Method for predicting milling residual stress field of titanium alloy
A residual stress and prediction method technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as poor prediction accuracy, heavy testing workload, and difficult control of residual stress field, achieving high accuracy, Effects of rapid prediction and robust design and analysis methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1, a kind of titanium alloy milling residual stress field prediction method based on exponential decay function
[0056] The prediction method of this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0057] Step 1: Determine the exponential decay function model of the milling residual stress field
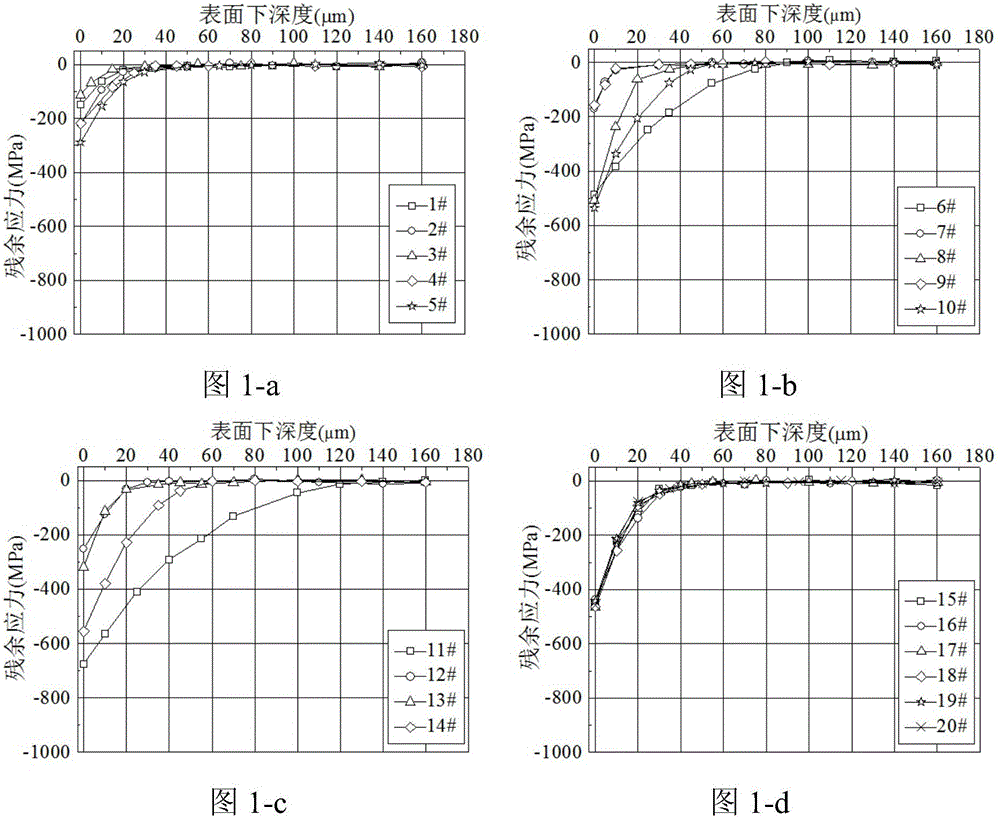
