Patents
Literature
54 results about "In vitro binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
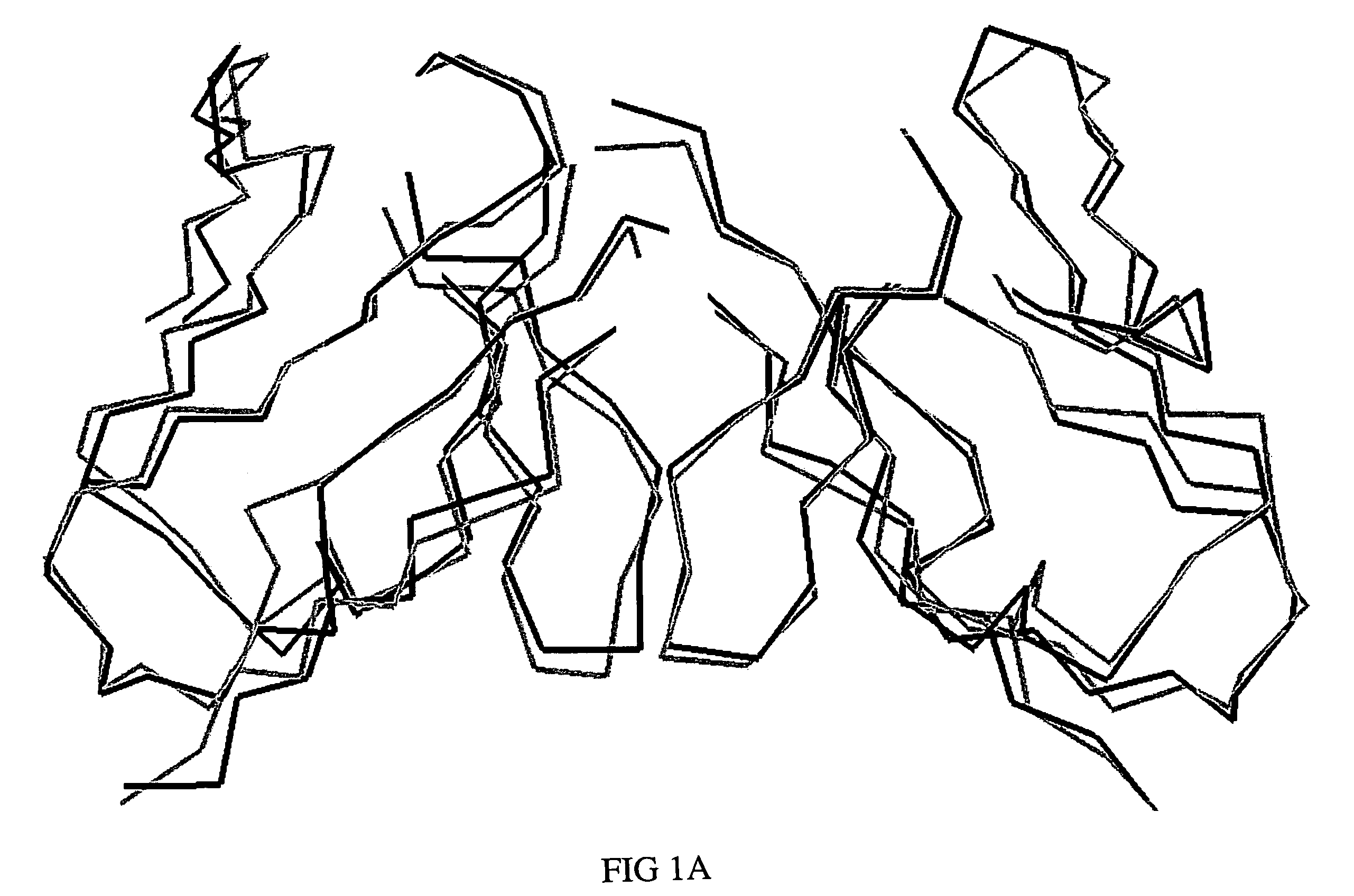
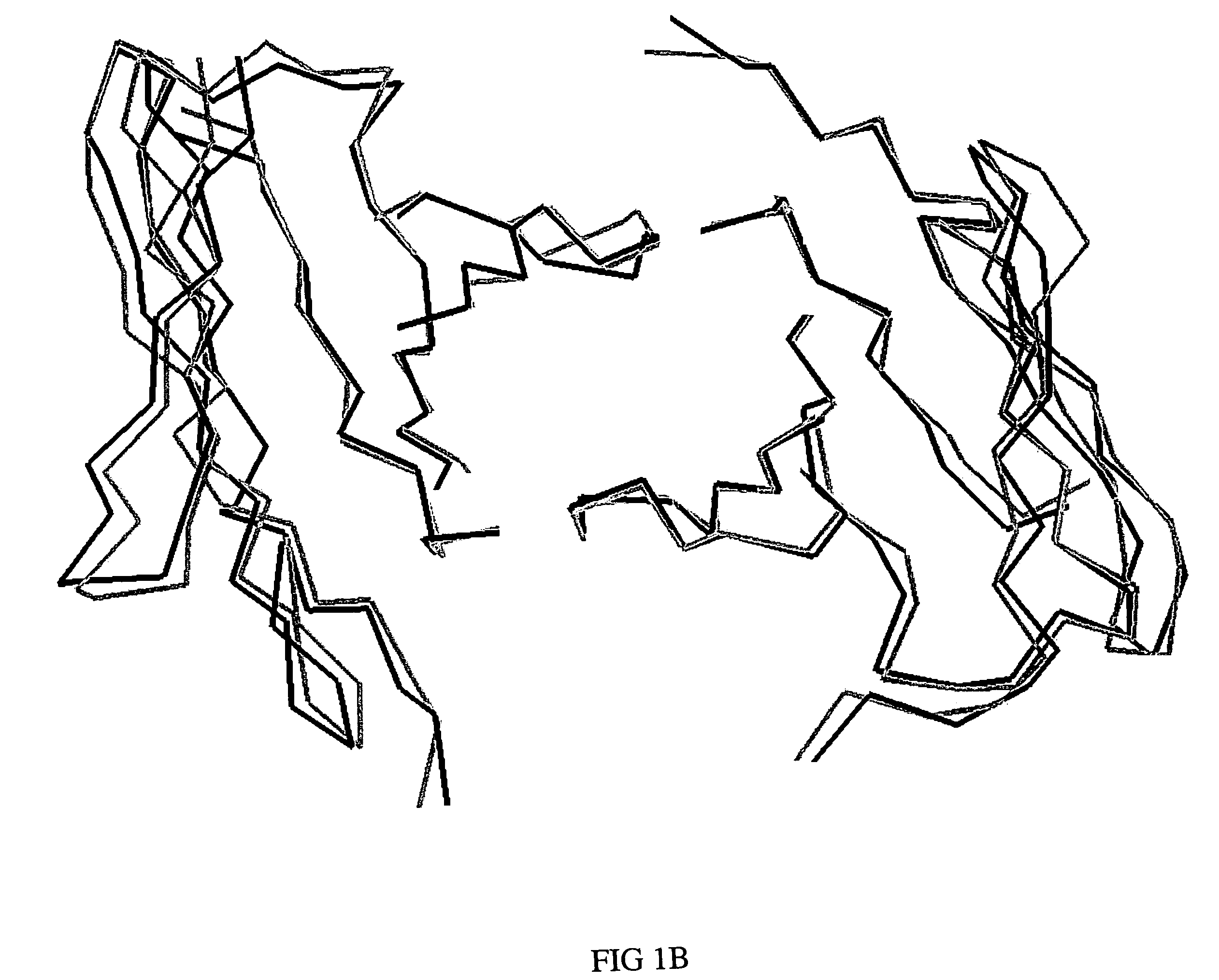
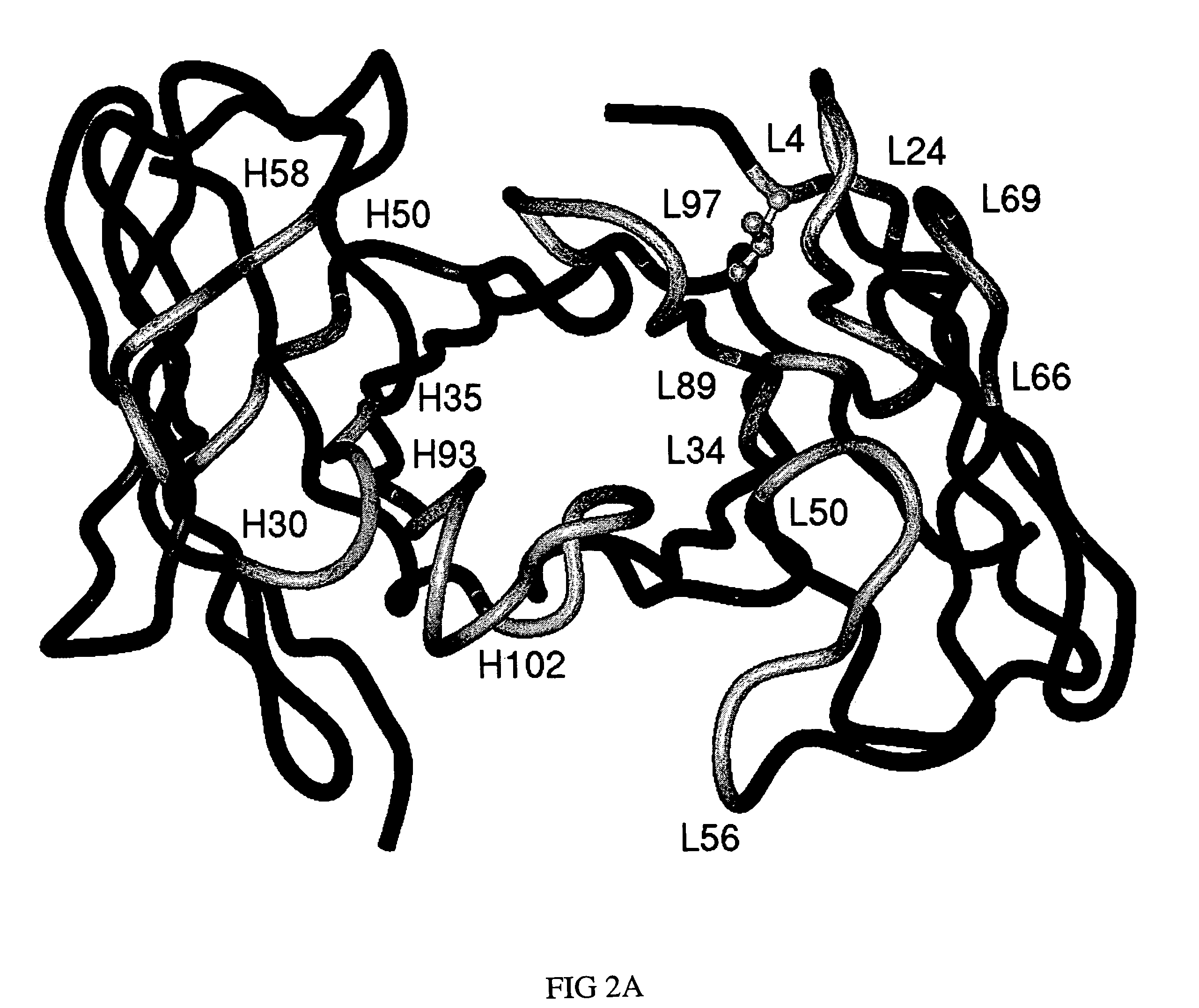
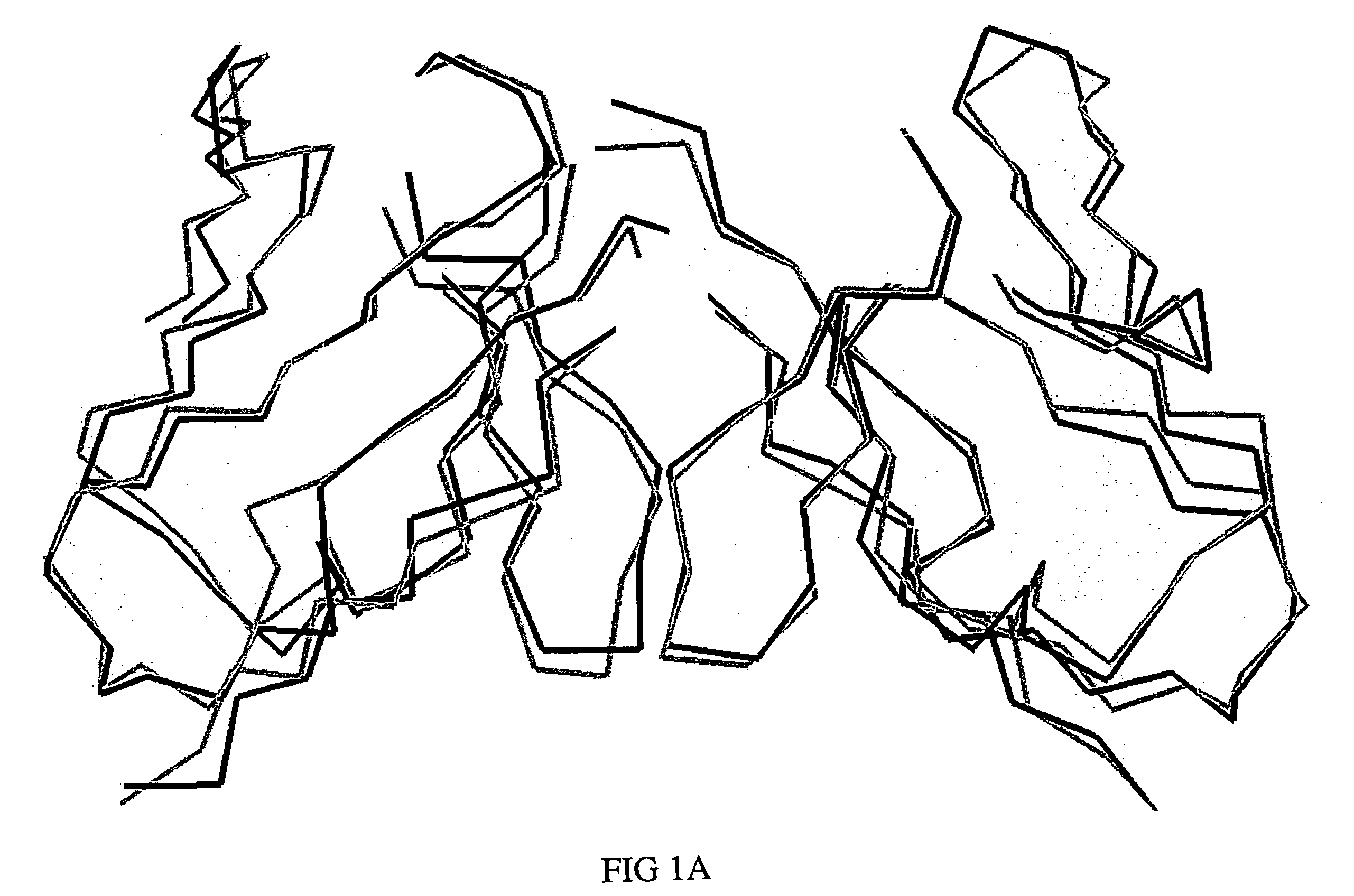
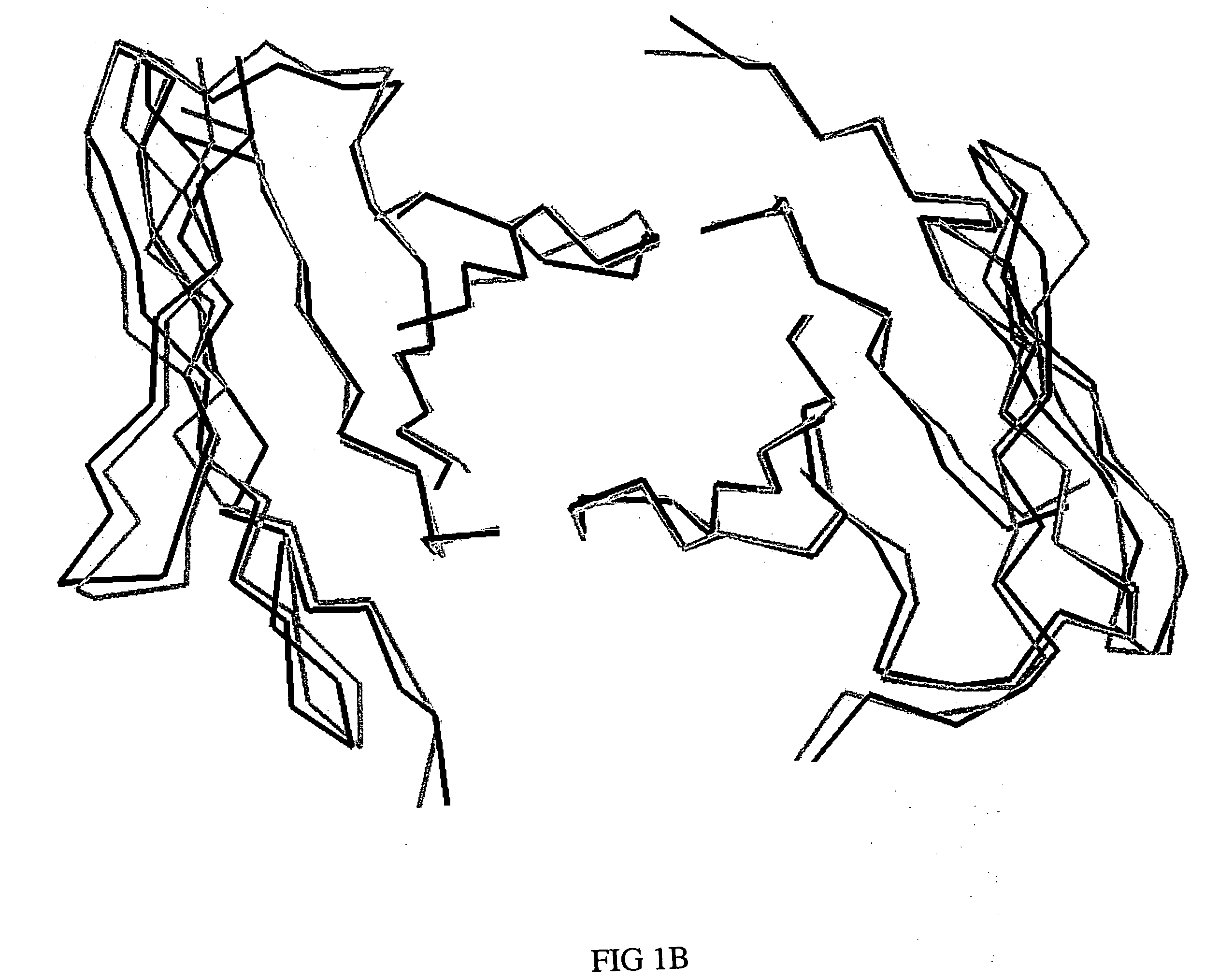
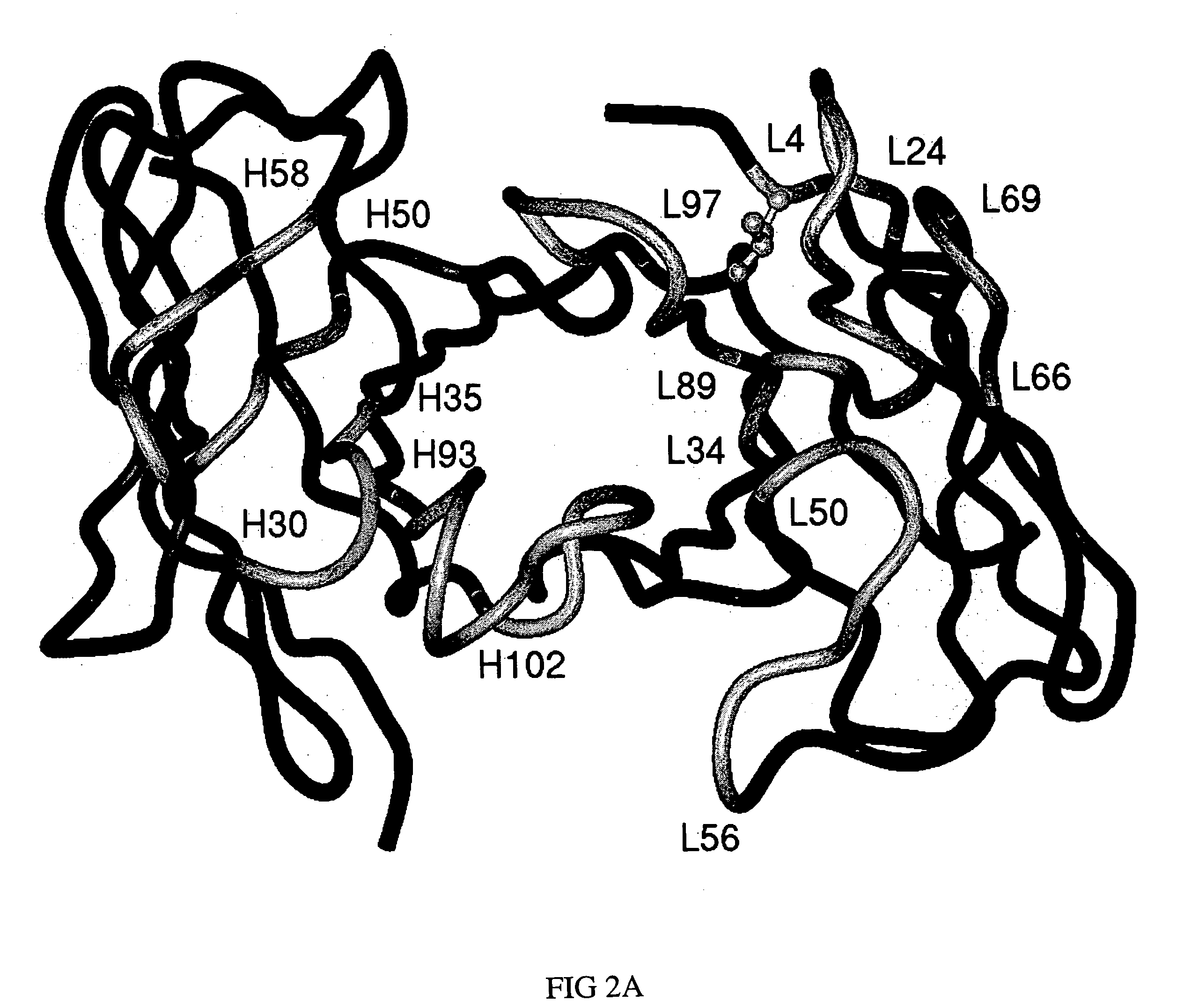
Humanized anti-CEA T84.66 antibody and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050244333A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAbnormal tissue growthCarcinoembryonic antigen
Embodiments of the present invention utilize a more efficient CDR grafting technique to generate humanized versions of the T84.66 antibody. The technique used to generate these antibodies utilizes crystallographic structural data to select an immunoglobulin framework having maximum structural overlap with a non-human donor molecule. This technique was used to develop humanized T84.66 antibodies exhibiting in vitro binding affinity and specificity for carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) nearly identical to that of T84.66 and the ability to specifically target tumors expressing CEA in vivo.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
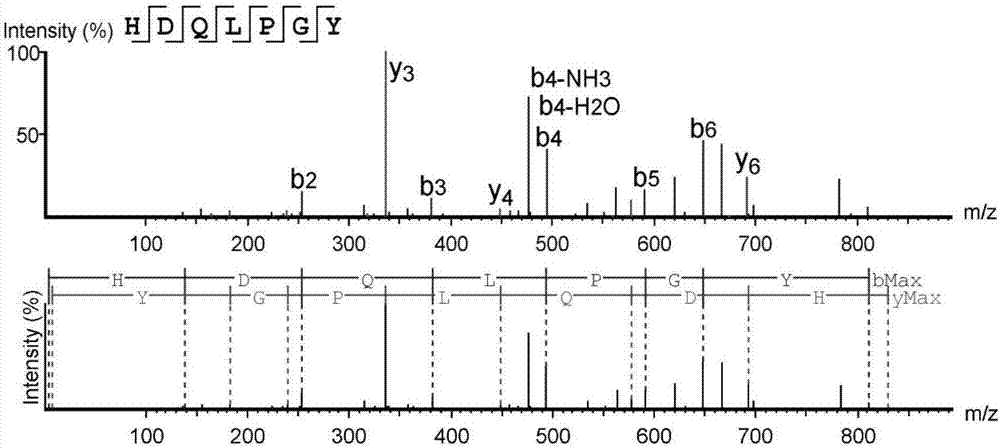
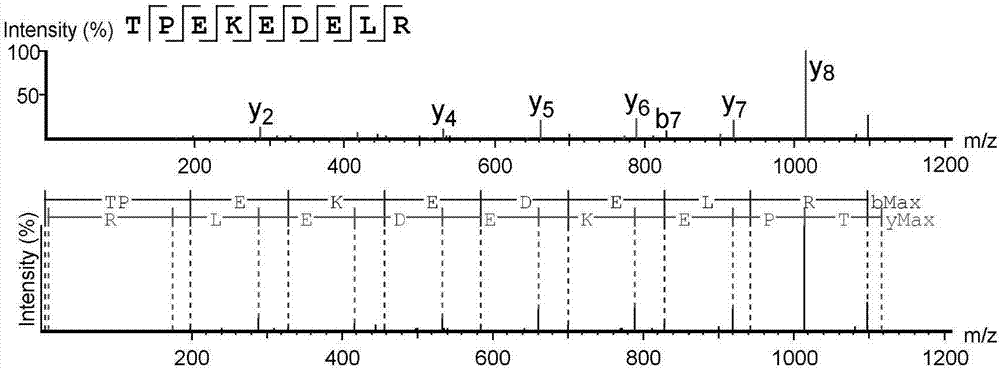
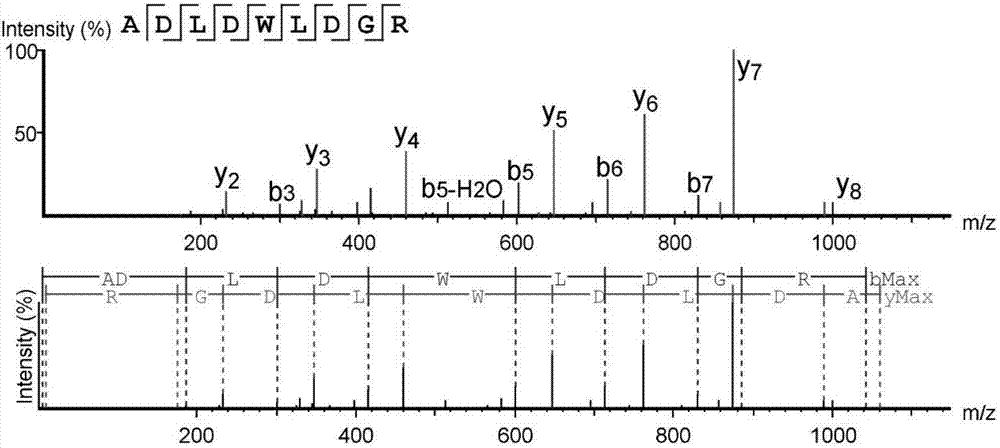
High-throughput active peptide screening method based on tandem mass spectrum and molecular docking
InactiveCN107132360AQuick searchEasy to operateBiological testingProtein targetHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to the field of medicine, and discloses a high-throughput screening method for active polypeptides based on tandem mass spectrometry and molecular docking. The invention uses modern biochemical technology to extract and prepare mixed polypeptides from marine molluscs, fish and other animals. After preliminary activity separation, the active site / component group is determined, and the amino acid sequence of all polypeptides in the active site / component group is identified by LC-MS / MS method. In the molecular docking software, all polypeptide sequences are homologously modeled, and then imported Molecular docking software docks with the target protein, analyzes the binding rate of the polypeptide and the target protein, and evaluates its inhibitory / activating activity, and screens the confirmed active polypeptide through solid-phase synthesis combined with in vitro activity evaluation to verify the accuracy of the screening. The invention has the advantages of fast and efficient search for marine active polypeptides, strong operability and important application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Tumor specific target polypeptide and application thereof
ActiveCN102060909ASmall molecular weightStrong penetrating powerPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesScreening methodTumor specific
The invention relates to a polypeptide capable of specific tumor-binding. The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID No.1. According to the invention, phages specifically binding with lung cancer are obtained by means of a phage display in vivo screening method to determine sequence in order to synthesize the specific binding polypeptide. The polypeptide can achieve excellent in vitro binding with a plurality of tumor cells subsequent to the conjunction with poly(amidoamine) dendrimer nano material. As verified by in vitro experiments, the target polypeptide has a very hightumor targeting effect and can be widely used as a targeting agent in diagnostic imaging and targeted treatment of tumors.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
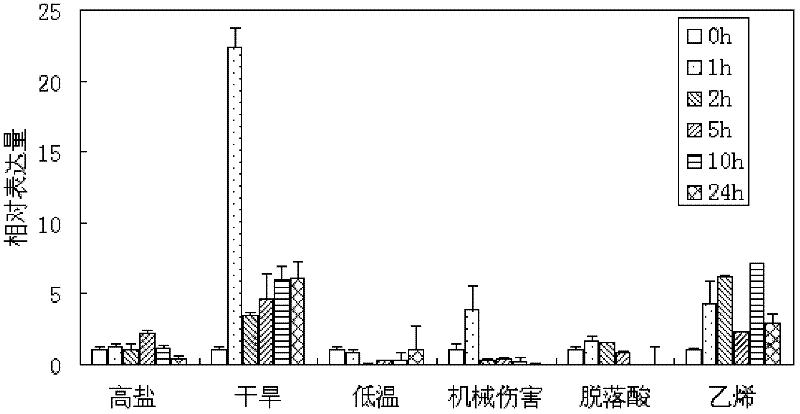
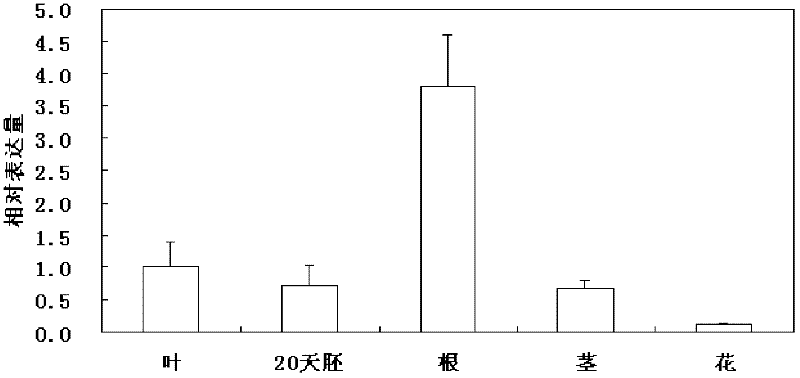
Soybean ethylene responsive factor (ERF) transcription factor, and coding gene and salt tolerance application thereof
InactiveCN102516377AImprove stress resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to a soybean ethylene responsive factor (ERF) transcription factor, and a coding gene and salt tolerance application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The amino acid sequence of the soybean ERF transcription factor is Sequence No.2, the amino acid sequence of the coding gene of the soybean ERF transcription factor is Sequence No.1, and the invention provides application of the soybean ERF transcription factor to salt tolerance of a transgenic plant. A GmERF7 transcription factor gene related with the soybean salt tolerance is cloned, and the expression mode of the gene in soybean, the in-vitro combination of the gene with an adversity element, and transcriptional regulation activity of the gene are researched, the salt tolerance of wild type tobacco and tobacco with trans GmERF7 gene is compared, basis is provided for the effective application of the soybean ERF transcription factor, and the invention has significance for improvement on stress resistance of plants, particularly cultivation of soybean varieties with high salt tolerance.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
