Method for improving bio-availability of sulfur by means of converting sulfur into polysulfide
A technology of sulfide and polysulfide, applied in the field of wastewater treatment, can solve the problems of low water solubility and low bioavailability of elemental sulfur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The synthesis of embodiment 1 soluble zerovalent sulfur
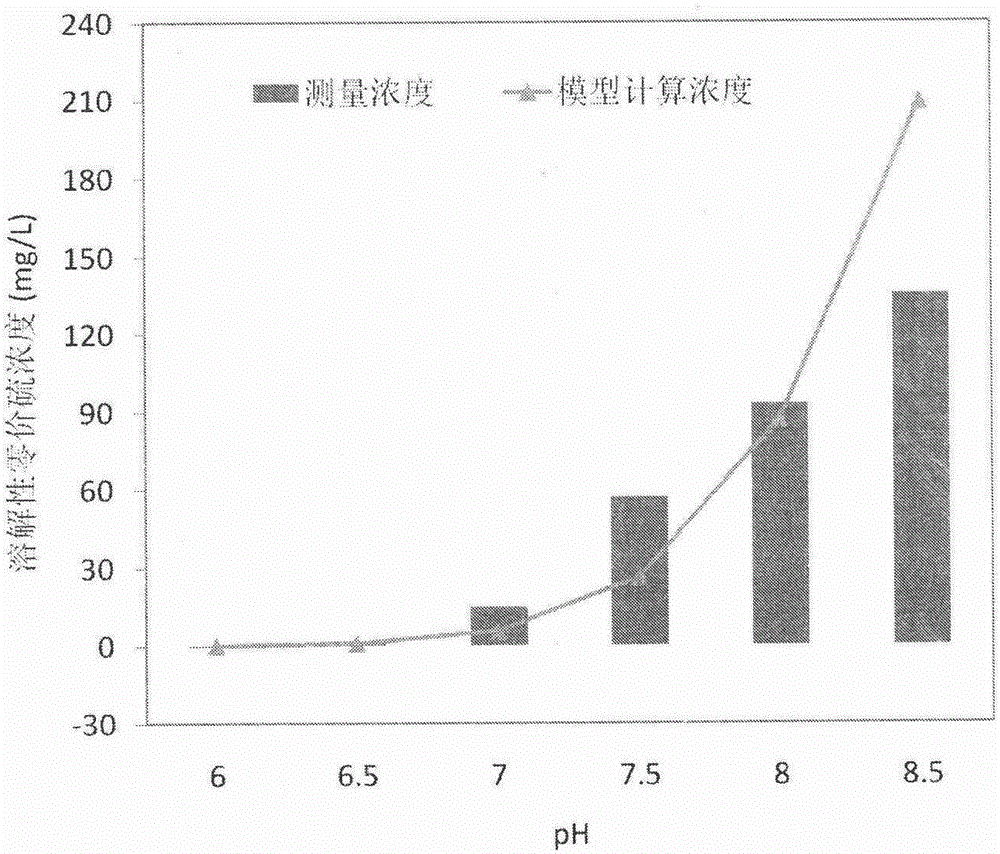
[0040] In this example, by setting six 200ml Erlenmeyer flasks with pH in the range of 6-8.5, the reaction equilibrium time and the equilibrium concentration of soluble zerovalent sulfur were explored. The synthesis of soluble zerovalent sulfur does not depend on the presence of microorganisms, that is, as long as there is S 0 and HS - , PS can be formed at a suitable pH.
[0041] refer to figure 1 , PS concentration was positively correlated with sulfide concentration and pH. When the pH is 8.5, it takes 2.5h to react to reach equilibrium, and the equilibrium concentration of soluble zerovalent sulfur is 135.00mg / L. However, when the pH drops to 6, the reaction equilibrium time is extremely short, and the soluble zerovalent sulfur is only 0.38 mg / L, making it almost impossible to synthesize. The relationship between the equilibrium concentration of dissolved zerovalent sulfur and pH in the figure is consist...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Effect of soluble zerovalent sulfur on sulfur reduction
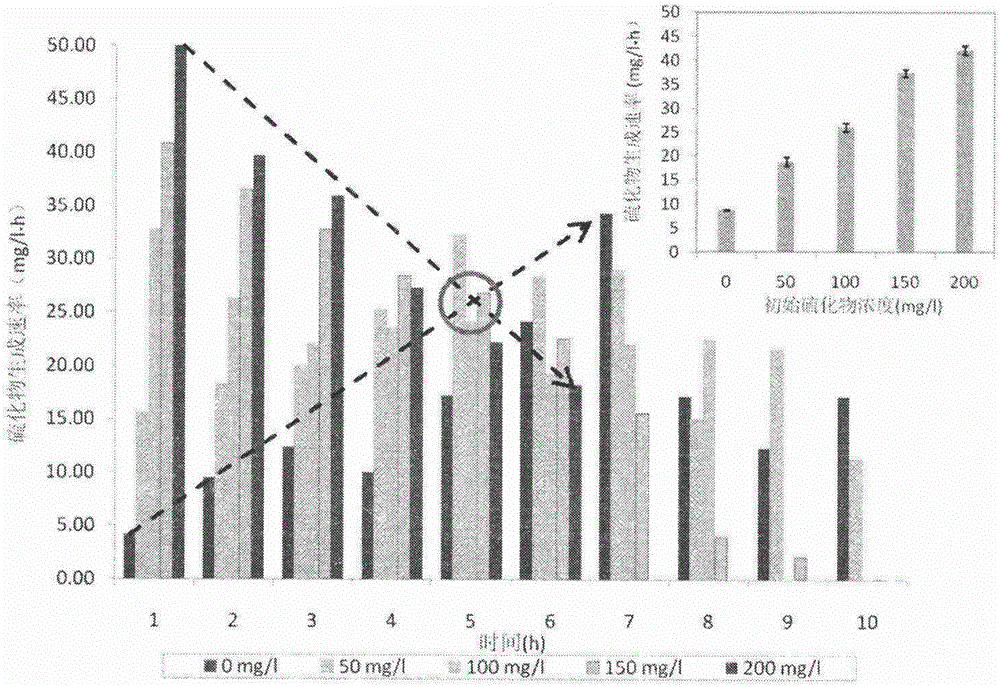
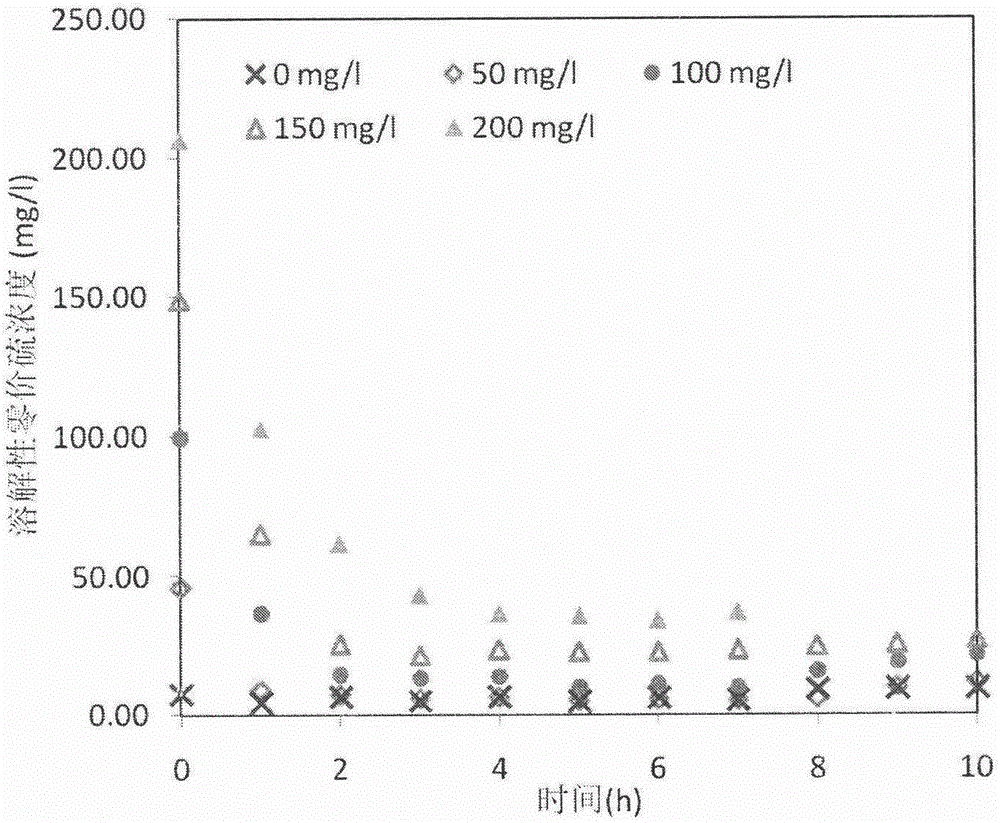
[0043] In this example, by setting 6 Erlenmeyer flasks (2.4L), the initial sulfide concentration is 0-200mg / L, glucose is used as the carbon source, the sludge concentration is 0.68gVSS / L, and the dosage of elemental sulfur is 5g / L. L, the initial pH is adjusted to the optimum range of 7.5 with HCL or NaOH.
