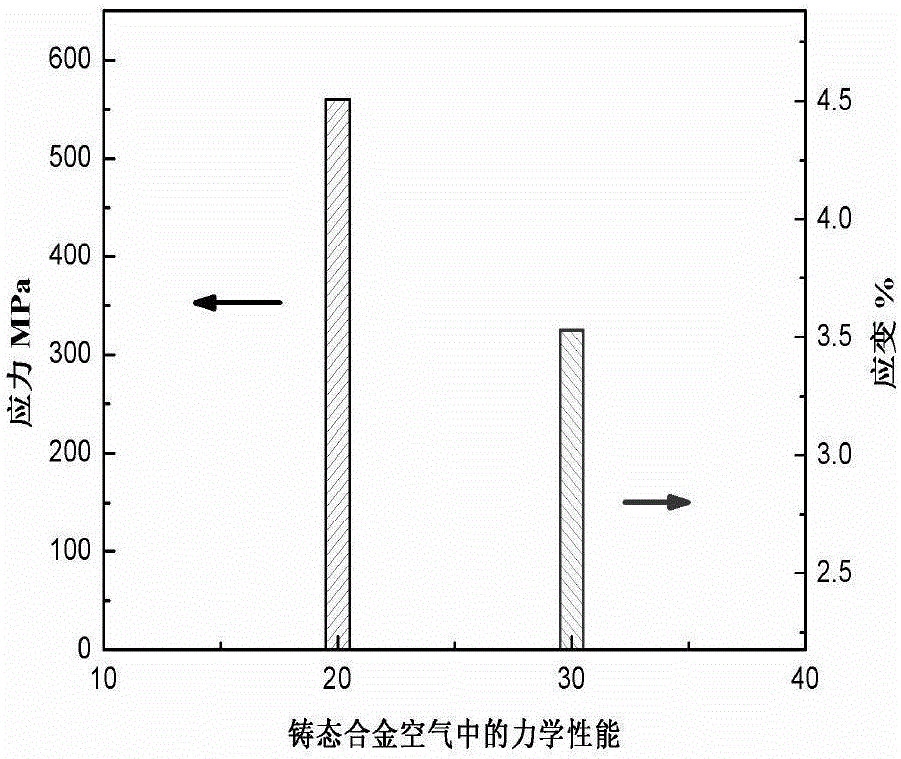
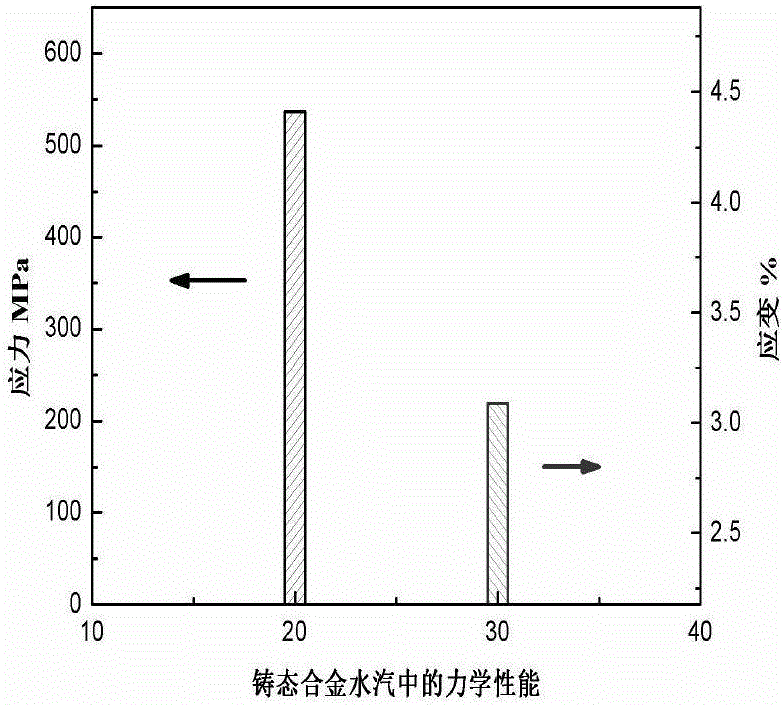
Heat treatment technology for improving brittleness of beta-phase solidification high Nb-TiAl alloy in water vapor environment
An alloy and environmental technology, applied in the field of intermetallic compounds, achieves the effects of simple operation, increased practical application and operability, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] This embodiment is a heat treatment process for improving brittleness resistance in a water vapor environment. The specific steps are:
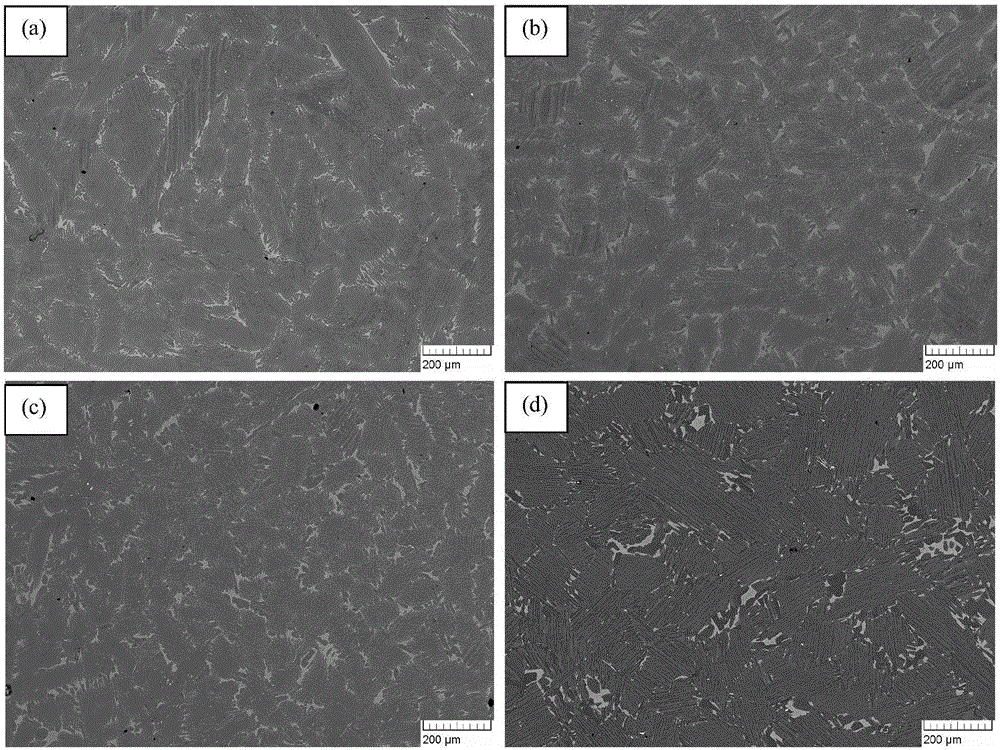
[0030] Step 1, prepare the sample. Samples were taken from ingots of β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloys of Ti-45Al-8.5Nb-(W,B,Y) obtained by electron beam melting. The microstructure of the β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloy ingot is as follows figure 1 as shown in a. The size of the β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloy sample is 100 × 30 × 30 mm. After ultrasonic cleaning and drying, the sample is placed in a heat treatment furnace, vacuumized and protected by argon gas. The vacuum degree is 5×10 -4 Pa.
[0031] Step 2, heat treatment. The sample was put into a box-type high-temperature heat treatment furnace, and the temperature was raised to 1240 °C in a stepwise manner with the furnace. Heating rate: the heating rate from room temperature to 900°C is 10°C / min; the heating rate above 900°C is 5°C / min. Then keep the sample heated to 1...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Step 1, prepare the sample. Samples were taken from ingots of β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloys of Ti-45Al-8.5Nb-(W,B,Y) obtained by electron beam melting. The microstructure of the β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloy ingot is as follows figure 1 as shown in a. The size of the β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloy sample is 100 × 30 × 30 mm. After ultrasonic cleaning and drying, the sample is placed in a heat treatment furnace, vacuumized and protected by argon gas. The vacuum degree is 1×10 -3 Pa.