CTL (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte) epitope peptide of foot-and-mouth disease virus type O and screening method of CTL epitope peptide
ActiveCN103864905AImprove bindingConvenient researchSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesCtl epitopeDisease
The invention discloses a CTL (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte) epitope peptide of a foot-and-mouth disease virus type O as well as a screening method and application of the CTL epitope peptide. The CTL epitope peptide is composed of nine amino acid residues, and the amino acid sequence of the CTL epitope peptide is as follows: Ala-Thr-Arg-Val-Thr-Glu-Leu-Leu-Tyr. The epitope peptide has relatively strong combining capacity with SLA (Swineleukocyteantigen)-I proteins from various strains of swine and can induce cytotoxic immune response so as to be suitable for preparing vaccines for preventing and controlling foot-and-mouth disease viruses of various strains of swine and wide in application range. According to the invention, a CTL simulated epitope peptide of a foot-and-mouth disease virus is combined with a single-chain molecule of SLA-I of six strains of constructed swine in vitro, thus a polypeptide which can be combined with a complex can be screened through mass spectrum measurement; in addition, a simulated epitope peptide which can be induced to generate the immune response capacity of T cells is determined through ELISPOT (Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay) detection. The invention provides a method for screening and authenticating the CTL epitope of the foot-and-mouth disease virus in a large scale, and lays the foundation for researching and preparing a multi-epitope vaccine of a foot-and-mouth disease.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Type A foot-and-mouth disease CTL (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) epitope peptide and screening method thereof
ActiveCN103724405AConvenient researchImprove bindingSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesCtl epitopeDisease
The invention discloses type A foot-and-mouth disease CTL (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) epitope peptide and a screening method thereof. The CTL epitope peptide consists of nine amino acid residues, and has an amino acid sequence of Ala-Met-Leu-Arg-Ala-Ala-Thr-Tyr-Tyr. The epitope peptide has stronger combining capability with SLA (swine leukocyte antigen)-?? proteins from pigs with different strains and causees cell toxicity immune response, and is applicable to the preparation of prevention and treatment vaccines for foot-and-mouth disease virus of pigs with various strains and wide in application range. According to the type A foot-and-mouth disease CTL epitope peptide and the screening method thereof, constructed SLA-I single-stranded molecules of pigs with six strains are utilized for in vitro combination with CTL simulated epitope peptide of foot-and-mouth disease virus, polypeptide which can be combined with complex is determined and screened by using a mass spectrum, and simulated epitope peptide which can induce the production of T cell immune response capability is determined through ELISPOT (enzyme linked immunospot assay) detection. The invention provides a method for screening and identifying a large number of foot-and-mouth disease virus CTL epitopes in the future, and lays a foundation for the development of multi-epitope vaccines for the foot-and-mouth disease of pigs.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
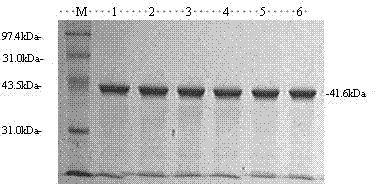
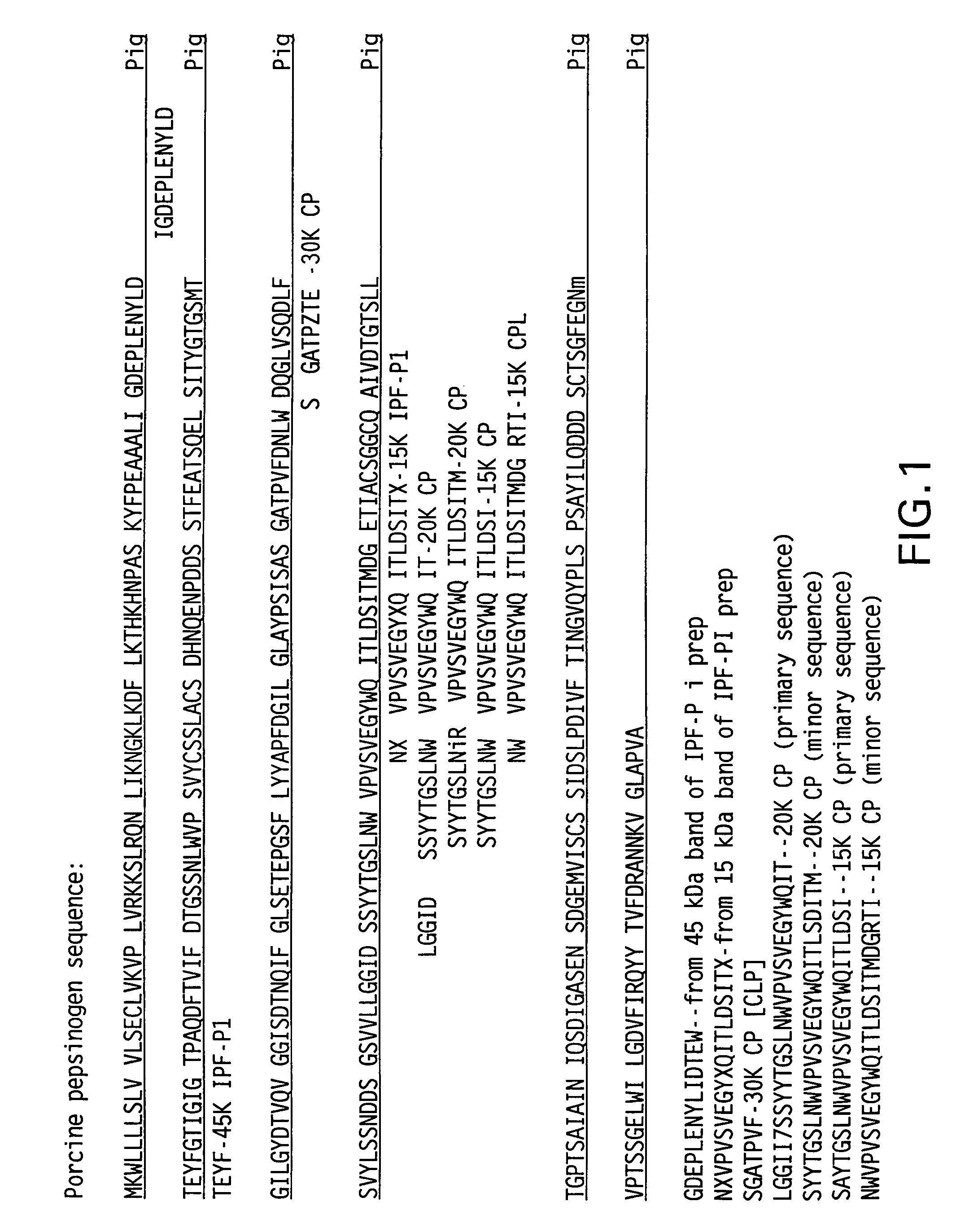
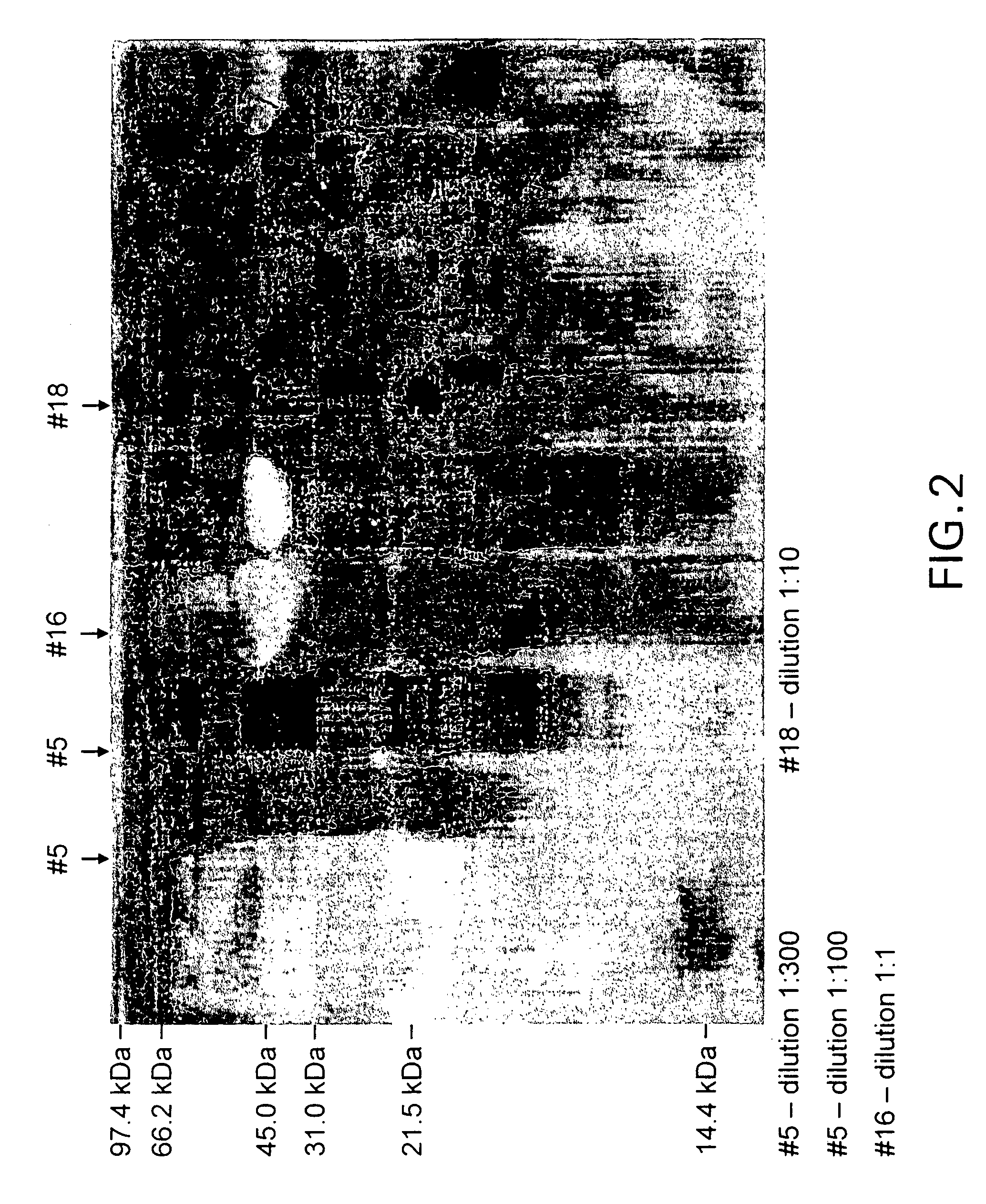
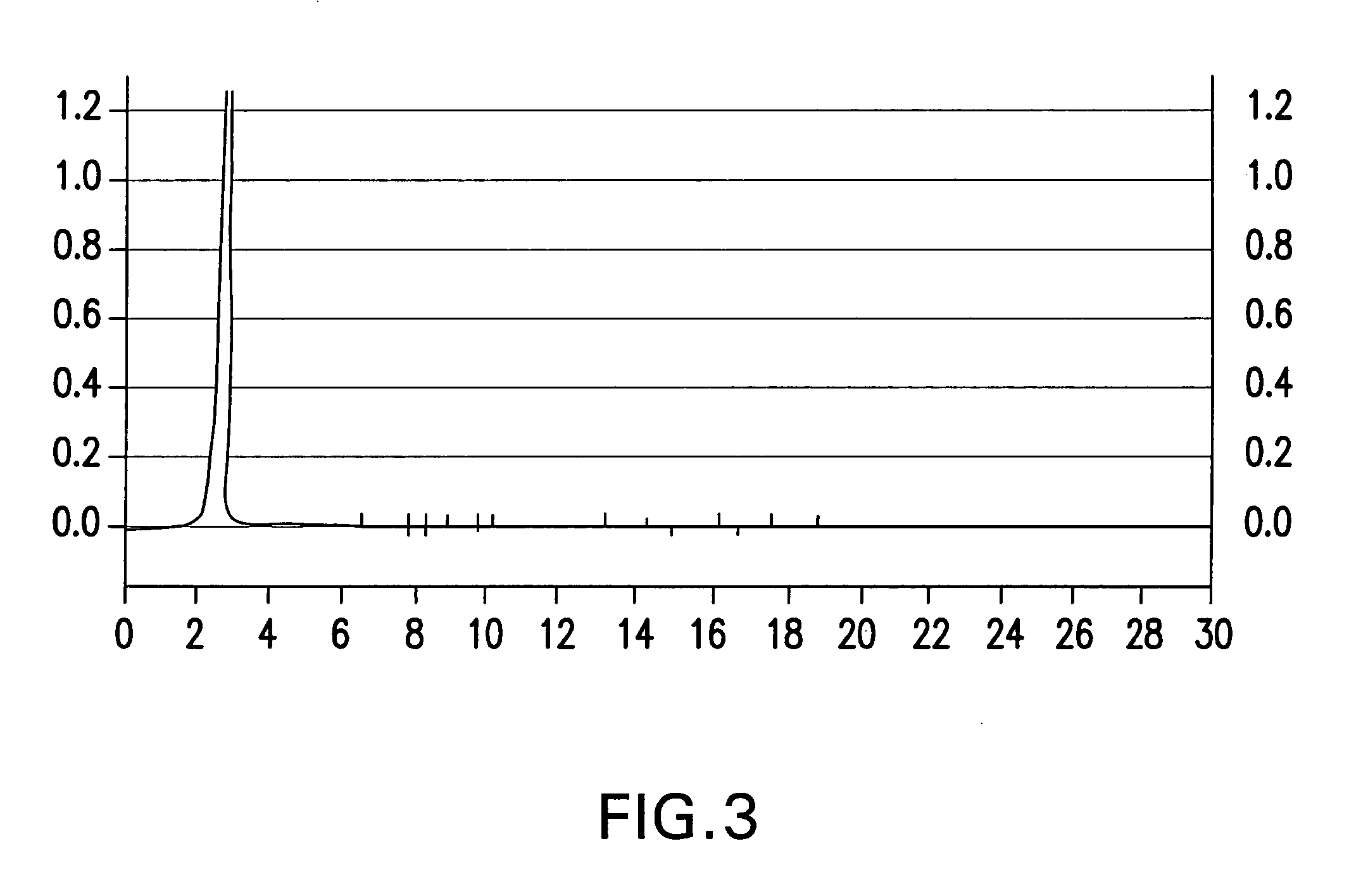
Irreversibly-inactivated pepsinogen fragment and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same for detecting, preventing, and treating HIV
An isolated antiviral peptide is characterized by the amino acid sequence GDEPLENYLDTEYF and a significant in vitro binding affinity for HIV-1 gp 120 and gp 41, and human CD4 cells. The peptide exhibits anti-retroviral activity in vivo, particularly anti-HIV-1 activity.
Owner:ZHABILOV TRUST THE
Method for superfine grinding of bamboo shoot dietary fibers
ActiveCN107173818AIncrease soluble dietary fiber contentStrong featuresFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentNitriteCholesterol
The invention discloses a method for superfine grinding of bamboo shoot dietary fibers. The method comprises the steps of preparing high-quality dietary fibers (compound enzyme enzymolysis process) and performing superfine grinding treatment. The condition for preparing the dietary fibers according to the compound enzyme enzymolysis process is mild, the extracted dietary fibers are high in biological activity, and meanwhile, the content of the soluble dietary fibers is increased to that of high-quality dietary fibers. The dietary fibers acquired according to an air jetting milling method have the grain size of 8.87mu m and the specific surface area of 1.29m<2> / g. The capacities of the bamboo shoot dietary fibers after superfine grinding for in-vitro binding with cholesterol, sodium cholate and nitrite are obviously enhanced and are respectively 11.95mg / g, 141.87mg / g and 1716.78mu g / g. The air jetting milling not only can obviously reduce the grain size of the bamboo shoot dietary fibers and can solve the problem of rough taste of the dietary fibers but also can increase the content of the soluble dietary fibers and can enhance the functional character of the dietary fibers, so that the air jetting milling is the optimal manner for the superfine grinding of the bamboo shoots at present.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Humanized Anti-cea t84.66 antibody and uses thereof
ActiveUS20080069816A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCarcinoembryonic Antigen PositiveIntravenous gammaglobulin
Embodiments of the present invention utilize a more efficient CDR grafting technique to generate humanized versions of the T84.66 antibody. The technique used to generate these antibodies utilizes crystallographic structural data to select an immunoglobulin framework having maximum structural overlap with a non-human donor molecule. This technique was used to develop humanized T84.66 antibodies exhibiting in vitro binding affinity and specificity for carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) nearly identical to that of T84.66 and the ability to specifically target tumors expressing CEA in vivo.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
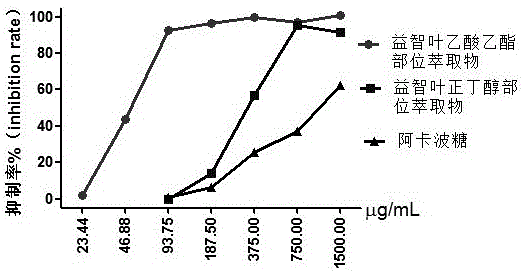
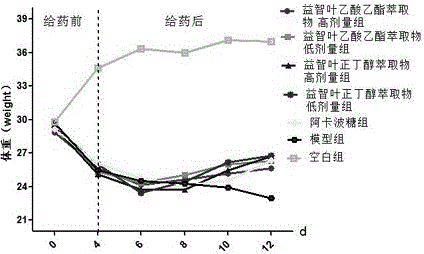
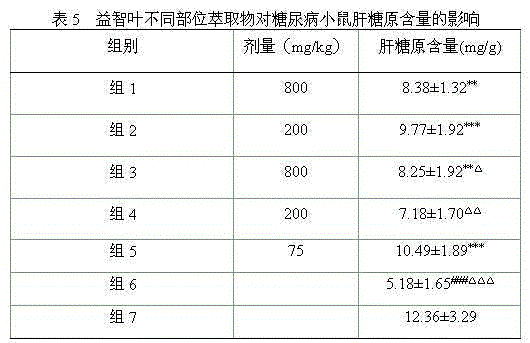
Alpinia oxyphylla leaf extract and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant extraction and particularly relates to alpinia oxyphylla leaf extract and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the alpinia oxyphylla leaf extract includes: taking alpinia oxyphylla leaves, adding ethanol, heating for extraction, and concentrating and drying extracted liquid to obtain ethanol total extract; dispersing the ethanol total extract into water, sequentially using petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and n-butanol for extraction, and volatizing solvent of each extract to respectively obtain petroleum ether part extract, ethyl acetate part extract and n-butanol part extract. In vitro and in vivo experiments show that the alpinia oxyphylla leaf extract has certain hypoglycemic effect in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
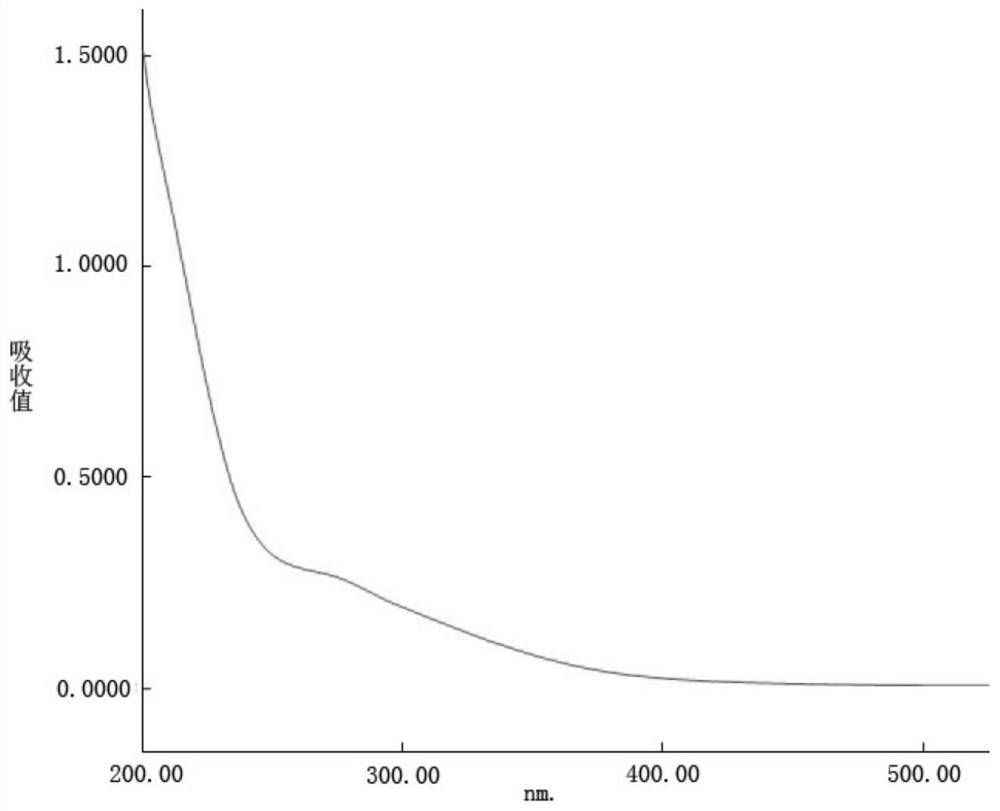
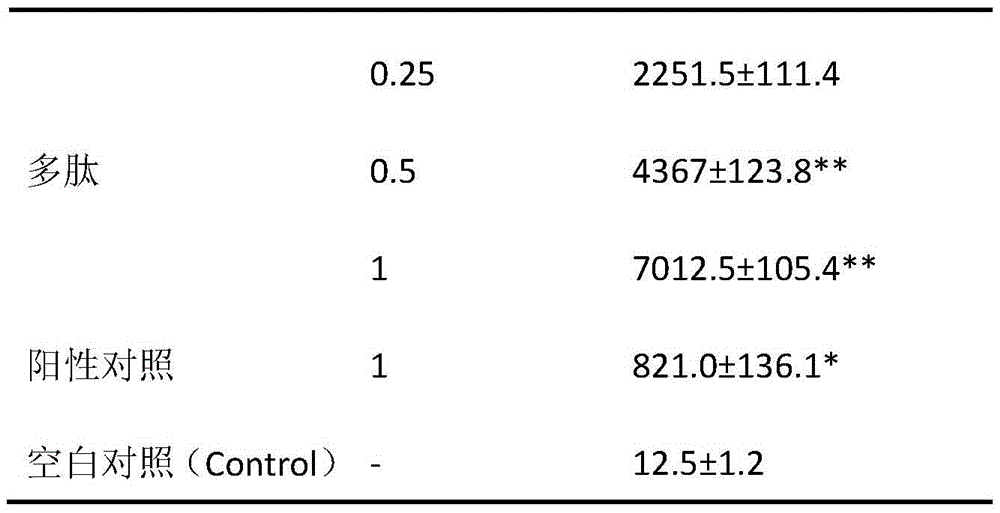
[18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same
InactiveCN105530961AIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsAntipyreticDiseaseRadioactive tracer
The present invention relates to an [18F]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, a synthesis thereof, and a method for evaluating biological results using the same. In the present invention, a fluoromethyl group-introduced fluorine-18 labeled radiotracer was prepared by introducing [18F]fluoroiodomethane, in which a prosthetic group diiodomethane is labeled with fluorine-18, into PBR28-OH through two stages, or substituting fluorine-18 using a triazolium triflate precursor in one stage at high yield. It was confirmed that, as a result of comparison and evaluation with exiting known [11C]PBR28 in view of in vitro binding affinity, fat affinity, and pharmacodynamic characteristics in a brain neuroinflammation model, the fluoromethyl group-introduced fluorine-18 labeled radiotracer had similar binding affinity and fat affinity to [11C]PBR28. Further, it was confirmed from the PET image comparison and evaluation in the brain neuroinflammation model that the fluoromethyl group-introduced fluorine-18 labeled radiotracer exhibited excellent selective / specific absorption in the inflammatory region more quickly and had high stability at the brain neuroinflammation site. According to the present invention, with respect to the synthesis of the novel fluoromethyl group-introduced fluorine-18 labeled radiotracer for PET targeting brain neuroinflammation and the diagnosis of brain neuroinflammation diseases, fluorine-18 having a relatively longer half-life than [11C]PBR28 was capable of being excellently labeled through the minimum structural change, and its excellent selective and specific imaging and pharmacodynamic advantages were verified, and thus a useful radiotracer for PET targeting brain neuroinflammation can be expected.
