Refrigeration cycle device
A refrigeration cycle and refrigerant technology, used in refrigerators, refrigeration components, refrigeration and liquefaction, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining superheat, increase in heat exchange, and deterioration of refrigeration cycle refrigeration coefficient, and achieve improved efficiency and improved refrigeration. The effect of coefficients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
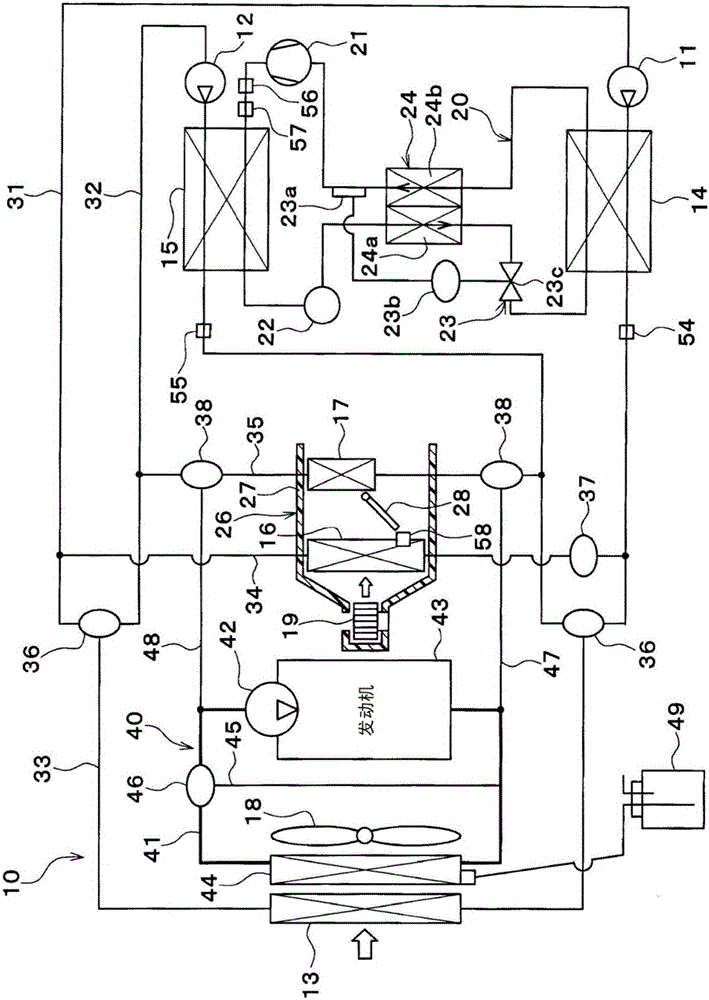
[0041] figure 1 The illustrated refrigeration cycle device 10 is used to air-condition the vehicle interior to an appropriate temperature. In the present embodiment, the refrigeration cycle device 10 is applied to a hybrid vehicle that obtains driving force for vehicle running from an engine (internal combustion engine) and a running electric motor.
[0042] The hybrid vehicle according to the present embodiment is configured as a plug-in hybrid vehicle capable of charging a battery (vehicle battery) mounted on the vehicle with electric power supplied from an external power supply (commercial power supply) when the vehicle is parked. As the battery, for example, a lithium ion battery can be used.
[0043] The driving force output from the engine is used not only for driving the vehicle but also for operating the generator. In addition, the electric power generated by the generator and the electric power supplied from the external power source can be stored in the battery, an...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0199] In the above-mentioned first embodiment, the high-pressure side refrigerant of the refrigerant circuit 20 heats the blown air blown toward the vehicle interior via the cooling water. Figure 9 As shown, the high-pressure side refrigerant of the refrigerant circuit 20 does not heat the blown air blown toward the vehicle interior through the cooling water.
[0200] The refrigerant circuit 20 has an indoor condenser 60 , an outdoor condenser 61 , an outdoor condenser bypass passage 62 , and a three-way valve 63 . The indoor condenser 60 and the outdoor condenser 61 are radiators that dissipate heat from the high-pressure side refrigerant in the refrigerant circuit 20 .
