In-vitro binding of immature dendritic cells mediated by NY-ESO-1 via polymeric structure domain
A technology of NY-ESO-1 and dendritic cells, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems affecting the natural history of tumors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
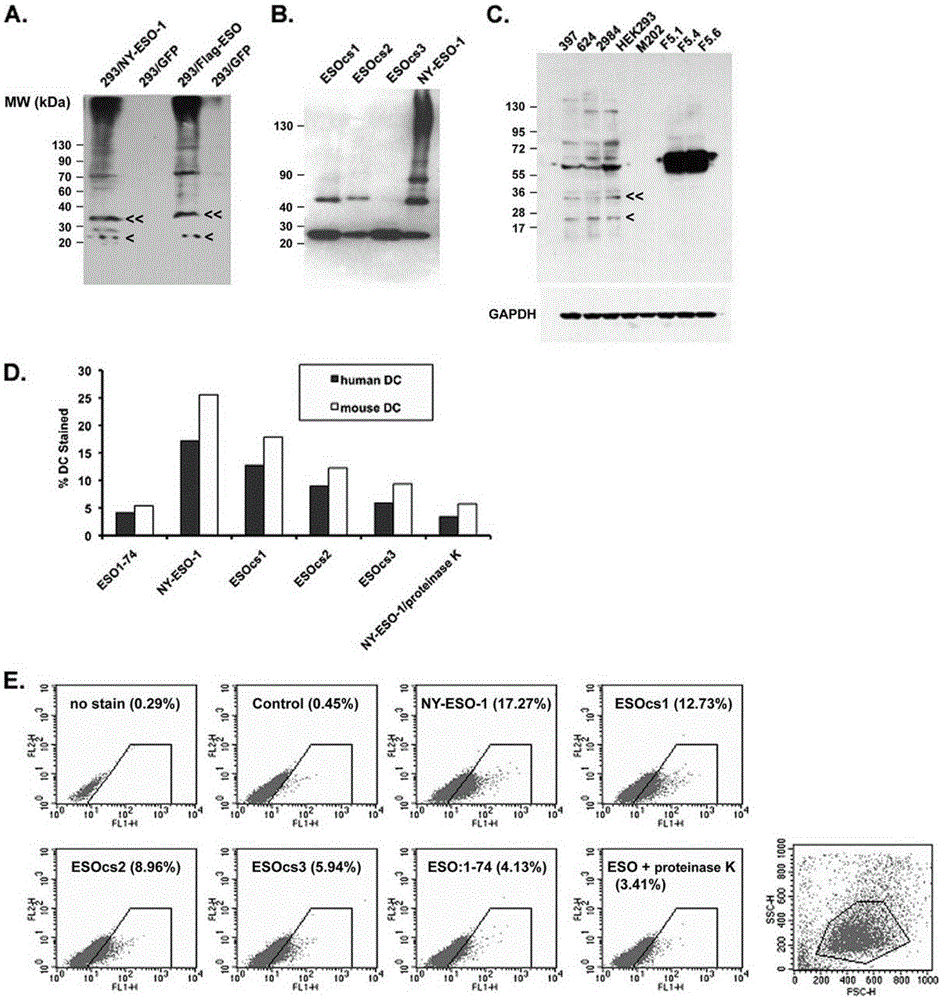
[0065] NY-ESO-1 protein can form multimeric structures even in loading buffer in the presence of regular concentrations of β-mercaptoethanol.
[0066] Experiments have found that NY-ESO-1 proteins obtained from bacteria and mammalian cells can form multimeric structures even in loading buffers with conventional concentrations of β-mercaptoethanol ( figure 1 A, B).
Embodiment 2
[0068] The polymerization reaction of NY-ESO-1 is mediated by its intermolecular disulfide bonds.
[0069] Cysteine in amino acid residues 75, 76, 78, 152 and 165 were replaced with serine. Three types of NY-ESO-1 with amino acid substitutions were: ESOcs1 with cysteine-serine substitutions at positions 75, 76, and 78, ESOcs2 with substitutions at positions 152 and 165, and ESOcs3 with mutations at all five positions. Purify these proteins and use Western blot to compare the oligomerization state between them ( figure 1 B). The results showed that the wild-type protein clearly showed the presence of dimers, tetramers and even multimers of 130 kDa. ESOcs1 and ESOcs2 showed mainly monomer and dimer structures, while the result of ESOcs3 showed mainly monomer. This experiment shows that the polymerization of NY-ESO-1 is due to the disulfide bonds between its molecules.
