A method of calculating a wetting speed for Sn-based solder and a Cu substrate
A technology of wetting speed and calculation method, which is applied in the direction of analyzing materials, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of incompetence in fixed point, positioning, dimensional accuracy limitation, complicated process, etc., and achieve the improvement of service reliability, volume reduction, volume small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
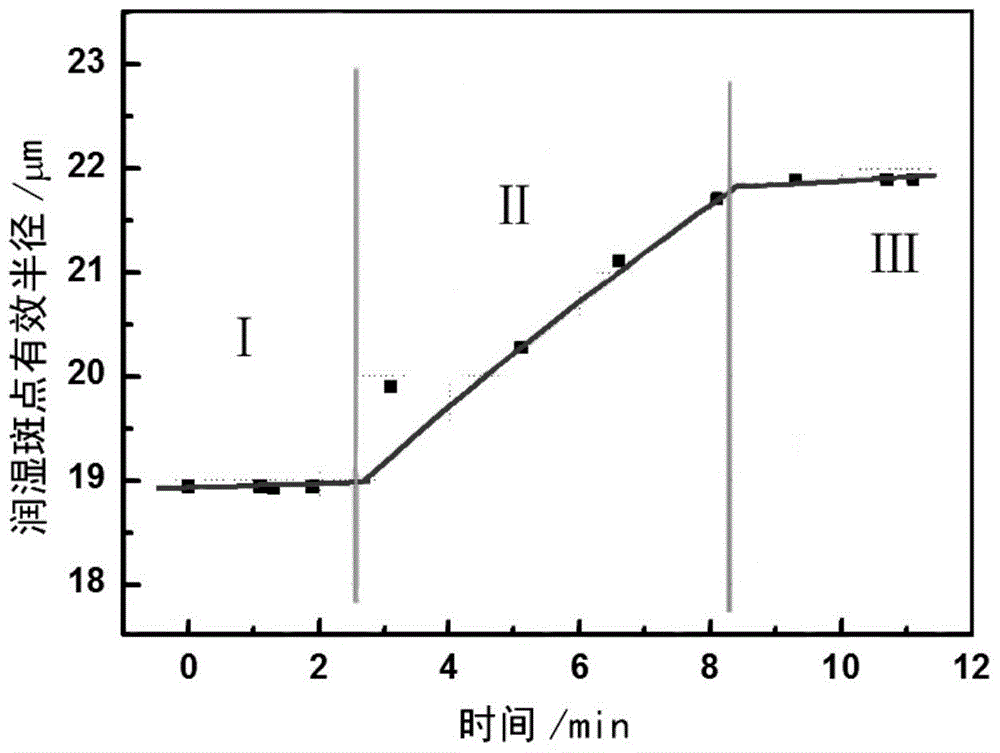
[0034] In this embodiment, a high-temperature metallographic microscope is used to observe the wetting process of Sn-based solder on the Cu substrate in situ and calculate the wetting speed. The specific process is as follows:
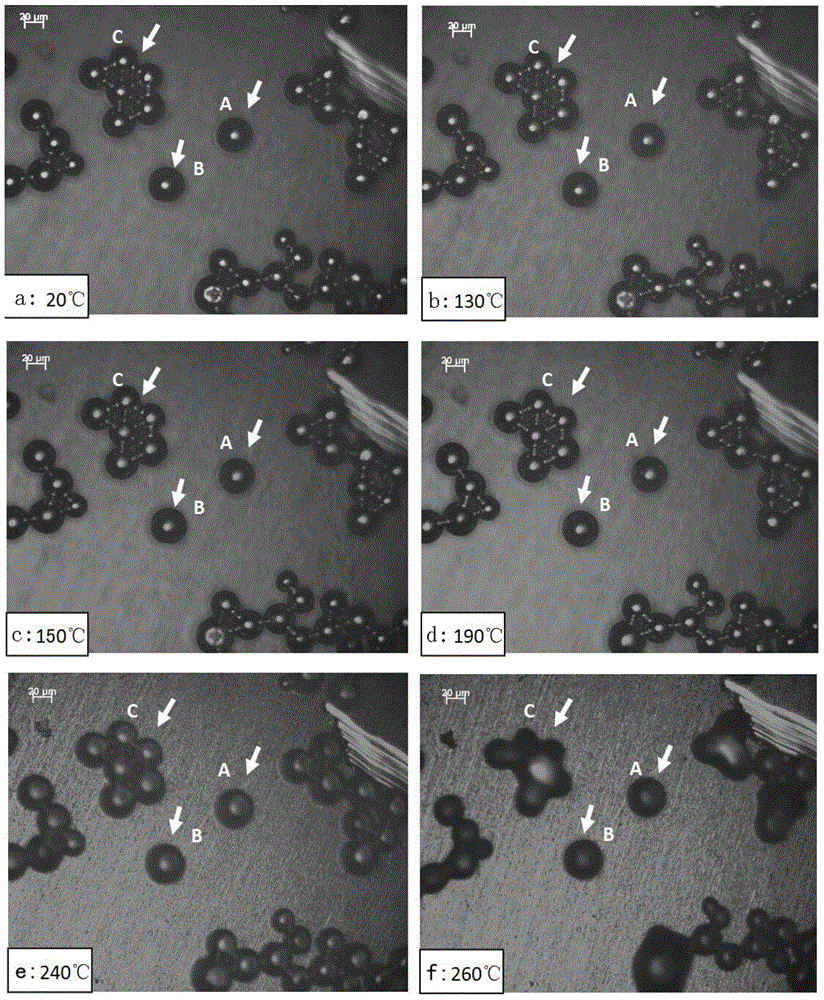
