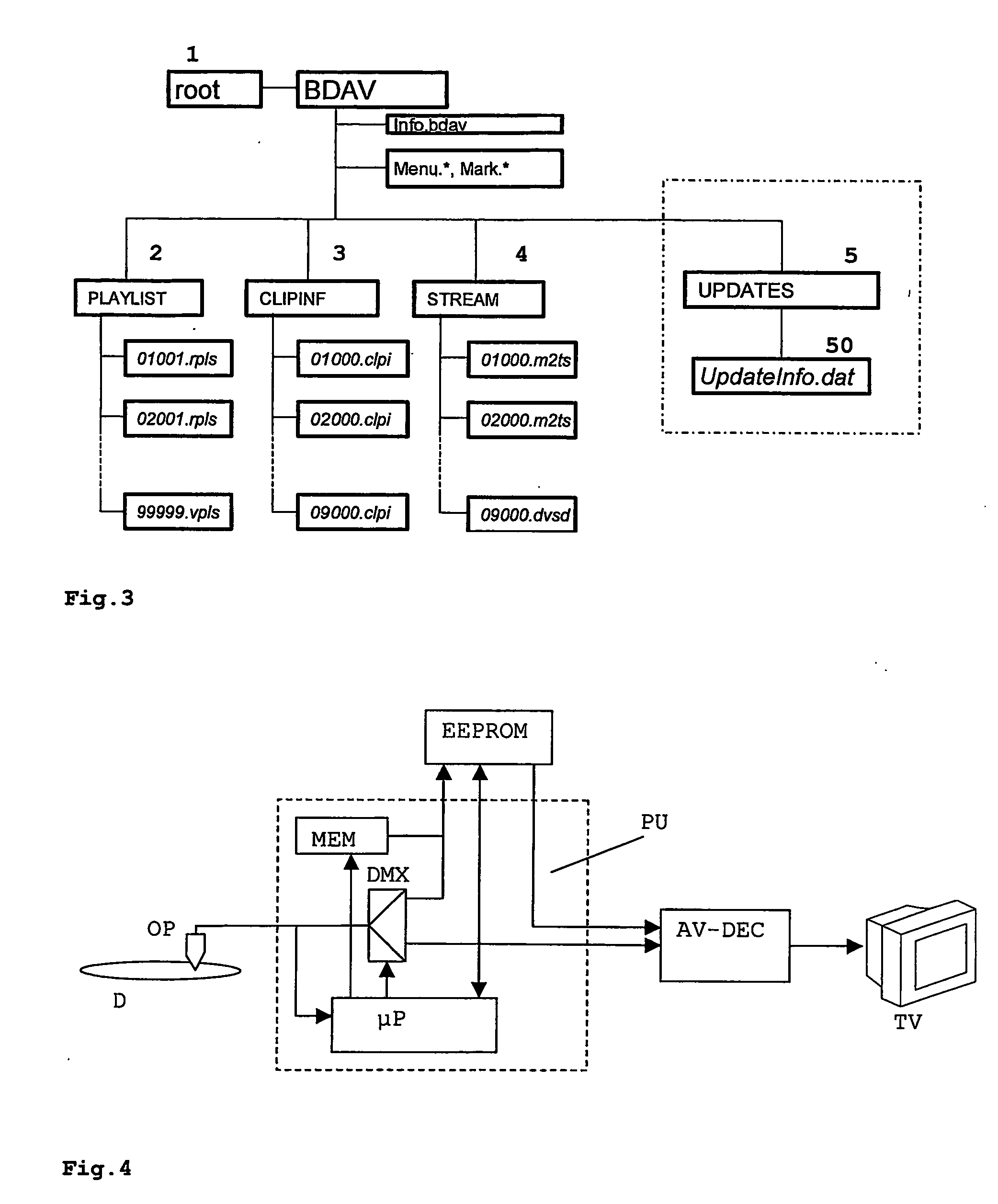
Removable Storage Medium for Audio-Visual Data
InactiveUS20070212026A1Easily obtainedEasily appliedColor television signals processingRecord information storageBlu-ray discDVD player
Playback devices, e.g. DVD players, for removable mass storage media used for the distribution of multimedia content contain a lot of firmware to control its functions. Typically, such firmware may be updated several times during the lifetime of the device. For playback devices that are already at a consumer's site and cannot be updated online, it is possible to update the firmware without using separate media, such as update-CDs, by storing firmware update data on removable storage media such as DVDs or Blu-ray discs that contain primarily audio-visual contents. Thus, it is possible to utilize unused storage space on e.g. optical discs, and to distribute and install firmware updates easily without requiring separate media or technical knowledge of the user.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
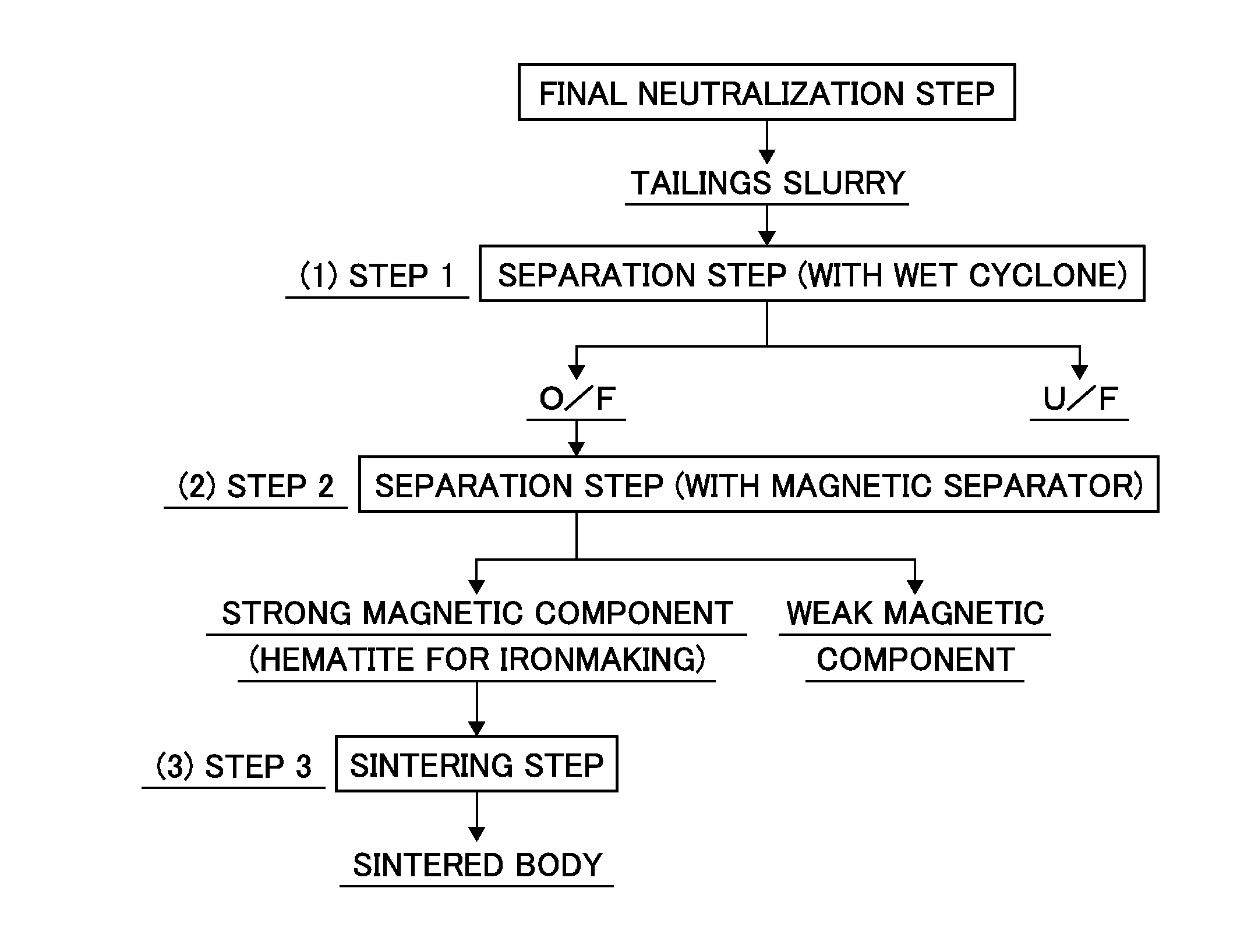
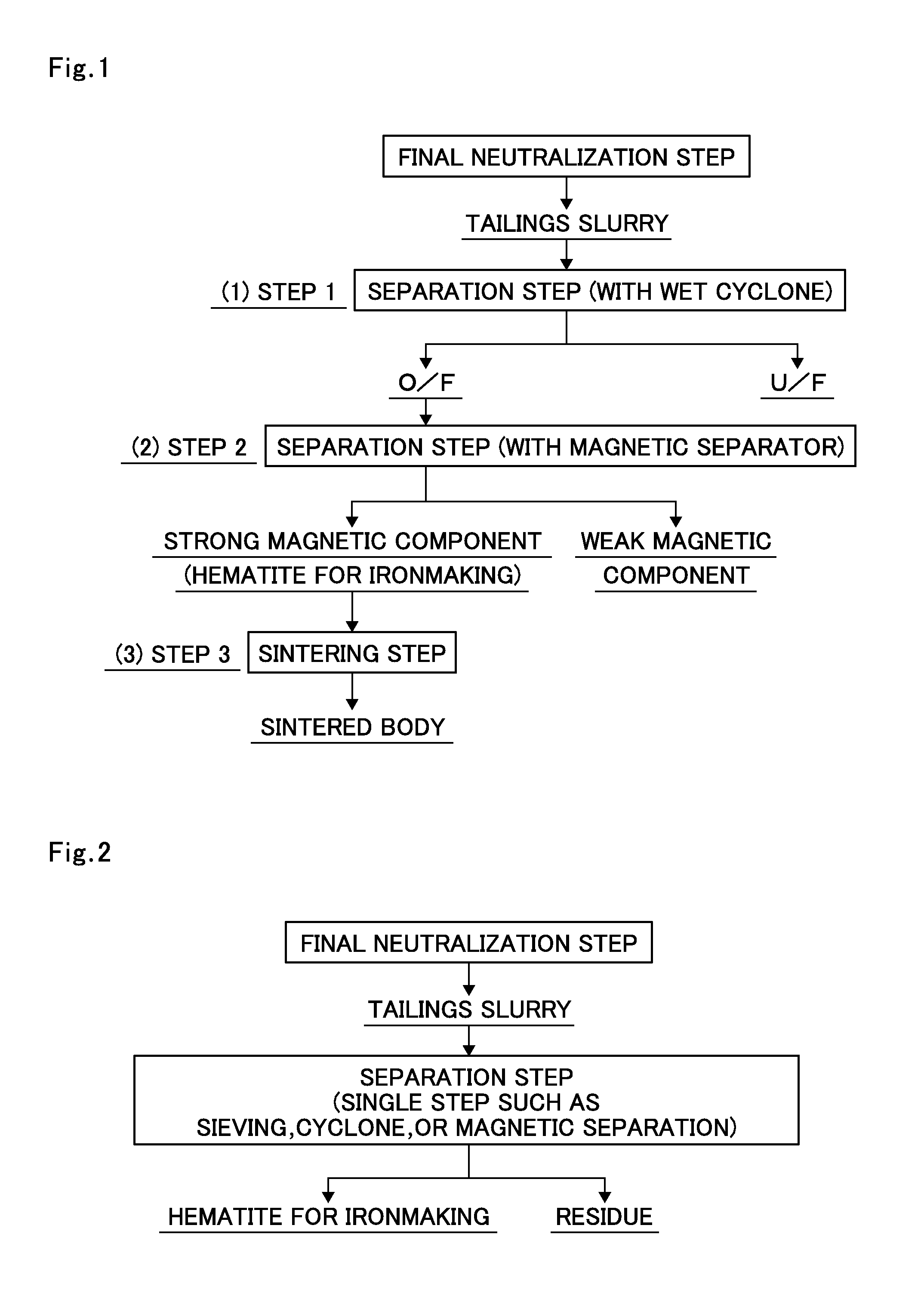
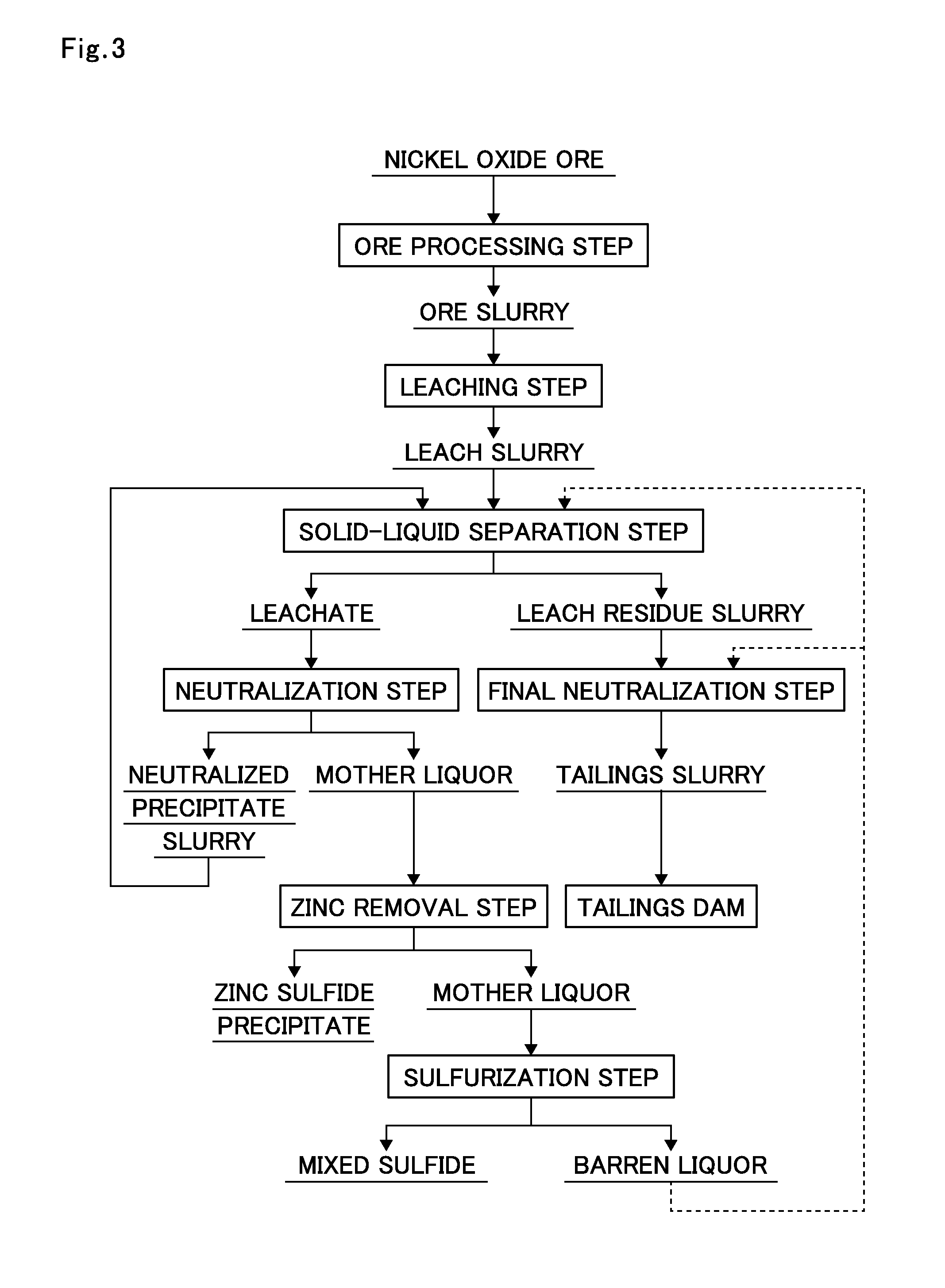
Process for producing hemataite for ironmaking
InactiveUS20160340201A1Easily obtainedEasy to getHigh gradient magnetic separatorsCentrifugal force sediment separationMagnetic separatorPhencyclone
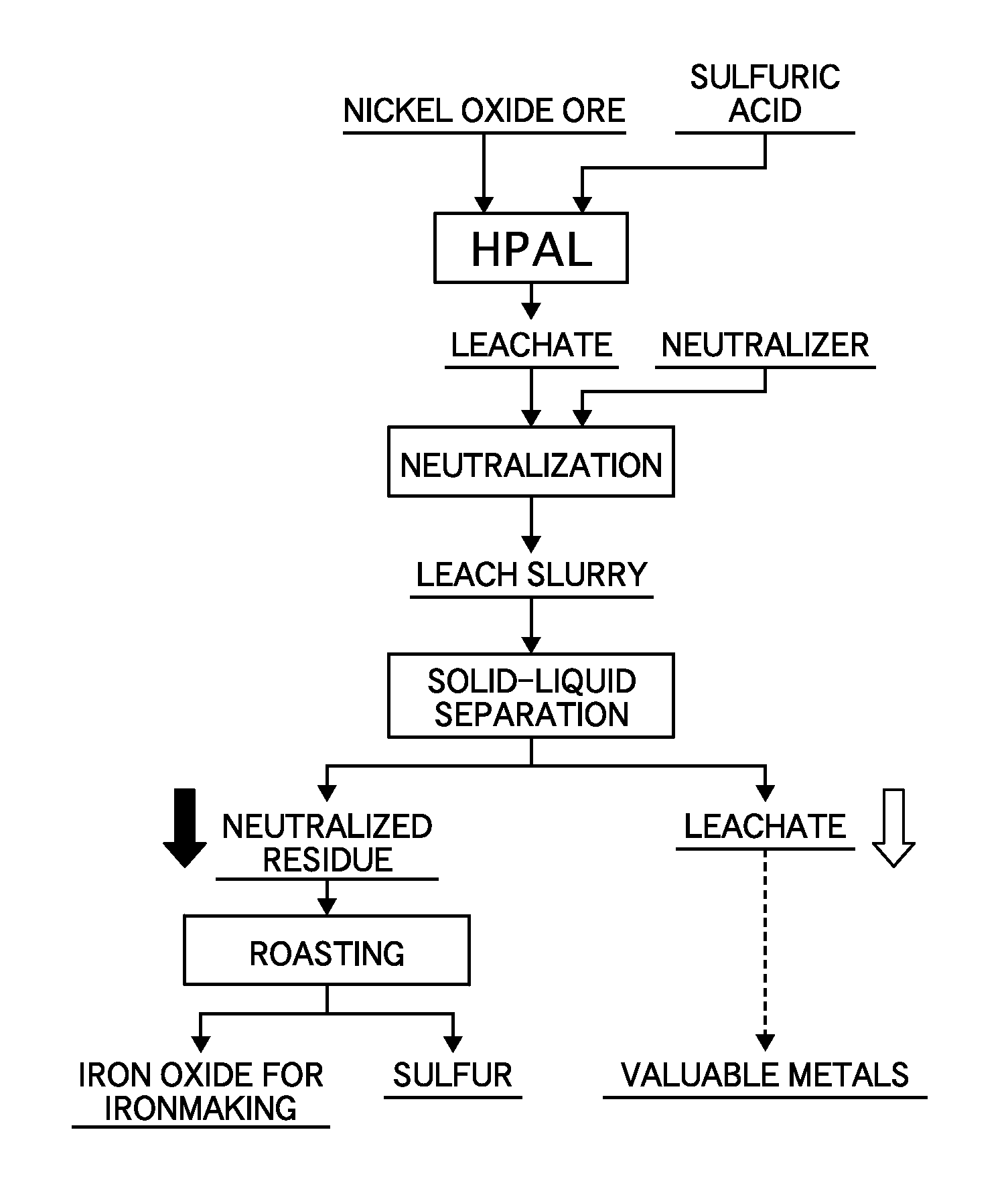
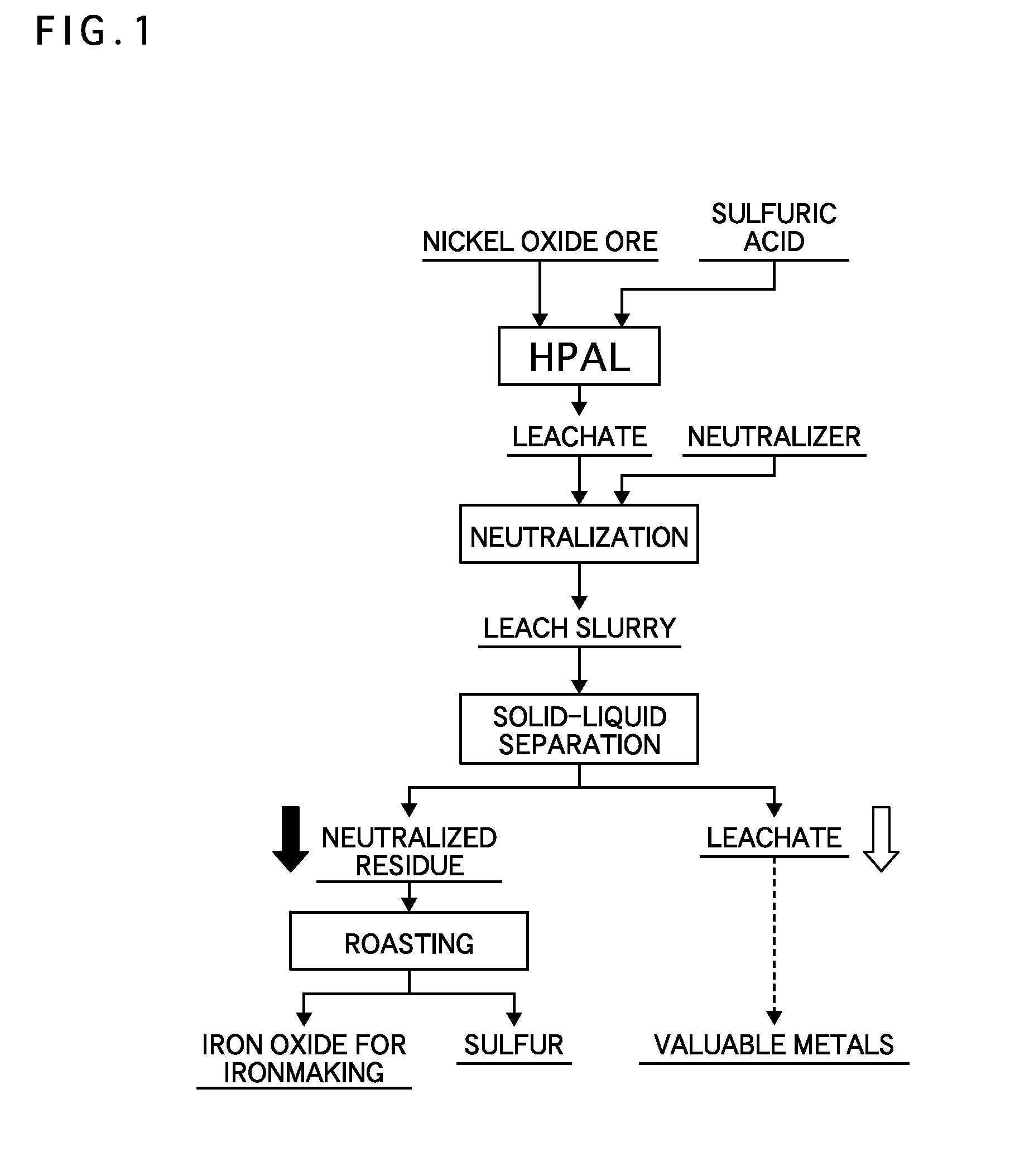
Proposed is a process for separating a leach residue from which a hematite-containing material that can be used as a raw material for ironmaking can be obtained, and provided is a production process of hematite for ironmaking from the leach residue. The process for producing hematite for ironmaking using, as a raw material, the leach residue in a slurry state obtained from a hydrometallurgical plant for nickel oxide ore utilizing a high pressure acid leach process comprises in sequence: a first step of separating the leach residue in a slurry state into an overflow and an underflow using a wet cyclone; a second step of separating the overflow into a strong magnetic component and a weak magnetic component using a strong-magnetic-field magnetic separator utilizing magnetic force; and a third step of sintering the separated strong magnetic component at a temperature of 1150 to 1350° C. to form a sintered body.