Bridge damage identification and assessment method based on long gauge length rigidity coefficient
A technology of stiffness coefficient and damage identification, applied in the testing, measuring devices, instruments, etc. of machine/structural components, can solve the problems of short life of electrical sensors, difficult to reflect local damage, and susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, so as to achieve rapid inspection and Effectiveness of monitoring, effective damage localization, and quantitative analysis of relative damage levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0027] A bridge damage identification and evaluation method based on long gauge stiffness coefficient, comprising the following steps:
[0028] (1) Build a distributed long-gauge-length strain sensor monitoring system: arrange several long-gauge-length strain sensors on the monitored bridge;
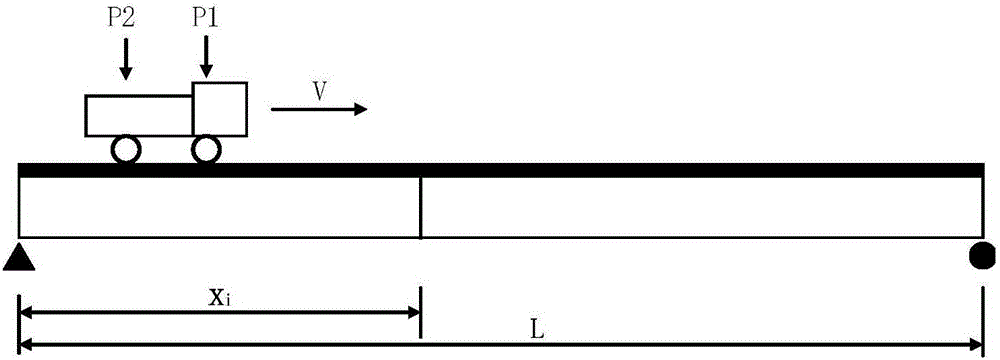
[0029] (2) Data collection when a single vehicle crosses the bridge: multiple collections of the long-gauge strain time history of a single vehicle passing through the monitored bridge span;
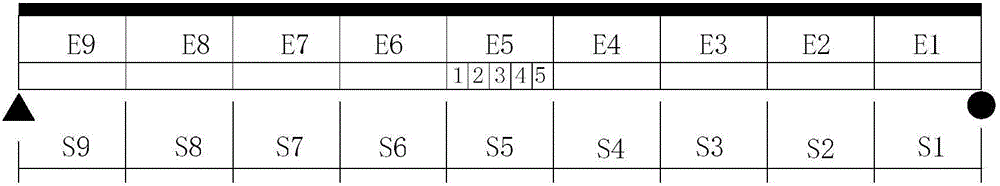
[0030] (3) Calculate the stiffness coefficients of all elements according to the distributed long gauge strain time history and the center coordinates of each sensor;
[0031] (4) The long gauge unit stiffness coefficient of each unit is formed into a matrix to form the long gauge unit stiffness coefficient matrix of the bridge;
[0032] (5) Bridge damage identification and bearing capaci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com