Owner:BIO IMAGING KOREA
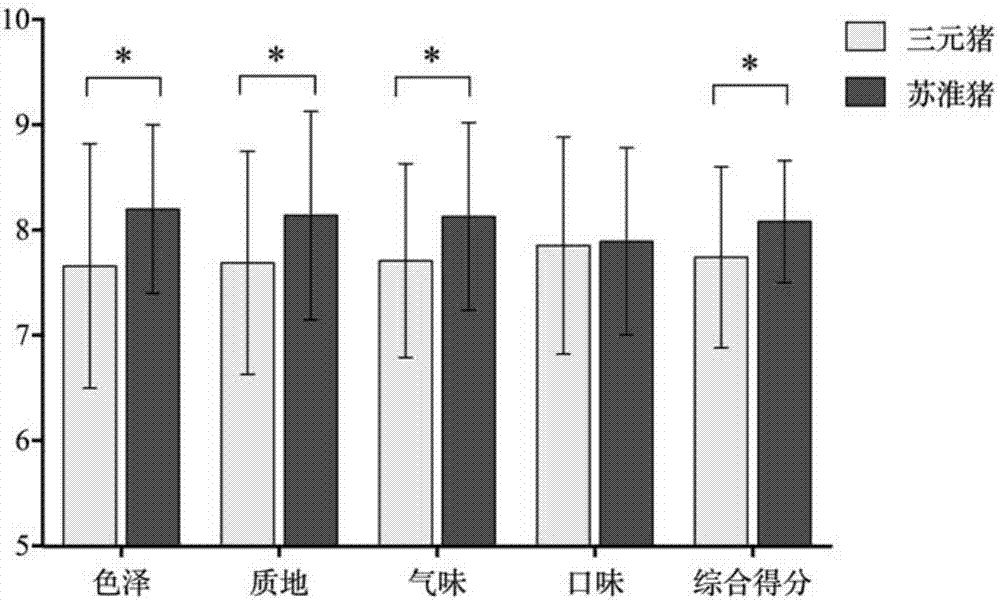
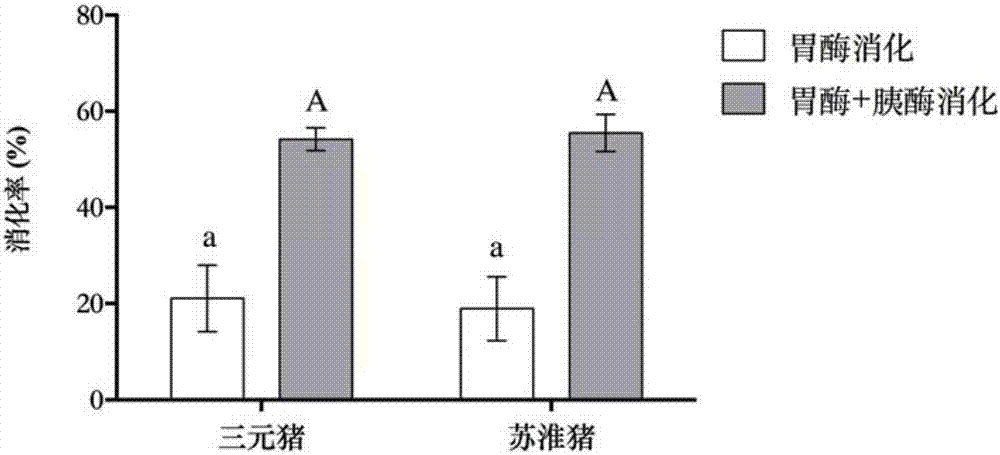
Method for making steamed pork belly with preserved greens by taking streaky pork of Suhuai pigs as raw material
ActiveCN107529414AGuaranteed nutritional qualityGuaranteed Flavor QualityFood scienceIn vitro digestionSolid-phase microextraction
The invention relates to the technical field of processing of meat products and in particular relates to a method for making steamed pork belly with preserved greens by taking streaky pork of Suhuai pigs as a raw material. The processing method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: taking streaky pork of Suhuai pigs and Shaoxing preserved vegetables as raw materials, cutting, coloring and slicing the streaky pork, cleaning and frying the preserved vegetables, blending juice, steaming, packaging, pre-cooling, quick-freezing and the like, thereby obtaining the steamed pork belly with preserved greens. Digestion conditions of foods in the in-vivo gastrointestinal tract are simulated by utilizing an in-vitro digestion model, and the bioavailability of the foods is reflectedby the food digestion degree. Moreover, flavor is an important index of sensory quality of foods and directly influences selections of consumers. The raw material selection is a basis of meat productprocessing. According to the process disclosed by the invention, the raw material varieties are subjected to process optimization by combining in-vitro digestion, headspace solid-phase micro-extraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and sensory evaluation. The invention aims to produce standardized steamed pork belly with preserved greens with excellent sensory quality and nutritional quality, and the requirements of consumers on food safety, health, convenience and rapidness are met.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Humanized anti-CEA T84.66 antibody and uses thereof
ActiveUS7273608B2In-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCarcinoembryonic Antigen PositiveIntravenous gammaglobulin
Embodiments of the present invention utilize a more efficient CDR grafting technique to generate humanized versions of the T84.66 antibody. The technique used to generate these antibodies utilizes crystallographic structural data to select an immunoglobulin framework having maximum structural overlap with a non-human donor molecule. This technique was used to develop humanized T84.66 antibodies exhibiting in vitro binding affinity and specificity for carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) nearly identical to that of T84.66 and the ability to specifically target tumors expressing CEA in vivo.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
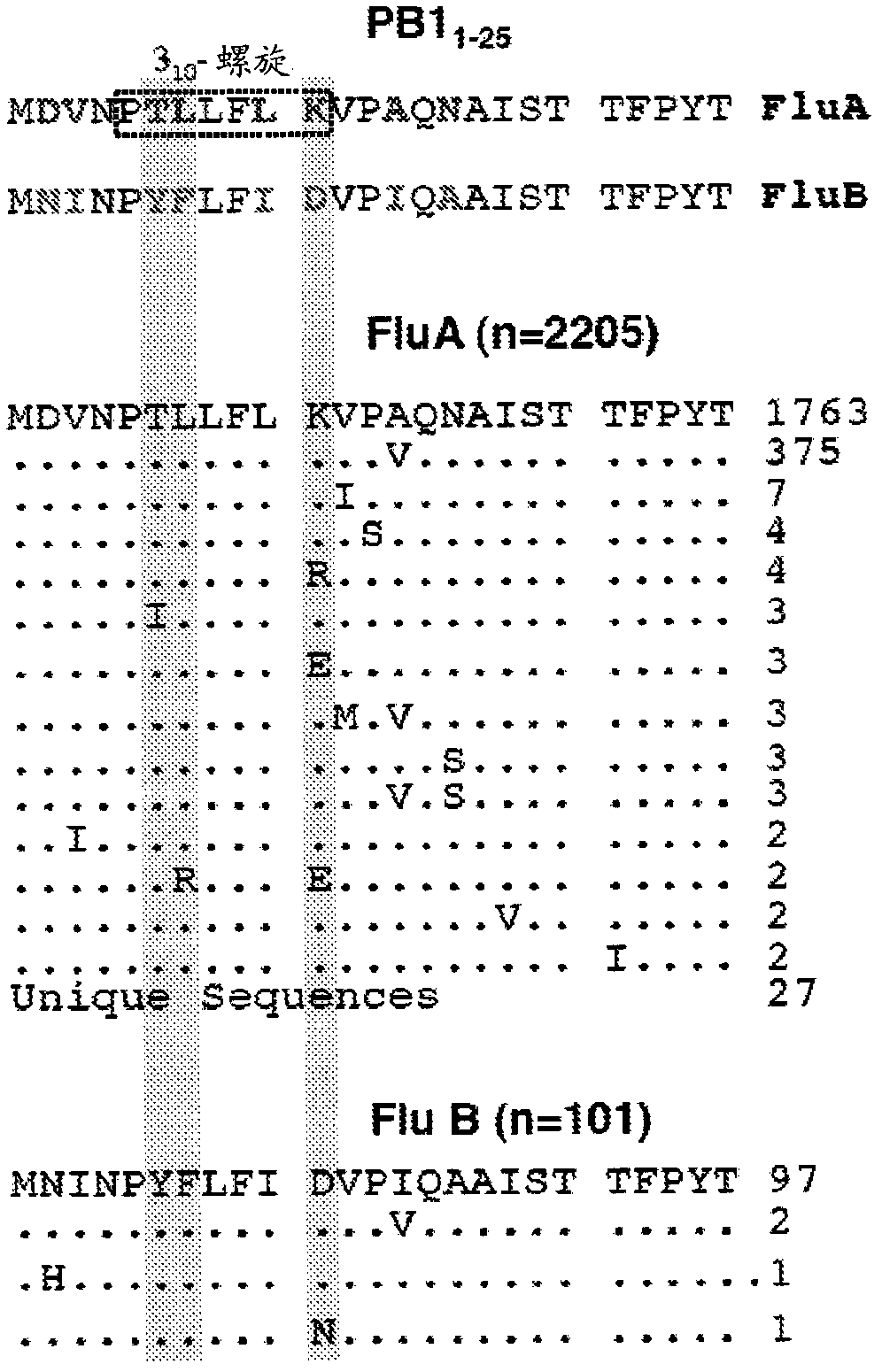
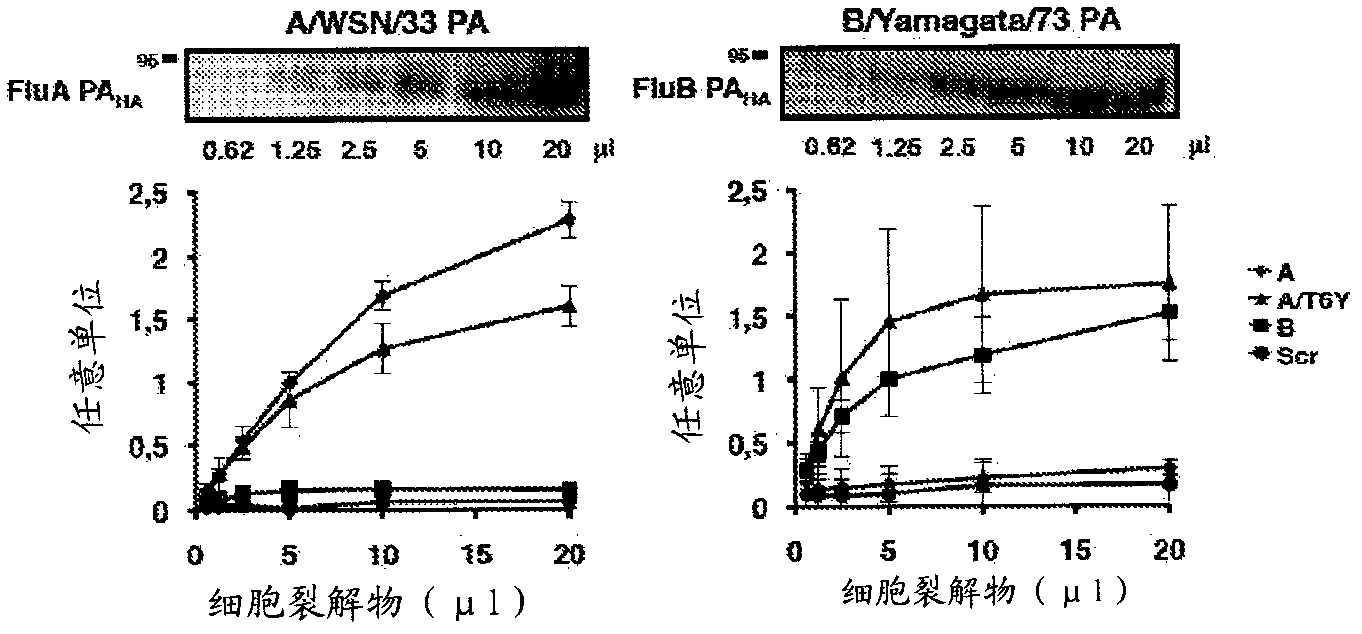
Influenza a and b virus replication-inhibiting peptides
A synthesized or isolated influenza virus replication-inhibiting peptide that competitively inhibits protein-protein interaction of the PA and PB1 of both influenza Virus Types A and B and novel in vitro binding screen to identify peptides with antiviral activity against influenza viruses of both type A and B is disclosed. In addition to the well-known pandemic influenza A viruses (such as the 1918 ''Spanish'' flu or H5N1), both type A and B viruses contribute greatly to the annual recurring epidemics that cause the vast majority of human cases and medical cost. Surprisingly, it was found that the novel virus replication-inhibiting, are able to inhibit protein-protein interaction of the PA and PB1 subunits of the heterotrimeric viral RNA polymerase complex of both influenza virus types A and B. The viral polymerase sub- unit interaction domain turned out as an effective target for the new antivirals, as correct assembly of the three viral polymerase subunits PB1, PB2 and PA is required for viral RNA synthesis and infectivity.
