Demodulation circuit used in a passive ultrahigh frequency radio-frequency identification label chip
A technology of radio frequency identification tags and demodulation circuits, applied in the field of analog integrated circuits, can solve the problems of increasing chip area and power consumption, complex structure, large area, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing chip area, improving sensitivity, and increasing working distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
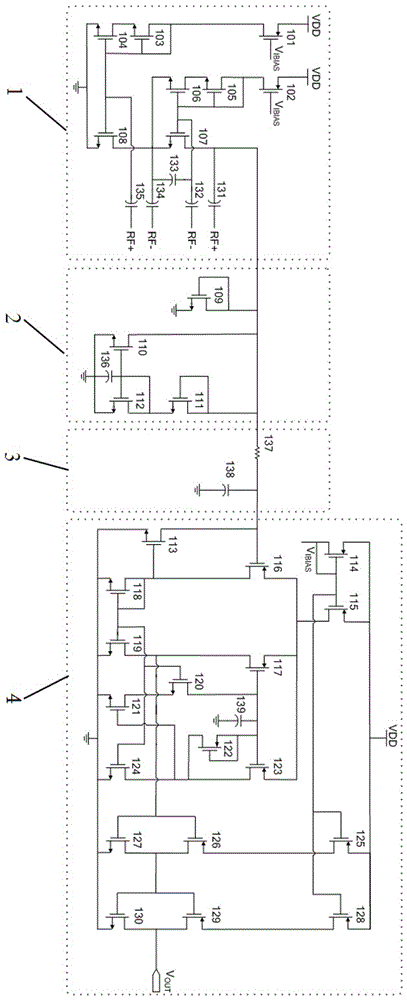
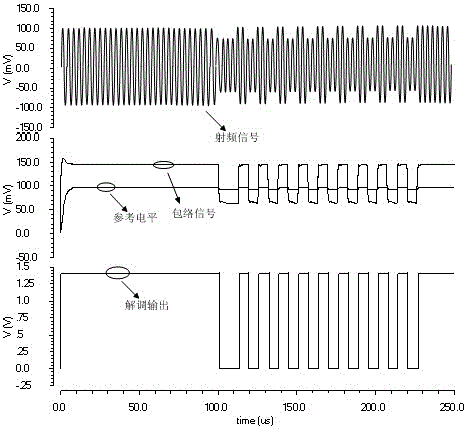
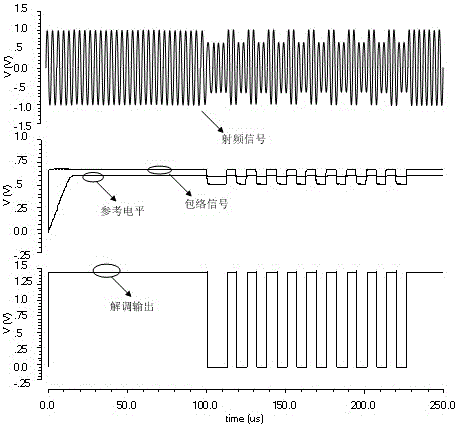
[0019] like figure 1As shown, the present invention includes an envelope detection circuit 1, a voltage limiting circuit 2, a low-pass filter circuit 3, a reference level generation and comparison output circuit 4 connected in series, and the envelope detection circuit 1 includes a first PMOS transistor 101 , the second PMOS transistor 102, the first NMOS transistor 103, the second NMOS transistor 104, the third NMOS transistor 105, the fourth NMOS transistor 106, the fifth NMOS transistor 107, the sixth NMOS transistor 108, the first capacitor 131, the second Capacitor 132, third capacitor 133, fourth capacitor 134, fifth capacitor 135, the sources of the first PMOS transistor 101 and the second PMOS transistor 102 are connected to high level, the grid of the first PMOS transistor 101 is connected to the second PMOS transistor 102 is connected to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com