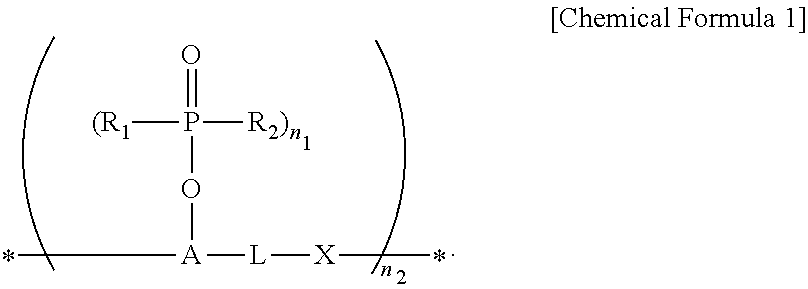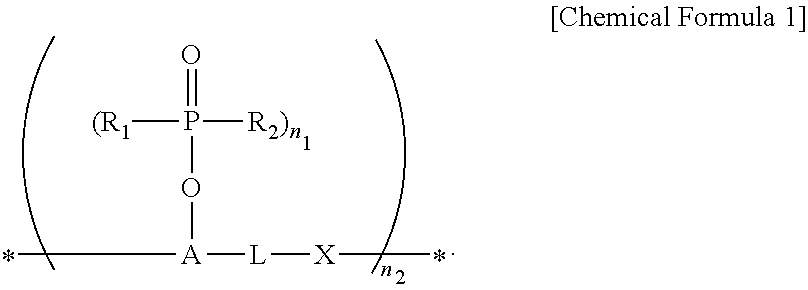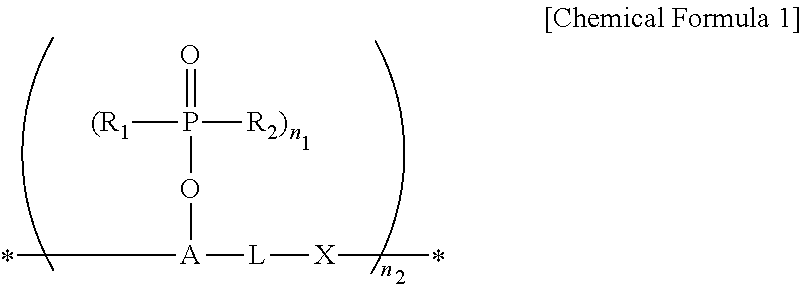Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Minimize reflectivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reflection type mask blank and reflection type mask and production methods for them
ActiveUS20050208389A1Accurately and quickly carry-outEasy to produceNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenReflective layer
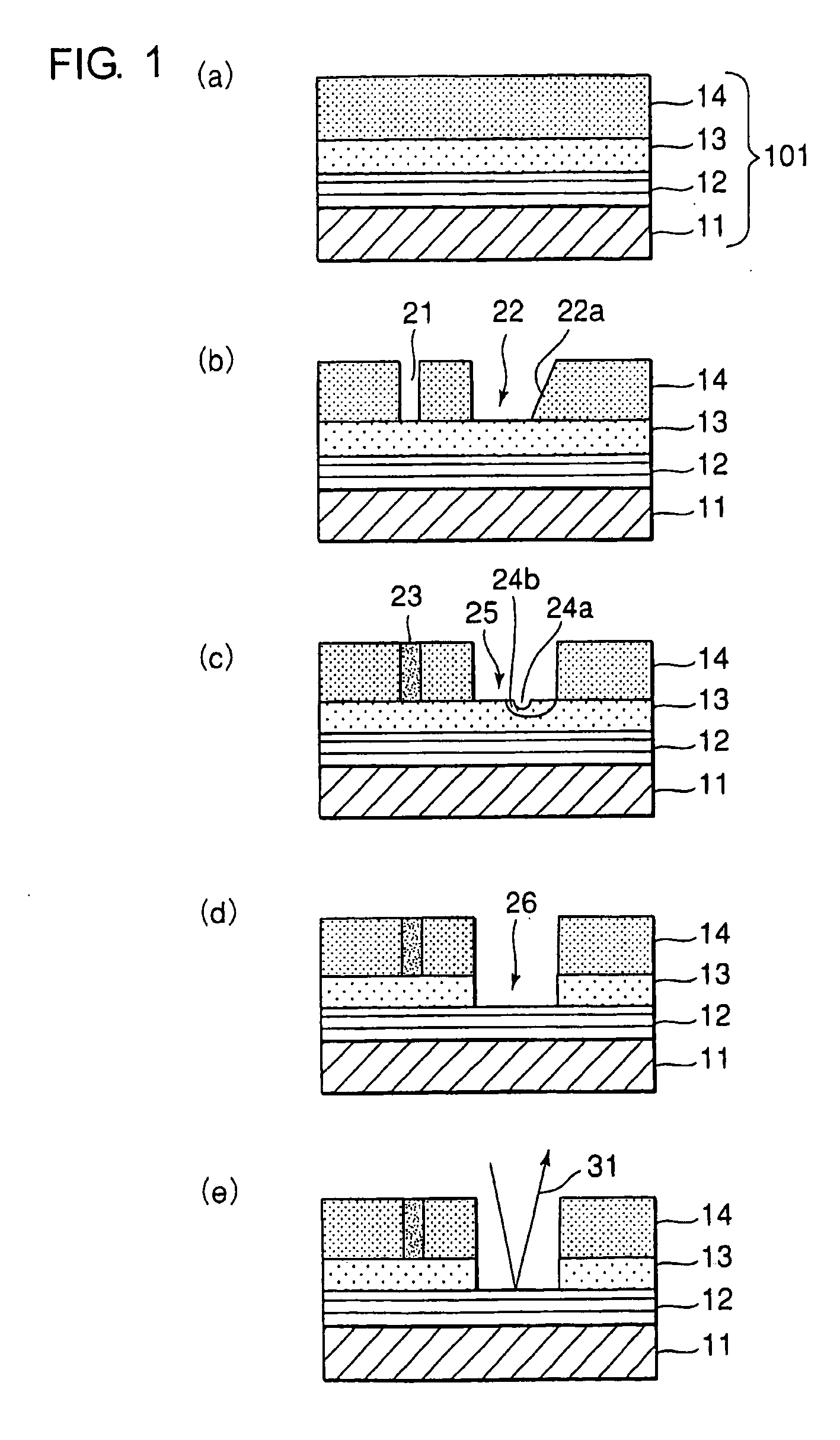
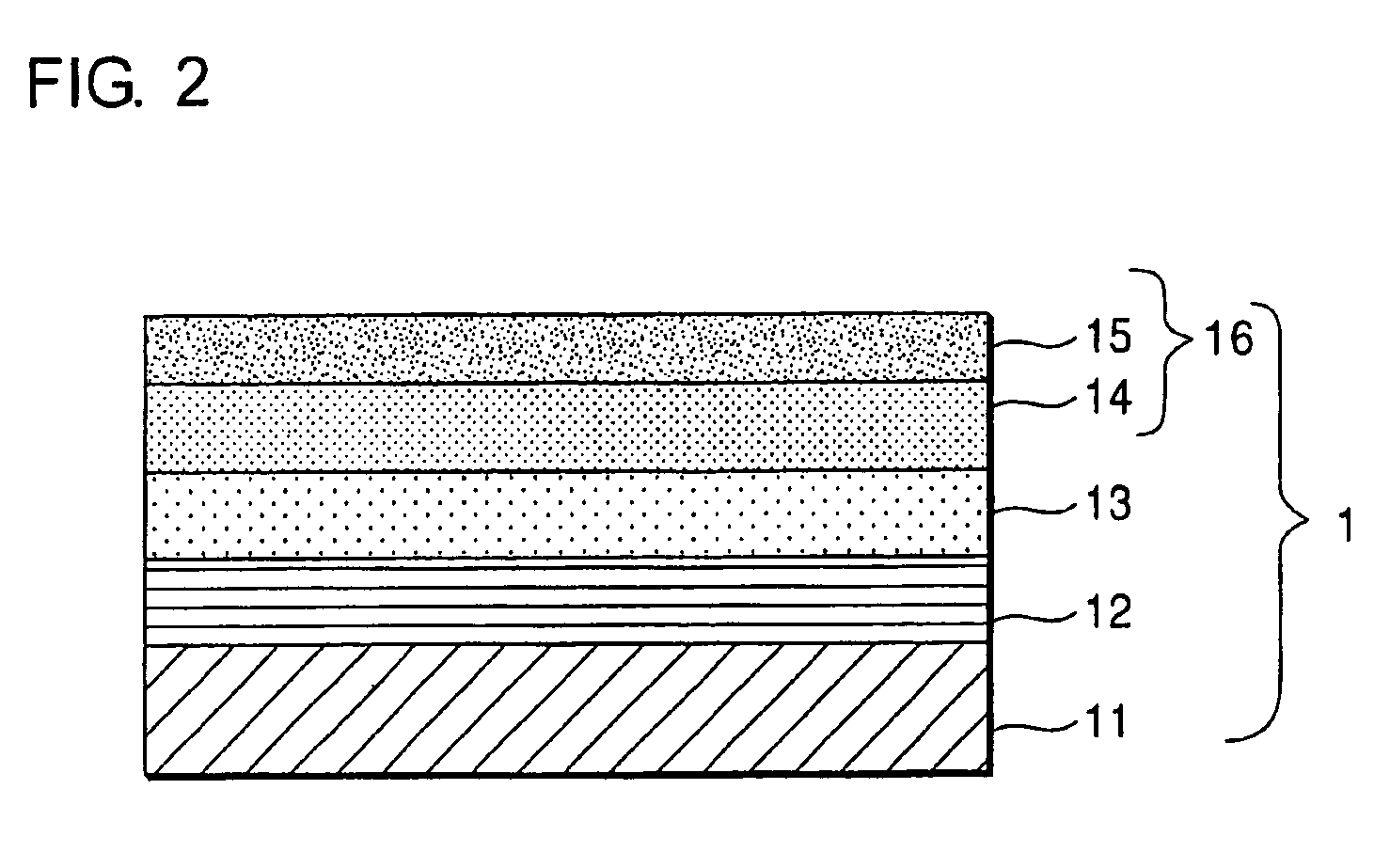
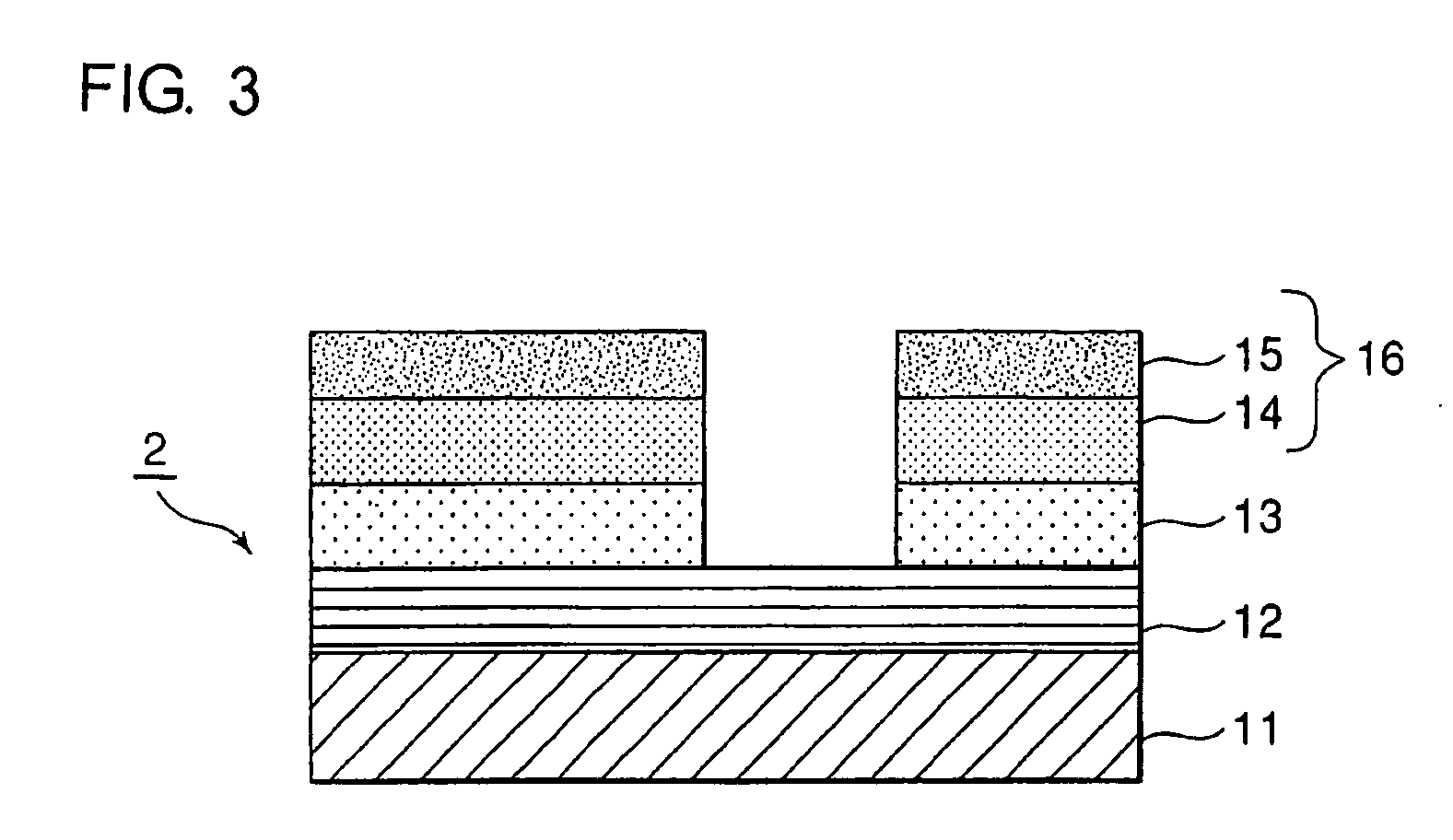
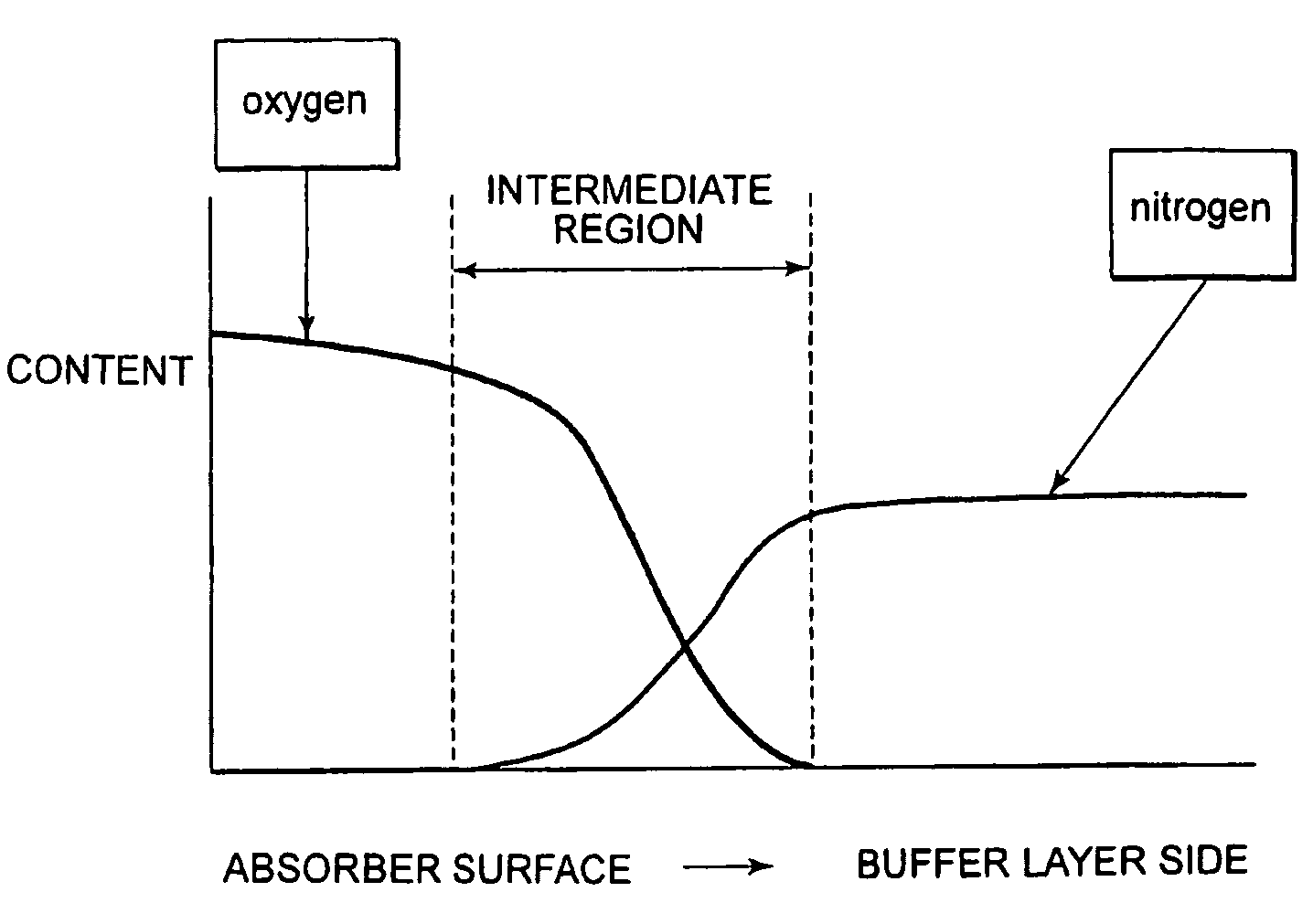
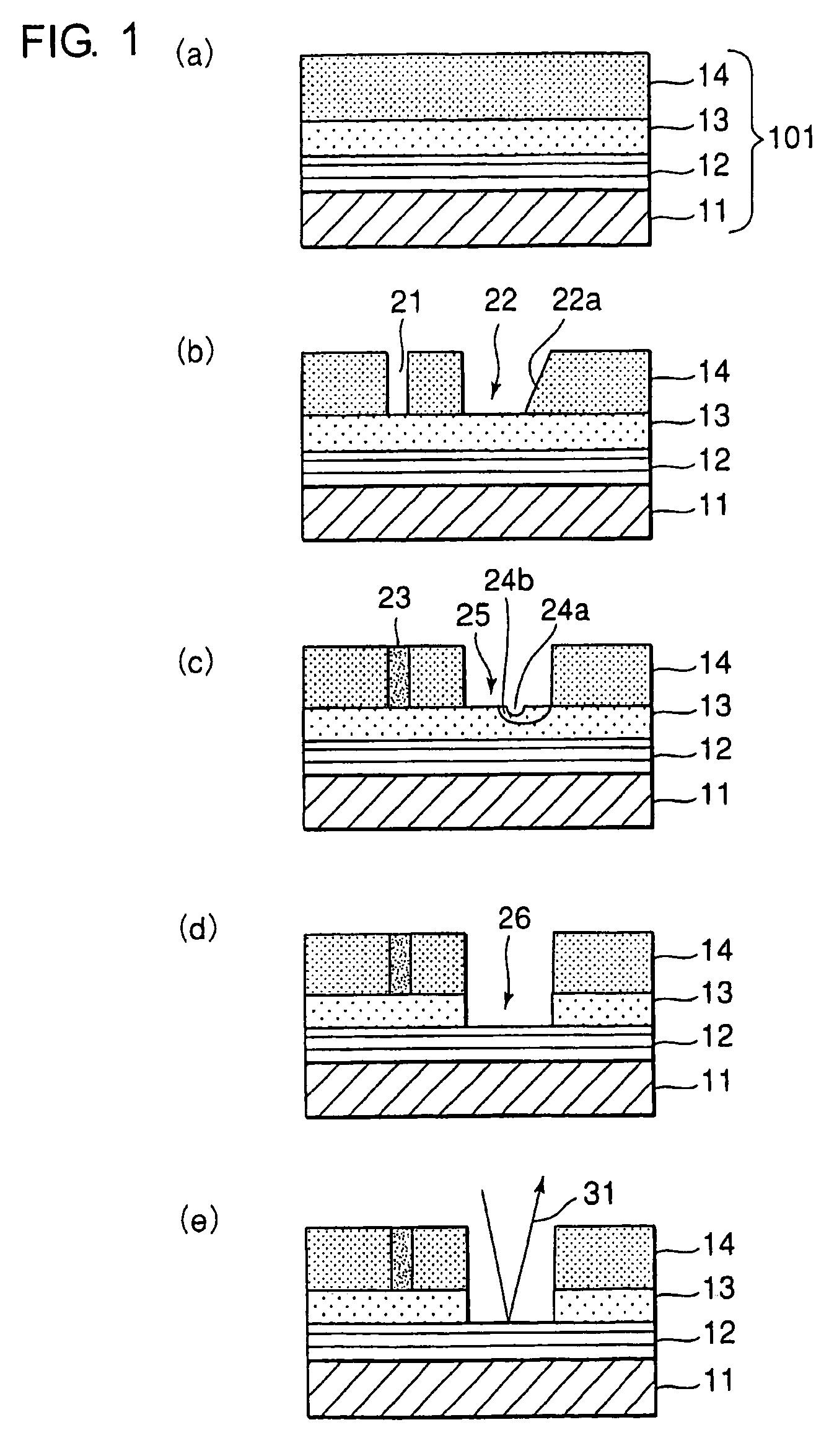
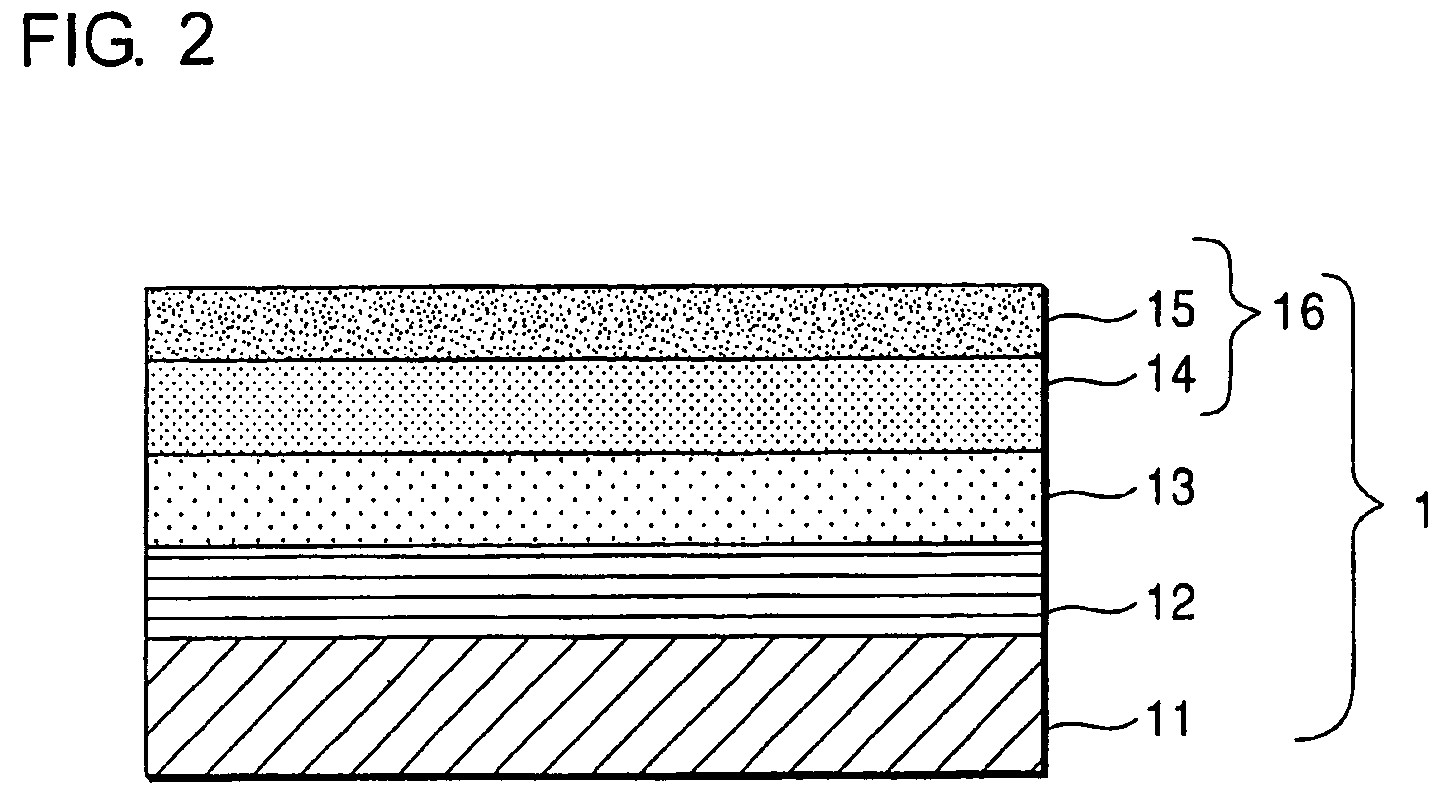
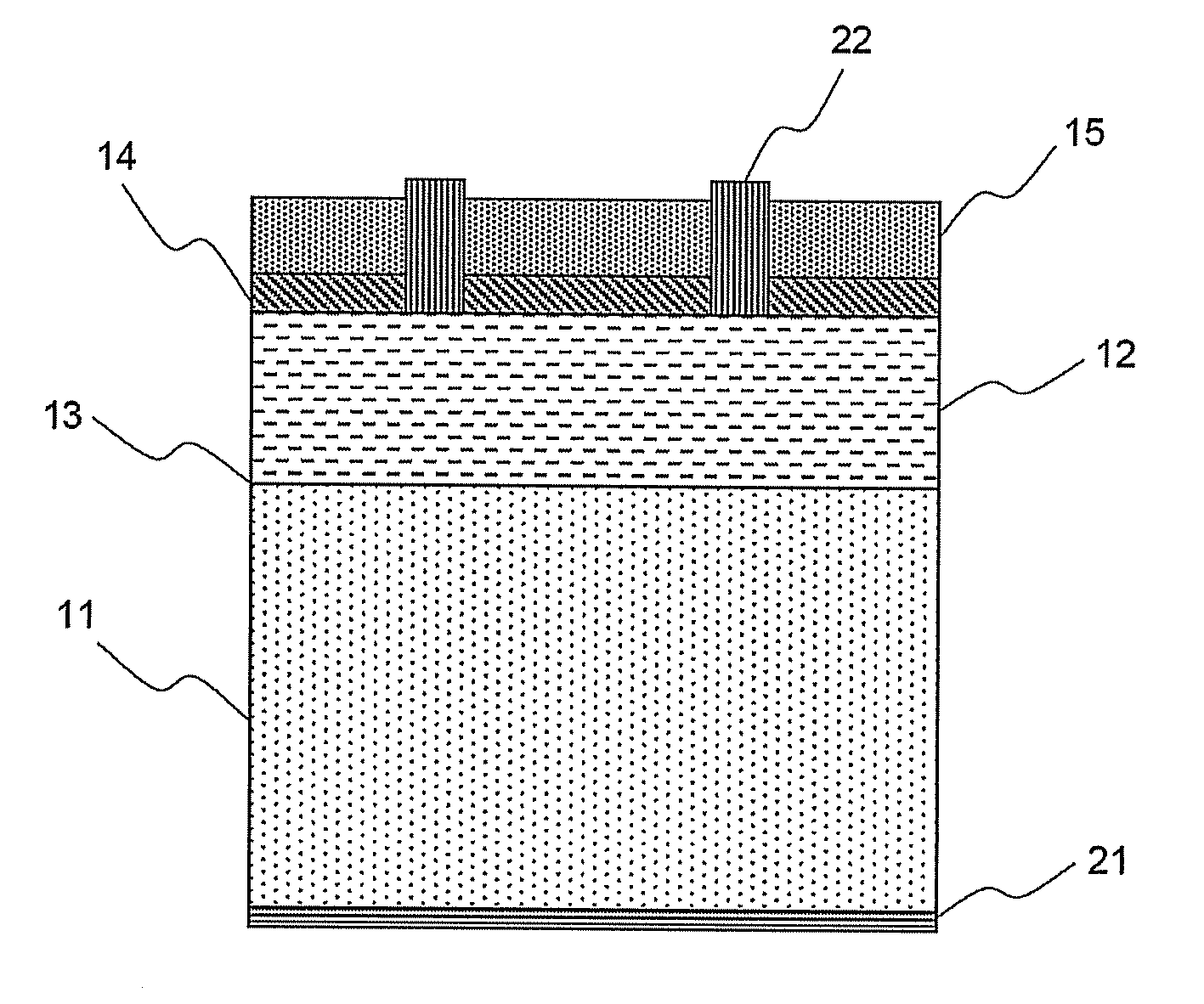
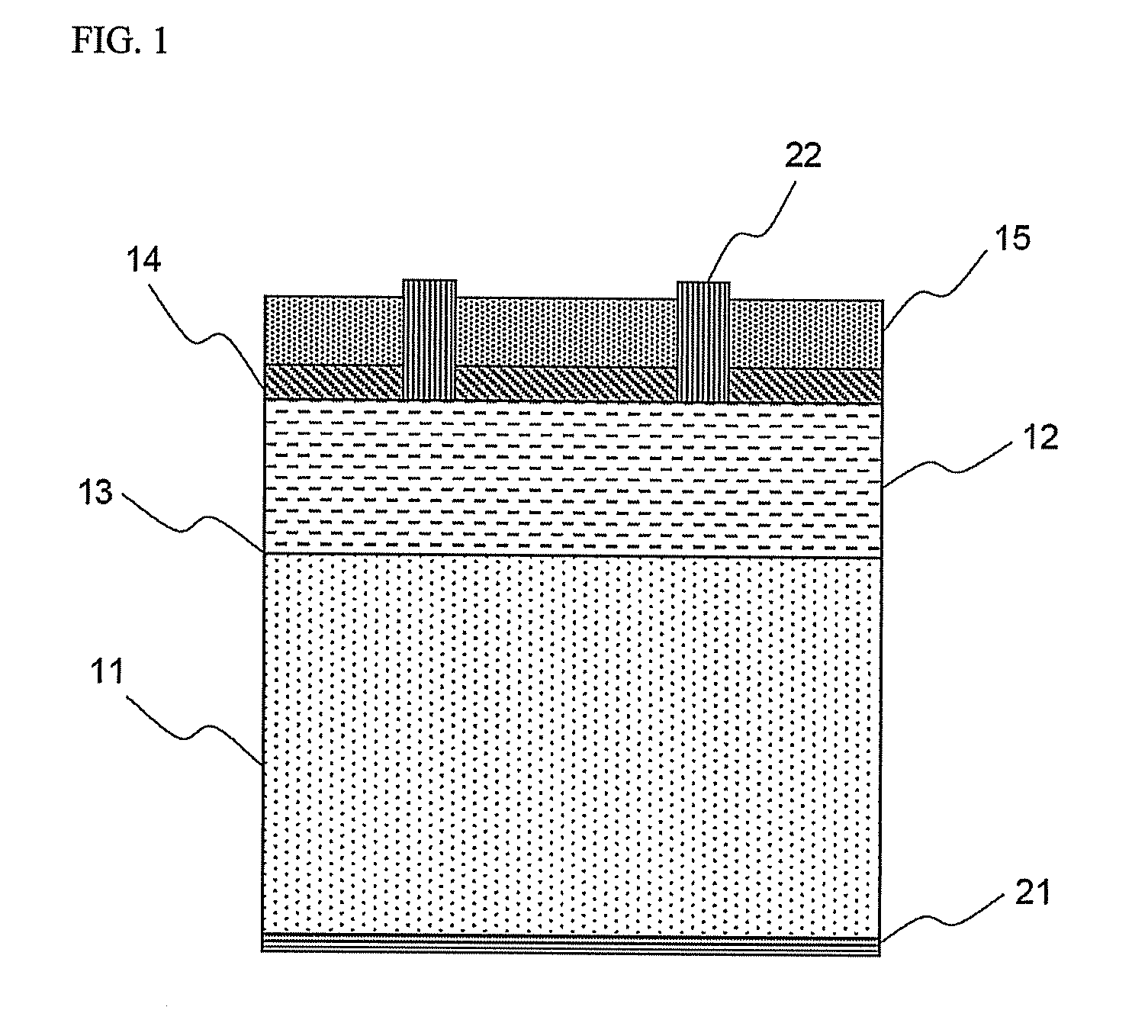
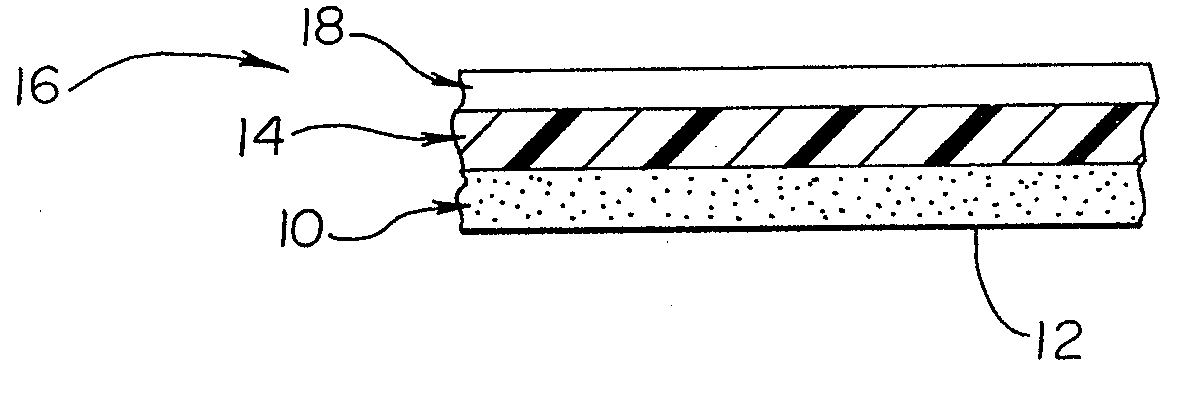
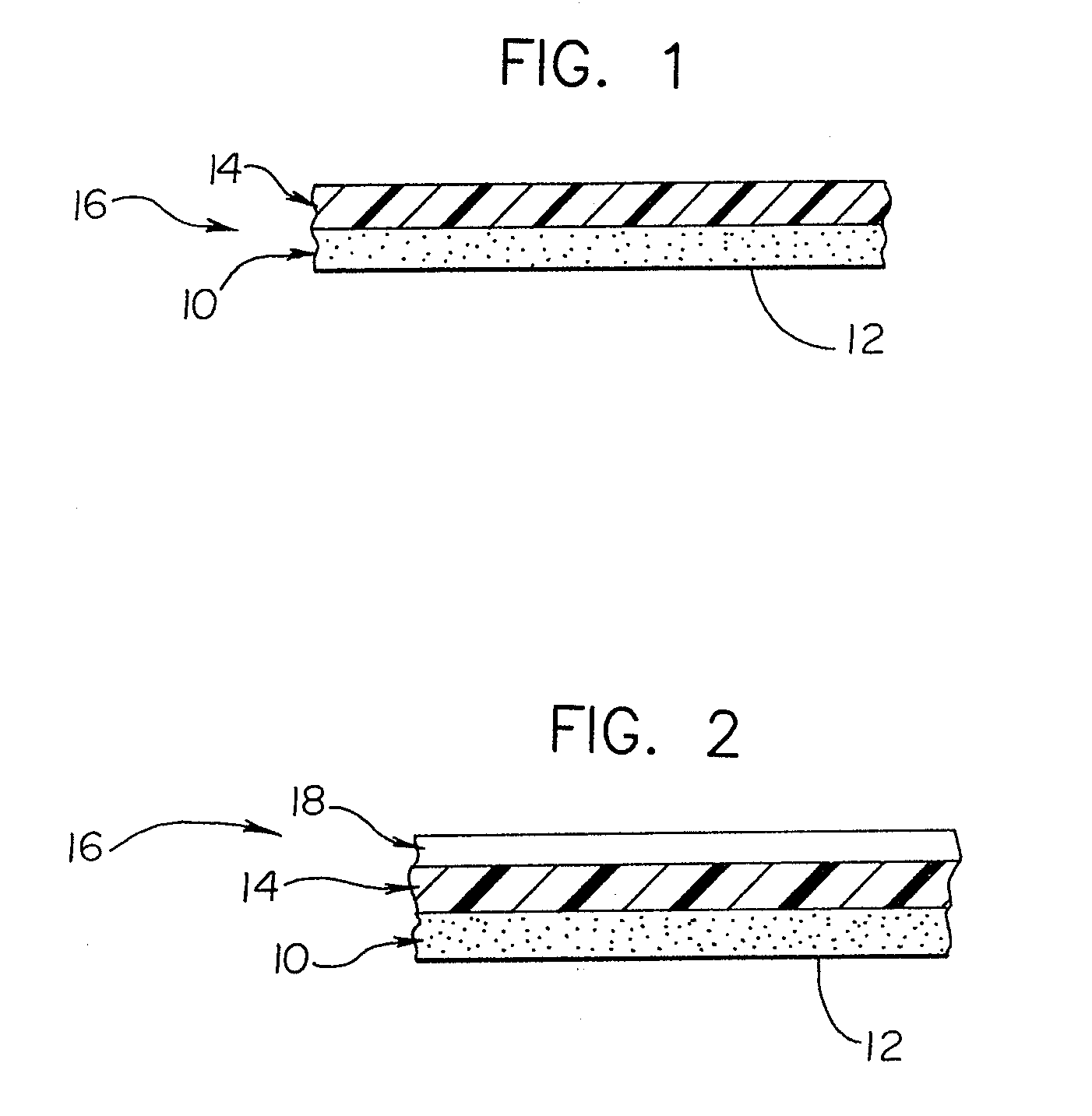
A reflective mask blank has a substrate (11) on which a reflective layer (12) for reflecting exposure light in a short-wavelength region including an extreme ultraviolet region and an absorber layer (16) for absorbing the exposure light are successively formed. The absorber layer (16) has an at least two-layer structure including as a lower layer an exposure light absorbing layer (14) formed by an absorber for the exposure light in the short-wavelength region including the extreme ultraviolet region and as an upper layer a low-reflectivity layer (15) formed by an absorber for inspection light used in inspection of a mask pattern. The upper layer is made of a material containing tantalum (Ta), boron (B), and nitrogen (N). The content of B is 5 at % to 30 at %. The ratio of Ta and N (Ta:N) falls within a range of 8:1 to 2:7. Alternatively, the reflective mask blank has a substrate on which a multilayer reflective film and an absorber layer are successively formed. In this case, the absorber layer is made of a material containing tantalum (Ta), boron (B), and nitrogen (N). The content of B is 5 at % to 25 at %. The ratio of Ta and N (Ta:N) falls within a range of 8:1 to 2:7.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Reflection type mask blank and reflection type mask and production methods for them
ActiveUS7390596B2Easy to produceLow costNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenLength wave
A reflective mask blank has a substrate (11) on which a reflective layer (12) for reflecting exposure light in a short-wavelength region including an extreme ultraviolet region and an absorber layer (16) for absorbing the exposure light are successively formed. The absorber layer (16) has an at least two-layer structure including as a lower layer an exposure light absorbing layer (14) formed by an absorber for the exposure light in the short-wavelength region including the extreme ultraviolet region and as an upper layer a low-reflectivity layer (15) formed by an absorber for inspection light used in inspection of a mask pattern. The upper layer is made of a material containing tantalum (Ta), boron (B), and nitrogen (N). The content of B is 5 at % to 30 at %. The ratio of Ta and N (Ta:N) falls within a range of 8:1 to 2:7. Alternatively, the reflective mask blank has a substrate on which a multilayer reflective film and an absorber layer are successively formed. In this case, the absorber layer is made of a material containing tantalum (Ta), boron (B), and nitrogen (N). The content of B is 5 at % to 25 at %. The ratio of Ta and N (Ta:N) falls within a range of 8:1 to 2:7.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Solar cell of high efficiency and process for preparation of the same