[0201] The interior condenser 60 is a refrigerant-air heat exchanger for exchanging heat between the high-pressure side refrigerant discharged from the compressor 21 and the blown air blown toward the vehicle interior. The indoor condenser 60 is a condenser for condensing the high-pressure side refrigeran...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
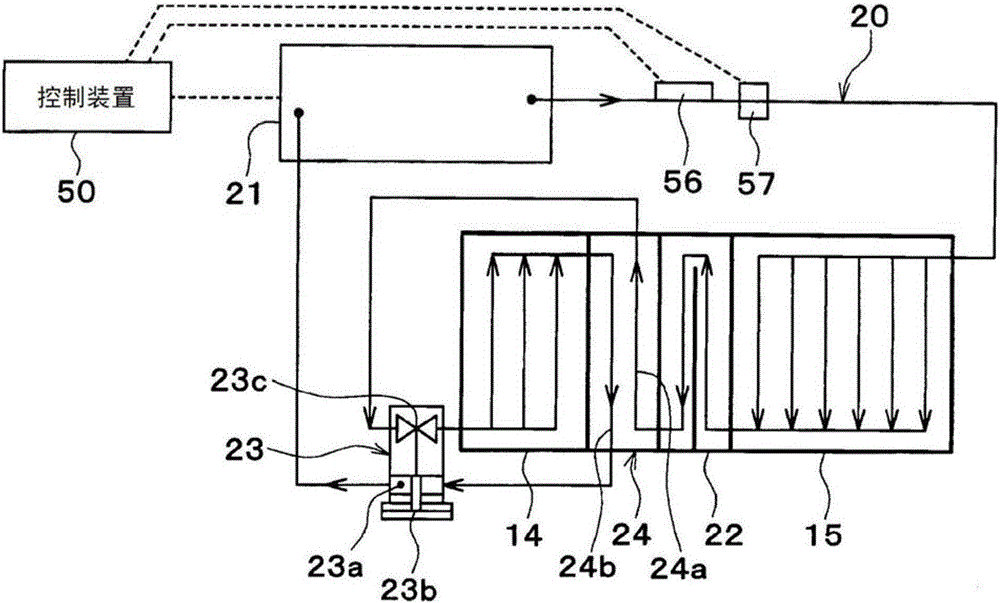
[0207] In the above-mentioned embodiment, the temperature type expansion valve 23 is used as the decompression device for decompressing and expanding the liquid-phase refrigerant flowing out of the cooling water heater 15, but in this embodiment, as Figure 10 As shown, the expansion valve 23 adopts an electric expansion valve 65 as a decompression device.
[0208] The electric expansion valve 65 changes the area (opening degree) of the throttle flow path 65b by an electric mechanism 65a. The throttle flow path 65 b is a decompression device for decompressing the high-pressure refrigerant that radiates heat in the cooling water heater 15 .
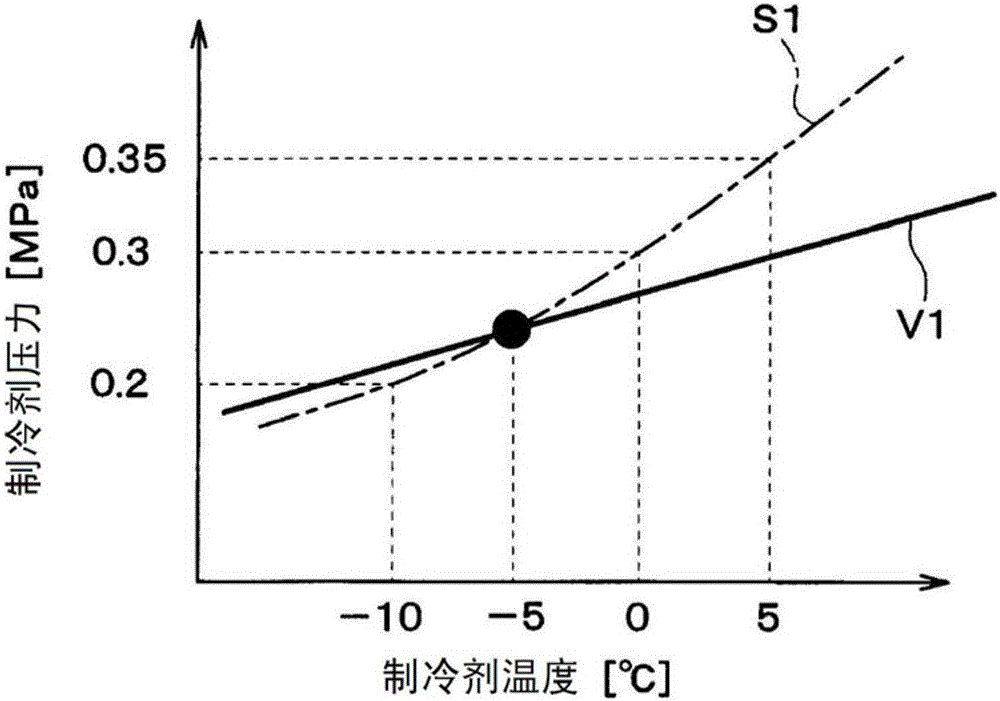
[0209] The operation of the electric mechanism 65 a is controlled by the control device 50 . The electric mechanism 65 a and the control device 50 are a superheat degree control unit that controls the degree of superheat of the low-pressure refrigerant that is heat-exchanged in the internal heat exchanger 24 .
[0210] The detection sign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com