Embodiment 3
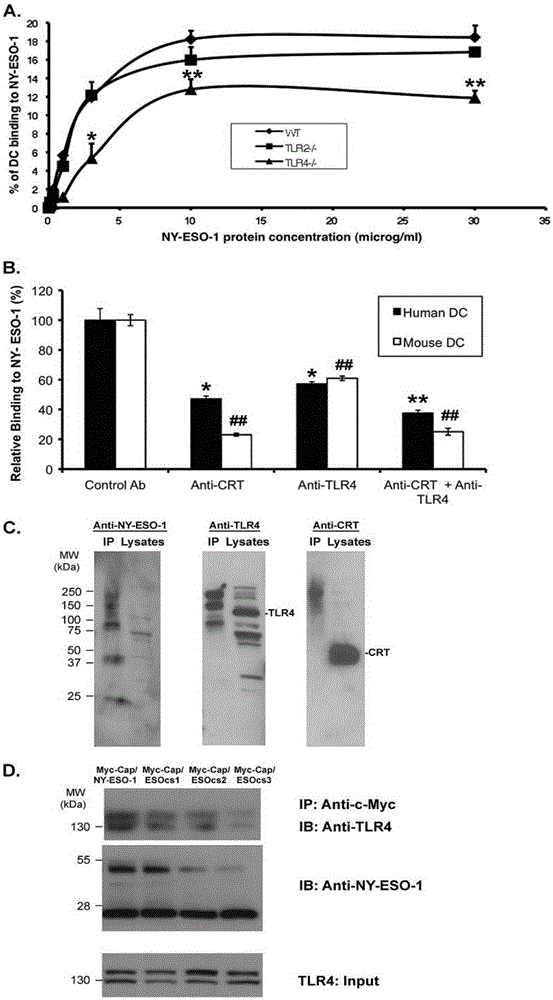
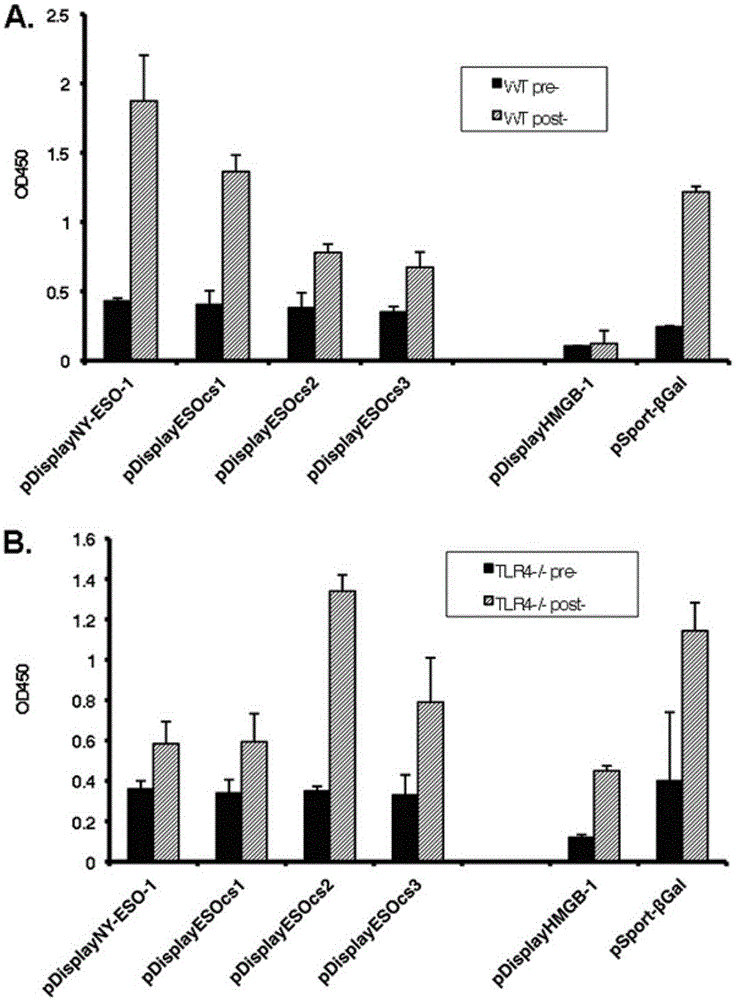
[0071] NY-ESO-1 binds to human and mouse immature dendritic cells in vitro and is related to its own polymeric structure.
[0072] Purify these proteins and use Western blot to compare the oligomerization state between them ( figure 1 B). The results showed that the wild-type protein clearly showed the presence of dimers, tetramers and even multimers of 130 kDa. ESOcs1 and ESOcs2 showed mainly monomer and dimer structures, while the result of ESOcs3 showed mainly monomer. This experiment shows that the polymerization of NY-ESO-1 is due to the disulfide bonds between its molecules. NY-ESO-1 present in cancer cells was also analyzed by Western blot for its protein aggregation in the loading buffer containing conventional concentrations of β-mercaptoethanol, and it was found that NY-ESO-1 mainly manifested as trimers and tetramers Dimeric and monomeric forms are rarely found (mutation 1C). Experiments show that NY-ESO-1 binds to human and mouse immature dendritic cells in vit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com