Wear-resisting material used for brake disc of high-speed train and preparation method for wear-resisting material
A technology of wear-resistant materials and high-speed trains, applied in the field of alloy steel materials, can solve the problems of obvious changes in friction coefficient with load and temperature, poor structure uniformity of as-cast brake disc materials, complicated preparation process, etc., to shorten the heat treatment cycle, Effect of improving tissue uniformity and reducing production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
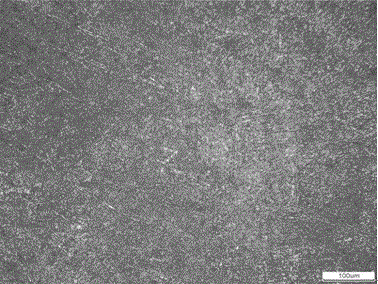
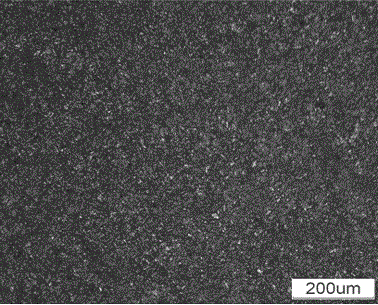
[0028] Weigh the sample as described in Table 1 above, use a 50Kg medium frequency induction furnace to melt the molten steel, add ferro-titanium and pure niobium, adjust the chemical composition of the molten steel, and then pour it. The as-cast sample was obtained by sand casting, and the metallographic structure of the as-cast sample is shown in figure 1 . Specimens for wire cutting heat treatment. The as-cast sample was heated to 900°C for 2 hours, water quenched, then kept at 600°C for 2 hours, and air-cooled. The metallographic structure of the sample after heat treatment is shown in figure 2 .
[0029] See Table 2 for the volumetric wear rates of the as-cast and heat-treated samples in Example 1 above under the conditions of a load of 100 N and a sliding speed of 45 m / s.
[0030] Table 2 Volume wear rate of as-cast and heat-treated states
[0031]
Embodiment 2
[0033] Weigh the sample as described in Table 1 above, use a 50Kg intermediate frequency induction furnace to melt the molten steel, add ferrotitanium, and adjust the alloying elements of the molten steel for pouring. The as-cast samples were obtained by sand casting, and the samples for heat treatment were processed by wire cutting. The as-cast sample was heated to 950°C for 1.5 hours, water quenched, then kept at 550°C for 1.5 hours, and air-cooled.
[0034] Under the same conditions, the friction coefficient of alloy steel is maintained at 0.35~0.40, and the volume wear rate is 3.45mm 3 / m.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Weigh the samples as described in Table 1 above, use a 50Kg medium frequency induction furnace to melt the molten steel, add pure niobium, adjust the chemical composition of the molten steel, and then pour. The as-cast samples were obtained by sand casting, and the samples for heat treatment were processed by wire cutting. The as-cast sample was heated to 1000°C for 1 hour, water quenched, then kept at 650°C for 2.5 hours, and air-cooled.
[0037] Under the same conditions, the friction coefficient of alloy steel is maintained at 0.33~0.37, and the volume wear rate is 2.96mm 3 / m.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| friction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| friction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| friction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com