InactiveUS20070175508A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyMinimize reflectivityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesP–n junctionFilm structure
Disclosed herein is a high-efficiency solar cell. More specifically, provided is a solar cell comprising a first conductivity type semiconductor substrate, a second conductivity type semiconductor layer formed on the first conductivity type semiconductor substrate and having a conductivity type opposite to that of the substrate, a p-n junction at an interface therebetween, a rear electrode in contact with at least a portion of the first conductivity type semiconductor substrate, a front electrode in contact with at least a portion of the second conductivity type semiconductor layer, and a silicon oxynitride passivation layer and a silicon nitride anti-reflective layer sequentially formed on a rear surface of the first conductivity type semiconductor substrate and / or a front surface of the second conductivity type semiconductor layer; and a process for preparing the same. Therefore, the solar cell according to the present invention can improve a photoelectric conversion efficiency by minimizing a reflectivity of absorbed light via provision of a dual reflective film structure composed of the passivation layer and anti-reflective layer, simultaneously with effective prevention of carrier recombination occurring at a semiconductor surface by the passivation layer. Further, the present invention enables a significant reduction of production costs by mass production capability via in situ continuous formation of the dual reflective film structure.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
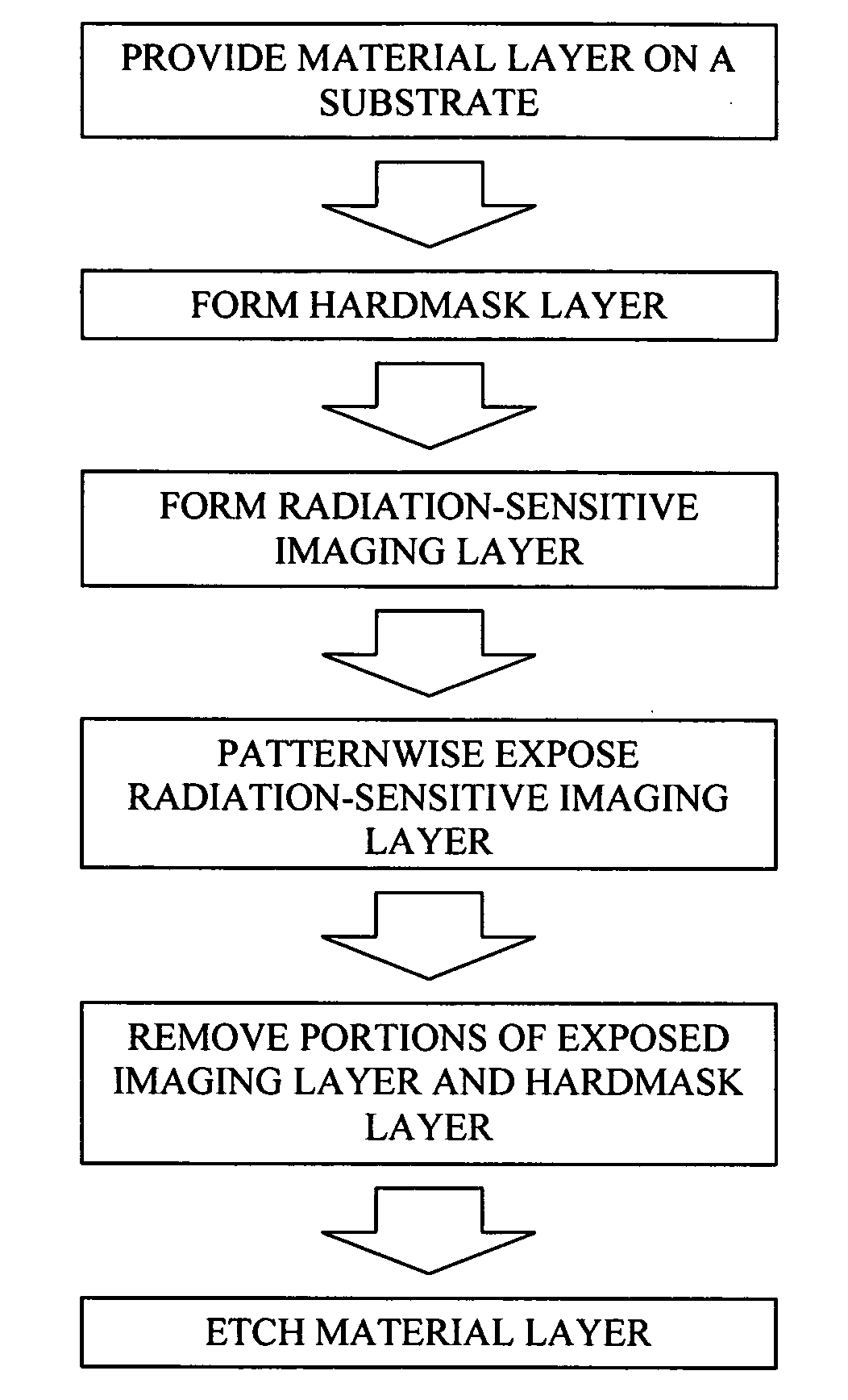
Hardmask composition having antirelective properties and method of patterning material on susbstrate using the same
ActiveUS20080305441A1Improve etch selectivitySolve the lack of resistancePhotosensitive materialsPhotoprinting processesPolymer scienceOrganic solvent
A hardmask composition includes an organic solvent and one or more aromatic ring-containing polymers represented by Formulae 1, 2 and 3:
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
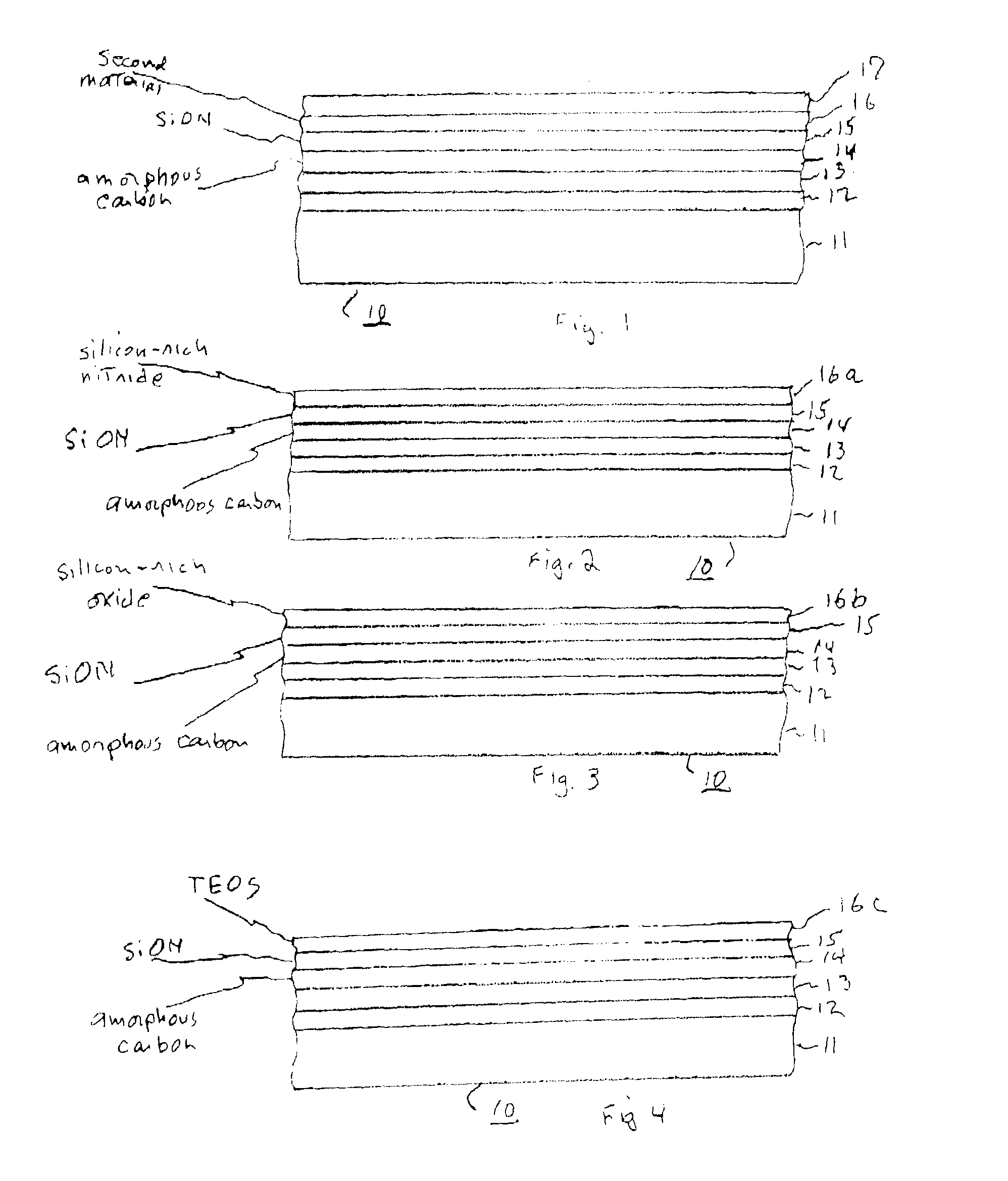
Capping layer for reducing amorphous carbon contamination of photoresist in semiconductor device manufacture; and process for making same
ActiveUS7109101B1Minimize reflectivityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAmount of substancePhotolithography
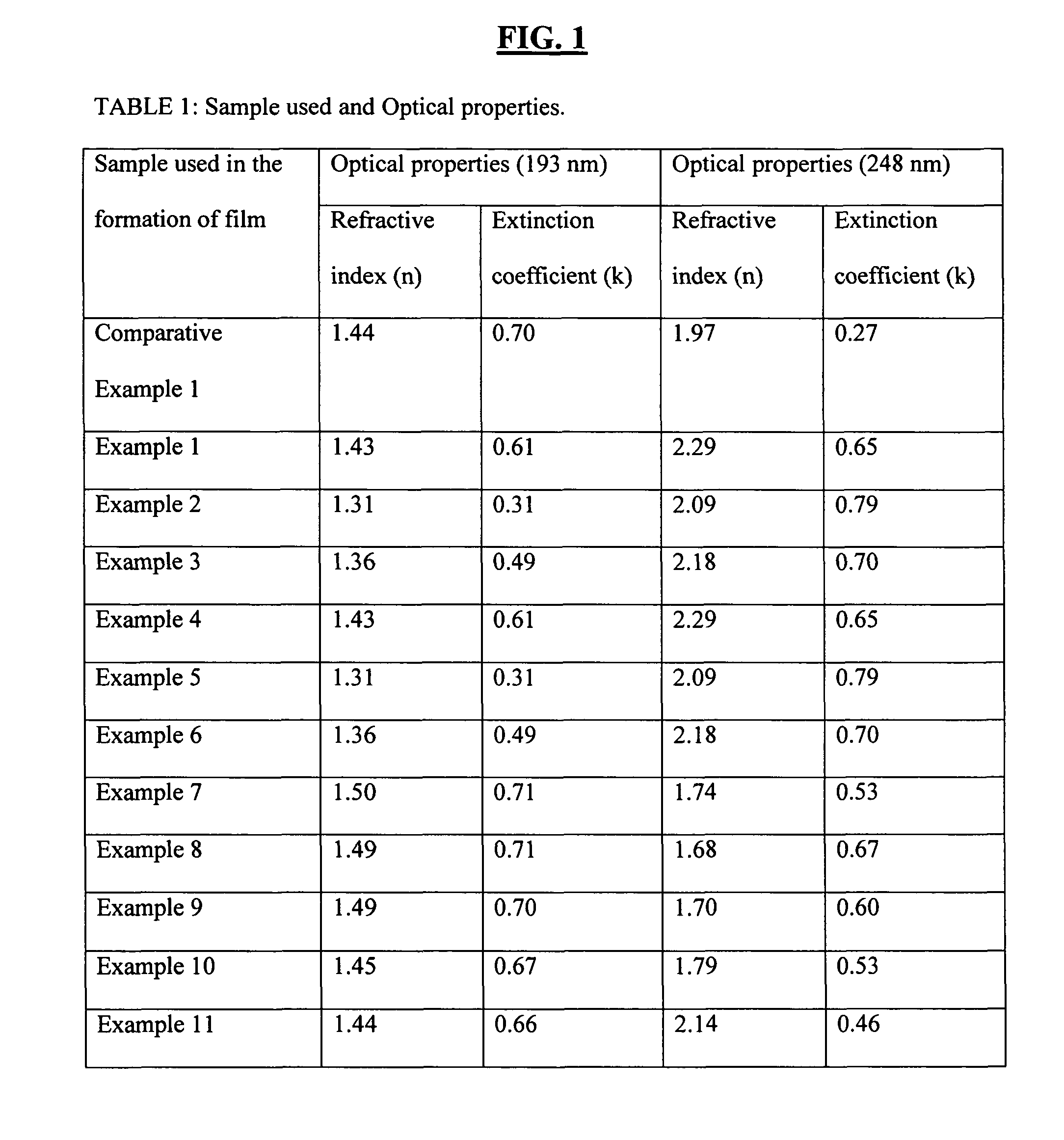
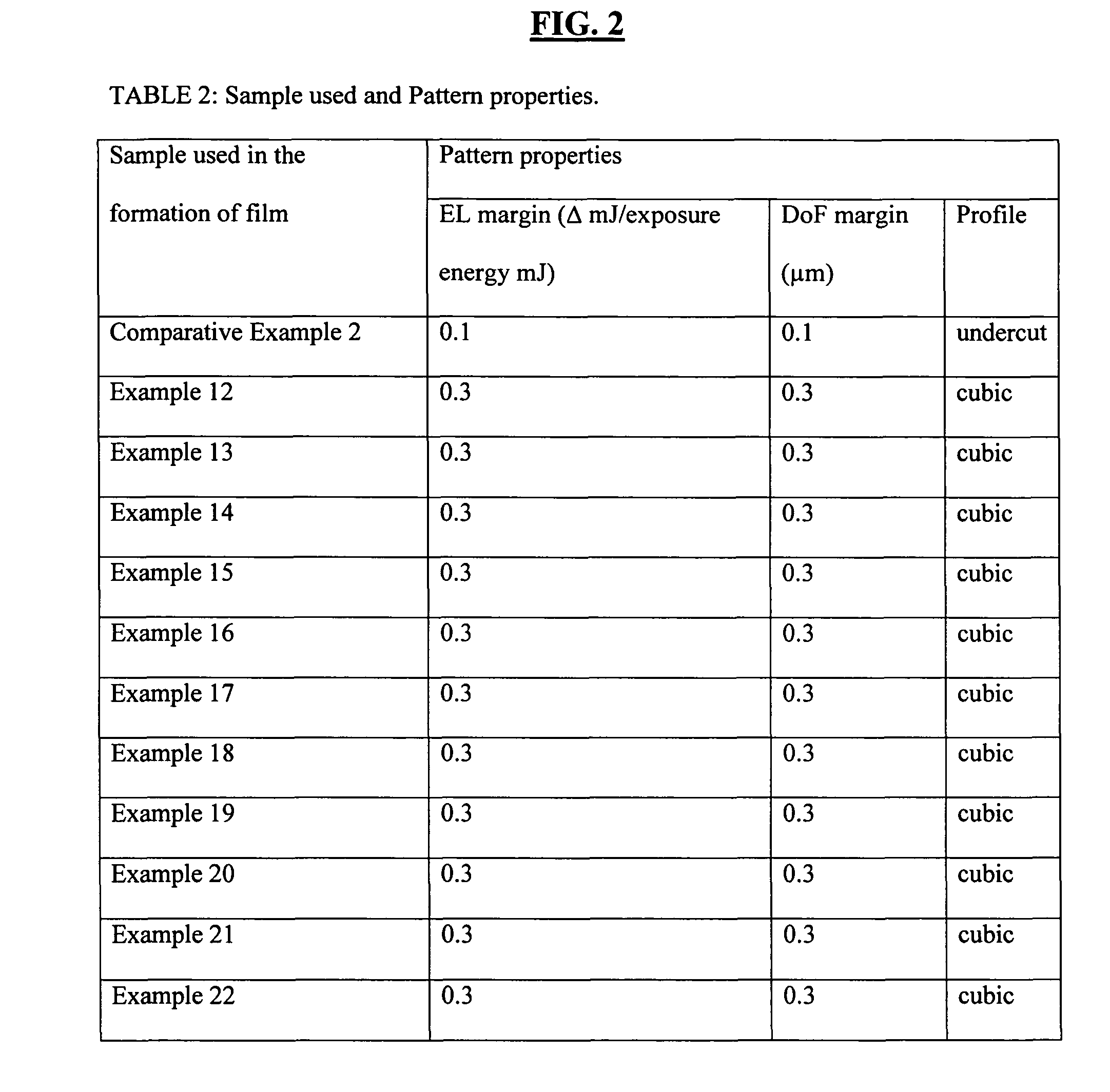
In the fabrication of semiconductor devices using the PECVD process to deposit hardmask material such as amorphous carbon, structure and process are described for reducing migration of species from the amorphous carbon which can damage an overlying photoresist. In one embodiment useful to 248 nm and 193 nm photolithography exposure wavelengths, amorphous carbon is plasma-deposited on a substrate to pre-defined thickness and pre-defined optical properties. A SiON layer is combined with a silicon-rich oxide layer, a silicon-rich nitride layer or a TEOS layer to create a capping layer resistant to species-migration. Layers are formulated to pre-determined thicknesses, refractive indices and extinction coefficients. The capping stacks constitute an effective etch mask for the amorphous carbon; and the hardmask properties of the amorphous carbon are not compromised. The disclosure has immediate application to fabricating polysilicon gates.