Planar MR Safety Cables for Biopotential Measurements
A magnetic resonance and safety technology, applied in the direction of measuring magnetic variables, measuring devices, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve the problems of increasing cable costs and not solving problems, and achieve the effect of reducing microphonic effects and electrostatic effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
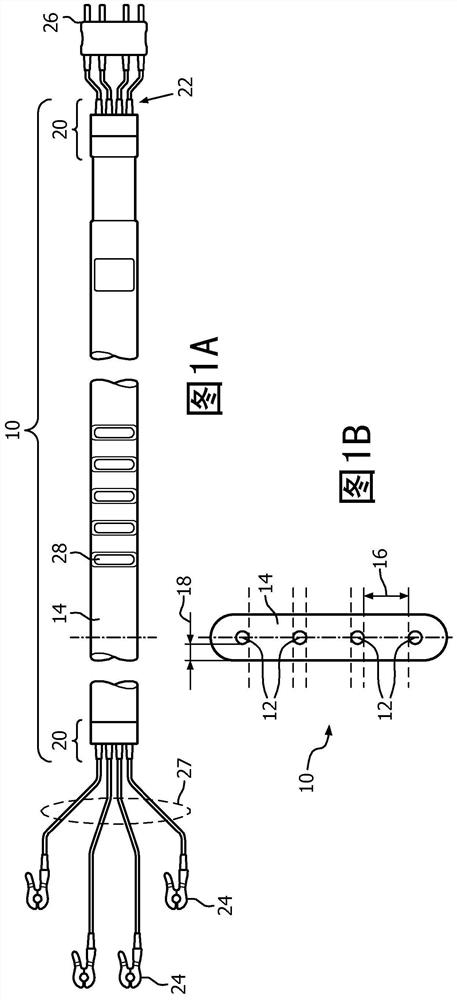
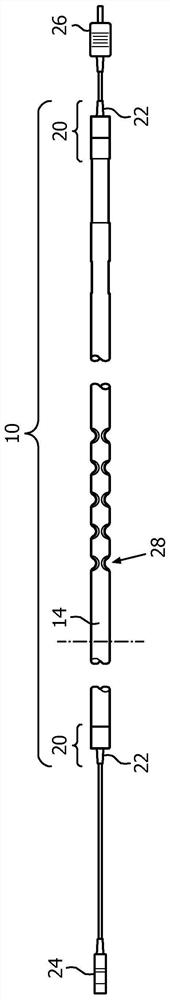
[0029] refer to Figure 1A , schematically illustrates an embodiment of a planar magnetic resonance (MR) safety cable 10 for biopotential measurements in top view. exist Figure 1B , the MR safety cable 10 is shown in cross-sectional view, and in Figure 1C , the MR security cable 10 is shown in side view. The cable 10 is shown with four controlled resistance conductive wires 12 arranged in a common plane and parallel to each other. In other embodiments, the cable can be configured to maintain any number of wires (eg, 4 to 12) in a common plane and parallel to each other. The wires transmit physiological signals, such as ECG signals in a strong magnetic field. The strong magnetic field can be that of a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanner. In one embodiment, the controlled resistance conductive lines include a distance 16 of at least 4mm between adjacent lines, although other distances are contemplated.
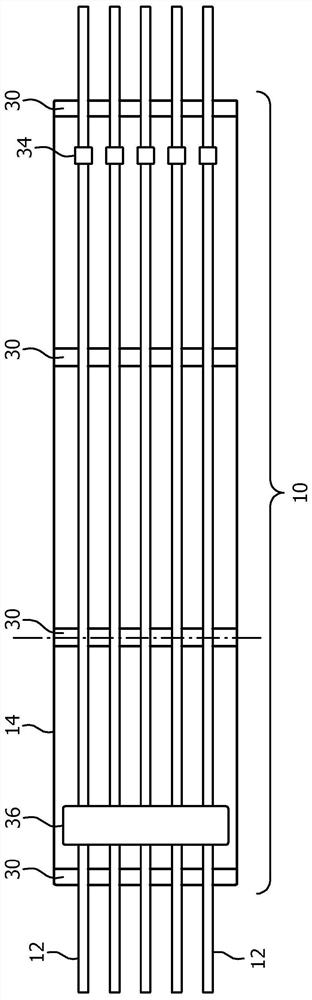
[0030] The cable 10 includes a rigid planar substrate 14 that ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com