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Pigment dispersions, block polymers and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20110136965A1Easily obtainedPolymerization conditions is mildInksOrganic dyesHeavy metalsDispersion stability
Disclosed is a pigment dispersion containing at least a pigment, a liquid medium and a high-molecular dispersant. The high-molecular dispersant is a block polymer represented by A-B or A-B-C, in which A, B and C each represent a polymer block and the A and C blocks may be the same or different. The block polymer and its production process are also disclosed. The high-molecular dispersant is free of problems of a smell, coloration, a heavy metal and cost, and its use can provide a pigment dispersion excellent in the dispersion stability of a pigment.
Owner:DAINICHISEIKA COLOR & CHEM MFG CO LTD +1
Novel asymmetrical bicipital lipid and tubular aggregate formed by using the same
InactiveUS20040120998A1Easily obtainedEasy to manufactureFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteEsterified saccharide compoundsMicrotubule cytoskeletonAqueous solution
The present invention offers a novel asymmetric double-headed lipid capable of forming a stable, nanometer scale micro-tubular aggregated material of containing a sugar and a carboxylic acid at each end. The present invention is an asymmetric double-headed lipid represented by the general formula R-NHCO-(CH2)n-COOH (I) (in the formula, R represents an aldopyranose radical from which the terminal reducing hydroxyl group is excluded and n is from six to twenty) and a hollow micro-tubular aggregated material formed from the asymmetric double-headed lipid. The external diameter of the micro-tubular aggregated material is 10-300 nm, and the length is 0.3-10 mum. The micro-tubular aggregated material can be manufactured by dispersing the asymmetric double-headed lipid described above in water at pH of two to eight, next heating to 80-100° C. to dissolve it and then gradually cooling the aqueous solution obtained.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
