Microbial analysis
A technology for microbial and mass spectrometry analysis, applied in the field of analysing microorganisms, can solve the problems of lack of, no successful analysis of lipid MALDI-MS, preventing widespread application, etc., to achieve the effect of simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0263] Embodiment 1-comparison of extraction solvents
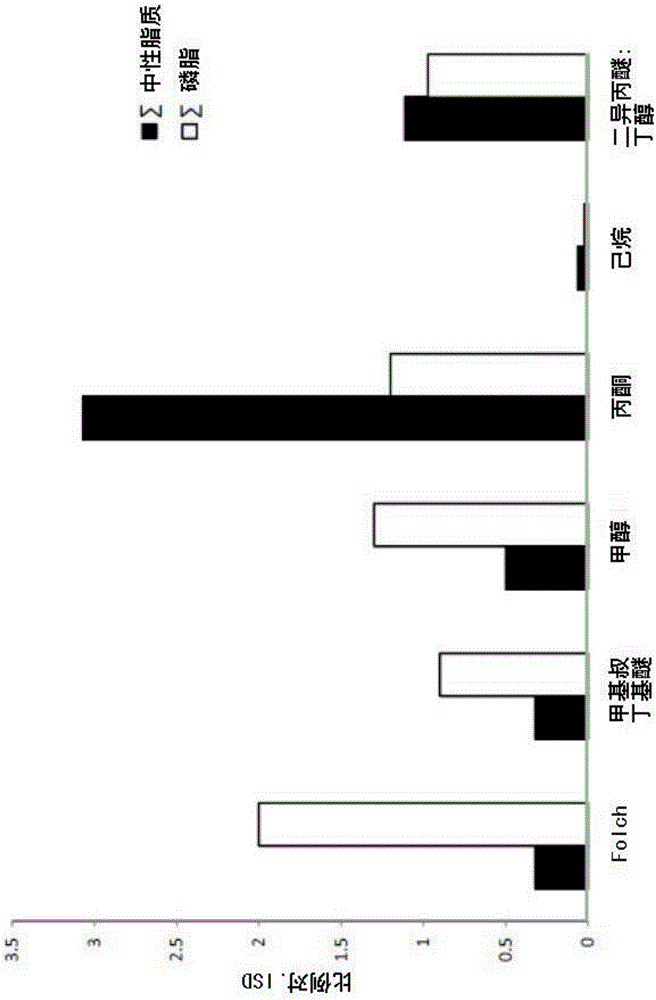
[0264] figure 1 The extraction efficiency of charged phospholipids (PLs) and neutral lipids (NLs) by 6 different organic solvents is shown. Extraction efficiencies were calculated based on the signal intensities of the corresponding lipid species in the MALDI-MS spectra.
[0265] It can be seen that Folch, MTBE and MeOH solvents preferentially allow the detection of PLs, while acetone favors the detection of NLs. Almost equal efficiencies were observed for both lipids when using DIPE / BuOH, with hexane having the worst results.
[0266] Based on these preliminary results, the use of Folch, MeOH and acetone in the lipid extraction step and in the MALDI-MS analysis of phospholipids from different bacterial, yeast and fungal species was further evaluated.
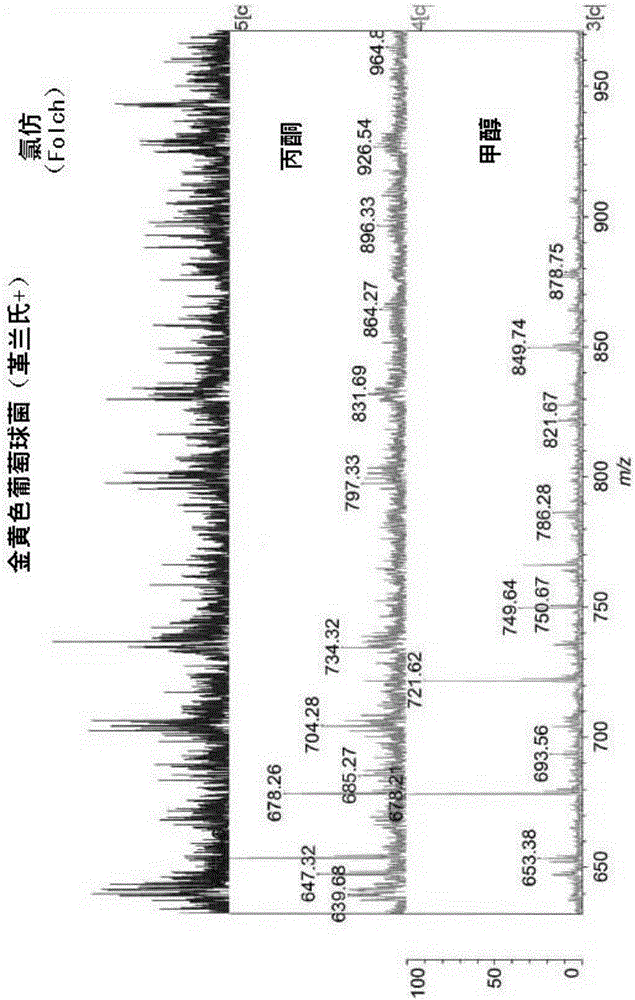
[0267] These three solvents were applied to Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus). From figure 2 It can be seen that methanol gives lipid MALDI-MS spectra w...
