Electromagnetically-driven micro mirror H-infinity control method and H-infinity control system
A technology for driving micromirrors and control methods, applied in general control systems, control/adjustment systems, adaptive control, etc., to achieve the effects of improving dynamic robust performance, reducing power consumption, and suppressing output noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
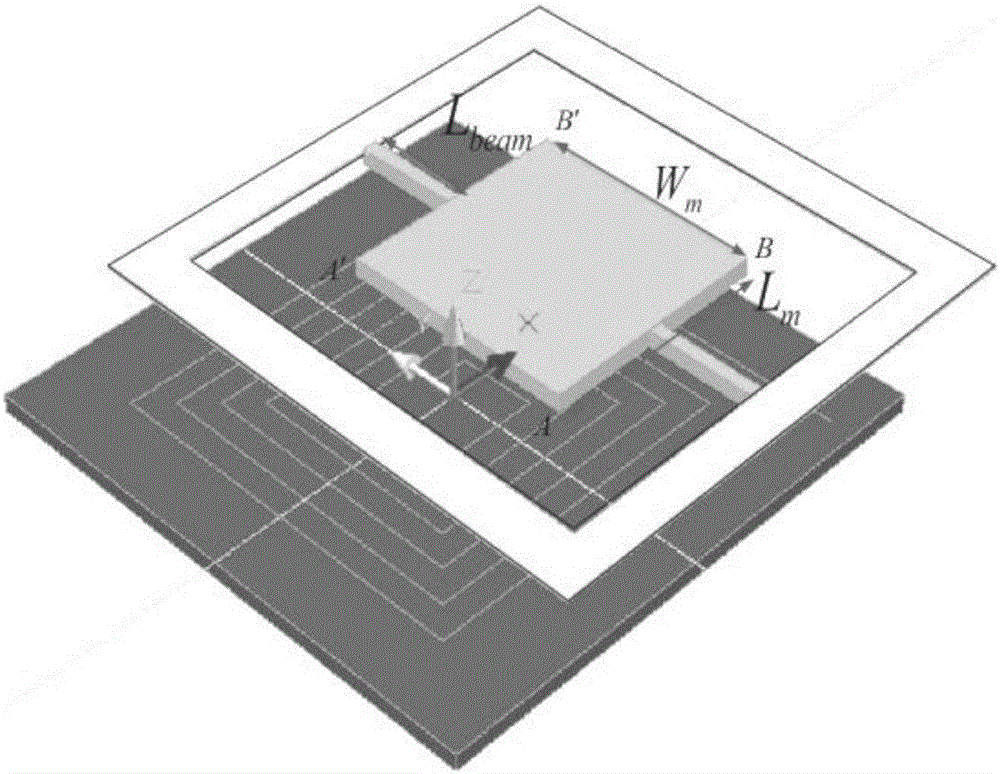
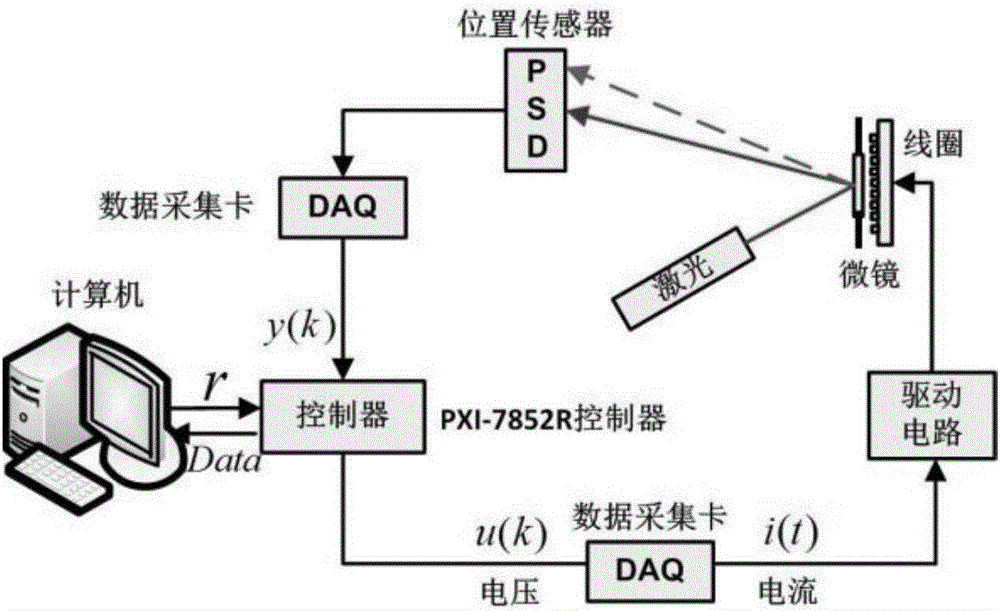
[0067] See Image 6 , Image 6 is the H of the electromagnetically driven micromirror disclosed in this embodiment ∞ Flow chart of the control method. The H of the electromagnetically driven micromirror disclosed in this embodiment ∞ The control method, on the basis of ensuring the good dynamic and static characteristics of the electromagnetic micromirror system, improves the dynamic robustness to unmodeled, reduces the power consumption of the controller, and suppresses the output noise.
[0068] Combine below Figure 1-Figure 6 , specifying an electromagnetically driven micromirror H ∞ The detailed procedure of the control method. as attached Image 6 As shown, the H of the electromagnetically driven micromirror ∞ The control method includes the following steps:
[0069] Step S1, selection of an optimization model.
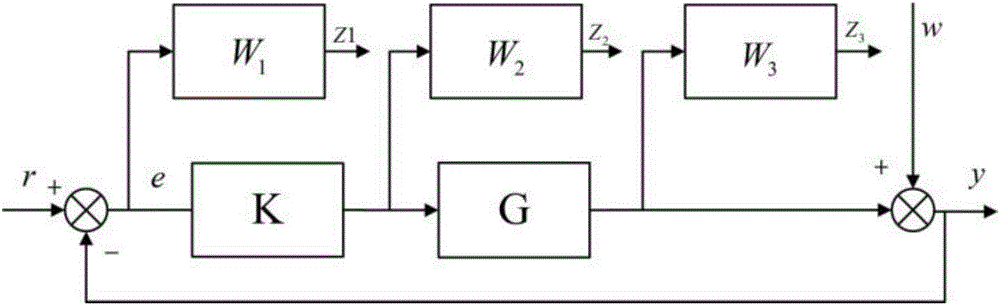
[0070] h ∞ The standard control models mainly include: a mixed sensitivity model for comprehensive design, a sensitivity minimization model for suppre...
Embodiment 2
[0110] This embodiment discloses an electromagnetically driven micromirror H ∞ control system, the H ∞ The control system includes:
[0111] The optimization model selection module, which selects the optimized H according to the target performance requirements ∞ standard control model, the H ∞ Standard control models include: mixed sensitivity model for comprehensive design, sensitivity minimization model for suppressing interference, and mixed sensitivity model for comprehensive design of system perturbation robustness model. For the above modes, let G be the transfer function of the controlled object, and K be H ∞ controller transfer function, W 1 , W 2 , W 3 is the weight function, let the system open-loop transfer function be L, where L=KG; let S=1 / (I+GK) -1 ,R=K / (I+GK) -1 ,T=GK / (I+GK) -1 , where S is the sensitivity function, which is the transfer function from external disturbance e to output y, which represents the ability of the system to suppress disturbance a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com