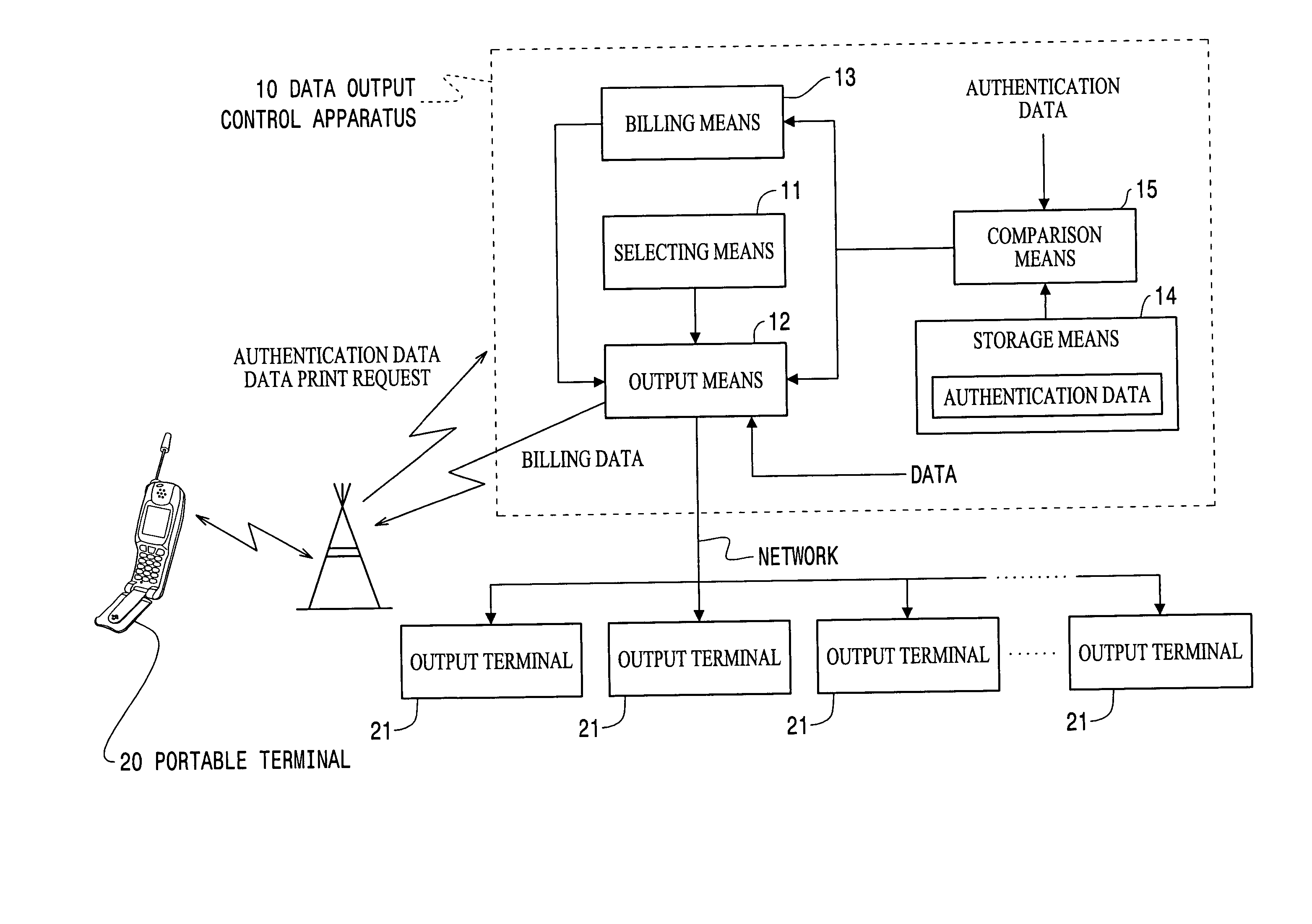
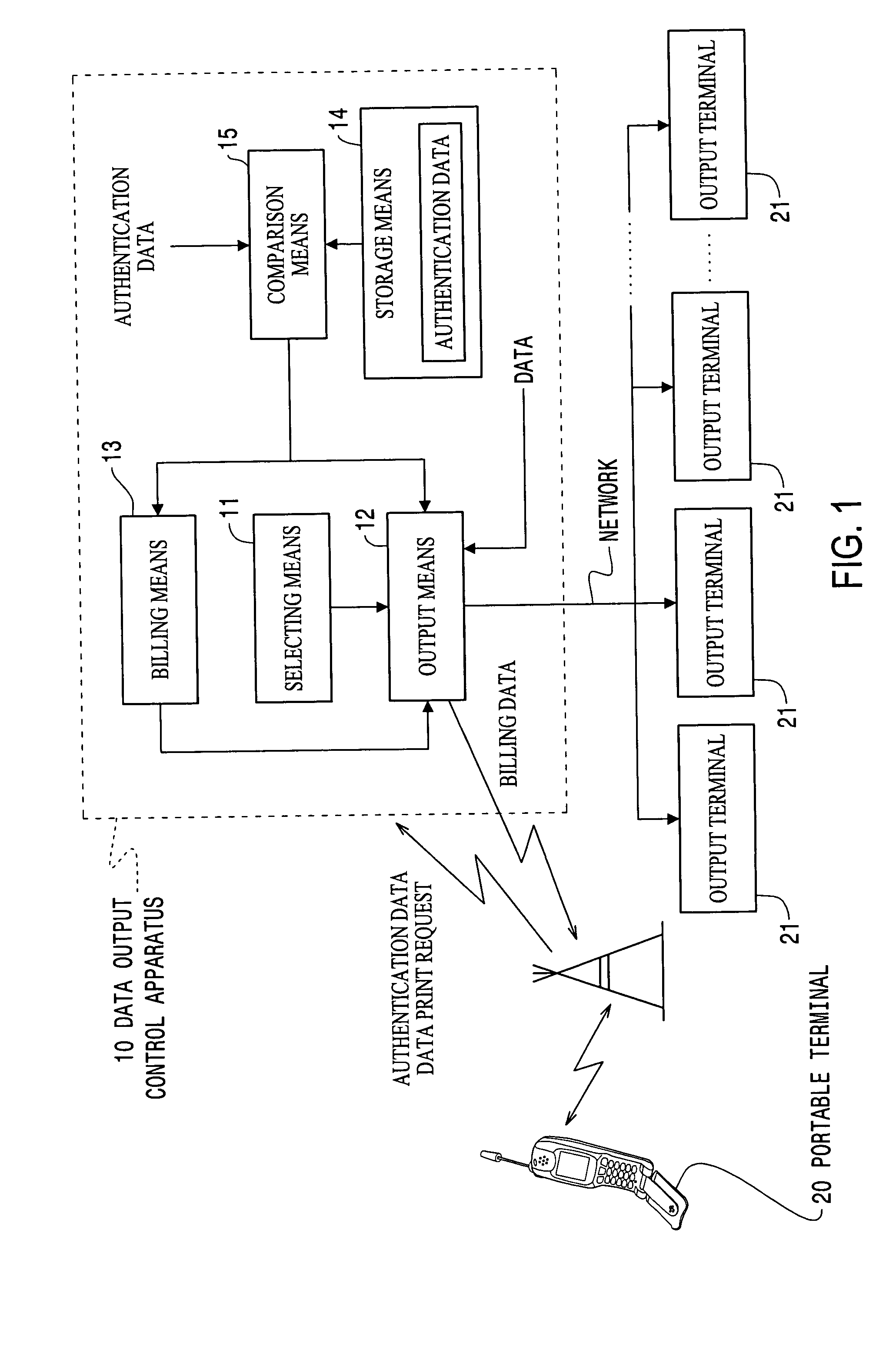
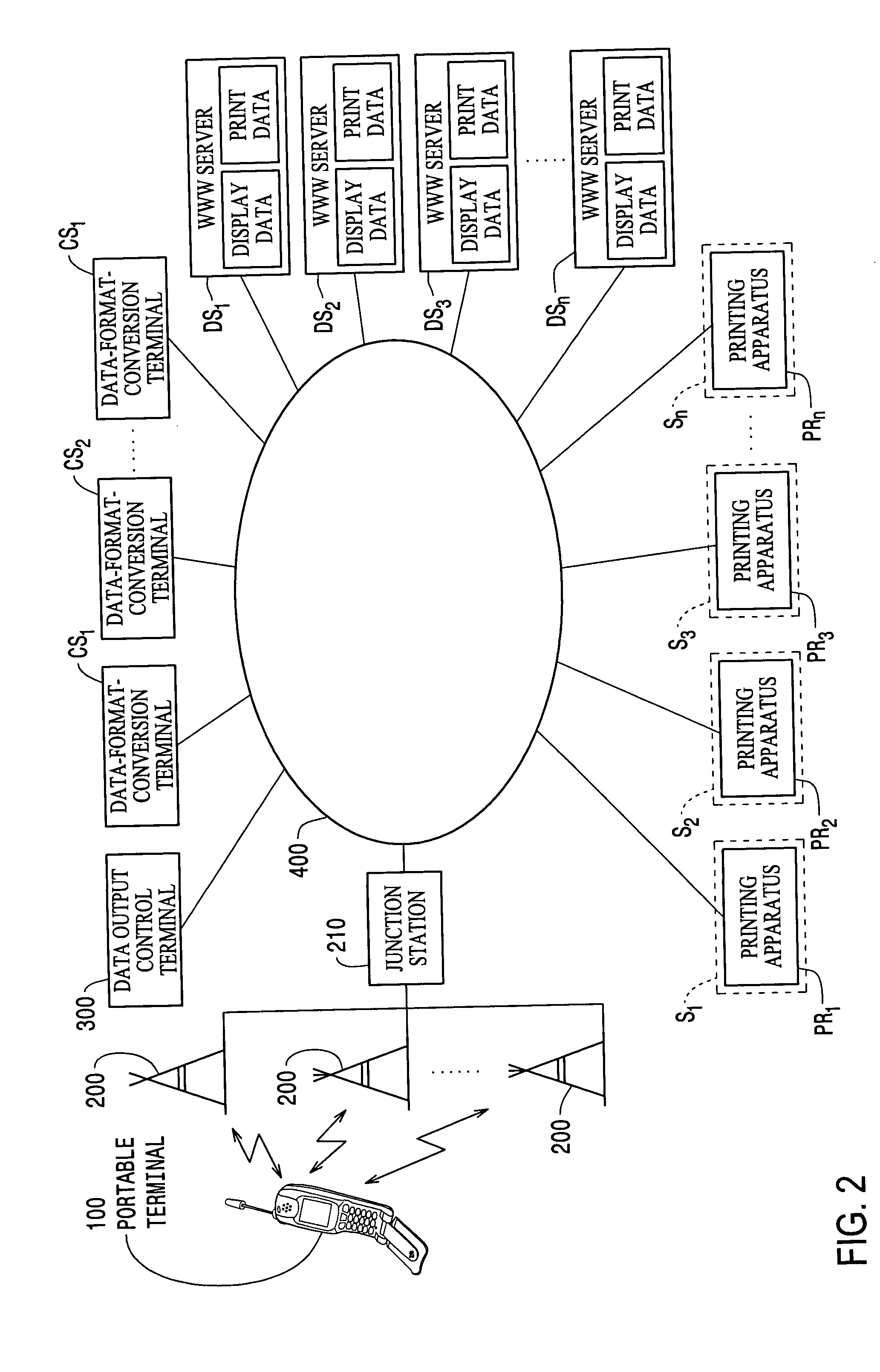
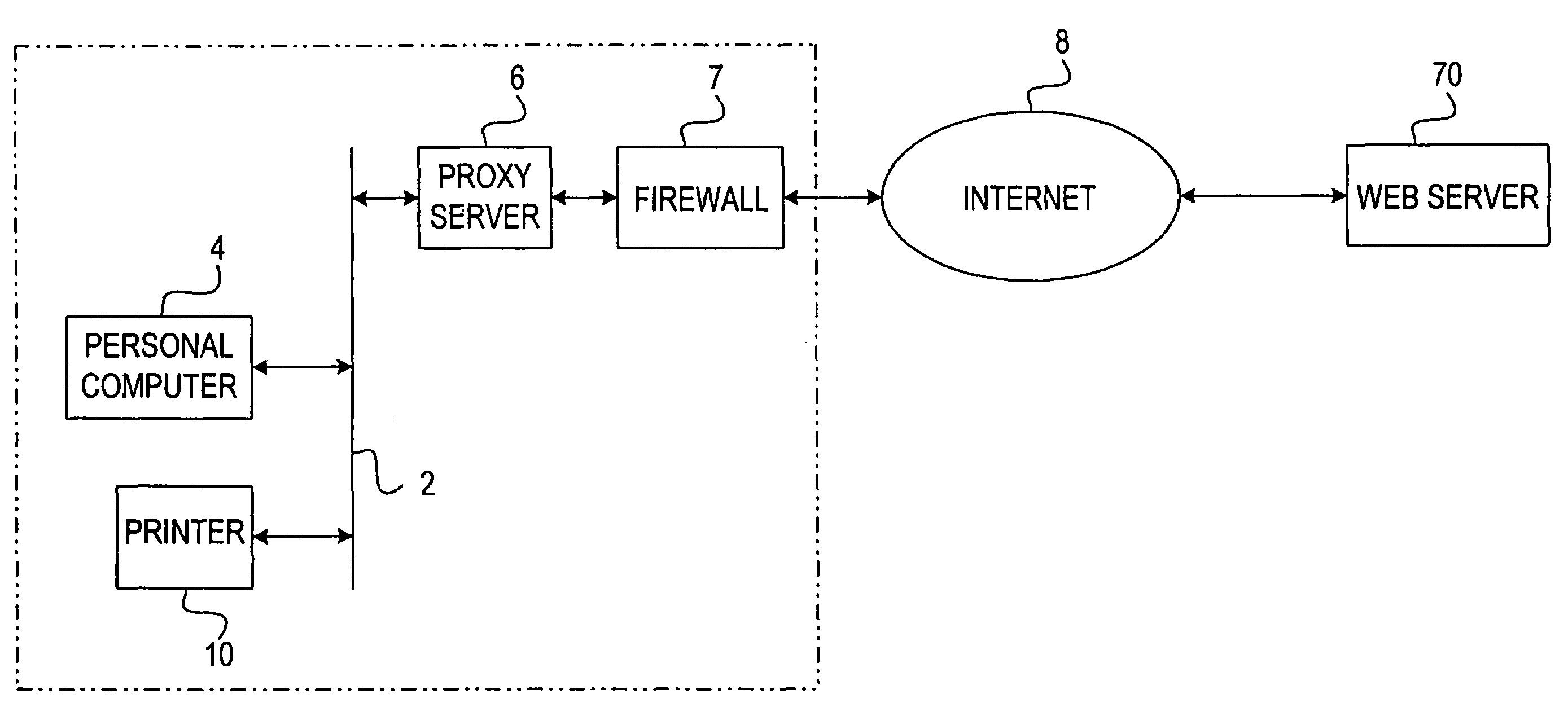
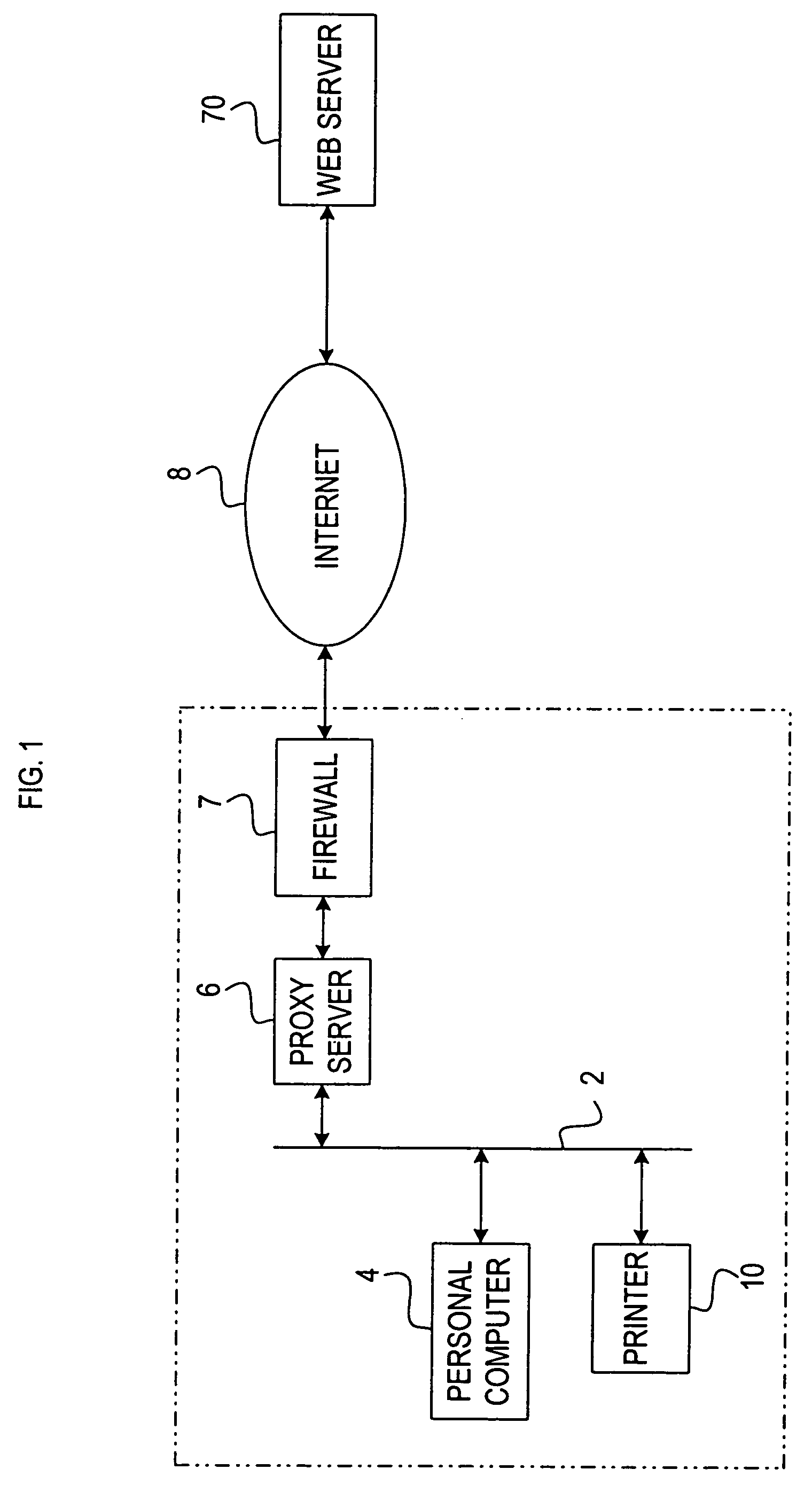
Data output control apparatus
InactiveUS20050131819A1Easily obtainedFavourable costAccounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementData selectionThe Internet
The invention provides a data output control apparatus which allows detailed information on a network to be readily obtained, which is advantageous with respect to cost, and which is suitable for specifically notifying the user of the service charge. A data output control terminal is communicatively connected via the Internet to a portable terminal carried by a user, printing apparatuses provided at various locations, and WWW servers. The data output control terminal obtains from a WWW server data associated with a data print request from the portable terminal, selects one of the plurality of printing apparatuses, and outputs the obtained data to the selected printing apparatus. Billing is executed in accordance with the result of use by the portable terminal of the print service provided by the data output control terminal. The billing is executed by summing the service charge and the call charge of the portable terminal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Insert injection molding method and jig
A radiator core support is made by an insert injection molding method. Four core members shaped in a triangular prism are built into a quadric-prism core and inserted into a rectangular tube, an upper radiator core support member. Then, an outwardly pressing member is inserted into a longitudinal slanted hole of the core to move and contact its members to the inner surfaces of the tube. The tube is located in a mold, into which molten molding material is injected. The tube is overmolded at the tops of a hood lock stay, and right and left side support members, being integrally formed out of rein. After cooling, drawing the pressing member from the core; then the core from the mold; and the molded part is removed from the mold.