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Flat panel display and method of fabricating the same
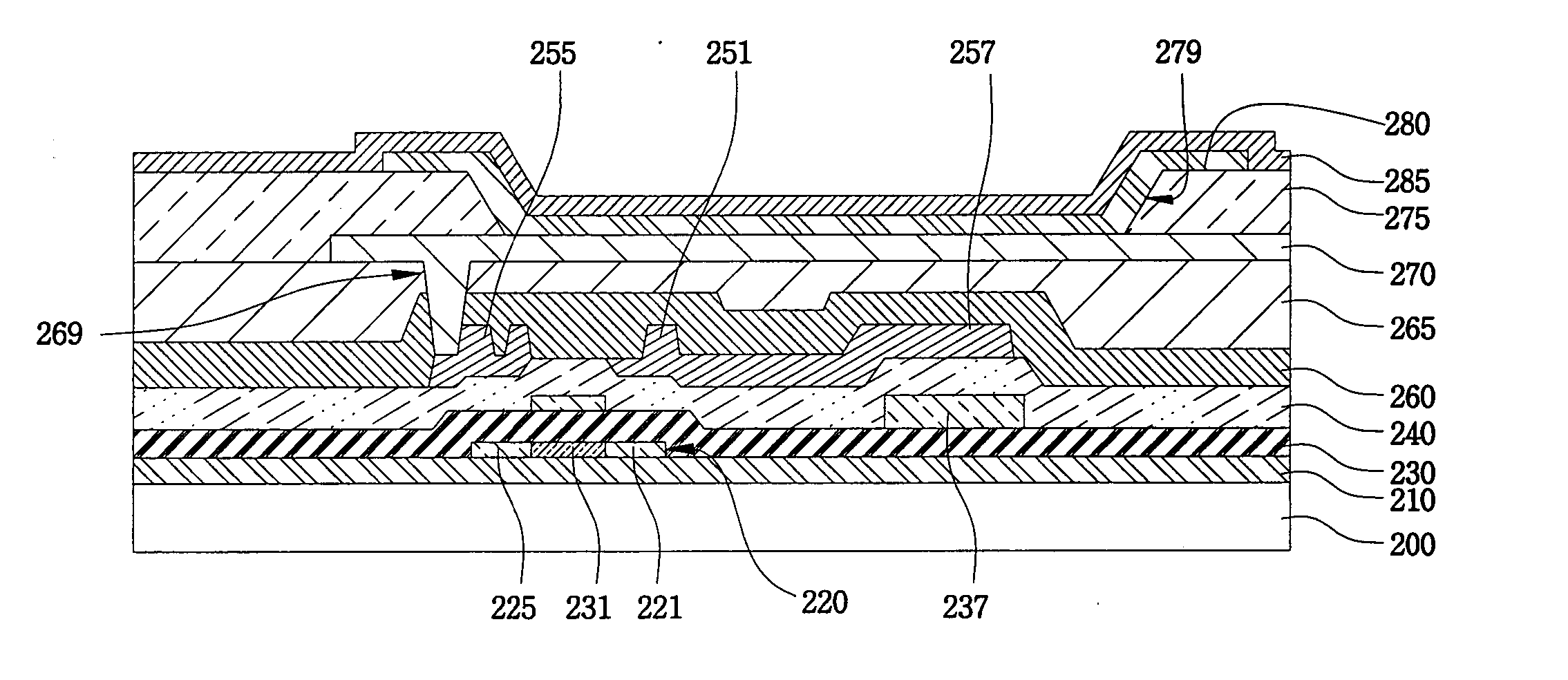
ActiveUS20050029926A1Increase contrastMinimize reflectivityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesThin membraneBlock layer
A light-emitting display device the same includes an insulating substrate having a thin film transistor formed thereon. The thin film transistor includes a source electrode and / or a drain electrode. A passivation layer is formed on the insulating substrate over at least a portion of the thin film transistor, and has a via hole formed therein, which electrically contacts either the source electrode or the drain electrode. A pixel electrode is formed in the via hole. A light-blocking layer is formed over an entire upper surface of the passivation layer except for an area corresponding to the pixel electrode. A planarization layer is formed on an upper surface of the light-blocking layer except for an area corresponding to the pixel electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Partitioned-cavity tunable fabry-perot filter
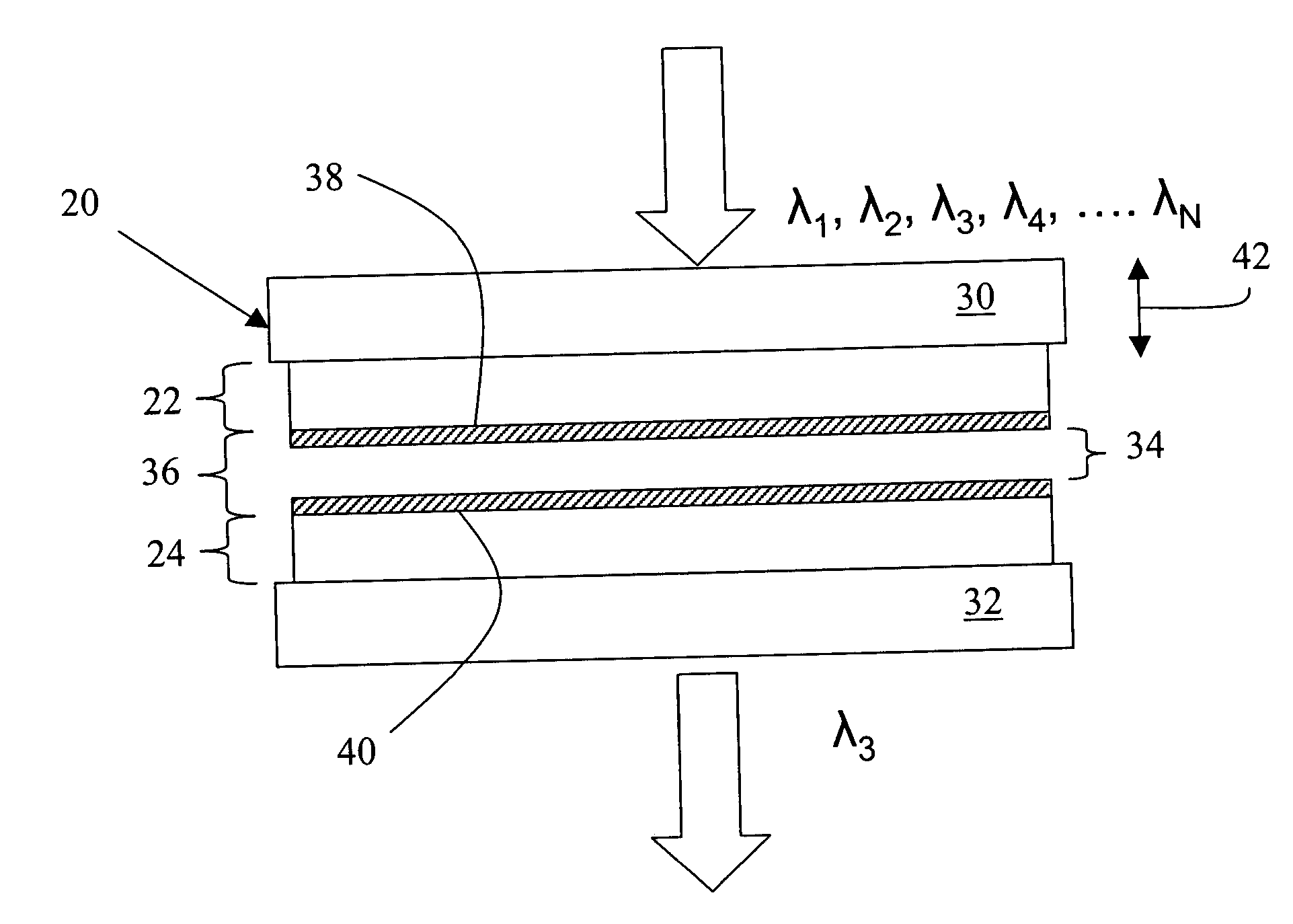
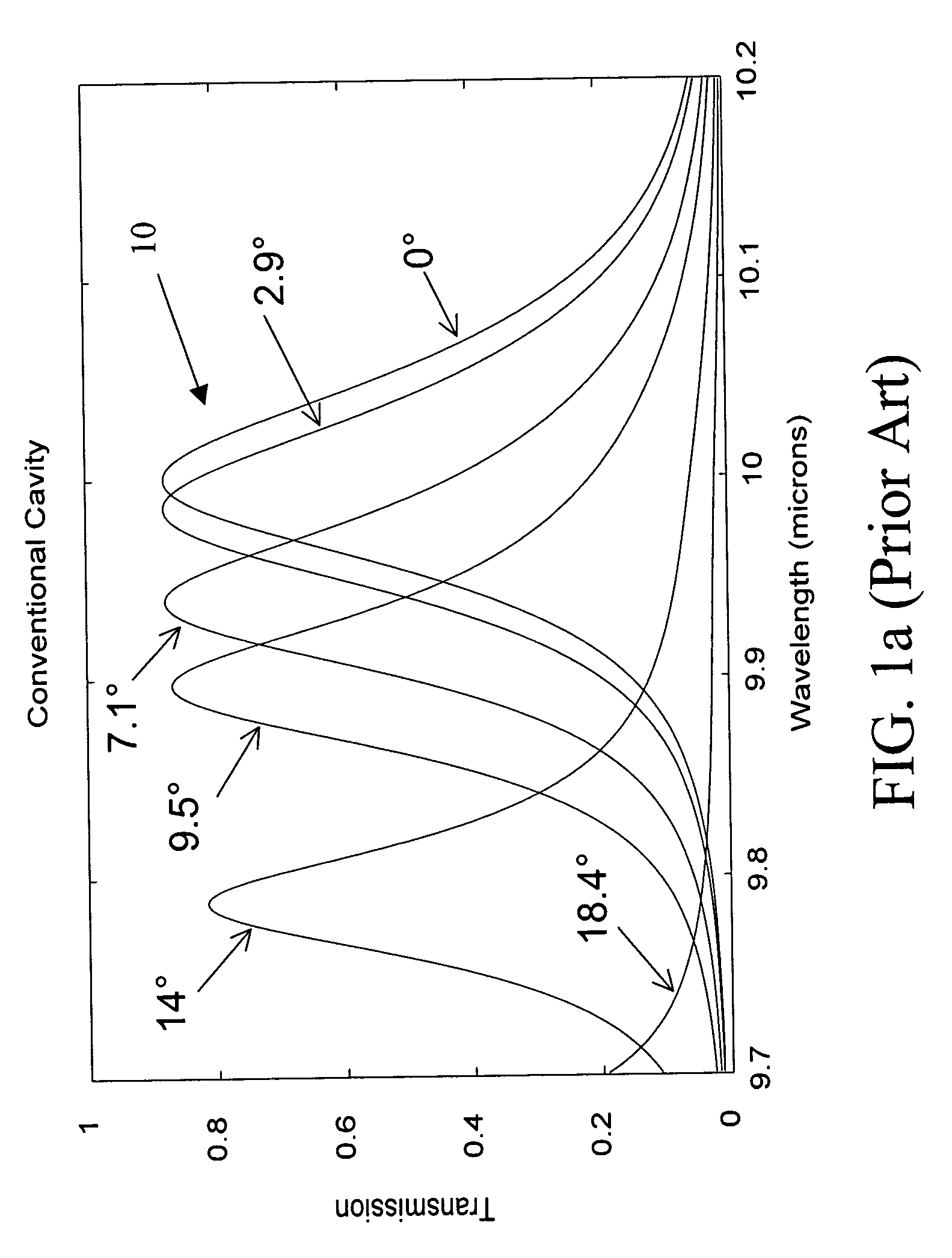
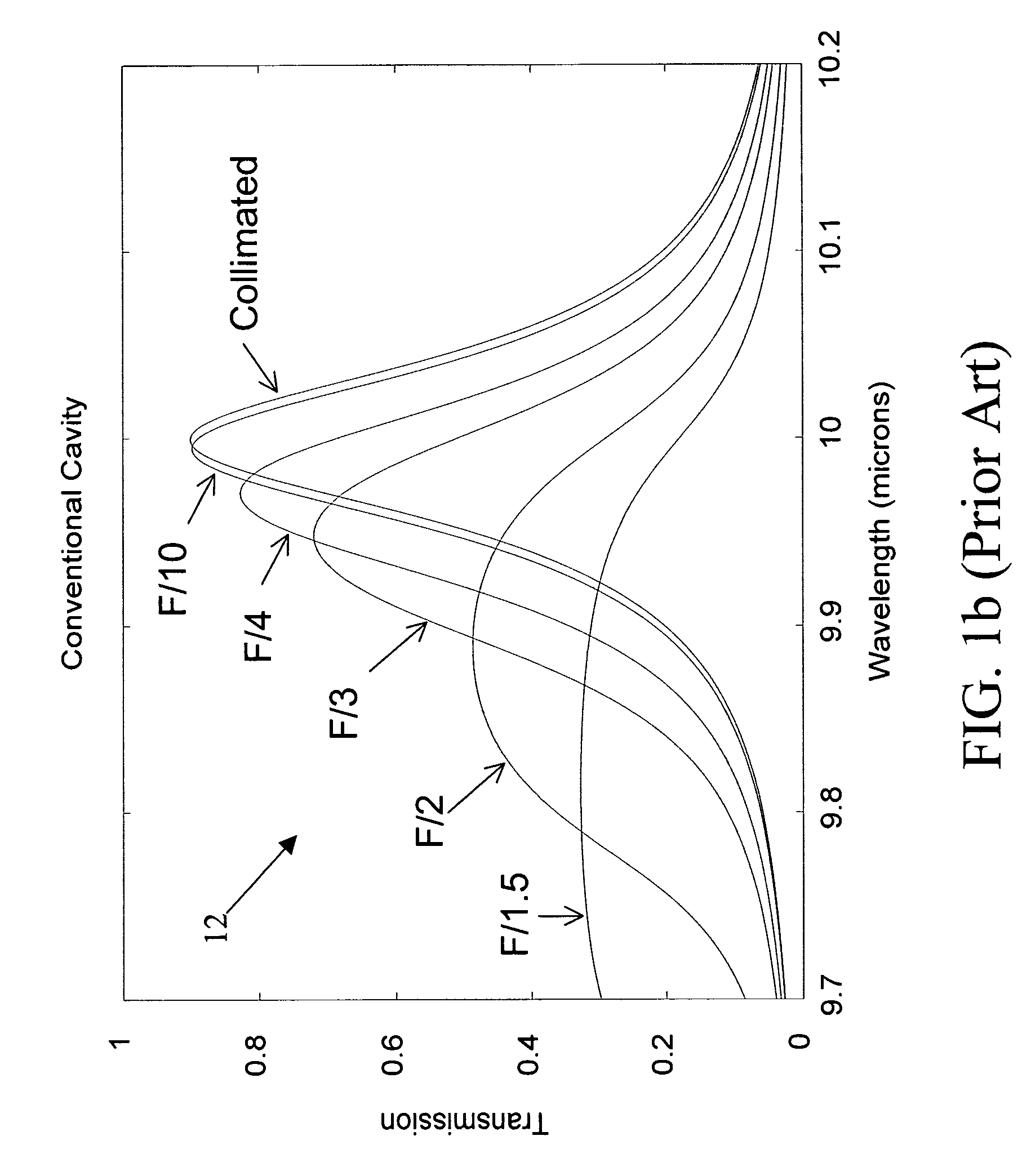
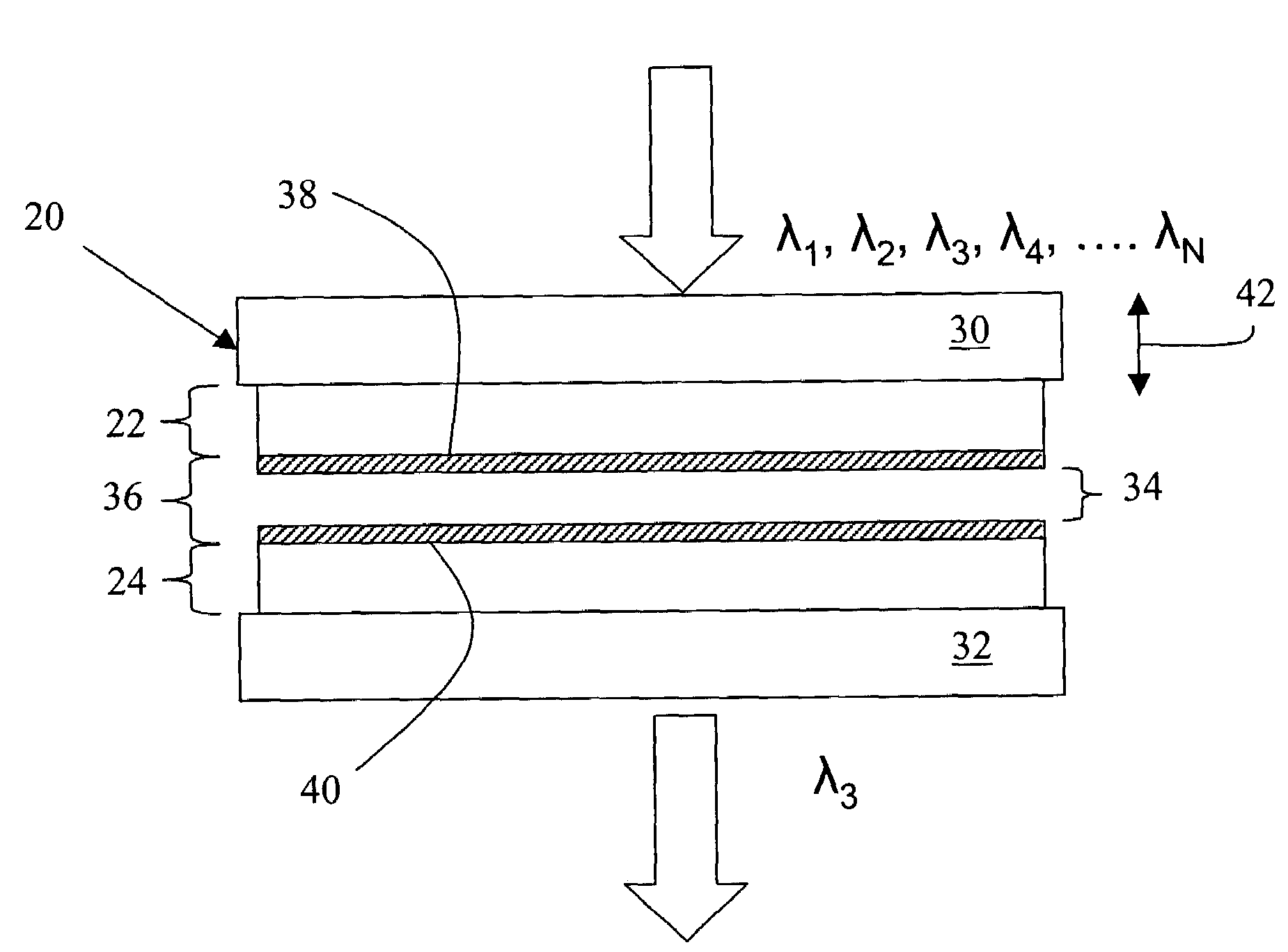
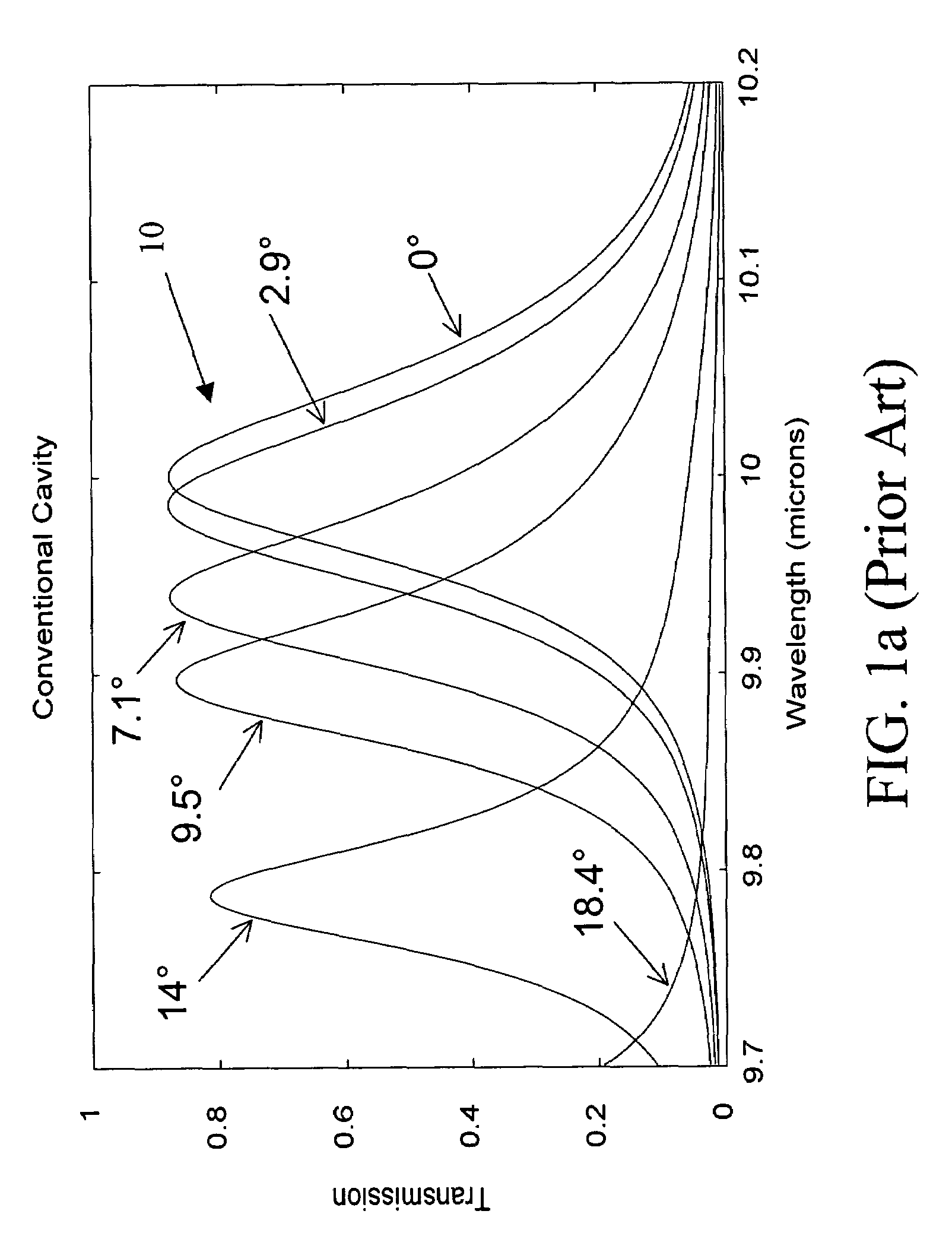
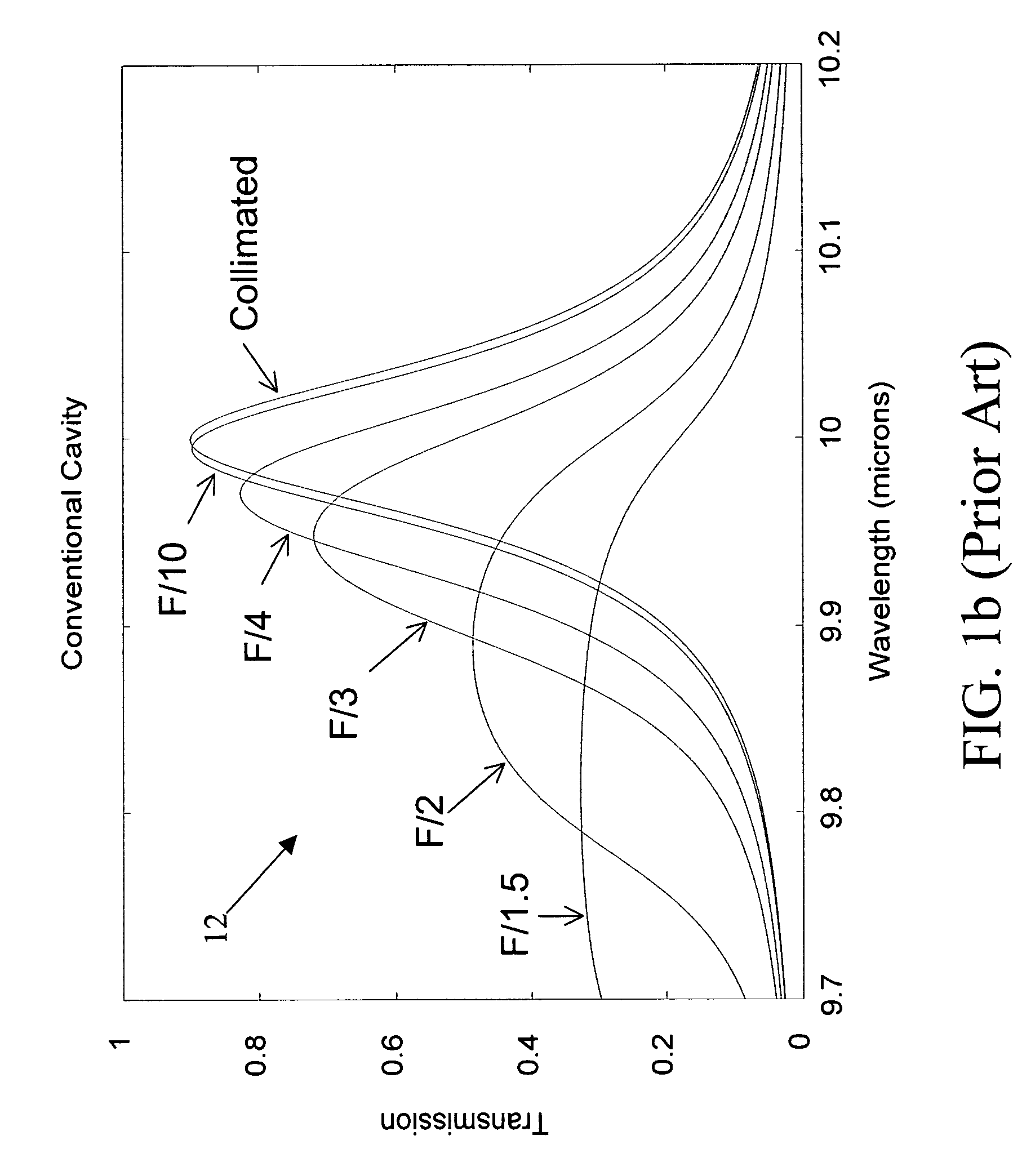
InactiveUS20050068541A1Less sensitiveLow F-numberSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionUsing optical meansAngle of incidenceMolecular physics
A tunable Fabry-Perot filter that is less sensitive to angle of incidence is formed by replacing the cavity (air gap) with a partitioned cavity that has an effective refractive index greater than one. The partitioned cavity includes a pair of partitioned cavity dielectric layers formed on the reflectors on either side of the variable air gap. Each of the dielectric layers has an optical thickness that is less than one fourth the shortest wavelength in the tuning range of the filter. The resulting three-layer partitioned cavity has an effective optical thickness substantially equal to an integral multiple (m) of one half the transmitted wavelength within the tuning range of the filter.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Surgical drape
InactiveUS20080078413A1Reduce glareReduce light intensityDiagnosticsRestraining devicesWound dressingTackifier
An adhesive composition having dispersed therein a broad spectrum antimicrobial agent for use in medical applications, such as an adhesive for surgical drapes, wound dressings and tapes, is provided. The adhesive is composed of acrylic polymers, tackifiers and a preferred antimicrobial agent, diiodomethyl-p-tolylsulfone. The subject adhesive composition may be formulated as either an essentially solventless hot melt, or as a solvent based system wherein an emulsion of the antimicrobial agent and the removal of excess solvent is avoided.