Owner:PIKE PHARMA
Preparation method of electrochemical sensor for chloramphenicol content detection
ActiveCN111398394AQuick responseImprove signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical biosensorSignalling molecules
The invention relates to a preparation method of an electrochemical sensor for chloramphenicol content detection. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using a metal nitrate compound as a raw material to prepare a metal organic framework material A; synthesizing an organic framework material B by using a hydrothermal synthesis method; preparing a metal organic framework material B / nucleic acid aptamer signal probe chain by using a crosslinking method; and preparing a gold nanoparticle / functionalized metal organic framework material A gold electrode by using an electrochemical deposition method. In vitro binding arched DNA structures, the content of chloramphenicol in the sample is indicated by increasing a signal molecule response signal carried by a signal molecule labeledmetal organic framework material B / nucleic acid aptamer signal probe chain and the electrochemical sensor for chloramphenicol content detection is obtained; compared with other methods for chloramphenicol content detection, the prepared novel electrochemical sensor is high in response speed, high in signal-to-noise ratio, high in sensitivity, good in repeatability and high in accuracy.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
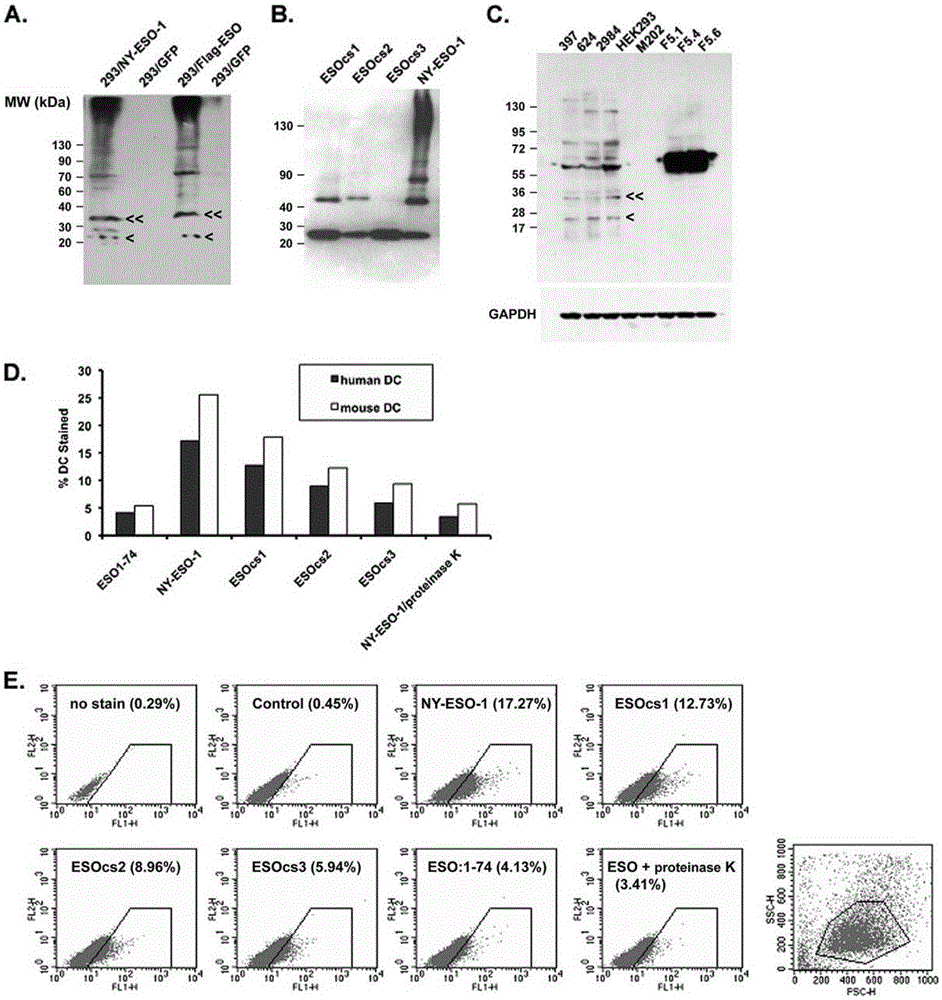
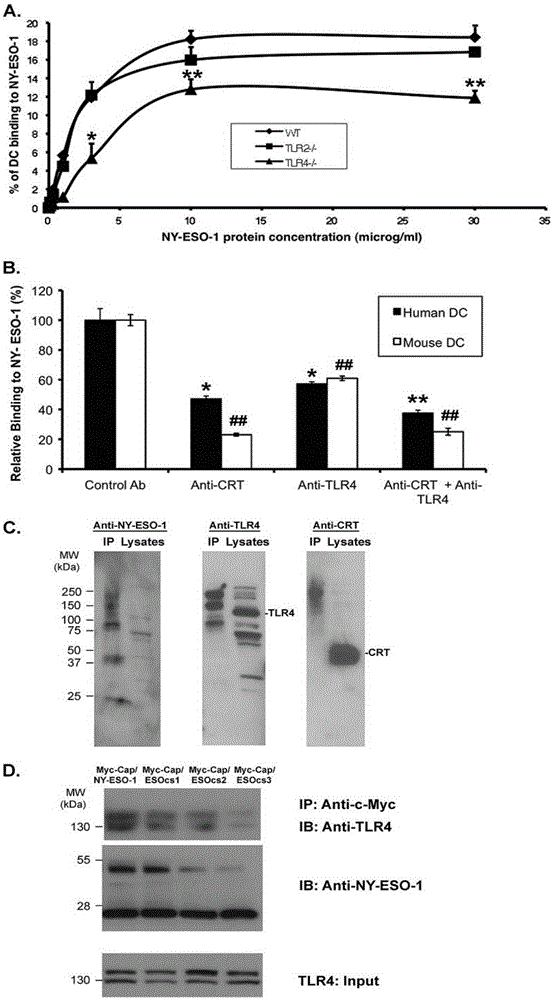
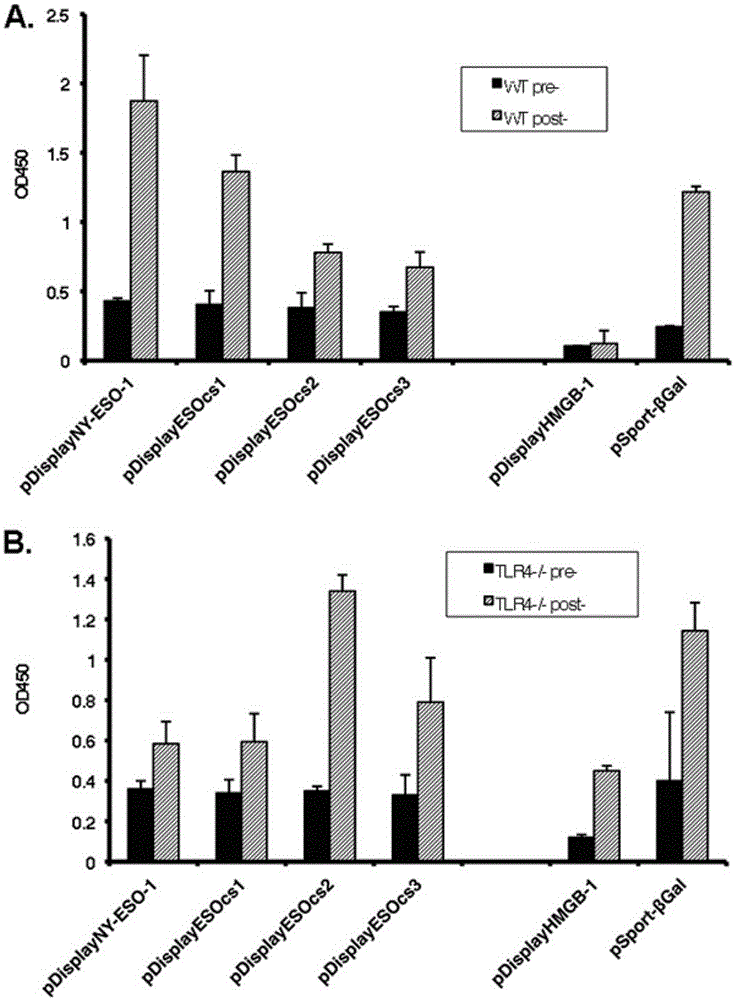
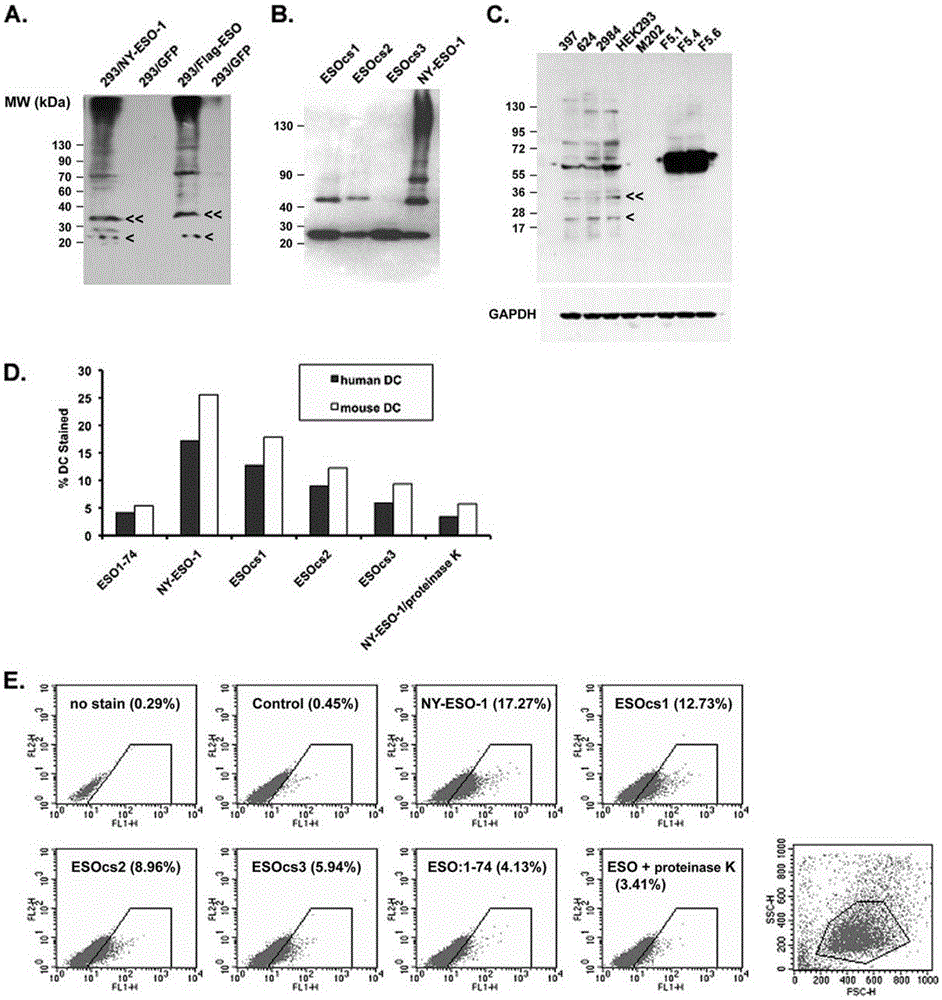
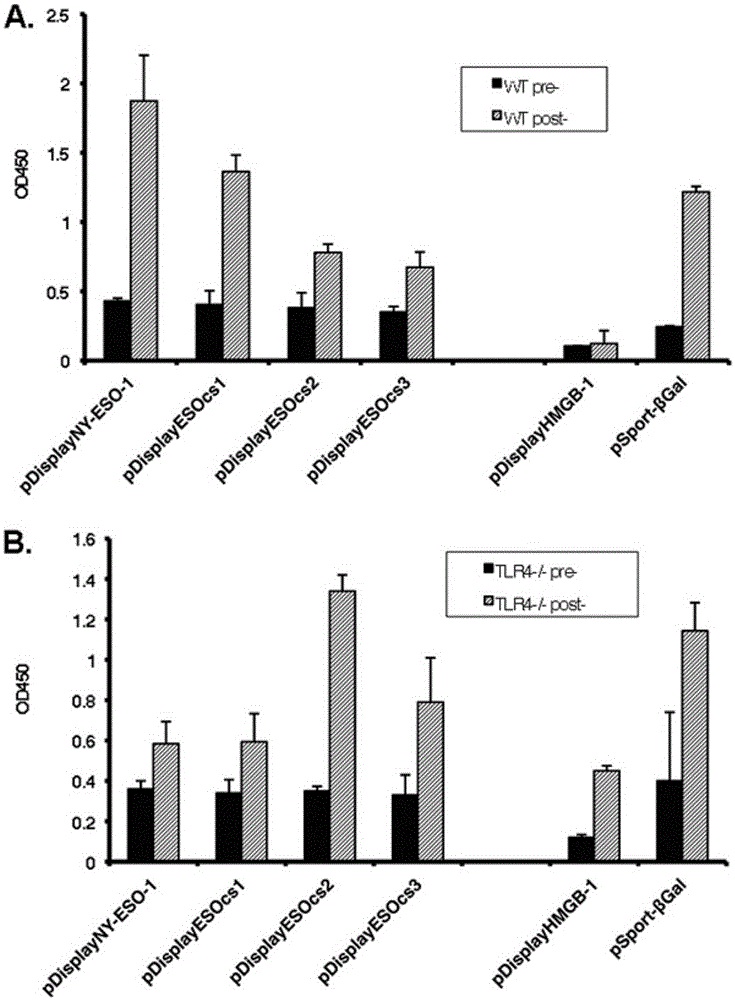
Applications of NY-ESO-1 as molecule adjuvant in enhancement of Art v1 (wtArt) allergen immune reaction
The present invention relates to the field of biomedicine, particularly to applications of NY-ESO-1 as a molecule adjuvant in enhancement of an Art v1 (wtArt) allergen immune reaction. According to the present invention, it is explored that the NY-ESO-1 protein can form a poly-structure even in a loading buffer containing beta-mercaptoethanol having a conventional concentration, the polymerization reaction of the NY-ESO-1 is mediated by the intermolecular disulfide bond, the binding of the NY-ESO-1 and the human / murine immature dendritic cells in vitro is related to the polymerization structure of the NY-ESO-1, TLR4 affects the in vitro binding of the NY-ESO-1 and the DC cells in bone marrow, the binding of the NY-ESO-1 and the human / murine immature dendritic cells can be performed through the action of calreticulin, the polymer oligomerization reduces the binding of TLR4 and NY-ESO-1, the polymer structure of the NY-ESO-1 and TLR4 in host participate into an immunoglobulin antibody reaction, and the improving of the art V1 (wtArt) and CA9 gene immunogenicity depends on the NY-ESO-1 gene fusion expression; and the test results prove that the NY-ESO-1 can be adopted as the molecule adjuvant in enhancement of the Art v1 (wtArt) allergen immune reaction.