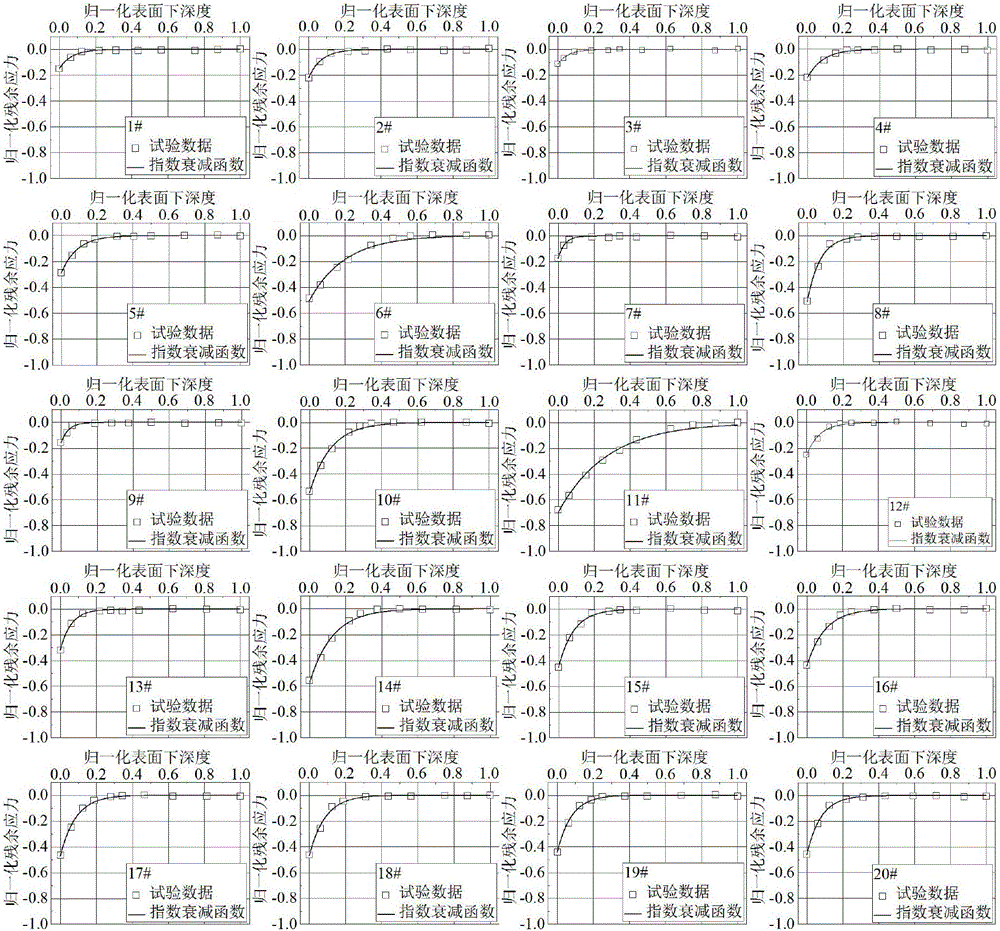
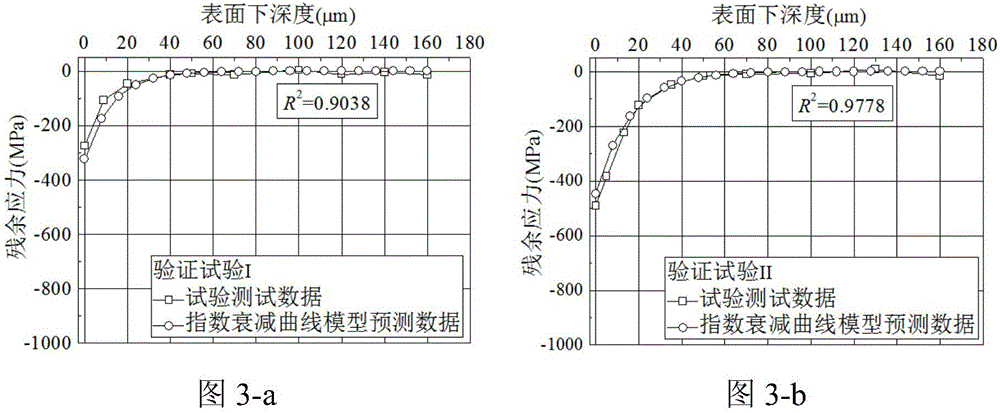
[0058] After milling, the surface layer of titanium alloy is in the state of residual compressive stress, and the residual compressive stress gradually decreases with the increase of the depth below the surface, and reaches the state of residual stress in the matrix. Therefore, an exponential decay function is proposed to describe the milling residual compressive stress curve.
[0059] σ(h)=Ae -λh
[0060] where σ is the residual stress; h is the subsurface depth; A is the initial value of the residual stress; λ is the exponential decay coefficient, which determines how fast the residual compressive stress field decays to a stable value.
[0061] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com