Owner:PADGET DAVID B +4
Hardmask composition having antirelective properties and method of patterning material on susbstrate using the same
ActiveUS7981594B2Improve etch selectivitySolve the lack of resistancePhotosensitive materialsPhotoprinting processesOrganic solventPolymer
A hardmask composition includes an organic solvent and one or more aromatic ring-containing polymers represented by Formula 1, 2 and 3:
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
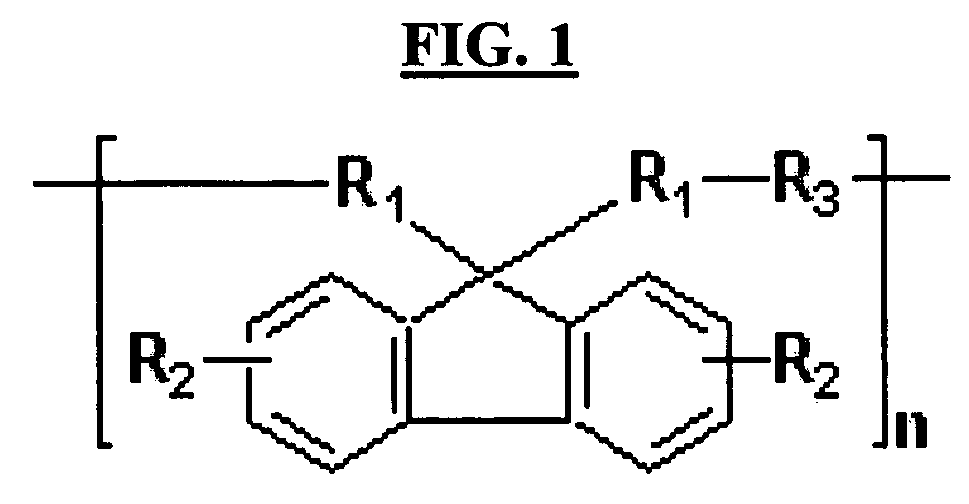
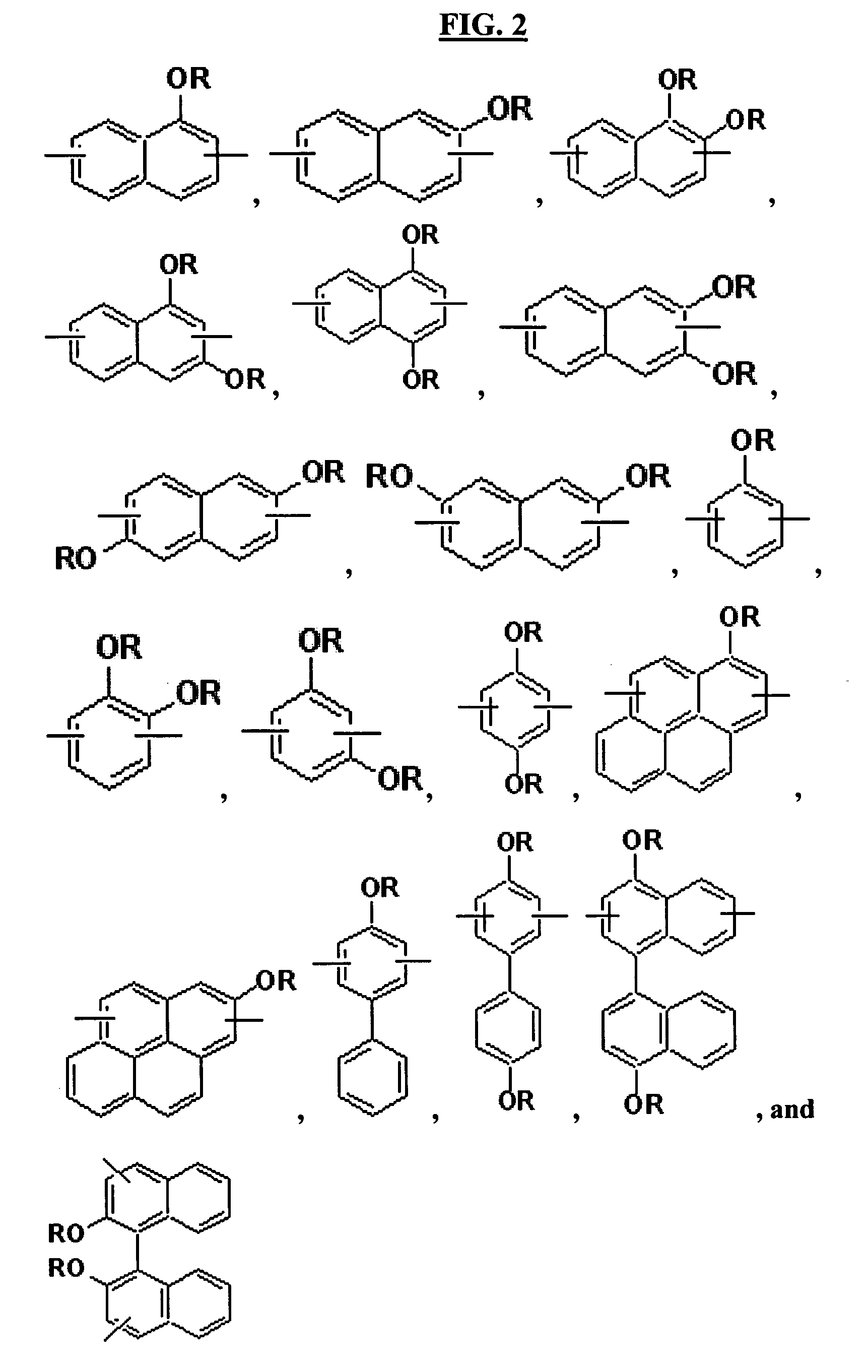
Aromatic ring-containing compound for a resist underlayer and resist underlayer composition
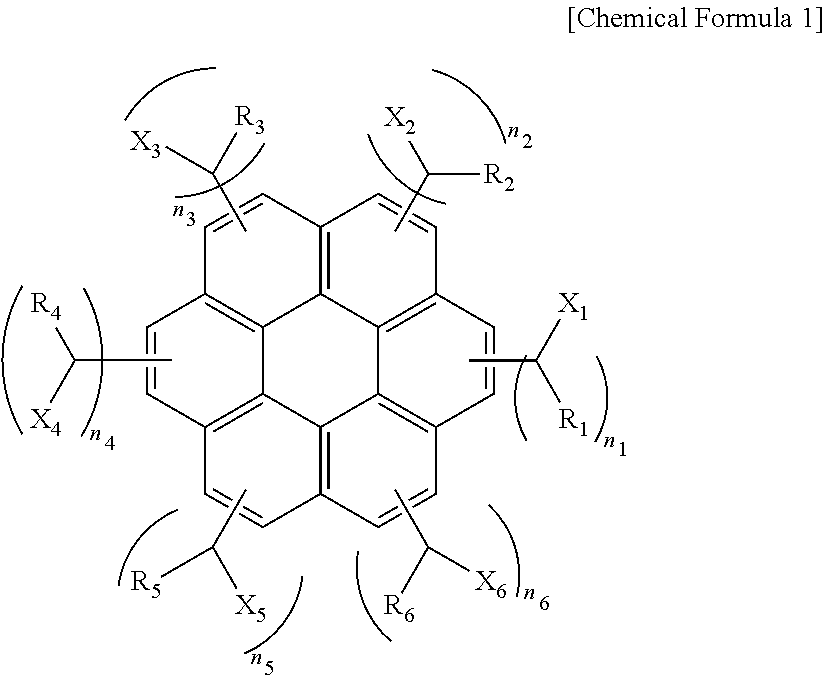
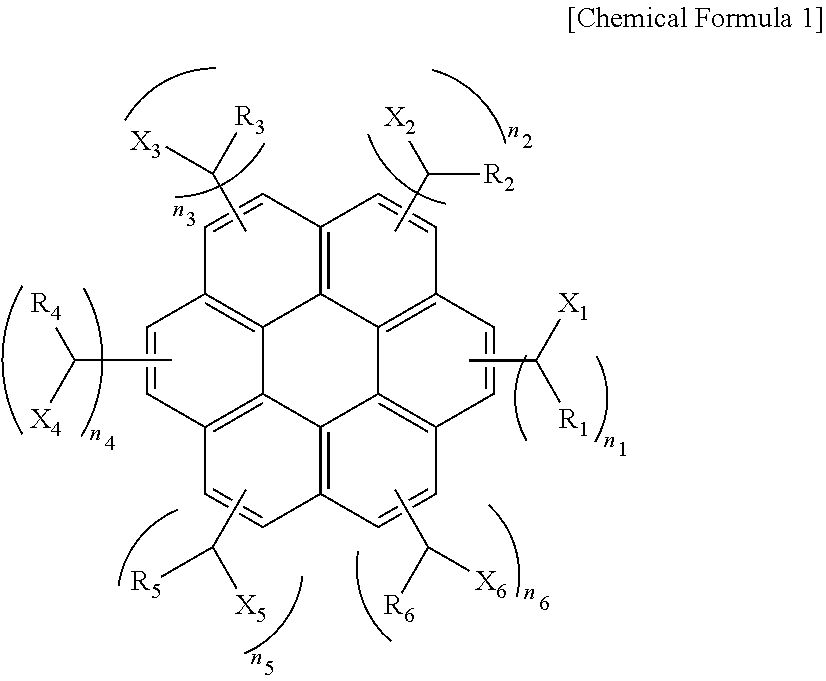
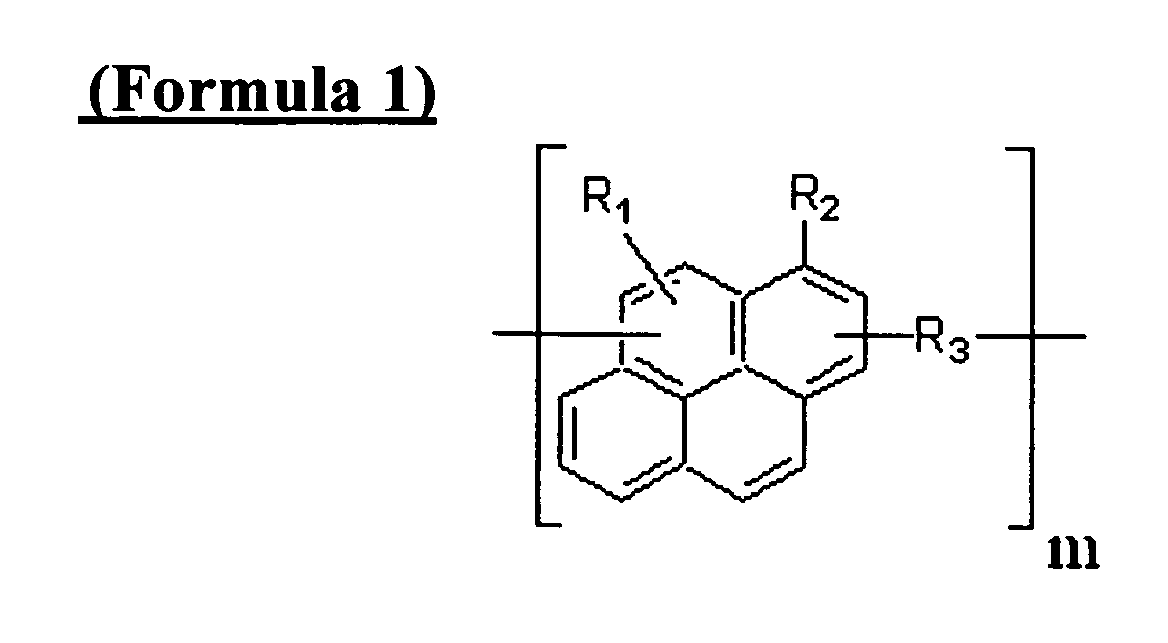
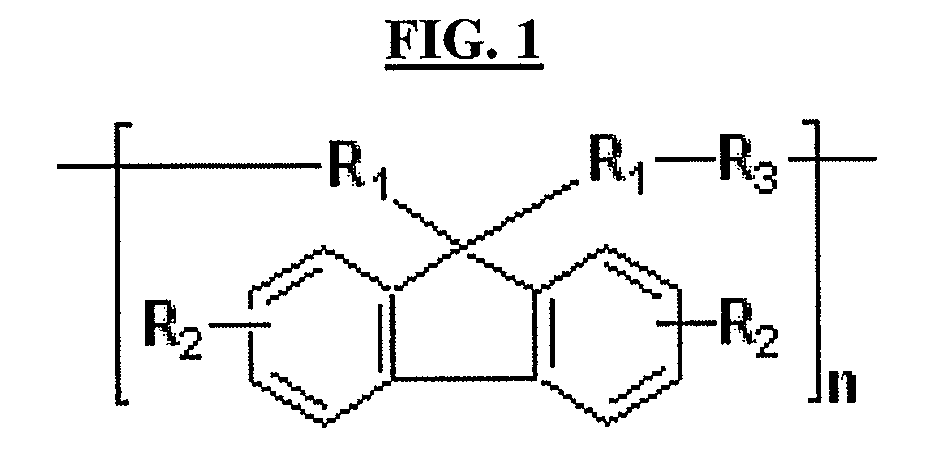
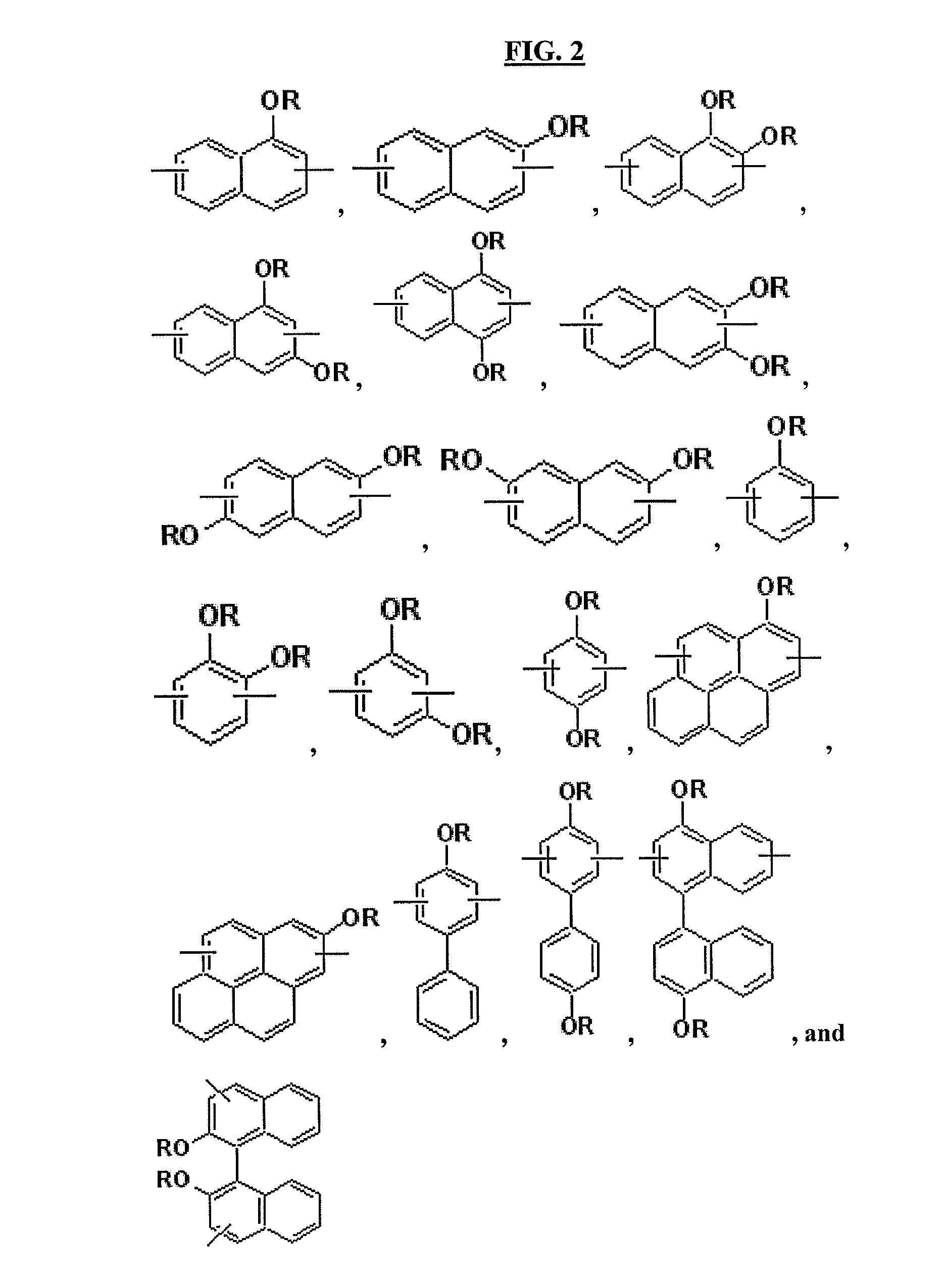
ActiveUS20110155944A1Excellent lithographic structureImprove etch selectivityOrganic chemistryMagnetic paintsResistAlkoxy group
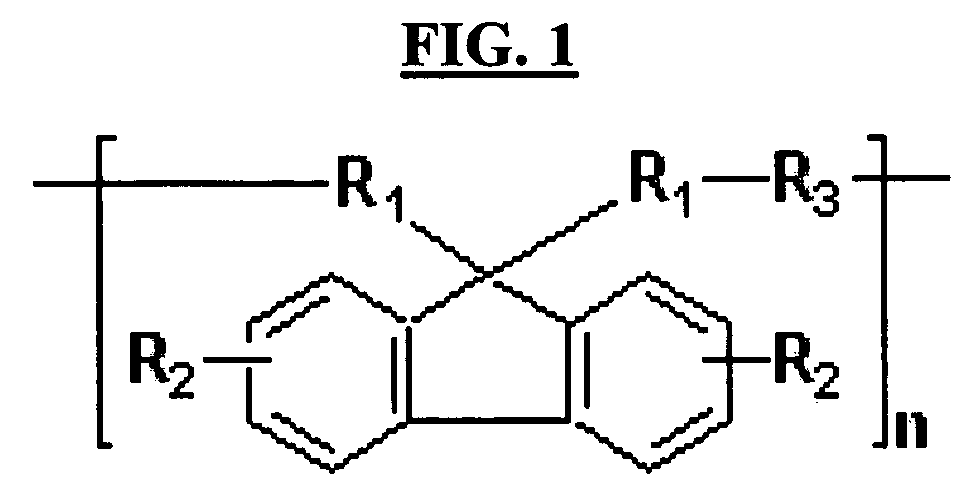
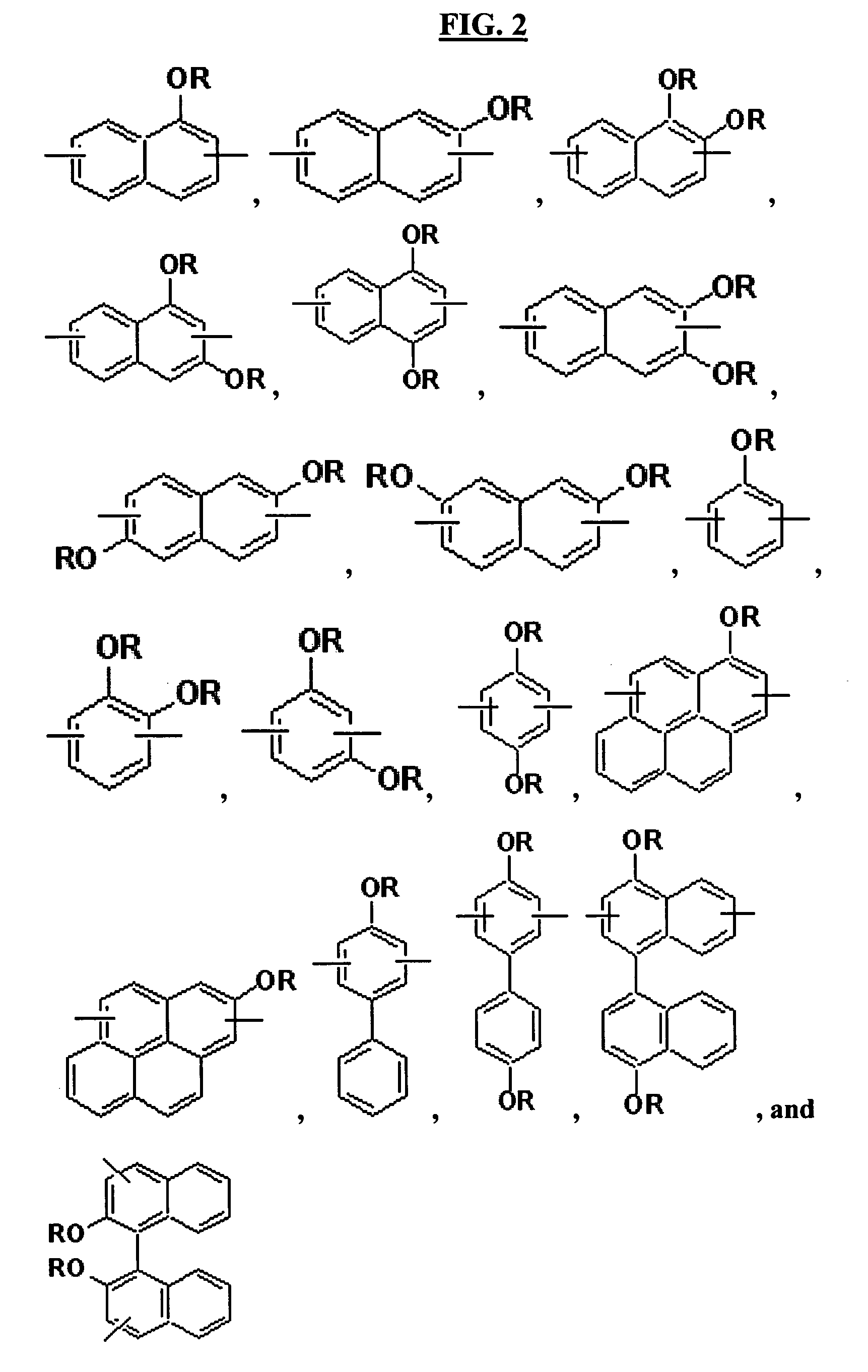
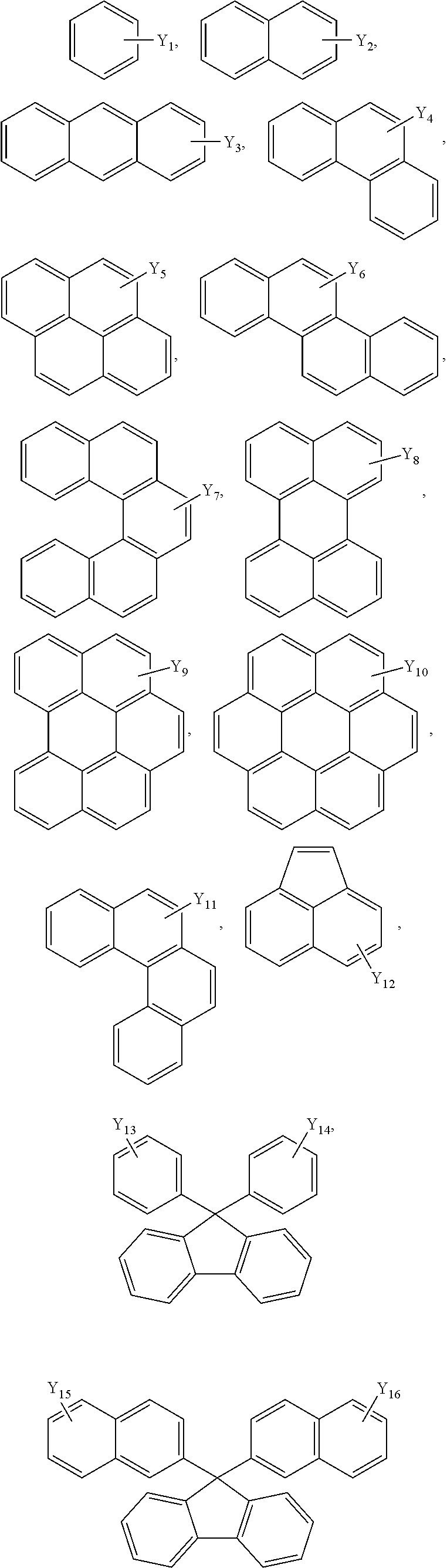
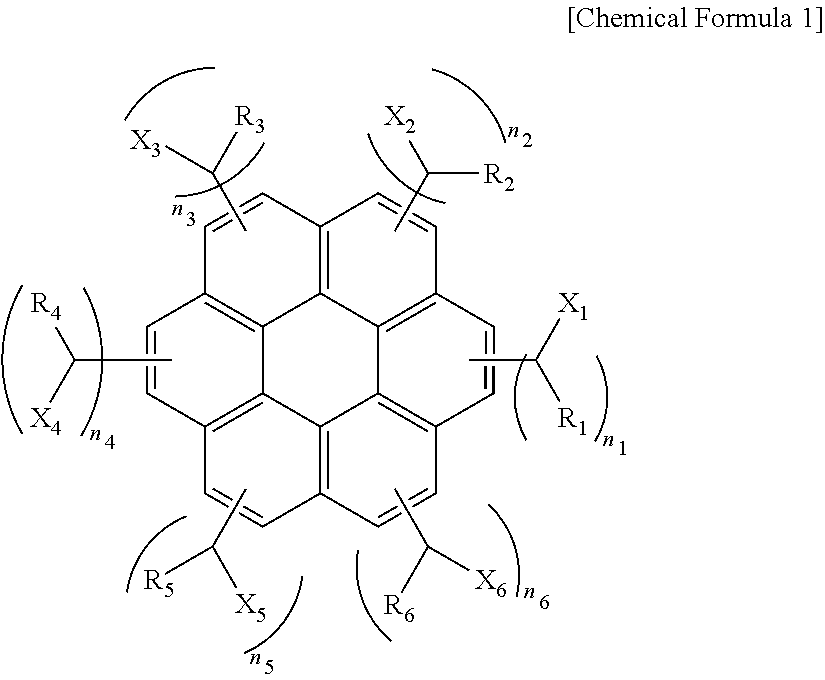
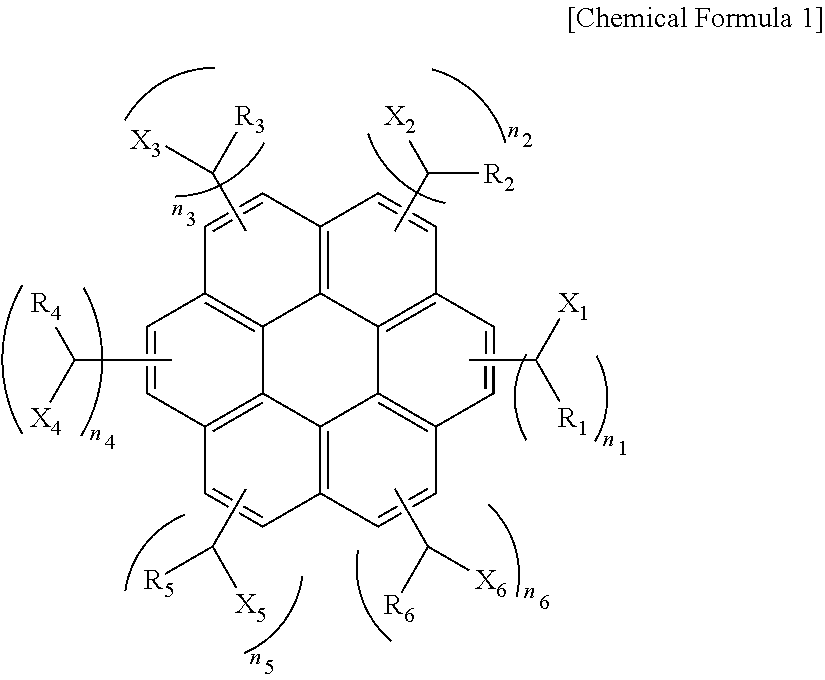
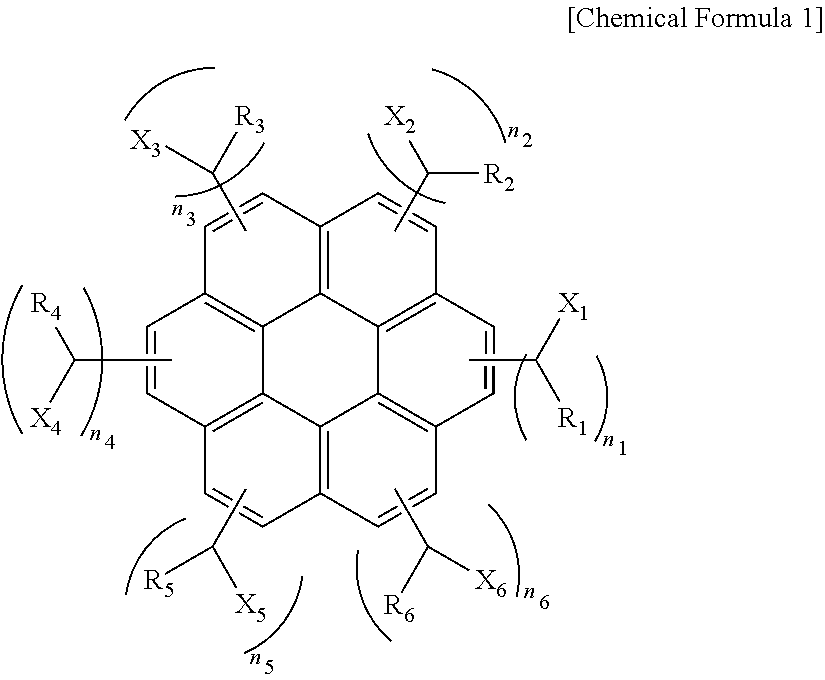
An aromatic ring-containing compound for a resist underlayer and a resist underlayer composition, the aromatic ring-containing compound being represented by the following Chemical Formula 1:wherein, in Chemical Formula 1, R1 to R6 are each independently a substituted or unsubstituted C1 to C10 alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C5 to C20 aromatic ring group, a substituted or unsubstituted C3 to C20 cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C3 to C20 cycloalkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C2 to C20 heteroaryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted C2 to C20 heterocycloalkyl group, X1 to X6 are each independently hydrogen, a hydroxy group (—OH), a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl amine group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, or an amino group (—NH2), n1 to n6 are each independently 0 or 1, and 1≦n1+n2+n3+n4+n5+n6≦6.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Hardmask composition, method of forming a pattern using the same, and semiconductor integrated circuit device including the pattern
ActiveUS20120153424A1Improve etch selectivitySufficient resistanceSolid-state devicesPhotomechanical apparatusSolventStructural unit
A hard mask composition, a method of forming a pattern, and a semiconductor integrated circuit device, the hard mask composition including a solvent; and a compound, the compound including a structural unit represented by the following Chemical Formula 1:
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
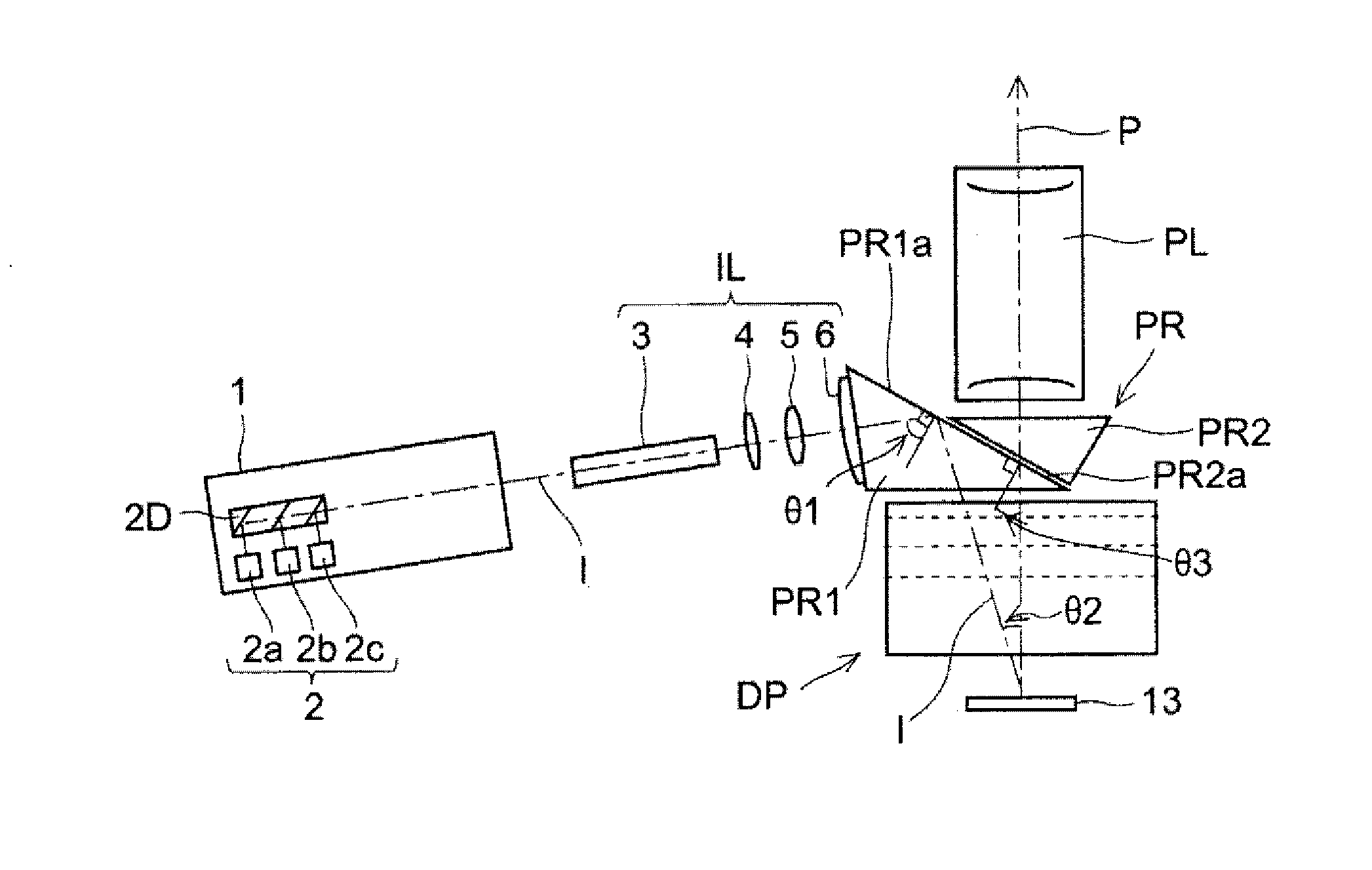
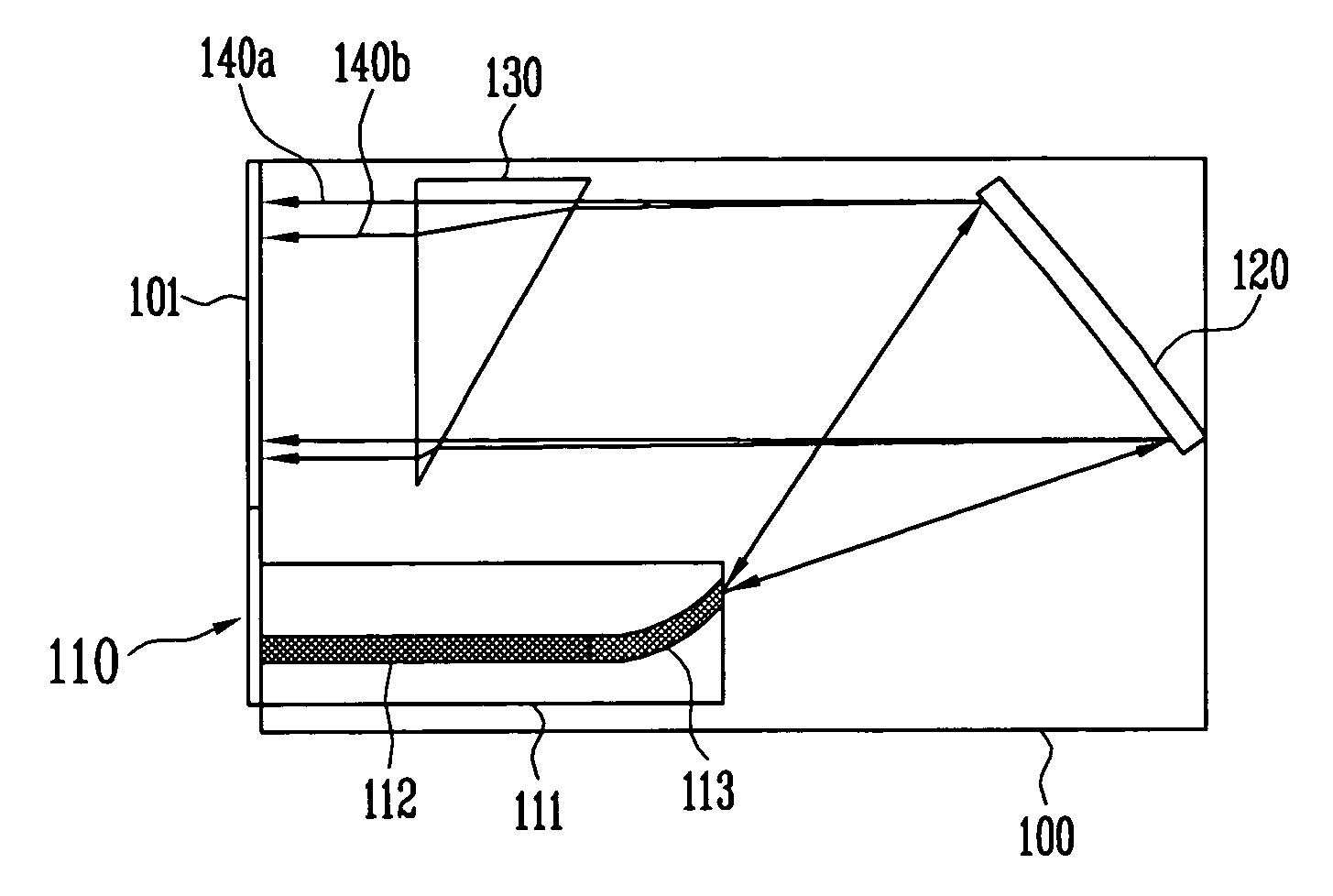
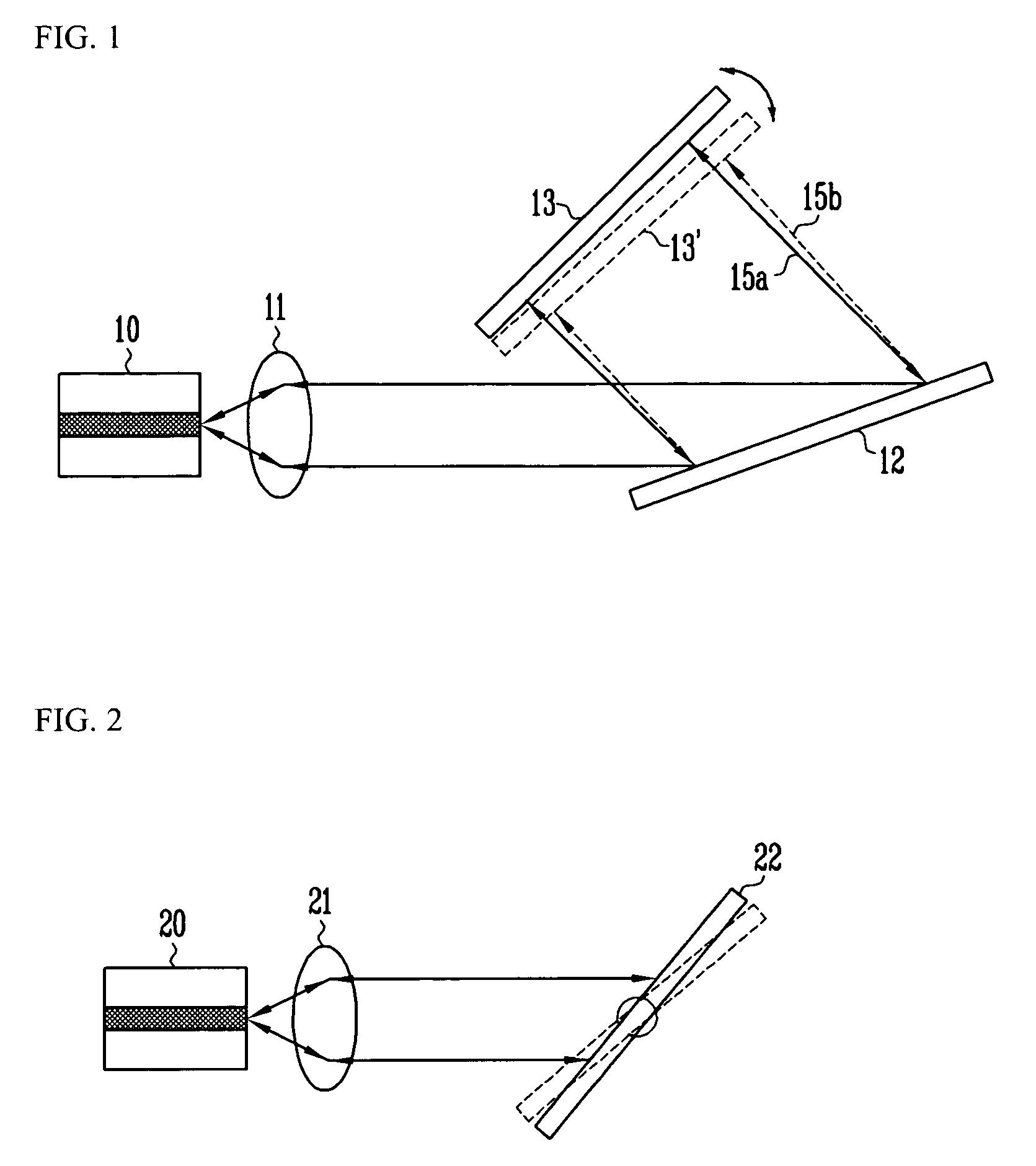
