A Tensor Representation Based Target Detection Method for Polarized Hyperspectral Images
A polarization hyperspectral and target detection technology, which is applied in image analysis, image enhancement, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of low information utilization rate and low accuracy of polarization hyperspectral image target detection, and achieve accurate target detection, reduce The effect of simplifying the calculation process and improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0053] Specific Embodiment 1: A tensor representation-based polarization hyperspectral image target detection method in this embodiment is specifically carried out in accordance with the following steps:
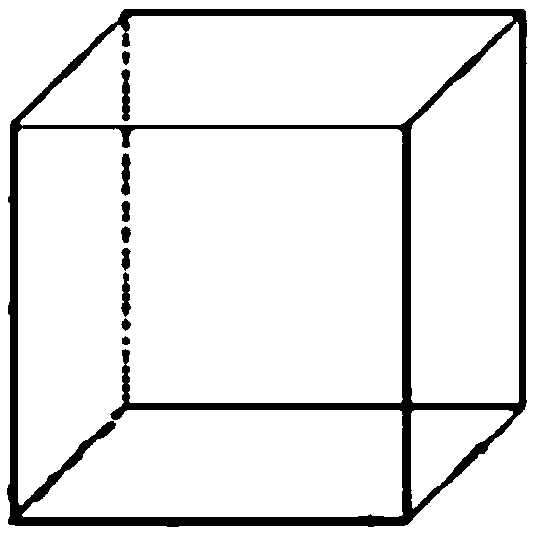
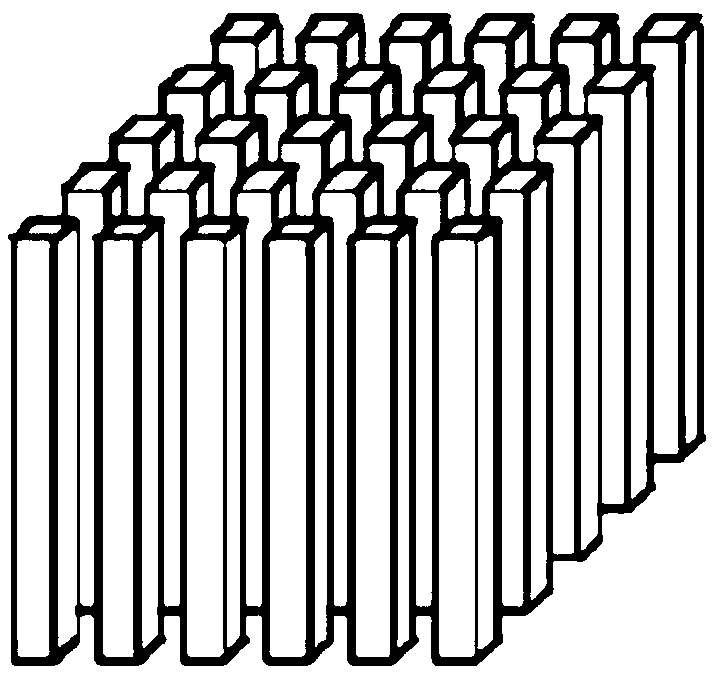
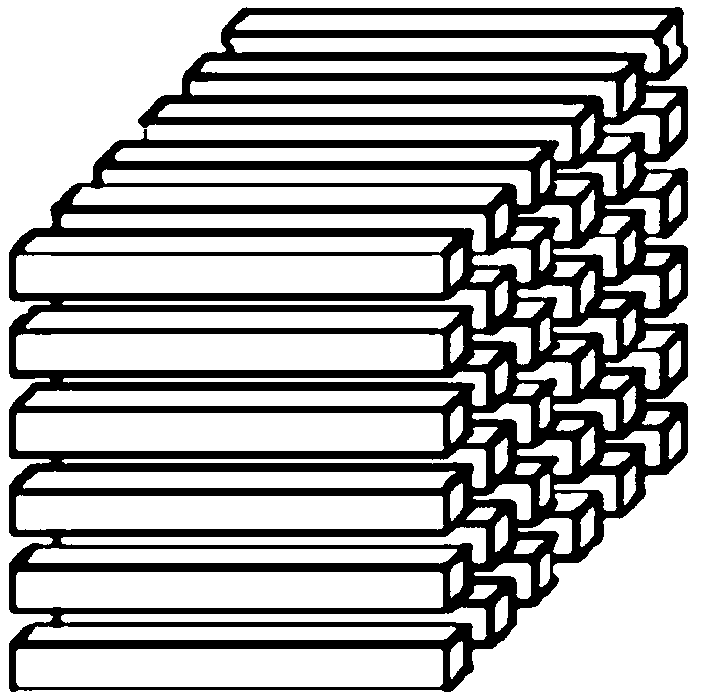
[0054] The concept of tensor was first proposed by Woldemar Voigt in the late 1790s. Later, Ricci and his students gradually perfected the concept of tensor and related operations in their research. From an algebraic point of view, the tensor can be regarded as a further extension of the matrix. The rows of the matrix are modulo-1 fibers, and the columns of the matrix are modulo-2 fibers. The third-order tensor has more tube fibers, such as Figure 1a , 1b , 1c, and 1d show the format of a third-order tensor. For the vector space U (1) ,U (2), ...,U (M) , defining their outer product space for tensors.
[0055] For the basic operations on tensors involved in the follow-up, this section makes a brief introduction. The first is the n-module expansion of the tensor, for...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0078] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: in said step two, on the basis of the data model of the polarized hyperspectral image under the tensor representation, the fourth-order tensor matching detection based on Tucker decomposition is obtained The model of the algorithm (FTMF) judges the detection result according to the model of the fourth-order tensor matching detection algorithm (FTMF) based on Tucker decomposition; the specific process is called:
[0079] Tucker decomposition is used for the training samples to extract the information of the target spectral dimension and polarization dimension, and the first principal component (i.e. the first column) of the factor matrix of the target spectral dimension and polarization dimension is selected to replace the target spectrum and polarization spectrum, and then according to the spectral dimension and polarization Spectral matched filter and polarization matched fil...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0081] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the spectral matching filter and polarization matching filter are constructed according to the information of the spectral dimension and the polarization dimension, and the fourth-order tensor matching detection based on Tucker decomposition is obtained The model of the algorithm (FTMF) judges the detection result according to the model of the fourth-order tensor matching detection algorithm (FTMF); the specific process is called:
[0082] Spectral Matched Filter H 3 Constructed as follows:
[0083]
[0084] Among them, S 3 Indicates the target spectrum, R 3 =E(Y (3) Y (3) T ) is the data to be detected Y (3) The covariance matrix of , Represents a fourth-order tensor The 3-mode expansion, In is the size of the nth dimension of the image, the value of n is 1, 2, 3 or 4, and T is the transpose;
[0085] will pair the spectrally matched filter H3 and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com