Owner:CALSONIC KANSEI CORP
Rotation position detection device and air conditioner
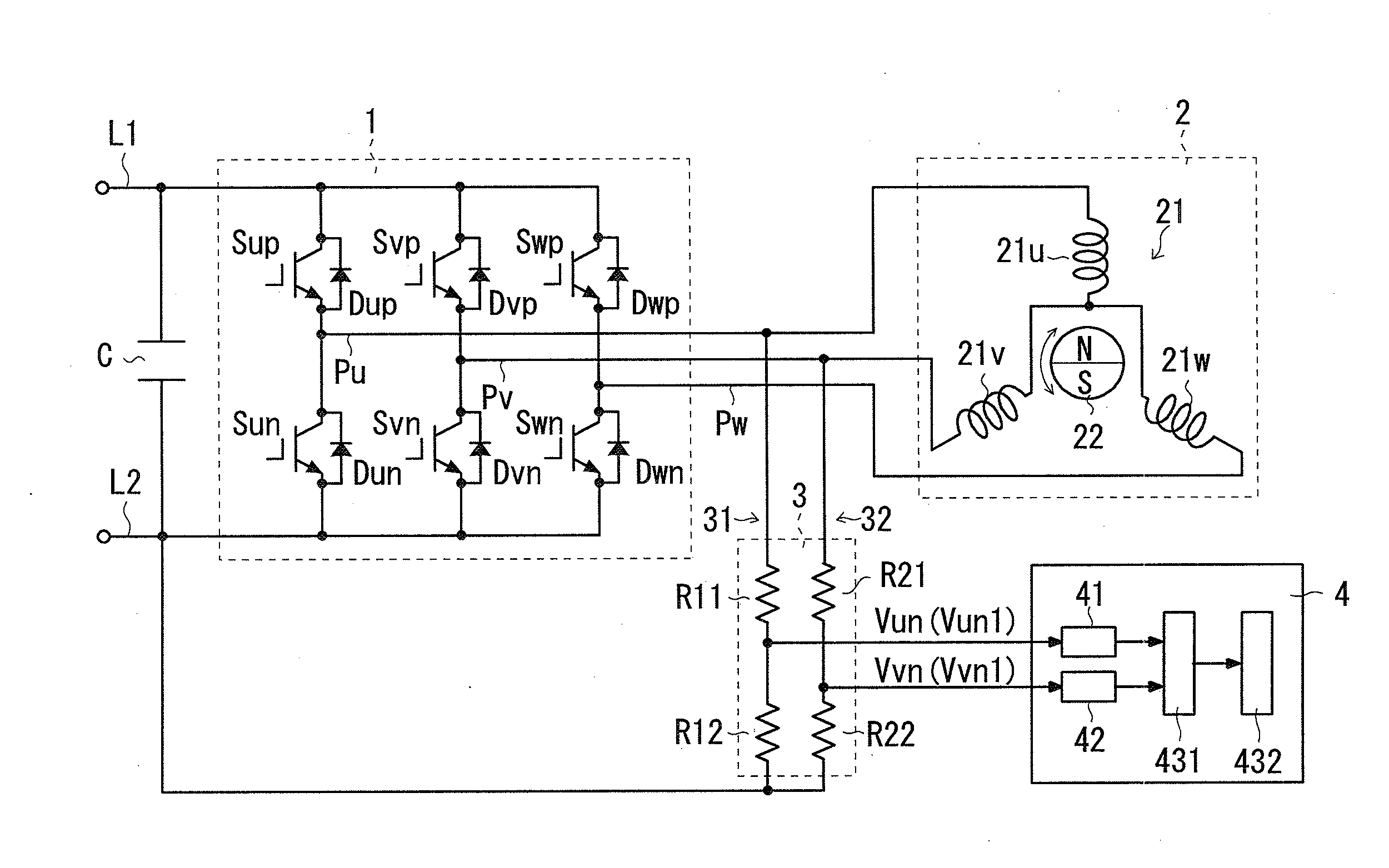
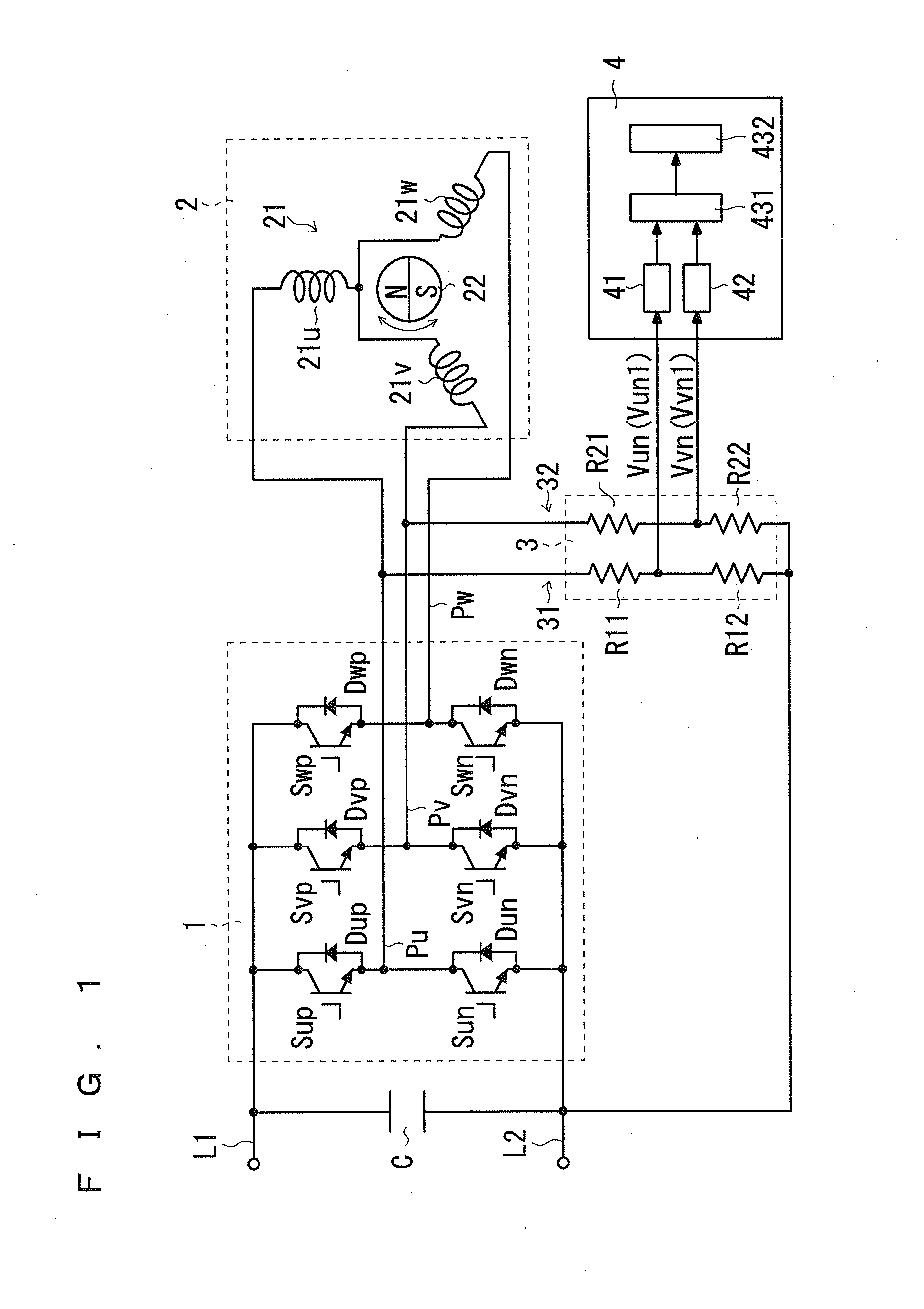
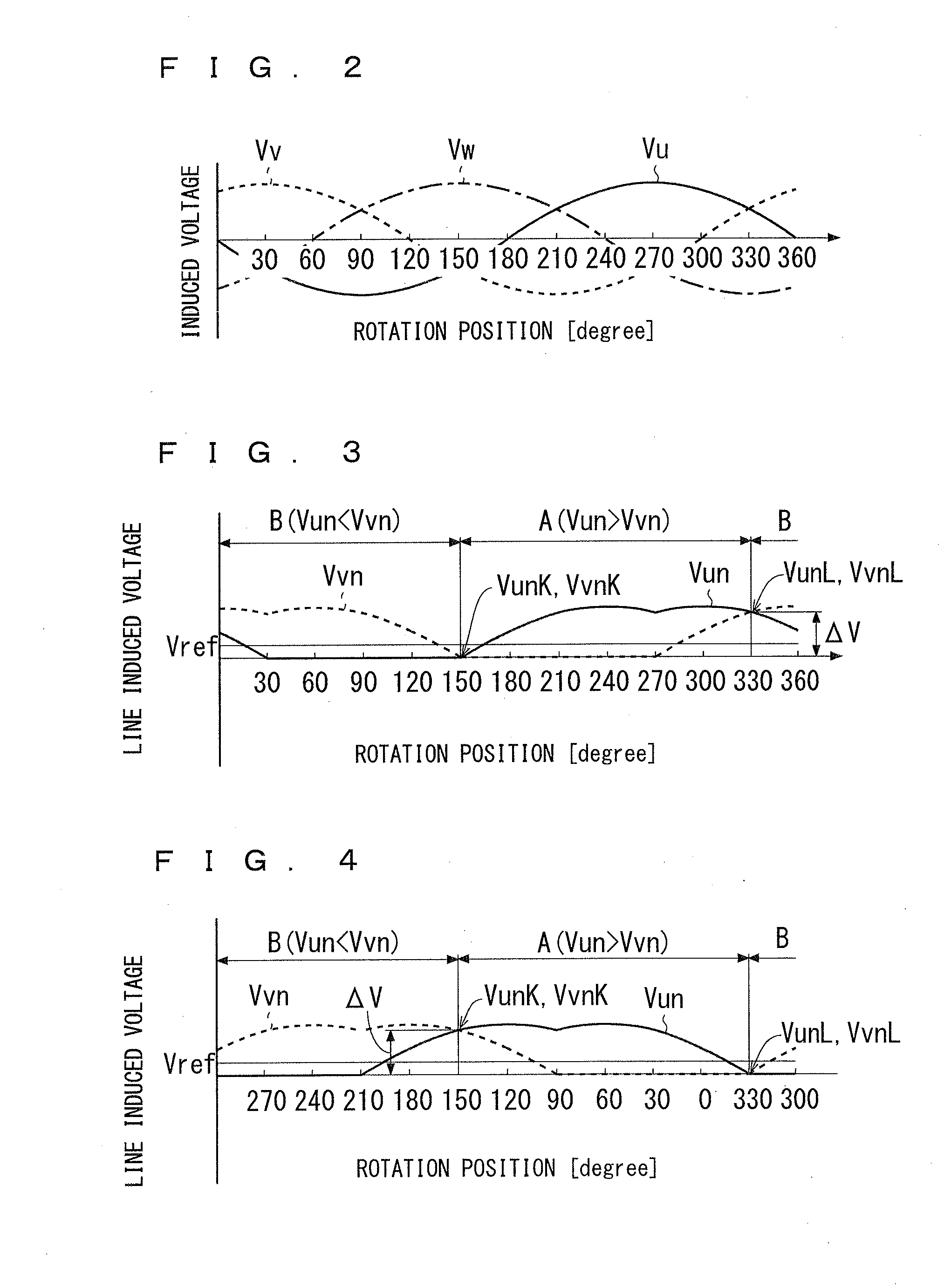
ActiveUS20150211894A1Improve estimation accuracyEasily obtainedSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor parameters estimation/adaptationMinimum phasePhysics
A detector detects whether or not a first line induced voltage and a second line induced voltage match each other, the first line induced voltage being a potential difference of a first phase potential of phase potentials relative to a reference potential, and the second line induced voltage being a potential difference of a second phase potential of the phase potentials other than the first phase potential relative to the reference potential. The phase potentials is outputted by the armature due to an induced electromotive force. The reference potential is any one of a minimum phase and a maximum phase. A rotation-position setting unit sets, to a predetermined value, an estimation value of a rotation position of the motor 2 at a point in time when the first line induced voltage and the second line induced voltage match each other.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Process for producing hydrofluoroolefin
InactiveUS20170158587A1Easily obtainedHigh purityPreparation by dehalogenationOrganic chemistry methodsChemistryMagnesium
To provide a method for producing a hydrofluoroolefin, wherein formation of an over-reduced product having hydrogen added to a material chlorofluoroolefin and an over-reduced product having not only chlorine atoms but also fluorine atoms in the chlorofluoroolefin replaced with hydrogen atoms, as by-products, is suppressed.A method for producing a hydrofluoroolefin, which comprises reacting a specific chlorofluoroolefin with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst supported on a carrier, to obtain a specific hydrofluoroolefin,wherein the catalyst is a catalyst composed of an alloy containing at least one platinum group element selected from the group consisting of palladium and platinum, and at least one second element selected from the group consisting of manganese, copper, aluminum, gold, lithium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, silver, zinc, cadmium, indium, silicon, germanium, tin, lead, arsenic, antimony and bismuth.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
