Method for quickly separating large quantity of PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) from human peripheral blood
A technology of human peripheral blood and separation method, which is applied in the field of rapid separation of PBMC from a large number of human peripheral blood, can solve the problems of unfavorable separation of PBMC and cell viability, long operation time, complicated separation method, etc., and achieves easy operation and reduced operation steps. , The effect of saving operation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
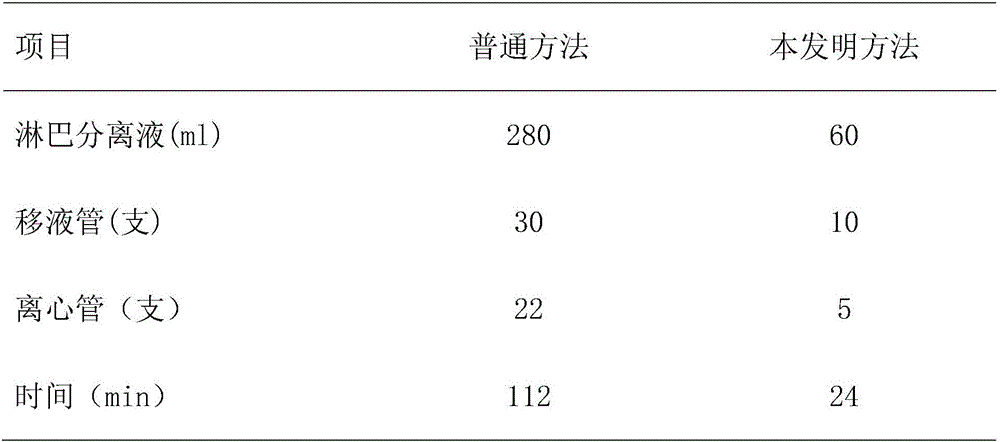
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] A method for rapidly separating a large amount of human peripheral blood PBMCs, comprising the steps of:
[0021] S1, sending human peripheral blood into a centrifuge tube for centrifugation;
[0022] S2. Absorb the sallow layer, and add physiological saline to it for dilution;
[0023] S3, sending the product obtained in S2 into a centrifuge tube containing lymphocyte separation liquid, wherein the product obtained in S2 is located in the upper layer of the lymphocyte separation liquid;
[0024] S4, centrifugal separation, the middle buffy coat layer was sucked, washed, and the supernatant was discarded by centrifugation to obtain PBMCs.
Embodiment 2
[0026] A method for rapidly separating a large amount of human peripheral blood PBMCs, comprising the steps of:
[0027] S1. Send 30ml of human peripheral blood into a centrifuge tube for centrifugation at a centrifugal speed of 1800rpm and a centrifugation time of 10min;
[0028] S2. After removing the upper layer of plasma, absorb the sallow layer, and add physiological saline to it for dilution;
[0029] S3, sending the product obtained in S2 into a centrifuge tube containing lymphocyte separation liquid, wherein the product obtained in S2 is located in the upper layer of the lymphocyte separation liquid;
[0030] S4, centrifugal separation, the middle buffy coat layer was sucked, washed, and the supernatant was discarded by centrifugation to obtain PBMCs.
Embodiment 3
[0032] A method for rapidly separating a large amount of human peripheral blood PBMCs, comprising the steps of:
[0033] S1. Send 180ml of human peripheral blood into a centrifuge tube for centrifugation at a centrifugation speed of 1800rpm and a centrifugation time of 10min;
[0034] S2. After removing the upper layer of plasma, absorb the sallow layer, and add physiological saline to it for dilution;
[0035] S3, sending the product obtained in S2 into a centrifuge tube containing lymphocyte separation liquid, wherein the product obtained in S2 is located in the upper layer of the lymphocyte separation liquid;
[0036] S4, centrifugal separation, the middle buffy coat layer was sucked, washed, and the supernatant was discarded by centrifugation to obtain PBMCs.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com