Method for assessing risks and weak links of power grid, with double fault probability characteristics considered
A weak link and failure probability technology, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, resources, etc., can solve the problems of probabilistic modeling without components, multiple failures, and high consumption of computing resources, so as to reduce the consumption of computing resources and the number of system states. , the effect of accurate calculation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
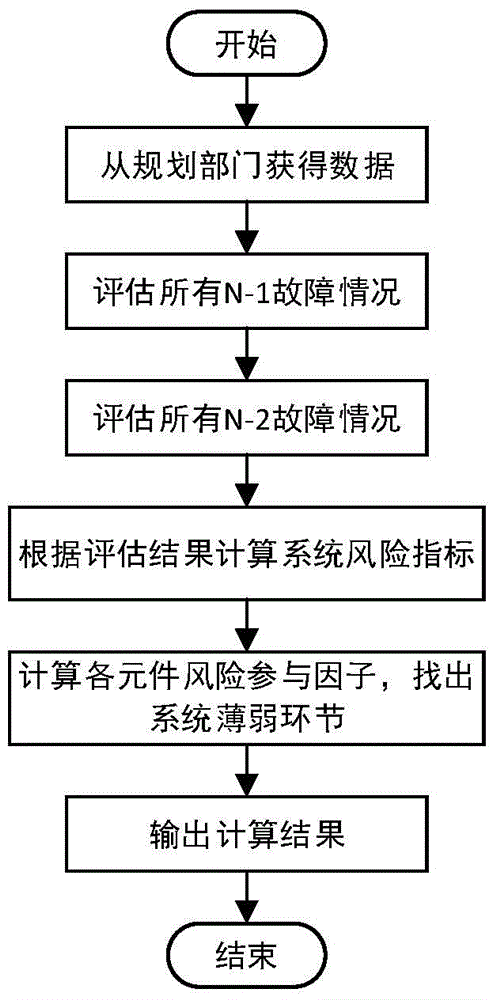
[0036] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings, but the content of the present invention is not limited to this.
[0037] Components in the present invention include generators, transformers, and transmission lines.
[0038] When applying the method of the present invention, it is necessary to obtain relevant data from the power grid planning department first. Basic system technical data, system operation constraint data, and component reliability data obtained from the power grid planning department;
[0039] The basic technical data of the system include node data, transmission line data, transformer data, load data and generator data;
[0040] The system operation constraint data includes the upper and lower limits of output of each generator set, the upper and lower limits of reactive power output of reactive power sources, the upper and lower limits of node voltage, and the upper and lower limits of branch power f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com