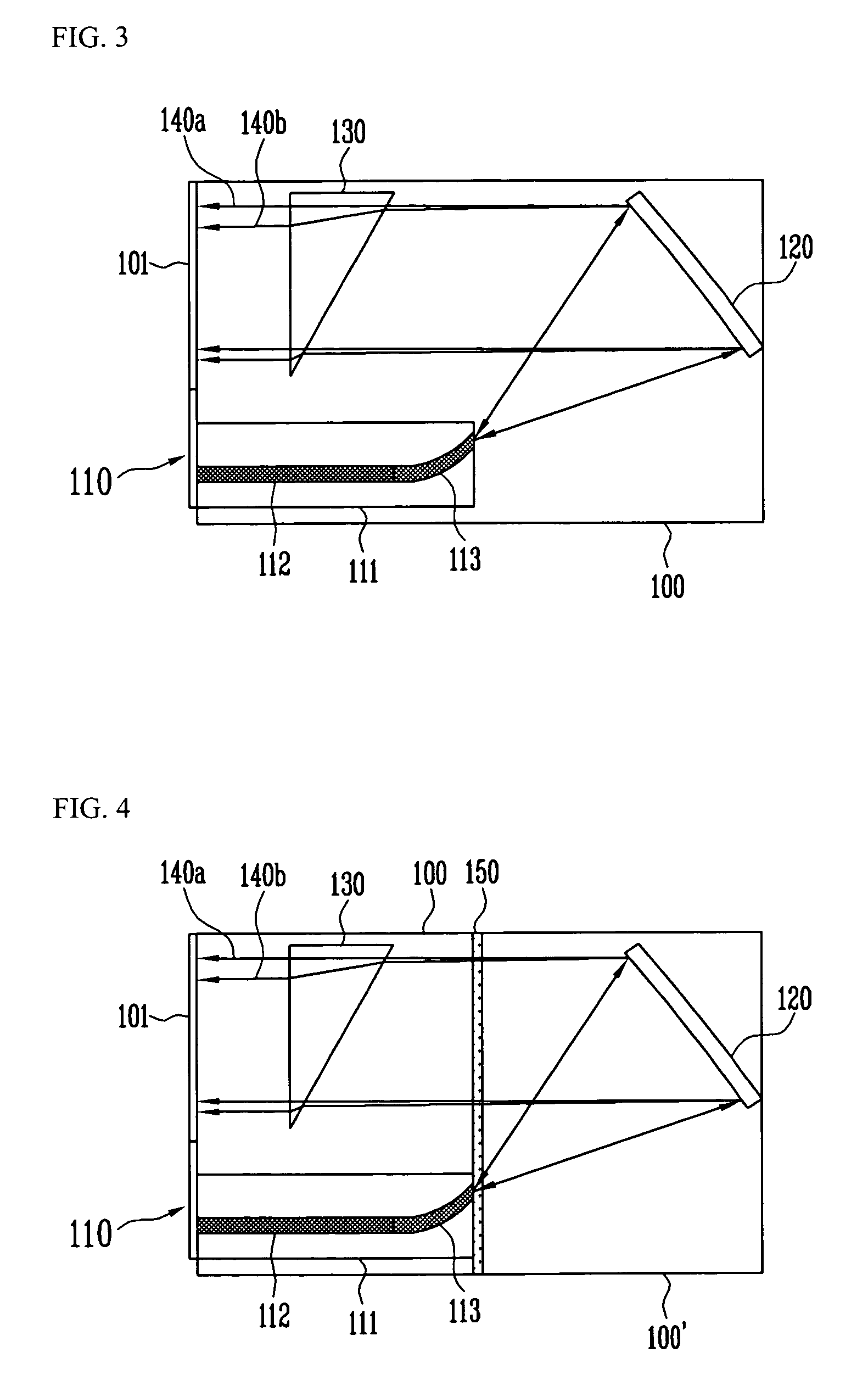
Prism for projection optical system and optical system having same
A prism for a projection optical system included in a projector including an illumination light source, an illumination optical system, and a projection optical system, includes: a first surface that totally reflects a beam of one of the illumination light and the projection light and transmits a beam of the other; and a second surface that is opposed to the first surface with an air gap therebetween and transmits a beam passing through the first surface, wherein the first surface has an antireflective film having an average reflectivity of a s-polarized reflectivity and a p-polarized reflectivity at a center angle of a transmitted beam of 2% or lower in three wavelength ranges including a first wavelength range of blue, a second wavelength range of green, and a third wavelength range of red.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Partitioned-cavity tunable fabry-perot filter
InactiveUS7319560B2Less sensitiveLow F-numberSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionUsing optical meansAngle of incidenceLength wave
A tunable Fabry-Perot filter that is less sensitive to angle of incidence is formed by replacing the cavity (air gap) with a partitioned cavity that has an effective refractive index greater than one. The partitioned cavity includes a pair of partitioned cavity dielectric layers formed on the reflectors on either side of the variable air gap. Each of the dielectric layers has an optical thickness that is less than one fourth the shortest wavelength in the tuning range of the filter. The resulting three-layer partitioned cavity has an effective optical thickness substantially equal to an integral multiple (m) of one half the transmitted wavelength within the tuning range of the filter.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
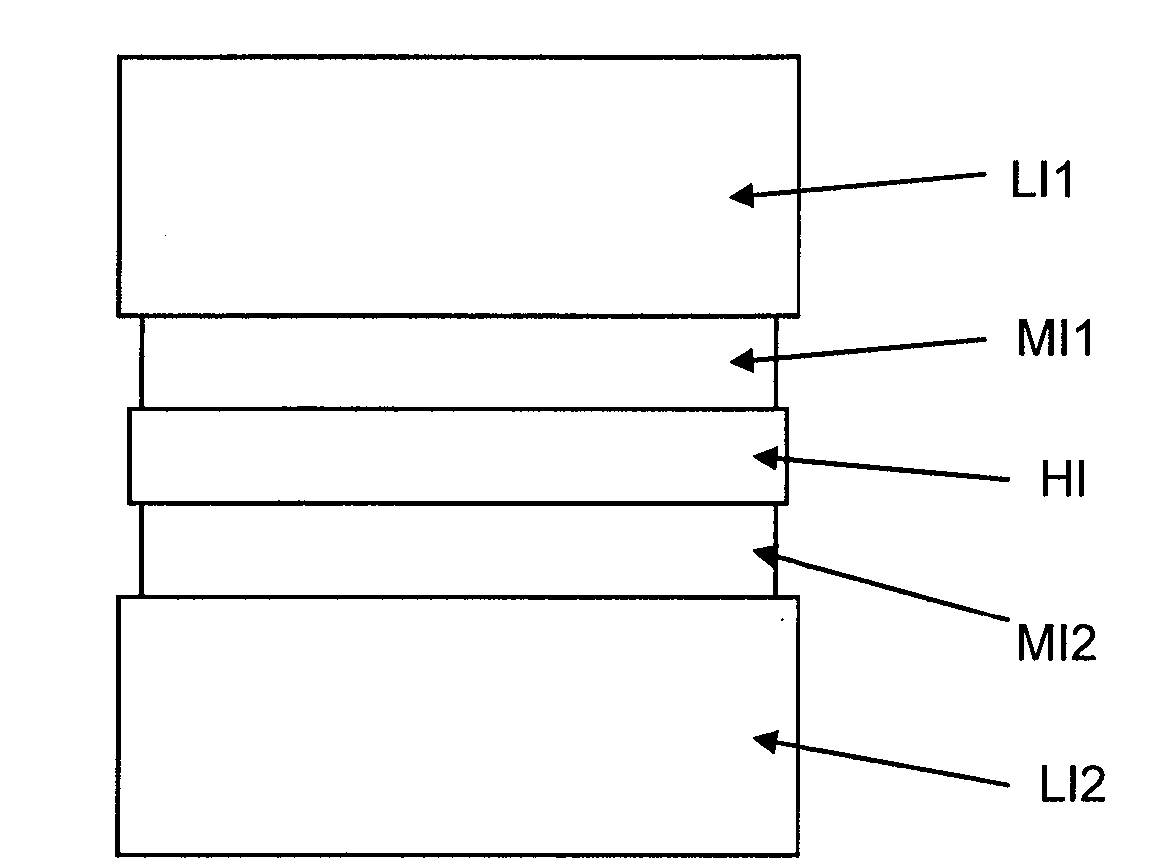
Optical structure to reduce internal reflections
ActiveUS20100297365A1Minimize internal reflectionInternal reflection be reduceLiquid crystal compositionsLayered productsComputational physicsRefractive index
A structure for reducing internal reflections in an optical system includes a stack of layers including a first layer having a first refractive index, a second layer having a second refractive index, a third layer having a third refractive index, a fourth layer having a fourth refractive index, and a fifth layer having a fifth refractive index. The second layer is arranged between the first layer and the third layer, and the fourth layer is arranged between the third layer and fifth layer. Further, the third refractive index is greater than the second and fourth refractive indexes, the second refractive index is greater than the first refractive index, and the fourth refractive index is greater than the fifth refractive index.
