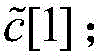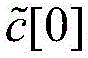Automatic adjustment method for dead-time compensation voltage value of motor driver
A motor driver and dead zone compensation technology, which is applied in the direction of controlling electromechanical brakes, controlling generators, motor generators, etc., can solve problems such as different and no real-time online detection, and achieve improved smoothness, steady-state and dynamic operation effects Superior, improved shock and distortion effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
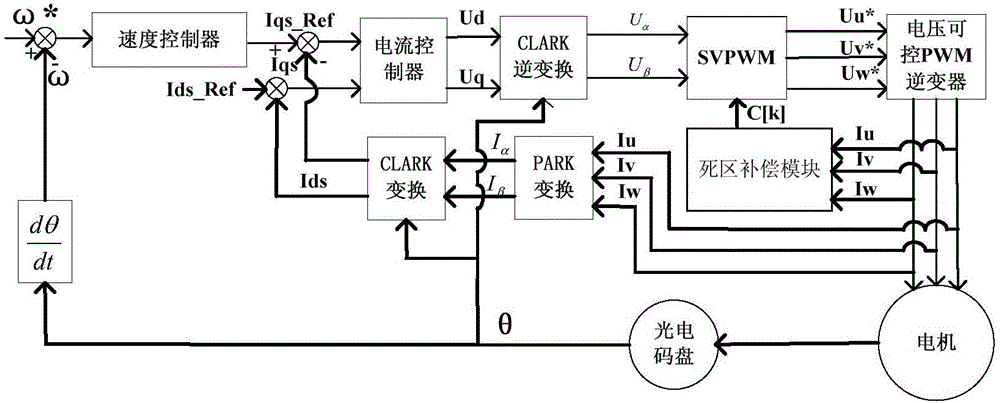
[0032] The automatic adjustment method of the dead-time compensation voltage value of the motor driver according to Embodiment 1 includes the following steps:
[0033] Step a, select at least 5 numbers c[0], c[1], c[2],...c[n] as the first screening dead zone compensation voltage value, n≥4;
[0034] Step b, the motor driver drives the asynchronous motor to rotate according to the selected first dead zone compensation voltage value c[0];
[0035] Step c, every preset time period T s Sampling the stator current I of the motor u once, and recorded separately as x u (k), where k=0,1,2,…2 N -1, N is a positive integer, M=2 N , f is the frequency of the stator current of the asynchronous motor; a total of 2 samples N end sampling after the number of times;
[0036] Step d, the stator current sampling value array x u (k) Perform Fourier transform to obtain the harmonic coefficient array X in the frequency domain u (k), where k=0,1,2,…2 N -1; Calculate the array number k c...
Embodiment 2
[0059] The method steps of Example 2 are similar to those of Example 1. The main difference is that Example 2 has been screened twice, while Example 2 has only been screened once. Therefore, the identification accuracy of Example 1 is better than that of Example 2, but The recognition speed of Example 2 is faster than that of Example 1.
[0060] The automatic adjustment method of the dead-time compensation voltage value of the motor driver according to Embodiment 1 includes the following steps:
[0061] Step a, select at least 5 numbers c[0], c[1], c[2],...c[n] as the first screening dead zone compensation voltage value, n≥4;
[0062] Step b, the motor driver drives the asynchronous motor to rotate according to the selected first dead zone compensation voltage value c[0];
[0063] Step c, every preset time period T s Sampling the stator current I of any phase of the motor u once, and recorded separately as x u(k), where k=0,1,2,…2 N -1, N is a positive integer, M=2 N , ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com