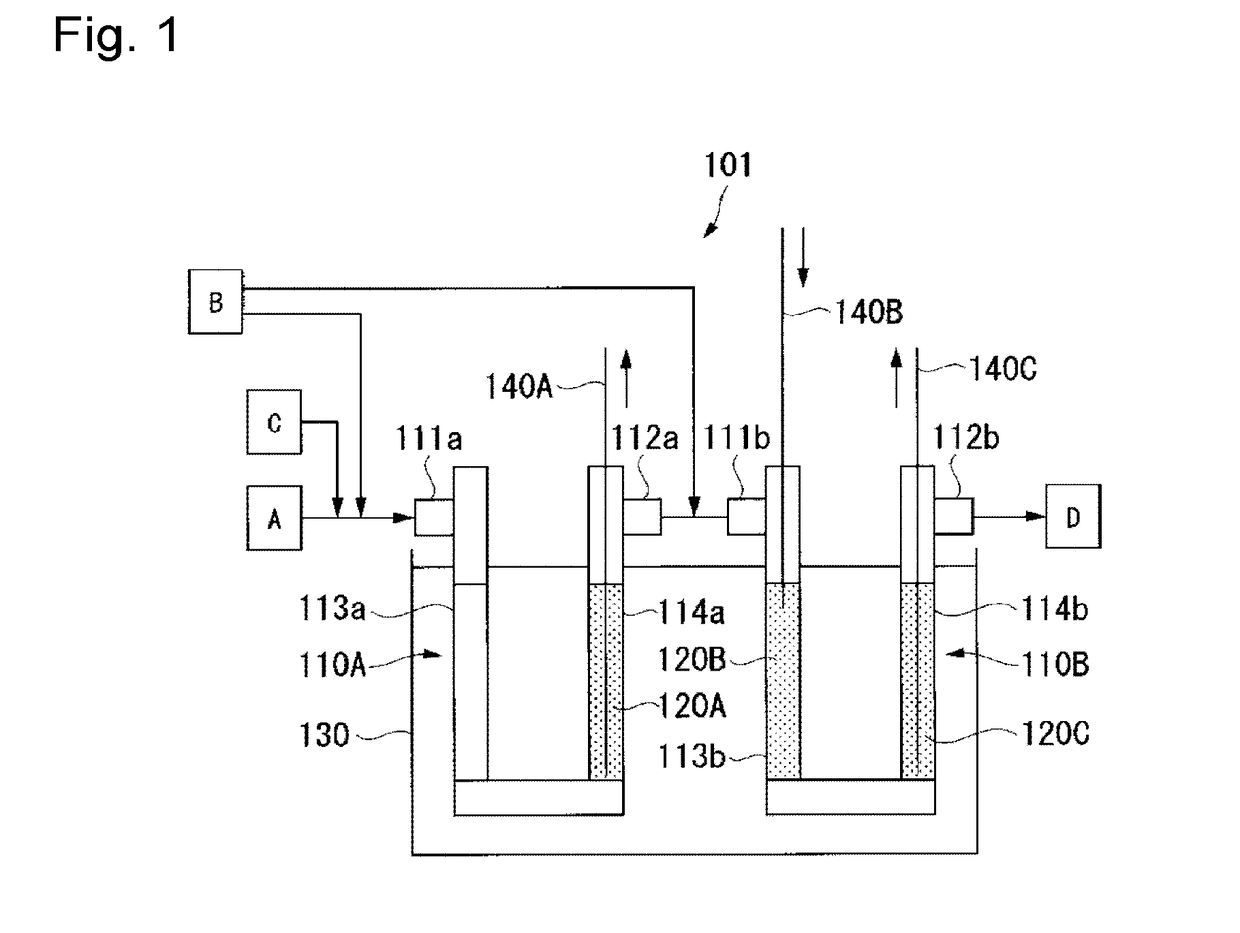
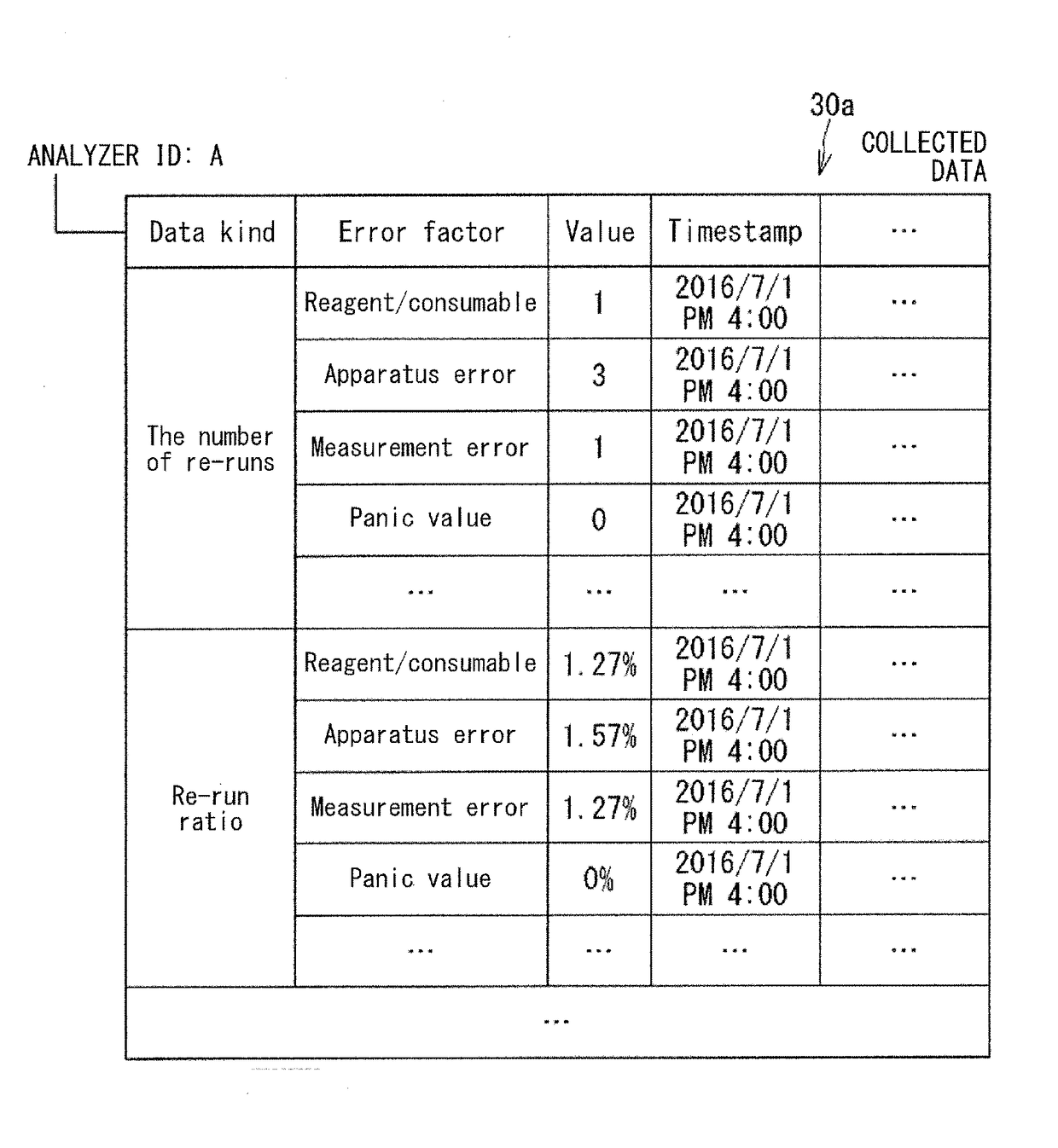
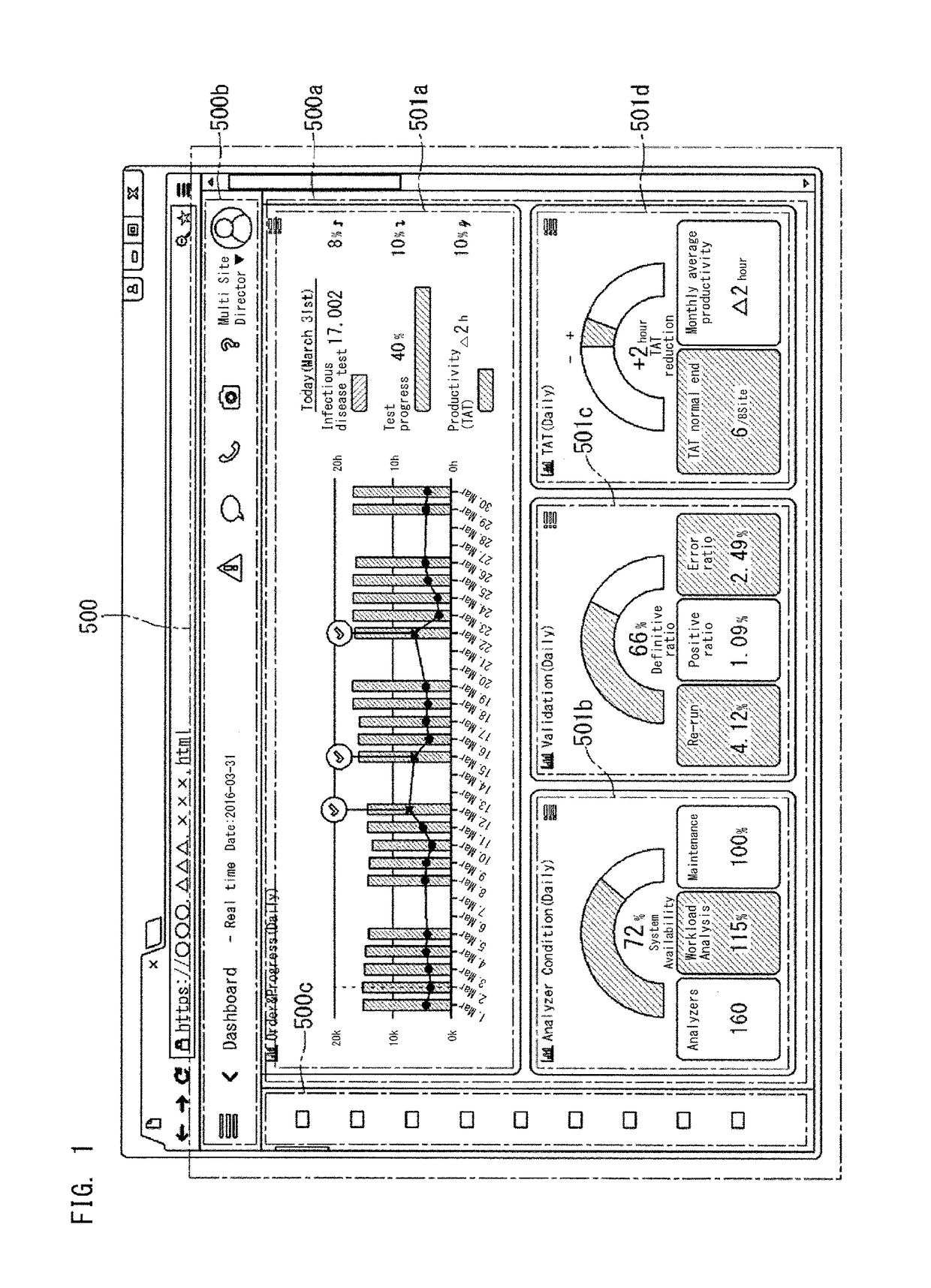
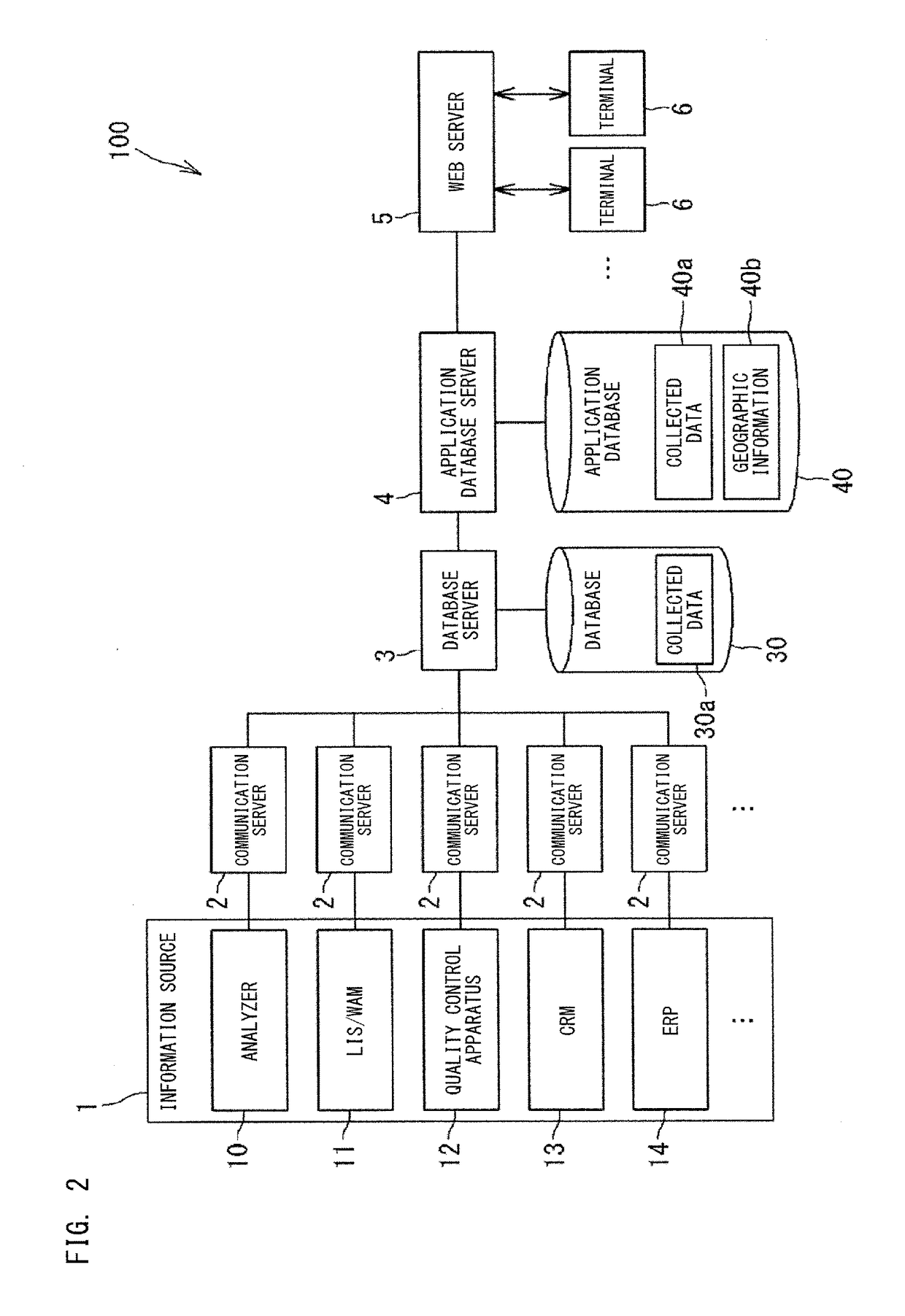
Information processing apparatus and method for clinical laboratory management
ActiveUS20180046781A1Easily obtainedEasy to getData visualisationComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionAnalyserInformation processing
To facilitate management of the entirety of one or a plurality of clinical laboratories. This information processing apparatus is used in management of a clinical laboratory in which an analyzer configured to analyze specimens is installed. The information processing apparatus includes: a communication section configured to communicate with a terminal operable by a user; and a controller configured to control display of the terminal via the communication section. On the basis of information collected from a plurality of analyzers installed in one or a plurality of clinical laboratories and from apparatuses relevant to the analyzers, the controller causes the terminal to display a screen including an index that indicates a status of the entirety of the one or the plurality of clinical laboratories. In response to the user selecting the index displayed in the screen, the controller causes the terminal to display the selected index so as to be divided in a plurality of categories.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Three-dimensional product having nanoporous surface and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100190403A1Easy to produceEasily obtainedMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationThree dimensional shapeNanometre
The present invention provides a method for producing a three-dimensional product having a nanoporous surface in which the pore density, pore size or pore size distribution can be easily and readily controlled. The invention combines two techniques: a method for producing a three-dimensional product in which a yarn is knitted or woven to finish into an arbitrary three-dimensional shape, and a method for transforming a surface consisting of a material in which nanoparticles are dispersed in a matrix to a nanoporous surface by immersing the surface in a liquid which dissolves the nanoparticles but does not dissolve the matrix.