Owner:UNIFIED INNOVATIVE TECH
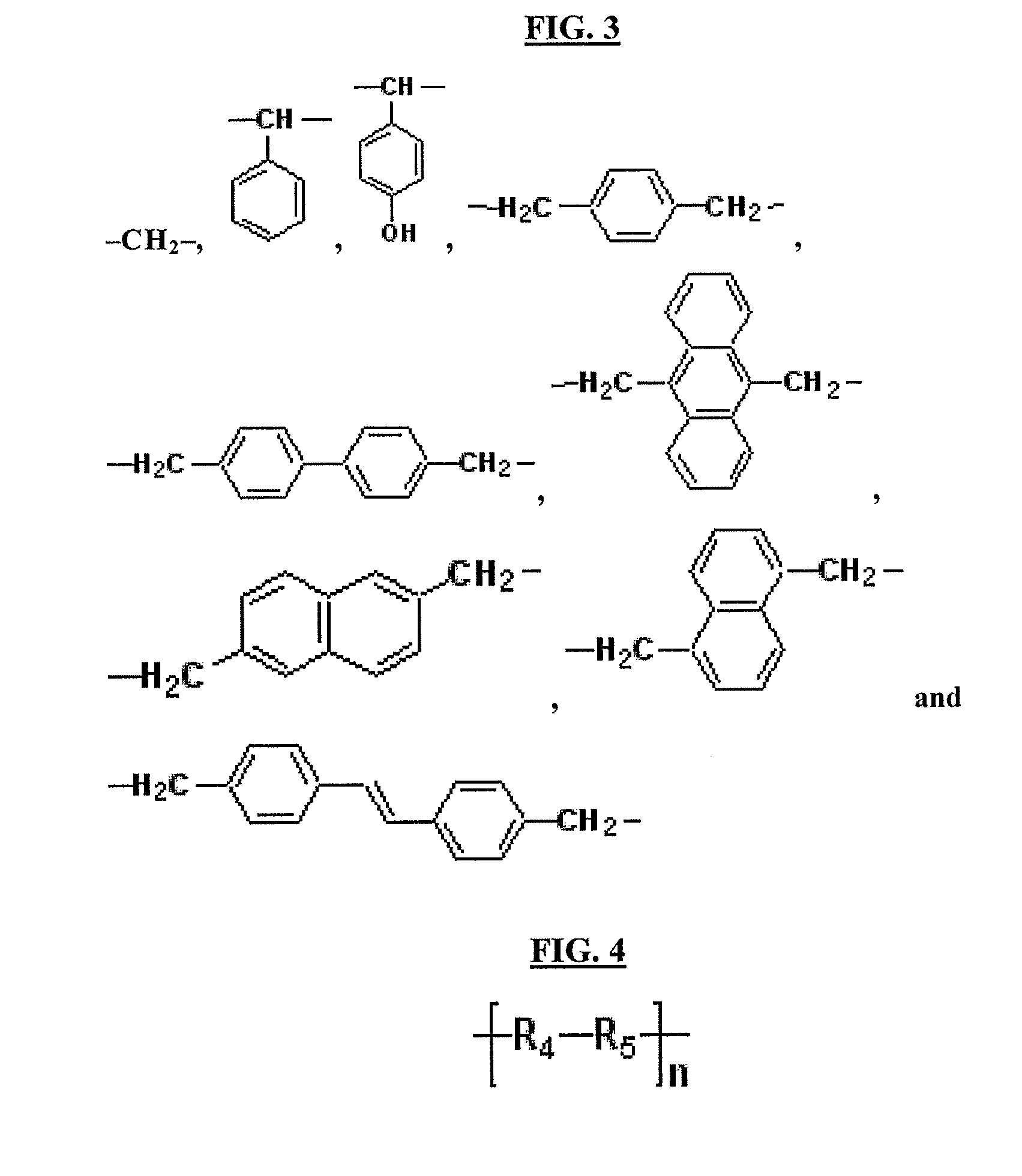
Aromatic ring-containing polymer, polymer mixture, antireflective hardmask composition, and associated methods
ActiveUS8420289B2Improve etch selectivitySolve the lack of resistancePhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive material processingPolymer sciencePolymer
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Hardmask composition having antireflective properties and method of patterning material on substrate using the same
ActiveUS20110275019A1Improve etch selectivitySolve the lack of resistancePhotosensitive materialsDiffusing elementsOrganic solventHard mask
A hardmask composition includes an organic solvent and one or more aromatic ring-containing polymers represented by Formulae 1, 2 and 3:
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Composition of anti-reflective hardmask
ActiveUS10189947B2Improve etch selectivityIncrease resistancePhotomechanical coating apparatusPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOrganic solventBiopolymer
Owner:CHOI SANG JUN
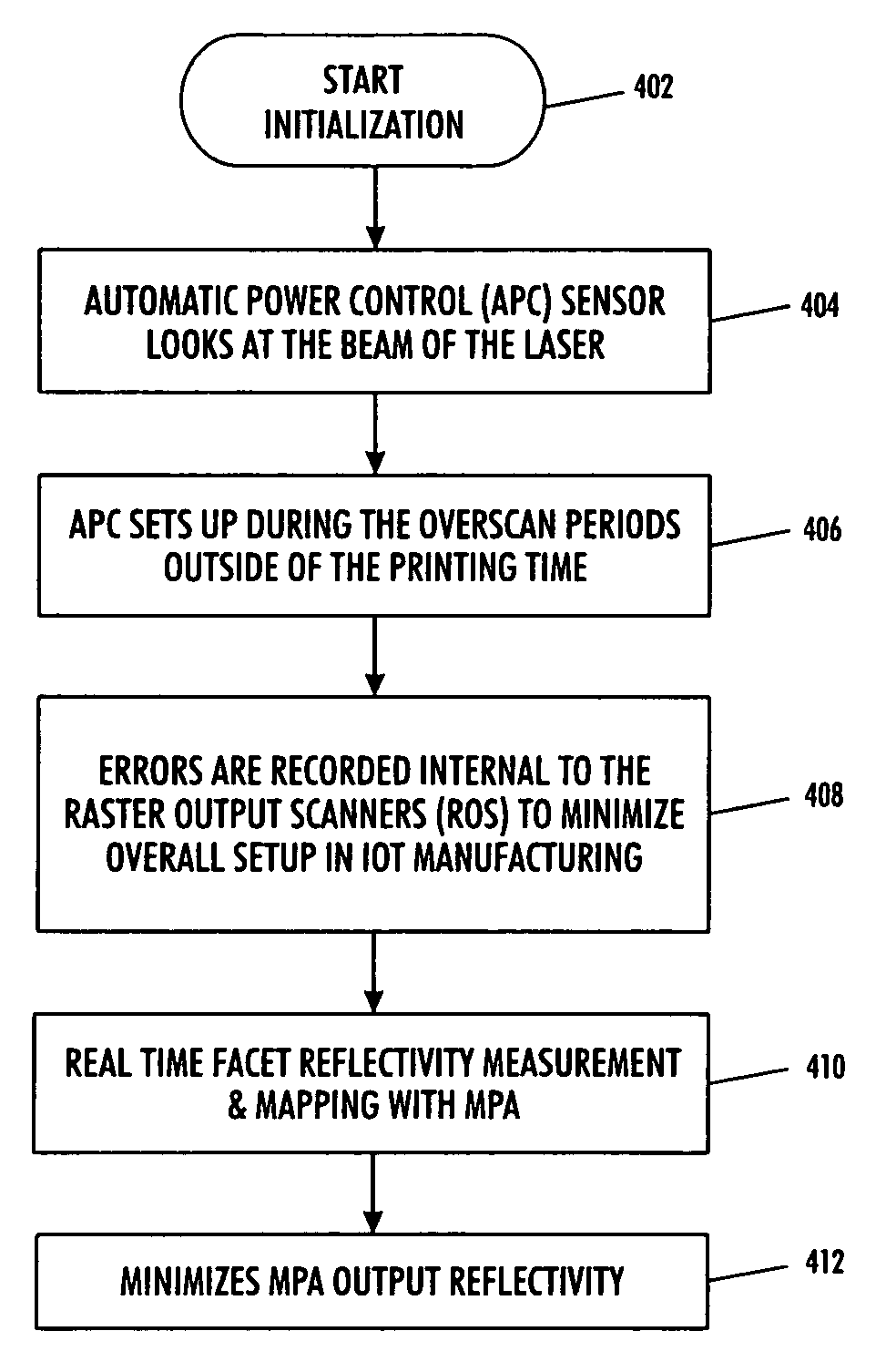
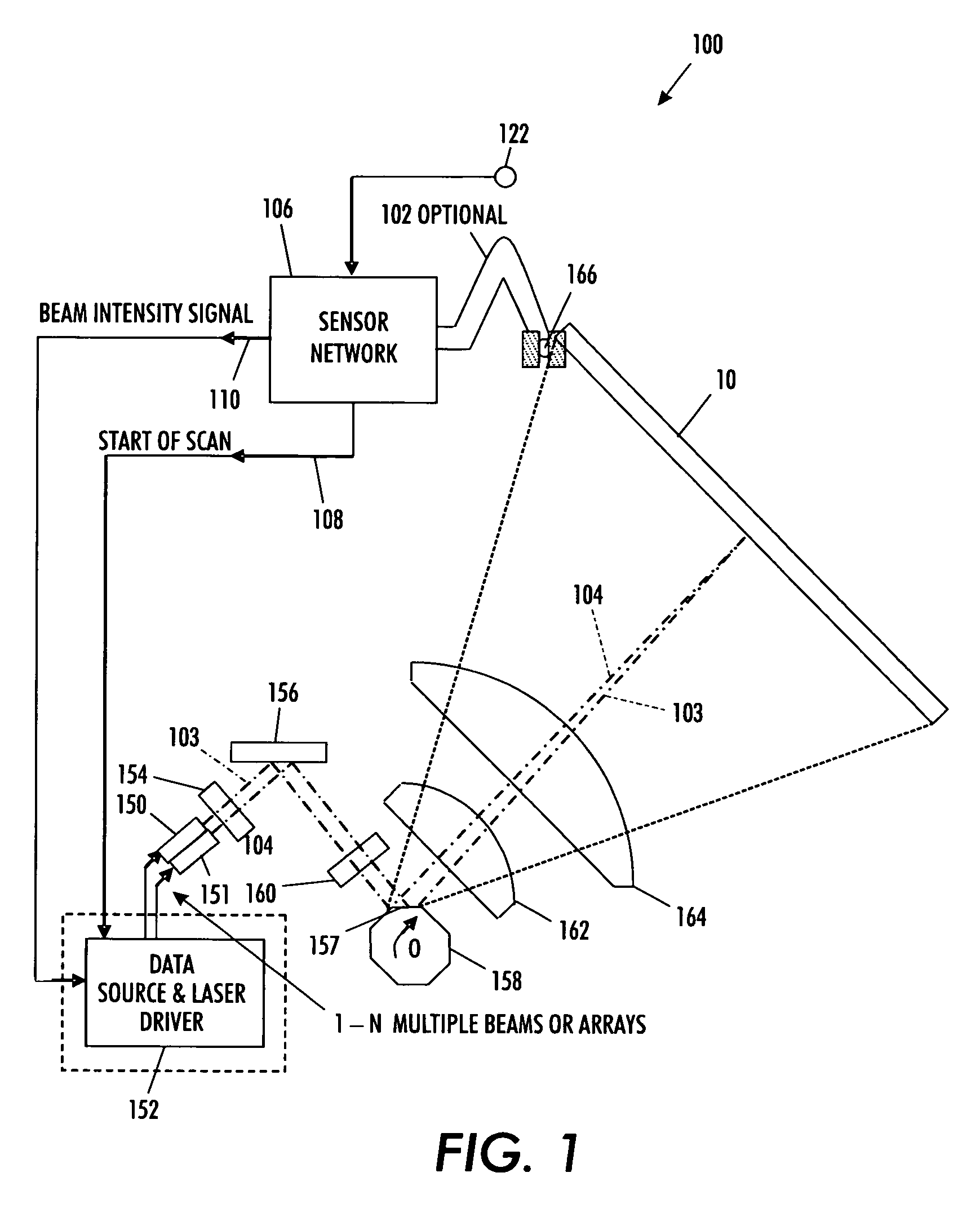
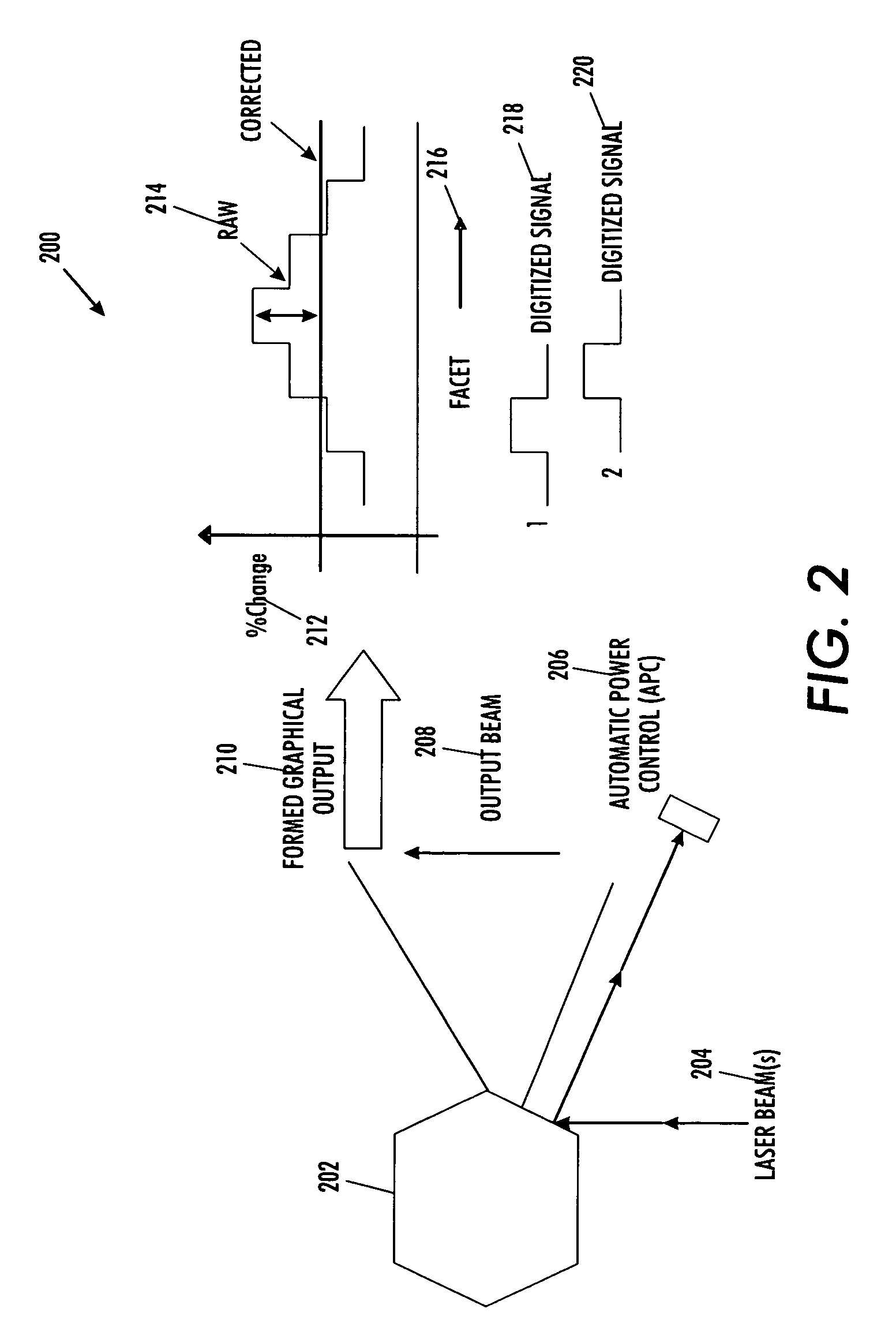
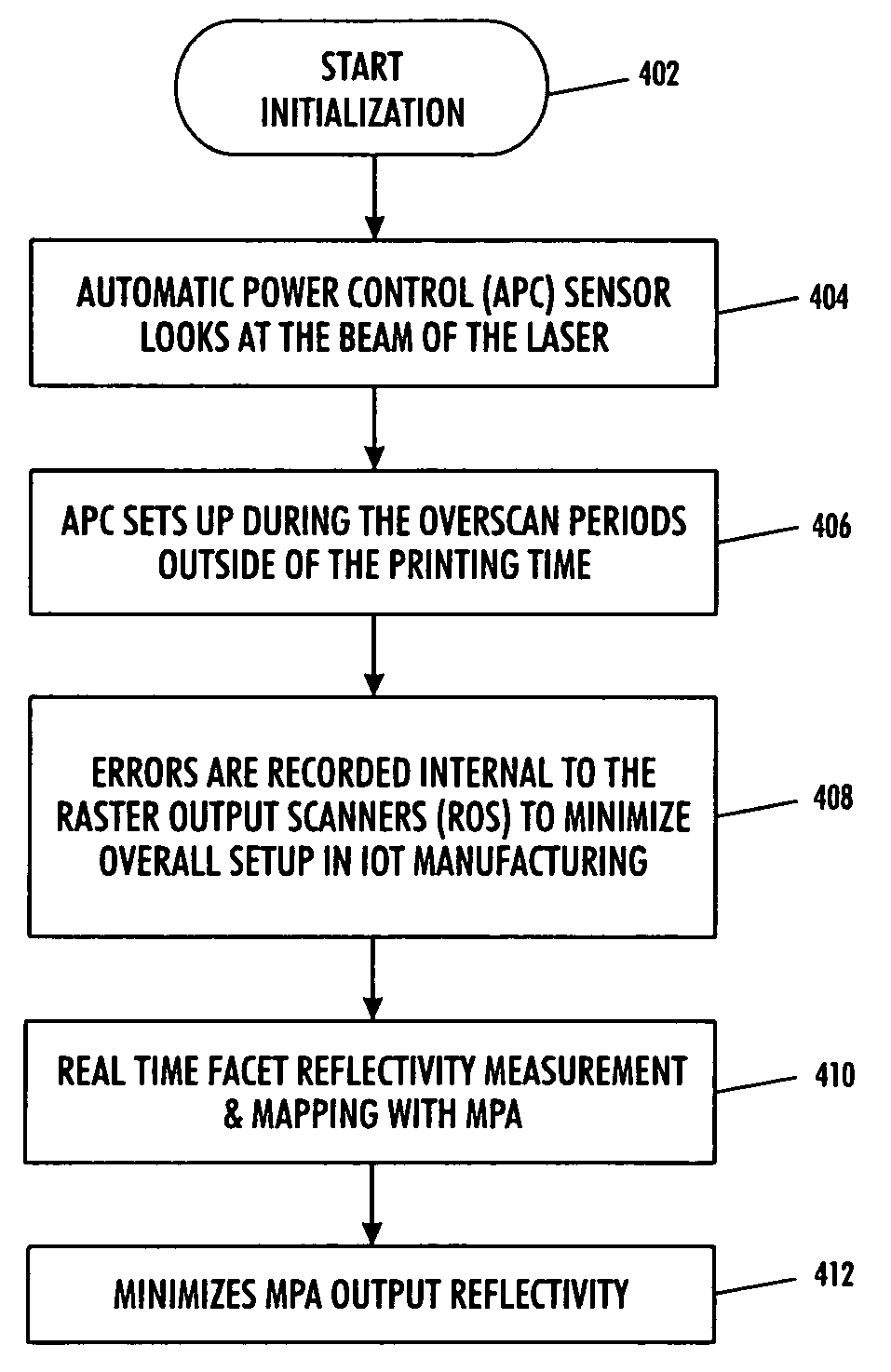
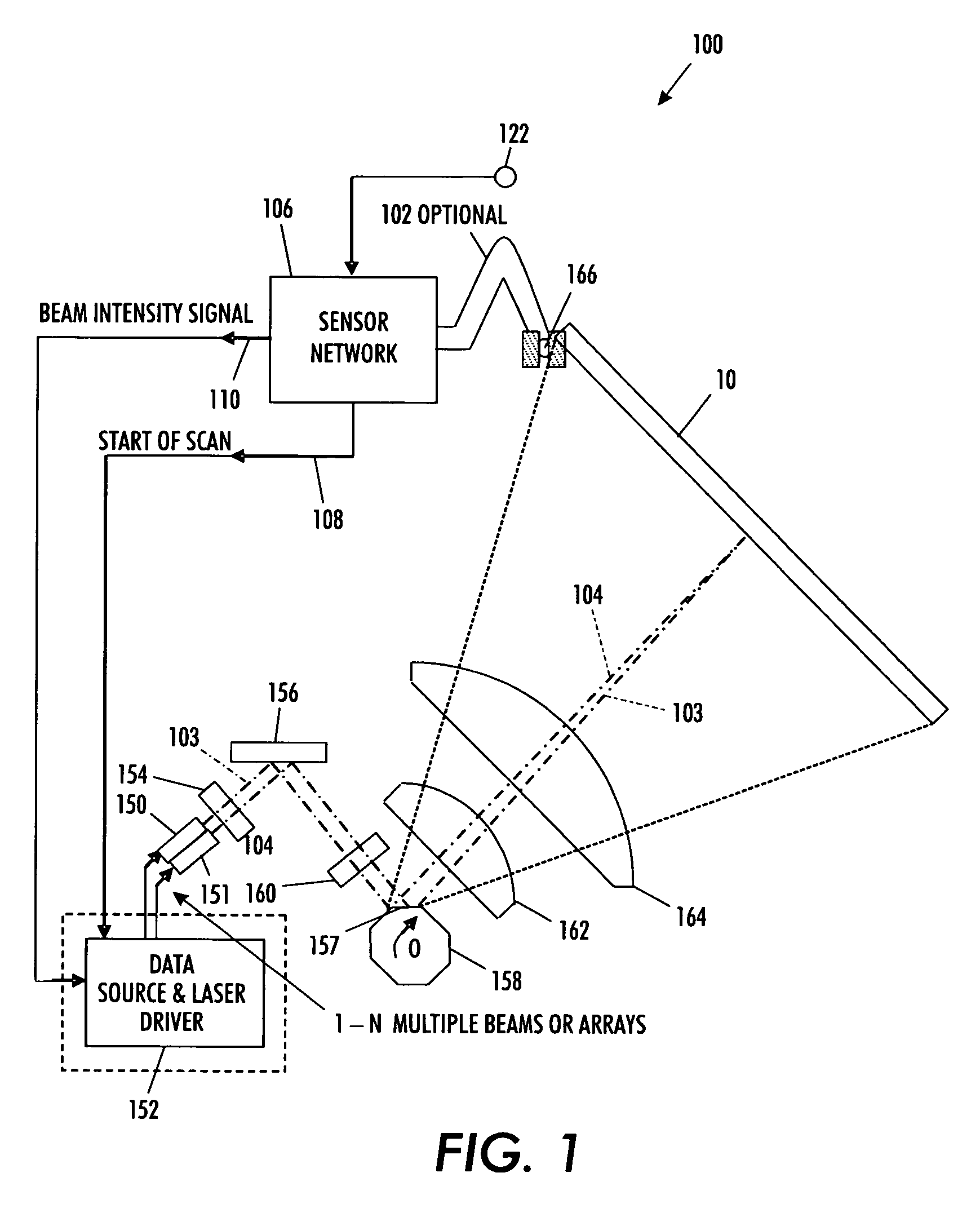
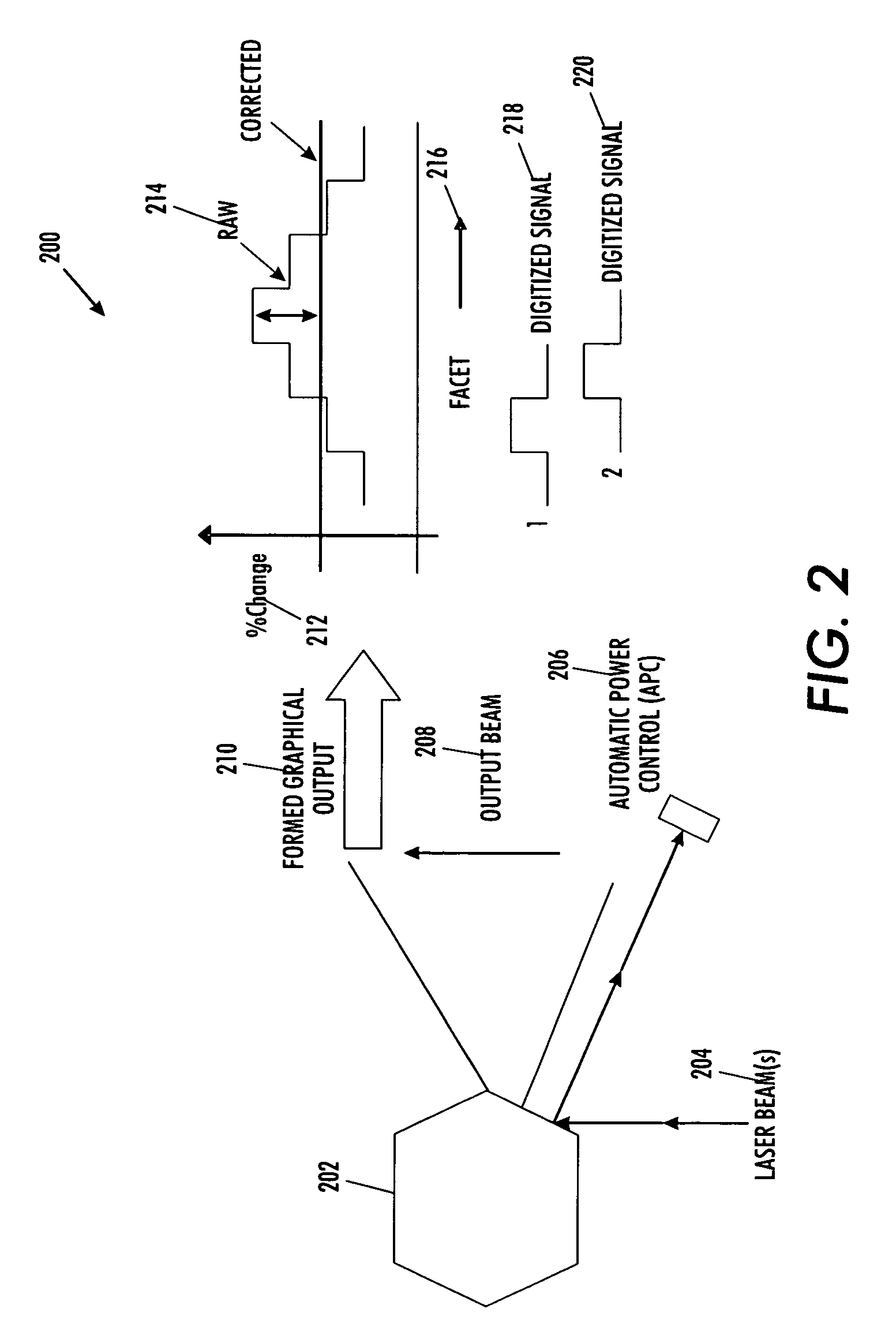
Motor polygon assembly (MPA) facet reflectivity mapping
InactiveUS7995089B2Data augmentationImprove system performanceInking apparatusGratingComputer terminal
A technique for minimizing motor polygon assembly output reflectivity using real time facet reflectivity measurements and mapping. An automatic power control sensor manages laser beams produced by the laser source associated with the system during overscan periods ‘outside’ of defined printing time. Errors are then recorded internal to the raster output scanner to minimize overall setup in the image output terminal.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Motor polygon assembly (MPA) facet reflectivity mapping
ActiveUS20080117281A1Minimizes MPA output reflectivityHigh outputInking apparatusGratingComputer terminal
A technique for minimizing motor polygon assembly output reflectivity using real time facet reflectivity measurements and mapping. An automatic power control sensor manages laser beams produced by the laser source associated with the system during overscan periods ‘outside’ of defined printing time. Errors are then recorded internal to the raster output scanner to minimize overall setup in the image output terminal.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Hardmask composition, method of forming a pattern using the same, and semiconductor integrated circuit device including the pattern
ActiveUS8741539B2Improve etch selectivitySufficient resistancePhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolventStructural unit
A hard mask composition, a method of forming a pattern, and a semiconductor integrated circuit device, the hard mask composition including a solvent; and a compound, the compound including a structural unit represented by the following Chemical Formula 1:
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
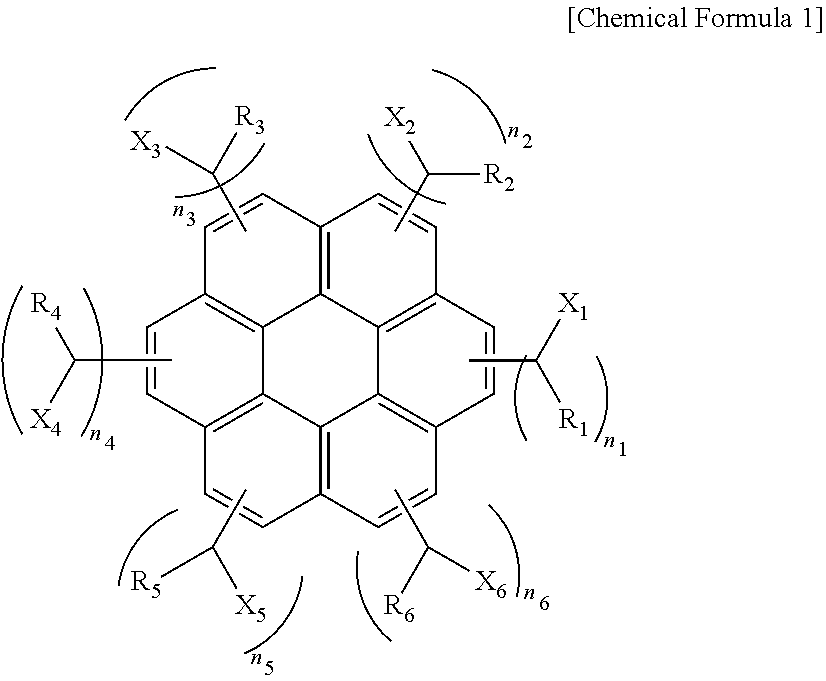
Aromatic ring-containing compound for a resist underlayer and resist underlayer composition
ActiveUS8637219B2Excellent lithographic structureImprove etch selectivityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationResistHydrogen
An aromatic ring-containing compound for a resist underlayer and a resist underlayer composition, the aromatic ring-containing compound being represented by the following Chemical Formula 1:wherein, in Chemical Formula 1, R1 to R6 are each independently a substituted or unsubstituted C1 to C10 alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C5 to C20 aromatic ring group, a substituted or unsubstituted C3 to C20 cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C3 to C20 cycloalkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C2 to C20 heteroaryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted C2 to C20 heterocycloalkyl group, X1 to X6 are each independently hydrogen, a hydroxy group (—OH), a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl amine group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, or an amino group (—NH2), n1 to n6 are each independently 0 or 1, and 1≦n1+n2+n3+n4+n5+n6≦6.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Tunable external cavity laser diode using variable optical deflector