[0035] 1. Wetting process of solder on copper sheet and morphology of wetting spots
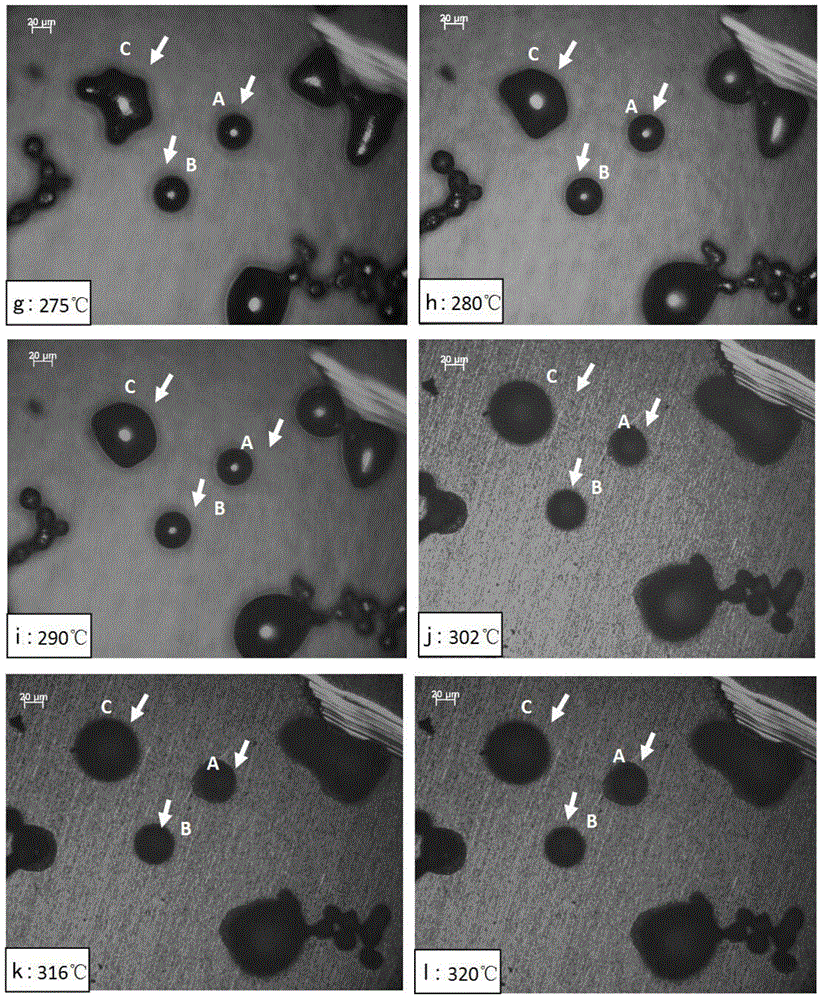
[0036] Put the Sn-based solder on the copper sheet, then place the sample in the hot stage of LinkamTHMS600, put the hot stage on the Axiophoto2imageE upright microscope, and pass 99.999% argon gas in the hot stage. The sample is heated up, the heating rate is set according to the melting of the solder, and the in-situ wetting process of the Sn-based solder on the Cu substrate is observed through a microscope. figure 1 It is the wetting process of Sn-based solder on the Cu substrate. It can be seen from the figure that some Sn particles are connected together, and some exist alone. The A and B particles that exist alone are the objects of observation and analysis. . ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com