Owner:EMPIRE TECH DEV LLC
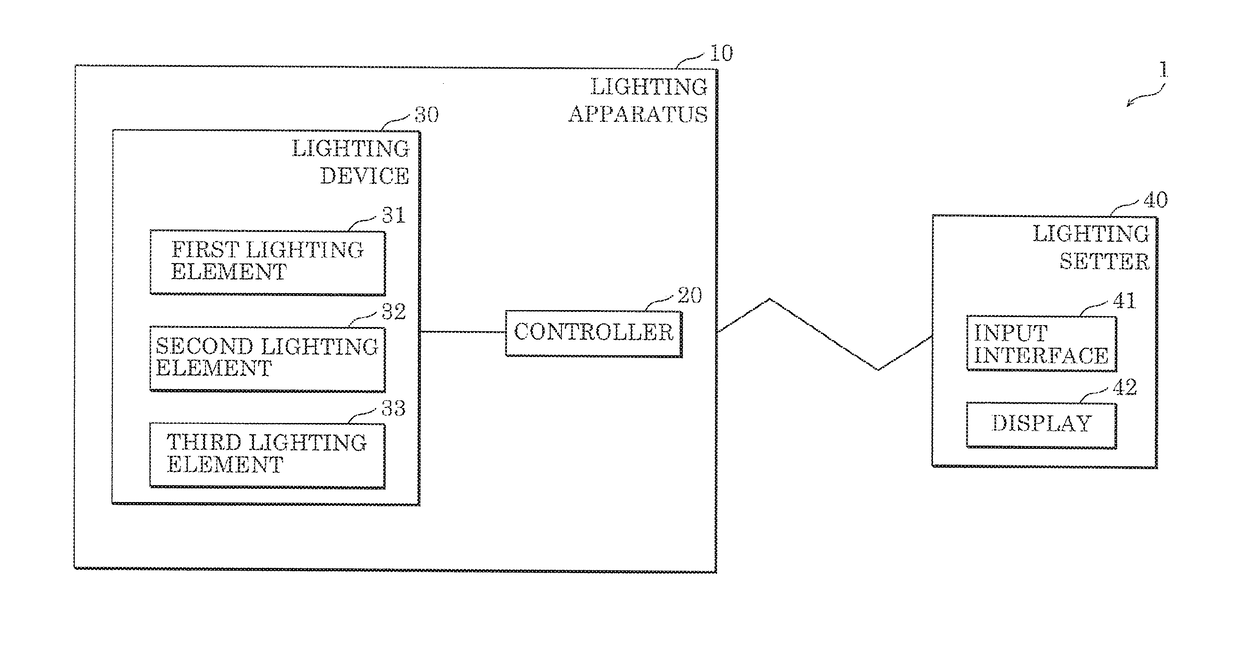
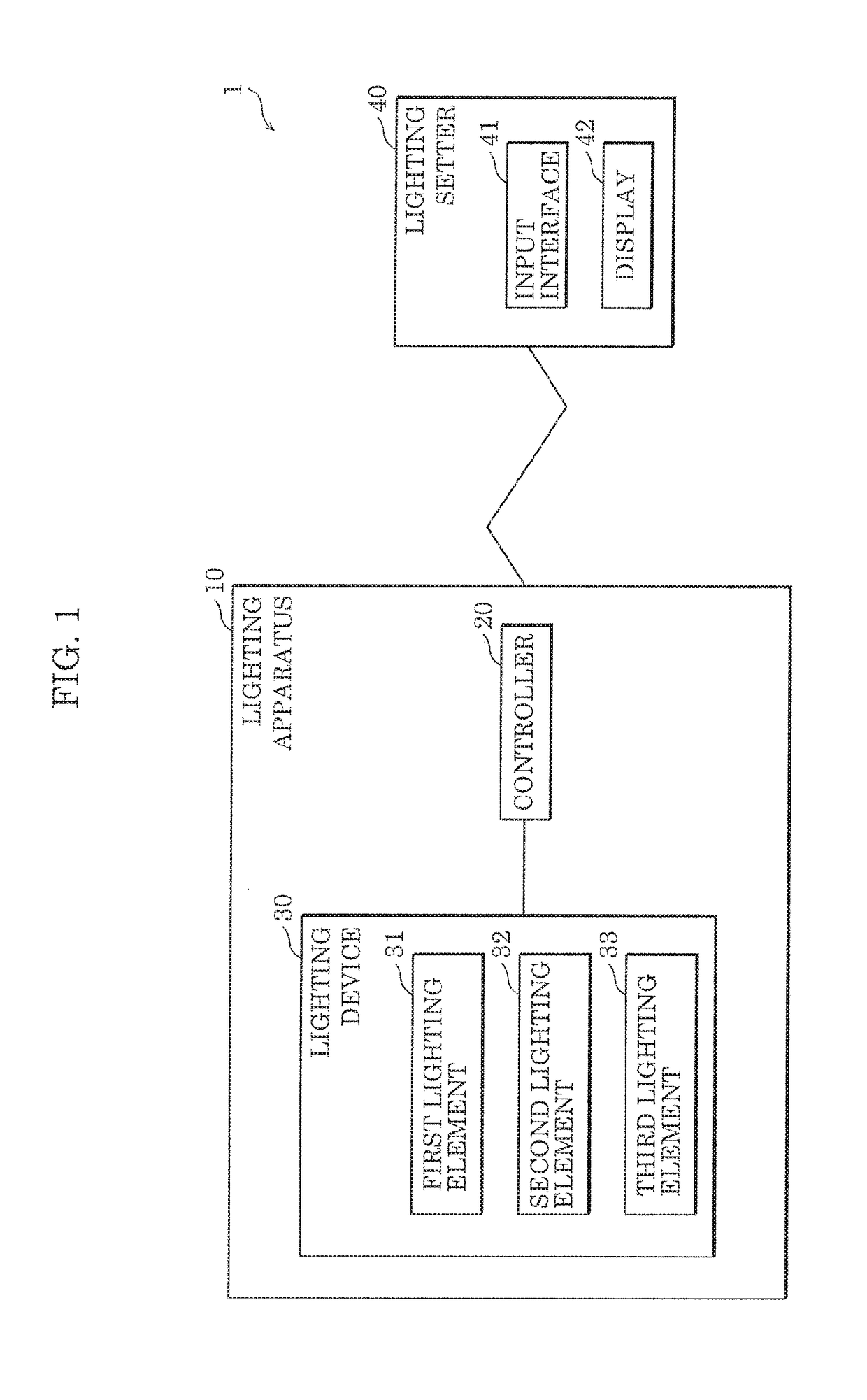
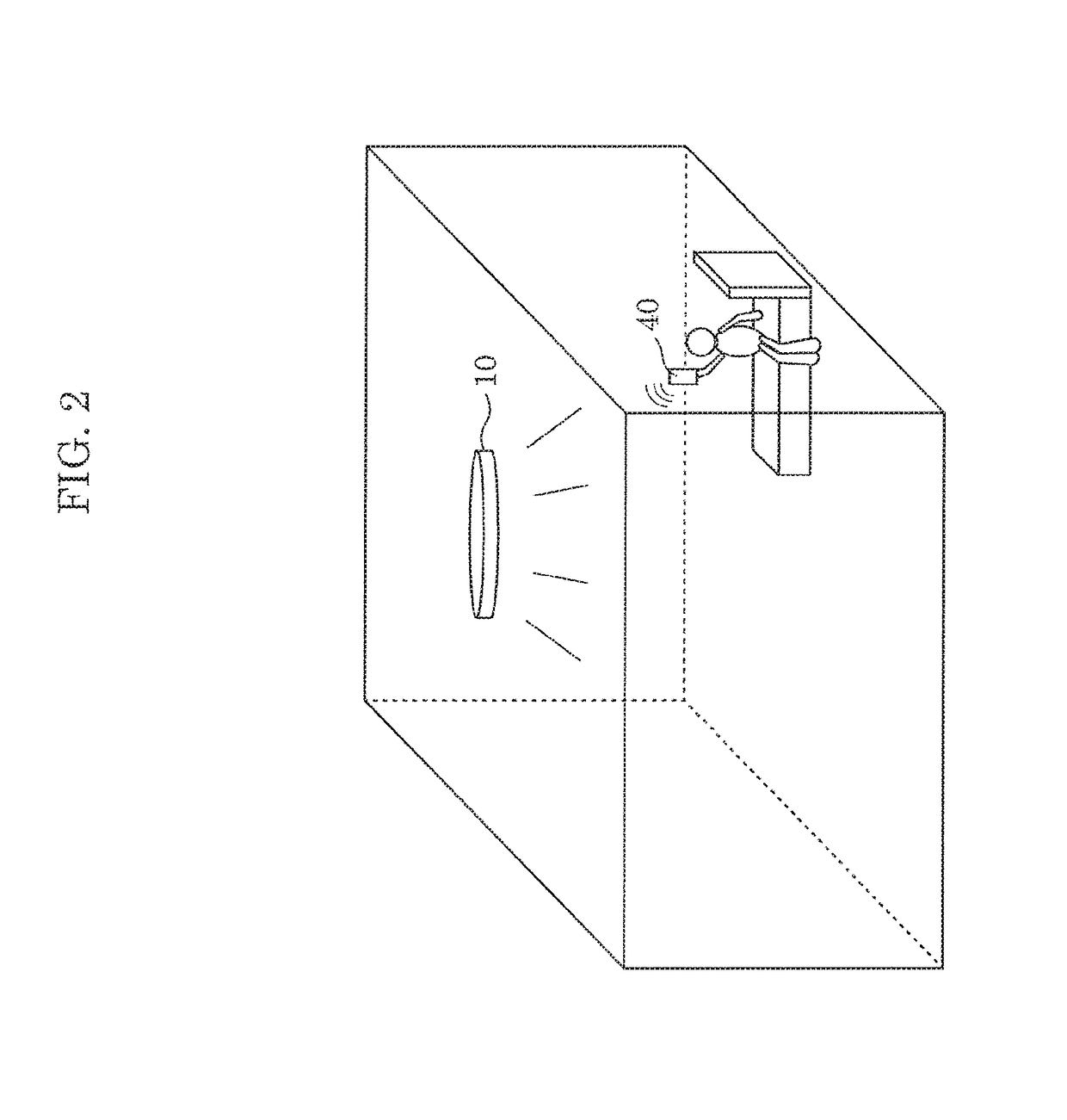
Lighting apparatus and lighting system
ActiveUS20180063912A1Easily obtainedSimple contentElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLighting systemEngineering
A lighting apparatus includes: a lighting device; and a controller which receives from a lighting setter, an instruction for causing the lighting device to operate in a predetermined mode, causes the lighting device to operate in the predetermined mode according to first control content, and subsequently receiving the instruction, causes the lighting device to operate in the predetermined mode according to second control content which is modified from the first control content based on first subjective information input to the lighting setter, the first subjective information indicating feedback of a user on the first control content.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
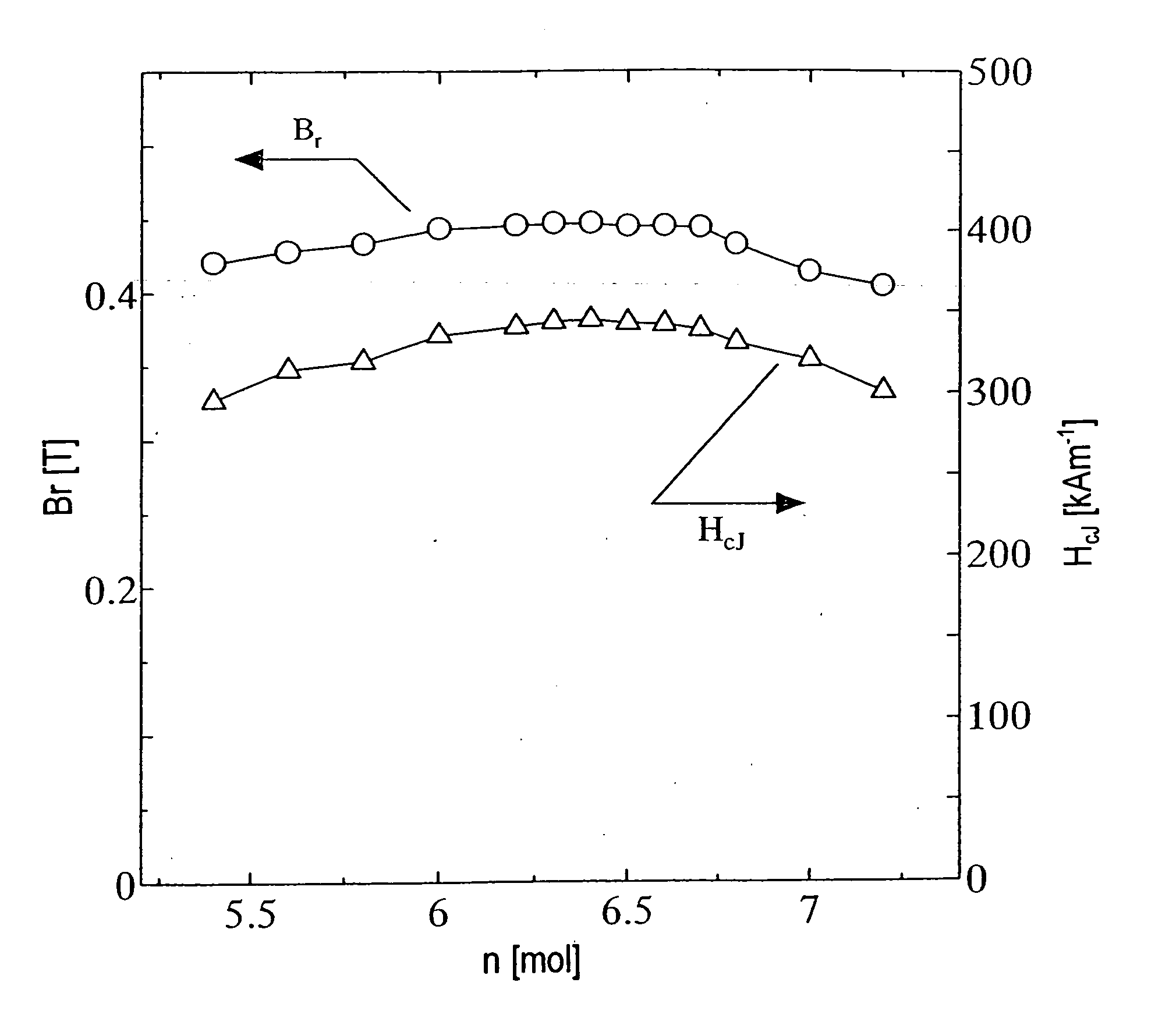
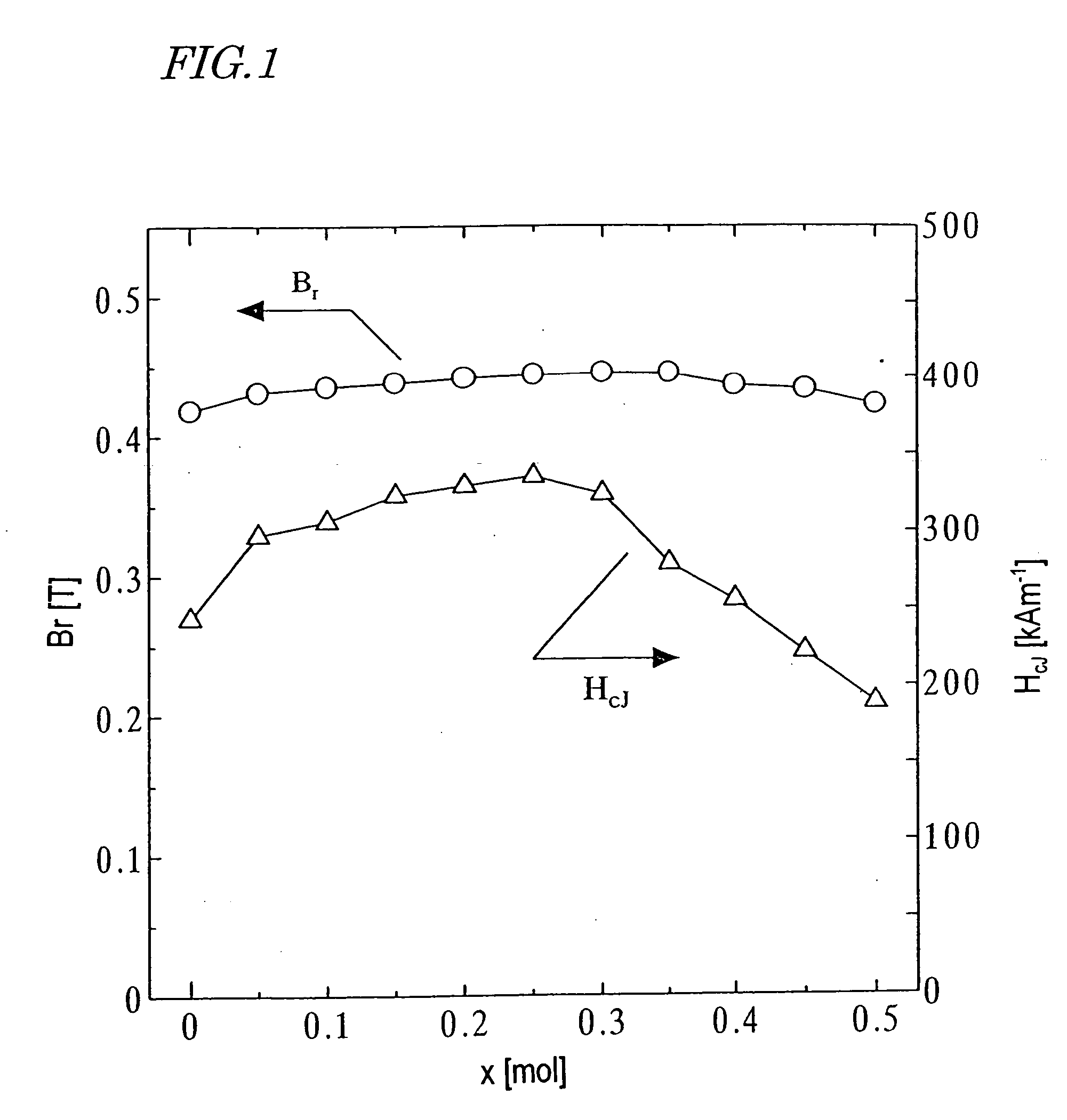
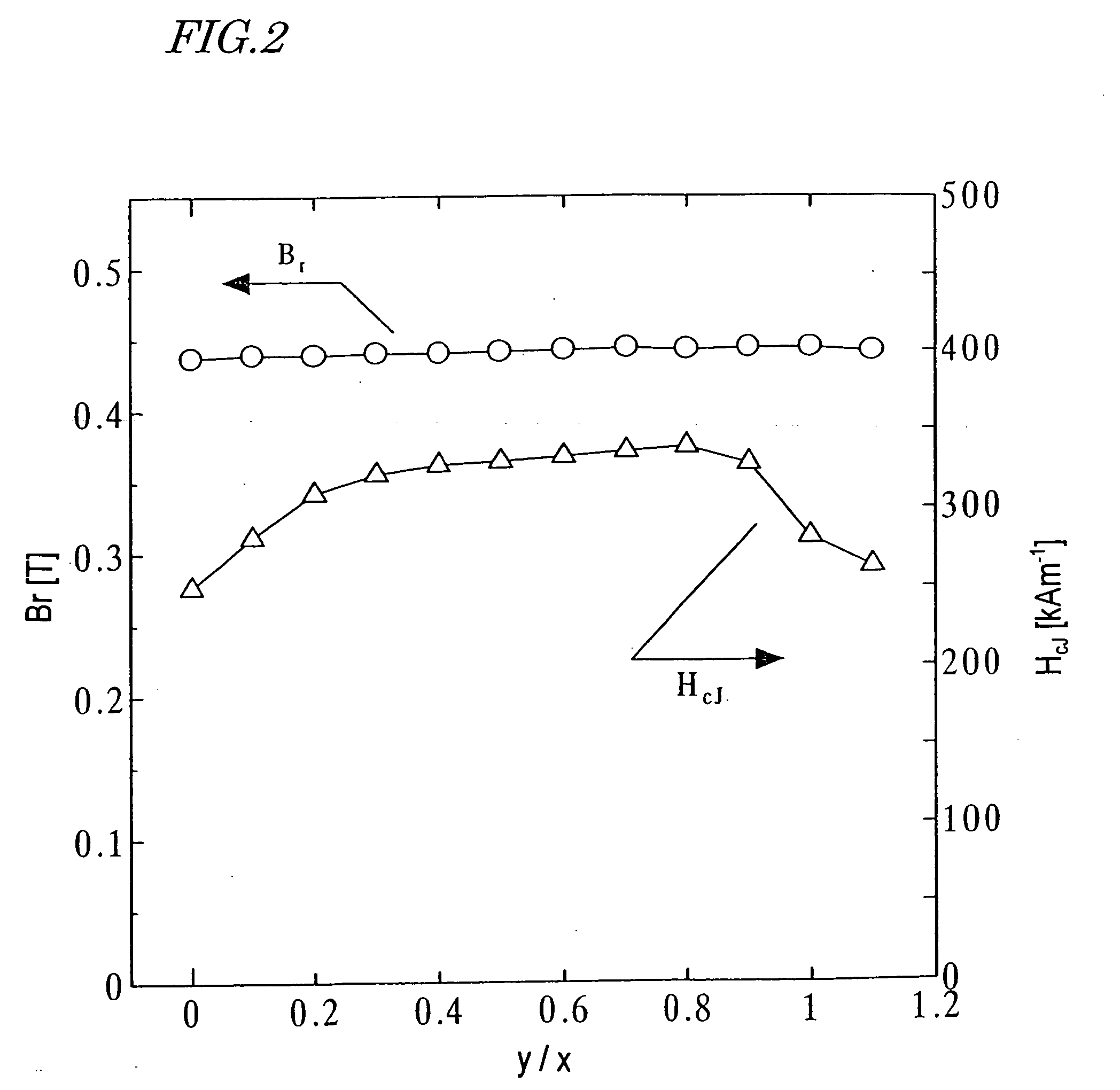
Permanent magnet and method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20040121188A1Easily obtainedEfficiently applicableMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageRare-earth elementMagnet
A ferrite magnet obtained by adding at least one element selected from the group consisting of Co, Ni, Mn and Zn to a ferrite having a hexagonal M-type magnetoplumbite structure, in which a portion of Sr, Ba, Pb or Ca is replaced with at least one element that is selected from the group consisting of the rare-earth elements (including