Owner:宁波美丽人生医药生物科技发展有限公司
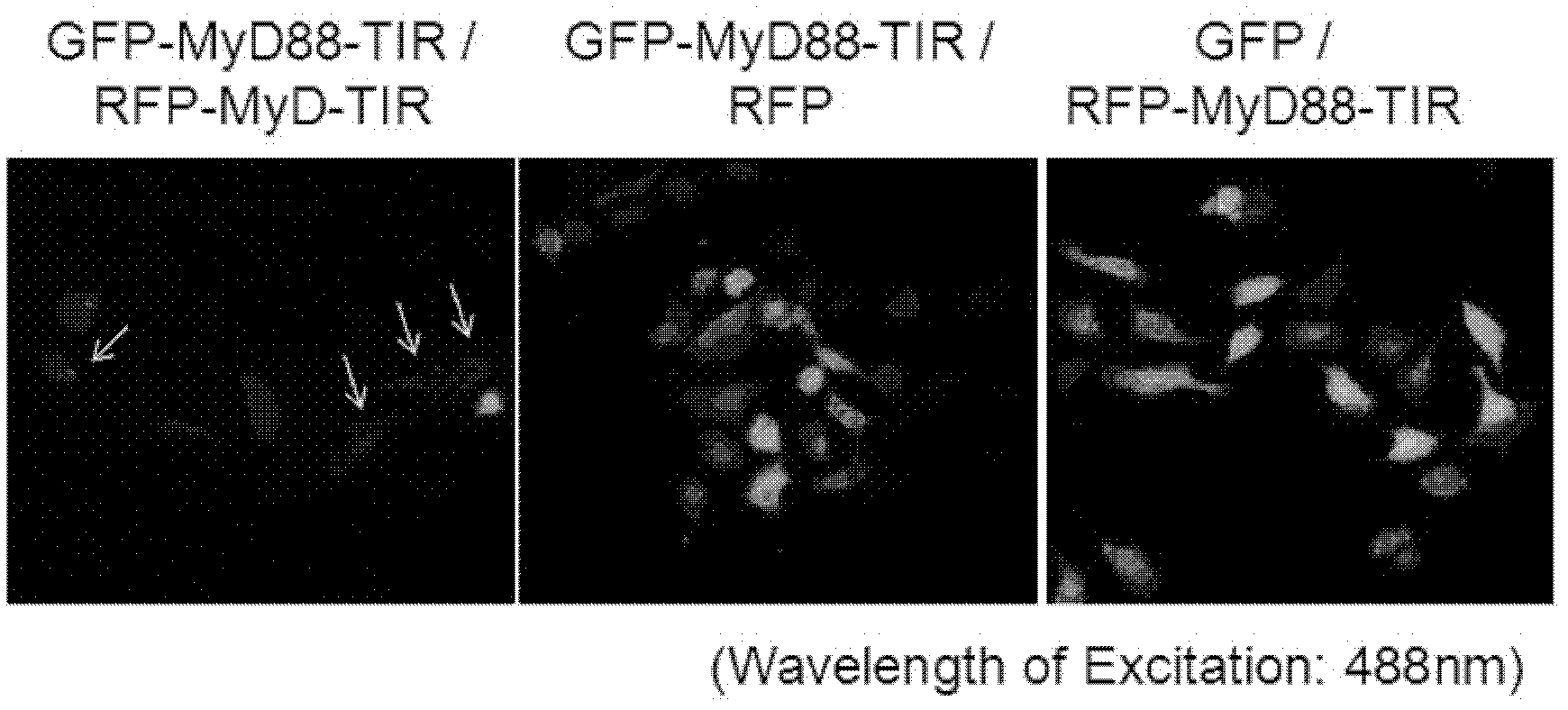
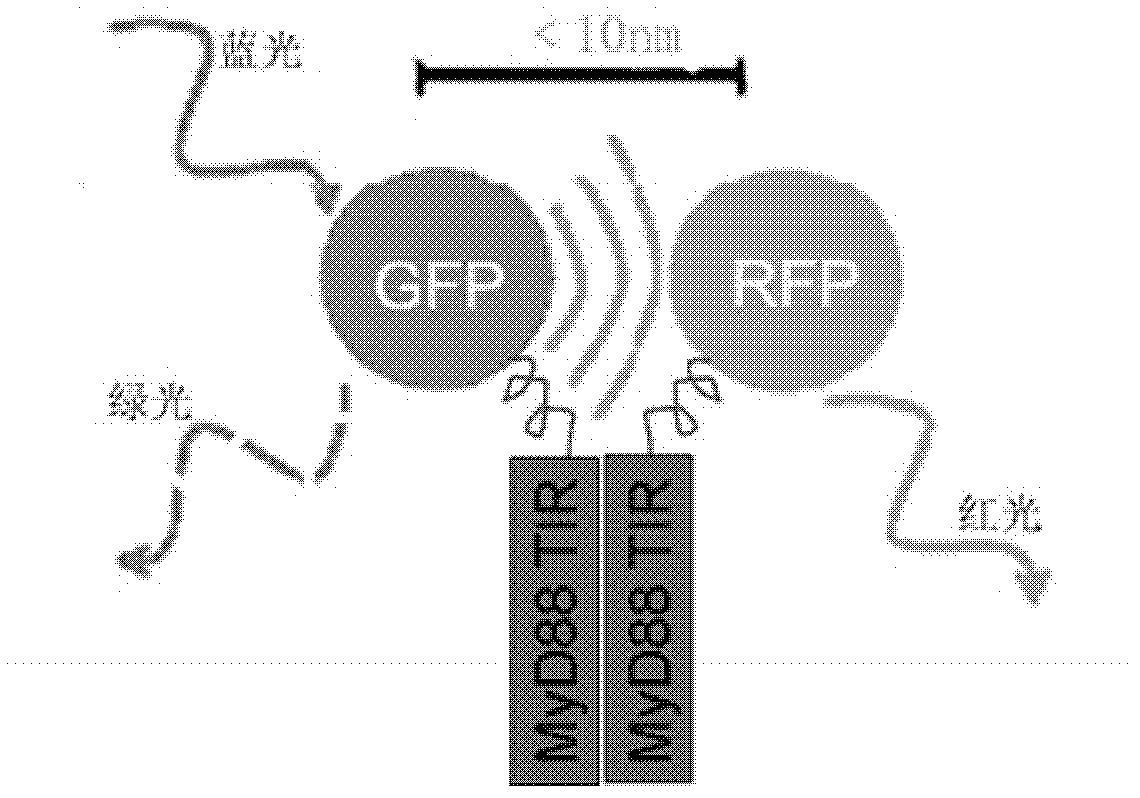
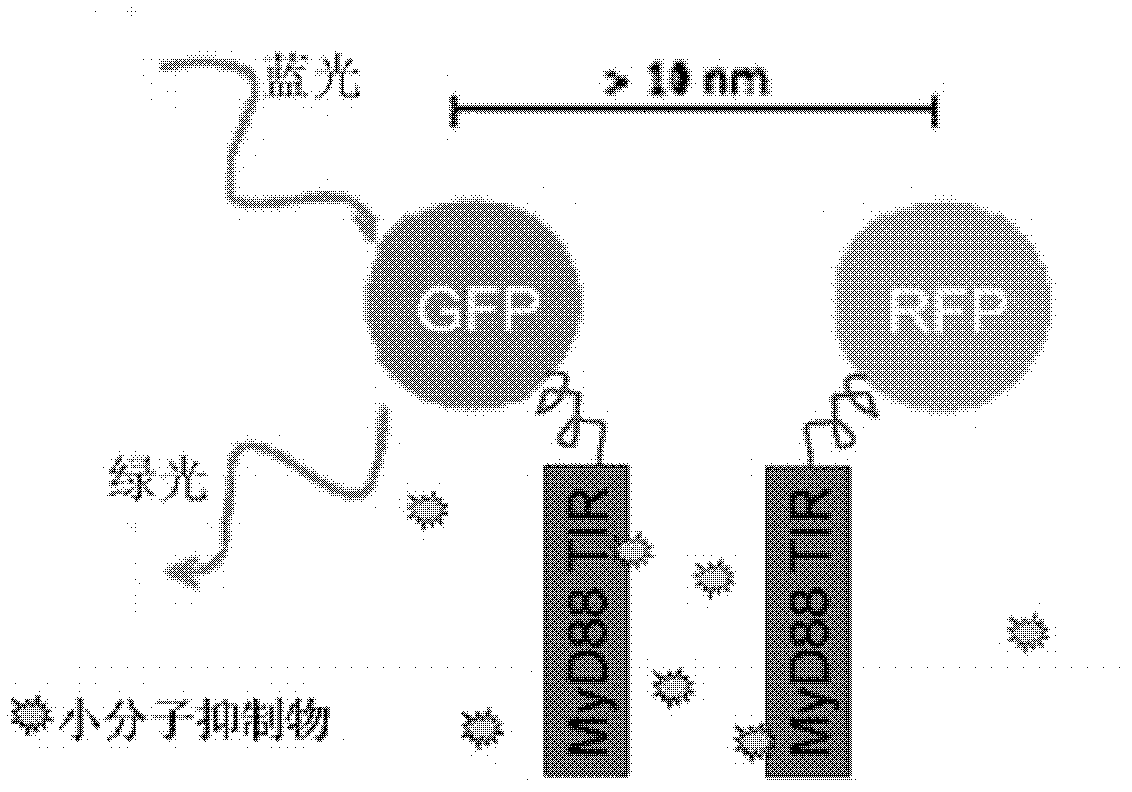
Anti-inflammatory inhibitor screening model taking MyD88TIR (myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 Toll/interleukin-1 receptor) dimerization as target point and application thereof
InactiveCN102321586AImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical synthesisDisease
The invention relates to an anti-inflammatory inhibitor screening model taking MyD88TIR (myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 Toll / interleukin-1 receptor) dimerization as a target point and application thereof. The anti-inflammatory inhibitor screening model taking the MyD88TIR dimerization as the target point is characterized in that: an MyD88TIR builds fusion protein plasmids together with protein genes GFP / RFP (Green fluorescent protein / Red fluorescent protein) of a fluorescence donor and a fluorescent receptor, and the fusion protein plasmids are transfected into mammalian cells to build dual-positive expression cell strains; the FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) phenomenon can be detected; when an MyD88TIR dimerization inhibitor exists in a culture medium, the cell strains which depend on dual-positive to express GFP-MyD88-TIR and RFP-MyD88-TIR are suggested, and whether the inhibitor directly blocks the interaction of the TIRs or not can be further determined according to in vitro binding analysis; and combined with the fluorescent FRET blocking results of eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic expression recombinant protein interaction analysis, the MyD88TIR dimerization inhibitor can be determined. The model can be used for widely screening commercialized small molecule libraries, self-prepared natural product components, or various chemical compounds, and modifiers, from which MyD88 dimerization inhibitory compounds are obtained to participate in the drug screening of MyD88 signal pathway-dependent chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
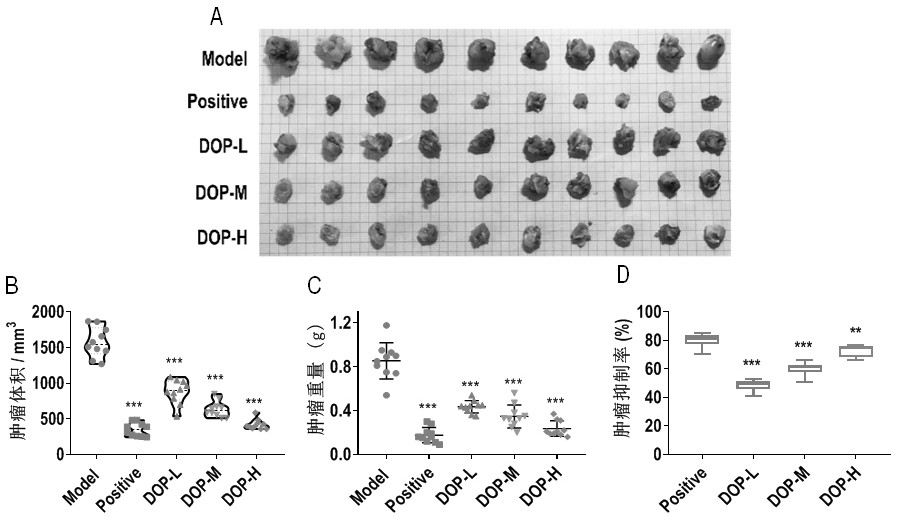
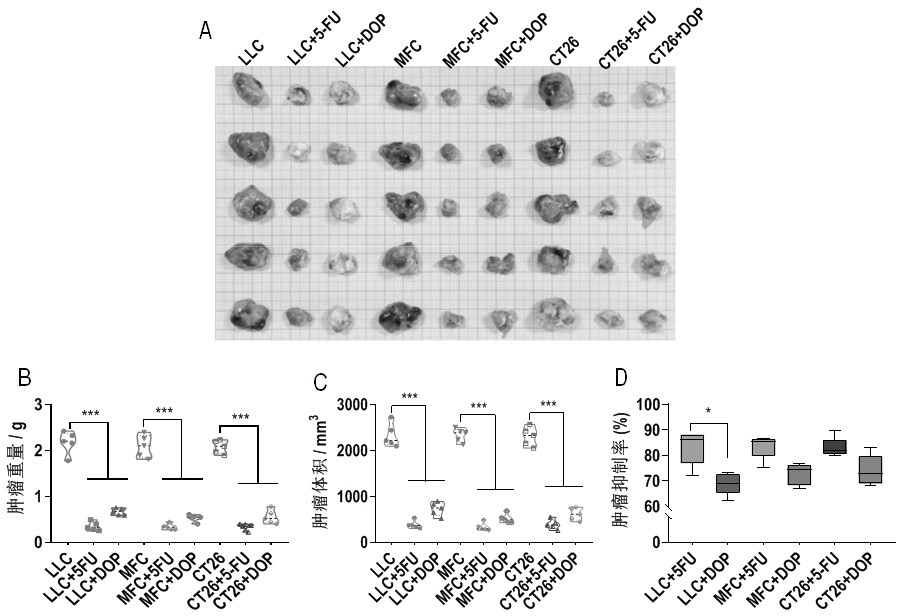
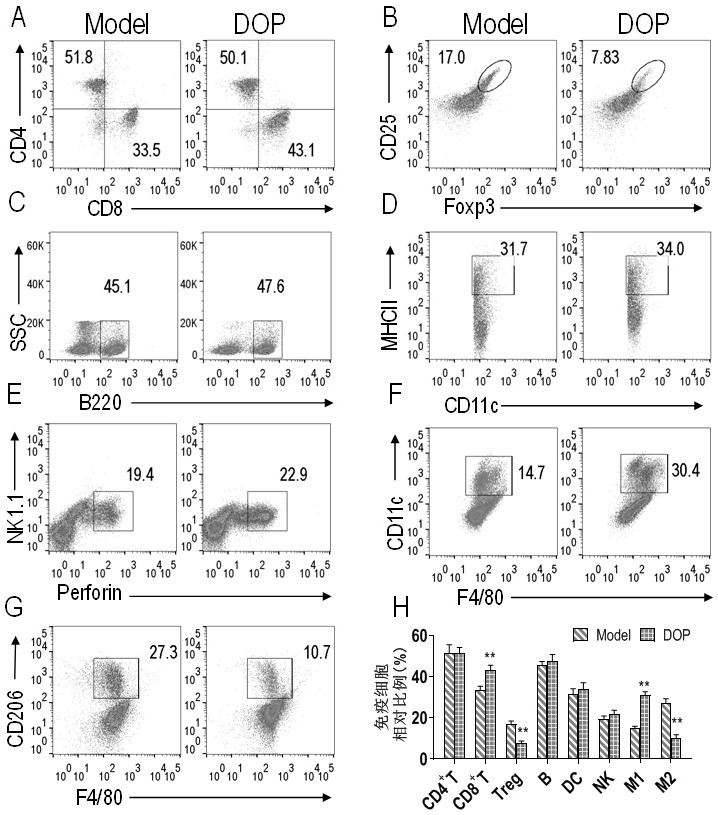
Application of dendrobium officinale polysaccharide in preparation of drug for treating tumors by targeting tumor-associated macrophages
InactiveCN112138018ACan exert anti-tumor effectPromote conversionOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsReceptorCD8
The invention relates to an application of dendrobium officinale polysaccharide in preparation of a drug for treating tumors by targeting tumor-associated macrophages, and belongs to the technical field of botanical drugs. Through the combination of in-vitro and in-vivo experiments, it is found for the first time that the dendrobium officinale polysaccharide can recognize TLR2 receptors on the surfaces of tumor-associated macrophage membranes in a targeted manner, the TAMs are induced to be polarized from M2 type to M1 type through mediation of the TLR2 receptors, then the tumor killing activity of CD8+T cells is promoted, immune escape generated by Tregs is inhibited, and therefore an anti-tumor effect is achieved synergistically. The application of the dendrobium officinale polysaccharide as the anti-tumor drug is developed, and a new possibility is provided for treating tumors by targeting the TAMs.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
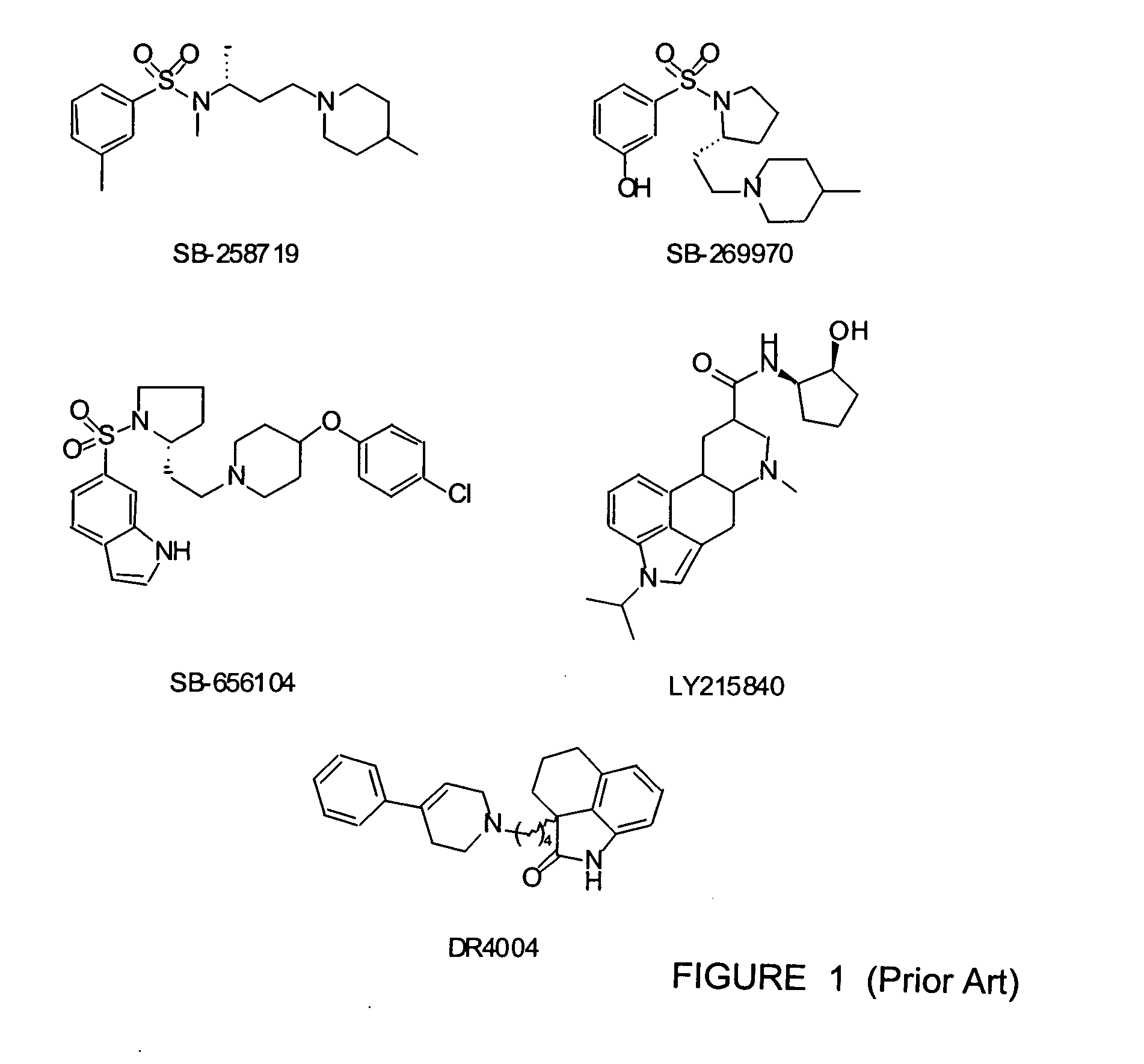
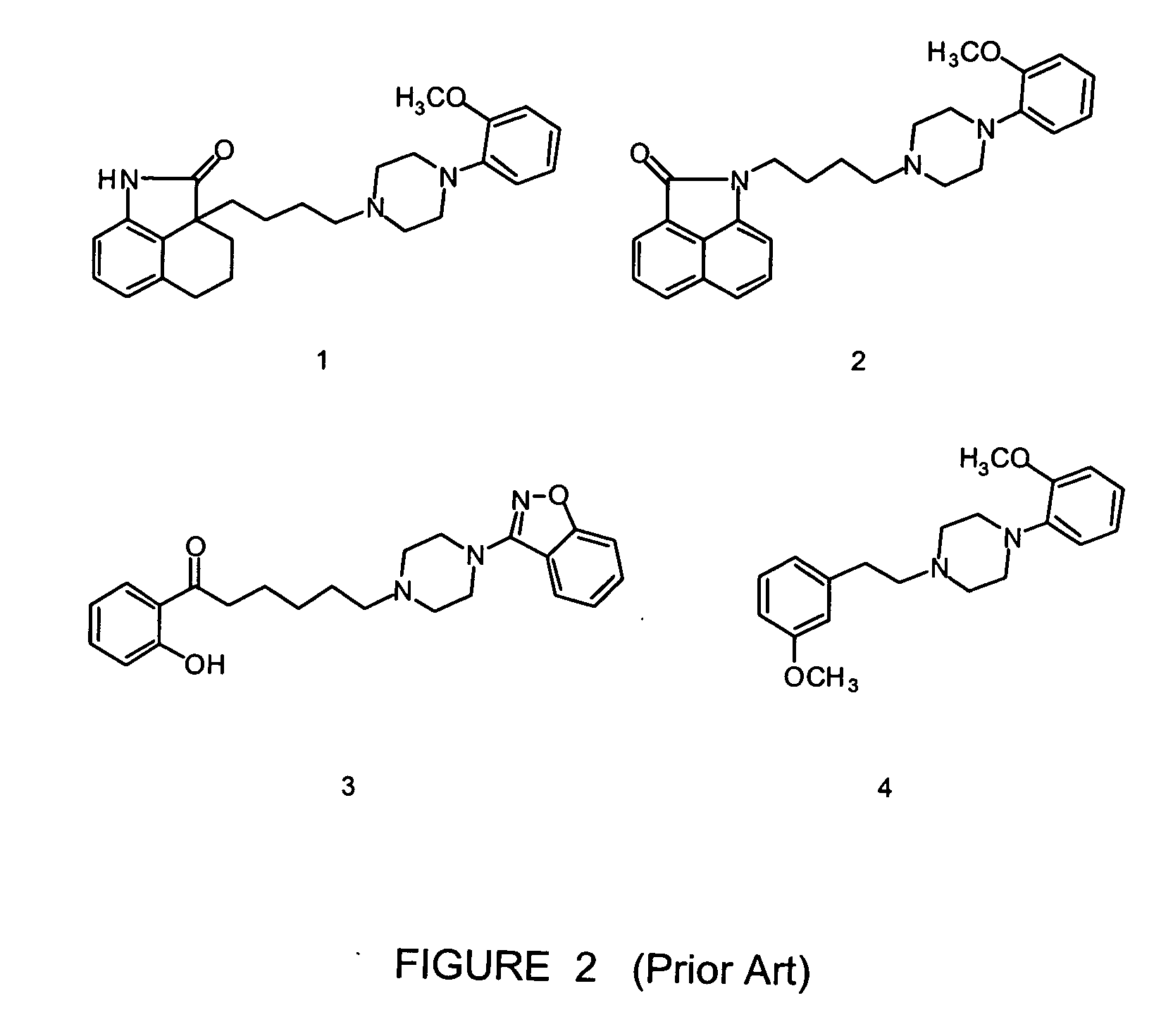
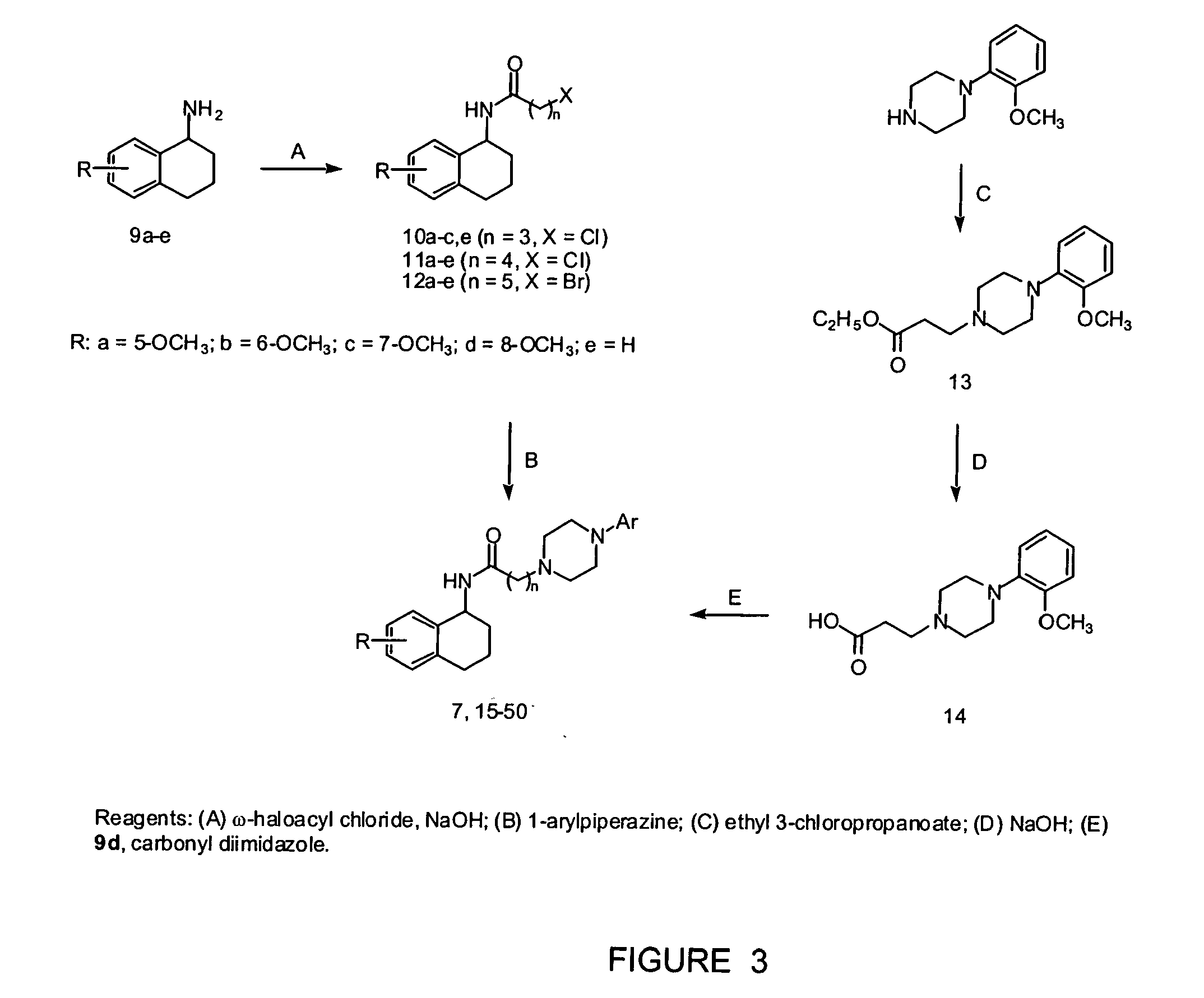
N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-4-phenyl-1-piperazinealkylamide derivatives, and therapeutic use thereof as 5-HT7 receptor ligands