[0044] figure 2 and image 3 In , it reflects the effect of dissolved zerovalent sulfur on the sulfur reduction rate and the concentration change of dissolved zerovalent sulfur.
[0045] 1). The initial sulfide concentration increased from 0mg / L to 200mg / L, and the initial dissolved zerovalent sulfur concentration rose from a very low value to 206.34mg / L, which increased the driving force of the sulfur reduction process. In the first 3 hours, the average rate of sulfur reduction under different initial sulfide concentrations showed a nearly linear increase, and the bioreduction rate of elementa...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The control of embodiment 3 soluble zerovalent sulfur
[0049] refer to Figure 4 , in the present embodiment, by setting 3 Erlenmeyer flasks (2.4L), the initial sulfide concentration is 0mg / L. With glucose as carbon source (TOC=40mg / L), the sludge concentration is 0.66gVSS / L, S 0 The dosage is 5g / L. The initial pH of the first Erlenmeyer flask was adjusted to 7.5 (NC) with HCL or NaOH, and 12.48mMFe was added to the second 2+ (C1), the third Erlenmeyer flask was adjusted to pH 6 with HCL, and its pH was kept constant throughout the experiment (C2).
[0050] After precipitating PS and sulfide, microorganisms will interact with S 0 direct contact. S at 9h 0 The reduction rate, C1 is only 2.5% of NC, while C2 has no obvious sulfide accumulation. After the experiment, the TOC of C1 and C2 did not change significantly, and the soluble zerovalent sulfur of the two during the reaction was also not detected. While under non-control conditions, the removal rate of TOC w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com