Y) and Bi and that always includes La, during the fine pulverization process thereof, and then subjecting the mixture to re-calcining and / or sintering process(es). By adding a small amount of the element such as Co, Ni, Mn or Zn to the ferrite already having the hexagonal M-type magnetoplumbite structure during the fine pulverization process thereof, the magnetic properties can be improved.
Owner:SUMITOMO SPECIAL METAL CO LTD
Service providing system for providing services using a devoted web page created by a web server provided outside and connected to a network
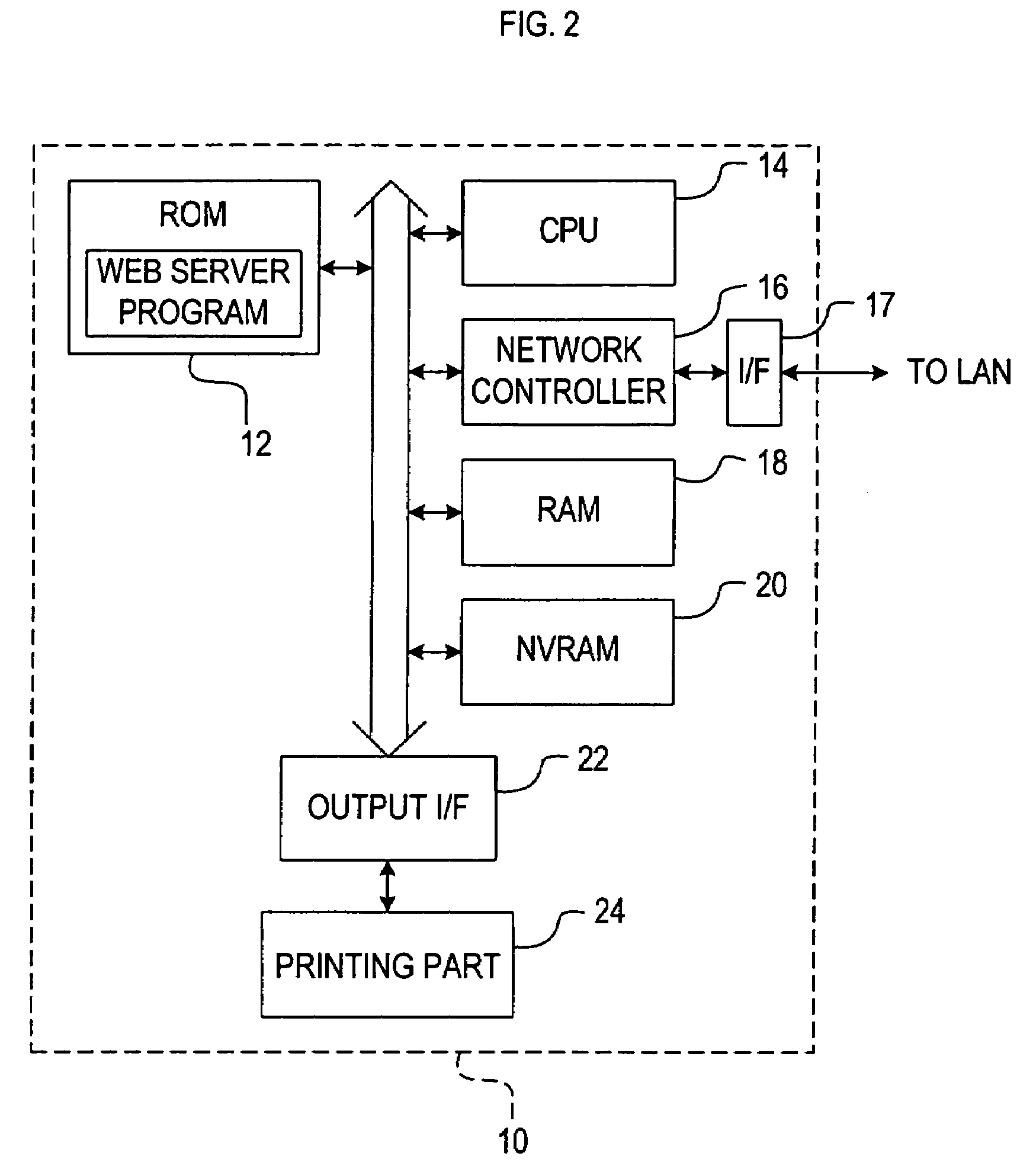
ActiveUS7325031B2Easily obtainedEasily arriveDigitally marking record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb serverService provision
A service providing system providing an improved comfortability when a user receives services offered using a web page. In the service providing system, a printer transmits information (e.g. the MAC address and information of status and consumables) related to the printer to a web server on the Internet. The web server creates a web page devoted to the printer, for providing services related to the printer (e.g. download of software already set up for the printer and indication of information of the consumables for the printer), based on the information received from the printer. With the service providing system, a user of the printer can receive services related to the printer by accessing to the web page through the web browser of a printer.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Production method for hematite for iron production
