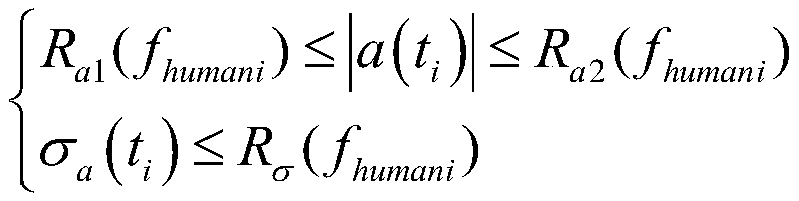An Adaptive Zero-speed Interval Detection Method for Pedestrian Navigation System
A technology for pedestrian navigation and zero-speed interval, applied in the field of pedestrian navigation and positioning, can solve the problems of false detection, missed detection, and strong randomness of pedestrian movement in detection results, and achieve the effect of simple detection means and improved detection accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
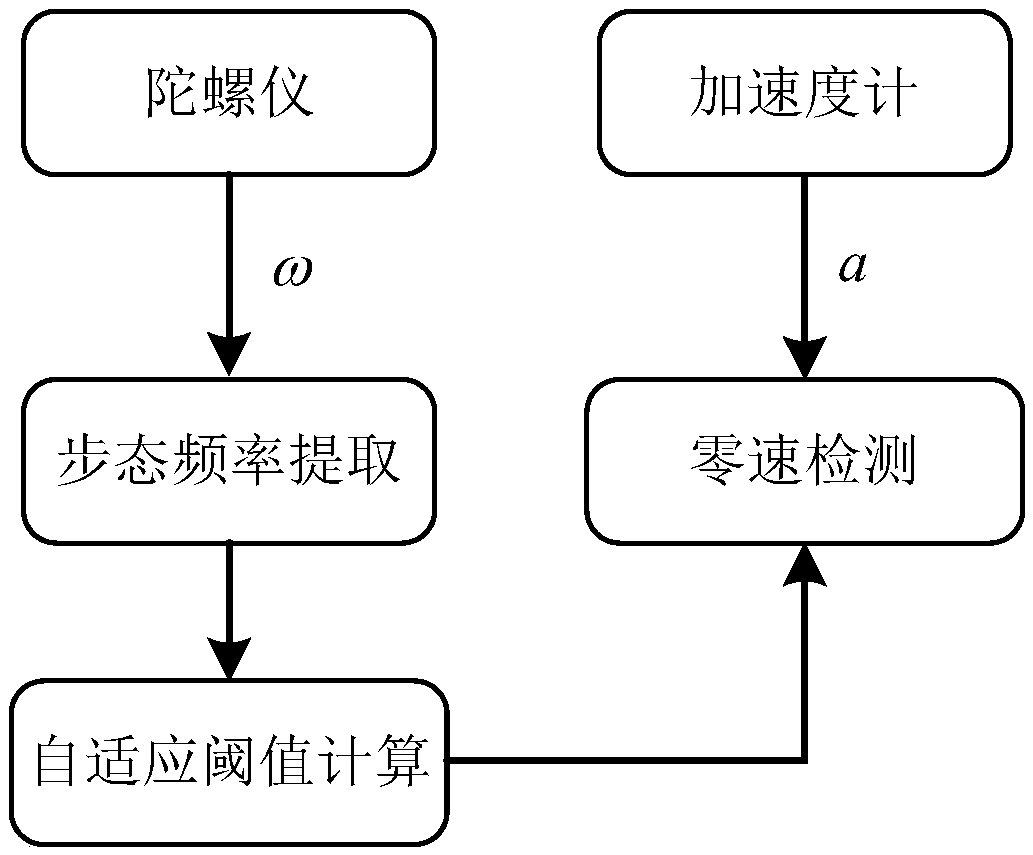
[0036] The invention provides an adaptive detection method for a zero-speed interval of a pedestrian navigation system, which is realized by the following steps:
[0037] Step 1, install the inertial measurement unit on the pedestrian's shoes, and use this measurement unit to measure and collect the data during the pedestrian's movement, including the angular rate output by the gyroscope and the acceleration output by the accelerometer, such as figure 1 shown. The inertial measurement unit coordinate axes x, y, and z point to the forward, rightward and vertical downward directions of the human body respectively, and the coordinate origin is at the center of the inertial measurement unit;
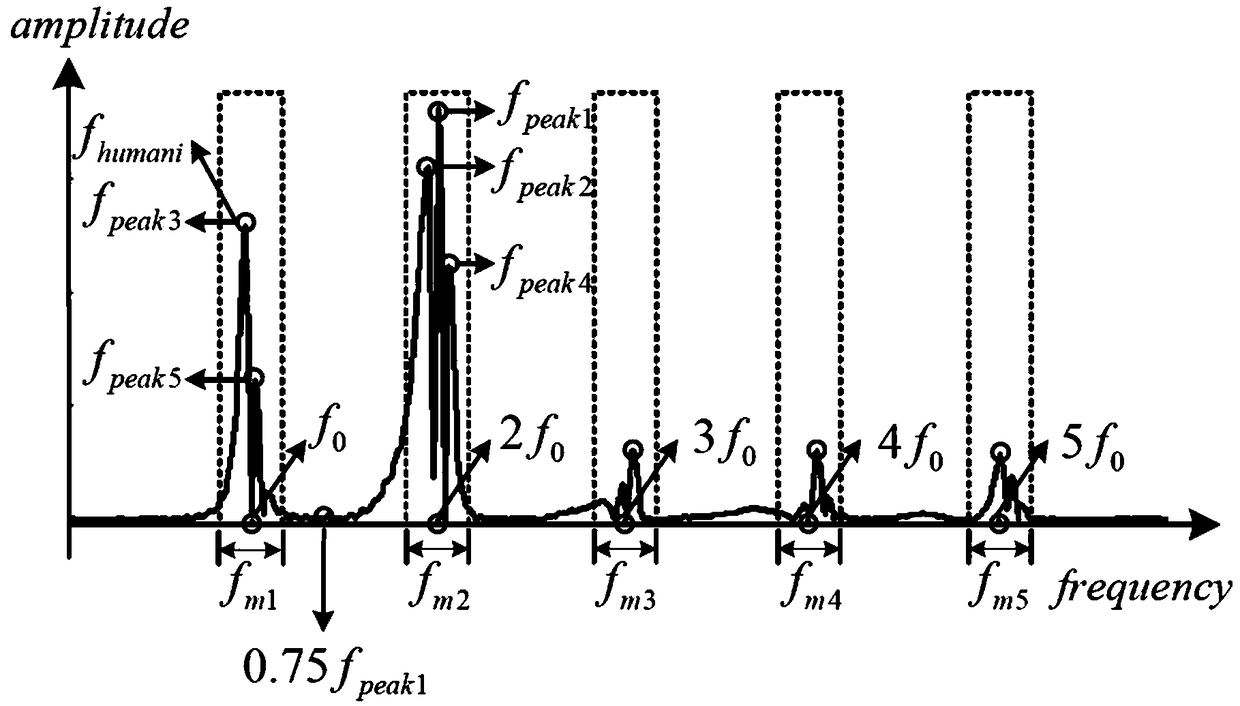
[0038] Step 2, analyzing the amplitude-frequency characteristics of the gyro data of any coordinate axis in the inertial measurement unit. Using the Fouri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com