[0035] Step 2, heat treatment. The sample was put into a box-type high-temperature heat treatment furnace, and the temperature was raised to 1220°C in a stepwise manner with the furnace. Heating rate: the heating rate from room temperature to 850°C is 8°C / min; the heating rate above 850°C is 4°C / min. Then keep the sample heated to 1220°C for 6 hours, and cool to room temperature with the furnace.
[0036] Experimental results such as figure 1 as shown in c. pass figure 1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Step 1, prepare the sample. Samples were taken from ingots of β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloys of Ti-45Al-8.5Nb-(W,B,Y) obtained by electron beam melting. The microstructure of the β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloy ingot is as follows figure 1 as shown in a. The size of the β-solidified high Nb-TiAl alloy sample is 100 × 30 × 30 mm. After ultrasonic cleaning and drying, the sample is placed in a heat treatment furnace, vacuumized and protected by argon gas. The vacuum degree is 1×10 -4 Pa.
[0039] Step 2, heat treatment. The sample was put into a box-type high-temperature heat treatment furnace, and the temperature was raised to 1260 °C in a stepwise manner with the furnace. Heating rate: The heating rate from room temperature to 950°C is 12°C / min; the heating rate above 950°C is 6°C / min. Then keep the sample heated to 1260°C for 9 hours, and cool to room temperature with the furnace.
[0040] Experimental results such as figure 1 shown in d. pass figure 1 D...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com