A series of N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-4-aryl-1-piperazinealkylamides was prepared and their affinity for serotonin 5-HT7, 5-HT1A, and 5-HT2A receptors was measured using in vitro binding assays. In relation to 5-HT7 receptor affinity, receptor binding studies indicated that: (i) the optimal alkyl chain length was five methylenes; (ii) an unsubstituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalenyl nucleus was selected for further substitutions; and (iii) the substitution pattern of the aryl ring linked to the piperazine ring played a significant role. Several compound with high affinity for 5-HT7 receptors were identified. Among them, 4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-piperazinehexanamide (28), 4-(2-acetylphenyl)-N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-piperazinehexanamide (34), 4-(2-methylthiophenyl)-N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-piperazinehexanamide (44), 4-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-piperazinehexanamide (46), 4-(2-methylphenyl)-N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-piperazinehexanamide (49) were assayed for the 5-HT7 receptor mediated relaxation of substance P-induced guinea-pig ileum contraction. Compounds 28, 44, and 49 behaved as full agonists, compound 34 as a partial agonist, whereas derivative 46 acted as an antagonist.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI BARI
Tumor immune response enhancing complex
InactiveCN106963940AGrowth inhibitionImprove inhibitory functionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor-specific antigenCell growth
The invention discloses a tumor immune response enhancing complex. The tumor immune response enhancing complex is formed through in vitro binding of tumor cell peptides, salmon ovarian peptides and heat shock protein 70, wherein the tumor cell peptides are peptides obtained from tumor cells and contain tumor specific antigen peptides. The tumor immune response enhancing complex can inhibit growth of tumor cells and meanwhile eliminate tumor necrosis factors, thereby greatly enhancing the function of inhibiting tumor growth.
Owner:JIANGSU FOOD & PHARMA SCI COLLEGE
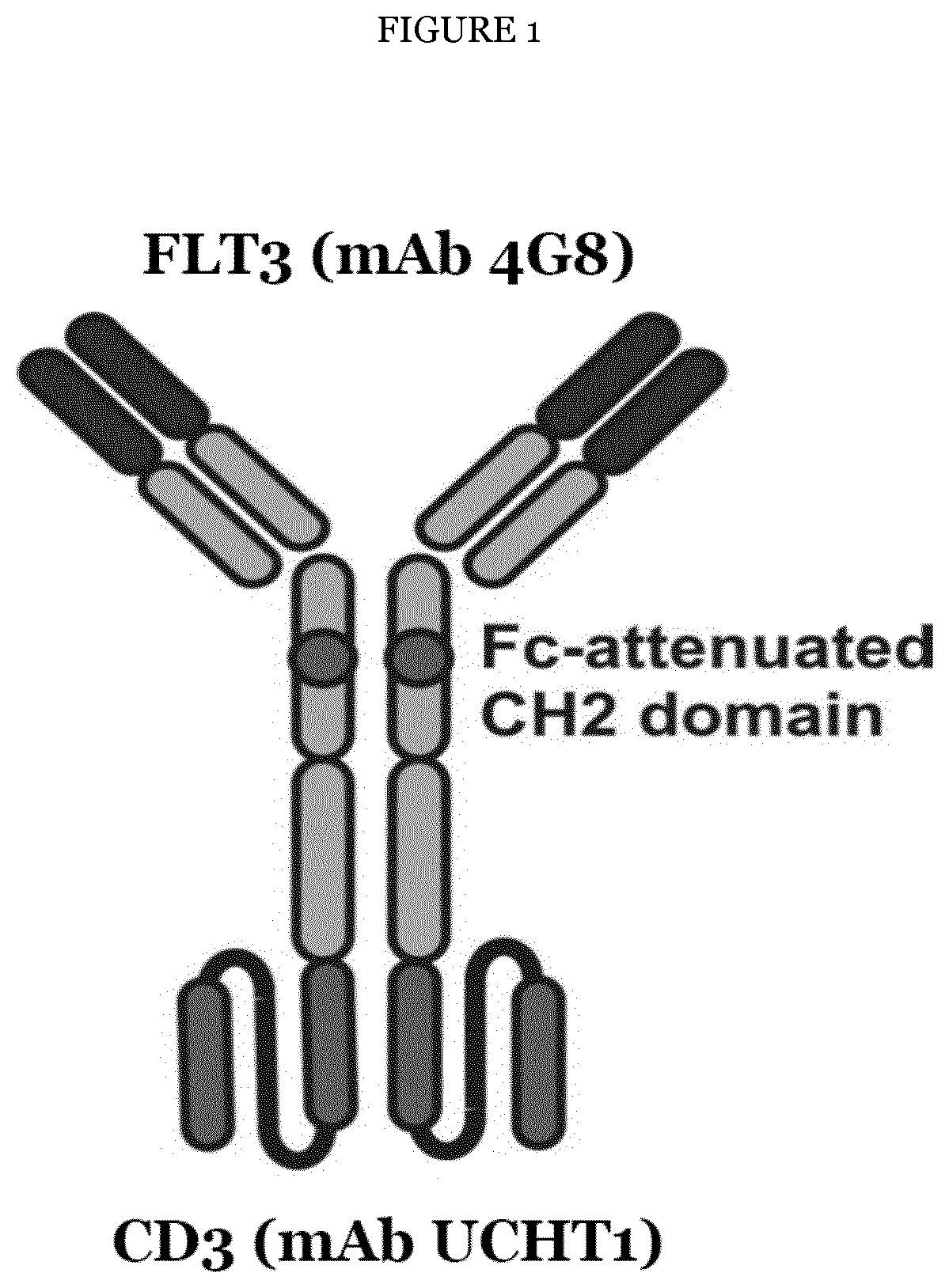
Improved Anti-FLT3 Antigen Binding Proteins
PendingUS20220056141A1Effective destructionEnhancing anti-tumor potencyHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesTyrosine
The present invention provides novel human fins related tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) antigen binding proteins, such as antibodies, having improved FLT3 binding affinity, and / or anti-tumor activity. The FLT3 antibodies of the invention were generated by mutation of a parent FLT3 antibody and tested in in vitro in binding assays as well as in vivo in a mouse tumor model and in human patient tumor samples. The antibodies of the invention are provided as monospecific constructs or in a bispecific FLT3×CD3 antibody format and show excellent target affinity and / or tumor cell killing. The present invention also relates methods for producing the antigen binding proteins of the invention as well as nucleic acids encoding them, vectors for and host cells for their expression. The invention further relates to methods of treating or diagnosing a disease such as leukemia using an FLT3 antigen binding protein (ABP) of the invention.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS +1
Complex of alpha-fetoprotein and inducers of apoptosis for the treatment of cancer
The invention relates to a composition comprising exogenous alpha-fetoprotein, a first compound reversibly bound to exogenous alpha-fetoprotein in vitro, and an unbound second compound wherein the first and second compound are anticancer drugs or combinations of anticancer drugs and wherein the second compound reversibly binds to recycled exogenous alpha-fetoprotein in vivo. A process for the butanol extraction of alpha-fetoprotein obtained from porcine blood and amniotic fluid during early embryogenesis and a process for the in vitro binding of alpha-fetoprotein and a first compound are also described. The invention also relates to a method of using these compositions to prevent, treat or inhibit a malignant neoplasm expressing an alpha-fetoprotein receptor.