InactiveUS20150050200A1Easily obtainedCheaply and stably procuredSolvent extractionSulfur compoundsBrown iron oxideSulfur content
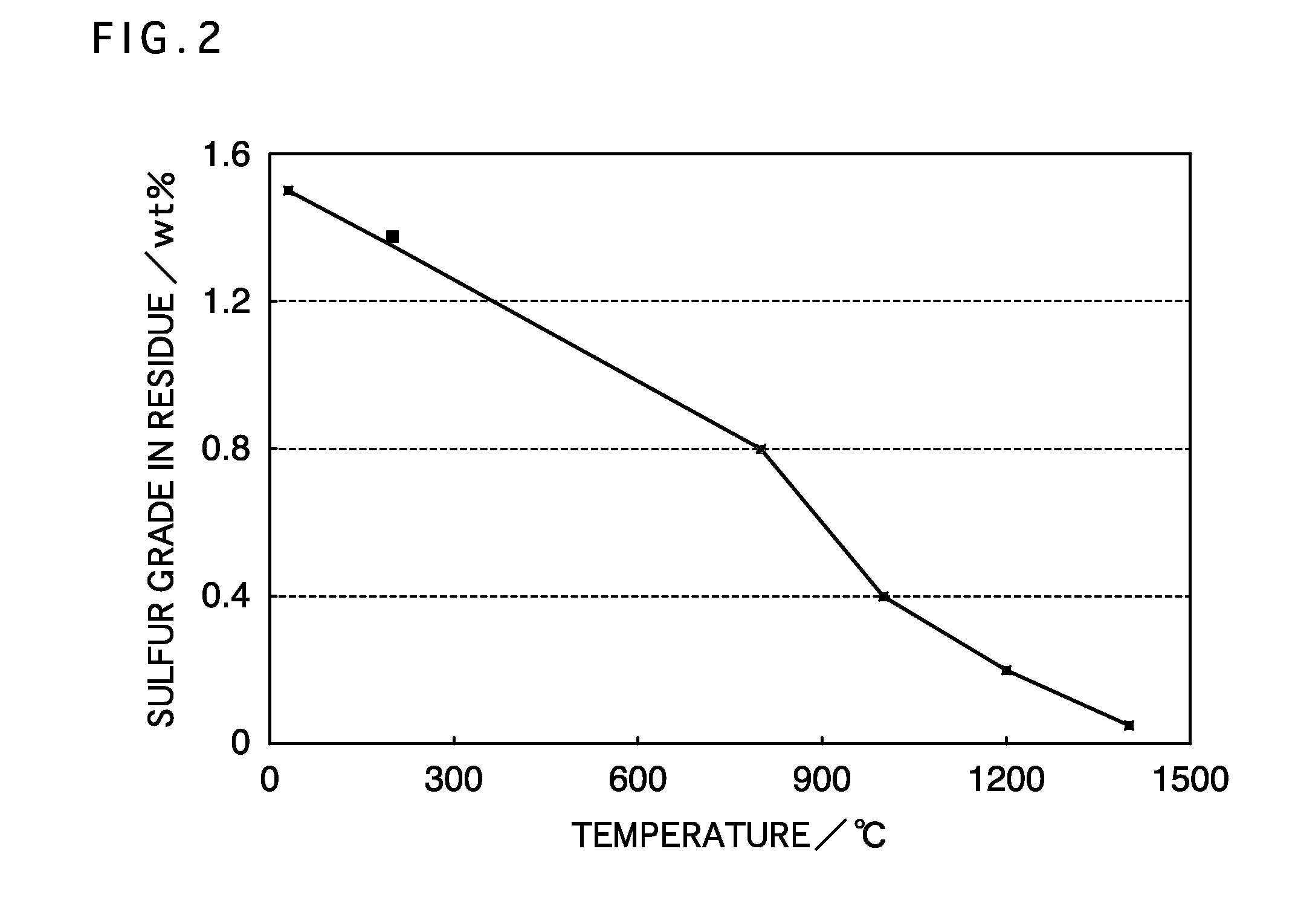
Provided is a production method for refining iron oxide (hematite), which has such a low sulfur content as to be used as a raw material for ironmaking from a leach residue containing iron oxide, the leach residue being produced by a high pressure acid leach (HPAL) process and being a raw material that can be cheaply and stably procured. In the method of producing (high purity) hematite for ironmaking by a process of adding an oxidant and sulfuric acid to nickel oxide ore and then leaching nickel, a leach residue obtained after the leaching of nickel is heated to 600° C. or more, and preferably 800° C. or more and 1400° C. or less.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Molecular detection/diagnosis reagent for tumor
ActiveUS20190010557A1Easily obtainedThe sampling process is convenientMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic separationCancer researchColorectal cancer
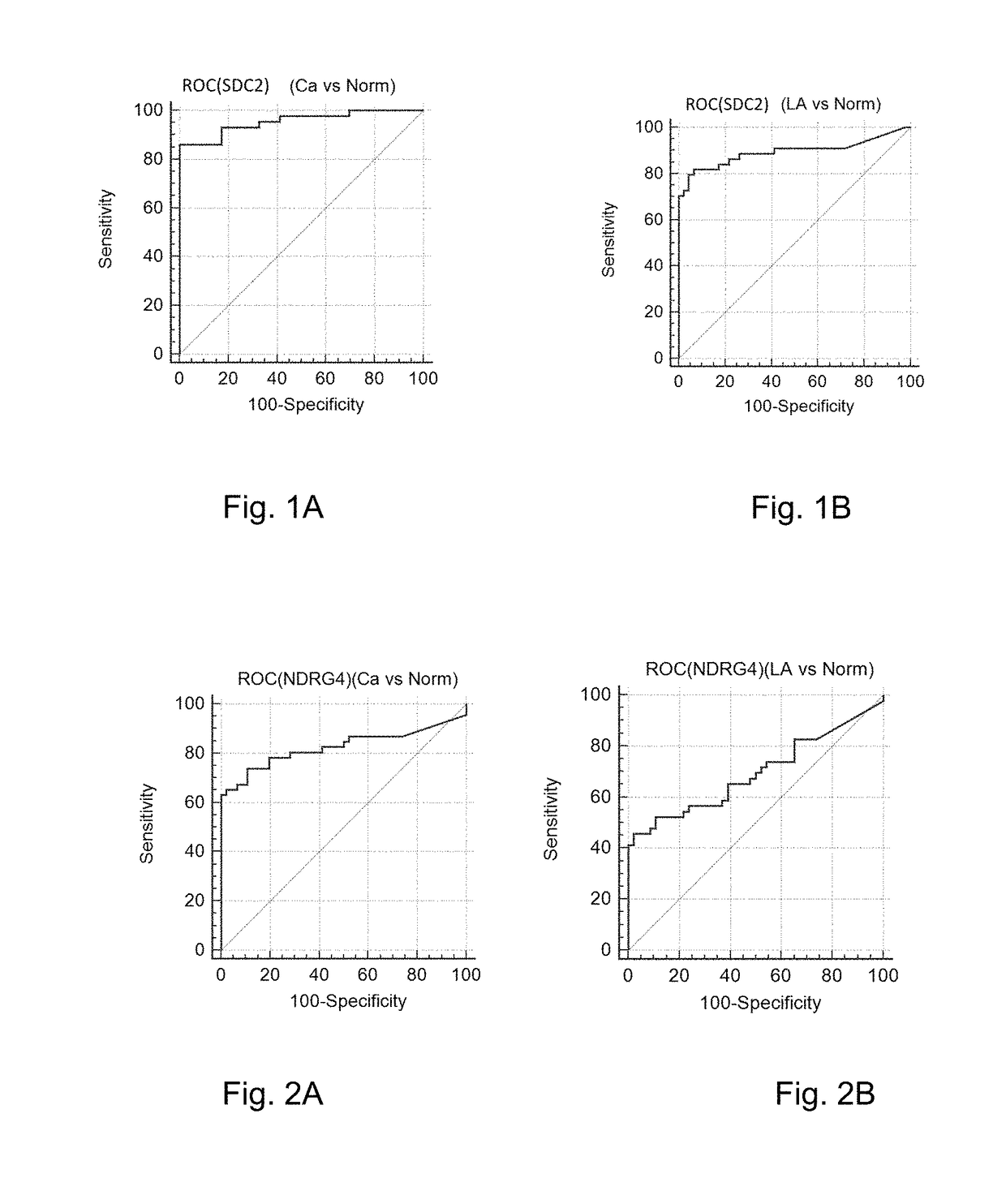
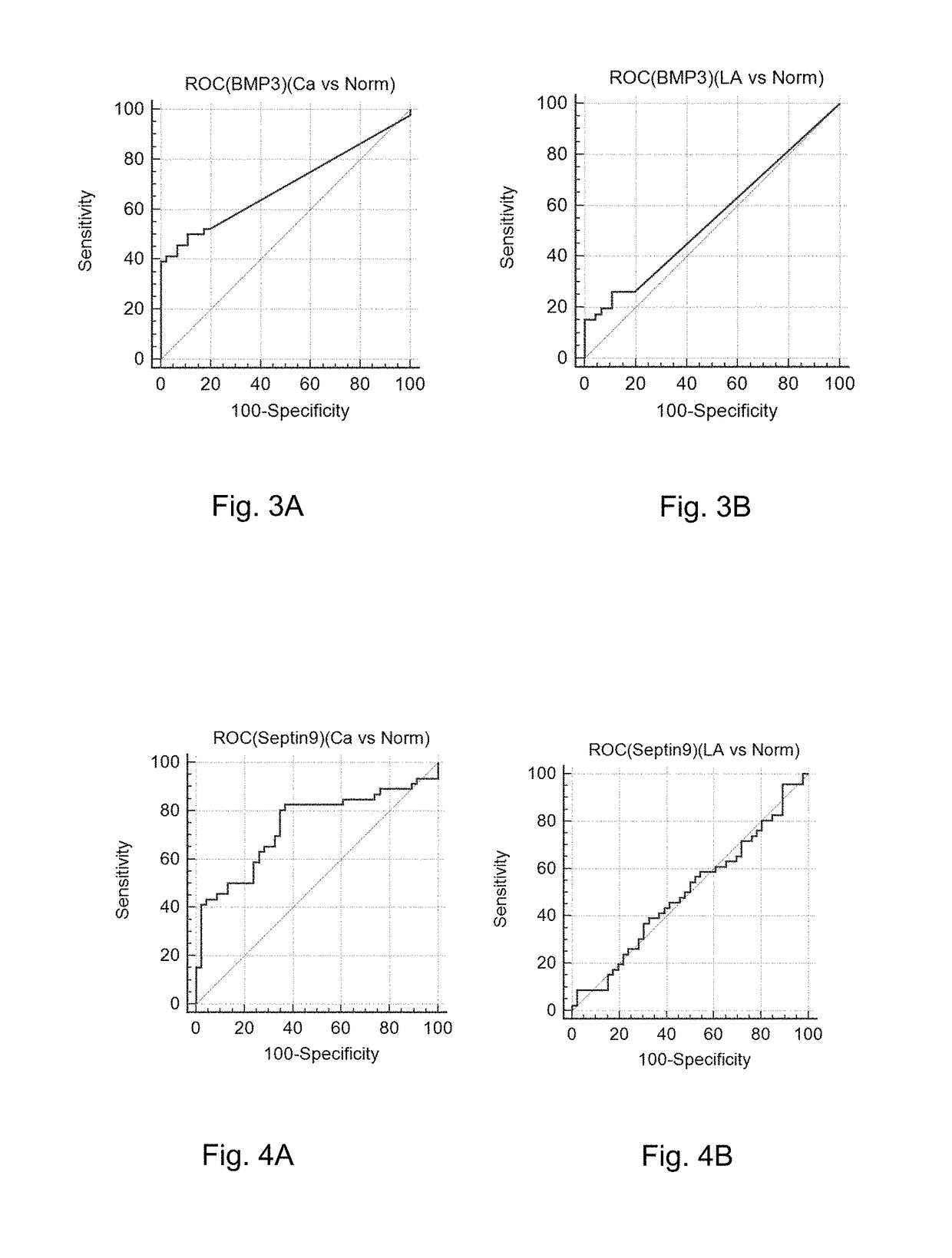
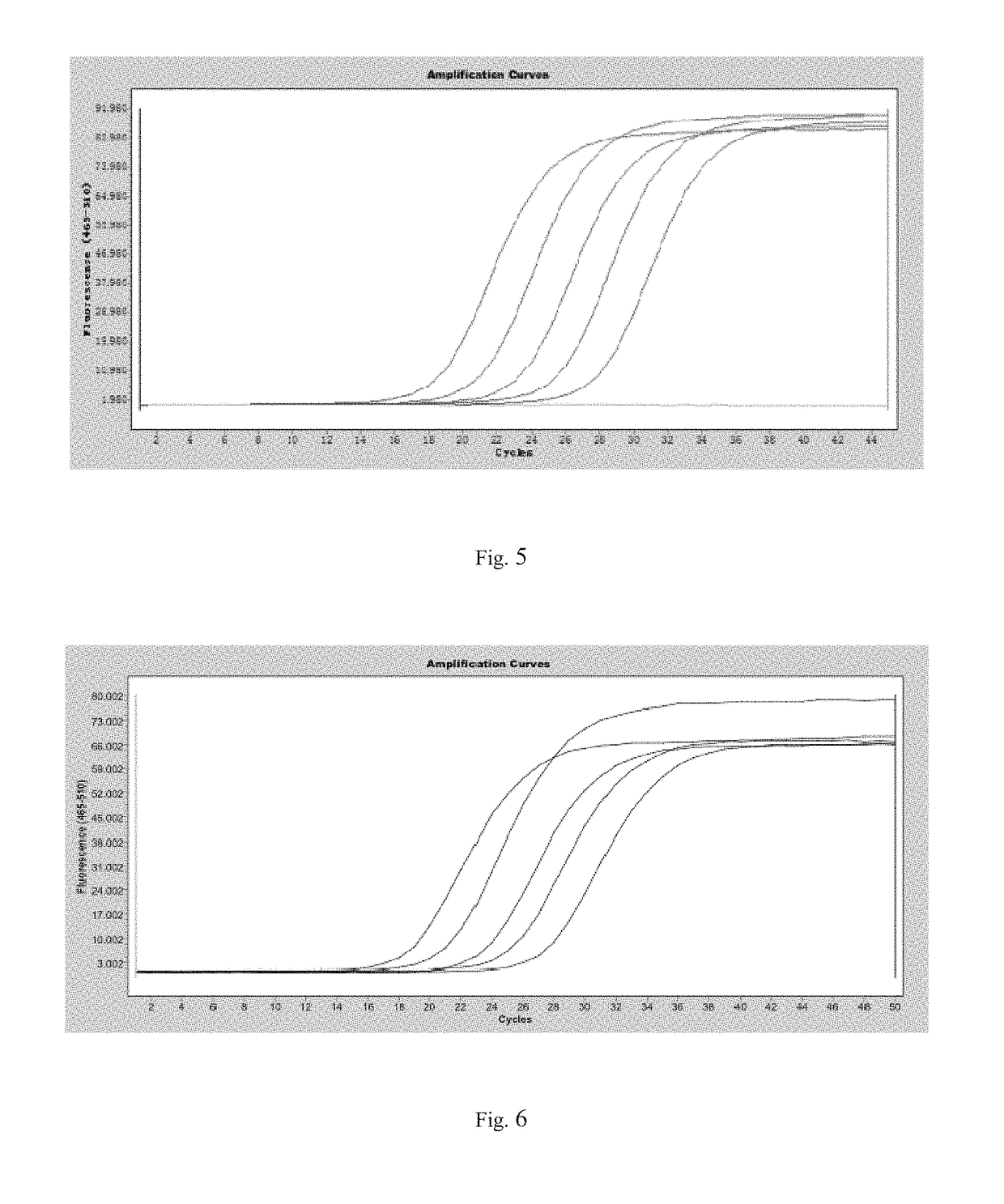
The present invention discloses a tumor molecular detection / diagnostic reagent, which takes excrement as a detection sample and includes an SDC2 gene methylation detection reagent. The methylation level of the SDC2 gene detected in the excrement has an extremely high relevance to the onset of the colorectal cancer. The sensitivity of the SDC2 gene in the excrement is 87 percent and the specificity is up to 98 percent or even higher than that in tissue.
Owner:CREATIVE BIOSCIENCES (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com