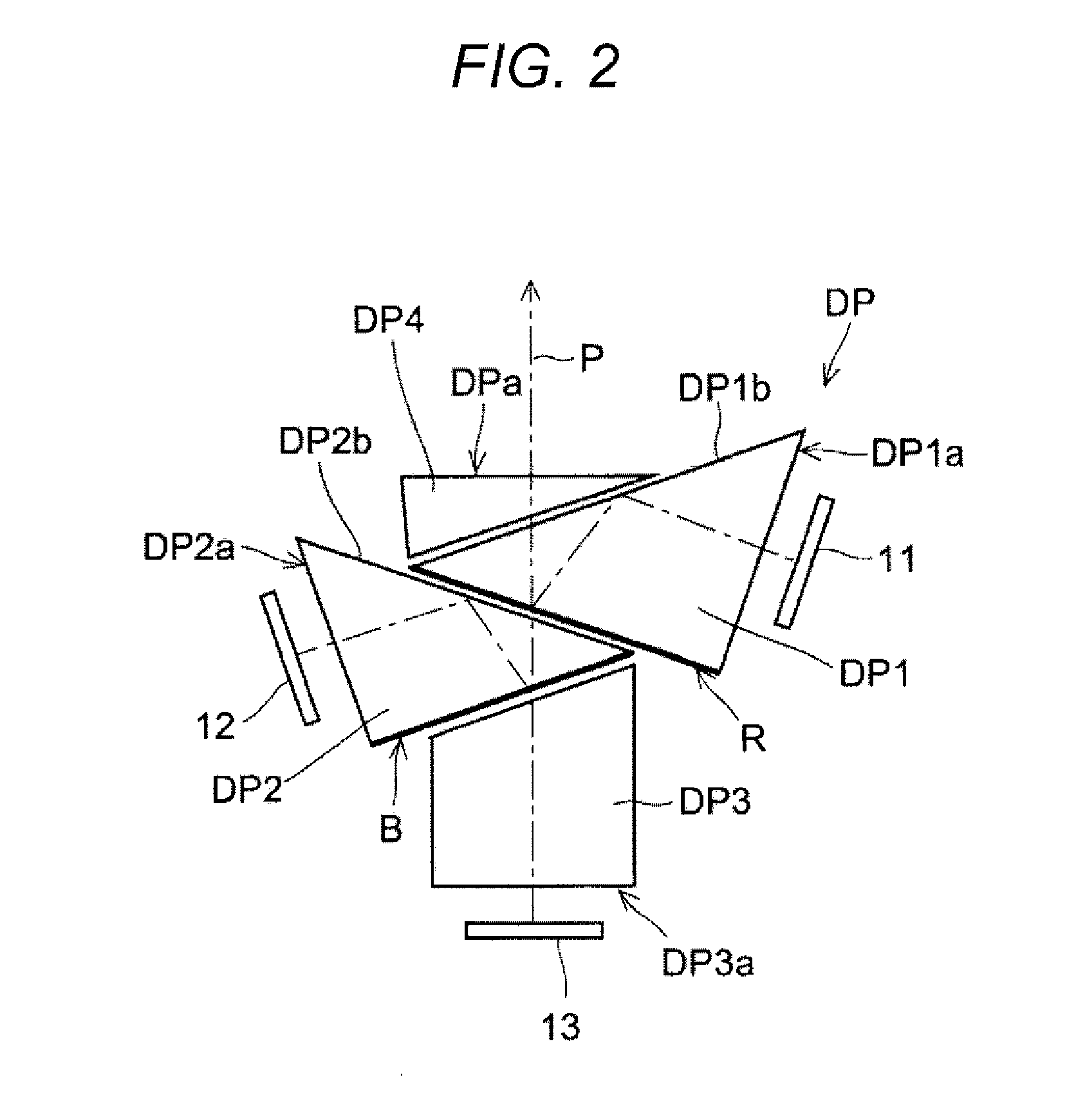
InactiveUS7212560B2Improve adjustabilityMinimize reflectivityLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser optical deviceExternal cavity laserRefractive index
Provided is a tunable external cavity laser diode using a variable optical deflector wherein the variable optical deflector, in which a refractive index varies according to an electrical signal, is arranged in a triangular shape between a concave diffraction grating and a reflective mirror. Since a resonant frequency is changed using the electrical signal rather than the mechanical movement, the stable operation and continuous high-speed tenability may be enabled. In addition, when the tunable external cavity laser diode according to the present invention is implemented in an InP / InGaAsP / InP slab waveguide, a variable time determined by the carrier lifetime may be reduced to several nanoseconds or less, the miniaturization is enabled, and the manufacturing costs are significantly reduced due to the process simplification. Moreover, when the concave diffraction grating is designed based on a silica (or polymer) based slab waveguide, the fabrication may be performed even by a lithography process having low resolution, thereby enhancing reproducibility and uniformity of the diffraction grating, and accordingly reducing the manufacturing costs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Composition of Anti-Reflective Hardmask
ActiveUS20170198096A1Improve etch selectivityIncrease resistancePhotomechanical coating apparatusPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOrganic solventBiopolymer
Owner:CHOI SANG JUN
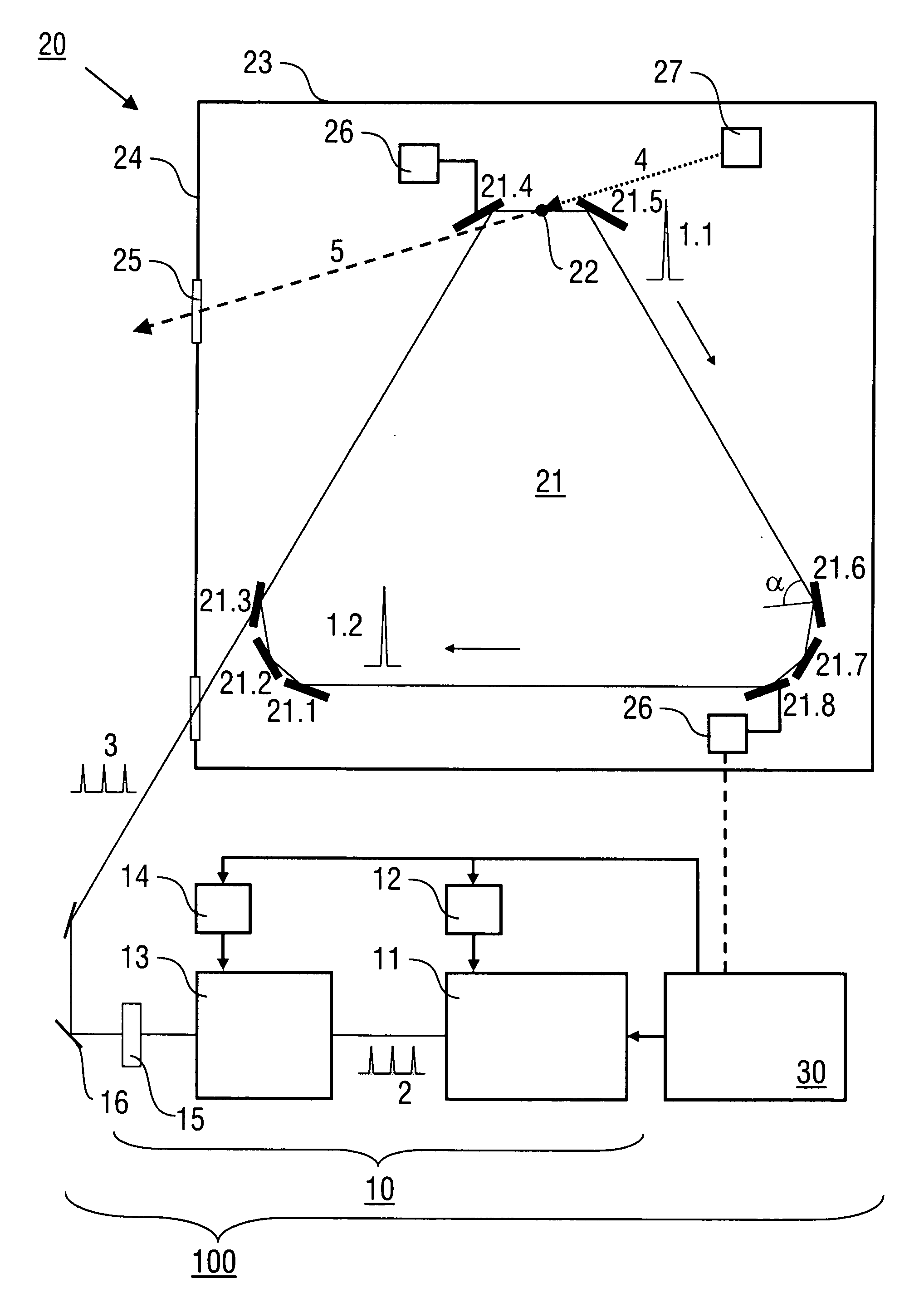
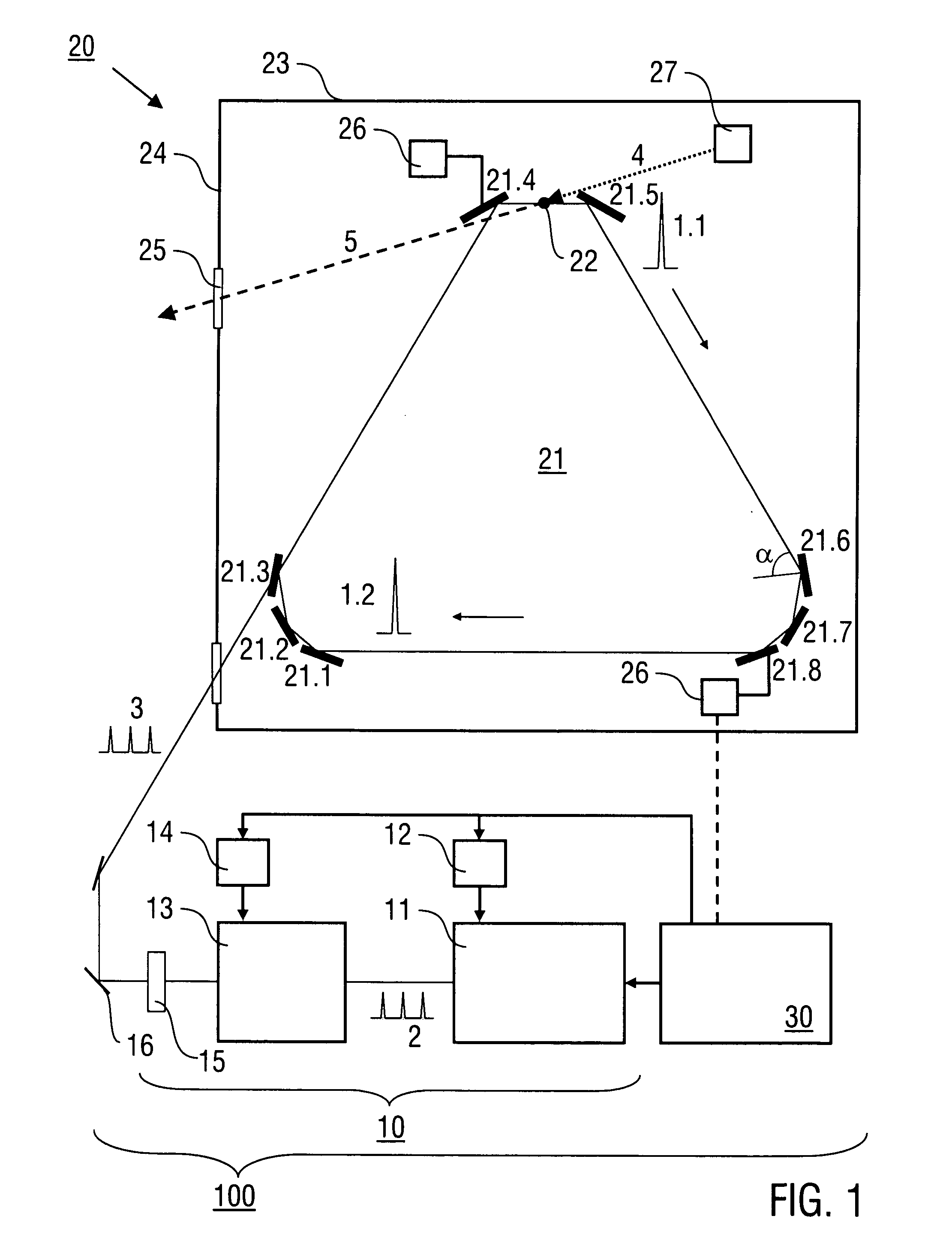
Method and laser device for generating pulsed high power laser light
InactiveUS20120275478A1Reflectivity lossMinimize reflectivityOptical devices for laserHigh power lasersLaser light
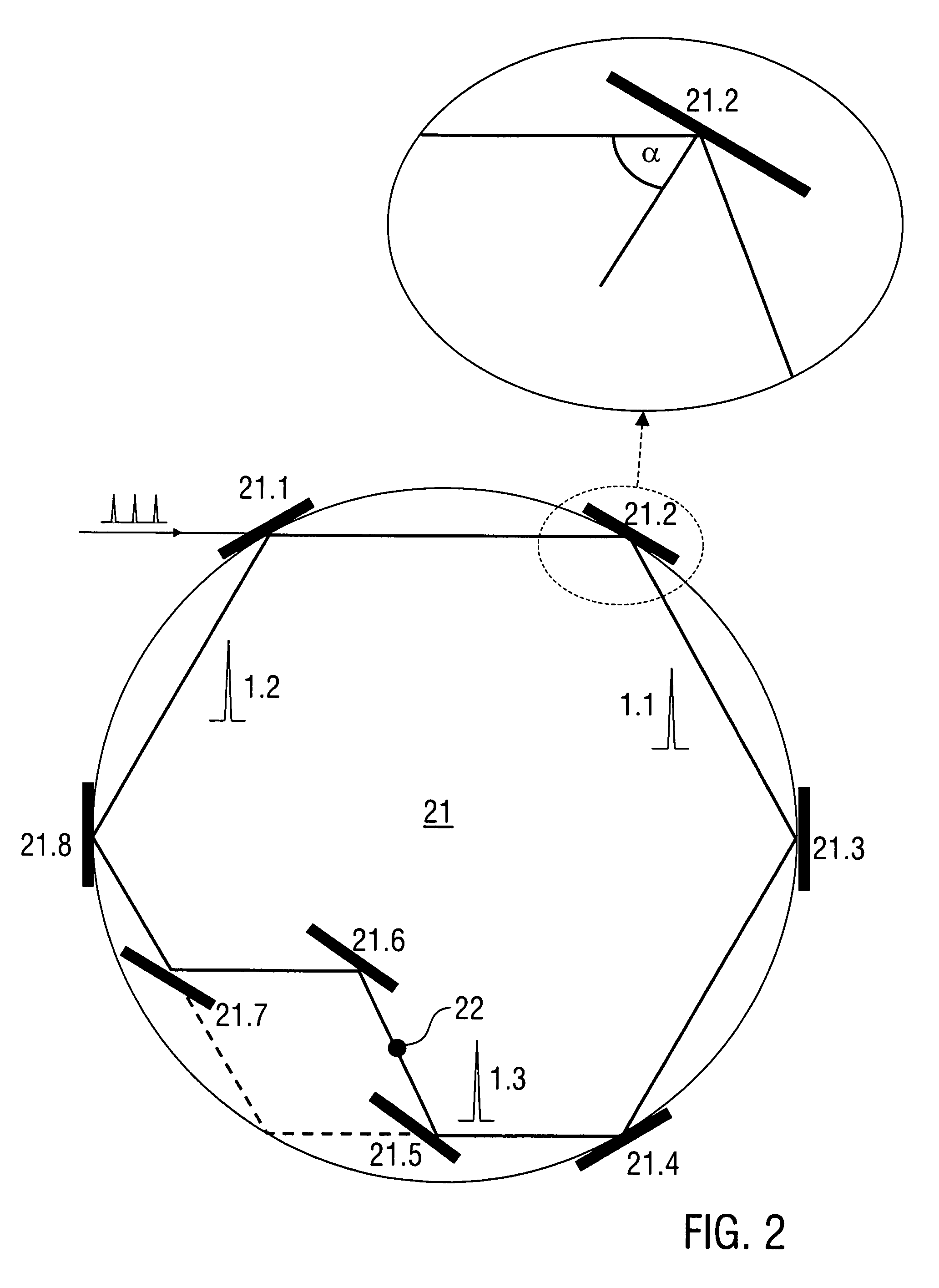
A method of generating pulsed laser light (1) comprises the steps of providing laser light pulses (2, 3) having a predetermined pulse repetition rate (frep) with a laser source device (10), coupling the laser light pulses into an enhancement cavity (21) with a plurality of cavity mirrors (21.1, 21.2, . . . ) and a predetermined cavity length (L), and coherent addition of the laser light pulses (2) in the enhancement cavity so that at least one cavity pulse (1.1, 1.2, . . . ) is formed, wherein the at least one cavity pulse (1.1, 1.2, . . . ) circulating in the enhancement cavity (21) irradiates all of the cavity mirrors (21.1, 21.2, . . . ) with an angle (α) of incidence of more than 45°. Furthermore, a laser device (100) being configured for conducting the method is described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
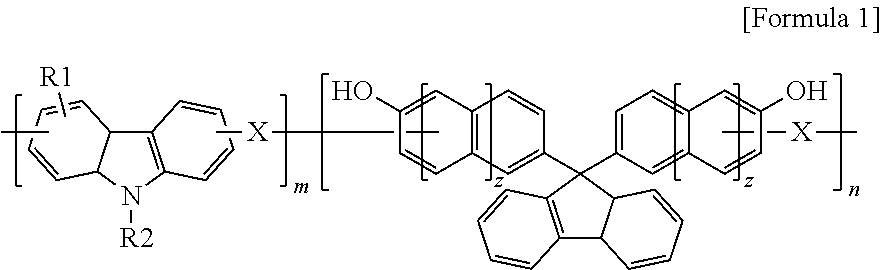
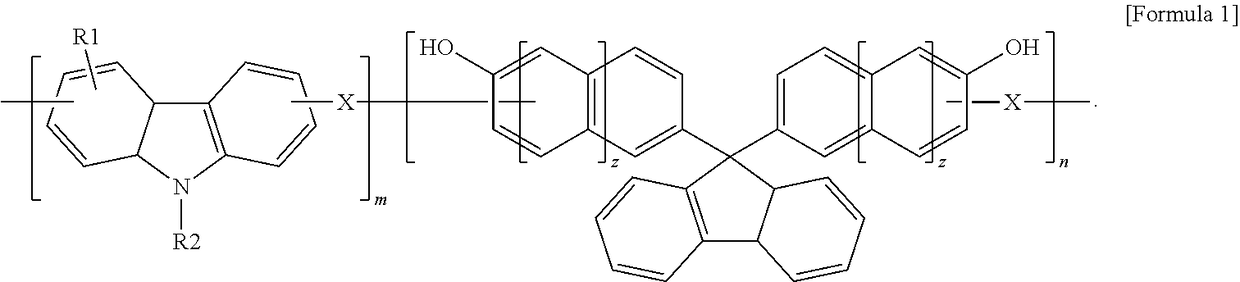
Anti-reflective hardmask composition
ActiveUS10858533B2Improve solubilityImprove etch selectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingsPolymer scienceTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
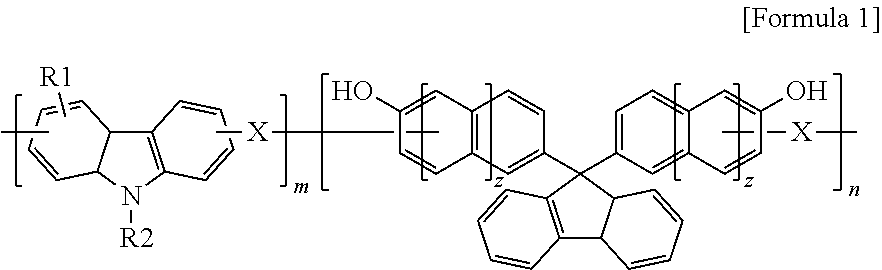
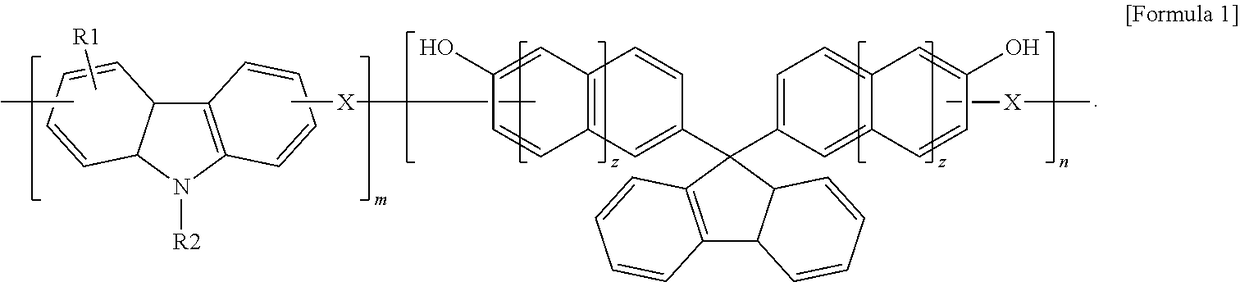
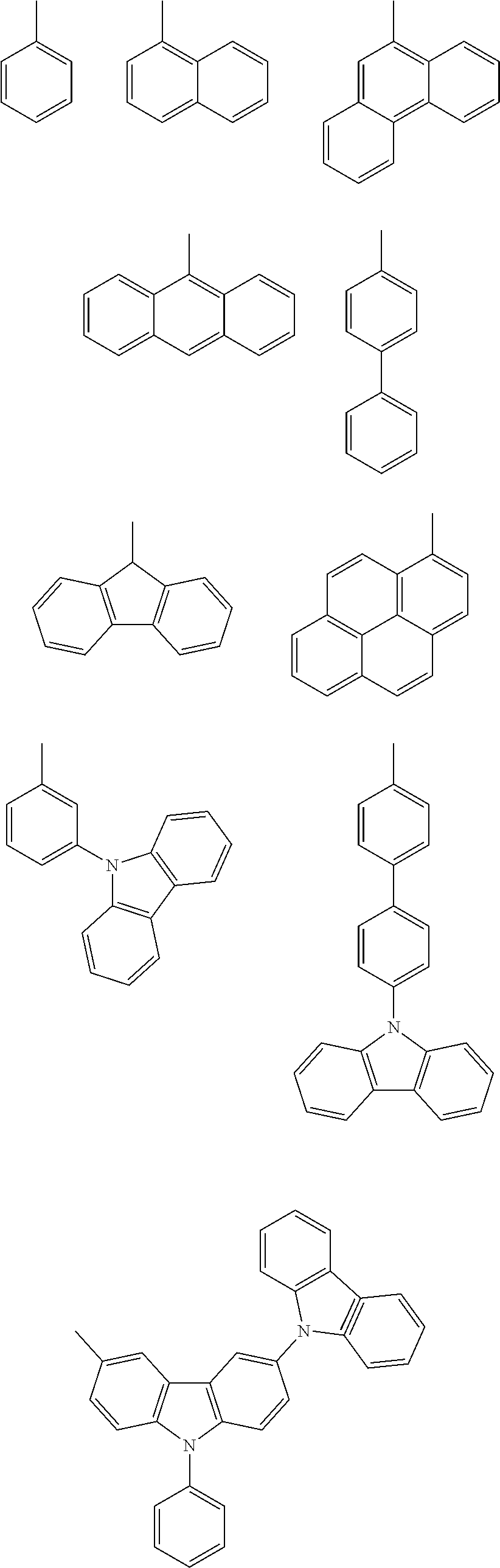
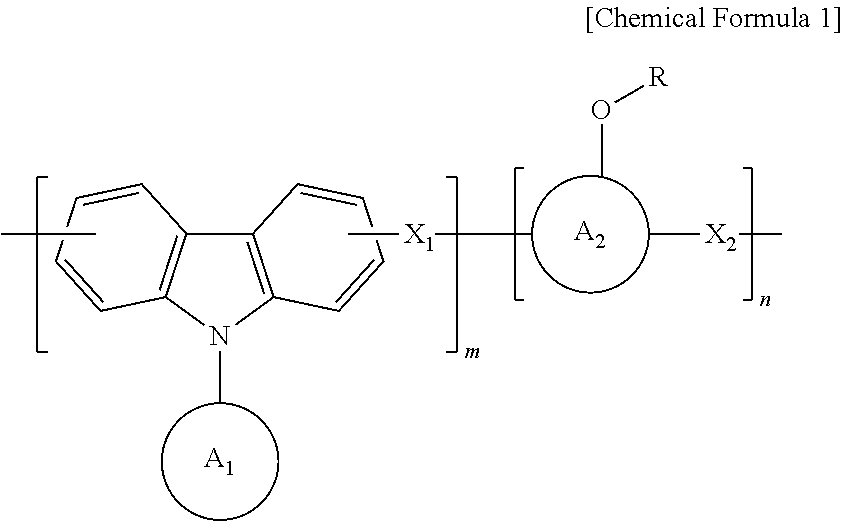
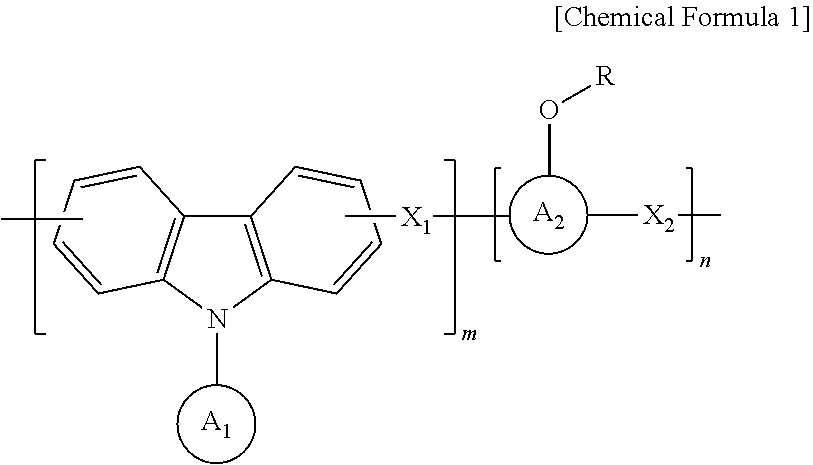
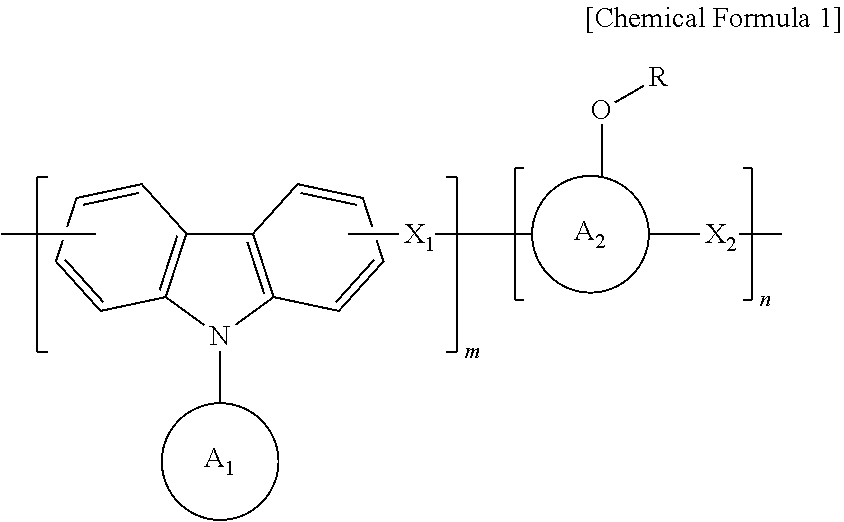
An anti-reflective hardmask composition contains: (a) an arylcarbazole derivative polymer represented by the following Chemical Formula 1 or a polymer blend containing the same; and (b) an organic solventin Chemical Formula 1, A1 and A2 are each independently a (C6-C40) aromatic aryl group and are the same as or different from each other,R is t-butyloxycarbonyl (t-BOC), ethoxyethyl, isopropyloxyethyl, or tetrahydropyranyl,X1 and X2 are each a polymerization linkage group derived from aldehyde or an aldehyde acetal monomer capable of being one-to-one polymerized with an arylcarbazole derivative and A2 in the presence of an acid catalyst,m / (m+n) is in a range of 0.05 to 0.8, anda weight average molecular weight (Mw) of an the polymer is in a range of 1,000 to 30,000.