Owner:PAK VLADIMIR +1
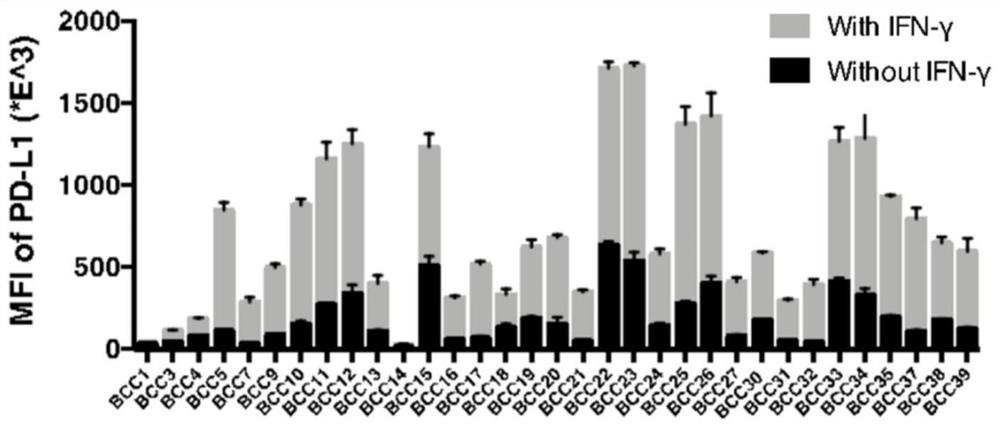
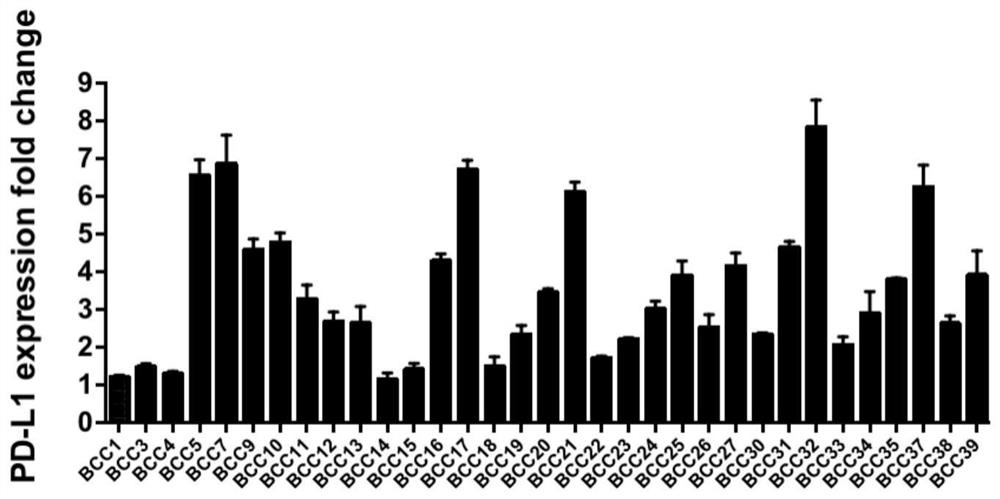
Method for dynamically and accurately detecting immunologic characteristics of primary tumor cells
PendingCN112986579ARealize formulationAchieve guidanceIndividual particle analysisBiological testingCarcinoma bladderOncology
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a method for detecting immunologic characteristics of primary tumor cells. The in-vitro detection method for the immunologic characteristics of the primary tumor cells comprises the following steps: culturing the primary tumor cells from different patient sources, establishing a bladder cancer primary tumor cell bank, detecting the expression level of PD-L1 before and after the primary cell IFN-gamma stimulation through a high-throughput flow detection platform, incubating the primary cells and the recombinant human PD-1-Fc chimeric protein, and detecting the binding capacity of the primary cells to the PD-1 protein. The immunotherapy effect of the corresponding patient is predicted in combination with the series of indexes. According to the invention, a convenient primary cell culture method and a high-throughput flow detection platform are utilized, and the individual prognosis evaluation of the in-vitro platform on cancer patients is realized by dynamically, quickly, accurately and quantitatively detecting the immune-related protein expression level and the in-vitro binding capacity of primary tumor cells.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and application of heterologous high expression of dypb active protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and particularly relates to a DypB active protein heterology high expression method and application. Aiming at the problem that existing DypB protein has no activity in hyterology expression and only can generate activity by being combined with heme in vitro, the invention provides the DypB active protein heterology high expression method and application. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of integrating related genes expressing the heme into host cells through genetic recombination to enable a host to have high-concentration heme, then constructing DypB into a recombinant vector and leading the recombinant vector into an expression host with high heme expression; thus, heterology high expression of the DypB active protein can be achieved. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the heme is integrated in the expression host to be synthesized into the related genes to improve the in-vivo accumulation concentration of the heme, then the DypB is expressed a lot through a cold induction mode, and the DypB has activity for degrading lignin after being expressed by the host.
Owner:四川爱奇生物科技有限公司
Construction method for distinguishing model of activity effect of PBDEs derivatives on enoyl-ACP reductase
ActiveCN112233730AAccurate calculation of activity effectsChemical property predictionHydrolasesReceptorReductase
The invention discloses a construction method for distinguishing a model of the activity effect of PBDEs derivatives on enoyl-ACP reductase. The construction method comprises the steps of receptor andligand modeling, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. The calculation result of the model is consistent with the result of an in-vitro binding activity determination experiment, and the result shows that the construction method of the model can accurately calculate the activity effect of the PBDEs derivatives on the enoyl-ACP reductase.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
A kind of O-type foot-and-mouth disease ctl epitope peptide and screening method
ActiveCN103864905BConvenient researchImprove bindingSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesCtl epitopeDisease
The invention discloses an O-type foot-and-mouth disease CTL epitope peptide, a screening method and application thereof. The CTL epitope peptide is composed of nine amino acid residues, and its amino acid sequence is: Ala-Thr-Arg-Val-Thr-Glu-? Leu-Leu-Tyr. The epitope peptide can have strong binding ability with SLA-I proteins derived from different strains of pigs and can cause cytotoxic immune response, and is suitable for the preparation of vaccines for the prevention and treatment of various strains of porcine foot-and-mouth disease viruses, and has a wide range of applications. The invention uses the constructed six-strain pig SLA-I single-chain molecule to bind the CTL mimetic epitope peptide of foot-and-mouth disease virus in vitro, mass spectrometry to screen the polypeptide that can bind to the complex, and through ELISPOT detection, it is determined that it can induce T cell immune response Capable mimotope peptides. The invention provides a method for screening and identifying a large number of CTL epitopes of foot-and-mouth disease virus in the future, and lays a foundation for developing a porcine foot-and-mouth disease multi-epitope vaccine.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Calprotectin participating in in-vitro binding of NY-ESO-1 and DC cells in bone marrow
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to calprotectin participating in in-vitro binding of NY-ESO-1 and DC cells in bone marrow. The inventor of the invention explores that the NY-ESO-1 protein can form a polymer structure even in loading buffer with beta-mercaptoethanol with the conventional concentration; the polymerization reaction of the NY-ESO-1 is mediated by intermolecular disulfide bond; binding of the NY-ESO-1 and immature dendritic cells of human and mice in vitro is associated with the polymerization structure of the NY-ESO-1; TLR4 influences the in-vitro binding of the NY-ESO-1 and the DC cells in the bone marrow; the binding of the NY-ESO-1 and the immature dendritic cells of human and the mice in vitro can be realized through the effect of the calprotectin; polymer oligomerization reduces the binding quantity of the TLR4 and the NY-ESO-1; the polymer structure of the NY-ESO-1 and the TLR4 in a host participate in the immuno-sphere antibody reaction; and improvement of Artv1(wtArt) and CA9 gene immunogenicity depends on the NY-ESO-1 gene fusion expression. The invention proves that the calprotectin participates in in-vitro binding of the NY-ESO-1 and the DC cells in the bone marrow.
Owner:宁波美丽人生医药生物科技发展有限公司
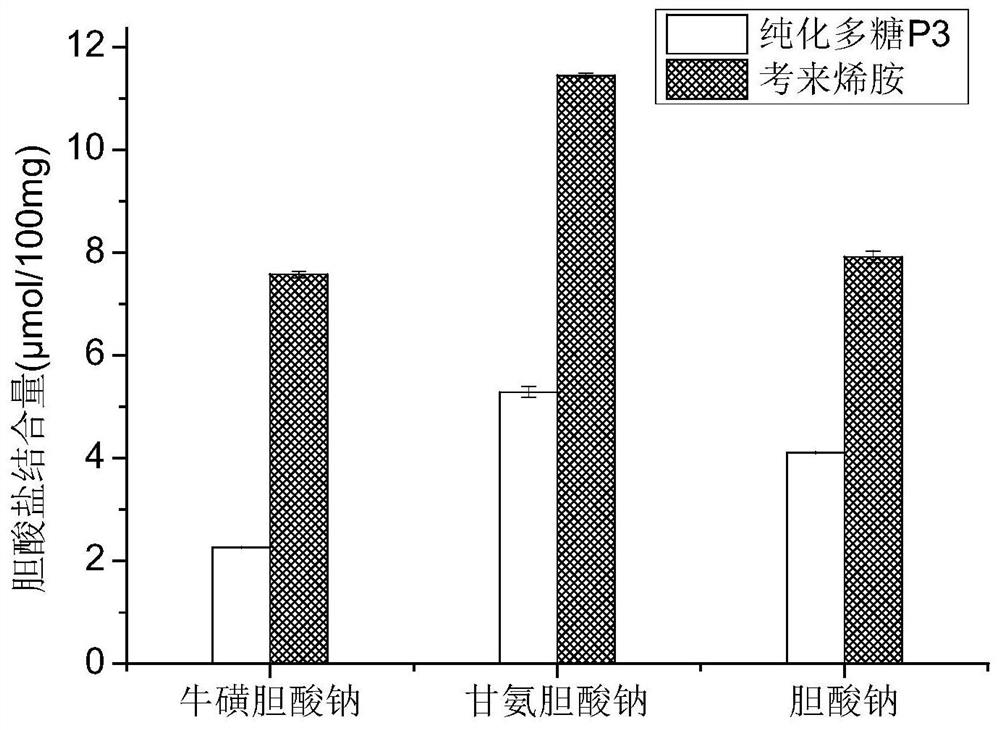
A myrtle polysaccharide p3, its separation method and its use in blood lipid-lowering drugs
ActiveCN109134679BLow costGood repeatabilityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCholic acidPharmaceutical Substances
The invention discloses a myrtle polysaccharide P3, its separation and purification method and its use in the preparation of blood lipid-lowering drugs. The polysaccharide contains the following molar percentages of monosaccharides: 9.97% of ribose, 2.40% of rhamnose, and 64.51% of arabinose , xylose 6.14%, mannose 5.39%, glucose 1.74%, galactose 9.85%. The experimental results of the present invention show that myrtle polysaccharide P3 has a certain ability to bind bile salts in vitro. With cholestyramine as a positive control, the binding rate of cholestyramine to each bile salt is calculated as 100%. The relative binding rates of myrtle polysaccharide P3 to sodium taurocholate, sodium glycocholate, and sodium cholate were 29.65%, 45.84%, and 51.90%, respectively.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Somatostatin receptor agonist polypeptide and its application
InactiveCN104045690BHigh activityImprove bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesDrug developmentLiver cancer
The invention relates to the field of medicine, in particular to a polypeptide capable of inhibiting the expression of somatostatin and treating liver cancer. Its sequence is GGLGLPFLATQNAAS, which is a brand-new sequence, which promotes the binding of somatostatin in vitro, and improves the survival rate of tumor-bearing mice in vivo, and has potential new drug development value.
Owner:ZHOUSHAN HOSPITAL
Protein A10 with arsenite and methyl arsenite combining capacity, engineering strain containing protein gene and application
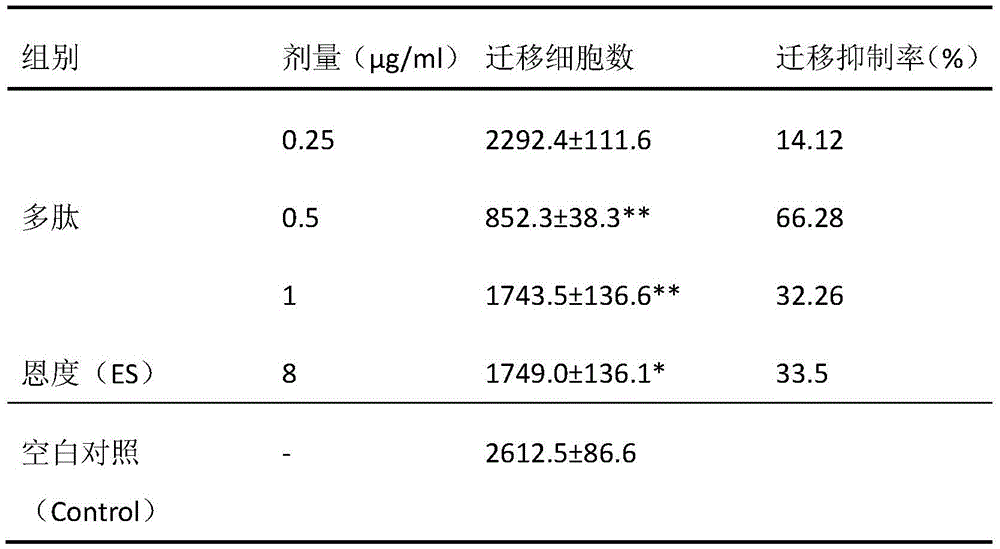
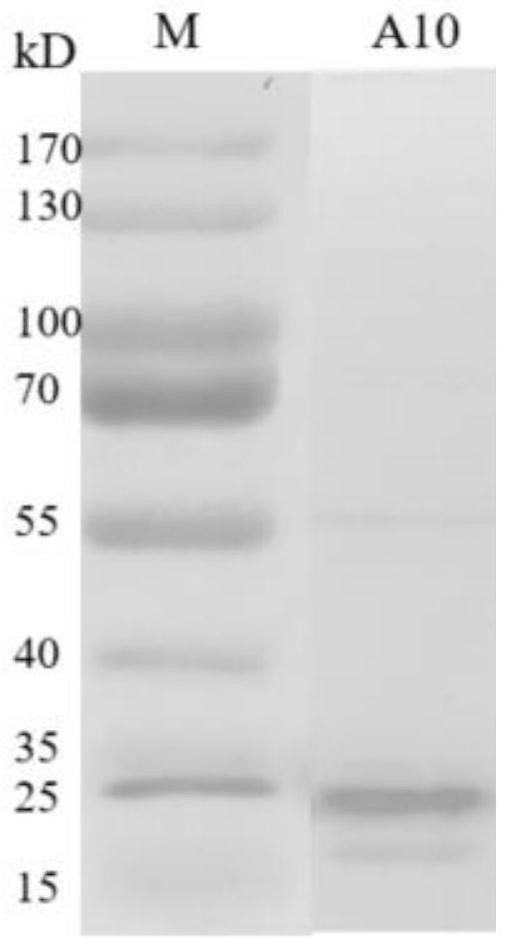
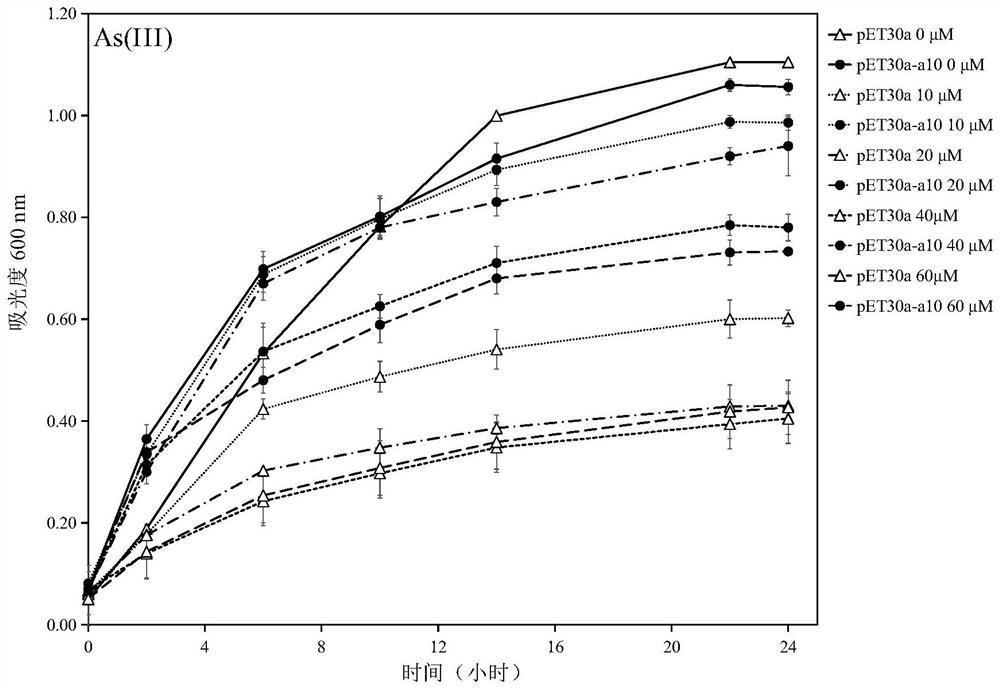
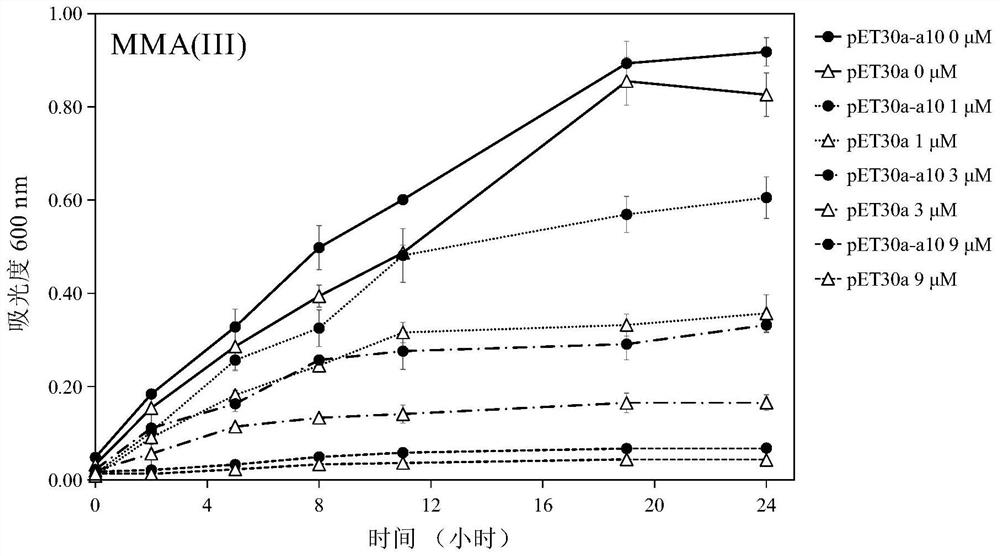
ActiveCN114605510AImprove bindingHigh removal rateBacteriaWater contaminantsProtein targetArsenic pollution
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com





![[18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same [18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/968fa248-169b-432d-ae39-6511ddb8404d/HDA0000939678010000011.PNG)
![[18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same [18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/968fa248-169b-432d-ae39-6511ddb8404d/HDA0000939678010000012.PNG)
![[18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same [18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/968fa248-169b-432d-ae39-6511ddb8404d/HDA0000939678010000021.PNG)