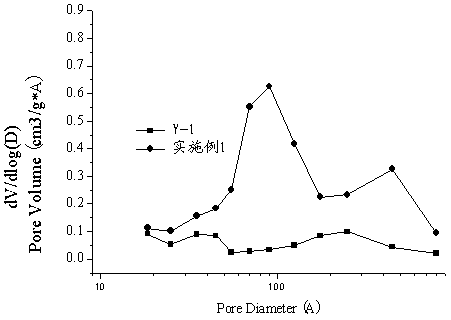
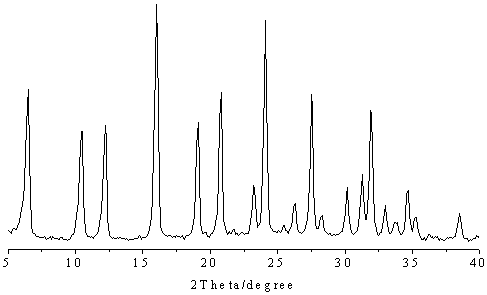
A kind of modification method of Y-type molecular sieve
A molecular sieve and modification technology, applied in molecular sieve catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, catalyst carriers, etc., to achieve the effects of increasing acid content, reducing silicon-aluminum ratio, and large mesopore structure distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Roast the Y-1 molecular sieve at 550°C for 4 hours, then contact the unsaturated olefin with the roasted Y-type molecular sieve, and roast it at 500°C for 2 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to carry out the carbon deposition reaction. Obtain the Y-type molecular sieve after carbon deposition;
[0024] (2) Under stirring conditions, add the Y-type molecular sieve after carbon deposition into the pressure-resistant container of 0.50mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, the mass ratio of molecular sieve addition to water in the solution is 1:8, and Seal the system, feed nitrogen to control the system pressure to 0.4MPa, then raise the temperature to 70°C, treat at a constant temperature for 2 hours, release the pressure, filter with suction until the pH value is less than 9, dry at 120°C for 12 hours, and finally bake at 550°C After 4 hours, a modified Y-type molecular sieve was obtained. The specific properties of molecular sieves are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0026] (1) Roast the Y-1 molecular sieve at 450°C for 6 hours, then contact the unsaturated olefin with the roasted Y-type molecular sieve, and roast it at 550°C for 2 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to carry out the carbon deposition reaction. Obtain the Y-type molecular sieve after carbon deposition;
[0027] (2) Under stirring conditions, add the Y-type molecular sieve after the carbon deposition into the pressure-resistant container of 0.80mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, the mass ratio of the molecular sieve to the water in the solution is 1:15, and Seal the system, feed air to control the system pressure to 0.6MPa, then raise the temperature to 80°C, treat at a constant temperature for 1 hour, release the pressure, filter with suction until the pH value is less than 9, dry at 110°C for 18 hours, and finally bake at 580°C After 4 hours, a modified Y-type molecular sieve was obtained. The specific properties of molecular sieves are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0029] (1) Roast the Y-1 molecular sieve at 600°C for 2 hours, then contact the unsaturated olefin with the roasted Y-type molecular sieve, and roast it at 480°C for 6 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to carry out the carbon deposition reaction. Obtain the Y-type molecular sieve after carbon deposition;
[0030] (2) Under stirring conditions, add the carbon-deposited Y-type molecular sieve into a pressure-resistant container of 0.60mol / L sodium hydroxide solution. The mass ratio of the amount of molecular sieve added to the water in the solution is 1:10, and Seal the system, feed nitrogen to control the system pressure to 0.2 MPa, then raise the temperature to 60°C, treat at a constant temperature for 3 hours, release the pressure, filter with suction until the pH value is less than 9, dry at 100°C for 24 hours, and finally roast at 520°C After 4 hours, a modified Y-type molecular sieve was obtained. The specific properties of molecular sieves are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com