Owner:CHOI SANG JUN +1
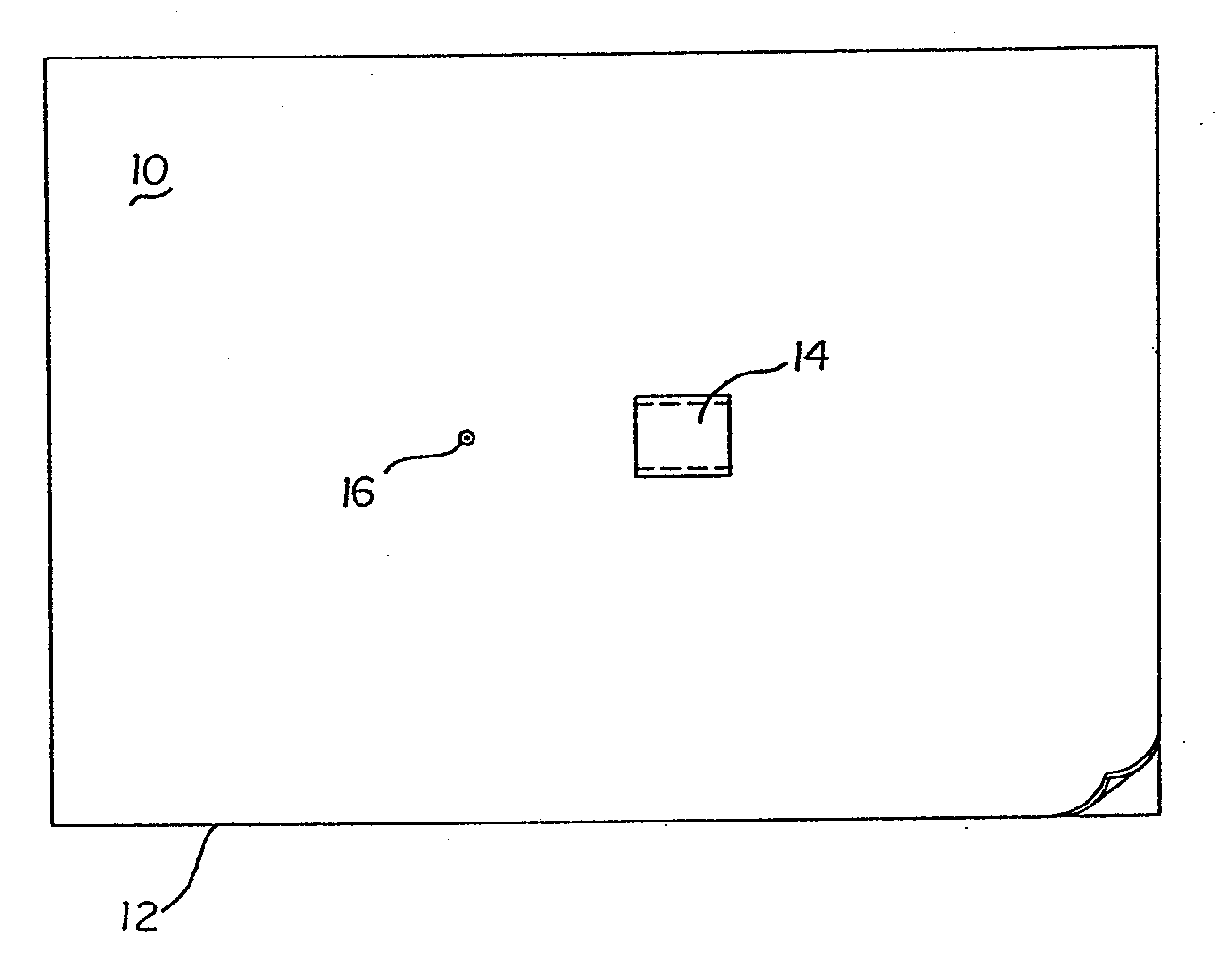
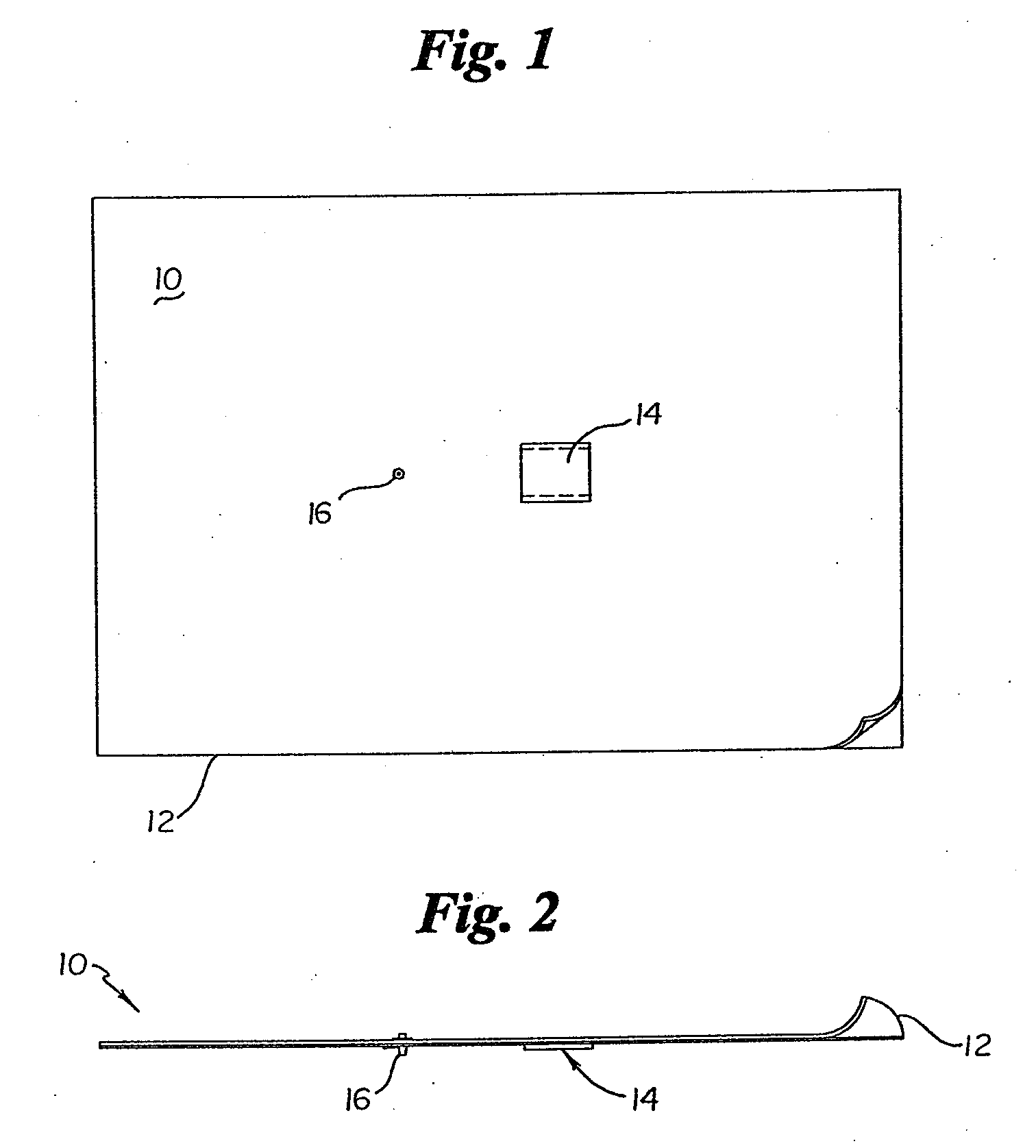
Minimally light reflective surgical drape
InactiveUS20070125389A1Reduce light intensityReduced luminance and glareRestraining devicesDiagnosticsLuminous intensityMedicine
A surgical drape manufactured or fabricated from a polymeric film having a low glare finish and a predetermined coloration for reducing the luminous intensity of light reflected from the surface thereof is provided. Such surgical drape thereby minimizes reflectivity therefrom, and thus eye strain and fatigue. The subject invention includes the use of colorants, dyes, pigments, etc. to form translucent polymeric surgical drapes that absorb a selected range of wavelengths from surface reflected light. More particularly, the use of coloring agents in combination with a textured surface yield a surgical drape possessing reduced luminance and glare, thereby mitigating eye strain and fatigue. The preferred range of reflected light, in order of preference, is 625-700 nm, 520-560 nm, 450-520 nm, 400-450 nm, 600-625 nm, and 560-600 nm.
Owner:MEDICAL CONCEPTS DEV
Hardmask compositions for resist underlayer films
ActiveUS7879526B2Easy to useMaintain good propertiesPhotosensitive materialsDecorative surface effectsResistOrganic solvent
Provided herein are hardmask compositions for resist underlayer films, wherein according to some embodiments of the invention, hardmask compositions include a polymer prepared by the reaction of a compound of Formula 1with a compound of Formula 2(R)m—Si—(OCH3)4-m (2)in the presence of a catalyst, wherein R is a monovalent organic group, n is an integer from 3 to 20, and m is 1 or 2; and an organic solvent.Also provided herein are methods for producing a semiconductor integrated circuit device using a hardmask composition according to an embodiment of the invention. Further provided are semiconductor integrated circuit devices produced by a method embodiment of the invention.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Optical structure to reduce internal reflections
ActiveUS8252390B2Lower refractive indexReduce optical reflectionLiquid crystal compositionsLayered productsTotal internal reflectionRefractive index
A structure for reducing internal reflections in an optical system includes a stack of layers including a first layer having a first refractive index, a second layer having a second refractive index, a third layer having a third refractive index, a fourth layer having a fourth refractive index, and a fifth layer having a fifth refractive index. The second layer is arranged between the first layer and the third layer, and the fourth layer is arranged between the third layer and fifth layer. Further, the third refractive index is greater than the second and fourth refractive indexes, the second refractive index is greater than the first refractive index, and the fourth refractive index is greater than the fifth refractive index.
Owner:UNIFIED INNOVATIVE TECH
Method for controlling the properties of DARC and manufacturing DARC
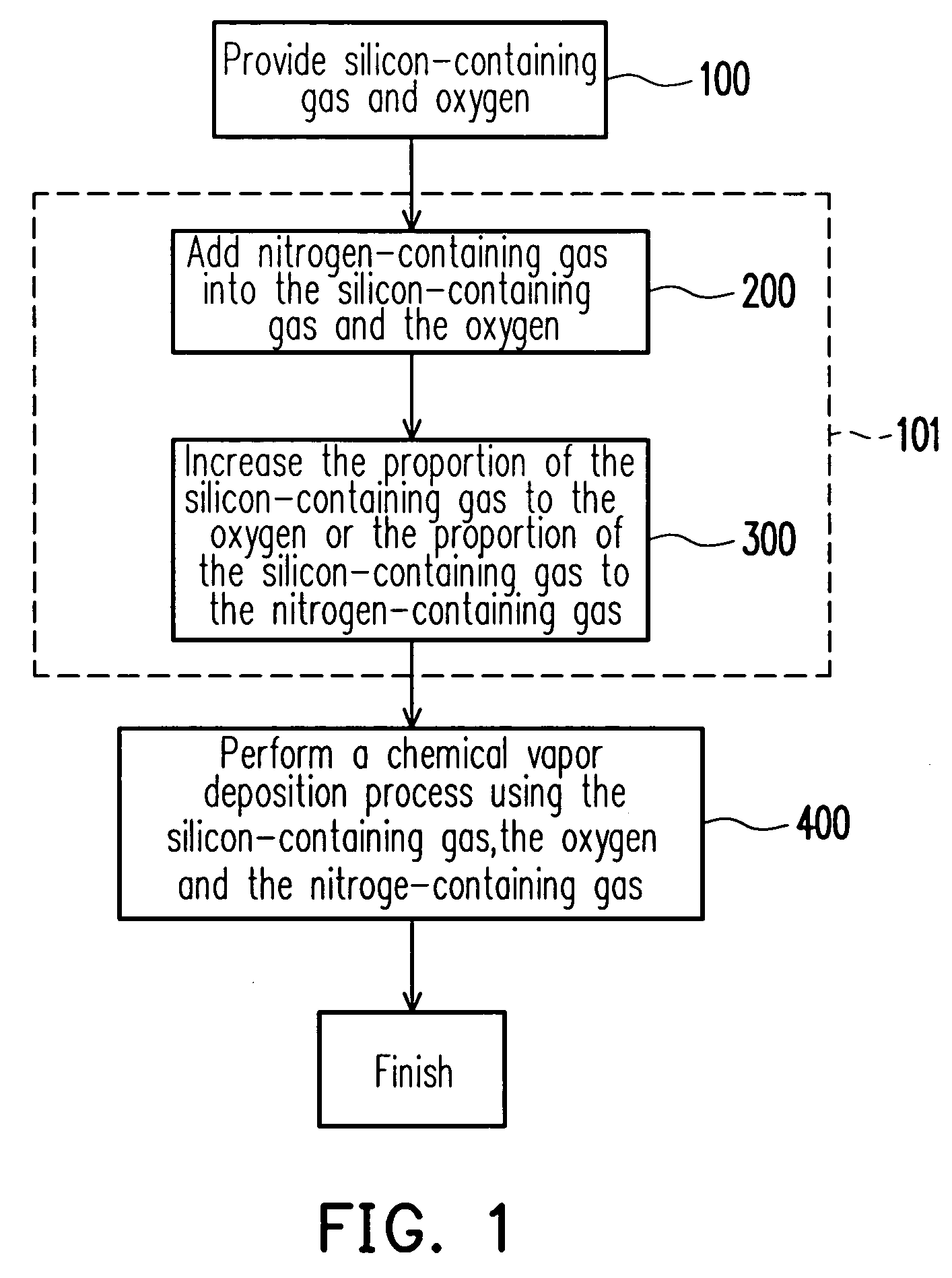
ActiveUS20060115991A1Reduce the differenceMinimize reflectivityPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingNitrogen
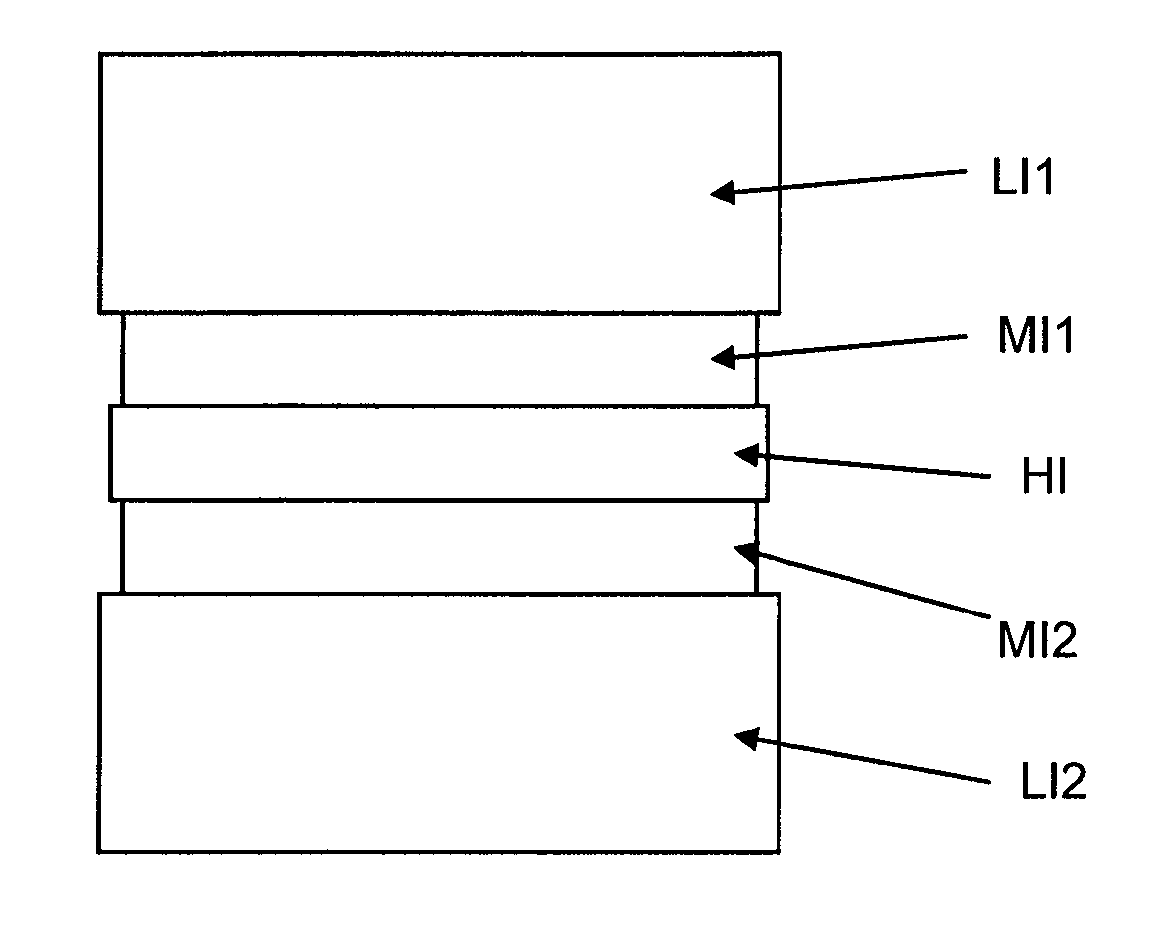
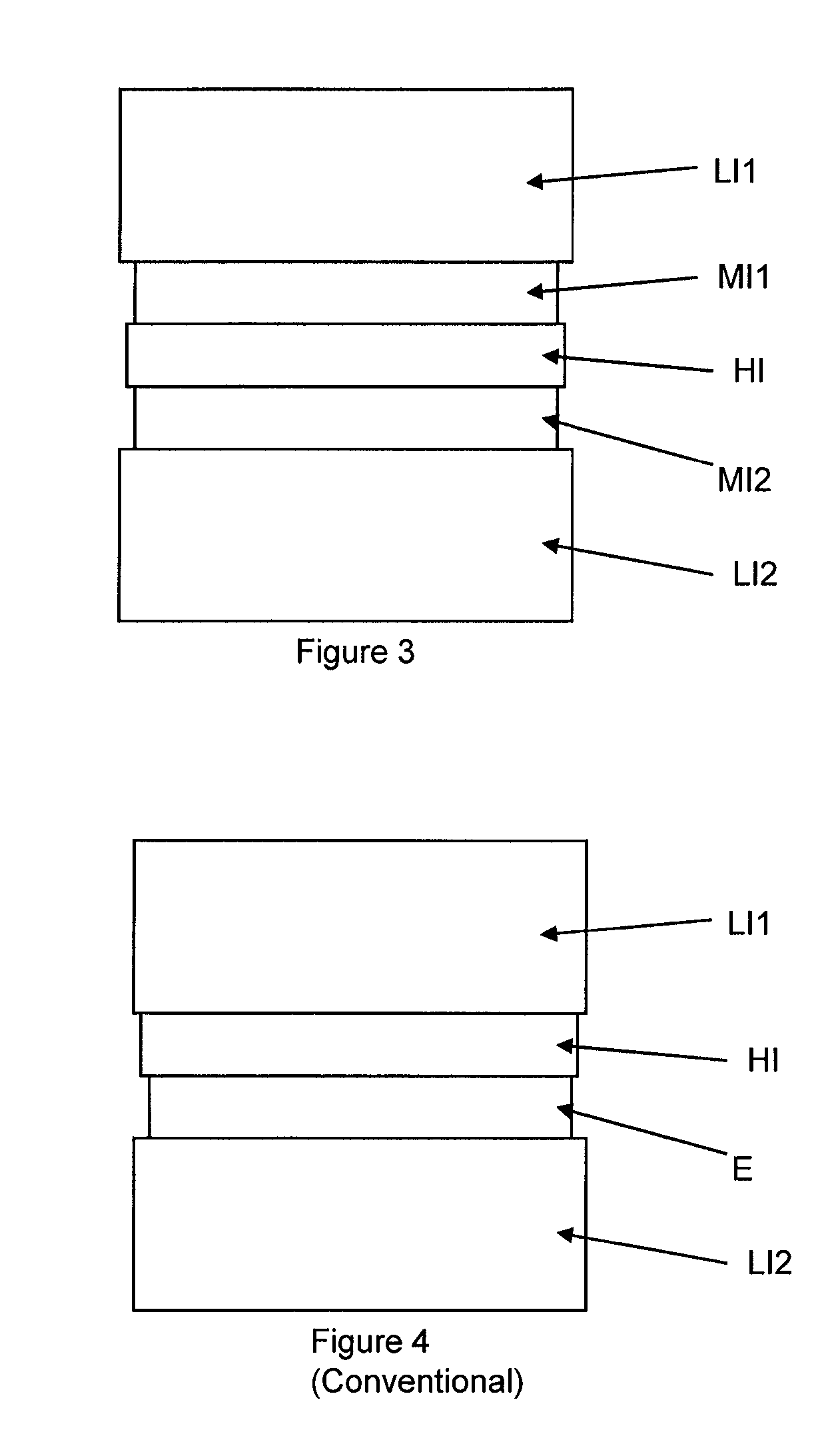
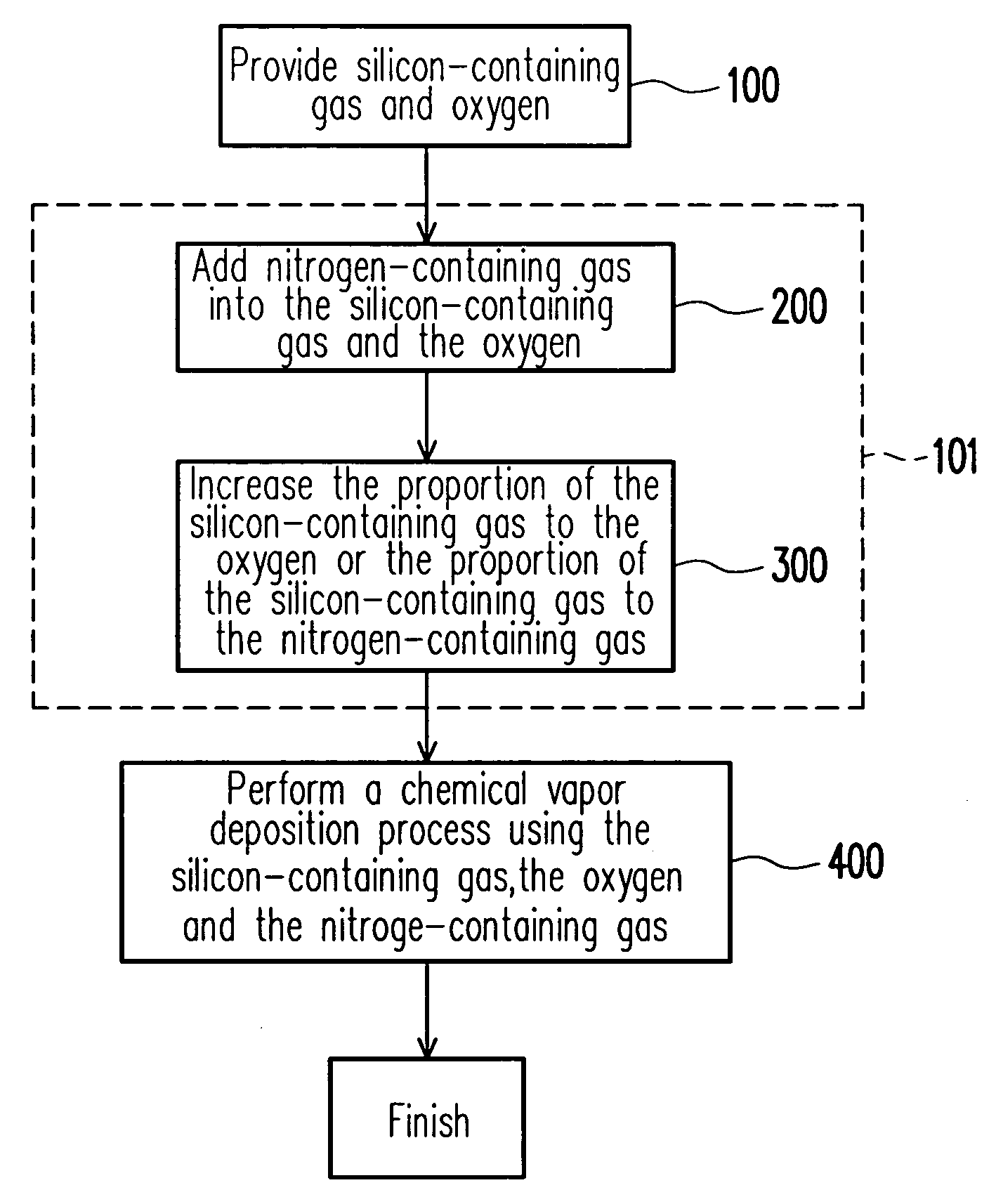
A method for controlling the properties of a dielectric anti-reflective coating (DARC) is provided. In the process of forming the DARC, a nitrogen-containing gas is added to a reaction gas comprising silicon-containing gas and oxygen for controlling the n value of the DARC. Furthermore, the proportion of the silicon-containing gas to the oxygen or the proportion of the silicon-containing gas to the nitrogen-containing gas is increased to control the k value of the DARC. By means of proper control of the n value and the k value, the DARC can have the lowest substrate reflectivity.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Anti-reflective hardmask composition
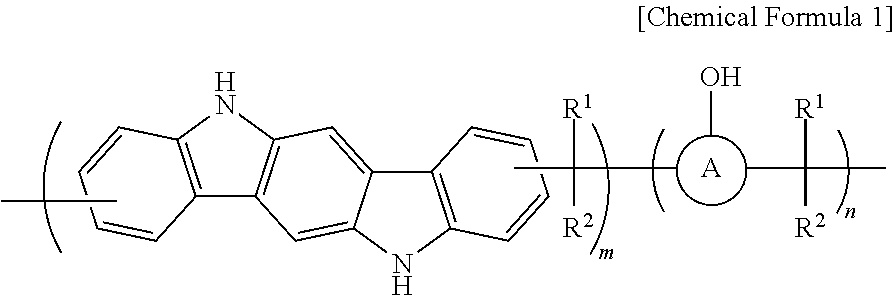
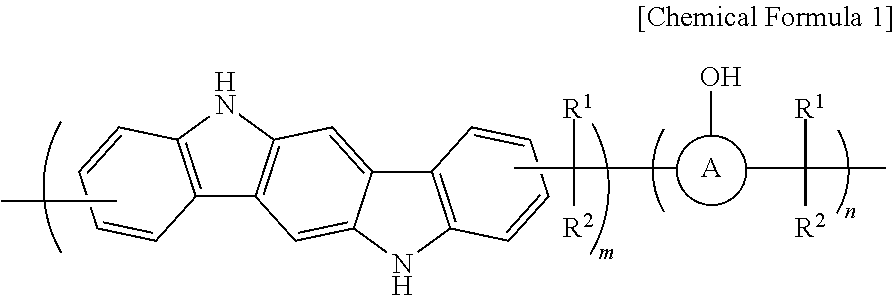
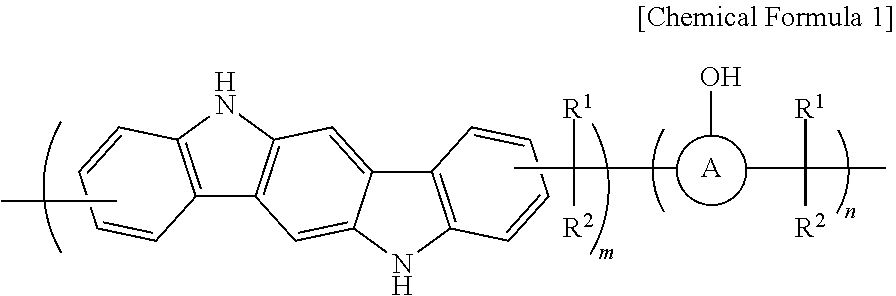
ActiveUS11493849B2Improve solubilityImprove etch selectivityAnti-reflective coatingsPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusPolymer scienceCarbazole
Provided is an anti-reflective hardmask composition including: (a) a polymer composed of an indolocarbazole represented by the following Chemical Formula 1 or a polymeric blend containing the same; and (b) an organic solvent.
Owner:OLAS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com