Embodiment 2
[0268] Example 2 - Comparison of matrix materials
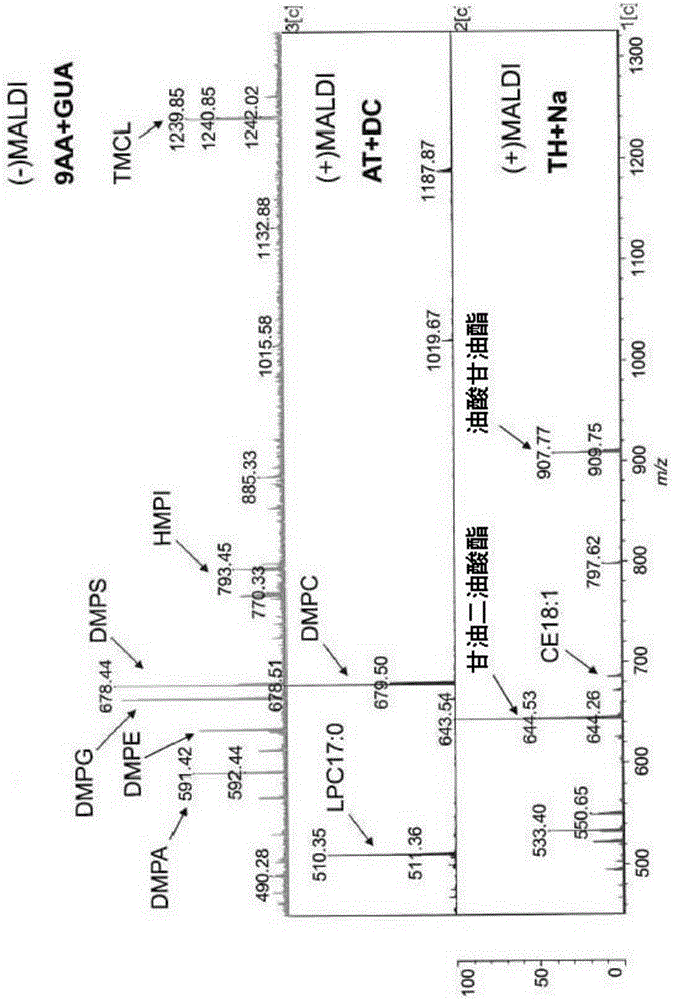
[0269] image 3 Three different mass spectra of the same sample containing mixtures of different lipid standards are shown. Mass spectra were obtained using different matrix substances according to the method described above. It can be seen that in the negative ion mode, 9AA-GUA allows detection of a large number of peaks. These correspond to anionic phospholipids.
[0270] It can also be seen that both ATT and THAP can return clear spectra in positive ion mode. Peaks in the ATT-DC spectrum correspond to cationic phospholipids, and THAP-Na peaks correspond to neutral lipids. It can be seen that in positive ion mode, fewer peaks were detected.
[0271] The inventors of the present application evaluated the selectivity of three different matrix materials for ionizing the different main PL species present in biofilms. The results are shown in Figure 4 .
[0272] The data show that in positive ion mode, cationic phosphol...
Embodiment 3
[0275] Example 3 - Effect of Culture Medium and Ionization Mode
[0276] Figure 5 Mass spectra from blood agar in the presence of methanolic lipid extraction solvent are shown. Several background peaks can be seen in the lipid profile mass range (m / z 700-1500) when measured in (+) MALDI mode but not (-) MALDL mode.
[0277] This is because blood agar contains some plasma lipids (e.g., derived from blood cells and lipoproteins), which are the main cationic PL- species (mainly LPC, PC and SM), and they are therefore preferentially in the (+) ion mode down is detected.
[0278] This problem can be circumvented in (+)MALDI mode by using minimal medium (without exogenous lipids) instead of blood agar. The resulting lipid mass profile is essentially the same, but contains fewer media contaminants. However, the use of minimal media often leads to less favorable culture conditions and to longer incubation times to obtain sufficient numbers of cells for analysis. This (-) mode al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com